Submitted:
26 October 2024
Posted:
28 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of Photophysical Properties of h-FTAA in Different Solvent Environments
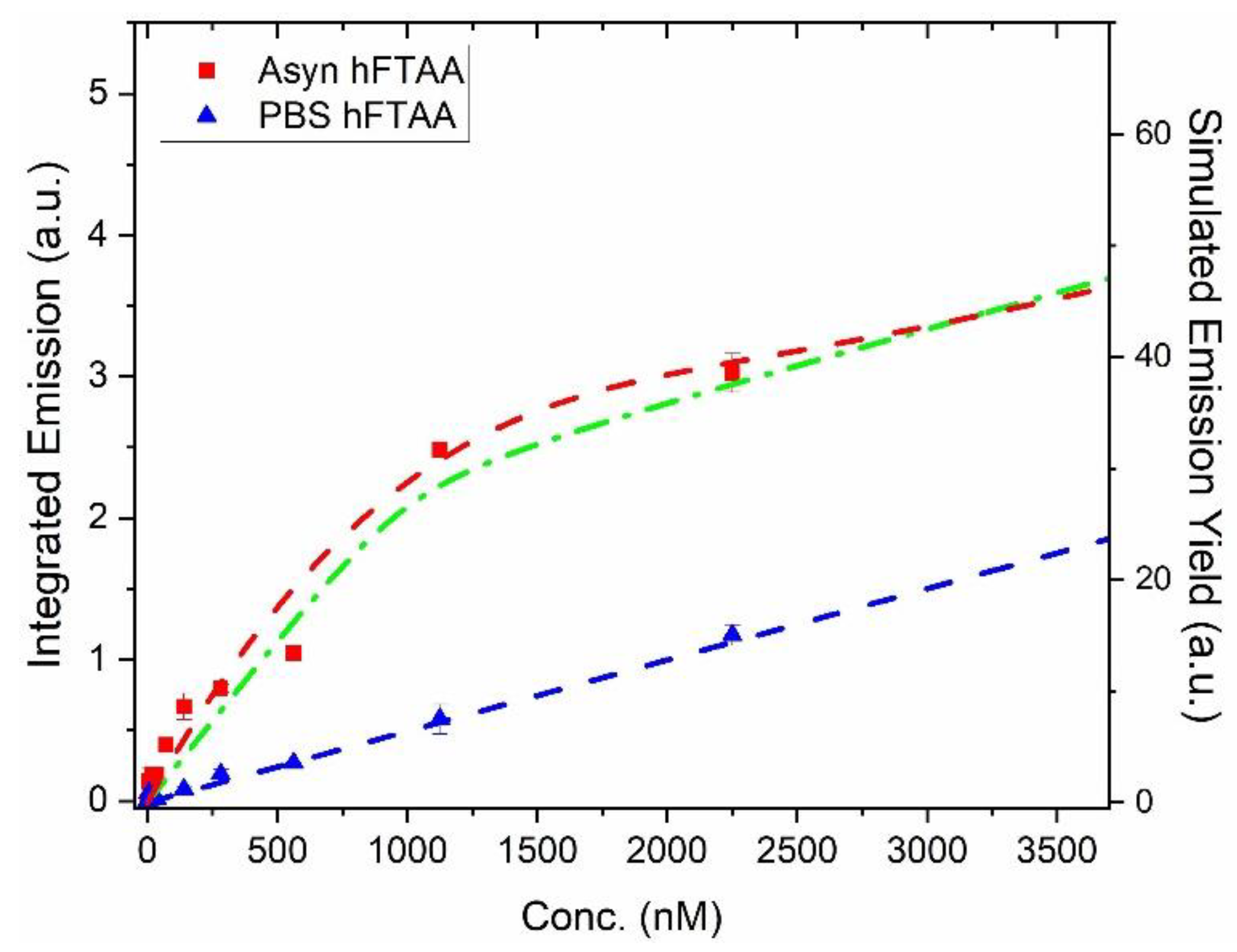
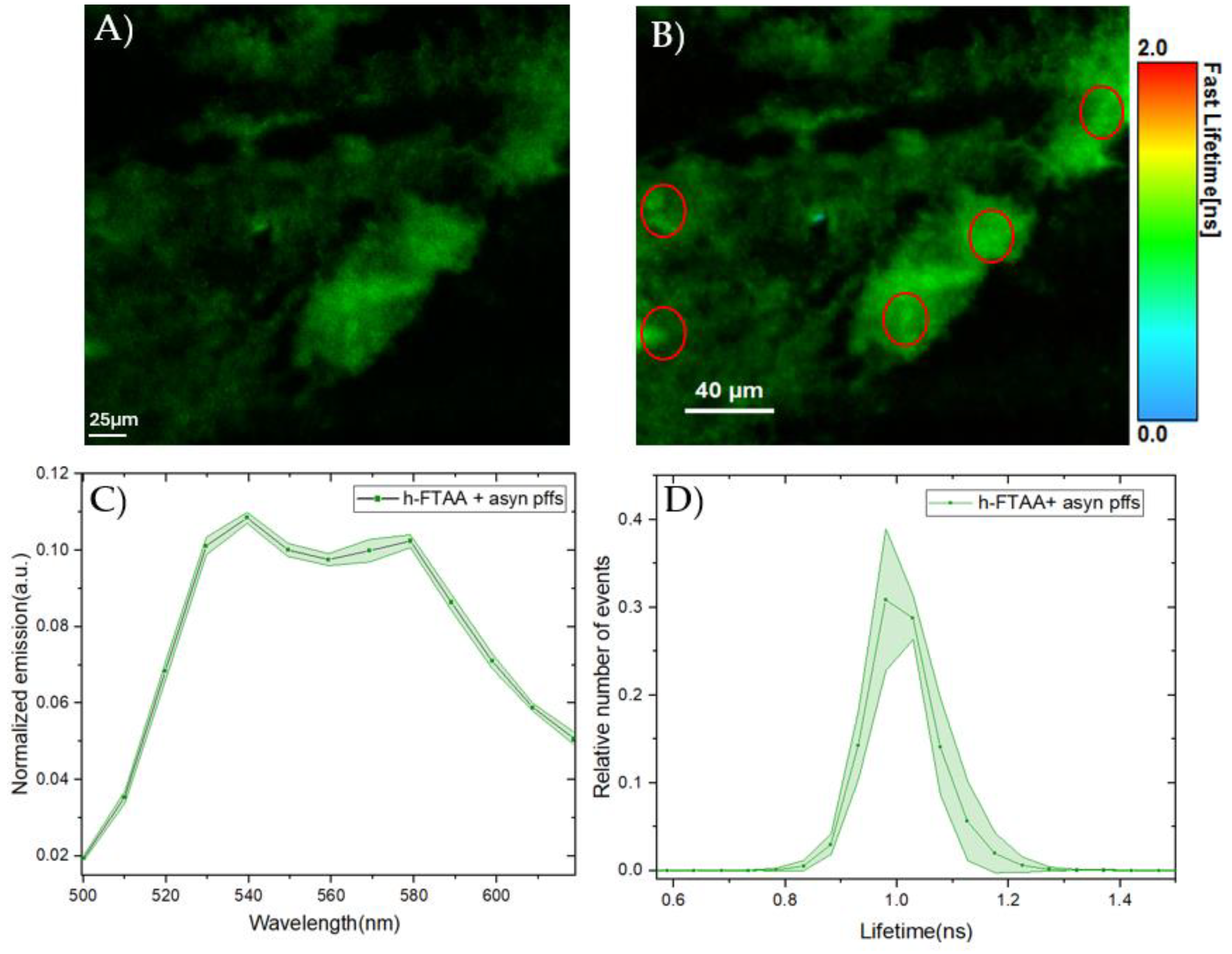
2.2. In Vitro Spectroscopic Evaluations of h-FTAA Binding to Human-αsyn Pre-Formed Fibrils
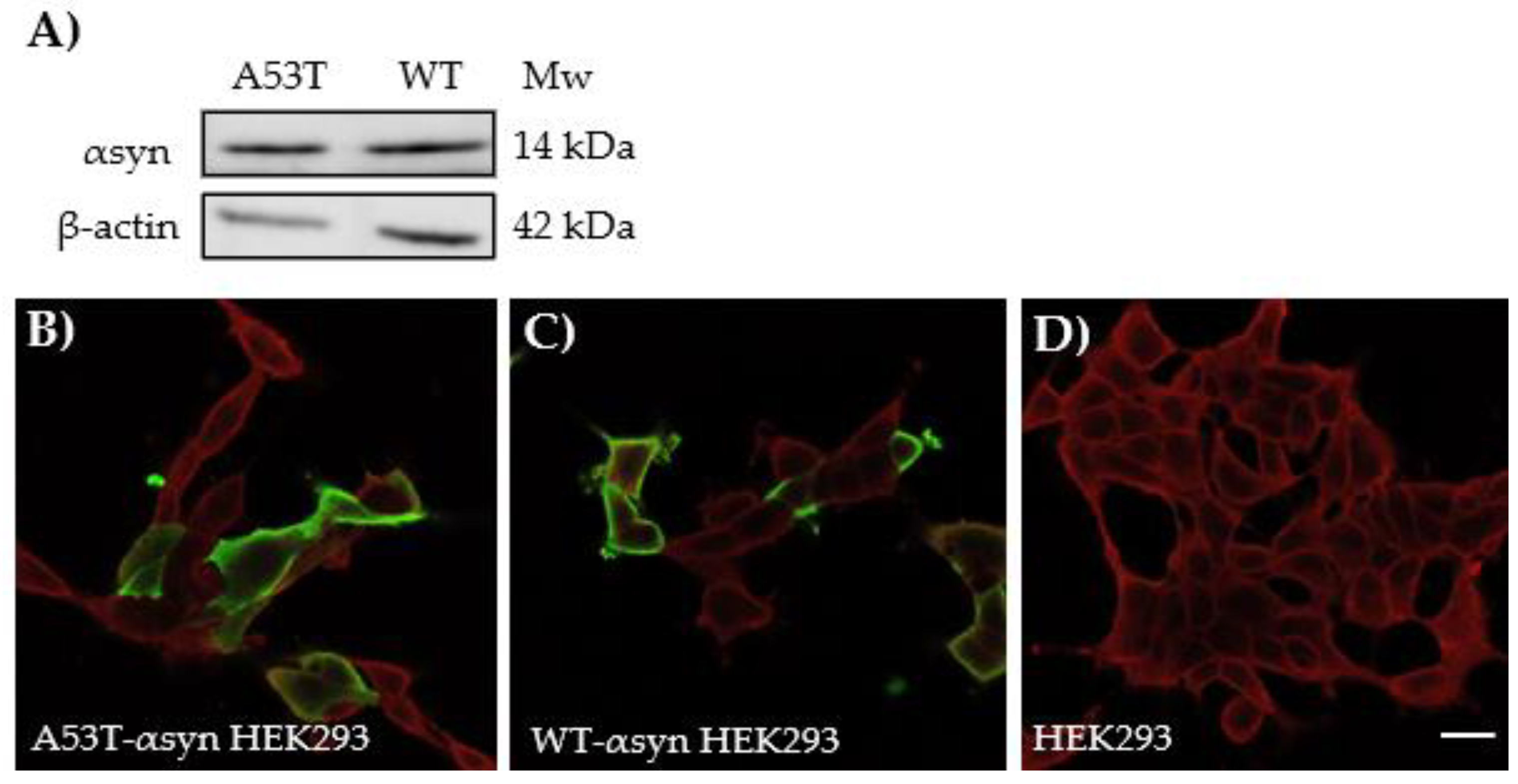
2.3. Characterization of αSyn Protein Expression in HEK293 Cells, Transiently Transfected with Human-A53T or Human-WT-αsyn
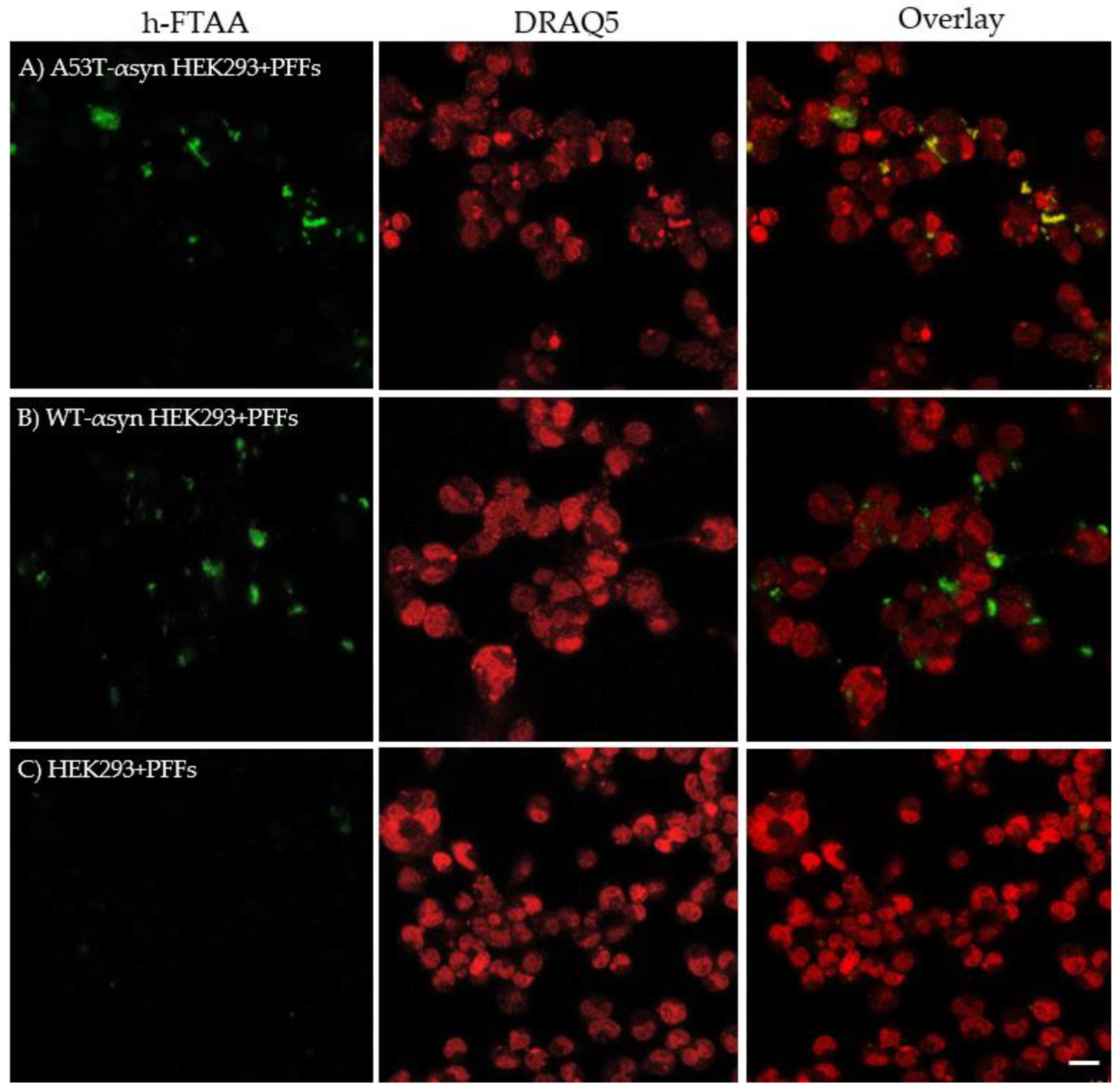
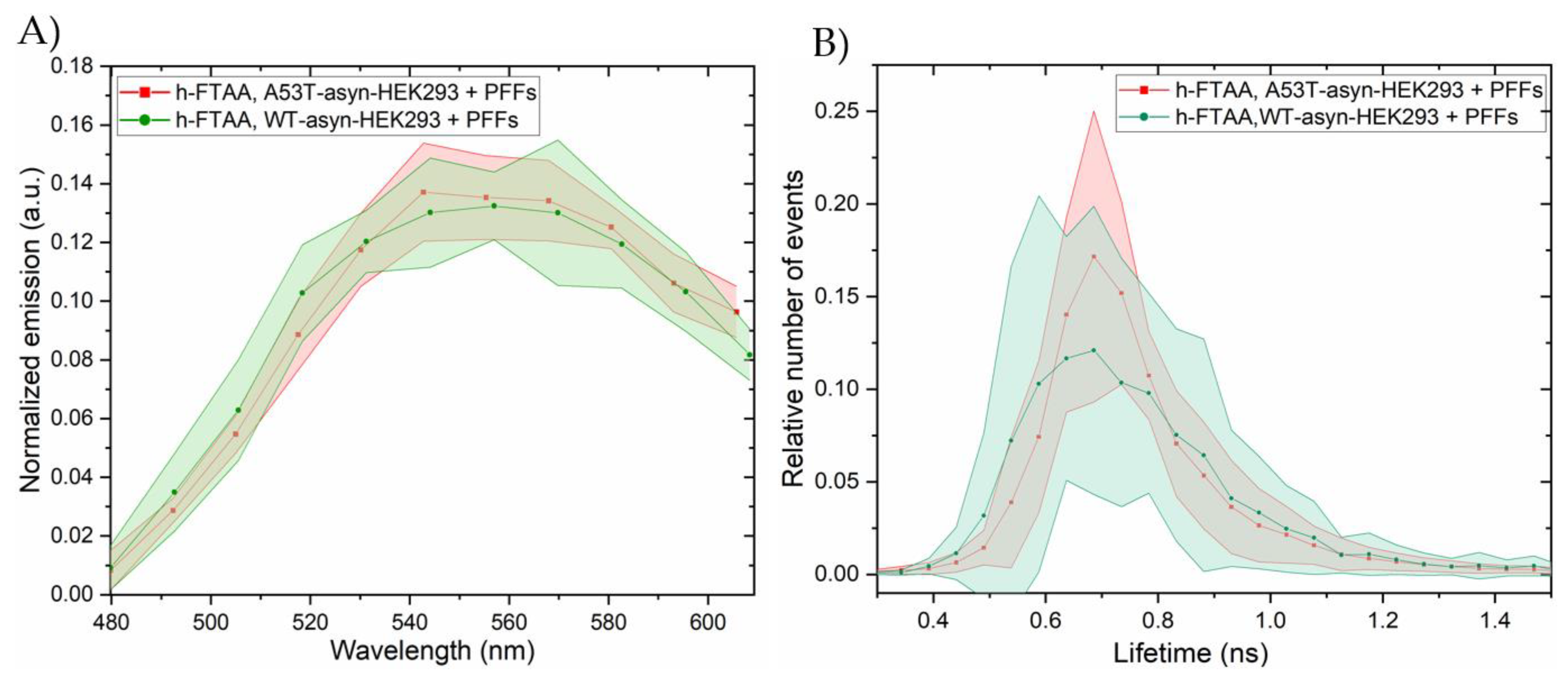
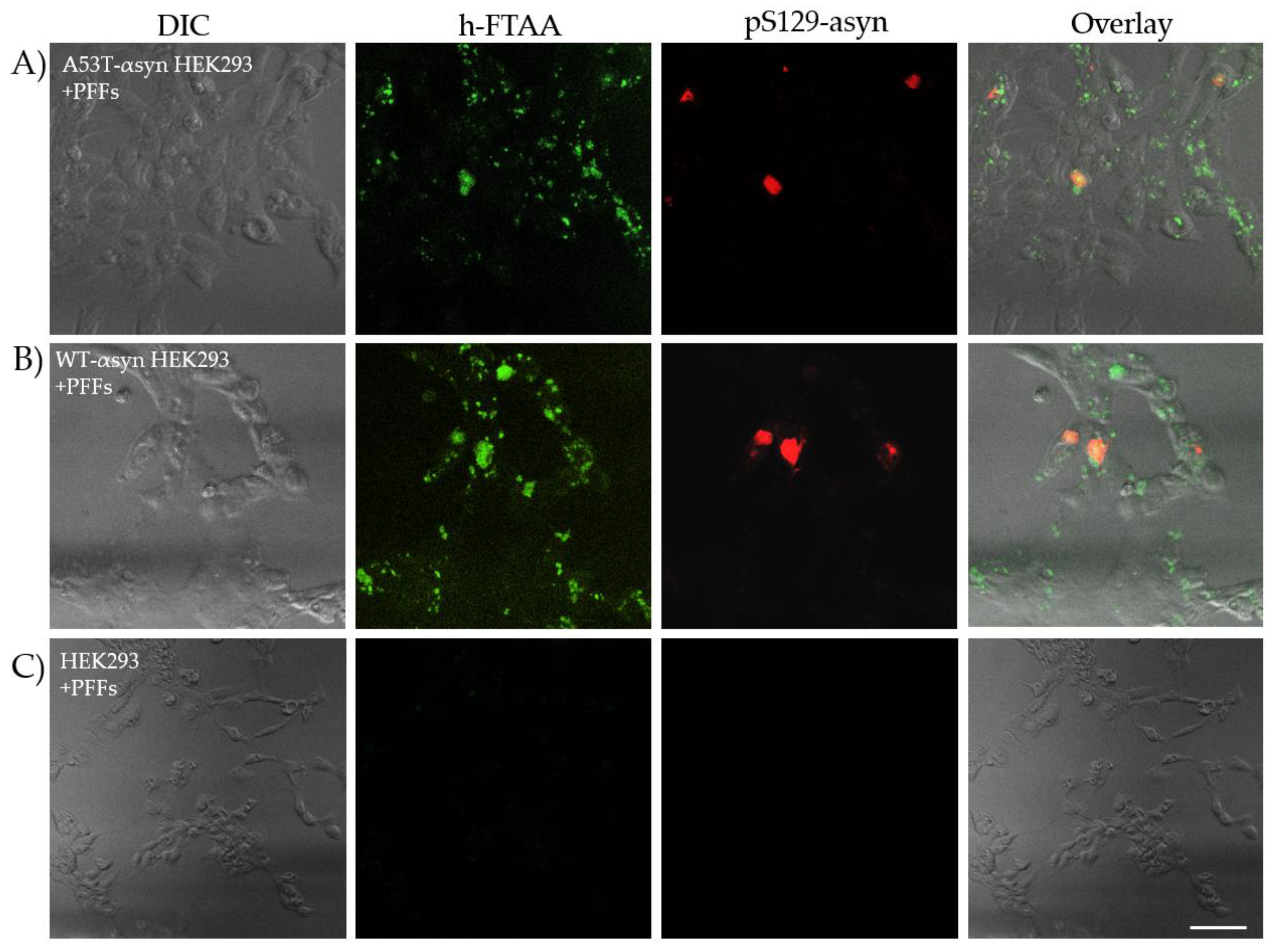
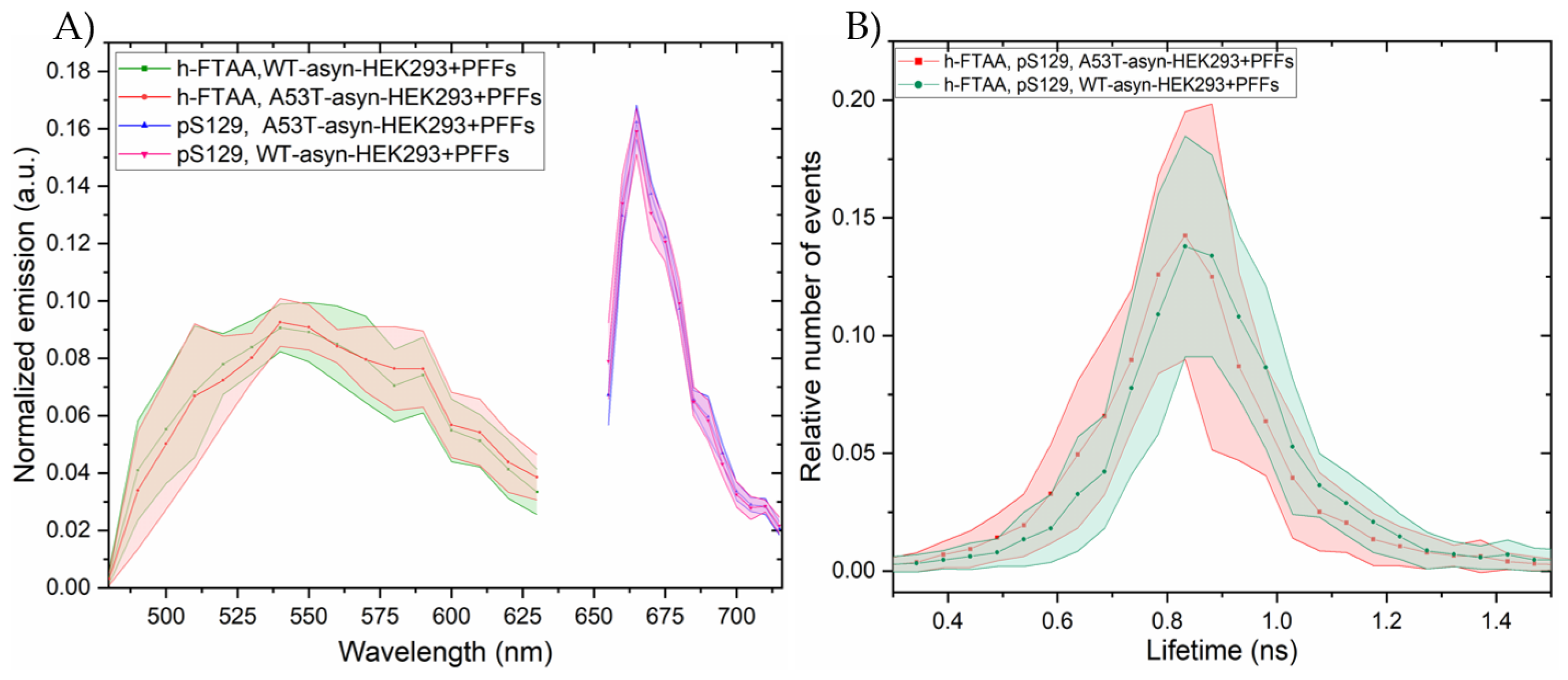
2.4. Hyperspectral Imaging and FLIM of αsyn Aggregates in HEK293 Cells
3. Discussion
4.1. Materials
4.2. Photophysical Measurements of h-FTAA in Solvents
4.3α. syn Fibril Formation
4.4. Emission of αsyn PFFs Together with h-FTAA and Simulation of Binding Curves
4.5. In-Vitro PFFs-h-FTAA Characterization Using Hyperspectral Imaging and FLIM
4.6. Cell Cultivation
4.7. Transfection with A53T or WT-αsyn
4.8. Seeding with αsyn PFFs
4.9. Staining with h-FTAA, DRAQ5 and Hyperspectral Microscopy
4.10. FACS for Assessing Transfection Efficiency
4.11. Western Blotting
4.12. Immunocytochemistry
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peelaerts, W.; Bousset, L.; Van der Perren, A.; Moskalyuk, A.; Pulizzi, R.; Giugliano, M.; Van den Haute, C.; Melki, R.; Baekelandt, V. α-Synuclein strains cause distinct synucleinopathies after local and systemic administration. Nature 2015, 522 (7556), 340-344. [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Gathagan, R. J.; Covell, D. J.; Medellin, C.; Stieber, A.; Robinson, J. L.; Zhang, B.; Pitkin, R. M.; Olufemi, M. F.; Luk, K. C.; et al. Cellular milieu imparts distinct pathological α-synuclein strains in α-synucleinopathies. Nature 2018, 557 (7706), 558-563. [CrossRef]
- Strohäker, T.; Jung, B. C.; Liou, S.-H.; Fernandez, C. O.; Riedel, D.; Becker, S.; Halliday, G. M.; Bennati, M.; Kim, W. S.; Lee, S.-J.; et al. Structural heterogeneity of α-synuclein fibrils amplified from patient brain extracts. Nature Communications 2019, 10 (1), 5535. [CrossRef]
- Peelaerts, W.; Baekelandt, V. ⍺-Synuclein Structural Diversity and the Cellular Environment in ⍺-Synuclein Transmission Models and Humans. Neurotherapeutics 2023, 20 (1), 67-82. [CrossRef]
- Holec, S. A. M.; Woerman, A. L. Evidence of distinct α-synuclein strains underlying disease heterogeneity. Acta Neuropathologica 2021, 142 (1), 73-86. [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ge, P.; Murray, K. A.; Sheth, P.; Zhang, M.; Nair, G.; Sawaya, M. R.; Shin, W. S.; Boyer, D. R.; Ye, S.; et al. Cryo-EM of full-length α-synuclein reveals fibril polymorphs with a common structural kernel. Nature Communications 2018, 9 (1), 3609. [CrossRef]
- Grazia Spillantini, M.; Anthony Crowther, R.; Jakes, R.; Cairns, N. J.; Lantos, P. L.; Goedert, M. Filamentous α-synuclein inclusions link multiple system atrophy with Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neuroscience Letters 1998, 251 (3), 205-208. [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Lv, S.; Xia, W.; Zhao, K.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, Q.; He, L.; Le, W.; Wang, Y.; et al. Heparin induces α-synuclein to form new fibril polymorphs with attenuated neuropathology. Nature Communications 2022, 13 (1), 4226. [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, S. O.; Uzunoğlu, G.; Nussbaum-Krammer, C. α-Synuclein Strains: Does Amyloid Conformation Explain the Heterogeneity of Synucleinopathies? Biomolecules 2021, 11 (7), 931.
- Schweighauser, M.; Shi, Y.; Tarutani, A.; Kametani, F.; Murzin, A. G.; Ghetti, B.; Matsubara, T.; Tomita, T.; Ando, T.; Hasegawa, K.; et al. Structures of α-synuclein filaments from multiple system atrophy. Nature 2020, 585 (7825), 464-469. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Murzin, A. G.; Peak-Chew, S.; Franco, C.; Garringer, H. J.; Newell, K. L.; Ghetti, B.; Goedert, M.; Scheres, S. H. W. Cryo-EM structures of Aβ40 filaments from the leptomeninges of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease and cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Acta Neuropathologica Communications 2023, 11 (1), 191. [CrossRef]
- Outeiro, T. F. Alpha-Synuclein Antibody Characterization: Why Semantics Matters. Mol Neurobiol 2021, 58 (5), 2202-2203. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. T.; Jagannath, S.; Francois, C.; Vanderstichele, H.; Stoops, E.; Lashuel, H. A. How specific are the conformation-specific α-synuclein antibodies? Characterization and validation of 16 α-synuclein conformation-specific antibodies using well-characterized preparations of α-synuclein monomers, fibrils and oligomers with distinct structures and morphology. Neurobiol Dis 2020, 146, 105086. [CrossRef]
- Björk, L.; Klingstedt, T.; Nilsson, K. P. R. Thiophene-Based Ligands: Design, Synthesis and Their Utilization for Optical Assignment of Polymorphic-Disease-Associated Protein Aggregates. ChemBioChem 2023, 24 (11), e202300044. [CrossRef]
- Aslund, A.; Sigurdson, C. J.; Klingstedt, T.; Grathwohl, S.; Bolmont, T.; Dickstein, D. L.; Glimsdal, E.; Prokop, S.; Lindgren, M.; Konradsson, P.; et al. Novel pentameric thiophene derivatives for in vitro and in vivo optical imaging of a plethora of protein aggregates in cerebral amyloidoses. ACS Chem Biol 2009, 4 (8), 673-684. [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Rodriguez, M.; Hou, S. S.; Snyder, A. C.; Dujardin, S.; Shirani, H.; Nilsson, K. P. R.; Bacskai, B. J. In vivo detection of tau fibrils and amyloid β aggregates with luminescent conjugated oligothiophenes and multiphoton microscopy. Acta Neuropathologica Communications 2019, 7 (1), 171. [CrossRef]
- Nyström, S.; Psonka-Antonczyk, K. M.; Ellingsen, P. G.; Johansson, L. B.; Reitan, N.; Handrick, S.; Prokop, S.; Heppner, F. L.; Wegenast-Braun, B. M.; Jucker, M.; et al. Evidence for age-dependent in vivo conformational rearrangement within Aβ amyloid deposits. ACS Chem Biol 2013, 8 (6), 1128-1133. [CrossRef]
- Klingstedt, T.; Blechschmidt, C.; Nogalska, A.; Prokop, S.; Häggqvist, B.; Danielsson, O.; Engel, W. K.; Askanas, V.; Heppner, F. L.; Nilsson, K. P. R. Luminescent Conjugated Oligothiophenes for Sensitive Fluorescent Assignment of Protein Inclusion Bodies. ChemBioChem 2013, 14 (5), 607-616. [CrossRef]
- Klingstedt, T.; Shirani, H.; Mahler, J.; Wegenast-Braun, B. M.; Nyström, S.; Goedert, M.; Jucker, M.; Nilsson, K. P. Distinct Spacing Between Anionic Groups: An Essential Chemical Determinant for Achieving Thiophene-Based Ligands to Distinguish β-Amyloid or Tau Polymorphic Aggregates. Chemistry 2015, 21 (25), 9072-9082. [CrossRef]
- Torre-Muruzabal, T.; Van der Perren, A.; Coens, A.; Gelders, G.; Janer, A. B.; Camacho-Garcia, S.; Klingstedt, T.; Nilsson, P.; Stefanova, N.; Melki, R.; et al. Host oligodendrogliopathy and α-synuclein strains dictate disease severity in multiple system atrophy. Brain 2022, 146 (1), 237-251. (acccessed 10/1/2024). [CrossRef]
- Klingstedt, T.; Ghetti, B.; Holton, J. L.; Ling, H.; Nilsson, K. P. R.; Goedert, M. Luminescent conjugated oligothiophenes distinguish between α-synuclein assemblies of Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Acta Neuropathologica Communications 2019, 7 (1), 193. [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, J.; Mahler, J.; Beschorner, N.; Kaeser, S. A.; Häsler, L. M.; Baumann, F.; Nyström, S.; Portelius, E.; Blennow, K.; Lashley, T.; et al. Amyloid polymorphisms constitute distinct clouds of conformational variants in different etiological subtypes of Alzheimer’s disease. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2017, 114 (49), 13018-13023. [CrossRef]
- Klingstedt, T.; Nilsson, K. P. R. Conjugated polymers for enhanced bioimaging. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects 2011, 1810 (3), 286-296. [CrossRef]
- BECKER, W. Fluorescence lifetime imaging – techniques and applications. Journal of Microscopy 2012, 247 (2), 119-136. [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, K.; Simon, R.; Sjölander, D.; Sigurdson, C. J.; Hammarström, P.; Nilsson, K. P. R. Multimodal fluorescence microscopy of prion strain specific PrP deposits stained by thiophene-based amyloid ligands. Prion 2014, 8 (4), 319-329. [CrossRef]
- Just, M. K.; Gram, H.; Theologidis, V.; Jensen, P. H.; Nilsson, K. P. R.; Lindgren, M.; Knudsen, K.; Borghammer, P.; Van Den Berge, N. Alpha-Synuclein Strain Variability in Body-First and Brain-First Synucleinopathies. Front Aging Neurosci 2022, 14, 907293. [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Calvo, P.; Bett, C.; Sevillano, A. M.; Kurt, T. D.; Lawrence, J.; Soldau, K.; Hammarström, P.; Nilsson, K. P. R.; Sigurdson, C. J. Generation of novel neuroinvasive prions following intravenous challenge. Brain Pathology 2018, 28 (6), 999-1011. [CrossRef]
- Sevillano, A. M.; Aguilar-Calvo, P.; Kurt, T. D.; Lawrence, J. A.; Soldau, K.; Nam, T. H.; Schumann, T.; Pizzo, D. P.; Nyström, S.; Choudhury, B.; et al. Prion protein glycans reduce intracerebral fibril formation and spongiosis in prion disease. J Clin Invest 2020, 130 (3), 1350-1362. [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, J. D.; Ulland, T. K.; Mahan, T. E.; Nyström, S.; Nilsson, K. P.; Song, W. M.; Zhou, Y.; Reinartz, M.; Choi, S.; Jiang, H.; et al. ApoE facilitates the microglial response to amyloid plaque pathology. J Exp Med 2018, 215 (4), 1047-1058. [CrossRef]
- Narhi, L.; Wood, S. J.; Steavenson, S.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, G. M.; Anafi, D.; Kaufman, S. A.; Martin, F.; Sitney, K.; Denis, P.; et al. Both Familial Parkinson’s Disease Mutations Accelerate α-Synuclein Aggregation *. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1999, 274 (14), 9843-9846. (acccessed 2024/08/01). [CrossRef]
- Giasson, B. I.; Duda, J. E.; Quinn, S. M.; Zhang, B.; Trojanowski, J. Q.; Lee, V. M.-Y. Neuronal α-synucleinopathy with severe movement disorder in mice expressing A53T human α-synuclein. Neuron 2002, 34 (4), 521-533.
- Sun, Y.; Hou, S.; Zhao, K.; Long, H.; Liu, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Su, X.-D.; Li, D.; Liu, C. Cryo-EM structure of full-length α-synuclein amyloid fibril with Parkinson’s disease familial A53T mutation. Cell Research 2020, 30 (4), 360-362. [CrossRef]
- Klingstedt, T.; Aslund, A.; Simon, R. A.; Johansson, L. B.; Mason, J. J.; Nyström, S.; Hammarström, P.; Nilsson, K. P. Synthesis of a library of oligothiophenes and their utilization as fluorescent ligands for spectral assignment of protein aggregates. Org Biomol Chem 2011, 9 (24), 8356-8370. [CrossRef]
- Rurack, K.; Spieles, M. Fluorescence Quantum Yields of a Series of Red and Near-Infrared Dyes Emitting at 600−1000 nm. Analytical Chemistry 2011, 83 (4), 1232-1242. [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, C.; Shirani, H.; Leira, P.; Rehn, D. R.; Linares, M.; Nilsson, K. P. R.; Norman, P.; Lindgren, M. Deciphering the Electronic Transitions of Thiophene-Based Donor-Acceptor-Donor Pentameric Ligands Utilized for Multimodal Fluorescence Microscopy of Protein Aggregates. ChemPhysChem 2021, 22 (3), 323-335. [CrossRef]
- Sundnes, M. L. Some Fluorescent Ligands for Studying Amyloid Uptake in Human Cell Models. Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), Trondheim,Norway, 2023. https://hdl.handle.net/11250/3096572.
- Herrmann, U. S.; Schütz, A. K.; Shirani, H.; Huang, D.; Saban, D.; Nuvolone, M.; Li, B.; Ballmer, B.; Åslund, A. K. O.; Mason, J. J.; et al. Structure-based drug design identifies polythiophenes as antiprion compounds. Science Translational Medicine 2015, 7 (299), 299ra123-299ra123. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C. G.; Meisl, G.; Horrocks, M. H.; Zetterberg, H.; Knowles, T. P. J.; Klenerman, D. Extrinsic Amyloid-Binding Dyes for Detection of Individual Protein Aggregates in Solution. Anal Chem 2018, 90 (17), 10385-10393. [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Swaminathan, P.; Björk, L.; Nakanishi, A.; Sato, H.; Zako, T.; Nilsson, K. P. R.; Lindgren, M. Spectroscopic Response of Chiral Proteophenes Binding to Two Chiral Insulin Amyloids. ChemPhotoChem n/a (n/a), e202400225. [CrossRef]
- Sundnes, M.; Swaminathan, P.; Lindgren, M.; Mohite, G.; Hellstrand, E.; Nyström, S.; Hammarström, P. The fluorescent amyloid ligand X34 binding to TTR tetramer and TTR fibrils: FRET and binding constants of a sequential two-step process. ChemPhotoChem Submitted, June 2024.
- Lee, M. K.; Stirling, W.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Qui, D.; Mandir, A. S.; Dawson, T. M.; Copeland, N. G.; Jenkins, N. A.; Price, D. L. Human α-synuclein-harboring familial Parkinson’s disease-linked Ala-53 → Thr mutation causes neurodegenerative disease with α-synuclein aggregation in transgenic mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2002, 99 (13), 8968-8973. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J. P.; Walker, D. E.; Goldstein, J. M.; de Laat, R.; Banducci, K.; Caccavello, R. J.; Barbour, R.; Huang, J.; Kling, K.; Lee, M.; et al. Phosphorylation of Ser-129 Is the Dominant Pathological Modification of α-Synuclein in Familial and Sporadic Lewy Body Disease *<sup></sup>. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2006, 281 (40), 29739-29752. (acccessed 2024/08/02). [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, H.; Hasegawa, M.; Dohmae, N.; Kawashima, A.; Masliah, E.; Goldberg, M. S.; Shen, J.; Takio, K.; Iwatsubo, T. α-Synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nature Cell Biology 2002, 4 (2), 160-164. [CrossRef]
- Delic, V.; Chandra, S.; Abdelmotilib, H.; Maltbie, T.; Wang, S.; Kem, D.; Scott, H. J.; Underwood, R. N.; Liu, Z.; Volpicelli-Daley, L. A.; et al. Sensitivity and specificity of phospho-Ser129 α-synuclein monoclonal antibodies. J Comp Neurol 2018, 526 (12), 1978-1990. [CrossRef]
- Lashuel, H. A.; Mahul-Mellier, A.-L.; Novello, S.; Hegde, R. N.; Jasiqi, Y.; Altay, M. F.; Donzelli, S.; DeGuire, S. M.; Burai, R.; Magalhães, P.; et al. Revisiting the specificity and ability of phospho-S129 antibodies to capture alpha-synuclein biochemical and pathological diversity. npj Parkinson’s Disease 2022, 8 (1), 136. [CrossRef]
- Sjöqvist, J.; Linares, M.; Lindgren, M.; Norman, P. Molecular dynamics effects on luminescence properties of oligothiophene derivatives: a molecular mechanics–response theory study based on the CHARMM force field and density functional theory. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2011, 13 (39), 17532-17542, 10.1039/C1CP21252D. [CrossRef]
- Chung, C. W.; Stephens, A. D.; Ward, E.; Feng, Y.; Davis, M. J.; Kaminski, C. F.; Kaminski Schierle, G. S. Label-Free Characterization of Amyloids and Alpha-Synuclein Polymorphs by Exploiting Their Intrinsic Fluorescence Property. Analytical Chemistry 2022, 94 (13), 5367-5374. [CrossRef]
- Graham, F. L.; Smiley, J.; Russell, W. C.; Nairn, R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol 1977, 36 (1), 59-74. [CrossRef]
- Holmqvist, S.; Chutna, O.; Bousset, L.; Aldrin-Kirk, P.; Li, W.; Björklund, T.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Roybon, L.; Melki, R.; Li, J.-Y. Direct evidence of Parkinson pathology spread from the gastrointestinal tract to the brain in rats. Acta Neuropathologica 2014, 128 (6), 805-820. [CrossRef]
- Uemura, N.; Yagi, H.; Uemura, M. T.; Hatanaka, Y.; Yamakado, H.; Takahashi, R. Inoculation of α-synuclein preformed fibrils into the mouse gastrointestinal tract induces Lewy body-like aggregates in the brainstem via the vagus nerve. Molecular Neurodegeneration 2018, 13 (1), 21. [CrossRef]
- Van Den Berge, N.; Ferreira, N.; Gram, H.; Mikkelsen, T. W.; Alstrup, A. K. O.; Casadei, N.; Tsung-Pin, P.; Riess, O.; Nyengaard, J. R.; Tamgüney, G.; et al. Evidence for bidirectional and trans-synaptic parasympathetic and sympathetic propagation of alpha-synuclein in rats. Acta Neuropathologica 2019, 138 (4), 535-550. [CrossRef]

| Solvent | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBS | |||||
| EtOH | |||||
| MeOH |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





