8-week-old male SD rats weighing 180 g to 200 g were provided by the Lab Center of the General Hospital of Northern Theater Command under the animal experiment license of No.: SCXK (Liao) 2020-0001. 8-week-old male SD rats were given sufficient water and food during the experiment to maintain the adaptive growth for one week.
HPL Stemulate (research-grade, No: ST-PL-NH100) was purchased from MineBio Life Sciences Ltd.
Allens spinal cord impactor was provided by the Trauma Laboratory of the General Hospital of Northern Theater Command. Brain solid positioner was provided by the Neurosurgery Laboratory of the General Hospital of Northern Theater Command. DiATOME ultra-thin diamond knife (3 mm, 45°) of LeicaLeica UC7 ultra-thin slicer and transmission electron microscope Hitachi-HT7700 were used. Main experimental reagents were obtained from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co, Ltd, including No: Servicebio G1102 electron microscope fixative, anhydrous ethanol and acetone, and 812 embedding agent (No: SPI 90529-77-4) was provided by Ted Pella Inc.
2.4. Experimental grouping, modeling and Methods
2.4.1 Experimental grouping
30 rats were randomly divided into 3 groups including Sham-operated Group, SCI group, and treatment group. For the rats in the treatment group, 2 mL HPL was injected intraperitoneally 30 minutes after surgery for 14 continuous days.
2.4.2 Modeling
After adult male SD rats were acclimatized and fed for 7 consecutive days, adult male SD rats were measured (standard body weight range: 200g-220g) and anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 1% sodium pentobarbital 40mg/kg. After the disappearance of the corneal reflex, male SD rats were immobilized in the prone position. An incision was made about 3 cm in the center of the T9-T11 spinal cord segment, the fascia was cut, and the muscle above the spinous process was removed. Mosquito forceps were adopted to remove the spinous process to expose the spinal cord completely, and a spinal cord impactor was adopted. An area with a diameter of 2 mm was selected and a 20-g weight was placed in free fall at a height of 5 cm from the spinal cord of male SD rats. After placing the 20g weight on the spinal cord of male SD rats for 5 seconds, it could be noticed that their hind limbs twitched, their tails swung, the tension of the hind limbs and tails disappeared, and they appeared to be reclining, implying the successful modeling process. After hemostasis in the surgical area, the muscles, fascia and skin of male SD rats were sutured sequentially, body temperature was maintained until postoperative recovery, and the bladder was massaged to urinate twice a day until they recovered the function of voluntary urination. During the operation, the rates were administered anesthetic drugs to achieve anesthesia and reduce pain. After the operation, ibuprofen analgesic drugs were given to relieve pain. During tissue collection, the arteries were anesthetized to collect blood and bleeding was continued until death. All animal treatments were in accordance with the Regulations for the Protection and Use of Laboratory Animals in the Northern Theater of Operations of the General Hospital of the Chinese People's Liberation Army (Ethical Approval No. 2023-24).
2.4.3 Main observation indicators
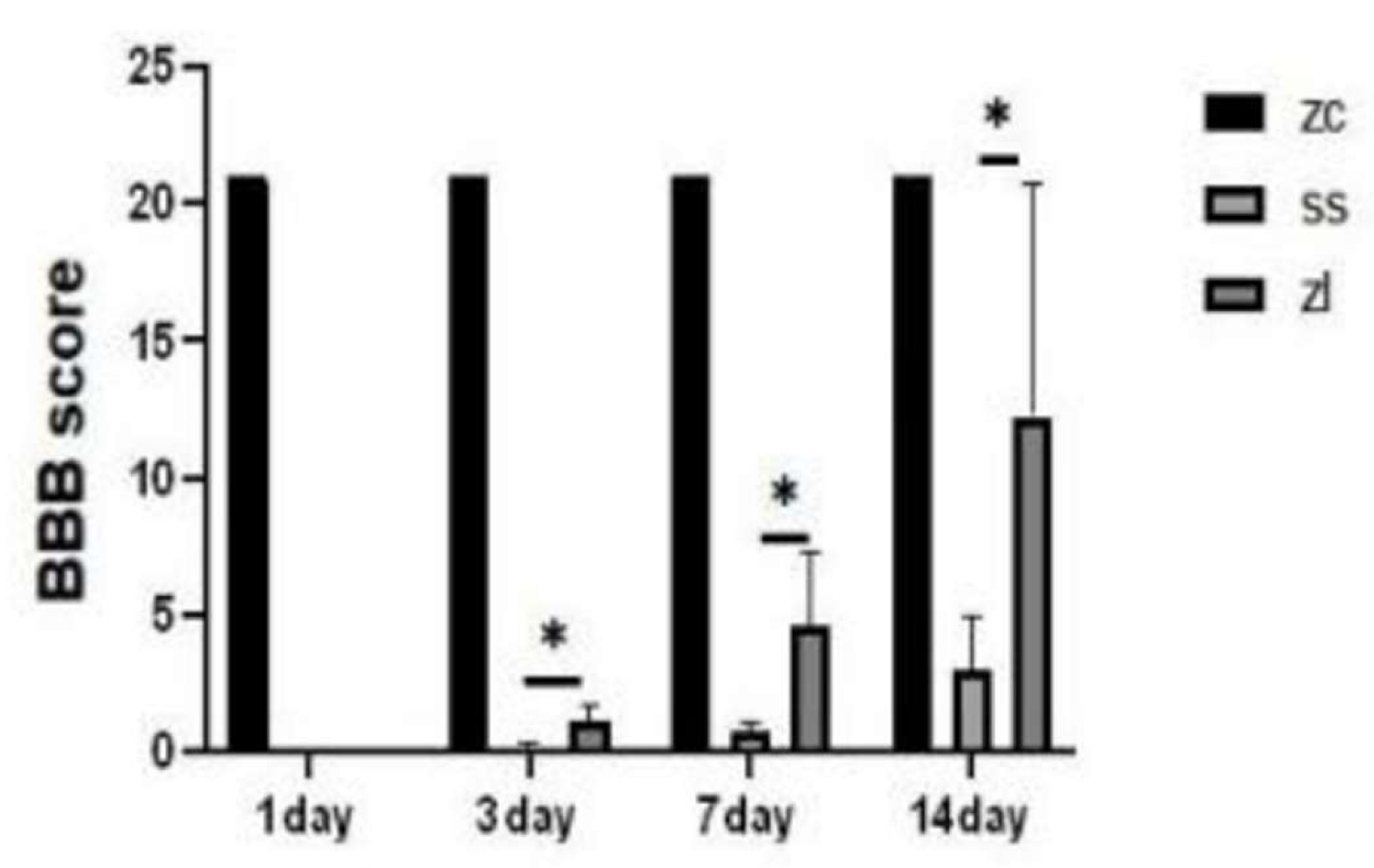
Postoperative daily Basso Beattie Bresnahan (BBB) score and incline plate tests were performed.
2.4.4 Preparation and sampling of specimens
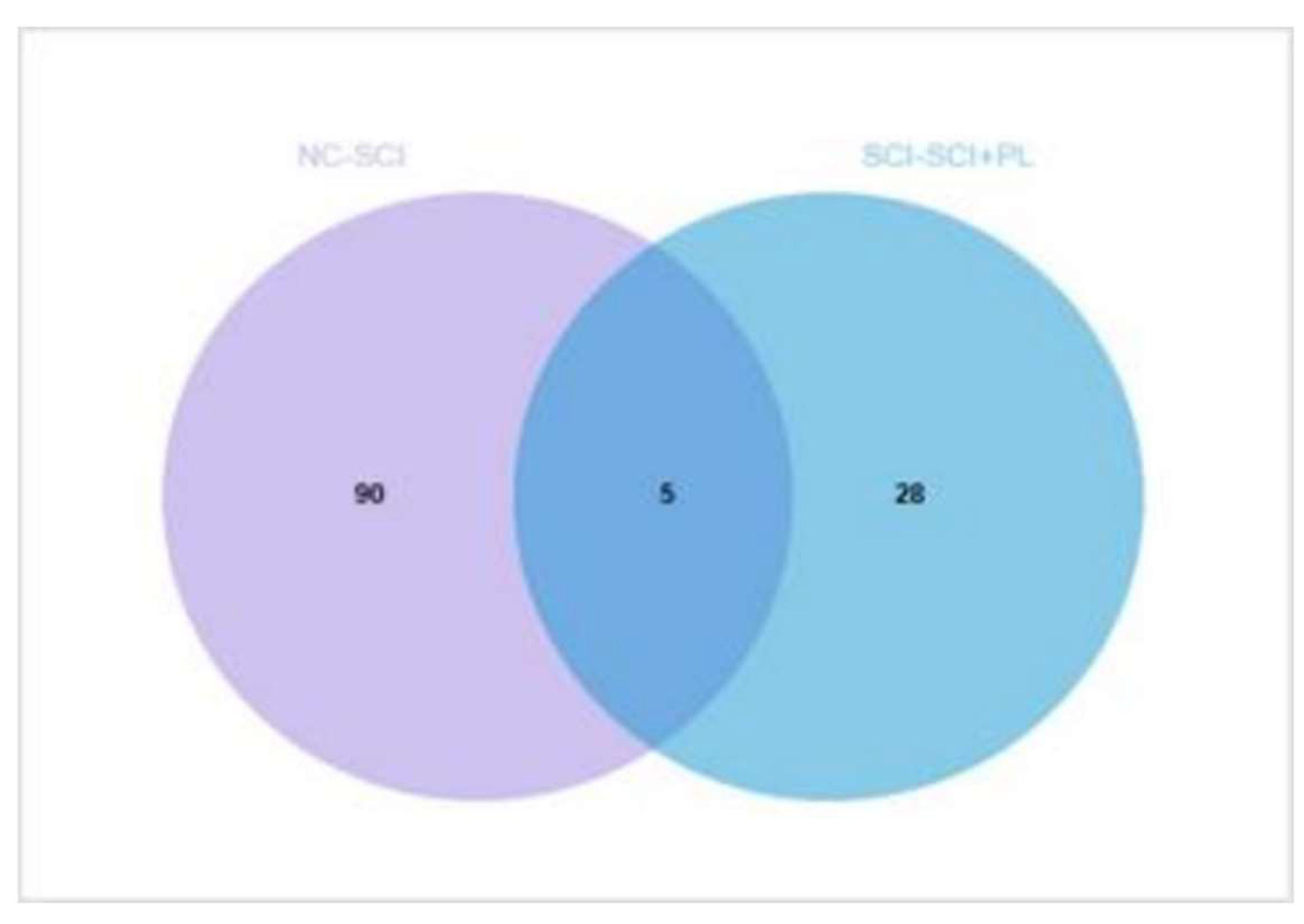
After anesthesia by intraperitoneal injection, the surgical area of SCI in rats was incised, and the spinal cord was gently and quickly removed from the rats, which was then either placed in formalin or washed in PBS and then frozen in a -80°C freezing tube. The spinal cords of three rats were randomly selected from the sham-operated, spinal cord injury and treatment groups, washed in PBS and stored in liquid nitrogen for proteomic analysis.
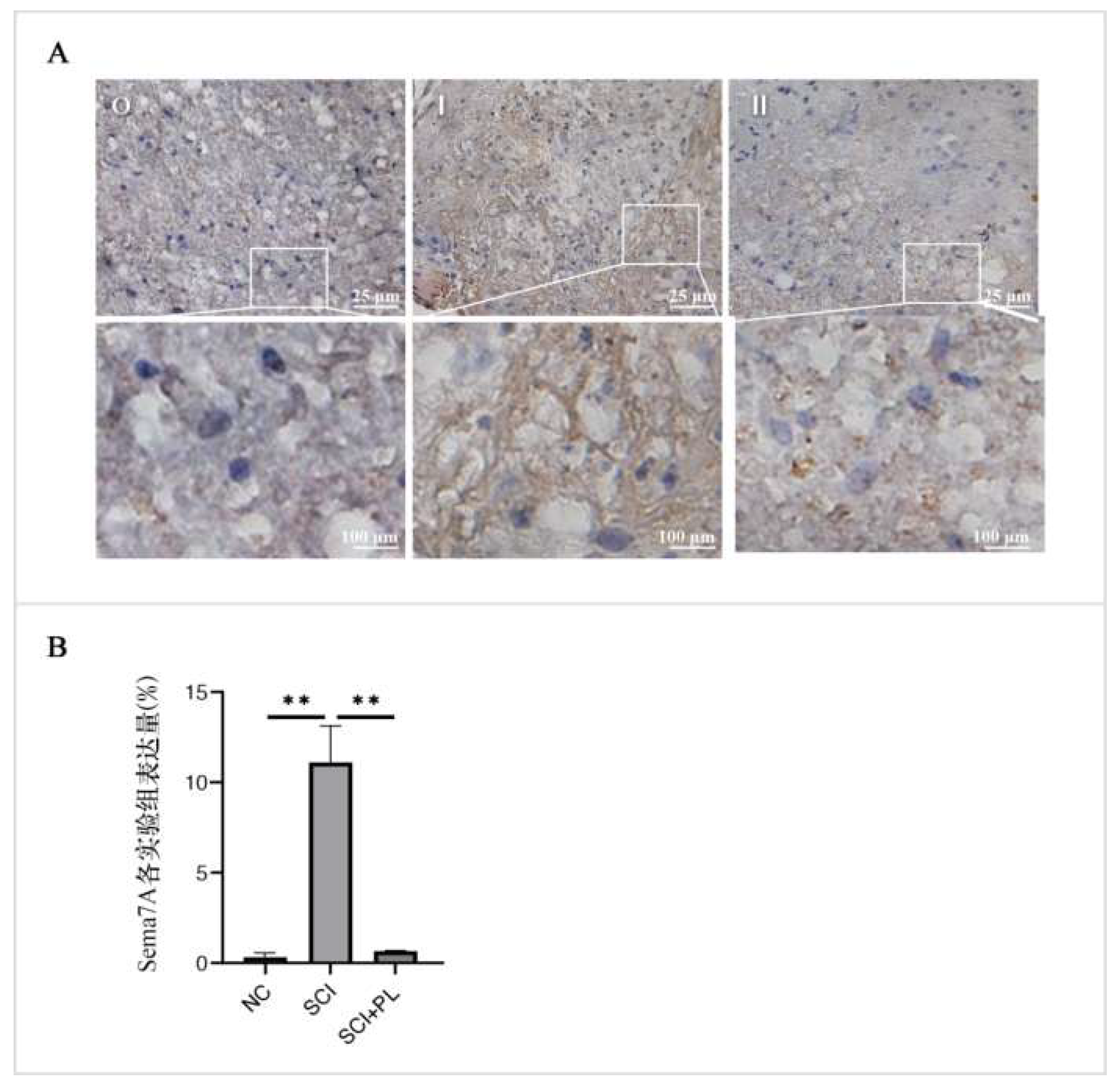
2.4.5 Immunohistochemical Staining
Step 1: Blocking treatment: treat with endogenous peroxidase blocker for 20 minutes.
Step 2: Soak in double distilled water 3 times for 5 minutes each time.
Step 3: Antigen repair: prepare 400-600 mL of 10 nM citric acid antigen repair solution (pH=6.0), put the slices into a beaker, seal the beaker mouth with cling film to prevent the repair solution from overflowing due to boiling, and then heat it in the microwave at high temperature for 10 minutes.
Step 4: After heating, add sterile double distilled water (DDW) to fill the liquid level, and heat it in a microwave for 40 minutes (medium to low temperature until thawed), and fill the liquid level with double distilled water every 10 minutes.
Step 5: After completing the antigen repair, cool the repair solution naturally at room temperature.
Step 6: After cleaning with DDW for 180 seconds, clean it for 3 times using photospace buffered saline (PBS) with 3 minutes each time.
Step 7: Perform primary antibody incubation, and store it in at 4 ℃, and raise the temperature to 37 ℃ in the next day. Then, perform a 5-minute PBS cleaning.
Step 8: Add reaction enhancer to the beaker, incubated continuously at room temperature for 20 minutes, and then performed PBS cleaning for 3 times with 3 minutes each time.
Step 9: Add goat anti-mouse/rabbit IgG/IgM H&L (HRP polymer), incubated at room temperature for 20 minutes, and then performed a PBS cleaning for 3 times with 3 minutes each time.
Step 10: Add DAB colorimetric solution dropwise (prepared in a 1:19 ratio when using), chose the staining time according to different antibodies, incubate at room temperature for 2 to 10 minutes, and gently rinsed DAB colorimetric solution with tap water after completing this experimental step.
Step 11: Re-dyeing: Stain it with hematoxylin for 50 seconds, cleaned with DDW for 3 minutes, and then performed PBS cleaning for 3 times with 5 minutes each time.
Step 12: Dehydration: Soak the slices in different concentrations of alcohol sequentially: 70 % (0 min), 80 % (1 min), 90 % (1 min), 95 % I (1 min), 95 % II (5 min), 100 % I (5 min), 100 % II (5 min), and 5 min.
Step 13: Transparent treatment: Treat it with xylene I and xylene II for 20 minutes each time.
Step 14: Used neutral resin to seal the slide, seal it with a glass slide (without residual small bubbles in the tissue), and dried it in the air naturally.
2.4.6 Tandem Mass Tag (TMT) Technology (Detected by Hangzhou Lianchuan Biotechnology Co, Ltd.)
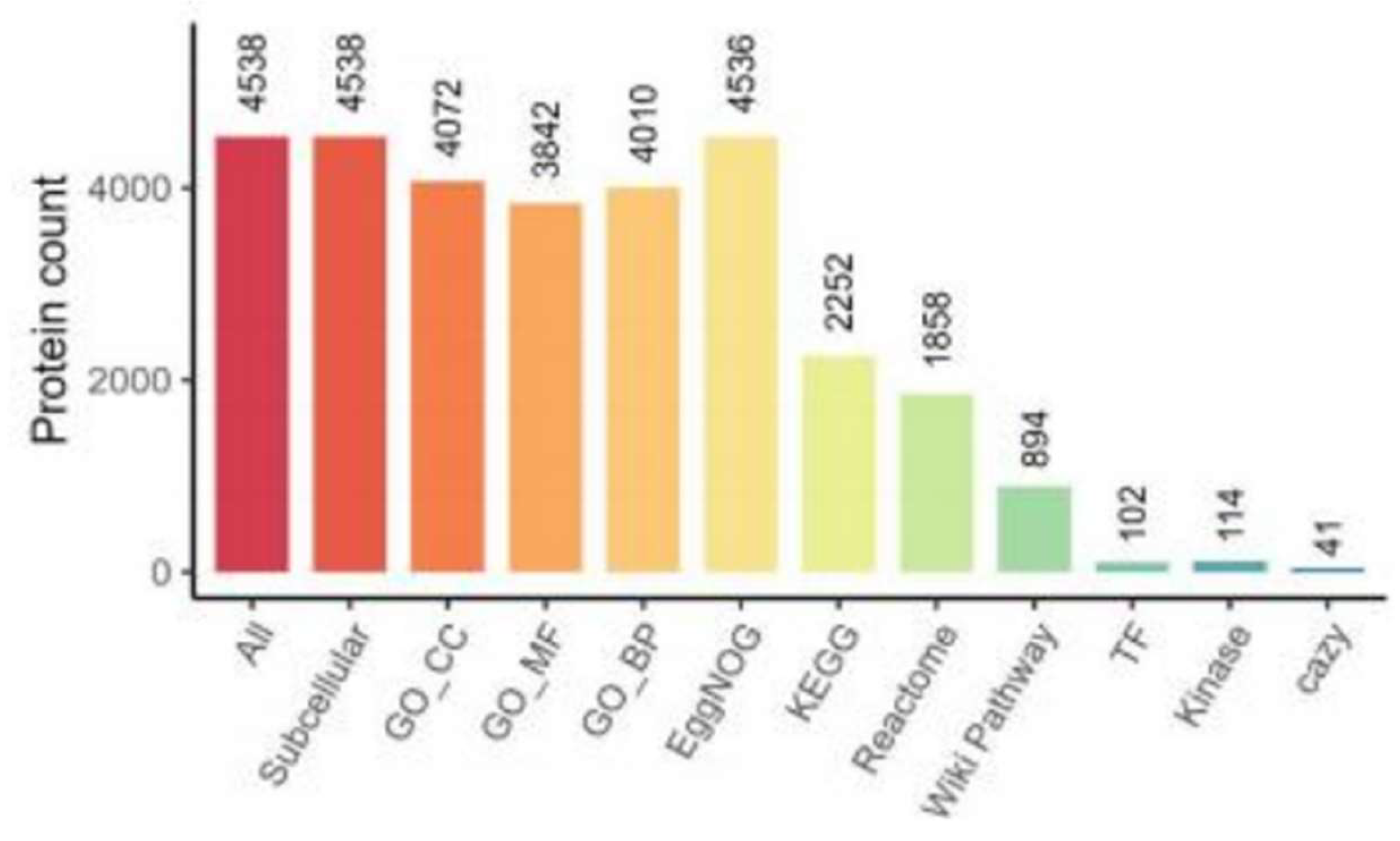
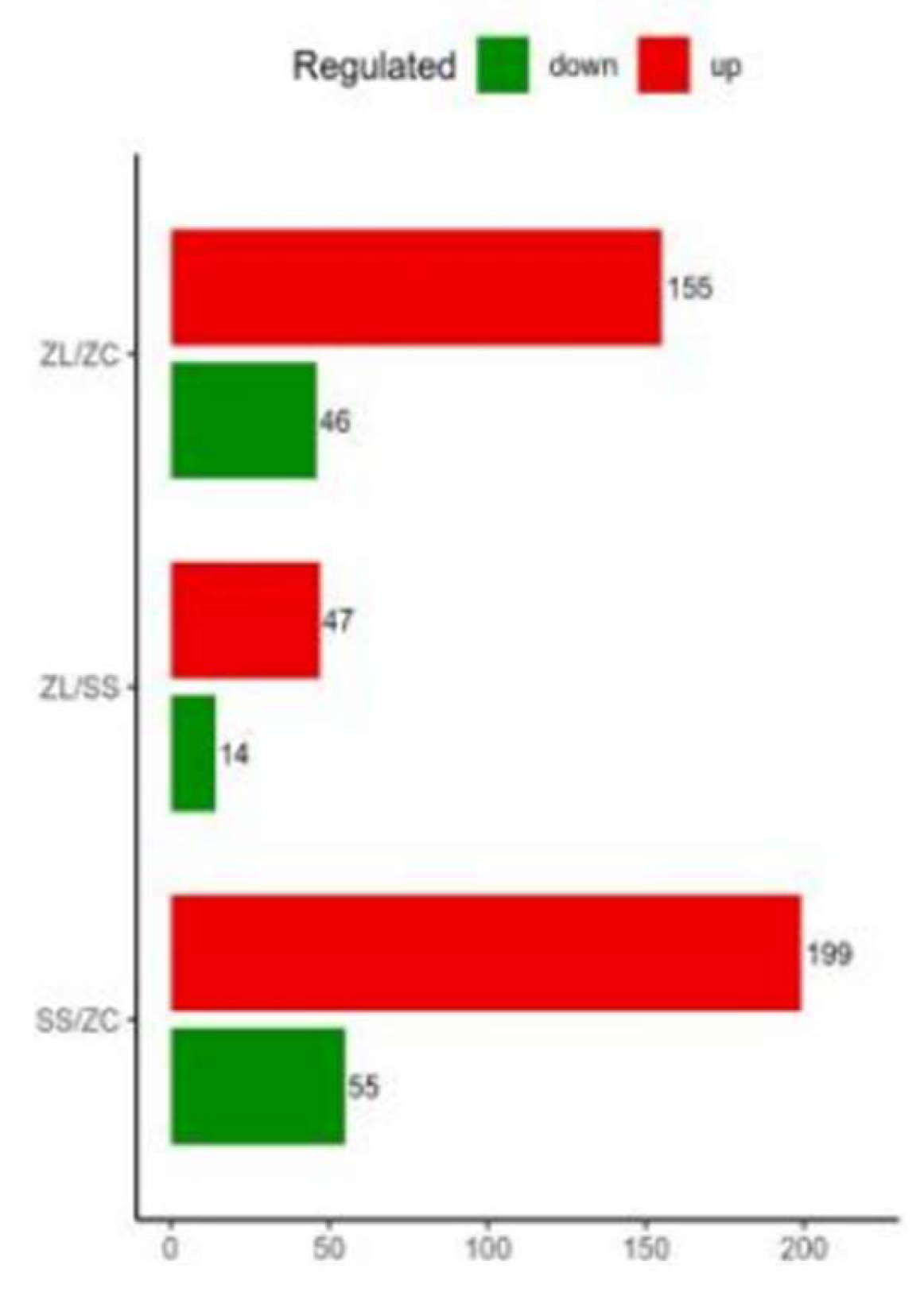
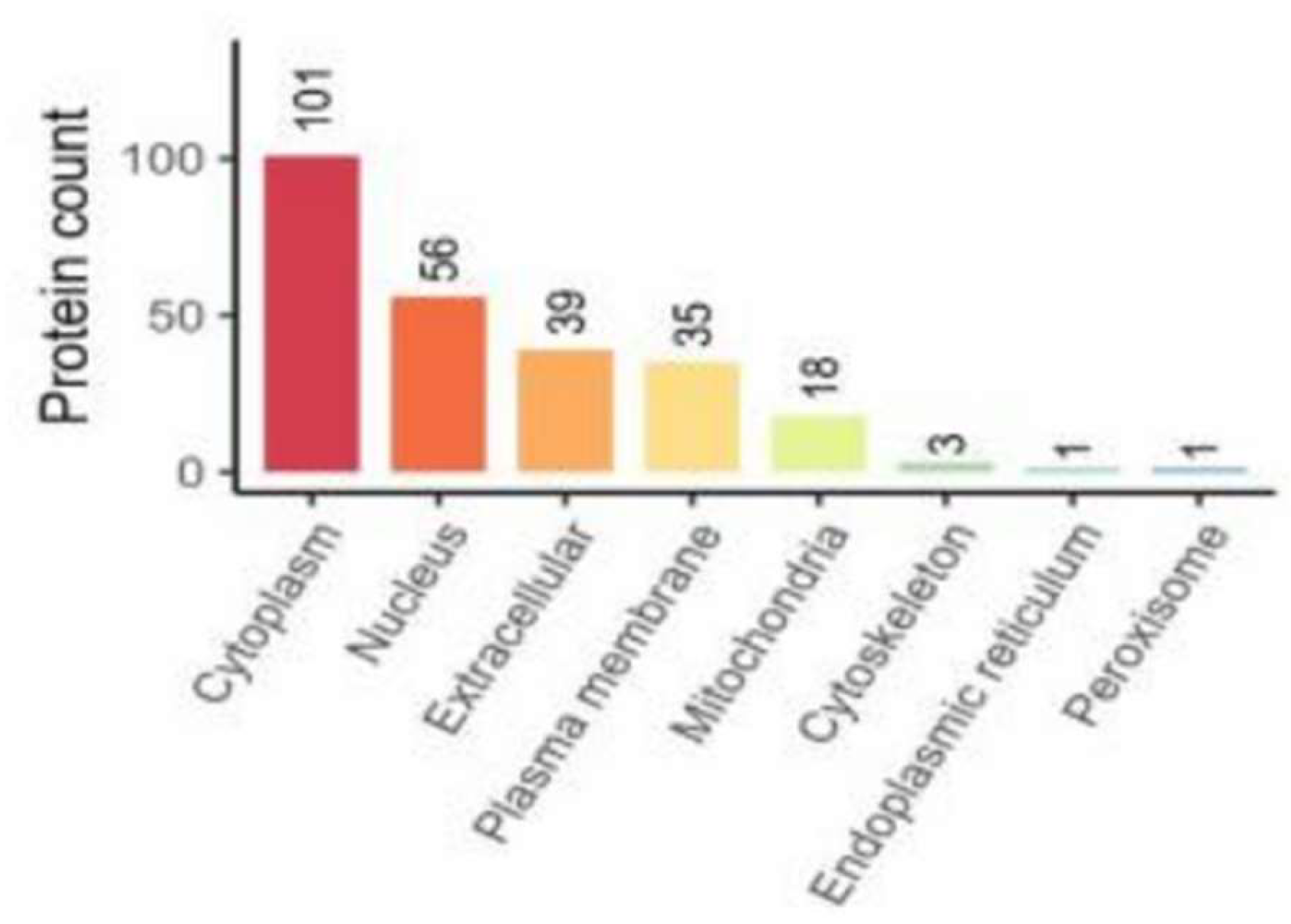
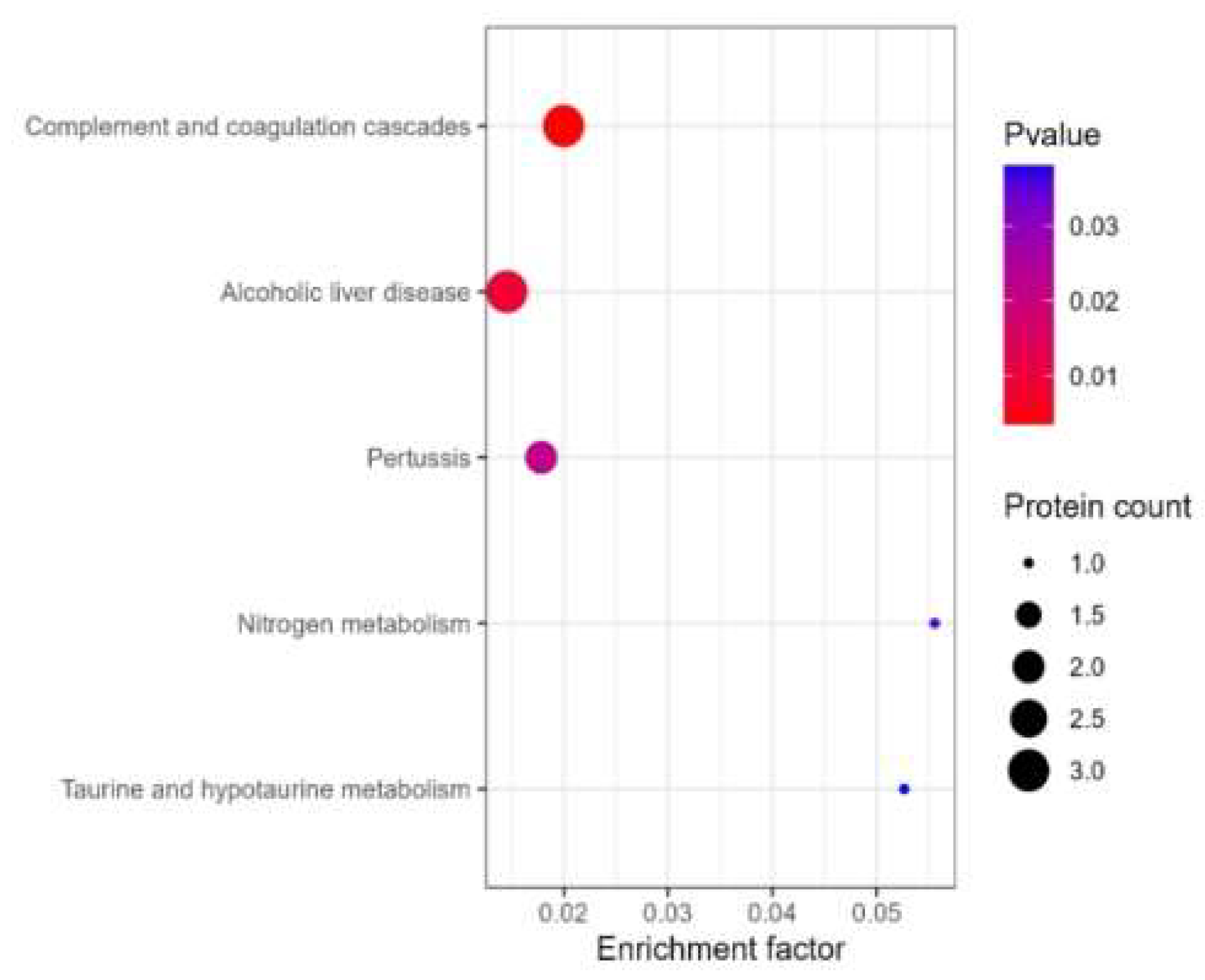
TMT technology was employed to detect 9 rat tissue samples using TMT labeled quantitative proteomics technology. The protein composition, expression level differences, and corresponding biological functions within the samples were analyzed. TMT (Tandem mass tag) is an in vitro stable isotope labeling protein quantification technique developed by ThermoFisher. This technology utilizes isotope reagents to simultaneously label up to 18 peptide samples (TMTpro-18plex). After mixing the labeled peptide samples in equal amounts, it can perform liquid chromatography separation and tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) detection to obtain primary and secondary mass spectrometry information for each peptide segment. In the secondary mass spectrometry, chemical bond cleavage releases TMT reporter ions, generating 18 reporter ion peaks in the low-quality region of the mass spectrometry, and the intensity of chemical bond cleavage can indicate the relative expression level information of the peptide segment in different samples. In addition, the mass to charge ratio of the peptide fragment ion peak in the secondary mass spectrometry can indicate the sequence information of the peptide segment. By retrieving these raw mass spectrometry data in the database, it can obtain qualitative and relative quantitative information of the protein.
2.4.7 Protein Extraction
(1) An appropriate amount of sample was added into a 2-mL centrifuge tube, and then an appropriate amount of steel beads and lysis buffer (50 mMTris-HCl, 8 M Urea), as well as a final concentration of 1X Roche Cocktail were added, and the mixture was placed on ice block for 5 minutes; (2) A grinder was used to crush and lysed the sample (frequency: 60 HZ, time: 2 min), centrifuged 20,000 g sample at 4°C for 15 min, and then extracted the supernatant; (3) DTT with a final concentration of 10 mM was added and water bath at 37 °C for 1 hour; (4) IAA with a final concentration of 20 mM was added, and placed in the dark for 30 minutes.
2.4.8 Protein Extraction Quality Control
(1) Bradford quantification: Added standard protein (0.2 μg/μL BSA) 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18 μL to the 96-well enzyme plate in sequence, then added 20, 18, 16, 14, 12, 10, 8, 6, 4, 2 μL of pure water in sequence, shake and mix, and then added 180 μL of Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 quantitative working solution to each well. Used a microplate reader to measure OD595, and created a linear standard curve based on OD595 and protein concentration. Diluted the protein solution to be tested to several times, add 180 μL of quantitative working solution to 20 μL of the protein solution, and read the OD595. Calculated the sample protein concentration based on the standard curve and sample OD595; (2) Used the SDS-PAGE method to sample 10 μg protein solution and add an appropriate amount of loading buffer, mix and heat at 95°C for 5 minutes, centrifuged 20,000g of the sample for 5 minutes, and then extract the supernatant an added it into the spotting holes filling with a 4-12 % SDS polyacrylamide gel, and applied 80V constant voltage electrophoresis for 20 minutes, followed by 120V constant voltage electrophoresis for 60 minutes. After applying electrophoresis, the SDS polyacrylamide gel was stained and destained, then removed and photographed.
2.4.9. Protease Hydrolysis
(1) Extracted 150 μg protein from each sample; (2) Added 3 μg Trypsin enzyme at a ratio of protein: enzyme=50:1, and enzymatically hydrolyzed at 37°C for 14-16 hours; (3) The enzymatically hydrolyzed peptides are desalted using a Waters solid- phase extraction chromatography column and vacuum-dried; (4) The dried peptide samples are reconstituted with pure water and stored at -20°C.
2.4.10. TMT Labeling
(1) Extracted an appropriate amount of peptide fragments from each sample, drain it under vacuum, and redissolve it into 30 μL solvent with 100 mM TEAB; (2) Added 100% anhydrous acetonitrile to the TMT labeling reagent for dissolution. Added each TMT label to each sample according to the ratio of TMT labeling: peptide=5:1, and made it stand for 1-2 hours at room temperature; (3) After labeling, added 5% hydroxylamine to each sample to a final concentration of 0.4 % to terminate labeling, then all the samples were mixed into a tube, shook and mixed well, part of the samples were extracted for labeling quality control, and the rest were drained.
2.4.11. High-pH Reversed-Phase Chromatography
After extracting equal amounts of peptide fragments from all samples, mixing them, diluting them with mobile phase A (5 % ACN, pH 9.8) and selecting samples,
they were separated using the UltiMate™ 3000 binary rapid separation system produced by Thermo Scientific. The model adopted was A 3.5μm 4.6x150mm Agilent ZORBAX 300ExtendC-18 liquid chromatography column was adopted to perform liquid-phase separation of the sample. Elute with a flow rate gradient of 0.3 mL/min: elute from 5% mobile phase B (97 % ACN, pH 9.8) to 21.5 % mobile phase B in 38 min, and elute from 21.5 % to 40 % mobile phase B in 20 min, elute from 40 % to 90 % mobile phase B in 2 min, 90 % mobile phase B for 3 min, and equilibrate with 5 % mobile phase B for 10 min. Monitor the elution peak at a wavelength of 214 nm and collect a component every 1 minute. Aggregate the samples according to the chromatographic elution peak pattern to obtain 10 components, and then freeze and drain the sample.
2.4.12 Mass Spectrometry (nano-flow liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
We re-solubilized the dried peptide sample with 0. 1 % FA, centrifuged the sample at 20,000 g for 10 minutes, and extracted the supernatant for sample selection. Separation was performed by EASY-nLC™ 1200 system produced by Thermo Scientific. We made the sample enter into the self-loaded liquid chromatography column C18 (100 μm inner diameter, 1.8 μm column particle size, approximately 35 cm column length), and was separated through the following effective gradient at a flow rate of 300 nL/min: 0~48 min, 8 % mobile phase B (98 % ACN, 0. 1 % FA) rises linearly to 32 %; 48~53min, mobile phase B rises from 32 % to 45 %; 53~55 min, mobile phase B rises from 45 % to 90 %; 55~62 min, 90 % mobile phase B. The peptide fragments separated by liquid phase were ionized by the nanoESI source and then entered the mass spectrometer Orbitrap Exploris™ 480 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Jose, CA) for DDA (Datadependent Acquisition) mode detection. Main parameter settings: ion source voltage is 2.2KV, primary mass spectrometry scanning range is 350~1,500m/z; resolution is set to 120,000; Normalized AGC Target is set to 300 %; secondary mass spectrometry fragmentation mode is HCD, and fragmentation Energy is set to 32 %; resolution is set to 45,000, and dynamic exclusion time is set to 60s. The starting m/z of the secondary mass spectrum is fixed at 110; the precursor ion screening conditions for secondary fragmentation are: charge 2+ to 6+; the Normalized AGC Target is set to 200 %, and the maximum ion injection time (MIT) is 120 ms.
2.4.13. Protein Identification and Quantification
We adopted MaxQuant software to conduct protein search, identification and quantitative analysis on the TMT-labeled mass spectrum raw data. The main parameters of MaxQuant that should be set are: select the MS2-based reporter
quantitative mode (TMT6plex, TMT10plex, TMT16plex or TMT18plex) , set trypsin to Trypsin/P enzyme, fixed modification to Carbamidomethyl(C), variable modification to Oxidation (M) and Acetyl (protein Nterm), select Match between runs
We extracted the proteins in the sample and then enzymatically hydrolyzed them, and labeled the enzymatically hydrolyzed peptides with TMT reagents and enriched and separated them. The peptides are detected using a high-performance liquid chromatography tandem high-resolution mass spectrometer to obtain a large amount of mass spectrometry data. We adopted MaxQuant (v2.1.4.0) software to identify the proteins in the samples. The identification conditions were: false positive spectrum (PSM FDR) < 0.01, false positive protein (Protein FDR) < 0.05.
2.5 Ethics Statement
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Northern Theater General Hospital: Northern Theater General Hospital Animal Medical Research Ethics Committee Branch(No. 2023-24). This study was performed in accordance with the ARRIVE guidelines.