Submitted:
21 October 2024
Posted:
24 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Sponge Implants
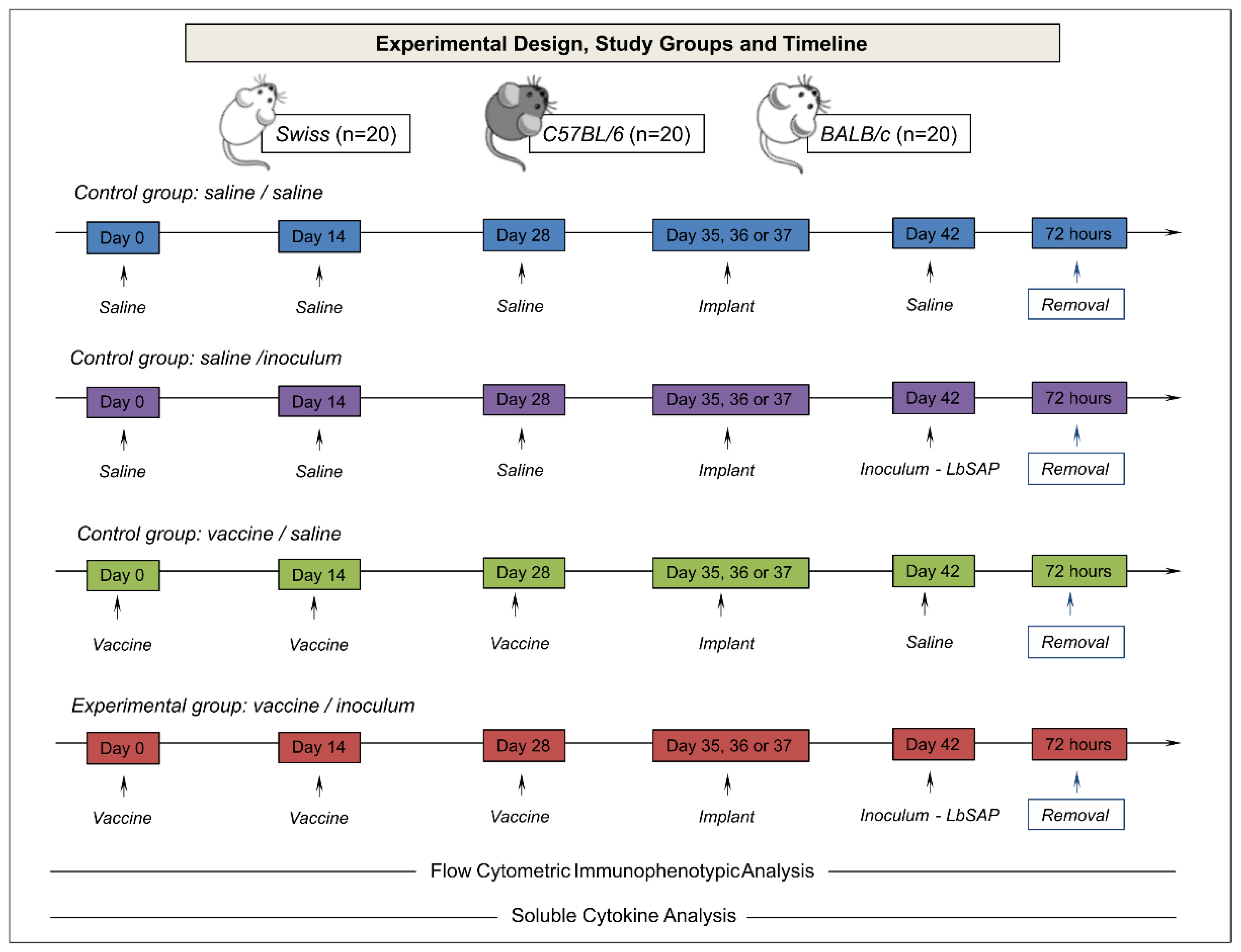
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Flow Cytometry Immunophenotyping
2.5. Soluble Cytokine Measurements
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Biomarker Signature Analysis
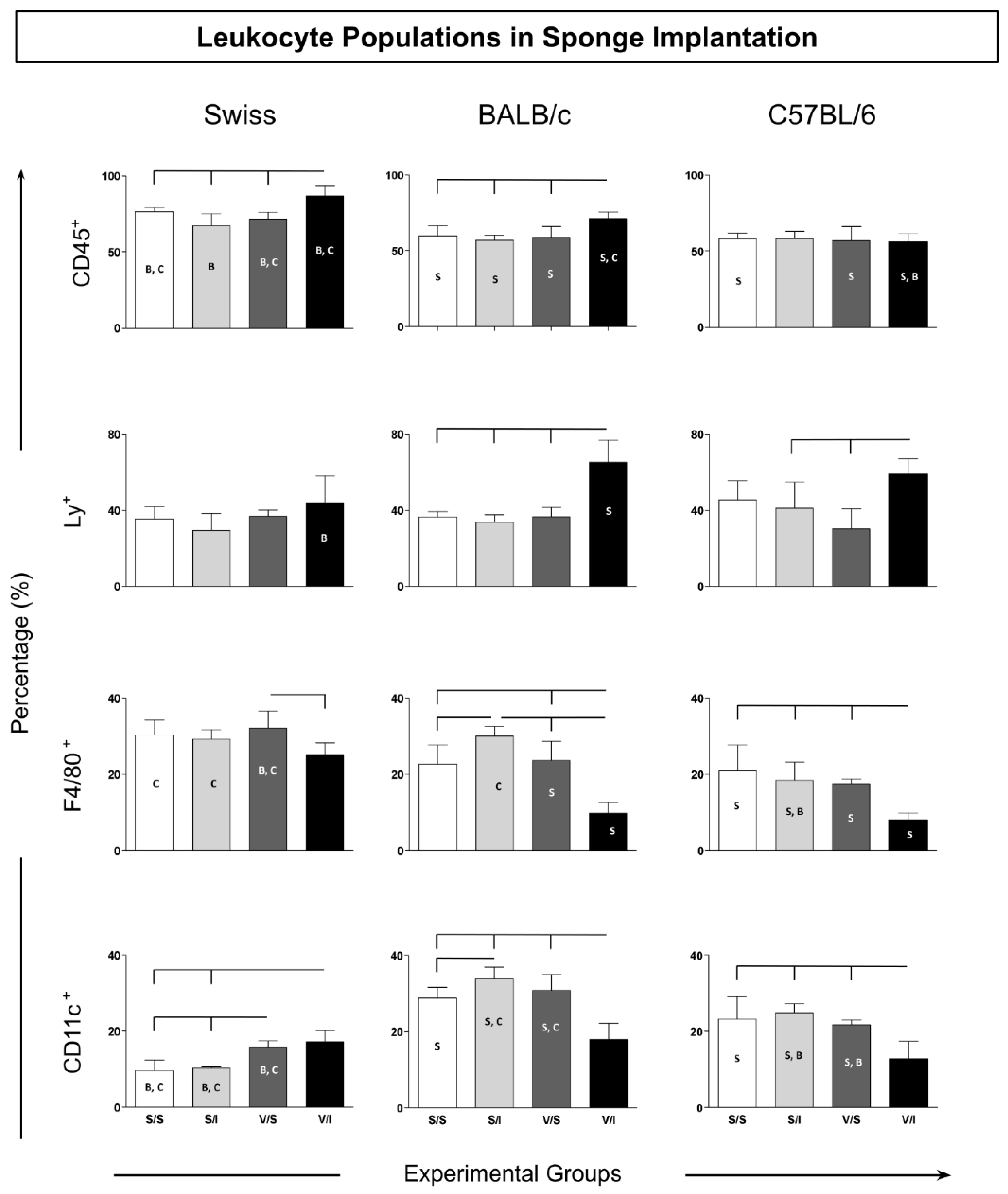
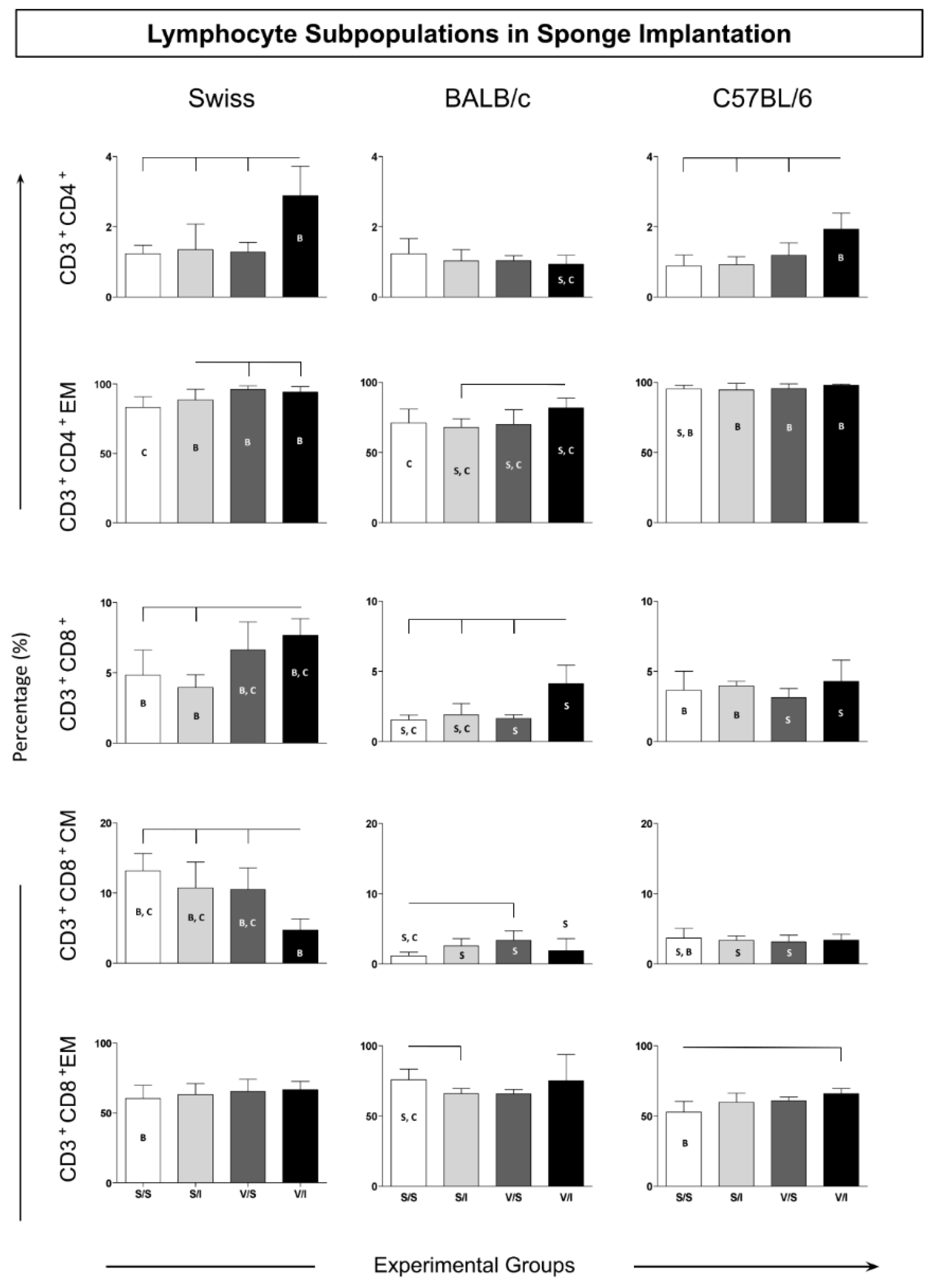
3. Results
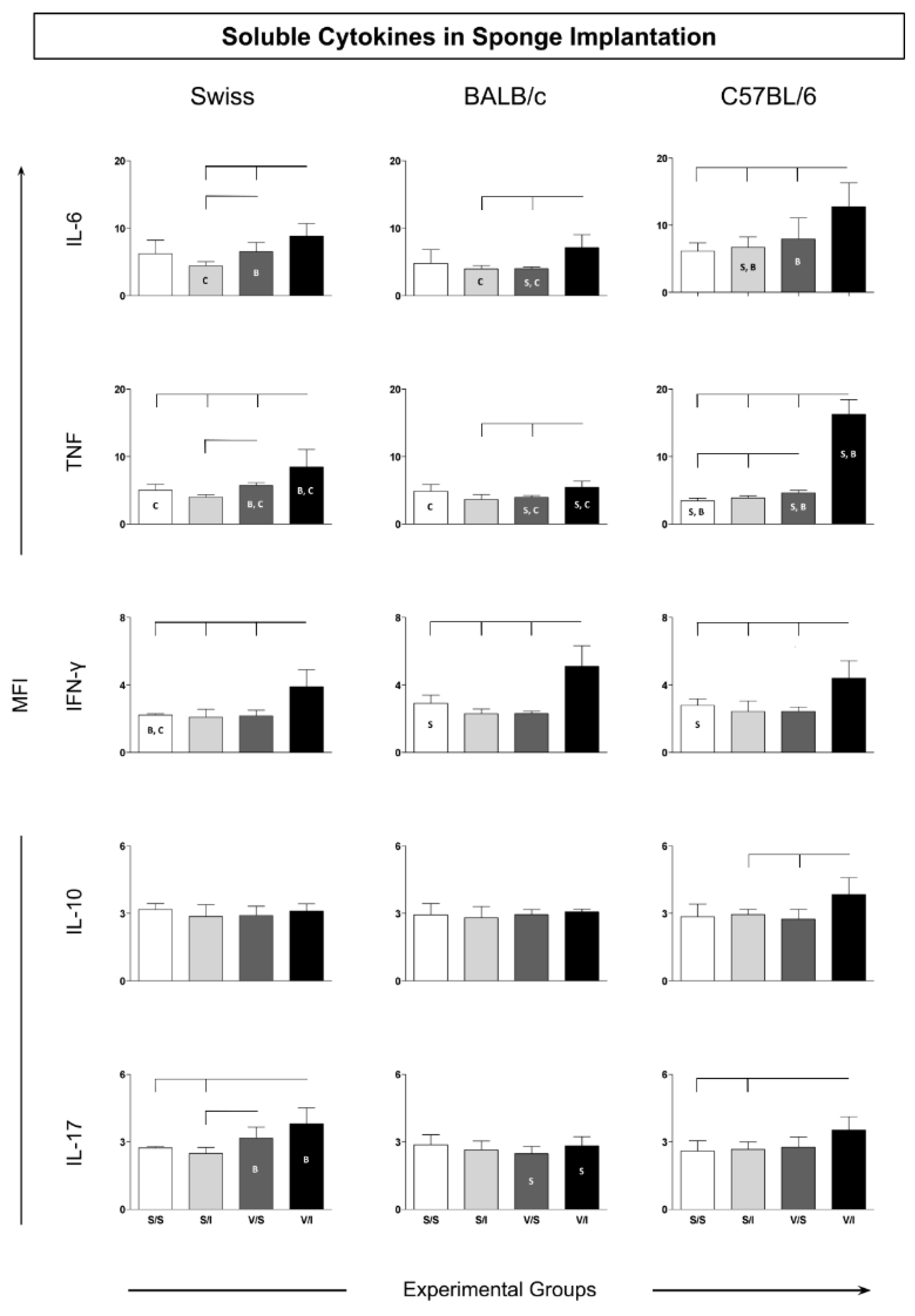
3.2. Cytokine Microenvironment in the Sponge Implants
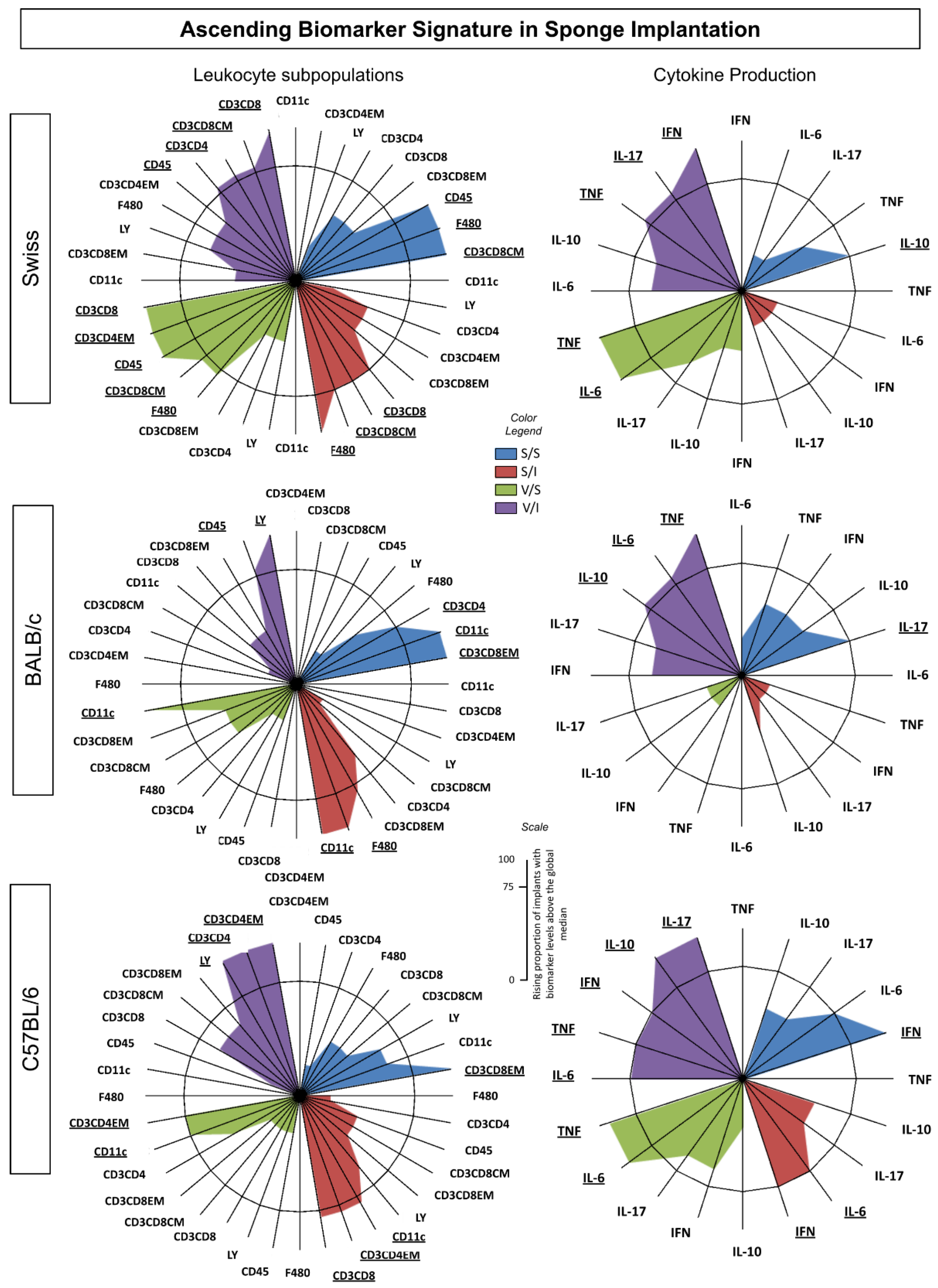
3.3. Ascendant Biomarker Signature Implants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrade, S.P.; Machado, R.D.P.; Teixeira, A.S.; Belo, A. V.; Tarso, A.M.; Beraldo, W.T. Sponge-Induced Angiogenesis in Mice and the Pharmacological Reactivity of the Neovasculature Quantitated by a Fluorimetric Method. Microvasc Res 1997, 54, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassini-Vieira, P.; Deconte, S.R. amos; Tomiosso, T.C. arla; Campos, P.P. eixoto; Montenegro, C. de F.; Selistre-de-Araújo, H.S. obreiro; Barcelos, L.S.; Andrade, S.P. assos; Araújo, F. de A. DisBa-01 Inhibits Angiogenesis, Inflammation and Fibrogenesis of Sponge-Induced-Fibrovascular Tissue in Mice. Toxicon 2014, 92, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabelo, L.F.G.; Ferreira, B.A.; Deconte, S.R.; Tomiosso, T.C.; dos Santos, P.K.; Andrade, S.P.; Selistre de Araújo, H.S.; Araújo, F. de A. Alternagin-C, a Disintegrin-like Protein from Bothrops Alternatus Venom, Attenuates Inflammation and Angiogenesis and Stimulates Collagen Deposition of Sponge-Induced Fibrovascular Tissue in Mice. Int J Biol Macromol 2019, 140, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, B.A.; Moura, F.B.R. de; Cassimiro, I.S.; Londero, V.S.; Gonçalves, M. de M.; Lago, J.H.G.; Araújo, F. de A. Costic Acid, a Sesquiterpene from Nectandra Barbellata (Lauraceae), Attenuates Sponge Implant-Induced Inflammation, Angiogenesis and Collagen Deposition in Vivo. Fitoterapia 2024, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, S.A.L.; Lima, L.D.C.; Andrade, S.P.; Silva-Cunha Junior, A. Da; Órefice, R.L.; Ayres, E.; Da Silva, G.R. Local Drug Delivery System: Inhibition of Inflammatory Angiogenesis in a Murine Sponge Model by Dexamethasone-Loaded Polyurethane Implants. J Pharm Sci 2011, 100, 2886–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, P.J. Sponge Implants as Models. Methods Enzymol 1988, 162, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.A.N.D.; Barcelos, L.S.; Campos, P.P.; Vasconcelos, A.C.; Teixeira, M.M.; Andrade, S.P. Sponge-Induced Angiogenesis and Inflammation in PAF Receptor-Deficient Mice (PAFR-KO). Br J Pharmacol 2004, 141, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belo, A. V.; Barcelos, L.S.; Ferreira, M.A.N.D.; Teixeira, M.M.; Andrade, S.P. Inhibition of Inflammatory Angiogenesis by Distant Subcutaneous Tumor in Mice. Life Sci 2004, 74, 2827–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelos, L.S.; Talvani, A.; Teixeira, A.S.; Cassali, G.D.; Andrade, S.P.; Teixeira, M.M. Production and in Vivo Effects of Chemokines CXCL1-3/KC and CCL2/JE in a Model of Inflammatory Angiogenesis in Mice. Inflammation Research 2004, 53, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, L.G.; Figueiredo, L.A.; Fernandes-Cunha, G.M.; De Miranda, M.B.; MacHado, L.A.; Da Silva, G.R.; De Moura, S.A.L. Methotrexate Locally Released from Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Implants: Inhibition of the Inflammatory Angiogenesis Response in a Murine Sponge Model and the Absence of Systemic Toxicity. J Pharm Sci 2015, 104, 3731–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanna, M.F.; Resende, L.A.; Aguiar-Soares, R.D. de O.; de Miranda, M.B.; de Mendonça, L.Z.; Melo Júnior, O.A. de O.; Mariano, R.M. da S.; Leite, J.C.; Silveira, P.; Corrêa-Oliveira, R.; et al. Kinetics of Phenotypic and Functional Changes in Mouse Models of Sponge Implants: Rational Selection to Optimize Protocols for Specific Biomolecules Screening Purposes. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2020, 8, 538203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, D.O.; Amaral, L.S.; Gomes, M.A.; Rocha, M.A.; Campos, P.R.; Cota, B.D.C.V.; Tafuri, L.S.A.; Paiva, A.M.R.; Silva, J.H.; Andrade, S.P.; et al. Metformin Inhibits Inflammatory Angiogenesis in a Murine Sponge Model. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2010, 64, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.S.; Saraswati, S.; Mathur, R.; Pandey, M. Brucine, a Plant Derived Alkaloid Inhibits Inflammatory Angiogenesis in a Murine Sponge Model. Biomedicine & Preventive Nutrition 2011, 1, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswati, S.; Pandey, M.; Mathur, R.; Agrawal, S.S. Boswellic Acid Inhibits Inflammatory Angiogenesis in a Murine Sponge Model. Microvasc Res 2011, 82, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaider, A.A.; Gader, A.G.M.A.; Almeshal, N.; Saraswati, S. Camel Urine Inhibits Inflammatory Angiogenesis in Murine Sponge Implant Angiogenesis Model. Biomedicine & Aging Pathology 2014, 4, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaider, A.A.; Abdel Gader, A.G.M.; Almeshaal, N.; Saraswati, S. Camel Milk Inhibits Inflammatory Angiogenesis via Downregulation of Proangiogenic and Proinflammatory Cytokines in Mice. APMIS 2014, 122, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, S.A.; Cardoso, C.C.; Orellano, L.A.; Reis, A.M.; Barcelos, L.S.; Andrade, S.P. Natriuretic Peptide Clearance Receptor Ligand (C-ANP4–23) Attenuates Angiogenesis in a Murine Sponge Implant Model. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2014, 41, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassini-Vieira, P.; Felipetto, M.; Prado, L.B.; Verano-Braga, T.; Andrade, S.P.; Santos, R.A.S.; Teixeira, M.M.; de Lima, M.E.; Pimenta, A.M.C.; Barcelos, L.S. Ts14 from Tityus Serrulatus Boosts Angiogenesis and Attenuates Inflammation and Collagen Deposition in Sponge-Induced Granulation Tissue in Mice. Peptides (N.Y.) 2017, 98, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, A.F.R.M.; Melo, M.M.; Campos, P.P.; Oliveira, M.S.; Oliveira, F.A.S.; Cassali, G.D.; Ferraz, V.P.; Cota, B.B.; Andrade, S.P.; Souza-Fagundes, E.M. Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory, Antiangiogenic and Antiproliferative Activities of Arrabidaea Chica Crude Extracts. J Ethnopharmacol 2015, 165, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellano, L.A.A.; Almeida, S.A.; Campos, P.P.; Andrade, S.P. Angiopreventive versus Angiopromoting Effects of Allopurinol in the Murine Sponge Model. Microvasc Res 2015, 101, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, B.A.; Deconte, S.R.; de Moura, F.B.R.; Tomiosso, T.C.; Clissa, P.B.; Andrade, S.P.; Araújo, F. de A. Inflammation, Angiogenesis and Fibrogenesis Are Differentially Modulated by Distinct Domains of the Snake Venom Metalloproteinase Jararhagin. Int J Biol Macromol 2018, 119, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, R.A.C.; Ferreira, B.A.; Moura, F.B.R. de; Costa Silva, T. da; Cavalcanti, F.; Franca, E. de F.; Sousa, R.M.F. de; Febronio, J. de L.; Lago, J.H.G.; Araújo, F. de A.; et al. Dehydrodieugenol B and Hexane Extract from Endlicheria Paniculata Regulate Inflammation, Angiogenesis, and Collagen Deposition Induced by a Murine Sponge Model. Fitoterapia 2020, 147, 104767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, L.G.; De Miranda, M.B.; De Moura, S.A.L.; Da Silva, G.R. Tacrolimus Delivered from Polymeric Implants Suppressed Inflammation and Angiogenesis in Vivo without Inducing Nephrotoxicity, Hepatotoxicity, and Myelosuppression. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 2018, 43, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mendonça, L.Z.; Resende, L.A.; Lanna, M.F.; Aguiar-Soares, R.D.D.O.; Roatt, B.M.; Castro, R.A.D.O.E.; Batista, M.A.; Silveira-Lemos, D.; Gomes, J.D.A.S.; Fujiwara, R.T.; et al. Multicomponent LBSap Vaccine Displays Immunological and Parasitological Profiles Similar to Those of Leish-Tec® and Leishmune® Vaccines against Visceral Leishmaniasis. Parasit Vectors 2016, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar-Soares, R.D.D.O.; Roatt, B.M.; Ker, H.G.; Moreira, N.D.D.; Mathias, F.A.S.; Cardoso, J.M.D.O.; Gontijo, N.F.; Bruna-Romero, O.; Teixeira-Carvalho, A.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; et al. LBSapSal-Vaccinated Dogs Exhibit Increased Circulating T-Lymphocyte Subsets (CD4+ and CD8+) as Well as a Reduction of Parasitism after Challenge with Leishmania Infantum plus Salivary Gland of Lutzomyia Longipalpis. Parasit Vectors 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar-Soares, R.D. de O.; Roatt, B.M.; Mathias, F.A.S.; Reis, L.E.S.; Cardoso, J.M. de O.; de Brito, R.C.F.; Ker, H.G.; Corrêa-Oliveira, R.; Giunchetti, R.C.; Reis, A.B. Phase I and II Clinical Trial Comparing the LBSap, Leishmune®, and Leish-Tec® Vaccines against Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis. Vaccines (Basel) 2020, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giunchetti, R.C.; Corrêa-Oliveira, R.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Teixeira-Carvalho, A.; Roatt, B.M.; Aguiar-Soares, R.D. de O.; Coura-Vital, W.; Abreu, R.T. de; Malaquias, L.C.C.; Gontijo, N.F.; et al. A Killed Leishmania Vaccine with Sand Fly Saliva Extract and Saponin Adjuvant Displays Immunogenicity in Dogs. Vaccine 2008, 26, 623–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giunchetti, R.C.; Corrêa-Oliveira, R.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Teixeira-Carvalho, A.; Roatt, B.M.; de Oliveira Aguiar-Soares, R.D.; de Souza, J.V.; das Dores Moreira, N.; Malaquias, L.C.C.; Mota e Castro, L.L.; et al. Immunogenicity of a Killed Leishmania Vaccine with Saponin Adjuvant in Dogs. Vaccine 2007, 25, 7674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, L.A.; Roatt, B.M.; Aguiar-Soares, R.D. de O.; Viana, K.F.; Mendonça, L.Z.; Lanna, M.F.; Silveira-Lemos, D.; Corrêa-Oliveira, R.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Fujiwara, R.T.; et al. Cytokine and Nitric Oxide Patterns in Dogs Immunized with LBSap Vaccine, before and after Experimental Challenge with Leishmania Chagasi plus Saliva of Lutzomyia Longipalpis. Vet Parasitol 2013, 198, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dores Moreira, N. Das; Vitoriano-Souza, J.; Roatt, B.M.; De Abreu Vieira, P.M.; Coura-Vital, W.; De Oliveira Cardoso, J.M.; Rezende, M.T.; Ker, H.G.; Giunchetti, R.C.; Carneiro, C.M.; et al. Clinical, Hematological and Biochemical Alterations in Hamster (Mesocricetus Auratus) Experimentally Infected with Leishmania Infantum through Different Routes of Inoculation. Parasit Vectors 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roatt, B.M.; Aguiar-Soares, R.D. de O.; Vitoriano-Souza, J.; Coura-Vital, W.; Braga, S.L.; Corrêa-Oliveira, R.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Teixeira-Carvalho, A.; de Lana, M.; Gontijo, N.F.; et al. Performance of LBSap Vaccine after Intradermal Challenge with L. Infantum and Saliva of Lu. Longipalpis: Immunogenicity and Parasitological Evaluation. PLoS One 2012, 7, e49780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, N. das D.; Giunchetti, R.C.; Carneiro, C.M.; Vitoriano-Souza, J.; Roatt, B.M.; Malaquias, L.C.C.; Corrêa-Oliveira, R.; Reis, A.B. Histological Study of Cell Migration in the Dermis of Hamsters after Immunisation with Two Different Vaccines against Visceral Leishmaniasis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 2009, 128, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, L.A.; Aguiar-Soares, R.D.D.O.; Gama-Ker, H.; Roatt, B.M.; De Mendonça, L.Z.; Alves, M.L.R.; Da Silveira-Lemos, D.; Corrêa-Oliveira, R.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Araújo, M.S.S.; et al. Impact of LbSapSal Vaccine in Canine Immunological and Parasitological Features before and after Leishmania Chagasi-Challenge. PLoS One 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitoriano-Souza, J.; Reis, A.B.; Moreira, N.D.; Giunchetti, R.C.; Correa-Oliveira, R.; Carneiro, C.M. Kinetics of Cell Migration to the Dermis and Hypodermis in Dogs Vaccinated with Antigenic Compounds of Leishmania Braziliensis plus Saponin. Vaccine 2008, 26, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitoriano-Souza, J.; Moreira, N. das D.; Menezes-Souza, D.; Roatt, B.M.; De Oliveira Aguiar-Soares, R.D.; Siqueira-Mathias, F.A.; De Oliveira Cardoso, J.M.; Giunchetti, R.C.; De Sá, R.G.; Corrêa-Oliveira, R.; et al. Dogs Immunized with LBSap Vaccine Displayed High Levels of IL-12 and IL-10 Cytokines and CCL4, CCL5 and CXCL8 Chemokines in the Dermis. Mol Immunol 2013, 56, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luiza-Silva, M.; Campi-Azevedo, A.C.; Batista, M.A.; Martins, M.A.; Avelar, R.S.; Lemos, D.D.S.; Camacho, L.A.B.; Martins, R.D.M.; Maia, M.D.L.D.S.; Farias, R.H.G.; et al. Cytokine Signatures of Innate and Adaptive Immunity in 17DD Yellow Fever Vaccinated Children and Its Association With the Level of Neutralizing Antibody. J Infect Dis 2011, 204, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, S.P.; Fan, T.P.D.; Lewis, G.P. Quantitative In-Vivo Studies on Angiogenesis in a Rat Sponge Model. Br J Exp Pathol 1987, 68, 755–766. [Google Scholar]
- Barcelos, L.S.; Coelho, A.M.; Russo, R.C.; Guabiraba, R.; Souza, A.L.S.; Bruno-Lima, G.; Proudfoot, A.E.I.; Andrade, S.P.; Teixeira, M.M. Role of the Chemokines CCL3/MIP-1α and CCL5/RANTES in Sponge-Induced Inflammatory Angiogenesis in Mice. Microvasc Res 2009, 78, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, J.B.; Campos, P.P.; Rocha, M.A.; Andrade, S.P. Cilostazol and Pentoxifylline Decrease Angiogenesis, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in Sponge-Induced Intraperitoneal Adhesion in Mice. Life Sci 2009, 84, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes-da-Silva, F.H.; Shrestha, D.; Salles, B.C.; Figueiredo, V.P.; Lopes, L.R.; Dias, L.; Barcelos, L. da S.; Moura, S.; de Andrade, S.P.; Talvani, A. Trypanosoma Cruzi Antigens Induce Inflammatory Angiogenesis in a Mouse Subcutaneous Sponge Model. Microvasc Res 2015, 97, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, S.A. de; Orellano, L.A.A.; Pereira, L.X.; Viana, C.T.R.; Campos, P.P.; Andrade, S.P.; Ferreira, M.A.N.D. Murine Strain Differences in Inflammatory Angiogenesis of Internal Wound in Diabetes. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 2017, 86, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, L.X.; Viana, C.T.R.; Orellano, L.A.A.; Almeida, S.A.; Vasconcelos, A.C.; Goes, A. de M.; Birbrair, A.; Andrade, S.P.; Campos, P.P. Synthetic Matrix of Polyether-Polyurethane as a Biological Platform for Pancreatic Regeneration. Life Sci 2017, 176, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheuermann, K.; Orellano, L.A.A.; Viana, C.T.R.; Machado, C.T.; Lazari, M.G.T.; Capettini, L.S.A.; Andrade, S.P.; Campos, P.P. Amitriptyline Downregulates Chronic Inflammatory Response to Biomaterial in Mice. Inflammation 2021, 44, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orellano, L.A.A.; de Almeida, S.A.; Pereira, L.X.; Machado, C.T.; Viana, C.T.R.; Andrade, S.P.; Campos, P.P. Implant-Induced Inflammatory Angiogenesis Is up-Regulated in Obese Mice. Microvasc Res 2020, 131, 104014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugya, Z.; Prechl, J.; Szénási, T.; Nemes, É.; Bácsi, A.; Koncz, G. Multiple Levels of Immunological Memory and Their Association with Vaccination. Vaccines 2021, 9, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giunchetti, R.C.; Silveira, P.; Resende, L.A.; Leite, J.C.; Melo-Júnior, O.A. de O.; Rodrigues-Alves, M.L.; Costa, L.M.; Lair, D.F.; Chaves, V.R.; Soares, I. dos S.; et al. Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis Biomarkers and Their Employment in Vaccines. Vet Parasitol 2019, 271, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, M.T.; Marchese, R.D.; Kierstead, L.S.; Tussey, L.G.; Wang, F.; Chirmule, N.; Washabaugh, M.W. Memory T Cells and Vaccines. Vaccine 2003, 21, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, R.A.; Luster, A.D. Redefining Memory T Cell Subsets. Trends Immunol 2020, 41, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprent, J.; Surh, C.D. Generation and Maintenance of Memory T Cells. Curr Opin Immunol 2001, 13, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, S.C.; Masopust, D. Understanding Subset Diversity in T Cell Memory. Immunity 2018, 48, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallusto, F.; Geginat, J.; Lanzavecchia, A. Central Memory and Effector Memory T Cell Subsets: Function, Generation, and Maintenance. Annu Rev Immunol 2004, 22, 745–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soon, M.S.F.; Engel, J.A.; Lee, H.J.; Haque, A. Development of Circulating CD4+ T-Cell Memory. Immunol Cell Biol 2019, 97, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, J.C.; Gonçalves, A.A.M.; de Oliveira, D.S.; Resende, L.A.; Boas, D.F.V.; Ribeiro, H.S.; Pereira, D.F.S.; da Silva, A.V.; Mariano, R.M. da S.; Reis, P.C.C.; et al. Transmission-Blocking Vaccines for Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis: New Progress and Yet New Challenges. Vaccines 2023, Vol. 11, Page 1565 2023, 11, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.A.M.; Ribeiro, A.J.; Resende, C.A.A.; Couto, C.A.P.; Gandra, I.B.; dos Santos Barcelos, I.C.; da Silva, J.O.; Machado, J.M.; Silva, K.A.; Silva, L.S.; et al. Recombinant Multiepitope Proteins Expressed in Escherichia Coli Cells and Their Potential for Immunodiagnosis. Microb Cell Fact 2024, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, D.S. de; Zaldívar, M.F.; Gonçalves, A.A.M.; Resende, L.A.; Mariano, R.M. da S.; Pereira, D.F.S.; Conrado, I. dos S.S.; Costa, M.A.F.; Lair, D.F.; Vilas-Boas, D.F.; et al. New Approaches to the Prevention of Visceral Leishmaniasis: A Review of Recent Patents of Potential Candidates for a Chimeric Protein Vaccine. Vaccines 2024, 12, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osero, B.O. ondo; Aruleba, R.T.; Brombacher, F.; Hurdayal, R. Unravelling the Unsolved Paradoxes of Cytokine Families in Host Resistance and Susceptibility to Leishmania Infection. Cytokine X 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaugh, M.P.; Foss, D.L. Inflammatory Cytokines and Antigen Presenting Cell Activation. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 2002, 87, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, G.; Ferrua, B.; Munro, P.; Boyer, L.; Mathal, N.; Gillet, D.; Marty, P.; Lemichez, E. Immunoadjuvant Properties of the Rho Activating Factor CNF1 in Prophylactic and Curative Vaccination against Leishmania Infantum. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0156363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, O.P.; Gidwani, K.; Kumar, R.; Nylén, S.; Jones, S.L.; Boelaert, M.; Sacks, D.; Sundar, S. Reassessment of Immune Correlates in Human Visceral Leishmaniasis as Defined by Cytokine Release in Whole Blood. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2012, 19, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.A.M.; Leite, J.C.; Resende, L.A.; Mariano, R.M. da S.; Silveira, P.; Melo-Júnior, O.A. de O.; Ribeiro, H.S.; de Oliveira, D.S.; Soares, D.F.; Santos, T.A.P.; et al. An Overview of Immunotherapeutic Approaches Against Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis: What Has Been Tested on Dogs and a New Perspective on Improving Treatment Efficacy. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Bhattacharya, P.; Joshi, A.B.; Ismail, N.; Dey, R.; Nakhasi, H.L. Role of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine IL-17 in Leishmania Pathogenesis and in Protective Immunity by Leishmania Vaccines. Cell Immunol 2016, 309, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitta, M.G.R.; Romano, A.; Cabantous, S.; Henri, S.; Hammad, A.; Kouriba, B.; Argiro, L.; El Kheir, M.; Bucheton, B.; Mary, C.; et al. IL-17 and IL-22 Are Associated with Protection against Human Kala Azar Caused by Leishmania Donovani. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2009, 119, 2379–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, M.S.L.; Carregaro, V.; Lima-Júnior, D.S.; Costa, D.L.; Ryffel, B.; Duthie, M.S.; De Jesus, A.; De Almeida, R.P.; Da Silva, J.S. Interleukin 17A Acts Synergistically With Interferon γ to Promote Protection Against Leishmania Infantum Infection. J Infect Dis 2015, 211, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giunchetti, R.C.; Silveira, P.; Resende, L.A.; Leite, J.C.; Melo-Júnior, O.A. de O.; Rodrigues-Alves, M.L.; Costa, L.M.; Lair, D.F.; Chaves, V.R.; Soares, I. dos S.; et al. Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis Biomarkers and Their Employment in Vaccines. Vet Parasitol 2019, 271, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




