The banking industry's performance has seen significant growth with the increased usage of technology in recent years. It is one of the most innovative industries, consistently adopting new technologies to provide efficient and advanced services to customers. Extensive literature explores the innovation of the banking industry and the advantages and opportunities it presents, with many researchers using models to identify customer behavior and technological acceptance. Among the most cited models are the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB), Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), and Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT), which are often used to explain how customers adopt IT-based services in the banking industry. These models have demonstrated the industry's ability to stay ahead in an ever-changing digital landscape and will continue to shape customer behavior and banking services in the future.
2.1. Technology Acceptance Model (TAM)
Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), it is one of the most widely-used models to examine the acceptance of technology in different IT-based services worldwide. TAM explains two primary factors that affect an individual's intention to use technological innovations: perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness. TAM aims to establish a relationship between users and a product and how users are influenced by it. It has been used extensively when considering the behavioral intention to use mobile banking applications. TAM explains why users may accept or reject information technology and provides insights into customer adoption behavior. Perceived ease of use, trust, and perceived usefulness beliefs are the two sets of TAM that determine behavioral intention to use technology, as reported by Jegatheesparan and Rajeshwaran, 2020. These factors have been recognized as important elements that explain technology acceptance, especially in the banking industry.
In summary, the Technology Acceptance Model has been valuable in identifying essential factors that influence technology adoption and has contributed to the understanding of customer behavior. As the banking industry continues to evolve and innovate with technology, models like TAM will play a critical role in shaping customer behavior and banking services in the future.
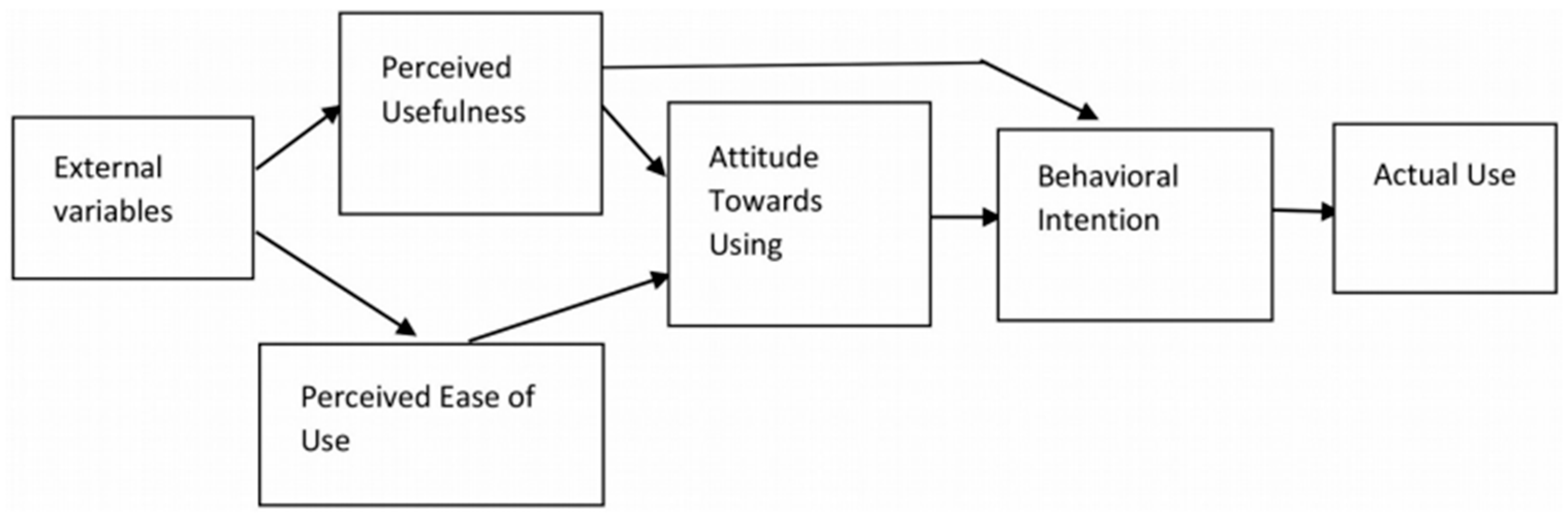
Figure 1.
Technology Acceptance Model (TAM). Source: Amadu, Muhammad, Mohammed, Owusu & Lukman (2018).
Figure 1.
Technology Acceptance Model (TAM). Source: Amadu, Muhammad, Mohammed, Owusu & Lukman (2018).
TAM is based on the idea that people's perceptions of the usefulness and ease of use of a technology, as well as their perceptions of the trustworthiness and riskiness of the technology, influence their intention to use the technology. The model includes the following components:
Perceived usefulness: the degree to which a person believes that using a technology will enhance their job performance or make their lives easier.
Perceived ease of use: the degree to which a person believes that using a technology will be effortless and straightforward.
Attitude towards using: the degree to which a person has a positive or negative evaluation of using the technology.
Behavioral intention: the degree to which a person intends or plans to use the technology.
Actual use: the degree to which a person uses the technology in practice.
TAM also includes the concepts of perceived risk and trust, which can influence the adoption of a technology. Perceived risk refers to the degree to which a person believes that using a technology may have negative consequences, such as financial loss or damage to reputation. Trust refers to the degree to which a person believes that the technology provider or developer is honest, reliable, and competent. Overall, TAM is a model that acknowledges the importance of trust and risk perceptions in shaping people's adoption behavior towards technology.
2.2. Empirical review of the study
According to the research done by Lakshika and Sajeewanie in 2019, they focused on examining the factors influencing customers' behavioral intention to use mobile banking applications in Sri Lanka. They investigated four antecedents, namely perceived risk, trust, convenience, and relative advantage to identify why most consumers do not use this innovative service. The study found that perceived risk, trust, convenience, and relative advantage all have a positive relationship with users' behavioral intention to use mobile banking applications. Users who perceive mobile banking as more convenient and advantageous are more likely to adopt it. Furthermore, users who perceive the mobile banking application as trustworthy and having less perceived risk related to security and privacy concerns are more likely to use it. In conclusion, their research emphasized that banks should focus on eliminating potential risks related to security and privacy, creating trust among customers, and making mobile banking applications more user-friendly and convenient. By doing so, banks can increase the acceptance and usage of mobile banking applications, ultimately leading to more satisfied customers and an increase in market share.
Moving on to the research done by Perera and Gunaratna , 2020, they investigated the impact of five service quality dimensions, namely tangibility, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy, on customer satisfaction with mobile banking. They used customer loyalty as the dependent variable, and customer satisfaction on mobile banking as the independent variable. The study employed several statistical techniques such as frequency statistics, descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation, regression model, and ANOVA to analyze the collected data. The results showed that all the mobile banking service quality attributes positively relate to customer satisfaction. Meaning, the better the service quality dimensions are in mobile banking, the more satisfied the customers will be, and the more likely they will remain loyal to their bank. Their research highlights the importance of ensuring high levels of service quality, including tangibility, reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy to increase customer satisfaction and loyalty towards mobile banking. By improving service quality, banks can provide a desirable mobile banking experience to their customers, ultimately leading to better business growth in the long term.
In the research study of Ayoobkhan in 2018, the author aimed to examine the factors influencing mobile banking adoption in the context of Sri Lanka. Self-administered questionnaires were distributed among respondents of Sampath banks in Ampara district, and data were analyzed using descriptive analysis, correlation analysis, and regression analysis.
The study found that perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, cost, trust, and perceived risk are significant factors influencing the adoption of mobile banking. The study revealed that respondents perceive mobile banking as more useful and easy to use, leading to increased adoption. Additionally, the lower the perceived cost and perceived risk, and the higher the trust in mobile banking, the more likely the customers will adopt it.
The findings of this study provide important insights for banks to promote the adoption of mobile banking in Sri Lanka. By enhancing the usefulness and ease of use of mobile banking applications, providing affordable and secure mobile banking services, and building trust among customers, banks can facilitate the adoption of mobile banking and improve their customer base. Ultimately, the adoption of mobile banking will lead to better customer service, increased efficiency, and sustainable growth for the banks.
Harshana and Wanniarachchige (2022) investigated the effect of the Covid-19 pandemic on the performance of Sri Lankan banks. The study included 18 licensed commercial banks, and data were collected for the year 2020. The authors used various statistical techniques, including correlation analysis, regression analysis, and t-tests to analyze the data. The results indicated that the Covid-19 pandemic has had a statistically significant adverse effect on bank performance in Sri Lanka. The financial performance of banks was negatively affected due to the economic slowdown caused by the pandemic. Moreover, the study found that the net interest margin, return on assets, and return on equity of banks were adversely impacted due to the pandemic. The research highlights the importance of banks being resilient during times of crisis. Banks need to adopt proactive measures to mitigate the impacts of external shocks like the Covid-19 pandemic on their performance. The study provides insights for banks to adopt appropriate risk management strategies, enhance their digital capabilities, and improve their funding structure to minimize the impact of crises on their operations. By doing so, banks can maintain their financial stability and meet the changing needs of their customers during uncertain times.
Yapabandara and Nagendrakumar (2022) have conducted a study to determine the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on the adoption of mobile banking in Sri Lanka. Using a stratified random sample from three districts, the study found that computer and internet literacy, perceived usefulness, and awareness were the most significant factors influencing online banking adoption. The results highlight the importance of improving digital literacy among customers and creating awareness of the benefits of mobile banking.
Jayarathne et al., (2022) examined the motives behind mobile payment adoption among customers and retailers in Sri Lanka during the pandemic. Their findings indicate that Performance expectancy and facilitating conditions are common motives, while Hedonic motivation and perceived technology security differ across urban and rural areas. The study underscores the need for banks to understand the unique needs of customers in different regions and tailor their offerings accordingly.
In conclusion, these studies shed light on various aspects of banking in Sri Lanka, including the adoption of mobile banking, factors influencing adoption, and the impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on bank performance
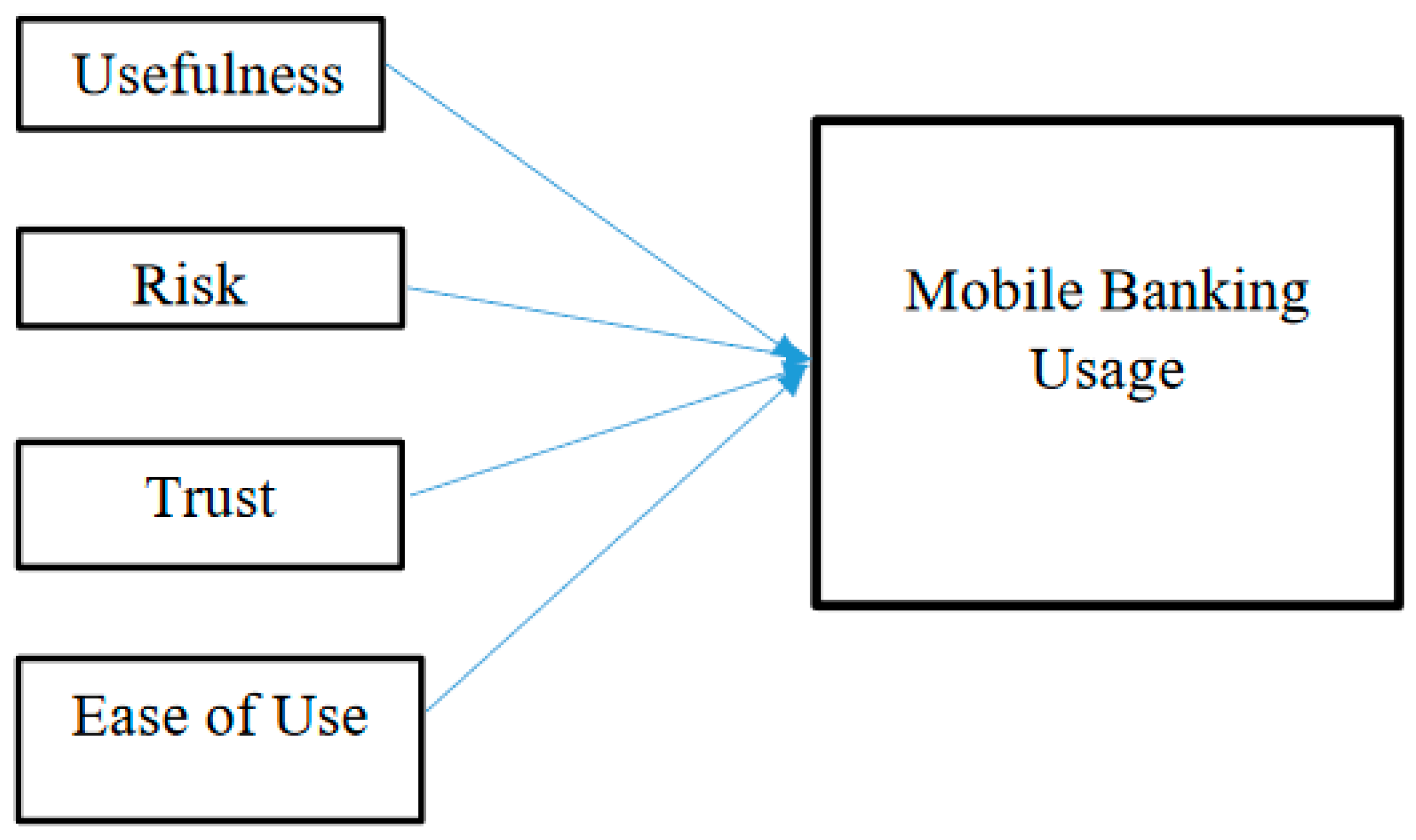
2.3. Variables for the Study
Ease of use is a very important factor, a customer considering when he purchase a product. A product should be easy to use to enhance the customer satisfaction. Ease of use is the most important factor for accept electronic banking (Upadhyay et al., 2017). And it will affect to attract the demand of the customers. Perceived ease of use refers that the degree in which a customer believes that using a particular system would be free of charge (Lakshika & Sanjeewanie, 2019). There are several determinants of the perceived ease of use as computer anxiety, perceived enjoyment, perception of external control and computer self-efficacy (Manel & Dias, 2022). In mobile banking ease of use directly affects to the acceptance of an information system. When compare the mobile banking with ATM transactions, mobile banking can easily use to do transactions and banking activities. Kahandawa and Wijenayake (2014) suggested that, there will be a positive impact and increase the satisfaction of the user, when he/she finds that the system is easy to use.
- 2.
Usefulness
Usefulness means the degree which a person believes that the using of particular system or technology increase his job performance (Wijesooriya & Sritharan, 2018). In their study Ravichandran and Madana (2016) also have proved it by mentioning that perceived usefulness is strongly connected with productivity. Because, in a workplace when employers use computers, it cause to improve their job performance, increase job effectiveness. There are several determinants of the perceived usefulness as image, output quality, job relevance and subjective norm (Manel & Dias, 2022). Moreover usefulness is a vital factor in Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) (Jagatheesparan & Rajeshwaran, 2020; Ayoobkhan, 2018; Wijesooriya & Sritharan, 2018; Ravichandran & Madana, 2016). If mobile banking is useful for someone he will motivate to use mobile banking very frequently and at the same time his satisfaction level also will increase.
- 3.
Risk
When a customer tries a new product the risk is always combined with it. On the service providers or suppliers side they also take a higher risk by offering the product or service as they deal with the customer’s satisfaction. 73.5% of mobile banking users expressed their concerns about the security of the mobile banking (Huili & Chunfang, 2011). As emphasized by Lakshika and Sanjeewanie (2019) perceived risk can be classified into five categories as security risk, performance risk, social risk, financial risk and time risk. Security risk refers the all the losses happen due to the frauds or hackers activities. When it comes to the mobile banking, security is a more concerning factor (Jegatheesparan & Rajeshwaran, 2020). Performance risk will arise due to the malfunctions of the mobile banking platforms. All the losses arise when using the mobile banking include in social risk. Financial risk arise due to the misuse of bank account and transaction errors. Time risk indicates the all the losses of time.
- 4.
Trust
The base for the success of a system is the customers’ trust. As mentioned by Ayoobkhan (2018) studies which investigate about the factors which affect to adopt and accept technology based services have identified trust as a key factor. Trust can be defined as the perception of the degree to which an exchange partner fulfil the consumer’s transactional obligations in the situations which are characterized as risk or uncertainty (Wijesooriya & Sritharan, 2018). Customer trust in mobile banking can be operationalized as the accumulation of customer beliefs about integrity, kindness, and ability, which can improve the customer's willingness to rely on mobile banking to obtain financial transactions (Alalwan et al., 2017).