Submitted:
24 October 2024
Posted:
25 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
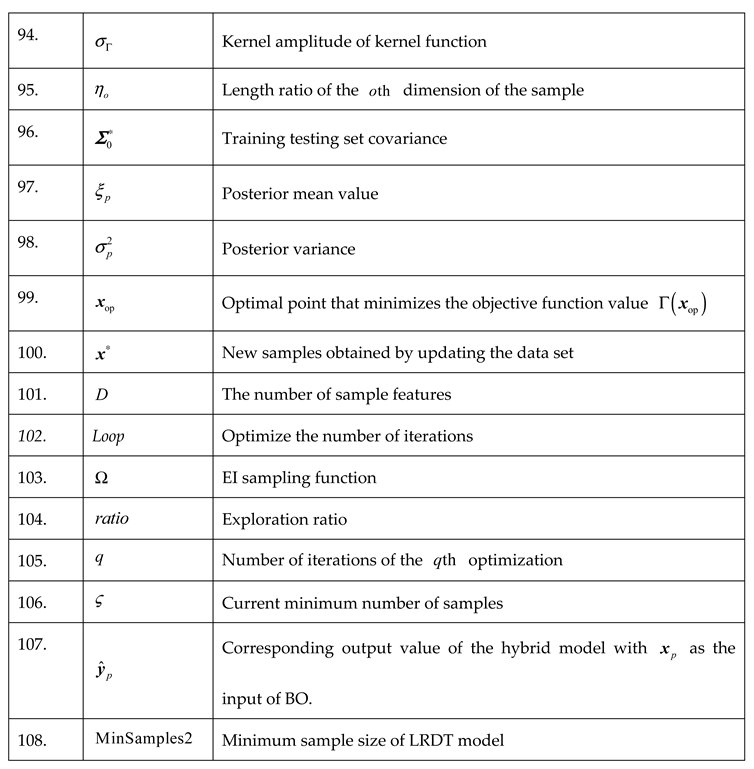
2.1. MSWI Process Description for Key Controlled Variables
2.2. Flue Gas Oxygen Content Control Description
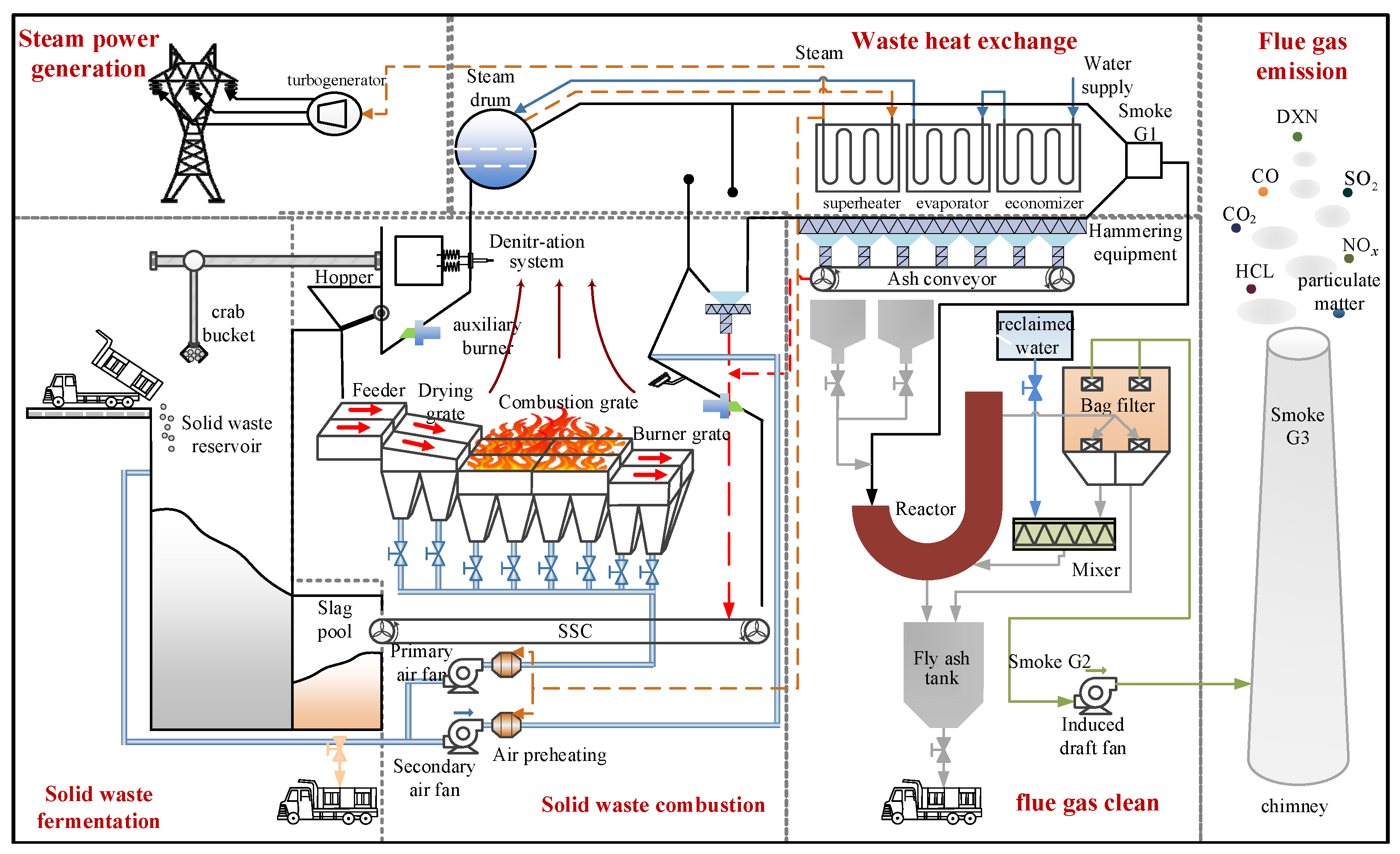
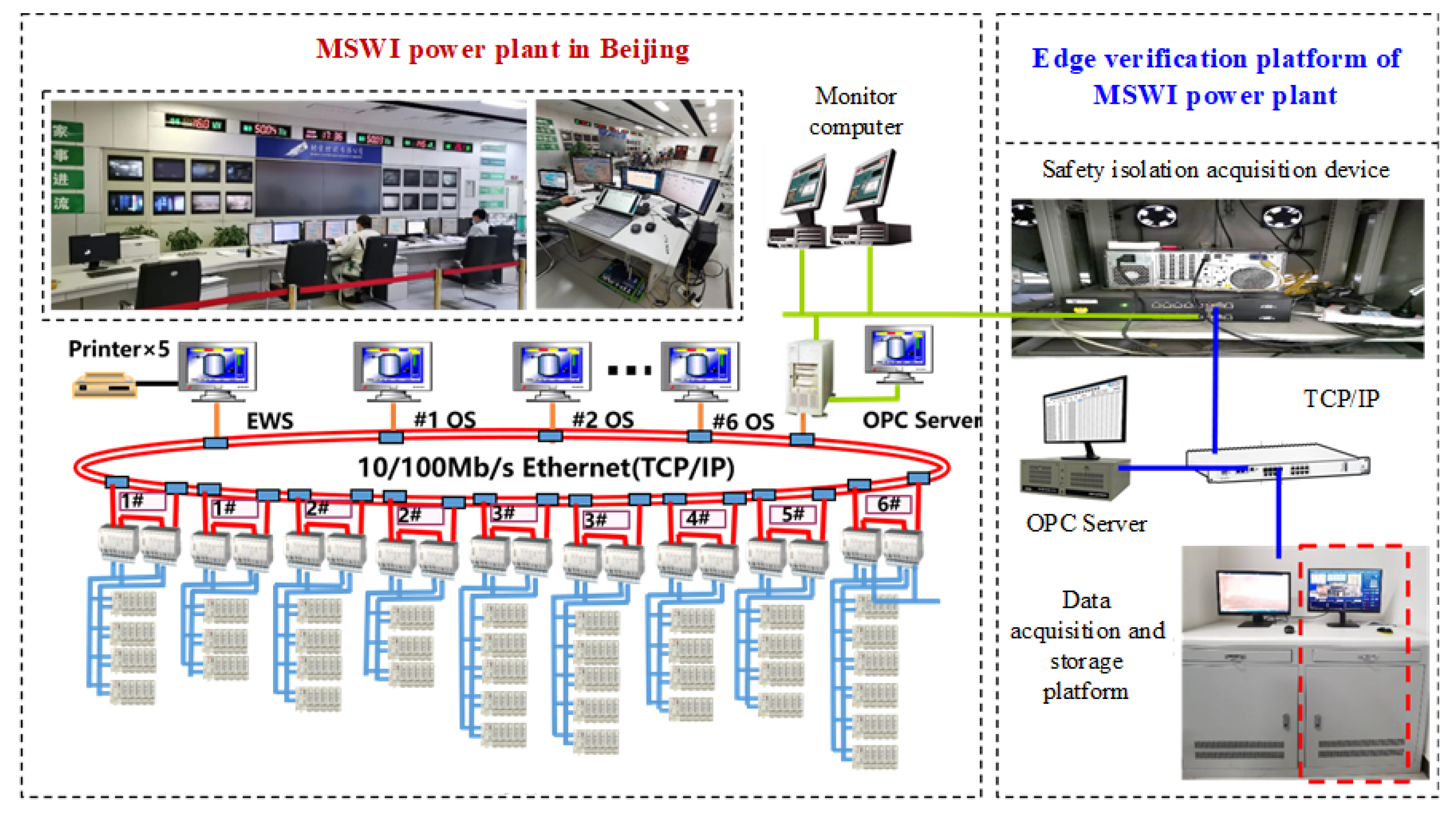
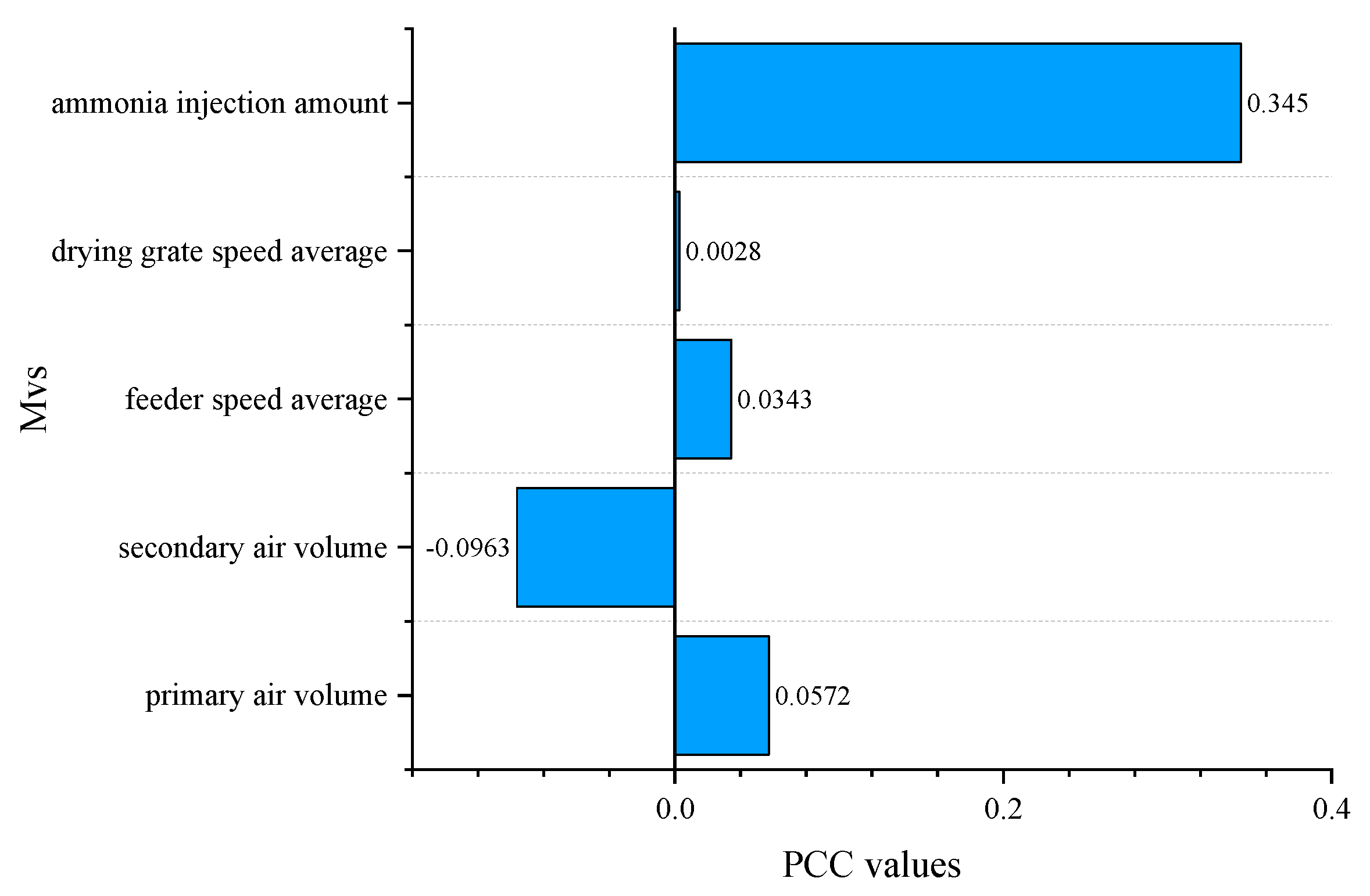
2.3. Data Acquisition Devices Description and Experimental Data Analysis
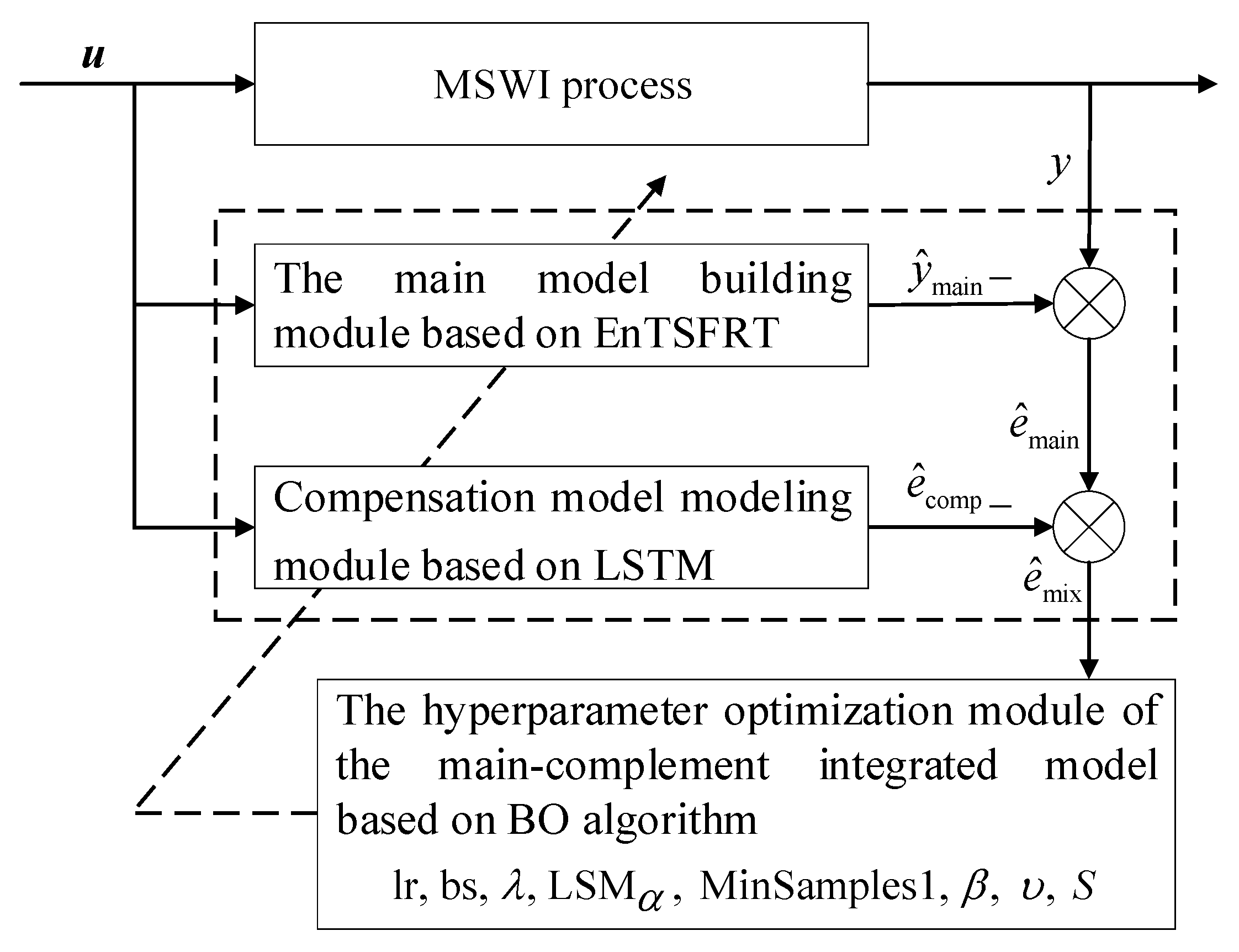
2.4. Modeling Strategy
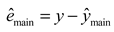
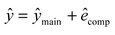
2.5. Algorithm Implementation
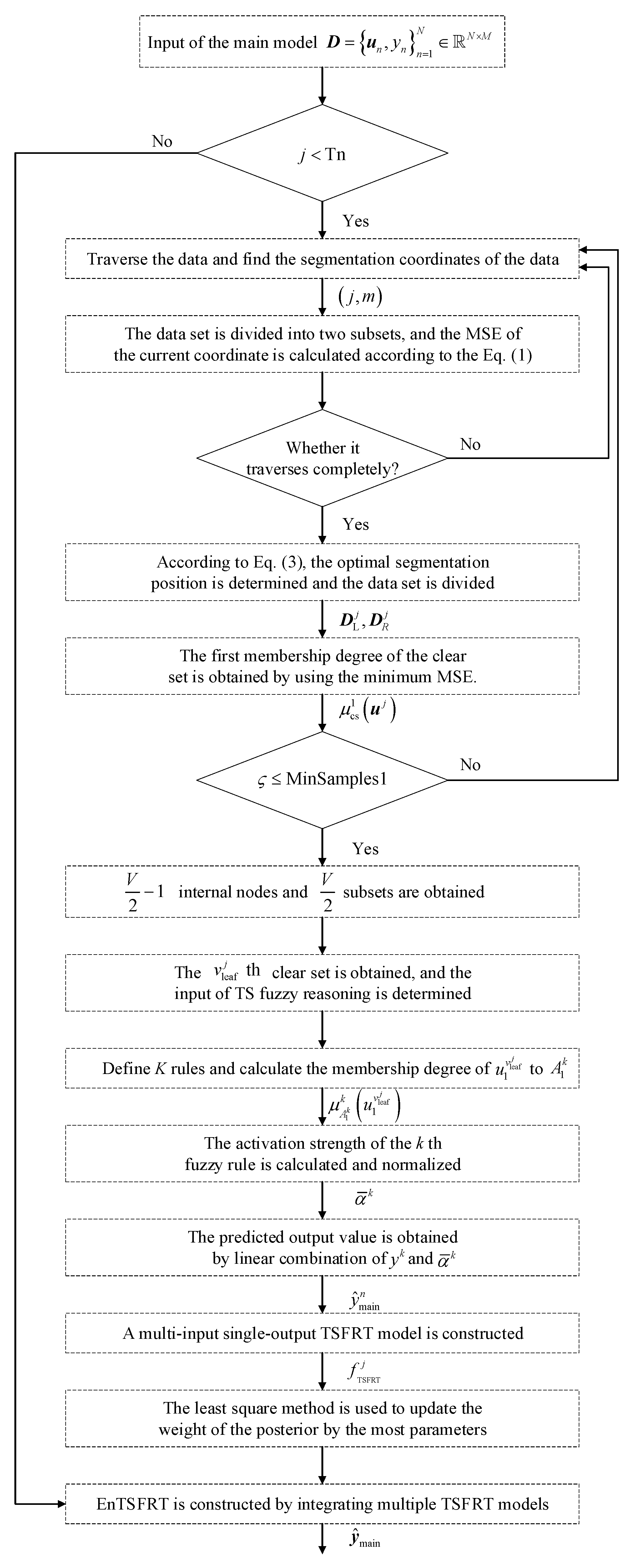
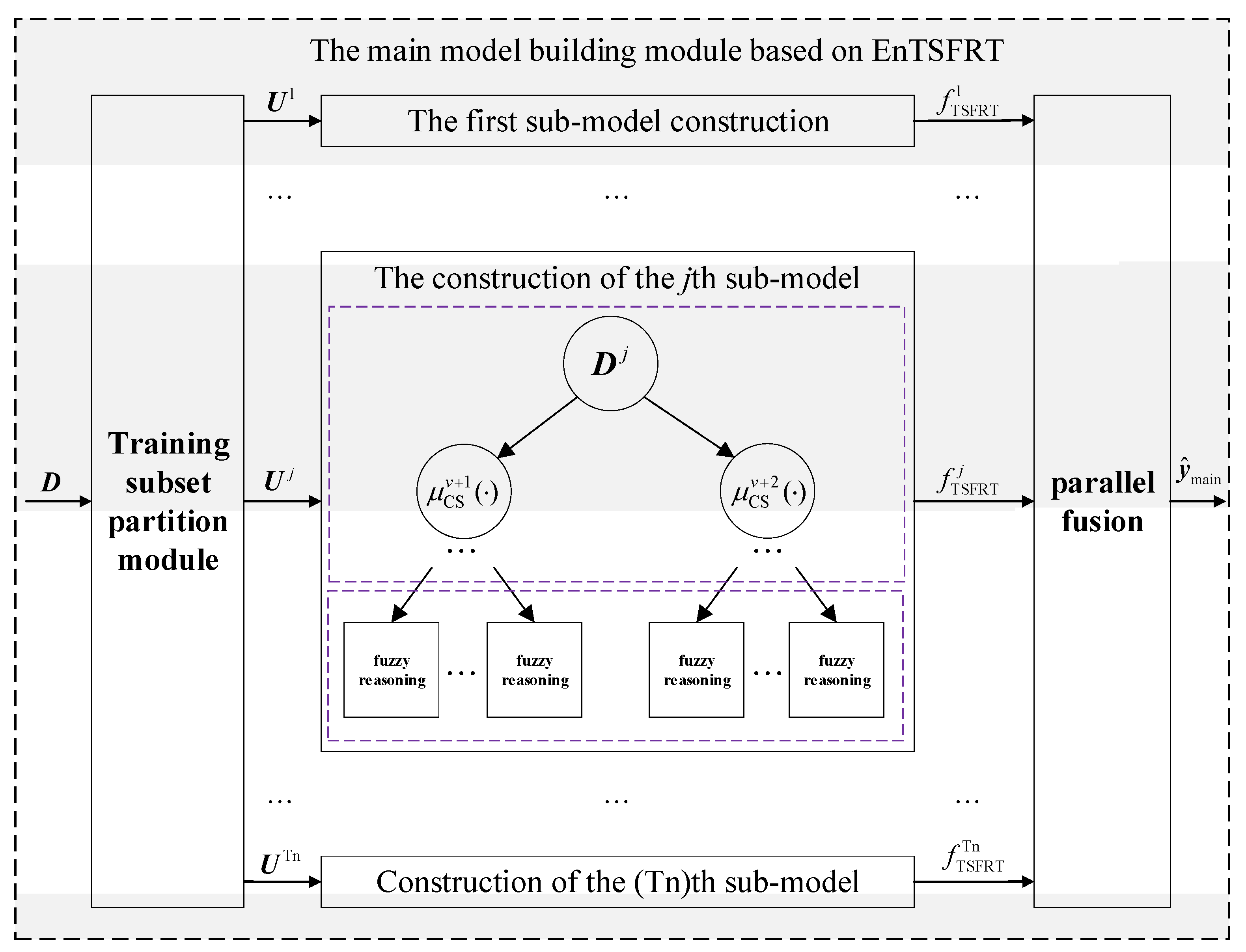
2.5.1. Main Model Construction Module Based on EnTSFRT
2.5.1.1. Training Subsets Partition Submodule
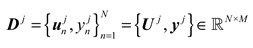
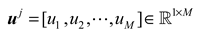
2.5.1.2. Sub-Model Construction Submodule
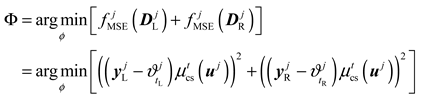
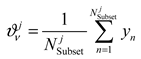
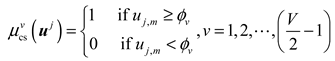
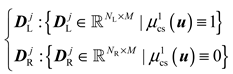
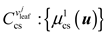
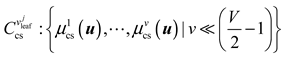
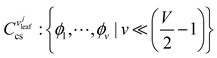
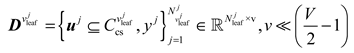
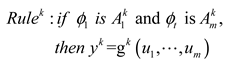
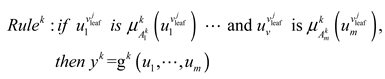
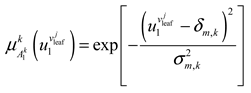
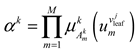
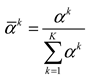
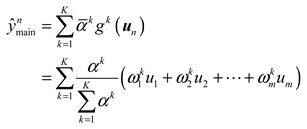
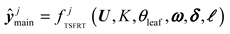
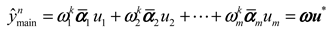
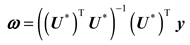
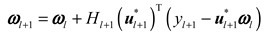
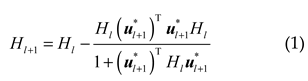
2.5.1.3. Parallel Fusion Submodule
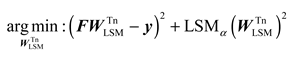
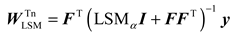
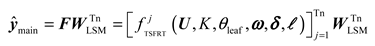
2.5.1.4. Flow Chart of Main Model Modeling
2.5.2. Compensation Model Construction Module Based on LSTM
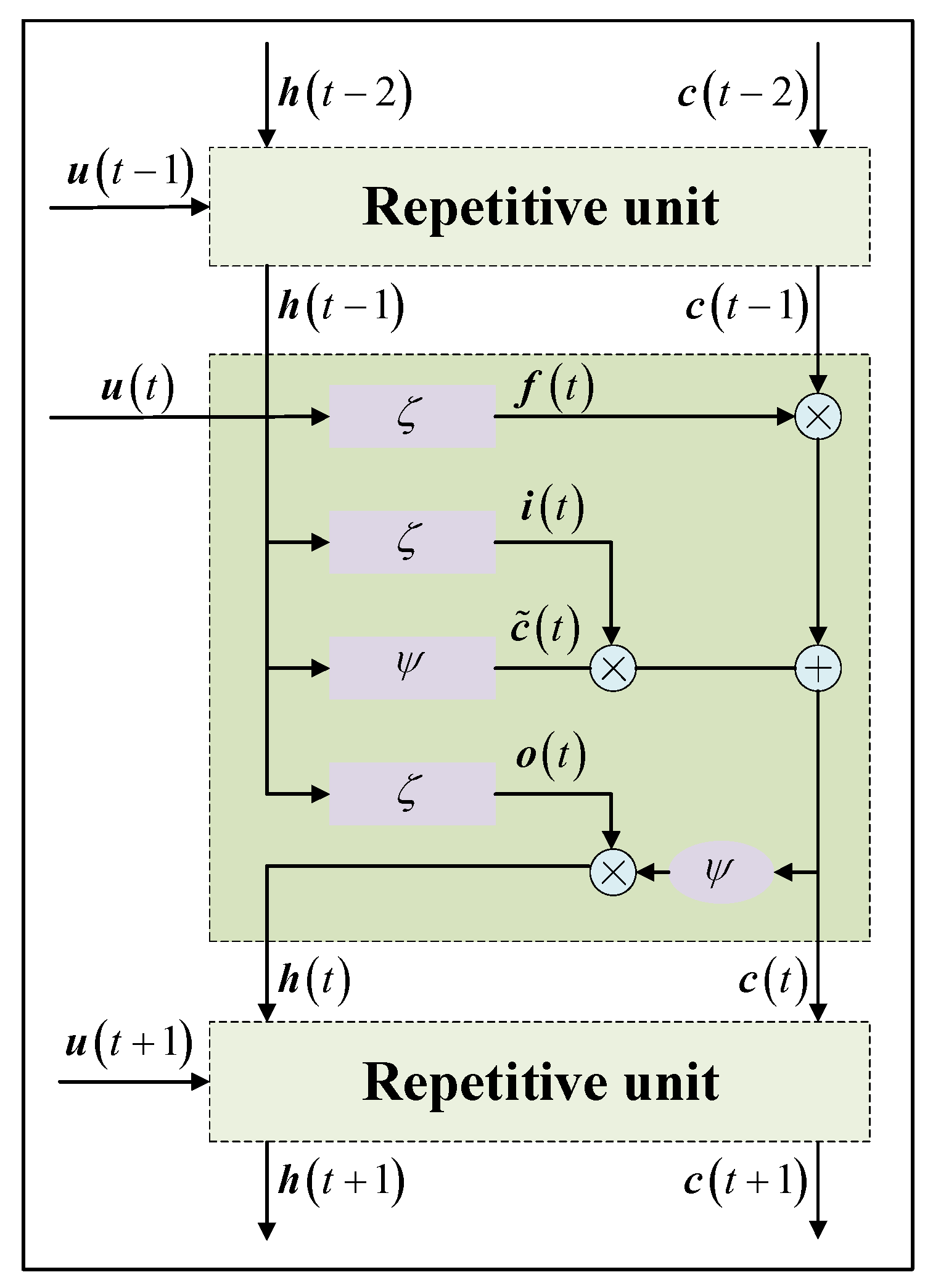
2.5.2.1. Forward Calculation Process
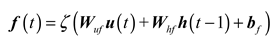
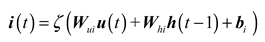
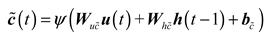
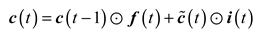
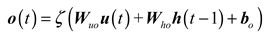
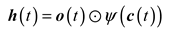
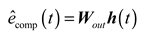
2.5.2.2. Back Propagation Process
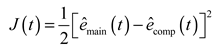
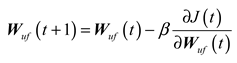
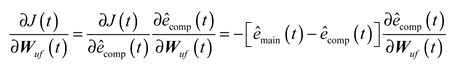
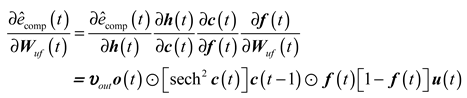
2.5.2.3. Flow Chart of Compensation Model Modeling
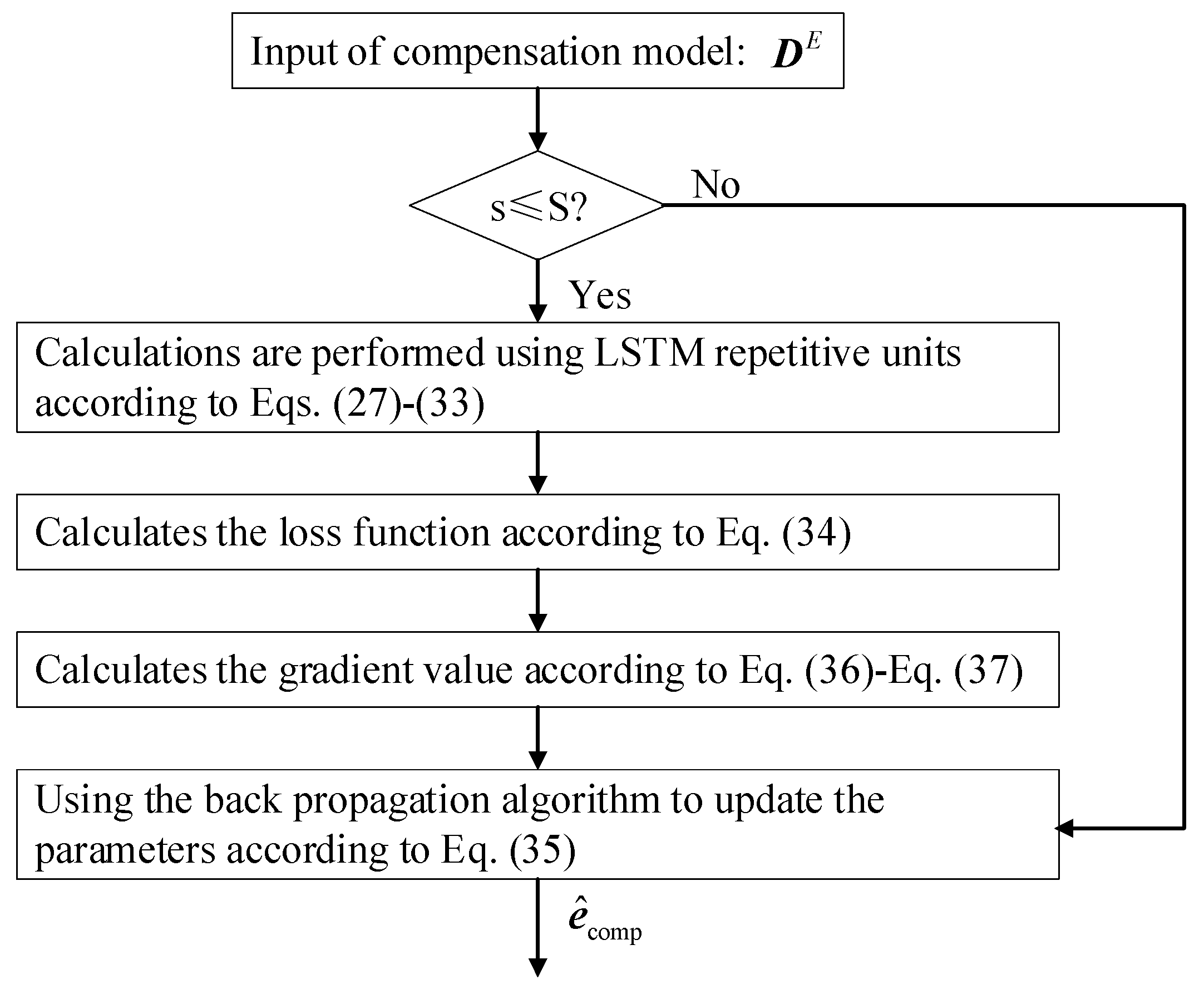
2.5.3. Hyperparameter Optimization Module Based on BO Algorithm
2.5.3.1. The Principle of BO Algorithm
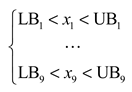

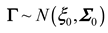
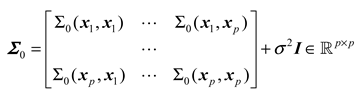
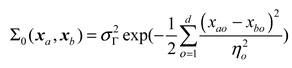
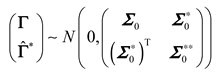
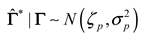
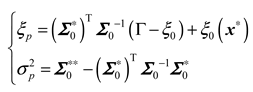
2.5.3.2. The Flow Chart of BO Algorithm
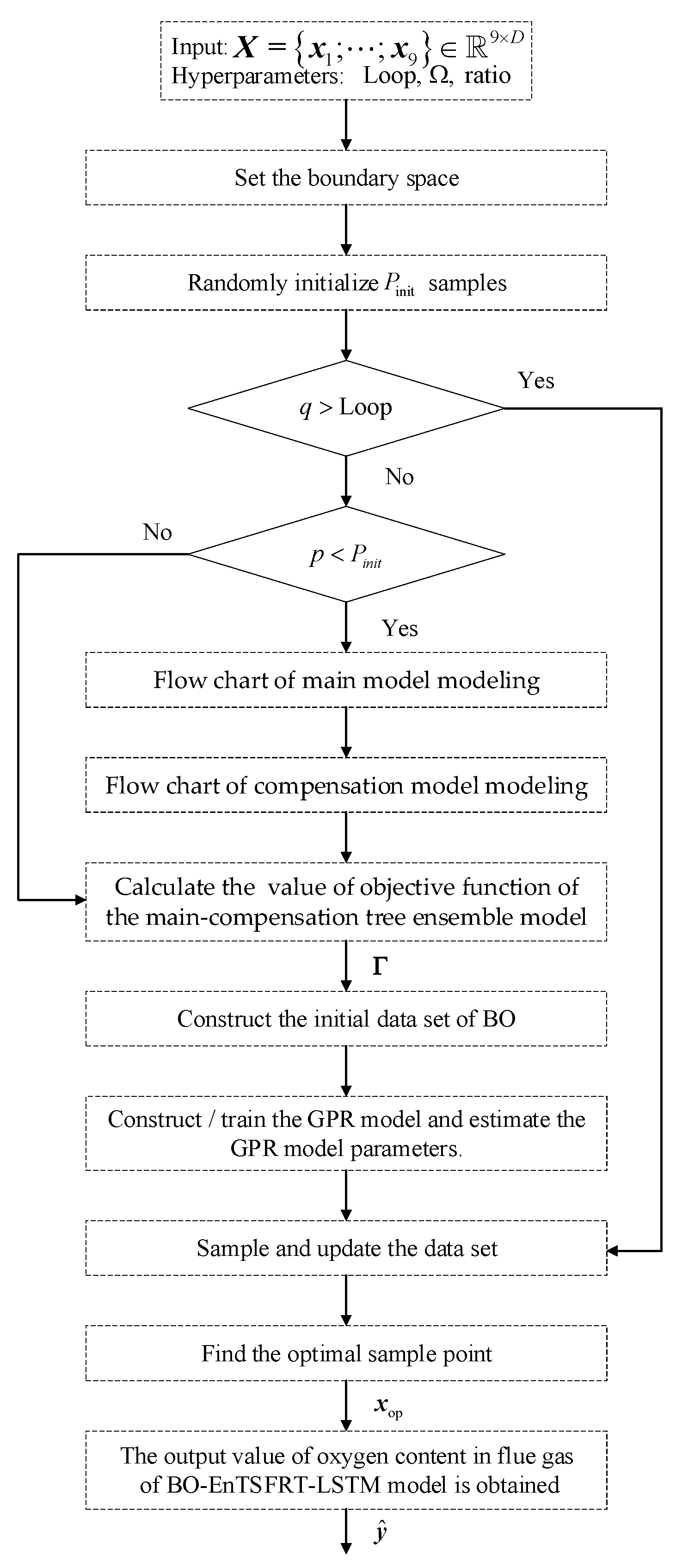
2.6. pseudo code
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance Metrics
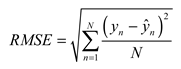
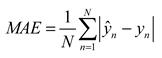
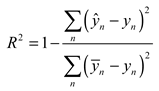
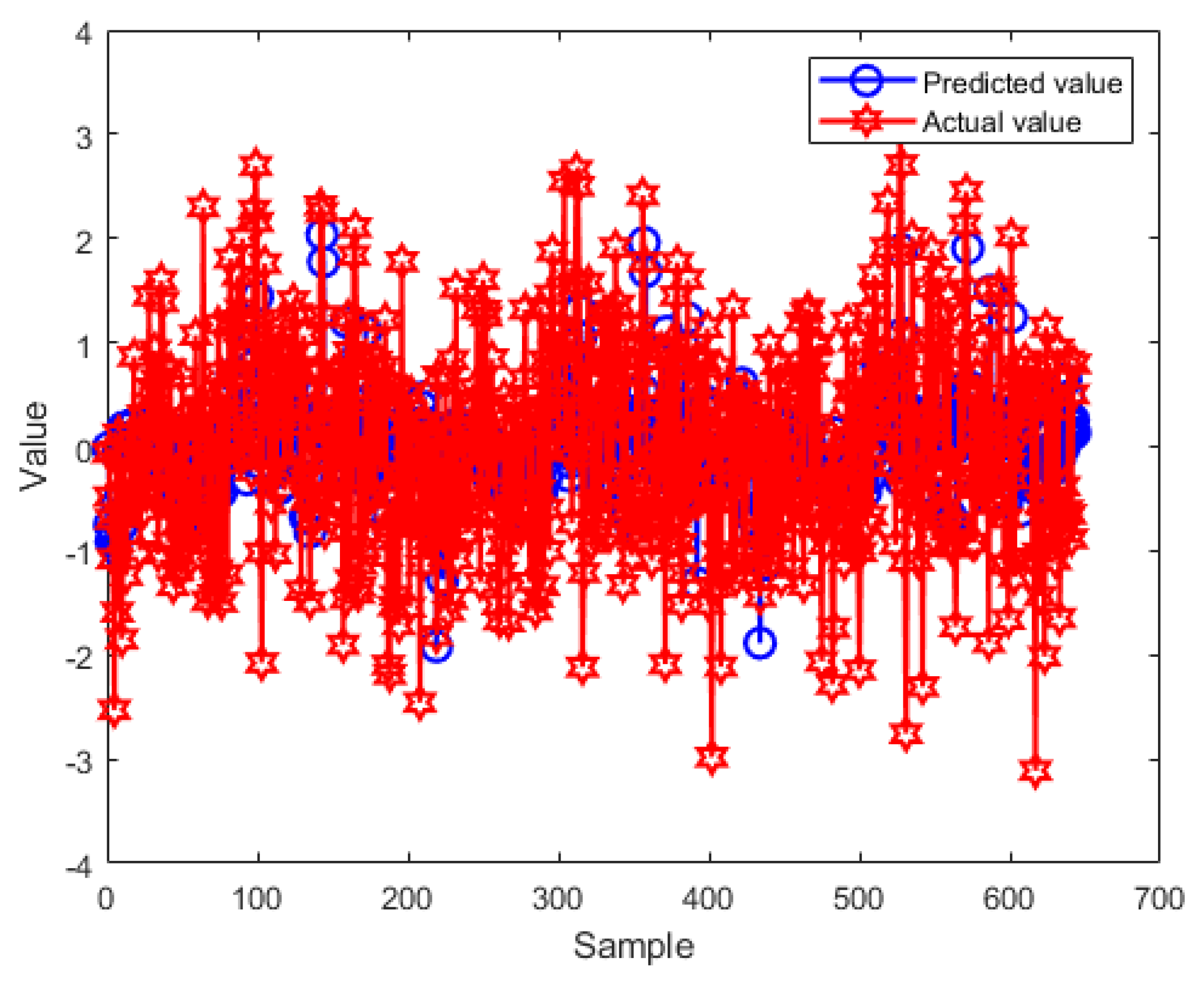
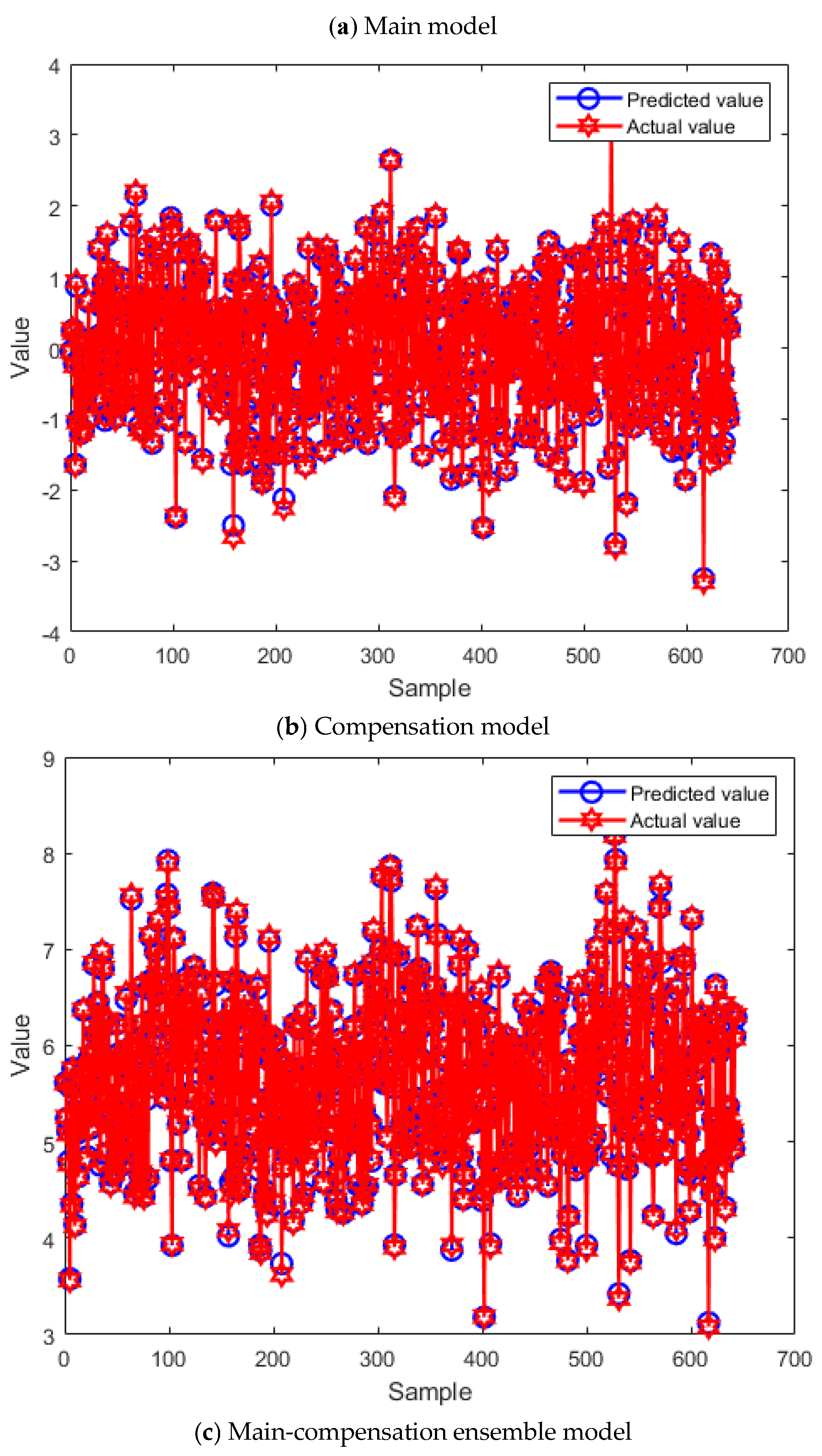
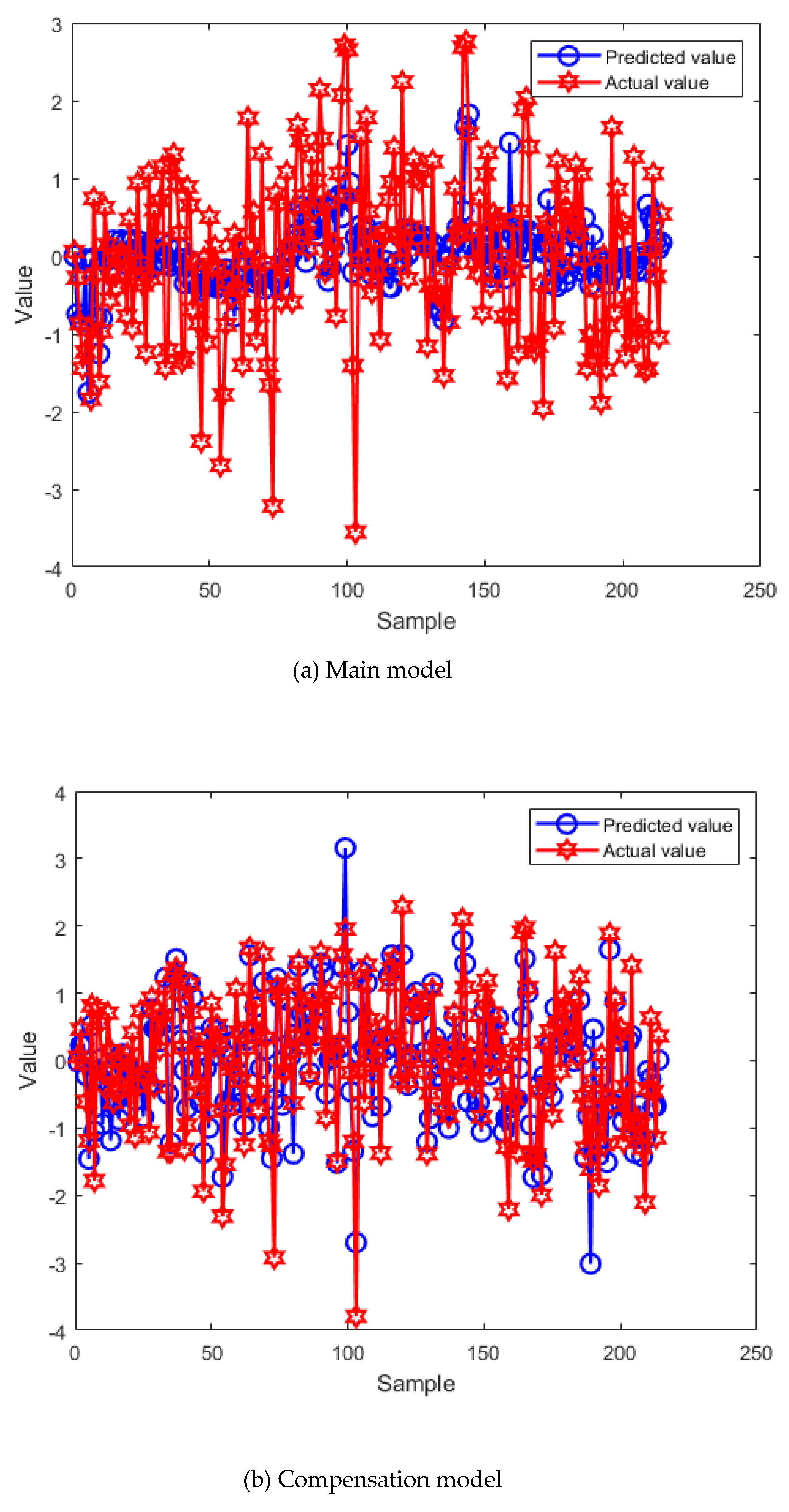
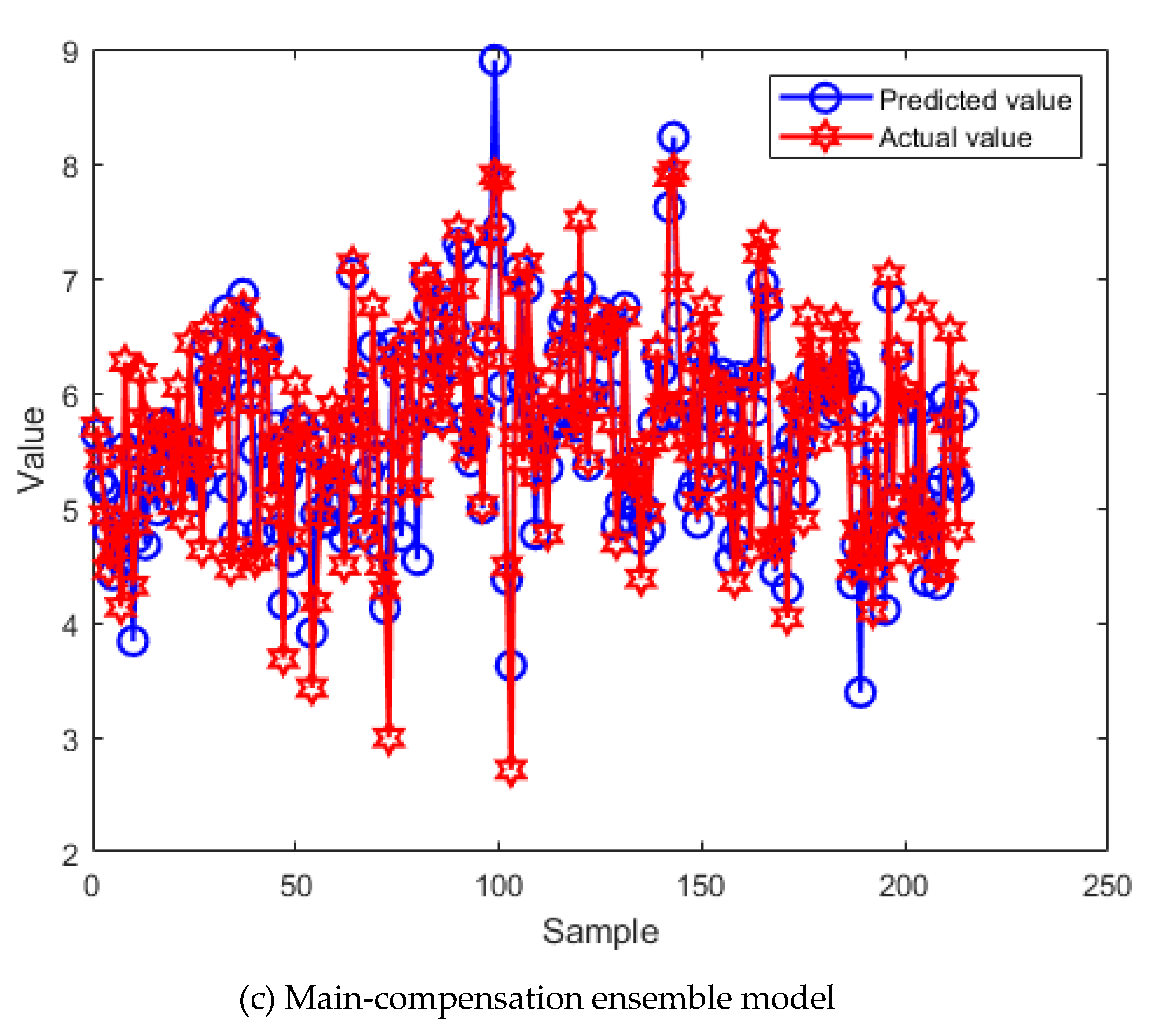
3.2. Experimental Results
3.3. Comparison and Discussion
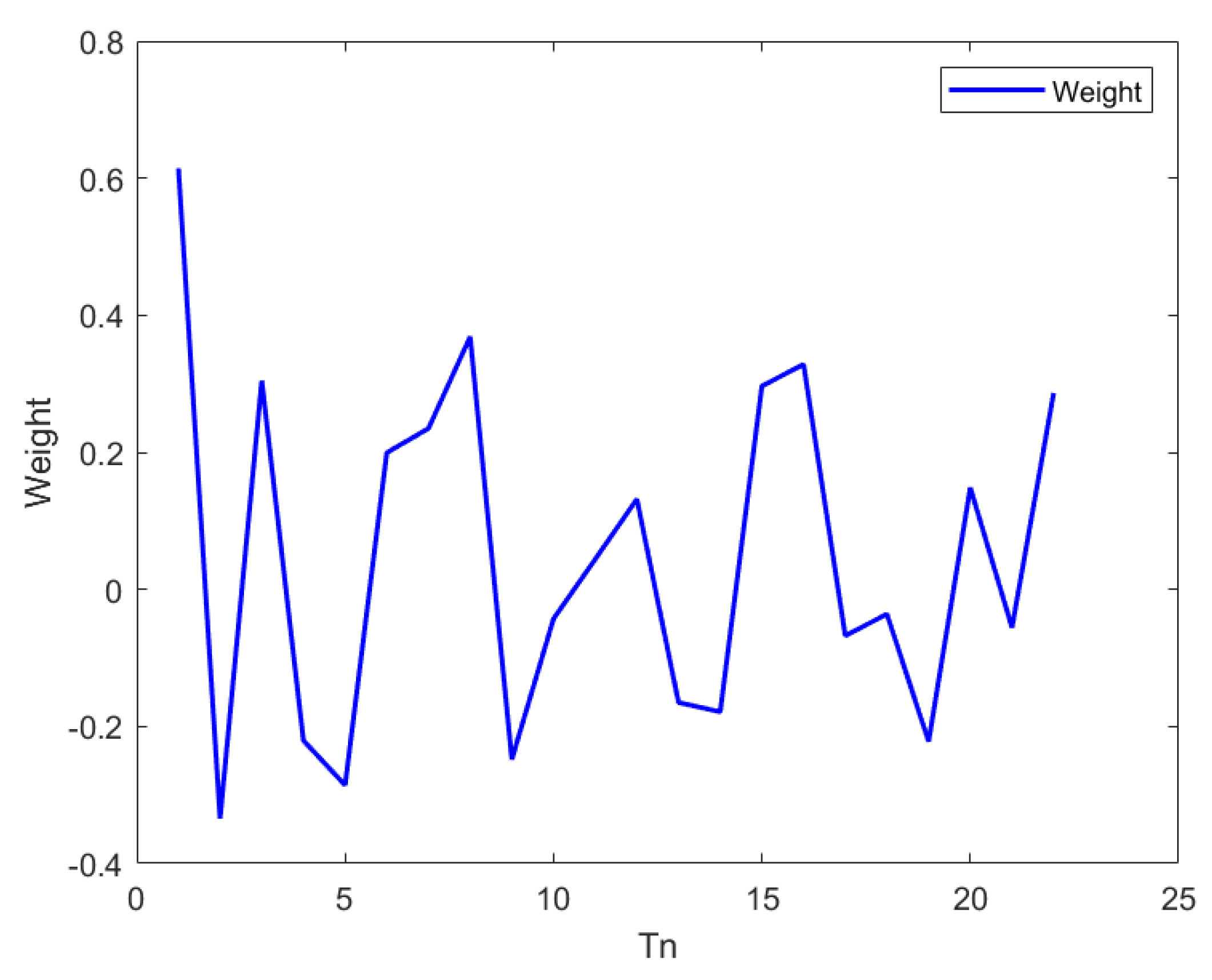
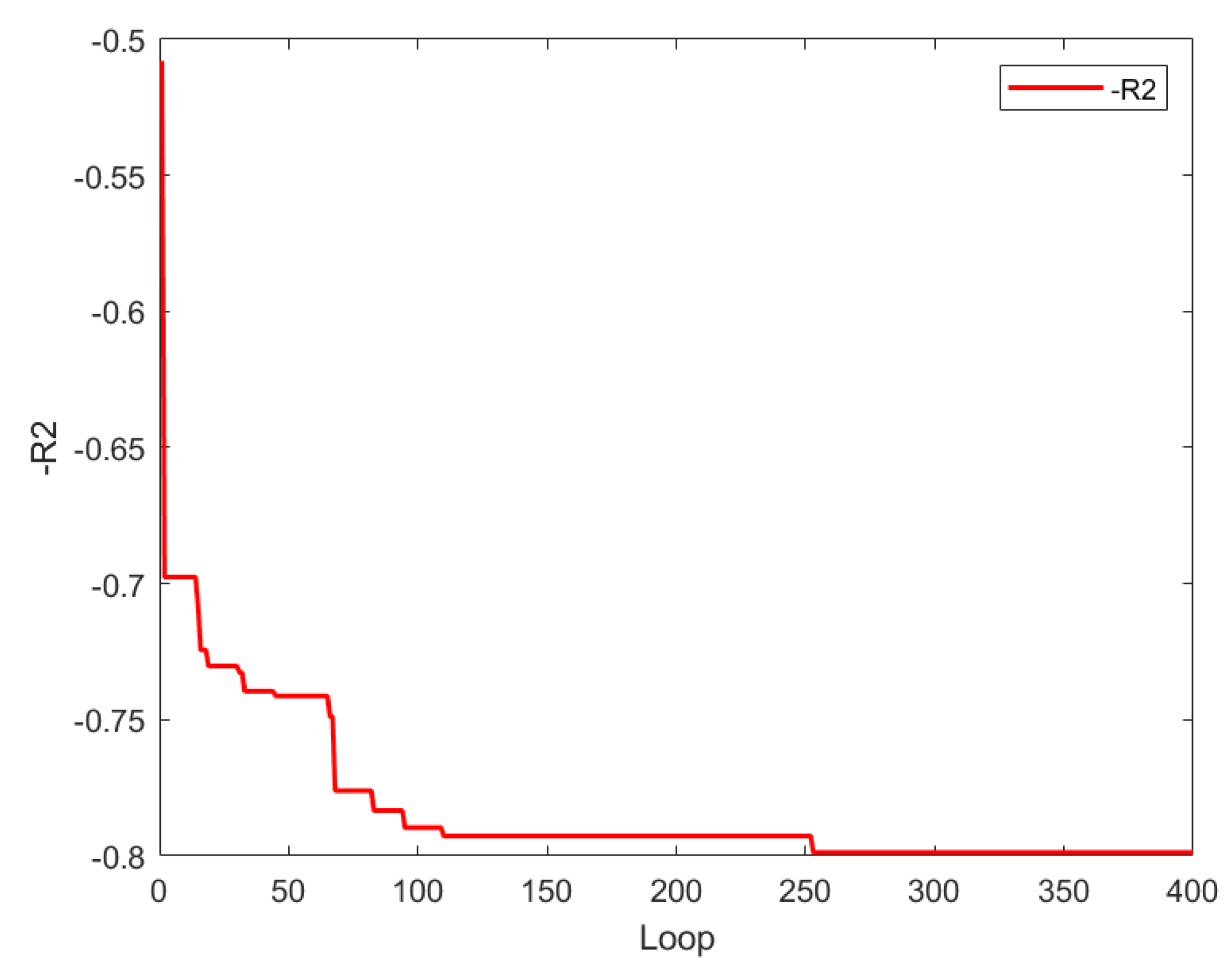
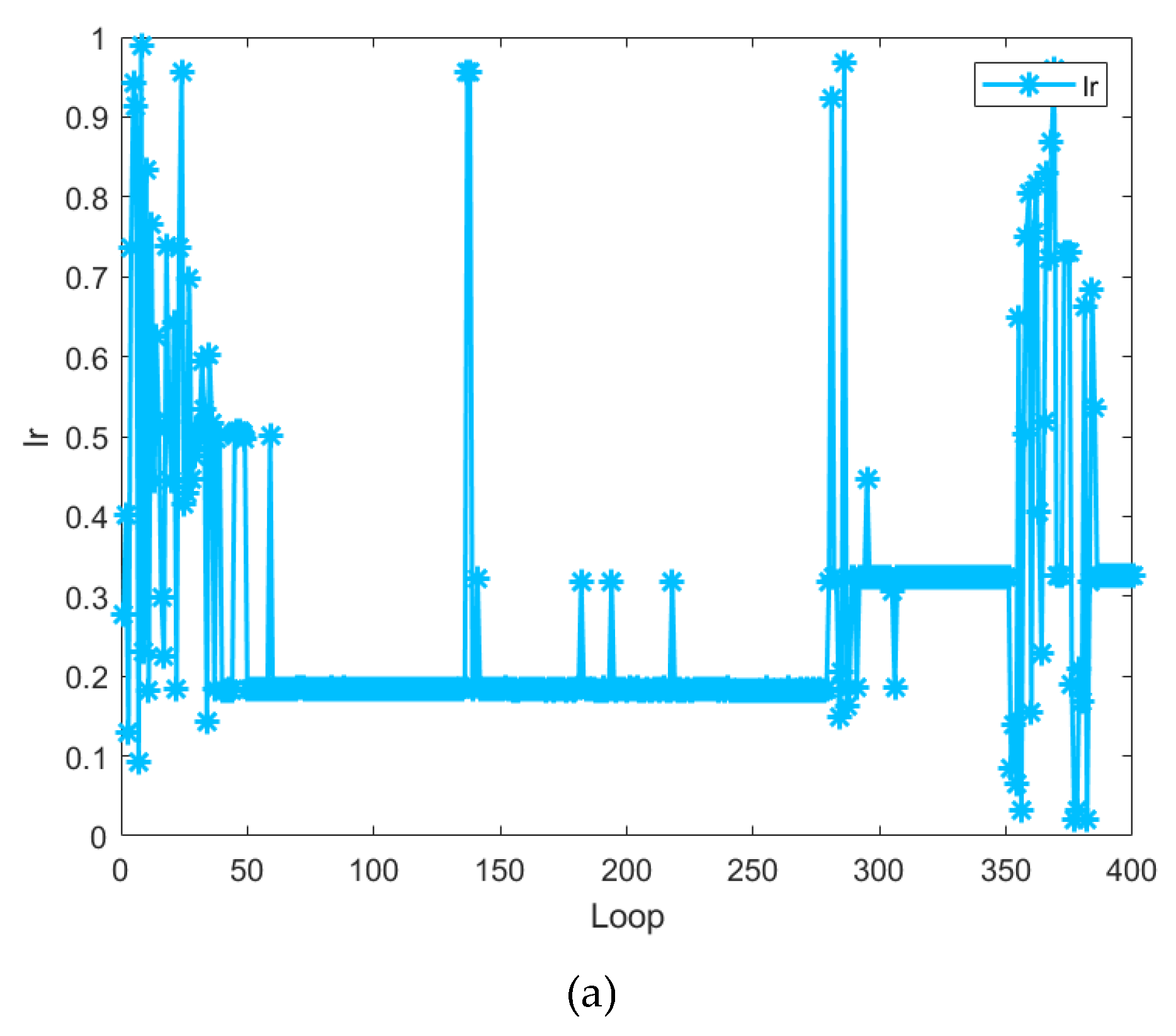
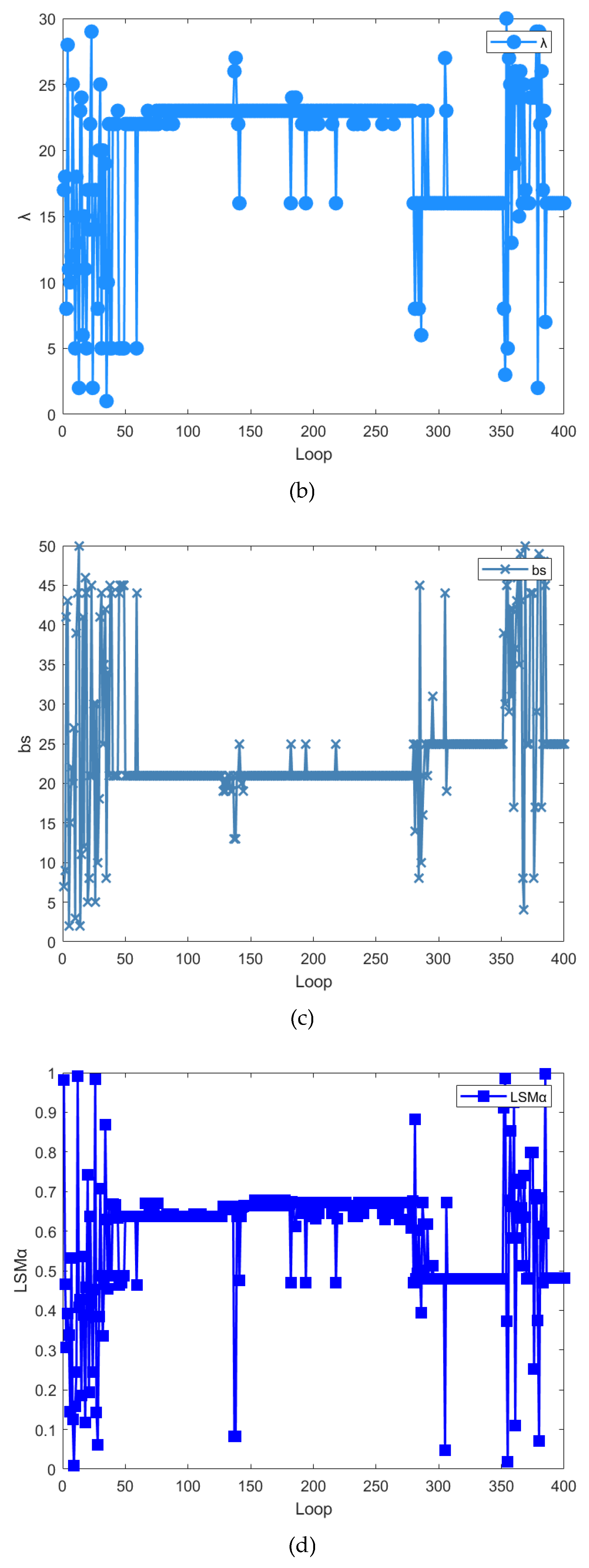
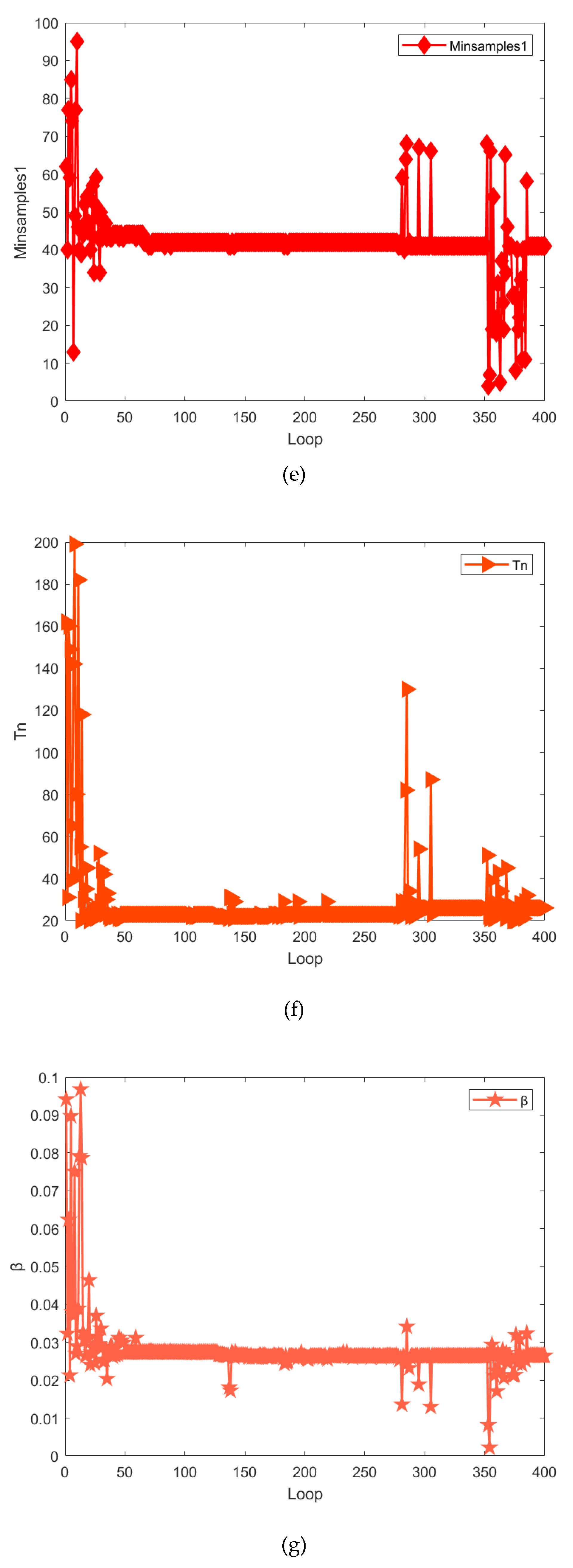
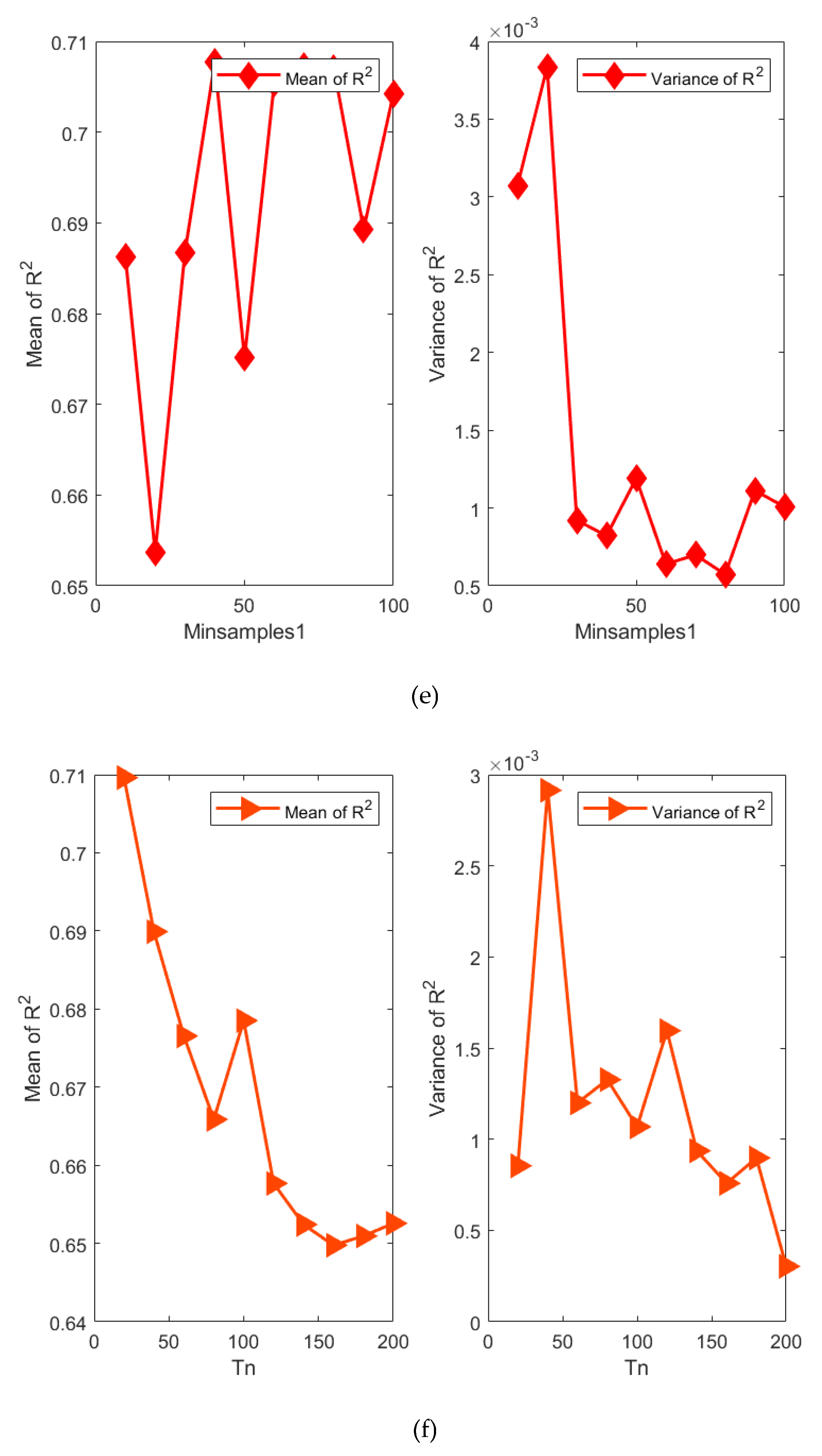
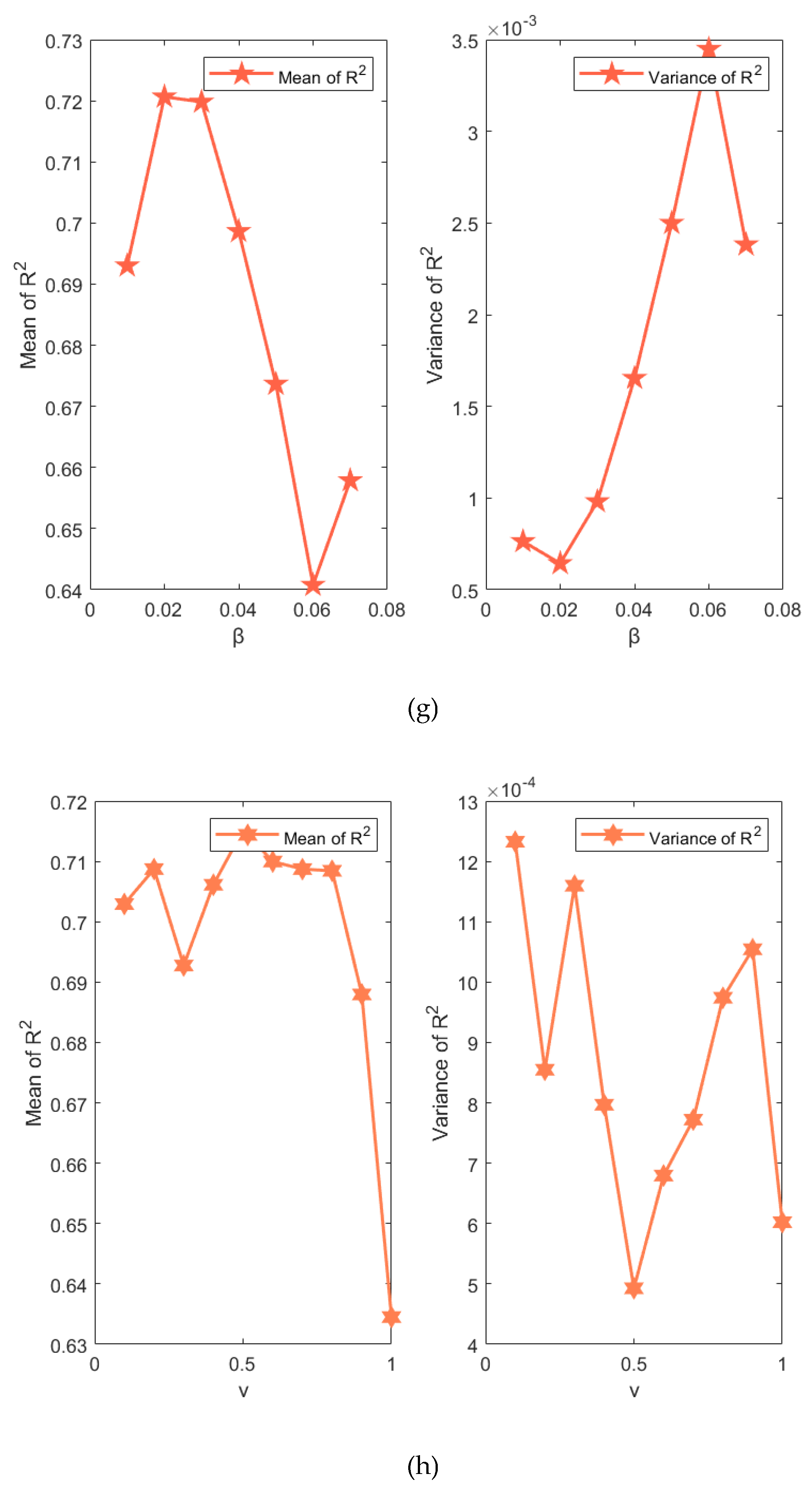
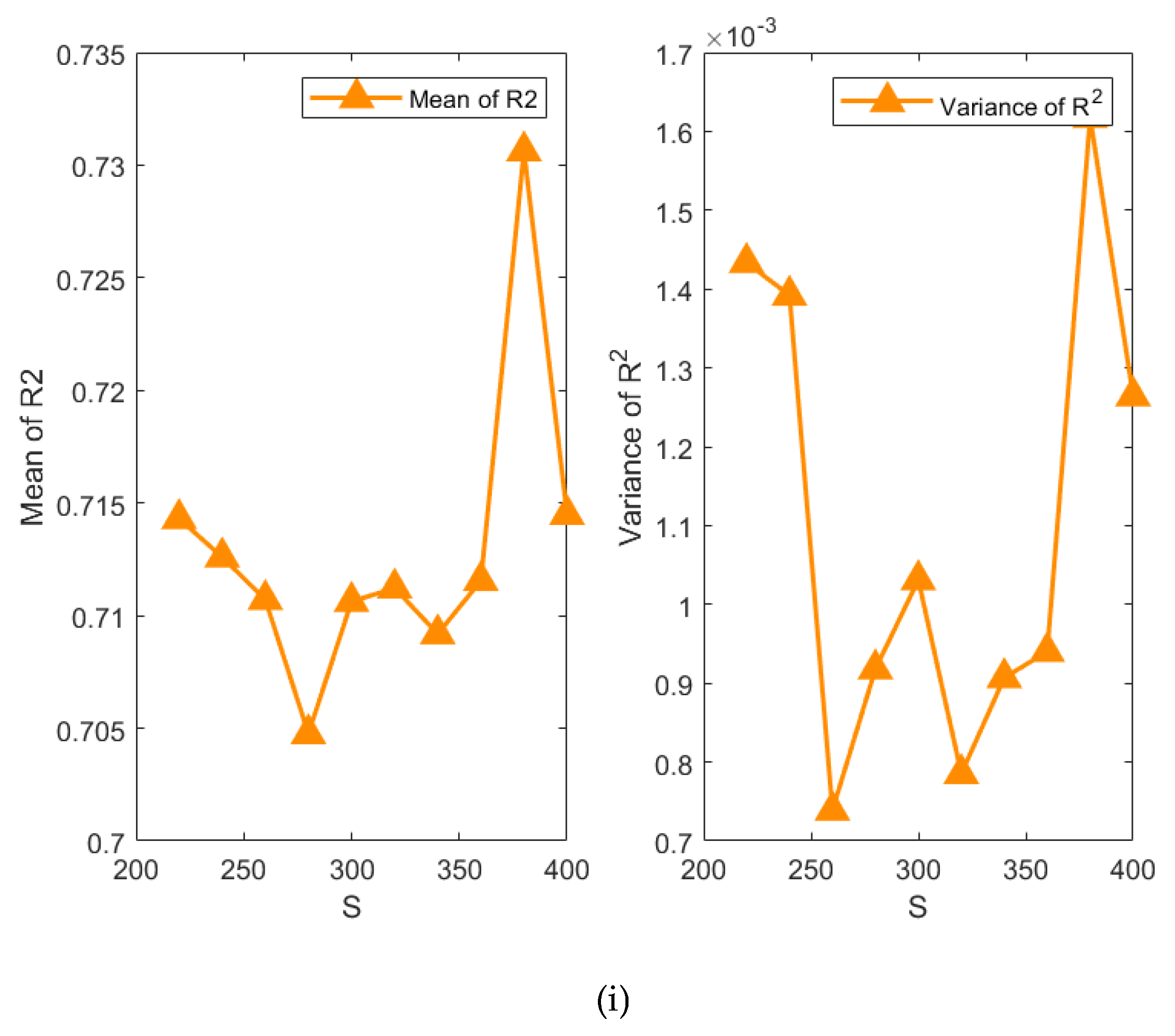
3.4. Hyperparameter Discussion
3.5. Comprehensive Analysis
4. Conclusion
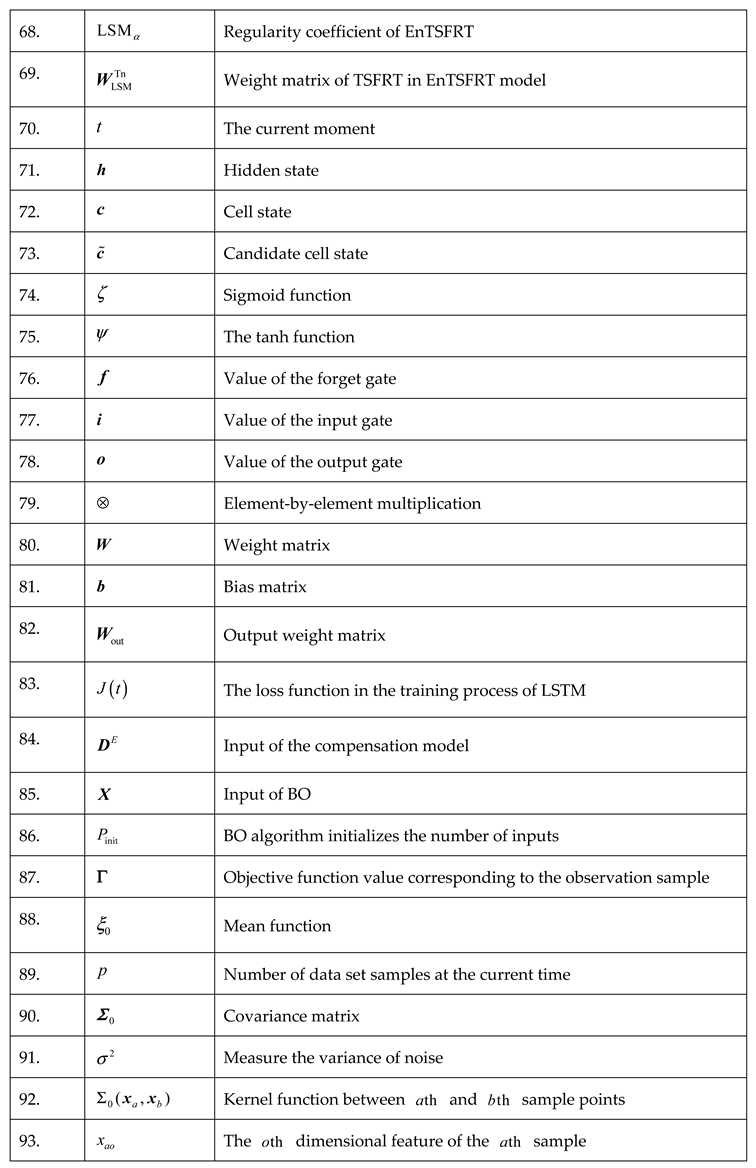
Appendix
|
|
References
- Jian, T.; Heng, X.; Wen, Y.; Jun-Fei, Q. Research status and prospect of intelligent optimization control of municipal solid waste incineration process. Acta Automatica Sinica 2023, 49, 2019–2059. [Google Scholar]
- An, C.; Jing-Rui, C.; Jing, C.; Chao, F.; Wei, W. Research on risks and countermeasures of “cities besieged by waste” in China-an empirical analysis based on DIIS. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences 2019, 34, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efforts to Promote the Realization of Carbon Peak Carbon Neutral Target. [Online]. Available: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/wsdwhfz/202111/t20211111_1303691.html.
- Ding, H.; Tang, J.; Qiao, J. (2021). Control Methods of Municipal Solid Wastes Incineration Process: A Survey. In 2021 40th Chinese Control Conference (CCC)(pp. 662-667). IEEE.
- Can-Lin, C.; Jian, T.; Heng, X.; Jun-Fei, Q. Early warning of dioxin emission in municipal solid waste incineration process based on fuzzy neural network confrontation generation. Control Theory & Applications 2024, 1–9.
- Pan, X.; Tang, J.; Xia, H. (2023). Flame combustion state identification based on CNN in municipal solid waste incineration process. In 2023 5th International Conference on Industrial Artificial Intelligence (IAI)(pp. 1-4). IEEE.
- Qiao, J.; Sun, J.; Meng, X. Event-triggered adaptive model predictive control of oxygen content for municipal solid waste incineration process. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering 2024, 21, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, S.; Xi, M.; Jun-Fei, Q. Data-driven predictive control of flue gas oxygen content in municipal solid waste incineration process. Control Theory & Applications 2024, 41, 484–495. [Google Scholar]
- Kai-Cheng, H.; Ai-Jun, Y.; Jian, T. Multi-objective robust prediction model of furnace temperature and flue gas oxygen content in municipal solid waste incineration process. Acta Automatica Sinica 2024, 50, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Ding, H.; Qiao, J. Adaptive multi-objective competitive swarm optimization algorithm based on kinematic analysis for municipal solid waste incineration. Applied Soft Computing 2023, 149, 110925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Meng, X.; Qiao, J. Event-Based Data-Driven Adaptive Model Predictive Control for Nonlinear Dynamic Processes. IEEE Transactions on Systems Man and Cybernetics: Systems 2024, 54, 1982–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ding, S.; Yang, Y.; Peng, K.; Qiu, J. A fault detection approach for nonlinear systems based on data-driven realizations of fuzzy kernel representations. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 26, 1800-1812. [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, M.; Cho, H.; Moon, I.; Kim, J. Multi-objective optimization of an explosive waste incineration process considering nitrogen oxides emission and process cost by using artificial neural network surrogate models[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection 2022, 162, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sildir, H.; Sarrafi, S.; Aydin, E. Optimal artificial neural network architecture design for modeling an industrial ethylene oxide plant. Computers & Chemical Engineering 2022, 163, 107850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimieh, A.; Mehriar, M.; Zamir, S.; Nostrati. Fuzzy-decision tree modeling for H2S production management in an industrial-scale anaerobic digestion process. Biochemical Engineering Journal 2024, 208, 109380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, J.; Chen, R.; Dai, H.; Ma, H.; Hu, G.; Xie, Y. Prediction of flue gas oxygen content of power plant with stacked target-enhanced autoencoder and attention-based LSTM. Measurement 2024, 235, 115036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai-Xu, D.; Jian, T.; Heng, X.; Jun-Fei, Q. MIMO controlled object modeling of municipal solid waste incineration process based on TS-FNN. Control Theory & Applications 2022, 39, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Lee, C. Neural-network-based fuzzy logic control and decision system. IEEE Transactions on Computers Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers 1991, 40, 1320–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Peng, R.; Mendel, J. Type-1 and interval type-2 fuzzy systems. IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine 2023, 18, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Xia, H.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, J.; Yu, W. Deep forest regression based on cross-layer full connection. Neural Computing and Applications 2021, 33, 9307–9328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, T.; Tian, H.; Cui, C.; Yu, W. (2023). Interpretable controlled object model of furnace temperature for MSWI process based on a novle linear regression decision tree. In 2023 35th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC)(pp. 325-330). IEEE.
- Xia, H.; Tang, J.; Yu, W.; et al. Takagi–Sugeno Fuzzy Regression Trees With Application to Complex Industrial Modeling. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. Inst. Electr. Electron. Eng. (IEEE) 2023, 31, 2210–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Zhang, W.; Huang, J.; Cui, C.; Qiao, J. Fuzzy reasoning based on truth-value progression: A control-theoretic design approach. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems 2023, 25, 1559–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Ma, K.; Lv, Y.; Fang, F.; Chang, T. Hybrid dynamic model of SCR denitrification system for coal-fired power plant. (2019). In 2019 IEEE 28th International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE)(pp. 106-111). IEEE.
- Luo, A.; Liu, B. (2022). Temperature prediction of roller kiln based on mechanism and SSA-ELM data-driven integrated model. In 2022 China Automation Congress (CAC)(pp. 5598-5603). IEEE.
- Dong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X. (2022). Intelligent compensation prediction of leaching process based on GRU neural network. In 2022 China Automation Congress (CAC)(pp. 1663-1668). IEEE.
- Xia, H.; Tang, J.; Yu, W.; Jun-Fei; Qiao. Dioxin emission modeling based on simulation mechanism and improved regression decision tree. Acta Automatica Sinica 2024, 50, 1001–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. The Annals of Statistics 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Deng, C.-H.; Zhao, L.-J. Research on the application of ellipsoid bound algorithm in hybrid modeling. Acta Automatica Sinica 2014, 40, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.; Meng, X.; Tang, J.; Qiao, J. NOx emission prediction for MSWI process based on dynamic modular neural network. Expert Systems with Applications 2023, 238, 122015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, J.; Xia, H.; Chen, J.; Yu, W.; Qiao, J. Heterogeneous ensemble prediction model of CO emission concentration in municipal solid waste incineration process using virtual data and real data hybrid-driven. Journal of Cleaner Production 2024, 445, 141313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, D.; Du, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q. Interpretable multi-task neural network modeling and particle swarm optimization of process parameters in laser welding. Knowledge-Based Systems 2024, 300, 112116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Tan, J.; Yu, J.; Gu, X.; Jiang, T. Online robust parameter design using sequential support vector regression based Bayesian optimization. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 2024, 540, 128649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Liu, G.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Wu, X. Intelligent optimization design of squeeze casting process parameters based on neural network and improved sparrow search algorithm. Journal of Industrial Information Integration 2024, 39, 100600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Tang, J.; Xia, H.; Wang, T.; Cui, C.; Pan, X. (2023). Furnace temperature control based on adaptive TS-FNN for municipal solid waste incineration process. In 2023 35th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC)(pp. 360-365). IEEE.
- Ding, H.; Tang, J.; Qiao, J. Dynamic modeling of multi-input and multi-output controlled object for municipal solid waste incineration process. Applied Energy 2023, 339, 120982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Tang, J.; Qiao, J. MIMO modeling and multi-loop control based on neural network for municipal solid waste incineration. Control Engineering Practice 2022, 127, 105280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, C.E.; Williams, C.K.I. Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning[M].MIT Press,2005.
- Rasmussen, C.E. Gaussian Processes in Machine Learning;[C]//Advanced Lectures on Machine Learning, ML Summer Schools 2003, Canberra, Australia, February 2-14, 2003, Tübingen, Germany, August 4-16, 2003, Revised Lectures.2003.
- Wen-Ju,. Y., Ying-Dong,. Z.; Hong-Hua,. Y. Prediction of sediment discharge in Jinghe River based on optimized BP neural network. Journal of China Hydrology 2024, 1–8.
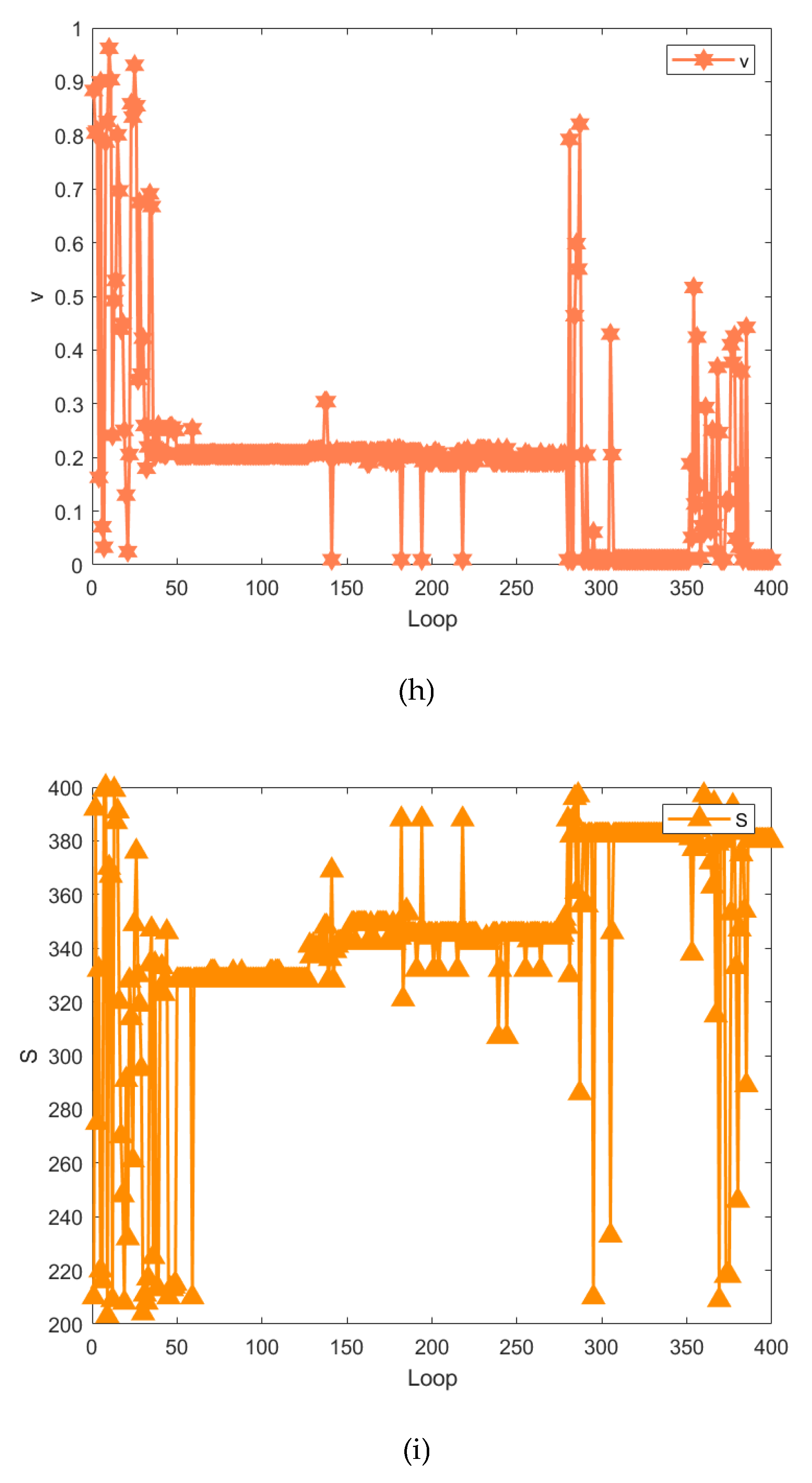
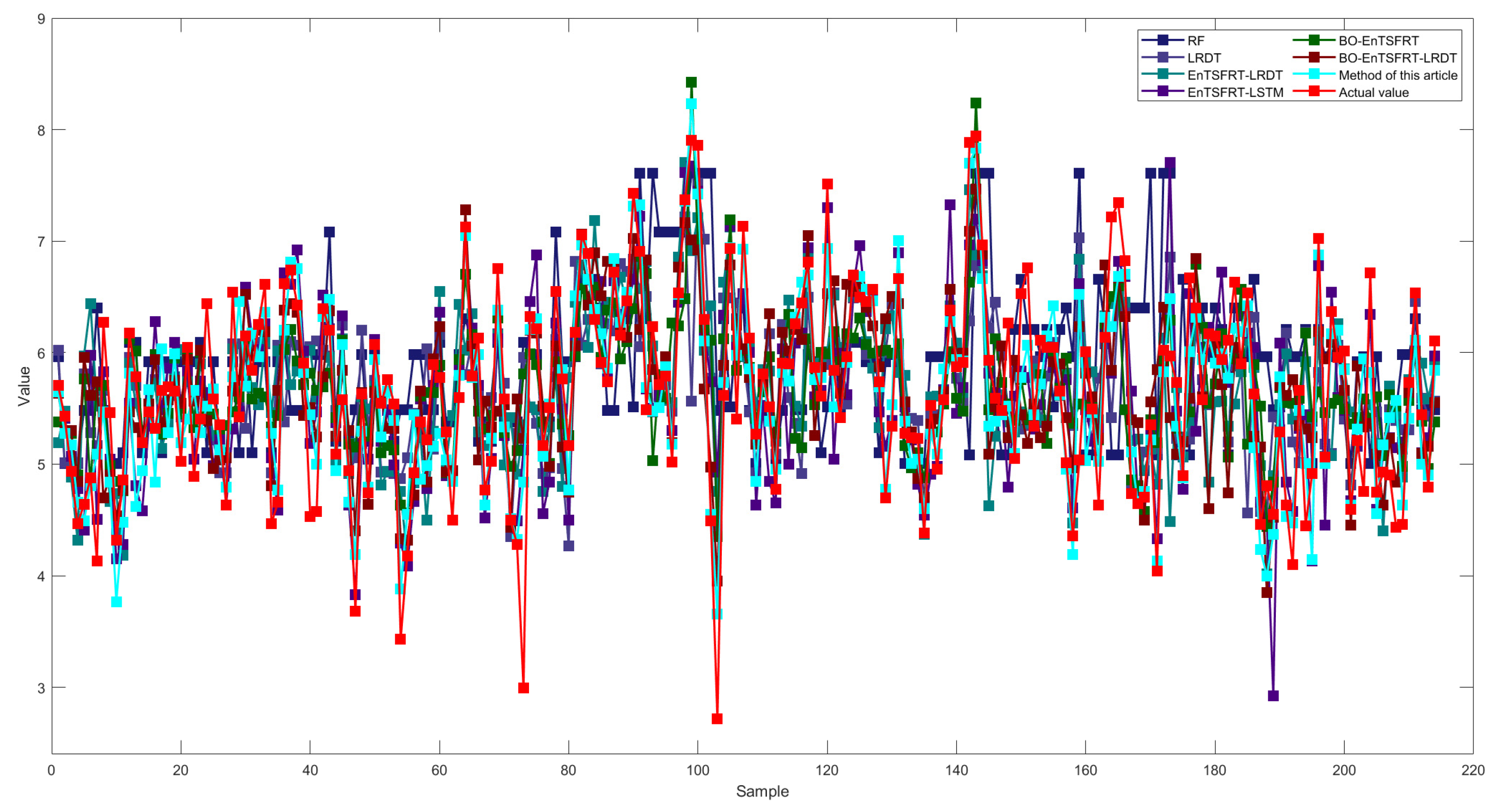
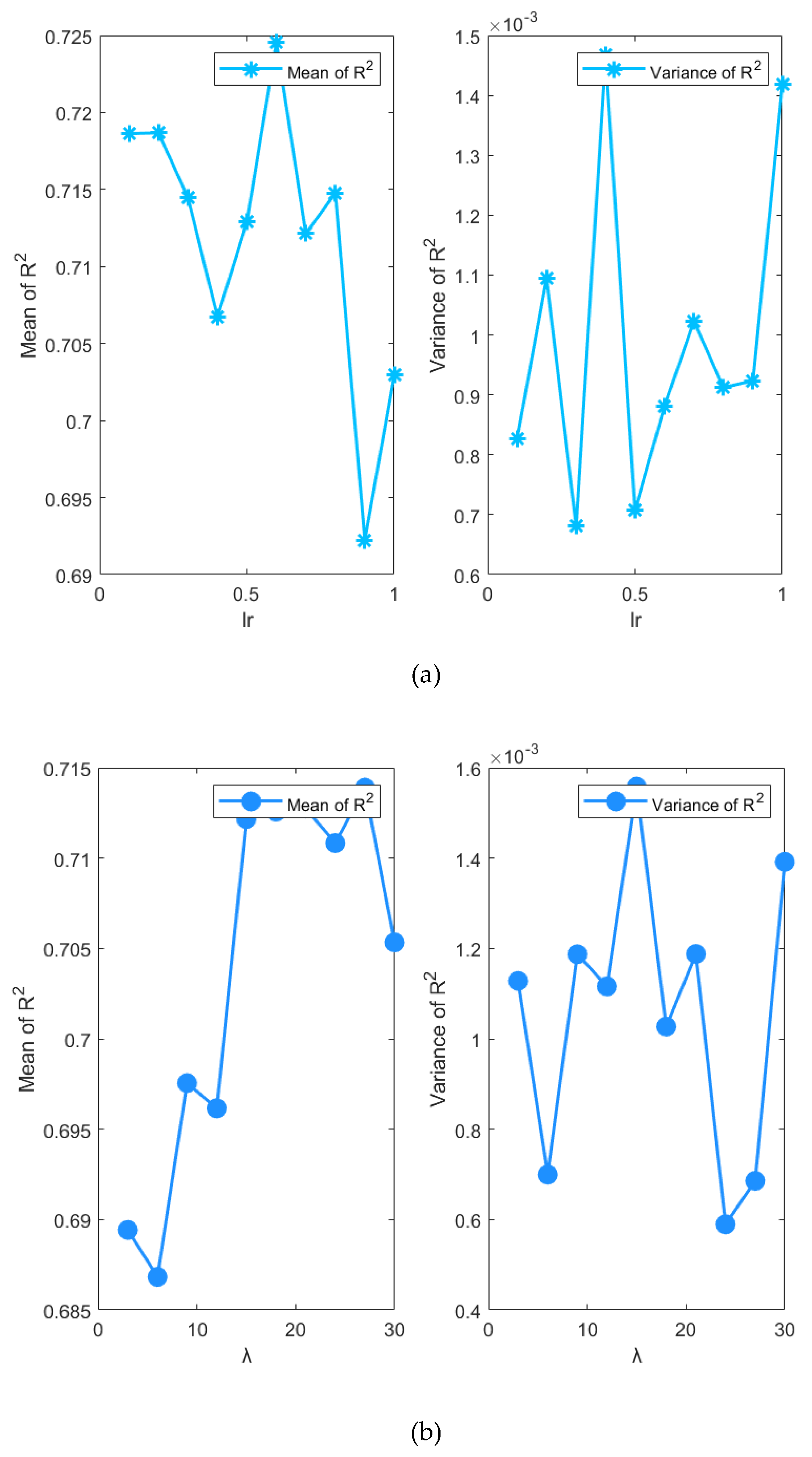
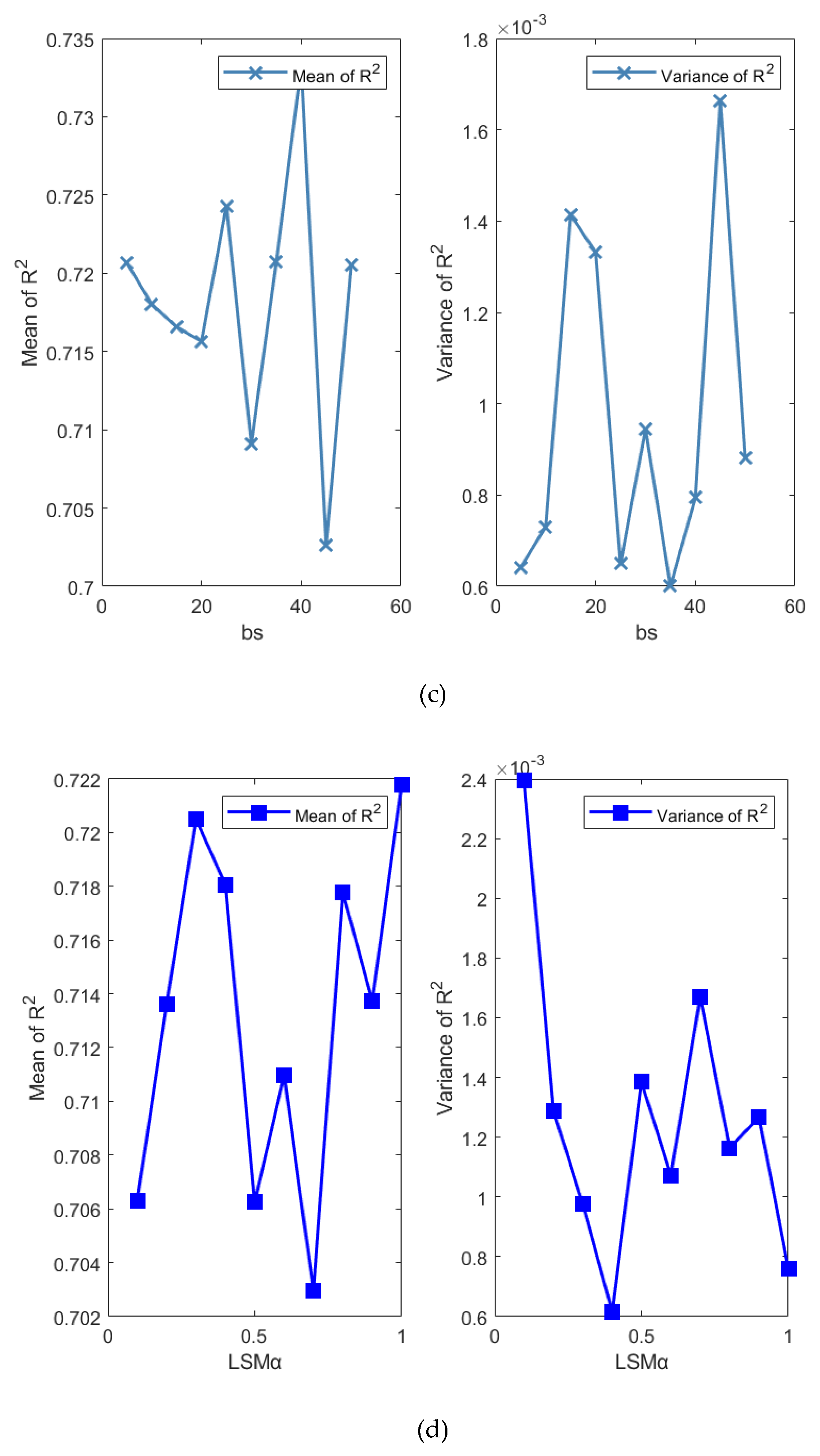
 |
| Dataset | Method | RMSE | MAE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | RF | 8.6432E-01±1.1677E-31 | 6.4993E-01±1.2975E-32 | -8.8061E-02±8.1092E-34 |
| LRDT | 5.2664E-01±5.1899E-32 | 4.0872E-01±1.2975E-32 | 5.9604E-01±1.2975E-32 | |
| EnTSFRT-LRDT | 4.4932E-01±1.1640E-04 | 3.5266E-01±8.4882E-05 | 7.0088E-01±2.0645E-04 | |
| EnTSFRT-LSTM | 4.5666E-02±4.1522E-04 | 3.3945E-02±1.6713E-04 | 9.9639E-01±1.7202E-05 | |
| BO-EnTSFRT | 6.4563E-01±9.0752E-05 | 5.1347E-01±6.8136E-05 | 5.8308E-01±1.5481E-04 | |
| BO-EnTSFRT-LRDT | 4.3465E-01±2.9193E-32 | 3.4153E-01±1.2975E-32 | 7.2484E-01±5.1899E-32 | |
| BO-EnTSFRT-LSTM | 2.6610E-02±5.8122E-06 | 2.0684E-02±3.3649E-06 | 9.9896E-01±3.8281E-08 | |
| Testing set | RF | 9.7815E-01±5.1899E-32 | 7.4468E-01±5.1899E-32 | -2.0272E-01±1.2975E-32 |
| LRDT | 7.6825E-01±0.0000E+00 | 5.9607E-01±5.1899E-32 | 2.5808E-01±0.0000E+00 | |
| EnTSFRT-LRDT | 7.3435E-01±3.5825E-04 | 5.7583E-01±1.6158E-04 | 2.4216E-01±1.4912E-03 | |
| EnTSFRT-LSTM | 5.7702E-01±1.0583E-03 | 4.2354E-01±6.3545E-04 | 5.8020E-01±2.1789E-03 | |
| BO-EnTSFRT | 8.5004E-01±5.7774E-04 | 6.7746E-01±2.1606E-04 | 3.1419E-01±1.4888E-03 | |
| BO-EnTSFRT-LRDT | 6.4225E-01±1.2975E-32 | 4.9011E-01±5.1899E-32 | 4.8149E-01±2.9193E-32 | |
| BO-EnTSFRT-LSTM | 4.3991E-01±2.0766E-04 | 3.1771E-01±1.1515E-04 | 7.5649E-01±2.4804E-04 |
| Model | Hyper Parameter | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Main Model | [0,1] | |
| [1, 30] | ||
| [1, 50] | ||
| [0, 1] | ||
| [1, 100] | ||
| [20, 200] | ||
| Compensation Model | [0, 0.1] | |
| [0, 1) | ||
| [200, 400] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





