Submitted:
21 October 2024
Posted:
22 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Study Population and Data Collection
2.3. Outcome Variables
2.4. Potential Covariates
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Participants
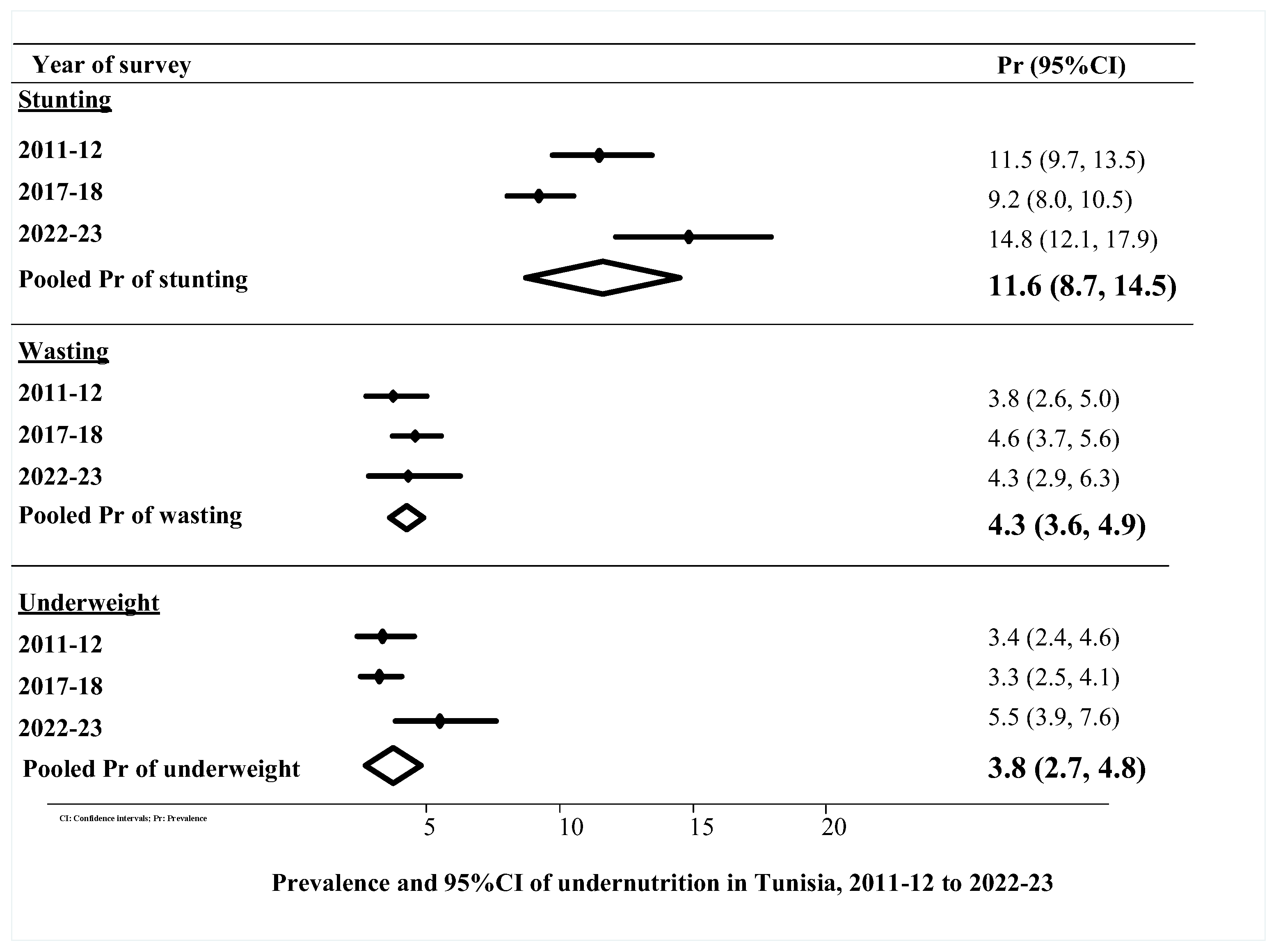
3.2. Prevalence and 95% CI of Undernutrition, 2011–12 to 2022–23
3.3. Trends in the Prevalence of Undernutrition from 2011–12 to 2022–23
3.4. Factors Associated with Undernutrition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), World Health Organization (WHO), International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank. Levels and trends in child malnutrition: UNICEF / WHO / World Bank Group Joint Child Malnutrition Estimates: Key findings of the 2023 edition. New York: UNICEF and WHO; 2023. CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- UNICEF Units for Children. From the First Hour of Life: Making the case for improved infant and young child feeding everywhere. 3 United Nations Plaza, New York, NY 10017, USA.
- Black RE, Allen LH, Bhutta ZA, Caulfield LE, De Onis M, Ezzati M, et al. Maternal and child undernutrition: global and regional exposures and health consequences. The lancet. 2008;371(9608):243-60. [CrossRef]
- Global Nutrition Report. Country Nutrition Profiles: Africa. 2024 Bristol UD.
- Djoumessi, YF. The impact of malnutrition on infant mortality and life expectancy in Africa. Nutrition. 2022; 103:111760.
- Atinmo T, Mirmiran P, Oyewole OE, Belahsen R, Serra-Majem L. Breaking the poverty/malnutrition cycle in Africa and the Middle East. Nutrition reviews. 2009;67(suppl_1):S40-S6. [CrossRef]
- Cho, R. How Climate Change Impacts the Economy. State of the Planet. Columbia Climate School. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- UNICEF for Every Child. Childhood diseases. [accessed 14 Aug 2024]. Available from: https://www.unicef.org/health/childhood-diseases.
- TARGET, S. An Investment Framework for Meeting the Global Nutrition Target for Stunting.
- Moore Tg, Arefadib N, Deery A, Keyes M, West S. The First Thousand Days: An Evidence Paper – Summary. Parkville, Victoria: Centre for Community, Child Health, Murdoch Children’s Research Institute.: 2017.
- Ochi A, Saidi Y. Socio-economic inequalities and their impact on children’s health and nutrition in Tunisia using generalized entropy measures. Regional Science Policy & Practice. 2024:100034. [CrossRef]
- Elmighrabi NF, Fleming CA, Agho KE. Wasting and Underweight in Northern African Children: Findings from Multiple-Indicator Cluster Surveys, 2014–2018. Nutrients. 2023;15(14):3207. [CrossRef]
- Elmighrabi NF, Fleming CA, Dhami MV, Agho KE. Childhood undernutrition in North Africa: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Global Health Action. 2023;16(1):2240158. [CrossRef]
- Elmighrabi NF, Fleming CA, Dhami MV, Elmabsout AA, Agho KE. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of childhood undernutrition in North Africa. Plos one. 2023;18(4):e0283685. [CrossRef]
- MICS Surveys. [accessed 0n 14 Aug 2024]. Available from: http://mics.unicef.org/] (http://mics.unicef.org/.
- Tunisia Datasets and reports. MICS UNICEF. 2024.
- World Health Organization. WHO child growth standards: length/height-for-age, weight-for-age, weight-for-length, weight-for-height and body mass index-for-age: methods and development. World Health Organization; 2006.
- Li Z, Kim R, Vollmer S, Subramanian SV. Factors associated with child stunting, wasting, and underweight in 35 low-and middle-income countries. JAMA network open. 2020;3(4):e203386-e. [CrossRef]
- Whye Lian C, Wan Muda WA, Mohd Hussin ZA, Ching Thon C. Factors associated with undernutrition among children in a rural district of Kelantan, Malaysia. Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health. 2012;24(2):330-42. [CrossRef]
- Tariq J, Sajjad A, Zakar R, Zakar MZ, Fischer F. Factors associated with undernutrition in children under the age of two years: secondary data analysis based on the Pakistan demographic and health survey 2012–2013. Nutrients. 2018;10(6):676. [CrossRef]
- Amaral TF, Matos LC, Teixeira MA, Tavares MM, Álvares L, Antunes A. Undernutrition and associated factors among hospitalized patients. Clinical nutrition. 2010;29(5):580-5. [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu M, Tinsae F, Haileslassie K, Seid O, Gebregziabher G, Yebyo H. Undernutrition status and associated factors in under-5 children, in Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Nutrition. 2015;31(7-8):964-70. [CrossRef]
- UNICEF, World Health Organization, World Bank. UNICEF-WHO-World Bank: Joint child malnutrition estimates - Levels and trends (2023 edition). 2023.
- UNICEF. At least one in four children live in poverty in the Middle East and North Africa. [accessed on 14 Aug. 2024]. Available from: https://www.unicef.org/press-releases/least-one-four-children-live-poverty-middle-east-and-north-africa#:~:text=Press%20release.
- World Bank Group. Poverty has fallen in the Maghreb, but inequality persists. [accessed on 14 Aug 2014]. Available from: https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/feature/2016/10/17/poverty-has-fallen-in-the-maghreb-but-inequality-persists.
- WID World. Global inequality data 2020 update. World inequality database. [accessed on 14 Aug 2024]. Available from: https://wid.world/news-article/2020-regional-updates/#:~:text=The%20World%20Inequality%20Lab%20releases,over%20time%2C%20countries%20and%20regions.
- Perez-Escamilla R, Bermudez O, Buccini GS, Kumanyika S, Lutter CK, Monsivais P, et al. Nutrition disparities and the global burden of malnutrition. Bmj. 2018;361. [CrossRef]
- Bhutta ZA, Das JK, Rizvi A, Gaffey MF, Walker N, Horton S, et al. Evidence-based interventions for improvement of maternal and child nutrition: what can be done and at what cost? The lancet. 2013;382(9890):452-77. [CrossRef]
- Marriott BP, White A, Hadden L, Davies JC, Wallingford JC. World Health Organization (WHO) infant and young child feeding indicators: associations with growth measures in 14 low-income countries. Maternal & child nutrition. 2012;8(3):354-70. [CrossRef]
- Zhao A, Gao H, Li B, Zhang J, Win NN, Wang P, et al. Inappropriate feeding behavior: one of the important causes of malnutrition in 6-to 36-month-old children in Myanmar. The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 2016;95(3):702. [CrossRef]
- World Food Program. Tunisia Country Strategic Plan (2022–2025). 2022.
- Datar A, Nicosia N, Shier V. Maternal work and children’s diet, activity, and obesity. Soc Sci Med. 2014; 107:196-204. [CrossRef]
- Faizan U, Rouster AS. Nutrition and hydration requirements in children and adults. 2020.
- Gatica-Domínguez G, Neves PA, Barros AJ, Victora CG. Complementary Feeding Practices in 80 Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Prevalence of and Socioeconomic Inequalities in Dietary Diversity, Meal Frequency, and Dietary Adequacy.. J nutr disorders ther. 2021;151(7):1956-64. [CrossRef]
- Lailatul M, Yuly S, Chrysoprase TA. Family support is the strongest predictor that influences mother’s self-efficacy level on complementary feedings practices among toddlers in Tengger tribe. Nutrition & Food Science. 2024;54(3):535-46. [CrossRef]
- Mekonen EG, Zegeye AF, Workneh BS. Complementary feeding practices and associated factors among mothers of children aged 6 to 23 months in Sub-saharan African countries: a multilevel analysis of the recent demographic and health survey. BMC Public Health. 2024;24(115). [CrossRef]
- Yalew BM, Amsalu F, Bikes D. Prevalence and factors associated with stunting, underweight and wasting: a community based cross sectional study among children age 6-59 months at Lalibela Town, Northern Ethiopia. J Nutr Disorders Ther. 2014;4(147):2161-0509.1000147. [CrossRef]
- Supadmi S, Laksono AD, Kusumawardani HD, Ashar H, Nursafingi A, Kusrini I, et al. Factor related to stunting of children under two years with working mothers in Indonesia. Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health. 2024; 26:101538. [CrossRef]
- Global Nutrition Report. Country Nutrition Profile: Tunisia. Bristol, UK: Development: 2024.
- UNICEF. Nutrition Porofile: Tunisia. 2010.
- Mertens A, Benjamin-Chung J, Colford Jr JM, Hubbard AE, van der Laan MJ, Coyle J, et al. Child wasting and concurrent stunting in low-and middle-income countries. Nature 2023;621(7979):558-67. [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui F, Salam RA, Lassi ZS, Das JK. The intertwined relationship between malnutrition and poverty. Frontiers in Public Health. 2020; 8:453. [CrossRef]
- Obasohan PE, Walters SJ, Jacques R, Khatab K. Risk factors associated with malnutrition among children under-five years in sub-Saharan African countries: a scoping review. International journal of environmental research and public health. 2020;17(23):8782. [CrossRef]
- Christian AK, Dake FA. Profiling household double and triple burden of malnutrition in sub-Saharan Africa: prevalence and influencing household factors. Public Health Nutrition. 2022;25(6):1563-76. [CrossRef]
- Sewor C, Jayalakshmi R. Trends of risk factors associated with childhood stunting and anaemia in Ghana: evidence from the Demographic Health Survey and Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey (2003–2017). Public Health Nutrition. 2024;27(1):e29. [CrossRef]
- Stewart CP, Iannotti L, Dewey KG, Michaelsen Kf, Onyango AW. Contextualising complementary feeding in a broader framework for stunting prevention. Maternal & child nutrition. 2013; 9:27-45. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. Infant and young child feeding.. 2023.
- Özaltin E, Hill K, Subramanian SV. Association of maternal stature with offspring mortality, underweight, and stunting in low-to middle-income countries. Jama. 2010;303(15):1507-16. [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. Maternal nutrition. [Accessed on 14 Aug 2024]: UNICEF for everychild. Available from: https://www.unicef.org/nutrition/maternal#:~:text=During%20pregnancy%2C%20poor%20diets%20lacking,and%20developmental%20delays%20for%20children.
- Delisle, HF. Poverty: the double burden of malnutrition in mothers and the intergenerational impact. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 2008;1136(1):172-84. [CrossRef]
- Popkin, BM. The shift in stages of the nutrition transition in the developing world differs from past experiences! Public health nutrition. 2002;5(1A):205-14. [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, S. Attacking the double burden of malnutrition in Asia and the Pacific: Asian Development Bank; 2001.
- Rachmah Q, Mahmudiono T, Loh SP. Predictor of Obese Mothers and Stunted Children in the Same Roof: A Population-Based Study in the Urban Poor Setting Indonesia. Front Nutr. 2021;6(8):710588. [CrossRef]
- Marshall NE, Lau B, Purnell JQ, Thornburg KL. Impact of maternal obesity and breastfeeding intention on lactation intensity and duration. Matern Child Nutr. 2019;15: e12732. [CrossRef]
- Adhikari D, Khatri RB, Paudel YR, Poudyal AK. Factors associated with underweight among under-Five children in Eastern Nepal: community-based cross-sectional study. Front Public Health. 2017; 5:350. [CrossRef]
- Moshi CC, Sebastian PJ, Mushumbusi DG, Azizi KA, Meghji WP, Kitunda ME, et al. Determinants of underweight among children aged 0–23 months in Tanzania. Food Science & Nutrition. 2022;10(4):1167-74. [CrossRef]
- Mukabutera A, Thomson DR, Hedt-Gauthier BL, Basinga P, Nyirazinyoye L, Murray M. Risk factors associated with underweight status in children under five: an analysis of the 2010 Rwanda Demographic Health Survey (RDHS). BMC Nutrition. 2016; 2:1-12. [CrossRef]
- Yisak H, Gobena T, F.t M. Prevalence and risk factors for under nutrition among children under five at Haramaya district, Eastern Ethiopia. BMC pediatrics. 2015; 15:1-7. [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. UNICEF’s approach to scaling up nutrition: For mothers and their children. United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) 2020.
- Black RE, Victora CG, Walker SP, Bhutta ZA, Christian P, De Onis M, et al. Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. The Lancet. 2013;382(9890):427-51. [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global nutrition targets 2025: low birth weight policy brief- external site opens in new window. Geneva: WHO, 2014.
- Scharf RJ, Stroustrup A, Conaway Mr, DeBoer Md. Growth and development in children born very low birthweight. Archives of Disease in Childhood-Fetal and Neonatal Edition. 2016;101(5): F433-F8. [CrossRef]
- Mayor, S. Low birth weight is associated with increased deaths in infancy and adolescence, shows study. British Medical Journal Publishing Group; 2016. [CrossRef]
- Ntenda, PA. Factors associated with non-and under-vaccination among children aged 12–23 months in Malawi. A multinomial analysis of the population-based sample. Pediatrics & Neonatology. 2019;60(6):623-33. [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, A. Low birthweight infants, infection, and immunity. 2001.
- Hviid A, Melbye M. The impact of birth weight on infectious disease hospitalization in childhood. American journal of epidemiology. 2007;165(7):756-61. [CrossRef]
- Amugsi DA, Mittelmark MB, Lartey A. An analysis of socio-demographic patterns in child malnutrition trends using Ghana demographic and health survey data in the period 1993–2008. BMC public health. 2013; 13:1-16. [CrossRef]
- Fotso, JC. Urban–rural differentials in child malnutrition: trends and socioeconomic correlates in sub-Saharan Africa. Health & place. 2007;13(1):205-23. [CrossRef]
- Statistiques Tunisie. Measuring Poverty, Inequalities and Polarization in Tunisia 2000-2010. Tunisia: National Institute of Statistics, 2012.
- Nasri, K. Poverty-alleviation programs in Tunisia: selection processes and targeting performance indicators at the regional level. International Journal of Social Economics. 2022;49(4):629-50. [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health and Population, National Nutrition Institute, UNICEF. Nutrition Agends for action a policy paper on scaling up nutrition interventions in Egypt; 2017.
- Vollmer S, Bommer C, Krishna A, Harttgen K, Subramanian SV. The association of parental education with childhood undernutrition in low-and middle-income countries: comparing the role of paternal and maternal education. International journal of epidemiology. 2017;46(1):312-23. [CrossRef]
- Karlsson O, De Neve J, Subramanian SV. Weakening association of parental education: analysis of child health outcomes in 43 low-and middle-income countries. International Journal of Epidemiology. 2019;48(1):83-97. [CrossRef]
- El Taguri A, Betilmal I, Mahmud SM, Ahmed AM, Goulet O, Galan P, et al. Risk factors for stunting among under-fives in Libya. Public health nutrition. 2009;12(8):1141-9. [CrossRef]
- El-Mouzan MI, Al-Salloum AA, Al-Herbish AS, Qurachi MM, Al-Omar AA. Effects of education of the head of the household on the prevalence of malnutrition in children. Saudi Med J. 2010;31(3):304-7.
- Bukit DS, Keloko AB, Ashar T. Father’s support and mother’s behavior in stunting prevention efforts. Journal of Health Science and Prevention. 2021;5(2):100-5. [CrossRef]
- Laksminingsih, E. Can early initiation to breastfeeding prevent stunting in 6–59 months old children? Journal of Health Research. 2018;32(5):334-41.
- Amer S, Kateeb E. Mothers’ Employment and Exclusive Breastfeeding Practices: A Brief Report from Jerusalem Governorate. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(3):2066. [CrossRef]
| Years 2011-12 (n=1271) | Years 2017-18 (n=1337) | Years 2022-23 (n=657) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area of residence | Total n (%) | Total n (%) | Total n (%) |
| Urban | 808 (63.56) | 831 (62.15) | 366 (55.77) |
| Rural | 463 (36.44) | 506 (37.85) | 291(44.23) |
| Wealth Index | |||
| Poorest | 344 (27.06) | 278 (20.79) | 116 (17.6) |
| Poorer | 295 (23.2) | 175 (13.12) | 191 (29.13) |
| Middle | 245 (19.26) | 257 (19.24) | 143 (21.73) |
| Fourth | 160 (12.6) | 391(29.23) | 88 (13.4) |
| Richest | 227 (17.88) | 235 (17.61) | 119 (18.13) |
| Sex of baby | |||
| Boy | 678 (53.37) | 726 (54.33) | 352 (53.64) |
| Girl | 592 (46.63) | 610 (45.67) | 305 (46.36) |
| Child age (months) | |||
| 0-5 | 337 (26.49) | 316 (23.65) | 150 (22.77) |
| 6-11 | 330 (25.99) | 321 (24.02) | 147 (22.36) |
| 12-17 | 302 (23.76) | 338 (25.26) | 166 (25.29) |
| 18-23 | 302 (23.76) | 362 (27.08) | 194 (29.58) |
| Mother’s age (years) | |||
| 15-34 | 938 (74.05) | 901 (67.88) | 391 (60.99) |
| 35-49 | 329 (25.95) | 426 (32.12) | 250 (39.01) |
| Father’s age (years) | |||
| 18-34 | 380 (33.11) | 374 (30.4) | 172 (28.04) |
| 35-44 | 598 (52.1) | 656 (53.3) | 320 (52.28) |
| 45+ | 170 (14.79) | 201 (16.3) | 121 (19.68) |
| Mother’s age at marriage (years) | |||
| ≤ 18 years | 44 (3.79) | 32 (2.55) | 27 (4.33) |
| >18 years | 1118 (96.21) | 1207 (97.45) | 590 (95.67) |
| Marital status | |||
| Married | 1148 (90.69) | 1231 (92.73) | 613 (95.45) |
| Not married | 118 (9.31) | 96 (7.27) | 29 (4.55) |
| Maternal education | |||
| Secondary and above | 771(60.91) | 973 (73.29) | 188 (30.51) |
| Primary | 354 (27.93) | 275 (20.73) | 339 (55.18) |
| No education | 141(11.16) | 79 (5.98) | 88 (14.31) |
| Father education | |||
| Secondary and above | 751(59.12) | 950 (71.1) | 193 (31.09) |
| Primary | 370 (29.9) | 288 (21.58) | 334 (53.82) |
| No education | 150 (11.8) | 98 (7.33) | 94 (15.09) |
| Maternal BMI (kgm-2) | |||
| ≤18.5 | 750 (64.12) | 878 (66.71) | 390 (65.1) |
| 19-25 | 380 (32.52) | 419 (31.84) | 182 (30.34) |
| 25+ | 39 (3.37) | 19 (1.45) | 27 (4.56) |
| Household members | |||
| 1-3 | 311(24.45) | 650 (48.65) | 116 (17.67) |
| 4-8 | 855 (67.31) | 677 (50.67) | 506 (76.97) |
| >8 | 105 (8.24) | 9 (0.68) | 35 (5.36) |
| Birth order | |||
| Non previous | 474 (37.28) | 770 (57.6) | 352 (53.51) |
| 1 | 601(47.3) | 354 (26.52) | 205 (31.19) |
| 2 or more | 196 (15.43) | 212 (15.88) | 101 (15.31) |
| Cooking fuel | |||
| Clean | 1270 (99.91) | 1333 (99.84) | 656 (99.83) |
| Un clean | 1(0.09) | 2 (0.16) | 1 (0.17) |
| Source of drinking water | |||
| Protected | 497 (62.74) | 725 (54.23) | 354 (53.9) |
| Unprotected | 474 (37.26) | 612 (45.77) | 303 (46.1) |
| Toilet facility | |||
| Improved | 784 (61.72) | 555 (41.53) | 298 (45.32) |
| Unimproved | 486 (38.28) | 781 (58.47) | 359 (54.68) |
| Listening to the radio | |||
| Not at all | 569 (44.9) | 722 (54.38) | 319 (49.78) |
| Yes | 698 (55.1) | 606 (45.62) | 321 (50.22) |
| Watching TV | |||
| Not at all | 22 (1.72) | 3 (2.33) | 31 (4.91) |
| Yes | 1245 (98.28) | 1296 (97.67) | 609 (95.09) |
| Reading newspaper | |||
| Not at all | 464 (42.9) | 105 (79.2) | 523 (81.57) |
| Yes | 617 (57.1) | 276 (20.8) | 118 (18.43) |
| Size of baby | |||
| Average | 824 (72.69) | 852 (69.85) | 418 (68.63) |
| Small | 161(14.23) | 154 (12.65) | 94 (15.4) |
| Large | 148 (13.08) | 213 (17.5) | 97 (15.97) |
| Diarrhoea last two weeks | |||
| No | 1115 (87.85) | 1173 (87.8) | 600 (92.03) |
| Yes | 154 (12.15) | 163 (12.2) | 52 (7.97) |
| Fever | |||
| No | 265 (20.83) | 1025 (76.82) | 542 (82.75) |
| Yes | 1006 (79.17) | 309 (23.18) | 113 (17.25) |
| Cough | |||
| No | 682 (53.74) | 934 (69.91) | 492 (75.18) |
| Yes | 587 (46.26) | 402 (30.09) | 163 (24.82) |
| Any infection | |||
| No | 137 (10.8) | 762 (57.03) | 444 (67.63) |
| Yes | 1134 (89.2) | 574 (42.97) | 213 (32.37) |
| Place of delivery | |||
| Government | 345 (27.14) | 1217 (99.73) | 604 (98.85) |
| Non-government | 926 (72.86) | 3 (0.27) | 7 (1.15) |
| Antenatal clinic visits | |||
| 8+ | 391(30.78) | 304 (22.72) | 165 (25.26) |
| 4-7 | 571(44.92) | 723 (54.06) | 315 (48.15) |
| 1-3 | 142 (11.18) | 139 (10.43) | 79 (12.06) |
| None | 167 (13.12) | 171(12.79) | 95 (14.53) |
| Delivery assistance | |||
| Skilled | 831 (65.4) | 1215 (90.92) | 601 (91.48) |
| Unskilled | 440 (34.6) | 121 (9.08) | 56 (8.52) |
| Mode of delivery | |||
| Non-caesarean | 16 (1.41) | 683 (56.12) | 325 (54.05) |
| Caesarean | 1113 (98.59) | 534 (43.88) | 276 (45.95) |
| Postnatal checkup (days) | |||
| 0-2 | 38 (3.02) | 180 (13.45) | 125 (18.98) |
| After 2 | 360 (28.32) | 206 (15.38) | 83 (12.65) |
| No | 872 (68.66) | 951(71.17) | 449 (68.36) |
| Early initiation of breast feeding | |||
| After 1 hr | 753 (59.26) | 858 (64.23) | 411 (62.49) |
| Withing 1 hr | 518 (40.74) | 478 (35.77) | 246 (37.51) |
| Ever breast feed | |||
| Yes | 555 (43.66) | 1135 (84.9) | 561 (85.39) |
| No | 716 (56.34) | 202 (15.1) | 96 (14.61) |
| Duration of breast feeding (months) | |||
| Up to 12 | 317 (24.95) | 564 (42.21) | 280 (42.56) |
| >12 | 954 (75.05) | 772 (57.79) | 377 (57.44) |
| Literacy | |||
| Yes | 309 (62.6) | 223 (17.85) | 346 (56.47) |
| No | 184 (37.4) | 1026 (82.15) | 266 (43.53) |
| Characteristics | Stunting | Wasting | Underweight | ||||||
| 2011-12 | 2022-23 | 2011-12 - 2022-23 | 2011-12 | 2022-23 | 2011-12 - 2022-23 | 2011-12 | 2022-23 | 2011-12 - 2022-23 | |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| Place of residence | |||||||||
| Urban | 9.3 | 16.4 | 7.0** | 2.9 | 4.8 | 1.8 | 2.9 | 6.2 | 3.3 |
| Rural | 15.1 | 12.8 | -2.4 | 5.2 | 3.6 | -1.7 | 4.2 | 4.7 | 0.5 |
| Wealth Index | |||||||||
| Poorest | 8.9 | 21.3 | 12.3 | 4.0 | 9.2 | 5.2 | 3.8 | 12.1 | 8.3 |
| Poorer | 14.3 | 15.5 | 1.3 | 4.6 | 3.4 | -1.2 | 3.2 | 4.3 | 1.1 |
| Middle | 4.6 | 12.7 | 8.1** | 2.3 | 4.9 | 2.6 | 2.2 | 7.2 | 5.1 |
| Fourth | 14.1 | 9.2 | -4.9 | 5.2 | 1.7 | - 3.6 | 2.6 | 1.6 | -0.9 |
| Richest | 17.1 | 14.4 | -2.7 | 3.2 | 2.3 | -0.8 | 4.8 | 2.3 | -2.5 |
| Sex of baby | |||||||||
| Boy | 12.9 | 16.5 | 3.7 | 4.8 | 6.3 | 1.5 | 4.7 | 7.5 | 2.8 |
| Girl | 9.9 | 12.8 | 2.9 | 2.7 | 2.0 | -0.7 | 1.8 | 3.2 | 1.4 |
| Child age (months) | |||||||||
| 0-5 | 16.0 | 27.8 | 11.8** | 6.6 | 8.2 | 1.6 | 6.9 | 15.7 | 8.9** |
| 6-11 | 5.1 | 7.8 | 2.7 | 4.4 | 1.5 | -2.9 | 2.6 | 4.6 | 2.0 |
| 12-17 | 15.5 | 13.6 | -1.9 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.7 | 2.3 | 1.7 |
| 18-23 | 9.3 | 10.9 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 5.5 | 3.21 | 3.0 | 1.2 | -1.8 |
| Mother’s age (years) | |||||||||
| 15-34 years | 11.1 | 17.2 | -0.4 | 3.9 | 4.2 | 0.3 | 3.7 | 6.6 | 2.9 |
| 35-49 years | 12.5 | 11.5 | -7.0 ** | 3.4 | 4.2 | 0.8 | 2.5 | 3.7 | 1.2 |
| Father’s age (years) | |||||||||
| 18-34 | 10.5 | 10.5 | 4.9 | 4 | 5.4 | 1.4 | 6.4 | 5.7 | -0.7 |
| 35-44 | 11.5 | 11.5 | 2.8 | 3.4 | 3.7 | 0.3 | 2.0 | 5.2 | 3.2** |
| 45+ | 12.0 | 12.0 | 5.3 | 3.9 | 4.3 | 0.4 | 3.1 | 6.5 | 3.4 |
| Mother’s age at marriage (years) | |||||||||
| ≤ 18 | 12.6 | 12.5 | -0.1 | 0.9 | 0.0 | -0.9 | - | - | 9.2 |
| >18 | 11.4 | 15.4 | 4.0 | 4 | 4.4 | 0.4 | 3.7 | 5.4 | 1.7 |
| Marital status | |||||||||
| Married | 11.3 | 15.2 | 3.9 | 3.7 | 4.3 | 0.6 | 3.6 | 5.6 | 2.0 |
| Not married | 13.8 | 10.8 | -3.0 | 4.7 | 2.7 | -2.1 | 1.0 | 2.5 | 1.5 |
| Maternal education | |||||||||
| Secondary and above | 10.1 | 13.1 | 3.05 | 3.8 | 0.6 | 2.2 | 3.9 | 5.8 | 1.9 |
| Primary | 11.0 | 16.3 | 5.2 | 3.3 | 3.4 | 0.2 | 1.6 | 4.0 | 2.4 |
| No education | 20.0 | 16.7 | -3.3 | 5.2 | 2.1 | -3.1 | 4.9 | 11.4 | 6.5 |
| Father education | |||||||||
| Secondary and above | 10.1 | 13.1 | 3.05 | 4.1 | 6.3 | 2.3 | 3.9 | 5.4 | 1.5 |
| Primary | 10.0 | 16.2 | 6.2 ** | 2.8 | 3.7 | 0.9 | 1.5 | 4.7 | 3.2** |
| No education | 21.6 | 15.4 | -6.3 | 4.9 | 1.2 | -3.6 | 5.4 | 10.0 | 4.6 |
| Maternal BMI (kgm-2) | |||||||||
| ≤18.5 | 6.3 | 8.5 | 2.2 | 5.9 | 6.5 | 0.6 | 4.6 | 6.6 | 2.0 |
| 19-25 | 19.7 | 23.6 | 3.9 | - | - | - | 1.0 | 3.9 | 2.9 |
| 25+ | 32.0 | 50.2 | 18.2 | - | - | - | 2.4 | - | -2.4 |
| Household members | |||||||||
| 1-3 | 9.8 | 11.3 | 1.51 | 6.3 | 10.2 | 3.9 | 4.5 | 3.5 | -1.0 |
| 4-8 | 12.3 | 15.9 | 3.62 | 2.7 | 3.0 | 0.3 | 3.3 | 6.0 | 2.7 |
| >8 | 10.2 | 9.7 | -0.49 | 4.9 | 3.0 | -1.9 | 1.0 | 5.5 | 4.5 |
| Birth order | |||||||||
| Non previous | 10.4 | 18.6 | 8.3 ** | 5.4 | 5.3 | -0.1 | 3.3 | 7.4 | 4.1** |
| 1 | 11.3 | 12.0 | 0.8 | 3.1 | 2.3 | -0.7 | 3.3 | 2.0 | -1.3 |
| 2 or more | 14.8 | 6.6 | -8.2 ** | 2.1 | 4.1 | 1.9 | 3.9 | 5.6 | 1.7 |
| Source of drinking water | |||||||||
| Protected | 11.6 | 13.9 | 2.3 | 3.7 | 4.2 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 5.3 | 1.3 |
| Unprotected | 11.3 | 15.8 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 4.3 | -0.01 | 2.4 | 5.7 | 3.3 |
| Toilet facility | |||||||||
| Improved | 11.6 | 12.7 | 1.1 | 3.7 | 4.7 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | -0.1 |
| Unimproved | 11.3 | 16.5 | 5.2 | 3.9 | 3.9 | - 0.01 | 2.4 | 6.8 | 4.3 ** |
| Listening to the radio | |||||||||
| Not at all | 10.6 | 15.2 | 4.6 | 3.1 | 4.1 | 1.0 | 2.4 | 5.4 | 3.0 ** |
| Yes | 12.2 | 14.9 | 2.7 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 0.2 | 4.2 | 5.6 | 1.3 |
| Watching TV | |||||||||
| Not at all | 20.1 | 25.8 | 5.7 | - | 3.8 | -1.0 | 2.9 | 8.4 | 5.6 |
| Yes | 11.3 | 14.4 | 3.1 | 3.9 | 4.2 | 0.1 | 3.4 | 5.3 | 1.9 |
| Read newspaper | |||||||||
| Not all | 9.0 | 15.0 | 6.0 ** | 2.0 | 4.5 | 2.5 | 1.7 | 6.1 | 4.4 ** |
| Yes | 10.9 | 15.3 | 4.4 | 4.9 | 2.9 | -2.0 | 4.2 | 2.6 | -1.7 |
| Size of baby | |||||||||
| Average | 11.6 | 16.2 | 4.6 | 3.7 | 5.1 | 1.4 | 3.6 | 5.1 | 1.6 |
| Small | 13.7 | 14.3 | 0.6 | 6.3 | 3.6 | -2.7 | 7.0 | 5.6 | -1.5 |
| Large | 8.7 | 12.5 | 3.8 | 1.4 | 1.3 | - 0.1 | 0.5 | 7.8 | 7.3 ** |
| Diarrhoea last two weeks | |||||||||
| No | 11.6 | 14.6 | 3.0 | 3.8 | 4.5 | 0.7 | 3.5 | 5.6 | 2.2 |
| Yes | 11.0 | 17.4 | 6.4 | 3.7 | 1.9 | -1.9 | 2.9 | 4.8 | 1.9 |
| Fever | |||||||||
| No | 15.5 | 15.8 | 0.28 | 4.5 | 4.4 | -0.1 | 3.3 | 6.1 | 2.8 |
| Yes | 10.4 | 10.3 | -0.13 | 3.6 | 3.5 | -0.1 | 3.4 | 2.5 | -0.9 |
| Cough | |||||||||
| No | 10.4 | 16.1 | 5.7 ** | 4.8 | 4.3 | -0.5 | 4.5 | 5.9 | 1.4 |
| Yes | 12.7 | 11 | -1.8 | 2.6 | 4.0 | 1.4 | 2.0 | 4.4 | 2.4 |
| Any infection | |||||||||
| No | 13.4 | 15.3 | 1.9 | 6.6 | 4.4 | -2.3 | 5.3 | 6.0 | 0.7 |
| Yes | 11.2 | 13.6 | 2.4 | 3.4 | 4.0 | 0.5 | 3.1 | 4.4 | 1.3 |
| Place of delivery | |||||||||
| Government | 7.9 | 15.3 | 7.4** | 3.9 | 3.2 | -0.6 | 3.0 | 4.4 | 1.3 |
| Non-government | 7.3 | 15.3 | 8.0 | 3.7 | 7.5 | 3.8 | 4.1 | 9.5 | 5.4 |
| Antenatal clinic visits | |||||||||
| 8+ | 14.3 | 19.9 | 5.6 | 3.2 | 7.1 | 3.9 | 4.0 | 3.9 | -0.2 |
| 4-7’ | 9.6 | 13.7 | 4.12 | 5.2 | 3.2 | -2.0 | 4.0 | 6.8 | 2.8 |
| 1-3’ | 11.3 | 14.3 | 2.1 | 0.3 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 1.4 | 3.9 | 2.5 |
| None | 11.2 | 10.1 | -1.1 | 3.3 | 4.7 | 1.4 | 1.1 | 5.3 | 4.2 |
| Delivery assistance | |||||||||
| Skilled | 11.0 | 15.3 | 4.3** | 3.8 | 4.4 | 0.6 | 3.8 | 5.7 | 1.9 |
| Unskilled | 12.4 | 8.5 | -3.9 | 3.8 | 2.9 | -0.9 | 2.6 | 2.9 | 0.3 |
| Mode of delivery | |||||||||
| Non-caesarean | 11.2 | 17.2 | 6.0** | 3.6 | 4.0 | 0.4 | 3.7 | 5.7 | 2.0 |
| Caesarean | 11.5 | 13.6 | 2.0 | 3.9 | 4.8 | 0.9 | 3.4 | 5.8 | 2.4 |
| Postnatal checkup | |||||||||
| 0-2 days | 14.0 | 16.5 | 2.6 | 13 | 7.7 | -5 .3 | 9.5 | 0.9 | -8.6 |
| After 2 days | 13.2 | 21.6 | 8.4 | 2.2 | 4.3 | 2.1 | 3.4 | 8.1 | 4.8 |
| No | 10.6 | 13.1 | 2.5 | 4.1 | 3.3 | -0.8 | 3.1 | 6.3 | 3.1 |
| Early initiation of breast feeding | |||||||||
| After 1 hr | 9.4 | 10.3 | 0.97 | 4.0 | 4.3 | 0.3 | 2.9 | 5.8 | 2.9 |
| Withing 1 hr | 14.5 | 22.2 | 7.7** | 3.4 | 4.1 | 0.7 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 1.0 |
| Ever breast feed | |||||||||
| Yes | 13.9 | 16 | -2.3 | 3.1 | 3.5 | 0.4 | 3.8 | 6.0 | 2.2 |
| No | 9.5 | 7.2 | 2.1 | 4.4 | 8.7 | 4.3 | 3.1 | 2.7 | -0.4 |
| Duration of breast feeding (months) | |||||||||
| Up to 12 | 13.5 | 17.9 | 5.4 | 4.1 | 3.6 | -0.5 | 4.7 | 9.7 | 7.4 ** |
| >12 | 10.8 | 12.5 | 2.7 | 3.7 | 4.7 | 1.0 | 2.9 | 2.3 | 1.7 |
| Literacy | |||||||||
| Yes | 10.2 | 16.9 | 6.7 ** | 3.1 | 3.8 | 0.7 | 1.2 | 6.6 | 5.5 ** |
| No | 19.3 | 13.6 | -5.7 | 4.7 | 4.4 | -0.30 | 4.9 | 4.4 | -0.5 |
| Characteristics | Stunting | Wasting | Underweight | ||||||||||
| Unadjusted | P | Adjusted | P | Unadjusted | P | Adjusted | P | Unadjusted | P | Adjusted | P | ||
| Years of survey | |||||||||||||
| 2012 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| 2018 | 0.72[0.54, 0.96] | 0.023 | 0.73 [0.52, 1.01] | 0.054 | 0.78 [0.45, 1.25] | 0.279 | 0.79 [0.47, 1.34] | 0.388 | 0.74 [0.44, 1.24] | 0.253 | 0.70[0.41, 1.20] | 0.191 | |
| 2023 | 1.34 [0.96, 1.87] | 0.088 | 1.22 [0.85, 1.74] | 0.284 | 1.12 [0.63, 1.10] | 0.689 | 1.16 [0.64, 2.12] | 0.620 | 1.66 [0.95, 2.91] | 0.074 | 1.70[0.94, 3.10] | 0.082 | |
| Area of residence | |||||||||||||
| Urban | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Rural | 1.35 [1.06, 1.74] | 0.017 | 1.08 [0.69, 1.67] | 0.745 | 1.09 [0.70, 1.69] | 0.717 | |||||||
| Wealth Index | |||||||||||||
| Poorest | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Poorer | 1.36 [0.92, 2.02] | 0.128 | 1.27 [0.84, 1.91] | 0.257 | 0.98 [0.50, 1.93] | 0.958 | 0.78 [0.42, 1.44] | 0.424 | |||||
| Middle | 0.56 [0.37, 0.86] | 0.008 | 0.52[0.33, 0.82] | 0.004 | 0.89 [0.45, 1.74] | 0.726 | 0.65 [0.32, 1.35] | 0.248 | |||||
| Fourth | 0.79 [0.53, 1.18] | 0.250 | .83 [0.54, 1.28] | 0.395 | 0.73 [0.35, 1.50] | 0.391 | 0.43 [0.21, 0.88] | 0.022 | |||||
| Richest | 1.20 [0.82, 1.76] | 0.349 | 1.29 [0.87, 1.92] | 0.210 | 0.82 [0.41, 1.64] | 0.580 | 0.66 [0.35, 1.24] | 0.199 | |||||
| Sex of baby | |||||||||||||
| Boy | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| Girl | 0.85 [0.66, 1.10] | 0.212 | 0.61 [0.39, 0.96] | 0.034 | 0.60 [0.37, 0.97] | 0.036 | 0.47 [0.29, 0.76] | 0.002 | 0.45[0.27, 0.74] | 0.002 | |||
| Child age | |||||||||||||
| 0 to 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 6 to 11 | 0.35[0.24, 0.52] | <0.001 | .26 [0.18, 0.39] | <0.001 | 0.52 [0.24, 1.76] | 0.004 | 0.42 [0.23, 0.77] | 0.006 | 0.45 [0.14, 0.44] | <0.001 | 0.20[0.10, 0.38] | <0.001 | |
| 12 to17 | 0.62 [0.45, 0.87] | 0,006 | .44 [0.31, 0.63] | <0.001 | 0.14 [0.07, 0.31] | <0.001 | 0.15 [0.07, 0.33] | <0.001 | 0.08 [0.03, 0.23] | <0.001 | 0.08[0.03, 0.22] | <0.001 | |
| 18-23 | 0.58 [0.42, 0.81] | <0.001 | 0.47 [0.33, 0.66] | <0.001 | 0.32 [0.18, 0.58] | <0.001 | 0.32 [0.17, 0.59] | <0.001 | 0.22 [0.12, 0.40] | <0.001 | 0.22[0.12, 0.42] | <0.001 | |
| Father’s age (years) | |||||||||||||
| 18-34 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 35-44 | 1.24 [0.91, 1.69] | 0.174 | 0.71 [0.43,1.19] | 0.196 | 0.54 [0.33, 0.88] | 0.014 | |||||||
| 45+ | 1.25 [0.85, 1.85] | 0.259 | 0.78 [0.39, 1.58] | 0.497 | 0.76 [0.39, 1.50] | 0.434 | |||||||
| Mother’s age at marriage (years) | |||||||||||||
| ≤ 18 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| >18 | 1.40 [0.50, 2.14] | 0.916 | 10.68[1.46, 78.0] | 0.020 | 10.12 [1.39,73.51] | 0.022 | 1.57 [0.22, 11.48] | 0.656 | |||||
| Birth order | |||||||||||||
| Non previous | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 0.87 [0.66, 1.16] | 0.347 | 0.76 [0.47, 1.23] | 0.263 | 0.62 [0.36, 1.07] | 0.085 | |||||||
| 2 or more | 1.08 [0.77, 1.52] | 0.663 | 0.56 [0.26, 1.19] | 0.132 | 1.19 [0.69, 2.09] | 0.532 | |||||||
| Household members | |||||||||||||
| 1-3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 4-8 | 1.38 [1.04, 1.83] | 0.024 | 0.53 [0.34, 0.84] | 0.006 | 1.27 [0.78, 2.07] | 0.344 | |||||||
| >8 | 1.12 [0.62, 2.02] | 0.704 | 0.95 [0.38, 2.35] | 0.910 | 0.82 [0.32, 2.07] | 0.672 | |||||||
| Size of baby | |||||||||||||
| Average | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Small | 1.34 [0.95, 1.88] | 0.092 | 1.48 [0.82, 2.68] | 0.197 | 1.86 [1.04, 3.31] | 0.035 | 1.90[1.04, 3.47] | 0.037 | |||||
| Large | 0.58 [0.36, 0.94] | 0.026 | 0.53 [0.25, 1.11] | 0.093 | 0.73 [0.36, 1.47] | 0.377 | 0.65[0.31, 1.34] | 0.241 | |||||
| Source of drinking water | |||||||||||||
| Protected | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Unprotected | 0.95 [0.74, 1.23] | 0.706 | 1.45 [0.93, 2.25] | 0.098 | 1.07 [0.68, 1.67] | 0.773 | |||||||
| Toilet facility | |||||||||||||
| Improved | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Unimproved | 1.03 [0.80, 1.32] | 0.812 | 1.26 [0.81, 1.96] | 0.306 | 1.26 [0.81, 1.96] | 0.306 | |||||||
| Listening to the radio | |||||||||||||
| Not at all | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||
| Yes | 0.07 [0.83, 1.37] | 0.618 | 1.13 [0.73, 1.75] | 0.598 | 1.34 [0.87, 2.08] | 0.189 | |||||||
| Watching TV | |||||||||||||
| Not at all | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Yes | 0.49 [0.29, 0.84] | 0.009 | 2.59[0.35, 18.86] | 0.349 | 0.43 [0.17, 1.08] | 0.072 | |||||||
| Read newspaper | |||||||||||||
| Not all | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Yes | 1.0 [0.75, 1.35] | 0.969 | 1.22 [0.75, 1.99] | 0.418 | 0.98 [0.59, 1.61] | 0.925 | |||||||
| Maternal education | |||||||||||||
| Secondary and above | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Primary | 1.37 [1.03, 1.82] | 0.033 | 0.93 [0.56, 1.56] | 0.780 | 0.84 [0.50, 1.40] | 0.504 | |||||||
| No education | 2.06 [1.4, 2.92] | <0.001 | 1.15 [0.59, 1.26] | 0.678 | 1.96 [1.04, 3.69] | 0.036 | |||||||
| Maternal BMI | |||||||||||||
| ≤18.5 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| 19-25 | 3.02 [2.32, 3.93] | <0.001 | 3.51 [2.69, 4.58] | <0.001 | - | 0.28 [0.15, 0.52] | <0.001 | 0.23[0.10, 0.54] | 0.001 | ||||
| 25+ | 9.27[5.35, 16.04] | <0.001 | 10.67 [5.97,19.08] |
<0.001 | - | 0.24 [0.03, 1.73] | 0.156 | 0.20[0.03, 1.61] | 0.13 | ||||
| Place of delivery | |||||||||||||
| Government | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Non government | 1.07 [0.66, 1.73] | 0.780 | 1.73 [0.83, 3.58] | 0.143 | 2.23 [1.14, 4.37] | 0.020 | |||||||
| Delivery assistance | |||||||||||||
| Skilled | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Unskilled | 1.06 [0.78, 1.43] | 0.708 | 0.90 [0.51, 1.60] | 0.727 | 0.71 [0.40, 1.26] | 0.241 | |||||||
| Antenatal clinic visits | |||||||||||||
| 8+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| 4-7’ | 0.70 [0.52, 0.95] | 0.020 | 0.73 [0.44, 1.22] | 0.232 | 1.23 [0.72, 2.11] | 0.456 | |||||||
| 1-3’ | 0.73 [0.47, 1.11] | 0.143 | 0.57 [0.26, 1.25] | 0.158 | 1.01 [0.48, 2.11] | 0.987 | |||||||
| None | 0.78 [0.53, 1.17] | 0.231 | 0.62 [0.30, 1.30] | 0.204 | 0.97 [0.47, 1.10] | 0.925 | |||||||
| Postnatal checkup | |||||||||||||
| 0-2 days | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| After 2 days | 0.91 [0.57, 1.45] | 0.697 | 0.35 [0.17,0.74] | 0.006 | 1.03 [0.46, 2.29] | 0.943 | |||||||
| No | 0.75 [0.51, 1.12] | 0.146 | 0.45 [0.25, 0.81] | 0.008 | 0.98 [0.49, 1.98] | 0.960 | |||||||
| Mode of delivery | |||||||||||||
| Non-caesarean | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Caesarean | 0.87 [0.66, 1.15] | 0.325 | 1.22 [0.76, 1.95] | 0.409 | 0.89 [0.54, 1.46] | 0.638 | |||||||
| Diarrhea last two weeks | |||||||||||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Yes | 1.11 [0.76, 1.61] | 0.598 | 1.02 [0.54, 1.93] | 0.945 | 0.92 [0.48, 1.79] | 0.809 | |||||||
| Fever | |||||||||||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Yes | 0.85 [0.66, 1.09] | 0.202 | 0.75 [0.48, 1.20] | 0.231 | 0.69 [0.44, 1.10] | 0.119 | |||||||
| Cough | |||||||||||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Yes | 1.02 [0.78, 1.32] | 0.907 | 0.68 [0.42, 1.09] | 0.107 | 0.58 [0.35, 0.96] | 0.035 | |||||||
| Any infection | |||||||||||||
| No | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Yes | 0.92 [0.72, 1.19] | 0.544 | 0.78 [0.50, 1.21] | 0.262 | 0.75 [0.48, 1.16] | 0.193 | |||||||
| Early initiation of breast feeding | |||||||||||||
| After 1 hr | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Withing 1 hr | 1.64 [1.28, 2.11] | <0.001 | 1.02 [0.66, 1.60] | 0.918 | 1.16 [0.74, 1.80] | 0.521 | |||||||
| Ever breast feed | |||||||||||||
| Yes | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| No | 0.77 [0.58, 1.02] | 0.073 | 1.41 [0.88, 2.27] | 0.149 | 0.85 [0.52, 1.39] | 0.510 | |||||||
| Duration of breast feeding | |||||||||||||
| Up to 12 months | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| >12 months | 0.79 [0.55, 1.14] | 0.207 | 0.67 [0.43, 1.04] | 0.076 | 0.42 [0.27, 0.65] | <0.001 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





