Introduction
E-commerce, the electronic exchange of goods and services, has witnessed unprecedented global growth, reshaping consumer behavior and business models. While developed economies have embraced e-commerce as a mainstream retail channel, developing countries like Nepal are also experiencing a surge in online transactions [
1]. This study focuses on the burgeoning e-commerce landscape in Nepal, investigating the factors driving its growth and the associated security challenges.
The rapid expansion of internet penetration, coupled with increasing smartphone ownership and urbanization, has laid the groundwork for e-commerce proliferation in Nepal [
2]. This digital transformation holds immense potential to boost economic growth, create employment opportunities, and enhance consumer convenience. However, the rapid growth of e-commerce has also brought forth a complex array of security risks, including data breaches, phishing attacks, and online fraud, which pose significant threats to both consumers and businesses.
To address this knowledge gap, this research aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the e-commerce ecosystem in Nepal, focusing on its growth trajectory, the nature of security challenges, and the effectiveness of existing security measures. By understanding the interplay between e-commerce development and security risks, this study seeks to contribute to the development of robust strategies for mitigating security threats and fostering a secure online marketplace in Nepal.
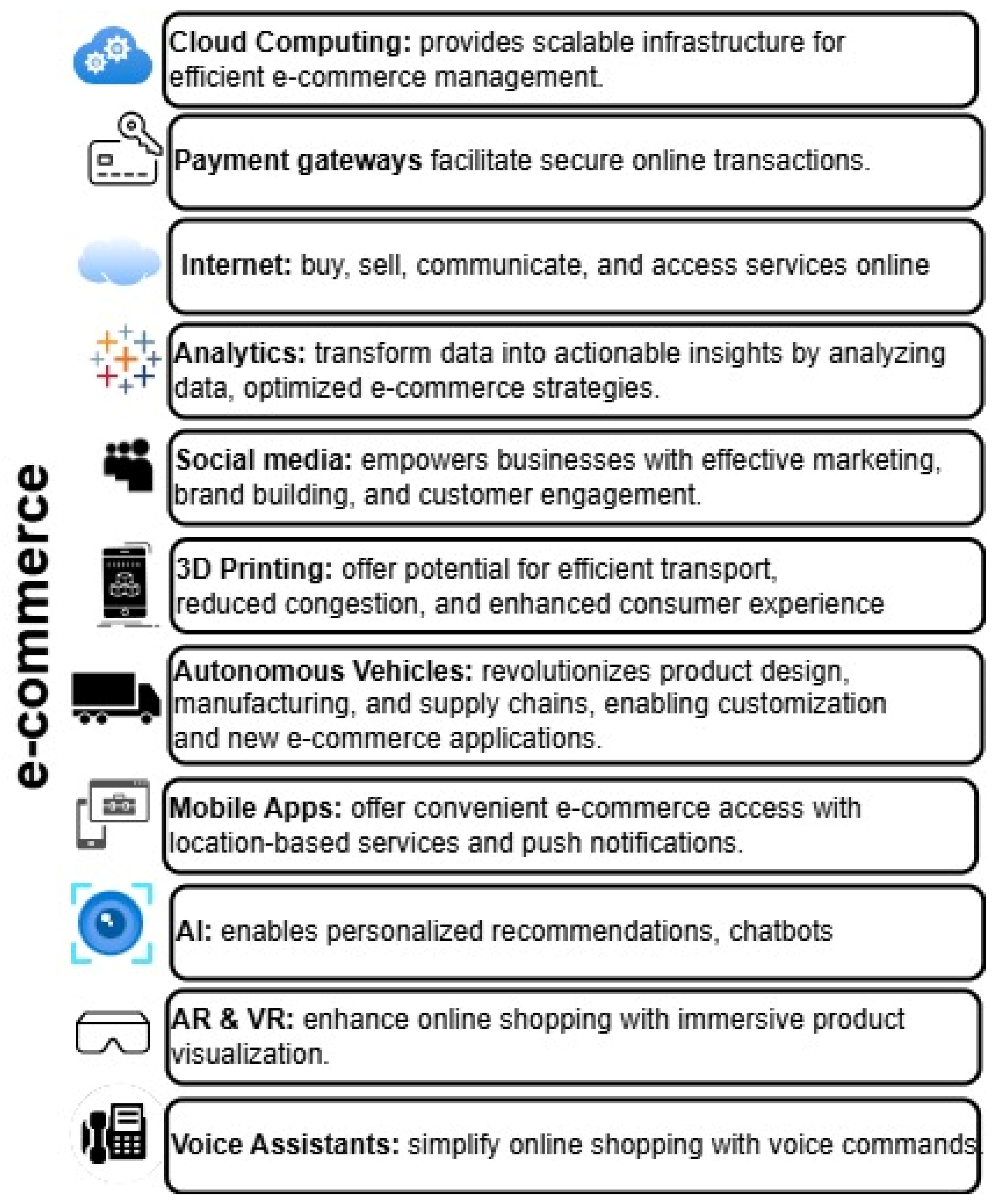
Several key facilitators, including the internet, payment gateways, analytics, social media, autonomous vehicles, and 3D printing, have played a pivotal role in shaping the e-commerce landscape [
3]. These facilitators, depicted in the accompanying figure, have collectively driven the growth and evolution of e-commerce.
Figure 1.
Key facilitators of e- commerce.
Figure 1.
Key facilitators of e- commerce.
The digital economy, a system reliant on digital technologies, has transformed traditional economic activities [
4]. E-commerce, facilitated by digital infrastructure, is a key component of the digital economy. To thrive in this digital age, organizations must adopt a strategic approach to e-commerce, aligning their corporate strategies with the opportunities and challenges presented by internet technologies [
5]. The internet transcends geographical boundaries, eliminating time constraints and rendering location less relevant [
6]
The rise of digital marketing has revolutionized the producer-consumer relationship, enabling companies to reach and engage with customers more effectively. [
7] As consumers spend increasing amounts of time and money online, digital marketing has become crucial for businesses to stay competitive. Digital marketing offers numerous benefits, including greater market presence, cost reduction, measurability, personalization, and improved communication. However, the growing reliance on digital channels also presents significant security challenges. Businesses must be vigilant in protecting their customers' data and preventing cyberattacks. Data breaches, phishing scams, and other online threats can have severe consequences for both businesses and consumers.
Rationale of the Study
Despite its potential for growth, Nepal's e-commerce sector has faced significant challenges, primarily due to the lack of a robust government framework [
8]. This is particularly evident when compared to developed countries, where online shopping has become a mainstream activity. While 90% of the population in developed countries engages in e-commerce, the adoption rate in developing nations like Nepal lags significantly, with less than half of the population participating in online transactions.[
9]
This disparity highlights the need for a supportive policy environment to foster the growth of e-commerce in Nepal. A well-defined legal and regulatory framework can address issues such as consumer protection, payment security, and data privacy, thereby creating a more conducive environment for businesses and consumers. Furthermore, the development of digital infrastructure, including reliable internet connectivity and payment systems, is essential for the successful adoption of e-commerce. By investing in these areas, the government can create the necessary conditions for businesses to thrive and consumers to benefit from the convenience and efficiency of online shopping.
Methodology
This research utilizes a quantitative approach to analyze e-commerce growth and security challenges in Nepal. Data was collected from government reports, industry publications, academic research, and reputable newspapers. This quantitative approach provided a structured and systematic way to analyze the growth of e-commerce and the prevalent security challenges in Nepal, contributing to a comprehensive understanding of the industry.
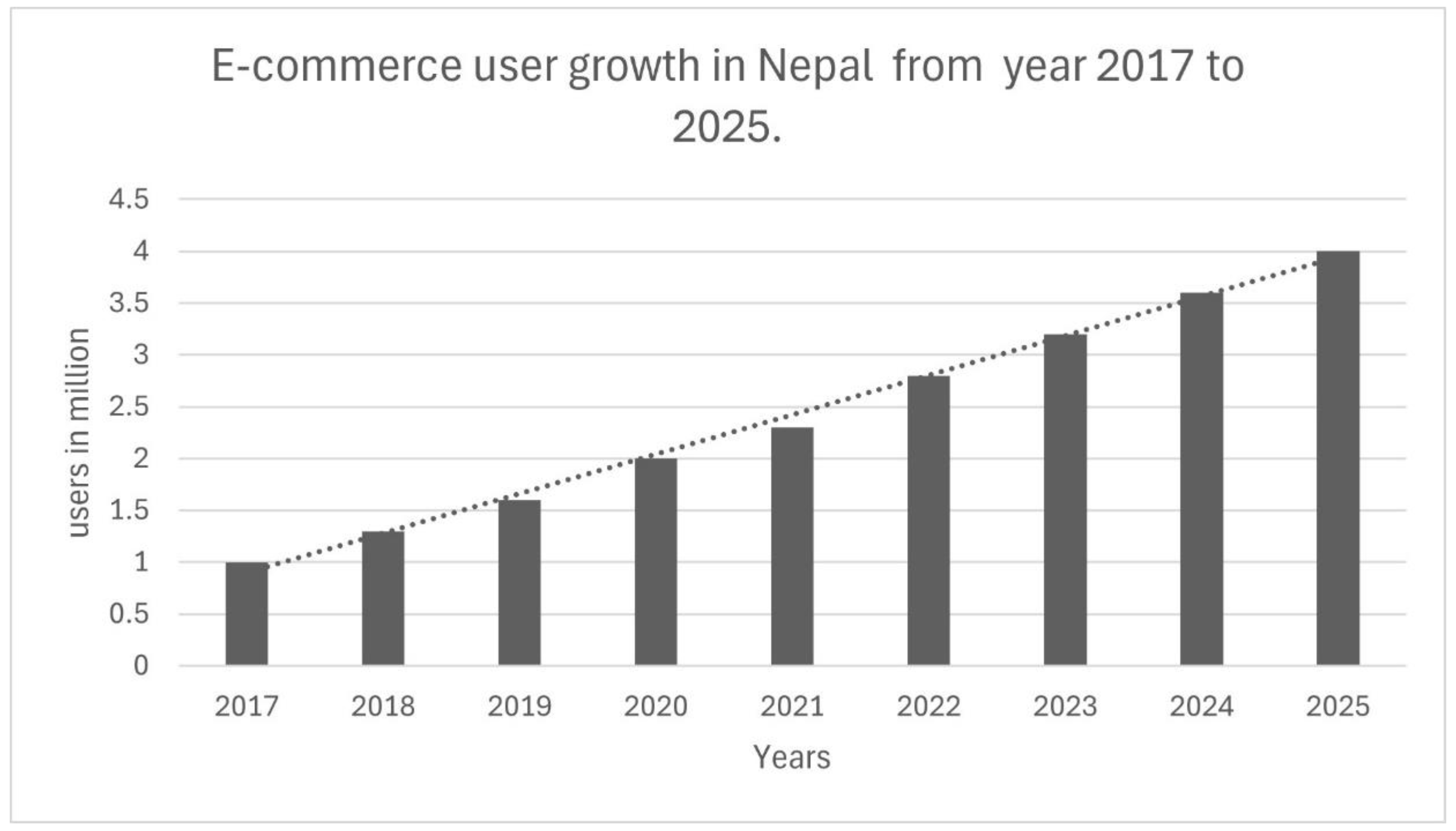
The Rise of E-Commerce in Nepal
The rapid growth of e-commerce in Nepal has been accompanied by challenges in supply chain management. Traditional methods have proven inadequate, leading to excessive costs and delays [
10]. To address these issues, e-businesses must adopt intelligent supply chains driven by information and communication technology (ICT). By focusing on customer-centric factors like security, personalization, affordability, and on-time delivery, businesses can gain a competitive advantage. However, existing research often overlooks the specific context of e-commerce, necessitating further studies to identify effective strategies for improving supply chain operations and enhancing customer satisfaction in Nepal's e-commerce sector.
Nepal's e-commerce landscape has observed significant expansion in current years, driven by several interconnected factors. The increasing internet penetration rate, coupled with the proliferation of smartphones, has empowered a growing number of Nepalese consumers to access online platforms and engage in digital commerce. The burgeoning middle class, with rising disposable incomes, has also fueled demand for a wider range of products and services available online. Online shoppers frequently purchase a wide range of products, including electronics, media, food, beauty products, fashion items, toys, beverages, furniture, and household essentials. Among these items, electronics consistently rank among the most popular purchases online. The growing variety of products available online has contributed to the increasing popularity of e-commerce.
Moreover, the government's initiatives to promote digital infrastructure and e-commerce have played a crucial role in creating a conducive environment for online businesses. The development of payment gateways, logistics networks, and digital literacy programs has facilitated the adoption of e-commerce by both consumers and merchants.
Despite the challenges posed by limited digital infrastructure in certain regions and a small domestic market, Nepal's e-commerce sector has demonstrated resilience and growth potential. A growing number of domestic and international e-commerce platforms have emerged, offering a diverse range of products, from electronics and fashion to groceries and pharmaceuticals.
The widespread adoption of online technologies has fundamentally transformed businesses into information-based operations. The internet has expanded the reach and scope of businesses, enabling them to operate on a global scale and connect with customers worldwide [
11]. This change in basic assumptions has profound implications for both marketers and customers. Marketers can now leverage digital networks to reach new audiences, personalize messaging, and track customer behavior. Customers, in turn, have an approach to a vast selection of goods and services, enhanced convenience, and greater price transparency.
According to Vaidya's research [
12], Nepali online consumers frequently encounter several problems when shopping on major e-commerce platforms like Daraz, Sastodeal, Hamrobazaar, SmartDoko, Esewapasal, and others. These common problems include:
Product Quality Issues: Receiving products that do not match descriptions or are of lower quality than expected.
Incorrect Products: Receiving the wrong product.
Limited After-Sales Support: Customers face difficulties in obtaining after-sales support, such as product returns, repairs, or replacements.
Limited Product Variety: Online stores might not have as wide a range of products as traditional brick-and-mortar stores, particularly for specialized items.
Payment Gateway Issues: Technical difficulties or limited payment options can hinder the checkout process and lead to customer frustration.
Language Barriers: For consumers who are not proficient in English, navigating online platforms and communicating with sellers is incredibly challenging.
Non-Delivery: Products failing to arrive at all.
Damaged Products: Receiving products in a damaged condition.
Unexpected Charges: Being charged additional fees not disclosed upfront.
Delayed Delivery: Products not arriving on time.
Difficulty in Warranty Claims and Refunds: Challenges in processing warranty claims and refunds.
Higher Prices: Being charged more than the advertised price.
Bulk Purchases Only: Products being available only for bulk purchases.
Poor Customer Service: Inadequate or unresponsive customer support.
Unavailable Services: Services not being available in urgent situations.
Incorrect Product Information: Receiving inaccurate information about products.
Delays on Arrival: Products arriving with significant delays.
A survey found that 57% of respondents in Nepal reported encountering challenges while shopping online [
12]. These issues highlight the need for e-commerce platforms in Nepal to address these problems and improve the overall customer experience.
E-Commerce Security Practices in Nepal
The rapid expansion of e-commerce in Nepal has unfortunately been accompanied by a growing number of security challenges. These threats pose significant risks to both consumers and businesses, hindering the overall growth of the sector.
Online shopping platforms, including websites, applications, and systems, are susceptible to vulnerabilities that can compromise the security of personal information. Data breaches, phishing attacks, and identity theft have become increasingly common, leading to financial losses and erosion of consumer trust. The lack of robust data protection regulations and consumer awareness further exacerbates these issues.
Nepal's Cyber Bureau data reveals a significant rise in cybercrime cases. From fiscal year 2022-23 to 2023-24, the total number of reported cases more than doubled, jumping from 9,013 to a staggering 19,730. This concerning trend is mirrored in online fraud cases, which make up a huge portion of overall cybercrime. While online fraud accounted for 20.35% (1,835 cases) in 2022-23, it saw a worrying surge in the following year, reaching 20.84% (4,112 cases) of all reported cybercrimes. [
13]
These statistics highlight the urgent need for enhanced cybersecurity measures to protect consumers and businesses from the growing threat of cybercrime.
The rapid expansion of e-commerce has brought forth several security challenges. Some of the usual challenges are:
Data Breaches: The collection and storage of personal and financial information online exposes businesses and consumers to the risk of data breaches. [
14]
Phishing Attacks: Phishing attacks are deceptive attempts to obtain personal information by using fraudulent emails or websites. [
15]
Online Fraud: Fraudulent activities, such as fake product listings and unauthorized transactions, pose risks to both consumers and businesses.
Cybercrime: Malicious activities like hacking, malware attacks, and ransomware can disrupt e-commerce operations and compromise data security.
Credit Card Fraud: Online shoppers are increasingly vulnerable to this type of fraud, with hackers targeting e-commerce databases to obtain sensitive card details. These malicious actors employ a variety of software programs to infiltrate e-commerce systems and steal card information.[
16]
Social Engineering: Social engineering is the manipulation of people to obtain confidential information or gain unauthorized access. [
17]
Insecure Payment Gateways: Vulnerabilities in third-party payment processors can lead to unauthorized access to payment data. [
18]
Lack of Customer Awareness: Customers may not be aware of common security threats and how to protect themselves when shopping online. [
19]
Addressing these problems and challenges is crucial for e-commerce businesses to provide a positive and satisfying customer experience. By offering high-quality products, transparent pricing, reliable payment options, timely delivery, strong security measures, and excellent customer support, businesses can build trust and loyalty among their customers.
Limitations of the Study
This research, while offering valuable insights into Nepal's e-commerce landscape and security challenges, has certain limitations. The availability and quality of data can influence the scope and depth of the study. Limited access to comprehensive data on e-commerce transactions, consumer behavior, and security incidents may restrict the research findings. The rapidly evolving nature of e-commerce and technology can make it challenging to keep pace with the latest trends and developments. Therefore, the findings of this analysis may not fully reflect the present state of the industry.
Furthermore, the data limitations stemming from relying on published journals may limit the generalizability of the findings to regions with different economic, technological, and cultural contexts. Addressing these limitations could be considered for future research to provide a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of e-commerce and security challenges in Nepal.
Conclusion
The burgeoning e-commerce sector in Nepal offers significant opportunities for economic growth, job creation, and enhanced consumer access to goods and services. However, the accompanying security challenges pose a substantial threat to its sustainability. This study underscores the urgent need for a concerted effort to address these challenges and foster a secure e-commerce ecosystem. Key findings reveal a disparity between the rapid expansion of e-commerce and the lagging implementation of robust safety measures. Data breaches, phishing attacks, and eroded consumer trust are prevalent, hindering the sector's potential.
To mitigate these risks, it is imperative to prioritize cybersecurity measures, enhance consumer awareness, and strengthen the regulatory framework. Organizations must invest in robust cybersecurity infrastructure, educate their employees about security best practices, and continuously monitor for emerging threats. By prioritizing security, businesses can build trust with their customers and protect their reputation, contributing to a more secure and sustainable e-commerce landscape in Nepal. Strengthening the regulatory framework is crucial for improving e-commerce security in Nepal. By establishing clear rules and regulations governing e-commerce activities, the government can create a more predictable and secure environment for businesses and consumers.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express their sincere gratitude to Dr. Naresh Kshetri, Assistant Professor in Computer Science at the School of Business and Technology, Emporia State University, Emporia, Kansas, USA, for generously providing references, research insights, and materials related to the topic. Additionally, we extend our thanks to Dr. Anjay Kumar Mishra for his valuable feedback, time, helpful suggestions, and support during the writing of this paper. We are also deeply indebted to the anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions, which have significantly enhanced the content, quality, and presentation of this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no personal or financial interests that could have influenced their research findings. This ensures that the research is objective and unbiased. The authors emphasize that their research has been conducted with complete objectivity, free from any external influences that might compromise the integrity of the results.
References
- Vaidya, R. Online Shopping in Nepal: Preferences and Problems. Journal of Nepalese Business Studies, 2019, 12, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokharel, S. Development in Digital Capitalism: Challenges and Prospects of Nepal. KMC Research Journal, 2023, 7, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V., Malviya. An overview of electronic commerce (e-Commerce). The journal of contemporary issues in business and government 2021, 27, 665–670. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoor, A. (2010). E-commerce: an introduction. Amir Manzoor.
- Rachmadewi, I. P., & Purnomo. The Role of e-Commerce: A Systematic Literature Review. iJIM, 2022, 16, 119. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, R. T. (2023). Electronic commerce: The strategic perspective.
- Melović, B., Jocović. The impact of digital transformation and digital marketing on the brand promotion, positioning and electronic business in Montenegro. Technology in Society, 2020, 63, 101425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajracharya, S., & Chatterjee. Challenges for online purchase intention: a qualitative study of e-commerce sector of Nepal. LBEF Res. J. Sci. Technol. Manage., 2023, 5, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Chapagai, S. (2022). Opportunities and challenges of e-commerce to customers: Comparative analysis of Nepal and Finland.
- Kalkha, H., Khiat. The rising trends of smart e-commerce logistics. IEEE Access, 2023, 11, 33839–33857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, S. K. , Vyas, L., Singh, S., & Joshi, M. (2023). Future of E-Commerce: A Robust Review. In Intelligent Sustainable Systems: Selected Papers of WorldS4 2022, Volume 2 (pp. 697-710). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
- Vaidya, R. Online shopping in Nepal: Preferences and problems. Journal of Nepalese Business Studies, 2019, 12, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybercrime cases spike in Nepal. (2024). @Kathmandupost; The Kathmandu Post. https://kathmandupost.com/national/2024/08/21/cybercrime-cases-spike-in-nepal#:~:text=Data%20from%20Nepal's%20Cyber%20Bureau,than%20doubled%2C%20skyrocketing%20to%2019%2C730.
- Singh, S. , & Singh, N. (2015, October). Internet of Things (IoT): Security challenges, business opportunities & reference architecture for E-commerce. In 2015 International conference on green computing and internet of things (ICGCIoT) (pp. 1577-1581). Ieee.
- ALadan, M. I. E-commerce security challenges: a taxonomy. Journal of Economics, Business and Management, 2016, 4, 589–593. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, D., Gupta, A., & Gupta, S. (2020, May). E-commerce security challenges: A review. In Proceedings of the international conference on innovative computing & communications (ICICC).
- Garcia, J. , Oburu, P., & Anand, S. (2022, October). The Commonalities in Social Engineering Attacks through E-Commerce Shopping Platforms & Online Gaming Programs. In 2022 3rd International Conference on Smart Electronics and Communication (ICOSEC) (pp. 778-783). IEEE.
- Oguta, G. C. Securing the virtual marketplace: Navigating the landscape of security and privacy challenges in E-Commerce. GSC Advanced Research and Reviews, 2024, 18, 084–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, S. A customer-centric view of E-commerce security and privacy. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).