Submitted:
21 October 2024
Posted:
22 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
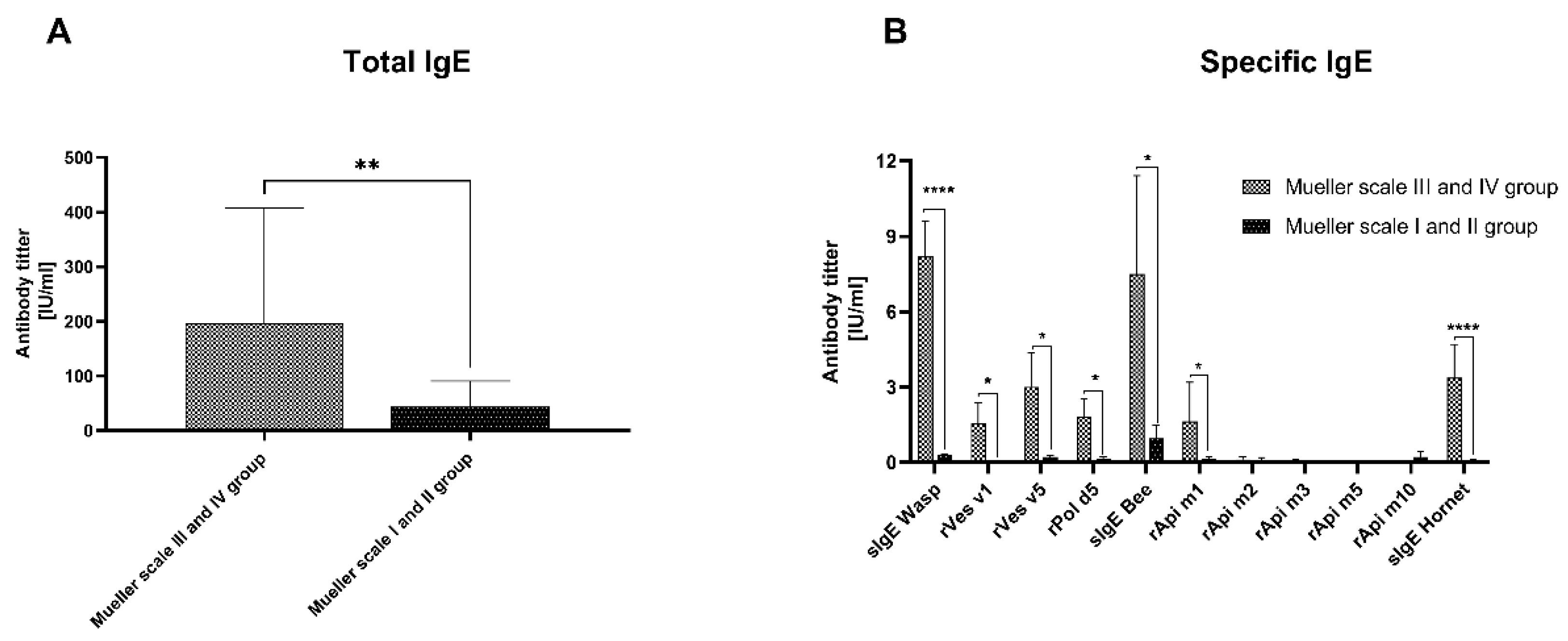
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. IgE Analysis
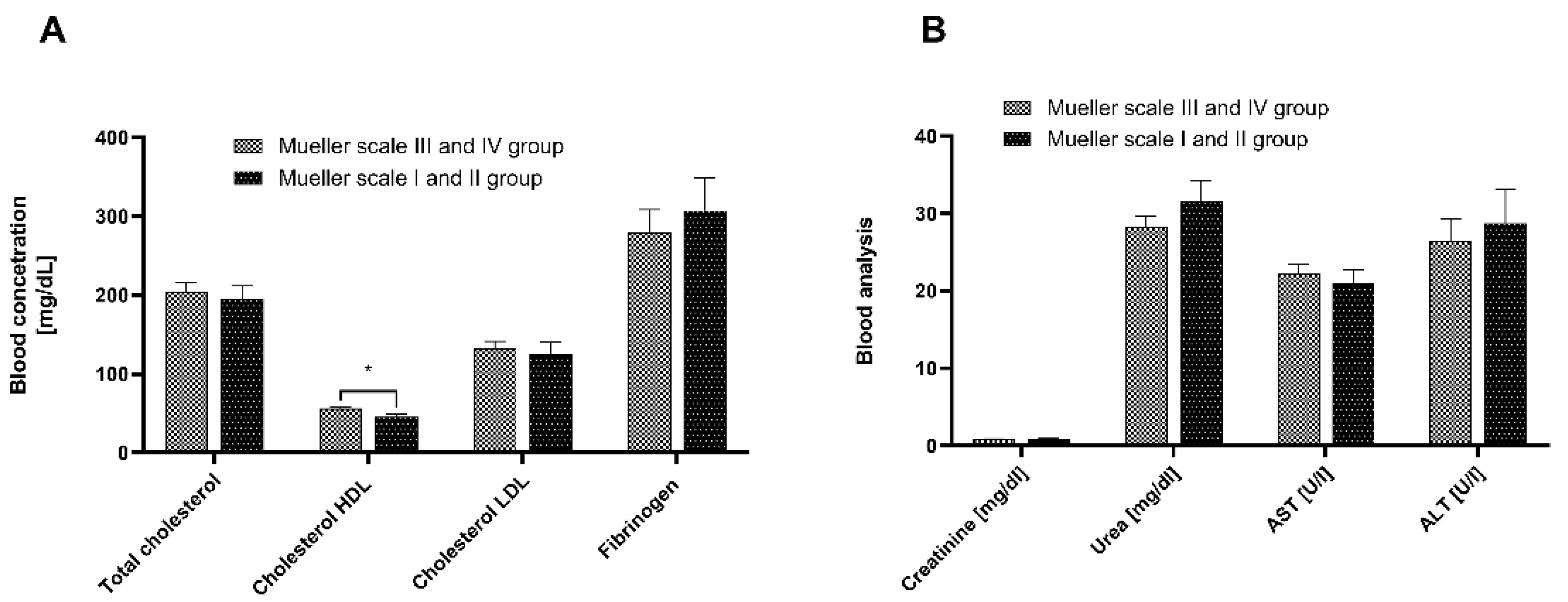
2.3. Blood Parameters Analysis
2.4. Biochemical Analysis
2.5. Immune System Parameters
2.6. Cells and Cytokines Indexes
- PLR (systemic inflammation index): Calculated from peripheral blood platelet (P) and lymphocyte (L) counts using the equation: PLR = P/L
- SII: Calculated from peripheral blood platelet (P), neutrophil (N), and lymphocyte (L) counts using the equation: SII = P × N/L
- SIRI: Calculated from peripheral blood monocyte (M), neutrophil (N), and lymphocyte (L) counts using the equation: SIRI = M × N/L
- NLR: Calculated from peripheral blood neutrophil (N) and lymphocyte (L) counts using the equation: NLR = N/L
- E/L: Eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (ELR),
- B/L: Basophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (BLR),
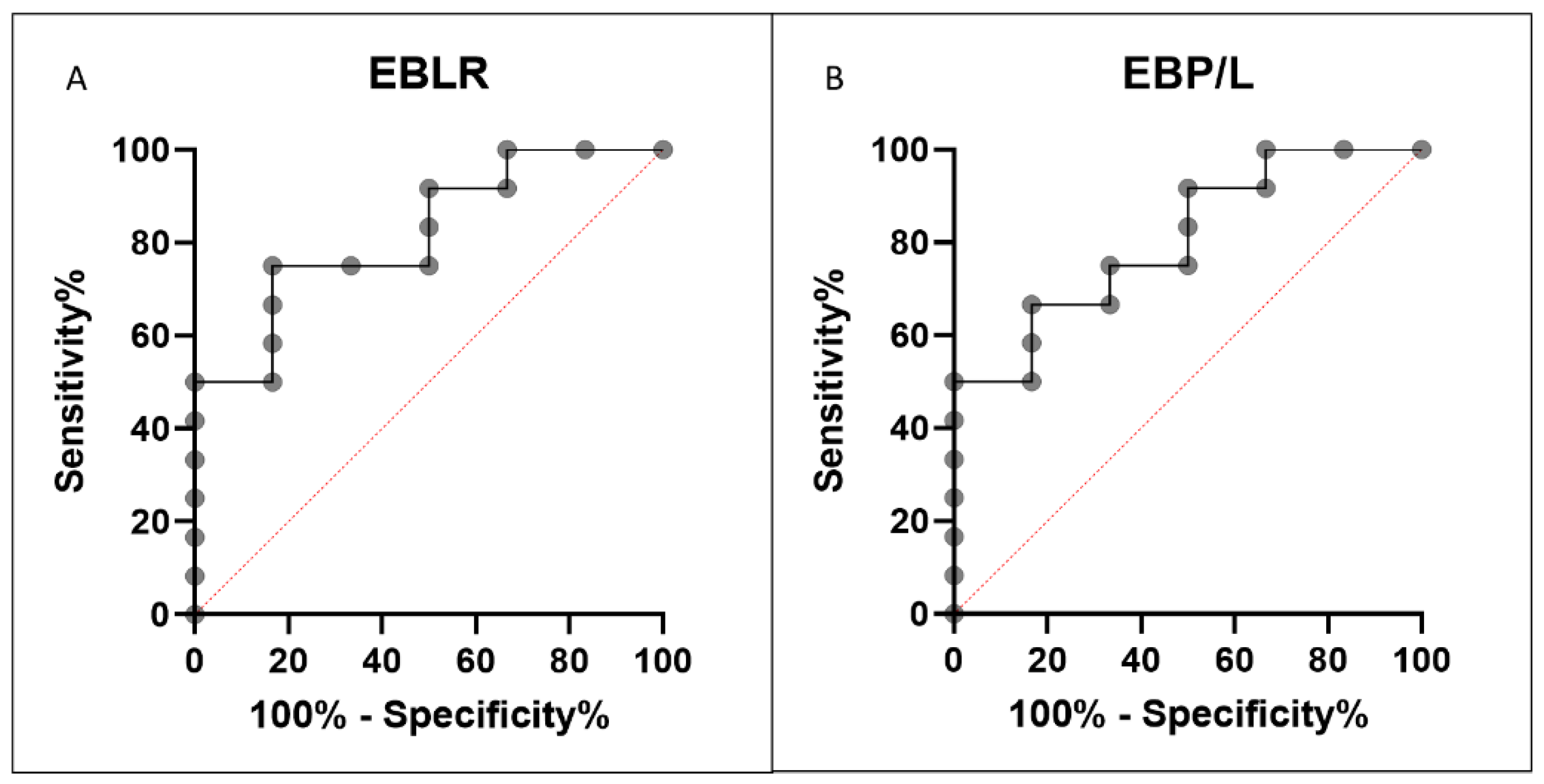
- E × B/L: Eosinophil × Basophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (EBLR),
- E × B × N/L: Eosinophil × Basophil × Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio,
- P × E/L: Platelet × Eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratio,
- P × B/L: Platelet × Basophil-to-lymphocyte ratio,
- E × B × P/L: Eosinophil × Basophil × Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio,
- N × M × E/L: Neutrophil × Monocyte × Eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratio.
- N × M × E × B/L: Neutrophil × Monocyte × Eosinophil × Basophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
- Th1/lymphocytes, Th2/lymphocytes, Th9/lymphocytes, Th17/lymphocytes, (Treg/lymphocytes)/103
- Th1/Th2, Th1/Th9, Th1/Th17, (Th1/Treg) × 103
- Th2/Th9, Th2/Th17, (Th2/Treg) × 103
- Th9/Th17, (Th9/Treg) × 10^3, (Th17/Treg) × 103
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. IgE Analysis
3.2. Blood Analysis
3.3. Biochemical Analysis
3.4. Index Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Müller U. [Insect sting allergy--clinical aspects, diagnosis and therapy]. Wien Med Wochenschr. 1989;139:150–6.
- Banks BEC, Shipolini RA. Chemistry and Pharmacology of Honey-bee Venom. Elsevier; 1986 [cited 2024 Mar 9]. p. 329–416. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9780125547703500115.
- Worm M, Moneret-Vautrin A, Scherer K, Lang R, Fernandez-Rivas M, Cardona V, et al. First European data from the network of severe allergic reactions (NORA). Allergy. 2014;69:1397–404. [CrossRef]
- Luo L, Kamau PM, Lai R. Bioactive Peptides and Proteins from Wasp Venoms. Biomolecules. 2022;12:527. [CrossRef]
- Nittner-Marszalska M, Kowal A, Szewczyk P, Guranski K, Ejma M. Wasp Venom Immunotherapy in a Patient With Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Central Nervous System Disease: Is it Safe? J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2017;27:127–9.
- Mueller UR, Mieller. Insect Sting Allergy, Clinical Picture, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Stuttgart New York; 1990.
- Graif Y, Romano-Zelekha O, Livne I, Green MS, Shohat T. Increased rate and greater severity of allergic reactions to insect sting among schoolchildren with atopic diseases. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2009;20:757–62. [CrossRef]
- Siracusa A, Folletti I, Gerth van Wijk R, Jeebhay MF, Moscato G, Quirce S, et al. Occupational anaphylaxis--an EAACI task force consensus statement. Allergy. 2015;70:141–52. [CrossRef]
- Feás X. Human Fatalities Caused by Hornet, Wasp and Bee Stings in Spain: Epidemiology at State and Sub-State Level from 1999 to 2018. Biology (Basel). 2021;10:73. [CrossRef]
- Feás X, Vidal C, Remesar S. What We Know about Sting-Related Deaths? Human Fatalities Caused by Hornet, Wasp and Bee Stings in Europe (1994-2016). Biology (Basel). 2022;11:282. [CrossRef]
- Ludman SW, Boyle RJ. Stinging insect allergy: current perspectives on venom immunotherapy. J Asthma Allergy. 2015;8:75–86. [CrossRef]
- Sturm GJ, Varga E-M, Roberts G, Mosbech H, Bilò MB, Akdis CA, et al. EAACI guidelines on allergen immunotherapy: Hymenoptera venom allergy. Allergy. 2018;73:744–64. [CrossRef]
- Bonifazi F, Jutel M, Biló BM, Birnbaum J, Muller U, EAACI Interest Group on Insect Venom Hypersensitivity. Prevention and treatment of hymenoptera venom allergy: guidelines for clinical practice. Allergy. 2005;60:1459–70. [CrossRef]
- Lawrence MG, Woodfolk JA, Schuyler AJ, Stillman LC, Chapman MD, Platts-Mills TAE. Half-life of IgE in serum and skin: Consequences for anti-IgE therapy in patients with allergic disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139:422-428.e4. [CrossRef]
- He Q, Wang S, Chen H, Long L, Xiao B, Hu K. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratios are independently associated with clinical outcomes of viral encephalitis. Front Neurol. 2023;13:1051865. [CrossRef]
- Azab B, Camacho-Rivera M, Taioli E. Average Values and Racial Differences of Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio among a Nationally Representative Sample of United States Subjects. PLoS One. 2014;9:e112361. [CrossRef]
- Demirkol S, Balta S, Cakar M, Unlu M, Arslan Z, Kucuk U. Red cell distribution width: a novel inflammatory marker in clinical practice. Cardiol J. 2013;20:209.
- Yenigun A, Sezen S, Calim OF, Ozturan O. Evaluation of the eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in pediatric patients with allergic rhinitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2016;30:e21-25. [CrossRef]
- Jiang Y, Ma W. Assessment of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Atopic Dermatitis Patients. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:1340–6. [CrossRef]
- Dogru M, Citli R. The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in children with atopic dermatitis: a case-control study. Clin Ter. 2017;168:e262–5. [CrossRef]
- Hagino T, Saeki H, Fujimoto E, Kanda N. The Eosinophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Acts as an Indicator for Improvement of Clinical Signs and Itch by Upadacitinib Treatment in Atopic Dermatitis. J Clin Med. 2023;12:2201. [CrossRef]
- Wawryk-Gawda E, Żybowska M, Ostrowicz K. The Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio in Children with Bronchial Asthma. J Clin Med. 2023;12:6869. [CrossRef]
- Arwas N, Shvartzman SU, Goldbart A, Bari R, Hazan I, Horev A, et al. Elevated Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Is Associated with Severe Asthma Exacerbation in Children. J Clin Med. 2023;12:3312. [CrossRef]
- Clinical significance of peripheral blood neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and plateletlymphocyte ratio in patients with asthma. Journal of Southern Medical University. 2017;37:84.
- Szymański Ł, Urbańska W, Ciepielak M, Cios A, Stankiewicz W, Stelmasiak M, et al. Time-dependent effect of desensitization with wasp venom on selected parameters of the immune system. Sci Rep. 2022;12:7206. [CrossRef]
- Urbańska W, Szymański L, Ciepelak M, Cios A, Stankiewicz W, Klimaszewska E, et al. Time-dependent cytokines changes in ultra-rush wasp venom immunotherapy. Sci Rep. 2023;13:10560. [CrossRef]
- Matuszewski M, Szarpak L, Pruc M, Pedrycz-Wieczorska A, Kilic M, Ak R, et al. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic biomarker for COVID-19 severity: a single center retrospective data analysis and systematic review with meta-analysis of 187 studies. Disaster and Emergency Medicine Journal. 2023;8:198–206. [CrossRef]
- Li C, Tian W, Zhao F, Li M, Ye Q, Wei Y, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index, SII, for prognosis of elderly patients with newly diagnosed tumors. Oncotarget. 2018;9:35293–9. [CrossRef]
- Dang H, Mao W, Wang S, Sha J, Lu M, Cong L, et al. Systemic inflammation response index as a prognostic predictor in patients with acute ischemic stroke: A propensity score matching analysis. Front Neurol. 2023;13:1049241. [CrossRef]
- Făgărășan I, Rusu A, Comșa H, Simu T-D, Vulturar D-M, Todea D-A. IL-6 and Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio as Markers of ICU Admittance in SARS-CoV-2 Patients with Diabetes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023;24:14908.
- Lee J, Lozano-Ruiz B, Yang FM, Fan DD, Shen L, González-Navajas JM. The Multifaceted Role of Th1, Th9, and Th17 Cells in Immune Checkpoint Inhibition Therapy. Frontiers in Immunology [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2024 Feb 1];12. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2021.625667. [CrossRef]
- Nahm, F.S. Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve: Overview and Practical Use for Clinicians. Korean J Anesthesiol 2022, 75, 25–36. [CrossRef]
- Tahir, N.; Zahra, F. Neutrophilia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2024.
- Rosales, C. Neutrophil: A Cell with Many Roles in Inflammation or Several Cell Types? Front Physiol 2018, 9, 113, doi:10.3389/fphys.2018.00113. [CrossRef]
- Day JH, Buckeridge DL, Welsh AC. Risk assessment in determining systemic reactivity to honeybee stings in sting-threatened individuals. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 1994;93:691–705. [CrossRef]
- Hollstein MM, Matzke SS, Lorbeer L, Forkel S, Fuchs T, Lex C, et al. Intracutaneous Skin Tests and Serum IgE Levels Cannot Predict the Grade of Anaphylaxis in Patients with Insect Venom Allergies. J Asthma Allergy. 2022;15:907–18.29. [CrossRef]
- Wilson AB, Deighton J, Lachmann PJ, Ewan PW. A comparative study of IgG subclass antibodies in patients allergic to wasp or bee venom. Allergy. 1994;49:272–80. [CrossRef]
- Reisman RE, DeMasi JM. Relationship of serum venom-specific IgE titers to clinical aspects of stinging insect allergy. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989;89:67–70. [CrossRef]
- Kopač P, Custovic A, Zidarn M, Šilar M, Šelb J, Bajrović N, et al. Biomarkers of the Severity of Honeybee Sting Reactions and the Severity and Threshold of Systemic Adverse Events During Immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9:3157-3163.e5. [CrossRef]
- Nittner-Marszalska M, Małolepszy J, Medrala W. [Evaluation of diagnostic value of skin test, venom specific antibodies against EgE and basophil histamine release test in hymenoptera allergy]. Pneumonol Alergol Pol. 1993;61:346–51.
- Warrington R. Lack of Correlation between Severity of Clinical Symptoms, Skin Test Reactivity, and Radioallergosorbent Test Results in Venom-Allergic Patients. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2006;2:62–7.
- Sturm GJ, Heinemann A, Schuster C, Wiednig M, Groselj-Strele A, Sturm EM, et al. Influence of total IgE levels on the severity of sting reactions in Hymenoptera venom allergy. Allergy. 2007;62:884–9. [CrossRef]
- van der Linden P-WG, Hack CE, Poortman J, Vivié-Kipp YC, Struyvenberg A, van der Zwan JK. Insect-sting challenge in 138 patients: Relation between clinical severity of anaphylaxis and mast cell activation. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 1992;90:110–8.
- Tomsitz D, Brockow K. Component Resolved Diagnosis in Hymenoptera Anaphylaxis. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2017;17:38. [CrossRef]
- Bilò MB, Ollert M, Blank S. The role of component-resolved diagnosis in Hymenoptera venom allergy. Curr Opin Allergy ClinImmunol. 2019;19:614–22. [CrossRef]
- Guan K, Li L-S, Yin J. Use of sIgE/T-IgE in Predicting Systemic Reactions: Retrospective Analysis of 54 Honeybee Venom Allergy Cases in North China. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016;129:2091–5.
- Hamilton RG, Williams PB, Specific IgE Testing Task Force of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology. Human IgE antibody serology: a primer for the practicing North American allergist/immunologist. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;126:33–8. [CrossRef]
- Gattinger P, Lupinek C, Kalogiros L, Silar M, Zidarn M, Korosec P, et al. The culprit insect but not severity of allergic reactions to bee and wasp venom can be determined by molecular diagnosis. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0199250. [CrossRef]
- Zhai G, Wang J, Liu Y, Zhou Y. Platelet-lymphocyte ratio as a new predictor of in-hospital mortality in cardiac intensive care unit patients. Sci Rep. 2021;11:23578. [CrossRef]
- Cansever M, Sari N. The association of allergic rhinitis severity with neutrophil-lymphocyte and platelet-lymphocyte ratio in children. North Clin Istanb. 2022;9:602–9. [CrossRef]
- Wang S, Pan X, Jia B, Chen S. Exploring the Correlation Between the Systemic Immune Inflammation Index (SII), Systemic Inflammatory Response Index (SIRI), and Type 2 Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity. 2023;16:3827. [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar MF, Coşgun M. Can the systemic immune inflammation index (SII) and the systemic inflammation response index (SIRI) predict the severity of coronary artery disease? Northwestern Med J. 2024;4:157–62.
- Ma R, Cui L, Cai J, Yang N, Wang Y, Chen Q, et al. Association between systemic immune inflammation index, systemic inflammation response index and adult psoriasis: evidence from NHANES. Front Immunol [Internet]. 2024 [cited 2024 Aug 25];15. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1323174/full. [CrossRef]
- Yin X, Zhang Y, Zou J, Yang J. Association of the systemic immune-inflammation index with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep. 2024;14:15129. [CrossRef]
- Tian T, Xie M, Sun G. Association of systemic immune-inflammation index with asthma and asthma-related events: a cross-sectional NHANES-based study. Front Med [Internet]. 2024 [cited 2024 Aug 25];11. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/medicine/articles/10.3389/fmed.2024.1400484/full. [CrossRef]
- Zeng-Yun-Ou Z, Zhong-Yu J, Wei L. Bidirectional associations between eosinophils, basophils, and lymphocytes with atopic dermatitis: A multivariable Mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1001911. [CrossRef]
| Mueller grade III and IV |
Mueller grade I and II |
p value (comparions betweenc diffrenet Mueller sclae gropus | Control | ||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| RBC [x 10^12/l] | 4.83 | 0.10 | 4.74 | 0.12 | 0.775 | 4.87 | 0.63 |
| HGB [g/dl] | 14.20 | 0.29 | 14.03 | 0.41 | 0.679 | 14.71 | 1.88 |
| HCT [%] | 41.87 | 0.82 | 41.26 | 1.02 | 0.805 | 43.03 | 5.61 |
| MCV [fL] | 86.77 | 0.95 | 87.16 | 0.99 | 0.851 | 88.31 | 3.50 |
| MCH [pg] | 29.49 | 0.36 | 29.60 | 0.46 | 0.944 | 30.26 | 1.38 |
| MCHC [g/dl] | 33.99 | 0.17 | 33.99 | 0.26 | 0.503 | 34.26 | 0.76 |
| PLT[x 10^9/l] | 253.30 | 12.25 | 266.47 | 17.86 | 0.876 | 251.34 | 60.76 |
| MPV [fL] | 10.91 | 0.19 | 11.07 | 0.24 | 0.353 | 9.13 | 0.88 |
| WBC [x10^9/L] | 6.46 | 0.32 | 7.12 | 0.36 | 0.617 | 6.09 | 1.74 |
| LYMPH w.b. [x10^3/µL] | 2.12 | 0.11 | 1.97 | 0.12 | 0.333 | 1.64 | 0.62 |
| LYMPH [%] | 33.45 | 1.69 | 28.65 | 2.03 | 0.062 | 27.09 | 7.66 |
| NEUT w.b. [x10^3/µL] | 3.60 | 0.30 | 4.42 | 0.37 | 0.073 | 3.76 | 1.33 |
| NEUT [%] | 54.27 | 2.07 | 60.92 | 2.46 | 0.035 | 61.41 | 8.80 |
| MONO w.b. [x10^3/µL] | 0.54 | 0.03 | 0.55 | 0.04 | 0.862 | 0.40 | 0.11 |
| MONO [%] | 8.40 | 0.29 | 7.80 | 0.56 | 0.322 | 6.57 | 1.44 |
| EO w.b. [x10^3/µL] | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.131 | 0.17 | 0.15 |
| EO [%] | 3.24 | 0.48 | 2.16 | 0.33 | 0.056 | 2.81 | 2.28 |
| BASO w.b. [x10^3/µL] | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.189 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| BASO [%] | 0.67 | 0.07 | 0.47 | 0.07 | 0.051 | 0.68 | 0.31 |
| Mueller grade III and IV | Mueller grade I and II | Control group | p value Mueller III-IV vs. Mueller I-II | p value Mueller III-IV vs. Control | p value Mueller II-II vs. Control | ||||
| Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | ||||
| PLR (P/L) | 131.700 | 9.776 | 143.800 | 13.310 | 168.000 | 8.900 | 0.727 | 0.0131 | 0.0684 |
| SII (P x N/L) | 515.900 | 77.730 | 655.600 | 88.360 | 619.600 | 43.380 | 0.092 | 0.0254 | 0.8898 |
| SIRI (NxM/L) | 1.065 | 0.164 | 1.354 | 0.216 | 0.947 | 0.065 | 0.057 | 0.5117 | 0.0871 |
| NRL (N/L) | 0.678 | 0.059 | 0.507 | 0.056 | 2.540 | 0.153 | 0.310 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| E/L | 0.093 | 0.012 | 0.075 | 0.010 | 0.078 | 0.007 | 0.183 | 0.1645 | 0.8239 |
| B/L | 0.021 | 0.002 | 0.018 | 0.002 | 0.024 | 0.001 | 0.343 | 0.2316 | 0.0279 |
| ((E*B)/L)*100 | 0.499 | 0.096 | 0.240 | 0.046 | 0.283 | 0.030 | 0.015 | 0.0463 | 0.3721 |
| (E*B*N)/L | 0.017 | 0.004 | 0.010 | 0.002 | 0.011 | 0.001 | 0.218 | 0.1633 | 0.9288 |
| P*E/L | 23.220 | 3.078 | 19.960 | 2.675 | 19.300 | 1.896 | 0.520 | 0.2539 | 0.7525 |
| P*B/L | 5.599 | 0.836 | 4.729 | 0.777 | 5.860 | 0.438 | 0.452 | 0.4435 | 0.1156 |
| (E*B*P)/L | 1.260 | 0.243 | 0.626 | 0.107 | 0.718 | 0.081 | 0.034 | 0.0388 | 0.633 |
| (N*M*E)/L | 0.181 | 0.036 | 0.176 | 0.029 | 0.112 | 0.011 | 0.546 | 0.1325 | 0.0432 |
| (N*M*E)/L | 0.048 | 0.011 | 0.045 | 0.008 | 0.036 | 0.004 | 0.749 | 0.7659 | 0.525 |
| N*M*E*B)/L | 0.010 | 0.003 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.438 | 0.0613 | 0.3744 |
| Mueller scale III and IV group | Mueller scale I and II group | p value | |||
| Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | ||
| Th1/lymphocytes | 577.43 | 260.81 | 584.08 | 235.30 | 0.981 |
| Th2/lymphocytes | 2413.08 | 1666.72 | 2041.60 | 1717.34 | 0.868 |
| Th9/lymphocytes | 115.72 | 17.57 | 107.85 | 17.62 | 0.666 |
| Th17/lymphocytes | 11.24 | 1.83 | 14.17 | 2.64 | 0.247 |
| (Treg/lymphocytes) / 103 | 34.86 | 10.99 | 68.18 | 26.02 | 0.289 |
| Th1/Th2 | 0.82 | 0.26 | 0.67 | 0.18 | 0.627 |
| Th1/Th9 | 3.88 | 1.25 | 4.38 | 1.13 | 0.713 |
| Th1/Th17 | 148.48 | 105.50 | 61.88 | 29.58 | 0.377 |
| (Th1/Treg) x 103 | 8.00 | 1.36 | 6.22 | 0.86 | 0.316 |
| Th2/Th9 | 13.40 | 6.73 | 15.17 | 11.45 | 0.875 |
| Th2/Th17 | 139.30 | 97.71 | 80.31 | 52.83 | 0.584 |
| (Th2/Treg) x 103 | 20.50 | 4.74 | 26.90 | 8.10 | 0.529 |
| Th9/Th17 | 43.52 | 33.96 | 13.99 | 8.47 | 0.333 |
| (Th9/Treg) x 103 | 4.97 | 1.35 | 2.68 | 0.56 | 0.150 |
| (Th17/Treg) x 103 | 0.70 | 0.16 | 0.49 | 0.09 | 0.290 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





