1. Introduction
Endometrial cancer (EC), a malignancy originating from the lining of the uterus, represents a significant public health concern due to its prevalence and impact on women’s health worldwide (Dobrzycka et al., 2024). It is the most common gynecologic cancer in developed countries and ranks second after cervical cancer in developing regions (Makker et al., 2021). The increasing incidence of EC, particularly in high-income countries, underscores the urgent need for effective prevention, early detection, and treatment strategies (Gordhandas et al., 2023). EC is characterized by its high incidence and significant mortality, especially among postmenopausal women. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the incidence of EC varies globally, with higher rates observed in North America, Europe, and Oceania, and lower rates in Asia and Africa (WHO, 2021). In the United States, EC is the fourth most common cancer in women, with an estimated 65,620 new cases and 12,590 deaths projected in 2020 (Siegel et al., 2020). In Europe, the incidence of EC is notably high, particularly in countries with aging populations and elevated obesity rates (Dobrzycka et al., 2024).
Conversely, in low-income countries, while the incidence is lower, mortality rates are higher due to limited access to early diagnostic services and effective treatment options (Bray et al., 2018). Historically, the incidence rates in African countries have been lower than in Western nations. However, recent trends indicate a rise in cases attributed to factors such as urbanization, lifestyle changes, and increasing obesity rates (Ferlay et al., 2020). According to Bray and co-workers (2024), the age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) of EC in Africa is approximately 4.3 per 100,000 women, which is lower than the global average of 8.4 per 100,000 women (Bray et al., 2024). Despite these lower incidence rates, significant variation exists across the continent, with higher rates reported in North Africa compared to Sub-Saharan Africa (WHO, 2021). Several factors contribute to the rising incidence of EC. These include increasing life expectancy, the prevalence of obesity, and the widespread use of unopposed estrogen therapy (Dobrzycka et al., 2024). Obesity is a particularly significant risk factor, as it is associated with increased estrogen levels due to the aromatization of androgens in adipose tissue, leading to endometrial hyperplasia and, subsequently, cancer (Ignatov and Ortmann, 2020). Other risk factors include early menarche, late menopause, nulliparity, and certain genetic predispositions such as Lynch syndrome (Gordhandas et al., 2023).
The impact of EC on women’s health extends beyond mortality and morbidity, affecting quality of life, reproductive health, and socioeconomic status (Dobrzycka et al., 2024). The disease often presents with symptoms such as abnormal uterine bleeding, pelvic pain, and weight loss, which can lead to significant psychological distress and physical discomfort (Amant et al., 2018). EC and its treatments, including surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, can lead to long-term side effects such as sexual dysfunction, lymphedema, and fatigue. These complications adversely affect the quality of life of survivors, necessitating comprehensive survivorship care plans that address physical, emotional, and social needs (Mahdy et al., 2021). For premenopausal women, EC poses a substantial threat to fertility. Standard treatment often involves hysterectomy, which precludes the possibility of future pregnancies. Fertility-sparing treatments, such as progestin therapy, are available but are appropriate only for select patients with early-stage, low-grade tumors (Factor and Pasamba, 2020). This highlights the need for early diagnosis and the development of less invasive treatment options. The socioeconomic impact of EC is profound, particularly in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) where healthcare resources are limited. Women in these regions often present with advanced disease due to lack of access to screening and diagnostic services, resulting in higher treatment costs and poorer outcomes (Bray et al., 2018). Moreover, the financial burden of cancer treatment can lead to catastrophic health expenditures, further exacerbating poverty and inequality.
Despite advancements in diagnosis and treatment, significant disparities exist in the burden of EC globally. Women in high-income countries benefit from better healthcare infrastructure, access to advanced diagnostic tools, and effective treatments, resulting in higher survival rates. In contrast, women in LMICs face numerous barriers, including limited awareness, inadequate healthcare facilities, and financial constraints, leading to delayed diagnosis and suboptimal treatment outcomes (Ferlay et al., 2020). Efforts to reduce the global burden of EC must focus on addressing these disparities through international collaboration, capacity building, and the implementation of cost-effective screening and treatment programs. Public health initiatives aimed at reducing obesity, promoting healthy lifestyles, and increasing awareness about the symptoms and risk factors of EC are crucial in mitigating its impact (Gordhandas et al., 2023).
Thus, EC remains a significant public health challenge with considerable implications for women’s health globally. Its rising incidence, particularly in high-income countries, coupled with the profound impact on quality of life, reproductive health, and socioeconomic status, underscores the need for comprehensive strategies to improve prevention, early detection, and treatment (Dobrzycka et al., 2024). Addressing global disparities through targeted interventions and international cooperation is essential in reducing the burden of this disease and enhancing outcomes for women worldwide (Gordhandas et al., 2023).
2. Importance of Genomic Studies in Cancer
Genomic studies have profoundly transformed the landscape of cancer research and treatment, ushering in an era of precision medicine where therapies are tailored to the genetic profiles of individual tumors (Chukkalore et al., 2023). This approach has been particularly impactful in understanding and treating EC, which has diverse molecular subtypes with distinct prognoses and therapeutic responses (Stan et al., 2024). Genomic studies have revealed that cancers are not homogeneous but consist of multiple subtypes with unique genetic and molecular characteristics. Identifying specific genetic mutations and pathways involved in cancer has led to the development of targeted therapies (Chukkalore et al., 2023). For instance, the discovery of mutations in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in EC has spurred the development of targeted inhibitors, improving treatment outcomes for patients with these genetic alterations (Makker et al., 2021). Genomic studies have facilitated the use of immunotherapy in cancer treatment. Tumors with high mutational burden, such as the MSI-H subtype of EC, are more likely to respond to immune checkpoint inhibitors like pembrolizumab (Makker et al., 2022; Bostan et al., 2024). Genomic studies have identified biomarkers that can predict disease prognosis and treatment response. For EC, biomarkers such as mutations in PTEN, PIK3CA, and ARID1A are associated with disease progression and survival outcomes (Moreira et al., 2022).
Advances in genomic technologies have enabled the development of liquid biopsies, which detect cancer-related genetic mutations and circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in blood samples. This non-invasive method holds promise for early cancer detection, monitoring disease progression, and assessing treatment response (Mishra et al., 2024). Genomic studies have elucidated mechanisms underlying resistance to conventional therapies. For example, alterations in the FGFR2 gene have been implicated in resistance to hormonal therapies in EC, leading to the exploration of FGFR inhibitors as a potential therapeutic option (Dixit et al., 2023). The advent of NGS has revolutionized genomic studies, allowing comprehensive profiling of tumor genomes. This technology has enabled the identification of novel genetic alterations and the development of multi-gene panels for cancer diagnosis and treatment selection (Scarano et al., 2024).
EC is a prime example of how genomic studies have advanced our understanding and treatment of cancer. The classification of EC into molecular subtypes has provided insights into tumor behavior and guided treatment decisions (Gotoh et al., 2024). For instance, patients with POLE ultramutated tumors have an excellent prognosis and may not require aggressive treatment, whereas those with copy number high tumors often benefit from more intensive therapy (Bostan et al., 2024; Paleari et al., 2021). Genomic studies have identified actionable mutations in EC, leading to the development of targeted therapies. The identification of mutations in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway has resulted in clinical trials testing inhibitors of this pathway, offering new hope for patients with advanced disease (Makker et al., 2021). Genomic profiling of endometrial tumors enables personalized treatment approaches. For example, patients with MSI-H tumors are now being treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors, demonstrating the impact of genomics on improving patient outcomes (Bostan et al., 2024). The integration of genomic data into clinical practice is exemplified by the use of molecular markers for risk stratification and treatment planning in EC. This approach ensures that patients receive the most appropriate and effective therapies based on their tumor’s genetic profile (Moreira et al., 2022).
Genomic studies have revolutionized cancer research and treatment, providing unprecedented insights into the molecular underpinnings of the disease. In EC, genomic advancements have led to improved classification, targeted therapies, and personalized medicine approaches, ultimately enhancing patient care and outcomes (Stan et al., 2024). Continued investment in genomic research is essential to further unravel the complexities of cancer and develop innovative strategies to combat this devastating disease. A comprehensive understanding of the genomic landscape of EC is indispensable in bridging the gap between genetic findings and clinical applications.
3. Genomic Landscape of Endometrial Cancer
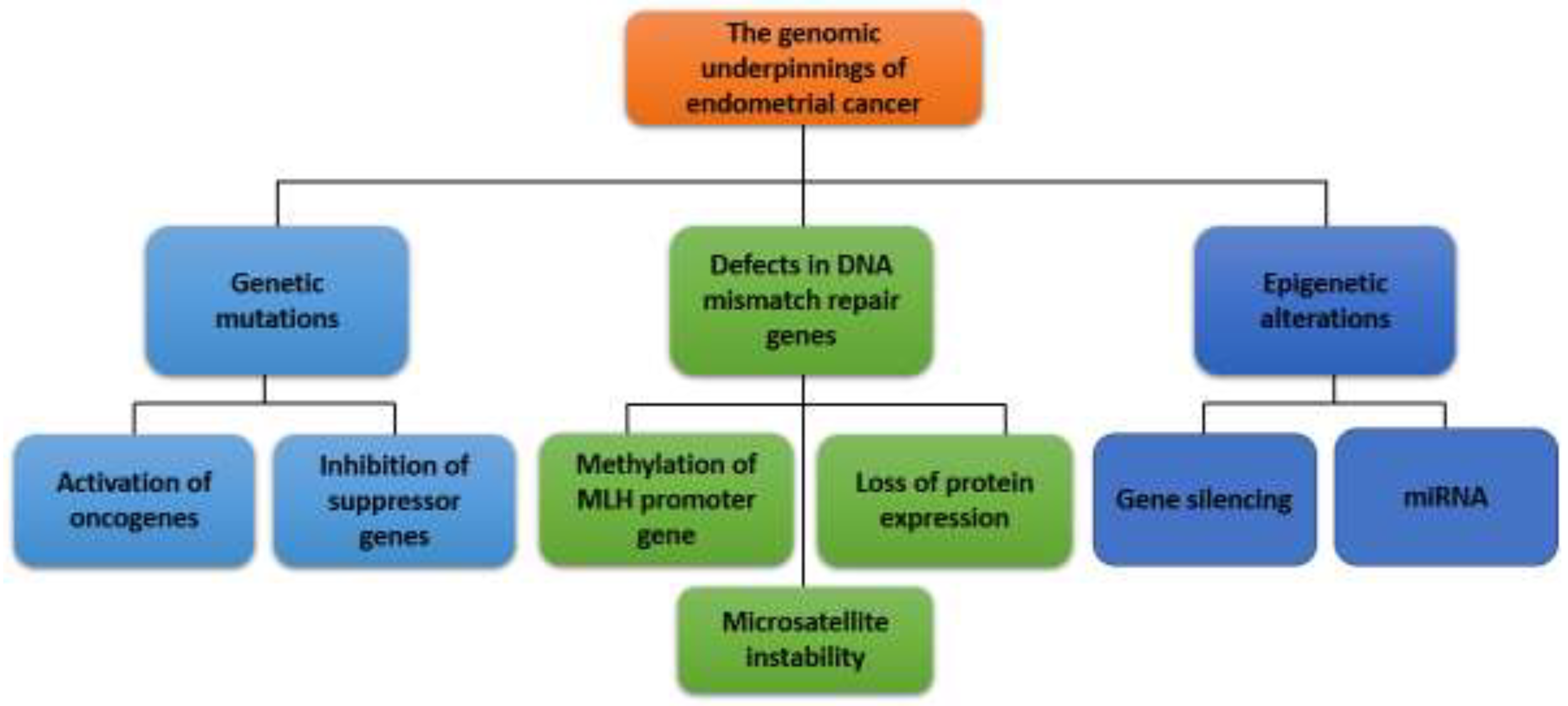
EC is a heterogeneous disease characterized by a variety of genetic and epigenetic alterations. It is a prevalent gynecological malignancy with significant genetic heterogeneity. As shown in
Figure 1, the pathogenesis of EC is a complex process of molecular mechanisms involved in the manifestation of genetic mutations, activation of oncogenes and inactivation of tumor suppressor genes, defects in the DNA MMR pathway, imbalance in hormonal signaling pathways, epigenetic changes, disorders in angiogenesis, and others. Understanding the genomic landscape of EC is crucial for improving diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis (Espinosa et al., 2024).
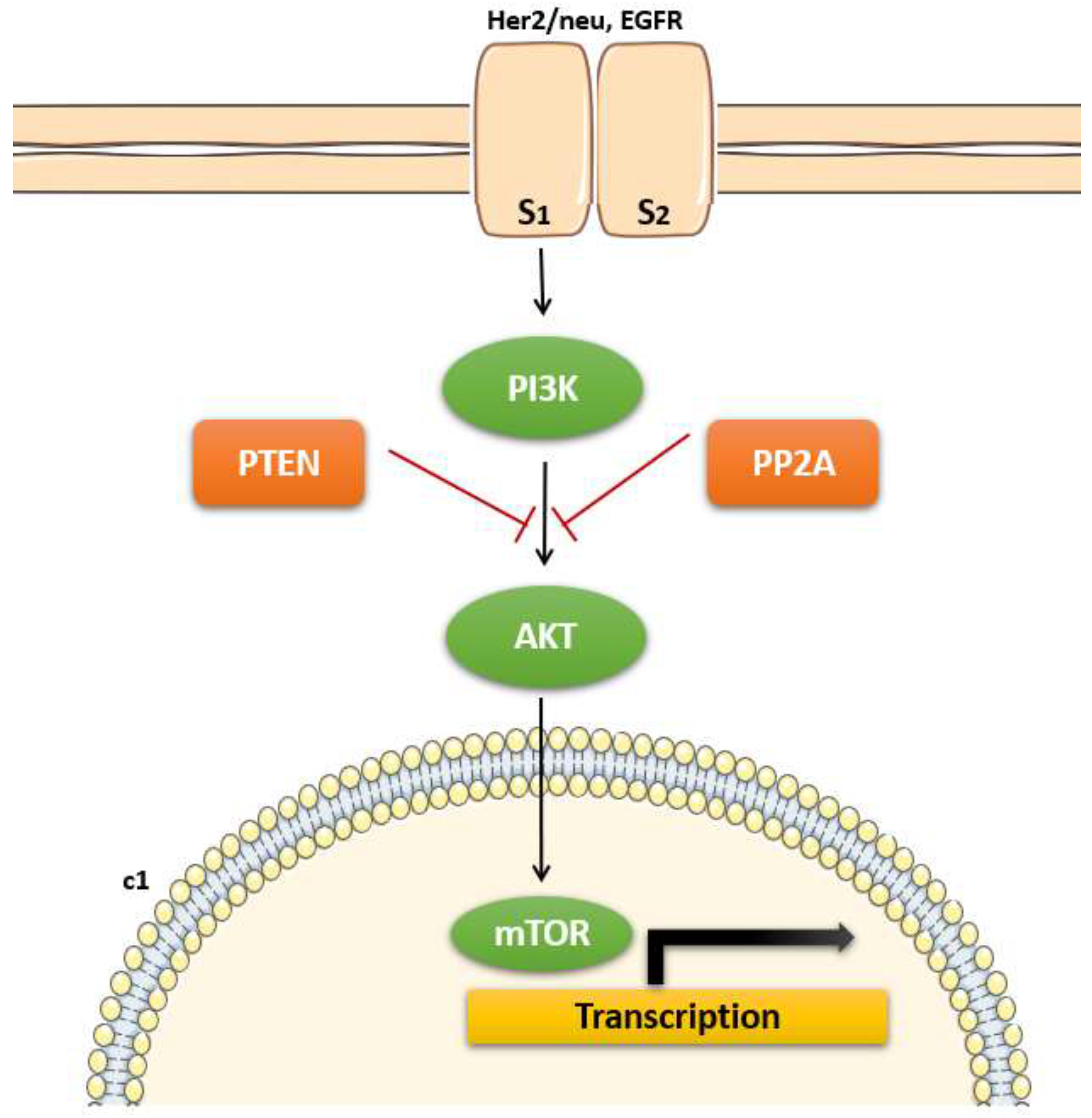
Among the various genetic alterations observed in EC, mutations in the PTEN (Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog) gene are particularly noteworthy due to their high frequency and critical role in tumorigenesis (Gotoh et al., 2024). The PTEN gene is one of the most frequently mutated genes among the most common genetic alterations in EC, occurring in approximately 40-80% of cases, particularly in endometrioid subtype which is more common and has a better prognosis compared to non-endometrioid types (Espinosa et al., 2024). It is a tumor suppressor gene located on chromosome 10q23, and it encodes a phosphatase involved in regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. PTEN mutations lead to the activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway thereby promoting loss of function and contributing to uncontrolled cell proliferation and survival, which are hallmarks of cancer (shown in
Figure 2). These mutations can include point mutations, insertions, deletions, and frameshift mutations, leading to a loss of PTEN protein function (Gotoh et al., 2024).
The PTEN protein acts as a phosphatase, dephosphorylating PIP3 (phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-triphosphate) to PIP2 (phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate), thereby antagonizing the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway (Southworth et al., 2024; Urick et al., 2019). This pathway is crucial for cell survival, growth, and proliferation. Loss of PTEN function results in unchecked activation of AKT, promoting cellular processes that lead to tumorigenesis, such as increased cell proliferation, survival, and migration (Urick et al., 2019). The presence of PTEN mutations in EC has significant clinical implications. Studies have shown that PTEN loss is associated with early-stage disease and favorable prognosis, particularly in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma (EEC) (Le et al., 2017). However, the prognostic significance of PTEN mutations can vary depending on the context of other genetic alterations and tumor subtypes. Additionally, PTEN status can influence therapeutic responses. For instance, tumors with PTEN mutations may be more sensitive to inhibitors targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, offering potential for targeted therapy in these patients. This has prompted ongoing research into PI3K pathway inhibitors and their efficacy in PTEN-mutant ECs (Le et al., 2017; Urick et al., 2019).
Recent research has focused on understanding the broader implications of PTEN mutations in the molecular landscape of EC (Urick et al., 2019). For example, next-generation sequencing and comprehensive genomic profiling have revealed that PTEN mutations often coexist with other genetic alterations, such as mutations in PIK3CA, ARID1A, and KRAS, suggesting a complex interplay of genetic events driving endometrial carcinogenesis. Moreover, studies have explored the role of PTEN mutations in the context of immune response and tumor microenvironment (Gotoh et al., 2024). Emerging evidence suggests that PTEN loss can affect immune cell infiltration and the expression of immune checkpoint molecules, thereby influencing the tumor’s response to immunotherapy (Urick et al., 2019). Therefore, PTEN mutations play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of EC, particularly in the endometrioid subtype. Their high prevalence and significant impact on tumor biology underscore the importance of PTEN as both a biomarker and a potential therapeutic target. Ongoing research continues to unravel the complexities of PTEN-related signaling pathways and their interactions with other molecular events, paving the way for more effective and personalized treatment strategies in EC (Stan et al., 2024).
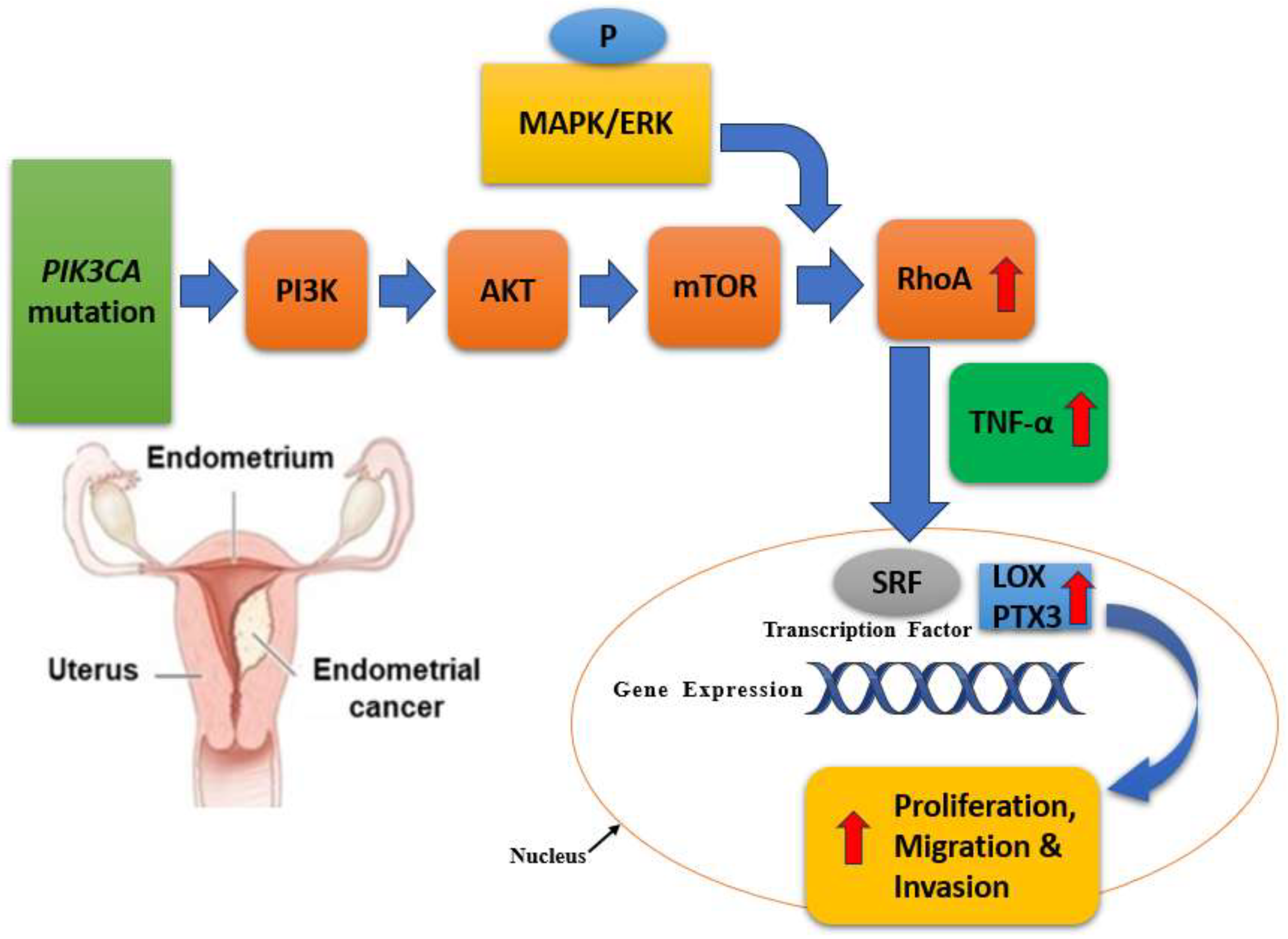
Mutations in the PIK3CA gene, which encodes the p110α catalytic subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K), are particularly significant and are present in about 40-50% of EC cases, with a higher frequency in endometrioid subtypes compared to non-endometrioid subtypes (Bostan et al., 2024). These mutations play a crucial role in the activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, contributing to tumorigenesis and progression in EC (Southworth et al., 2024). These mutations often occur in the helical (exon 9) and kinase (exon 20) domains of the gene, leading to gain-of-function alterations that enhance PI3K activity (Bostan et al., 2024; Paleari et al., 2021). The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is a critical regulator of cell growth, survival, and metabolism. As shown in
Figure 3, PIK3CA mutations result in constitutive activation of this pathway, leading to increased cell proliferation, survival, and angiogenesis, which are hallmarks of cancer (Bredin et al., 2023). This hyperactivation occurs through the phosphorylation and activation of AKT, which then promotes downstream signaling events crucial for tumor development and progression (Chukkalore et al., 2023). The presence of PIK3CA mutations in EC has several clinical implications. Some studies suggest that PIK3CA mutations are associated with a better prognosis in endometrioid endometrial carcinoma, though the results are not always consistent across different cohorts (Southworth et al., 2024). PIK3CA mutations have been targeted with specific inhibitors of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. For example, drugs like alpelisib (PIQRAY) have shown efficacy in PIK3CA-mutant cancers, including EC, making these mutations a potential biomarker for targeted therapy (Passarelli et al., 2023).
There is ongoing research into combining PI3K inhibitors with other treatments such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, given the role of PI3K pathway activation in modulating the tumor immune microenvironment (Mokhtari et al., 2020). Recent advances in genomic profiling have enhanced our understanding of PIK3CA mutations in EC. Comprehensive genomic analyses, such as those conducted by The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), have provided detailed insights into the co-occurrence of PIK3CA mutations with other genetic alterations, such as PTEN loss and ARID1A mutations, which collectively influence the disease phenotype and therapeutic response (Bostan et al., 2024; Paleari et al., 2021). Moreover, emerging research is focusing on the interaction between PIK3CA mutations and other molecular pathways, such as the MAPK pathway, to identify novel combinatorial treatment strategies (Paleari et al., 2021). For instance, preclinical studies have demonstrated synergistic effects of PI3K and MEK inhibitors in PIK3CA-mutant EC models, highlighting potential new avenues for treatment (Bostan et al., 2024). Thus, PIK3CA mutations are a significant driver of EC, particularly in the endometrioid subtype. These mutations lead to the activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, promoting tumorigenesis and offering potential targets for therapy. Understanding the prevalence, mechanisms, and clinical implications of PIK3CA mutations is essential for developing targeted therapies and improving patient outcomes in EC (Passarelli et al., 2023).
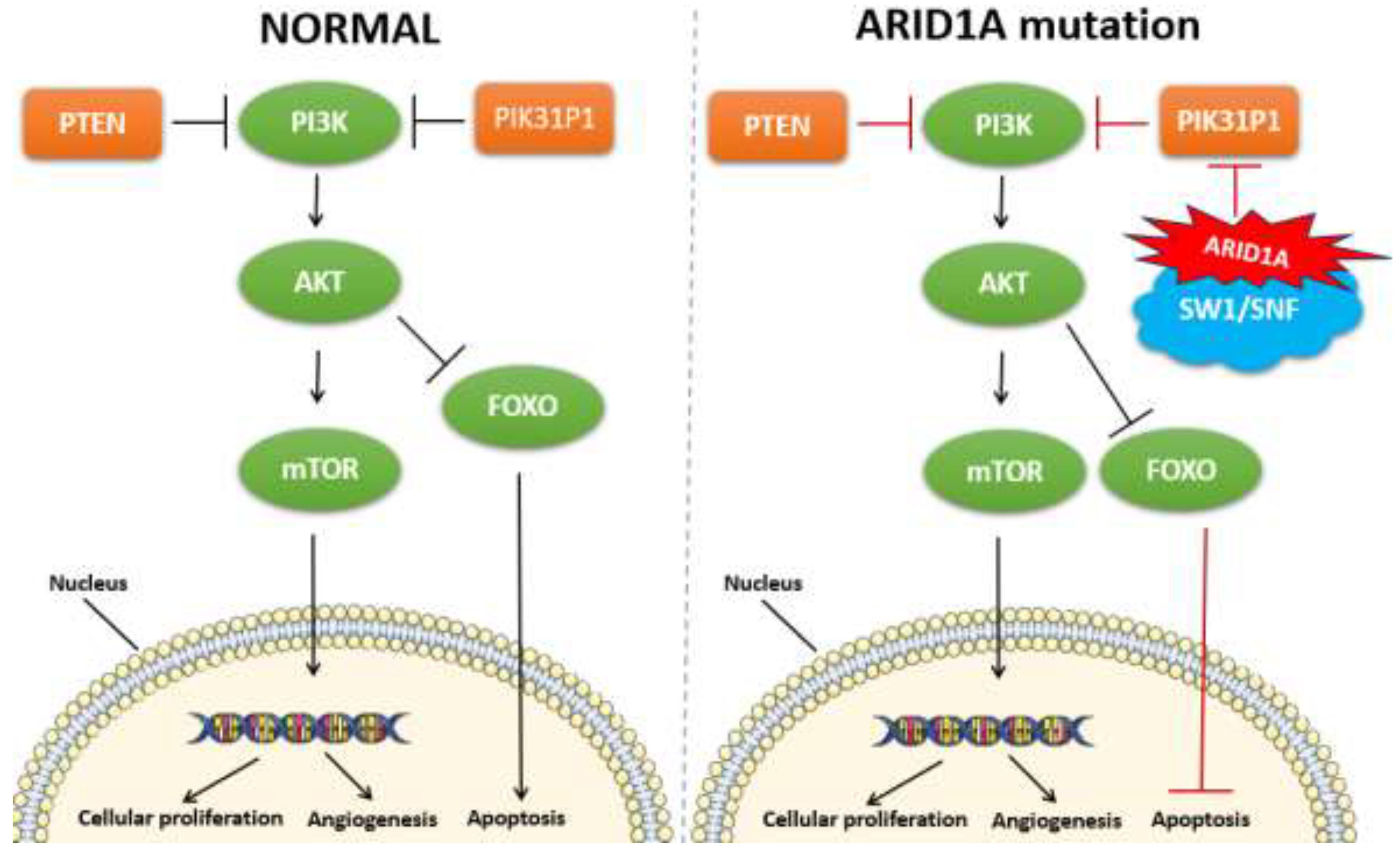
Among the genetic alterations implicated in EC, mutations in the ARID1A gene have garnered significant attention. ARID1A (AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 1A) is a crucial component of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, which plays a vital role in regulating gene expression and maintaining genomic stability. The loss or mutation of ARID1A disrupts these processes, contributing to the pathogenesis of EC. ARID1A mutations are found in approximately 30-50% of ECs and are associated with loss of function of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, which leads to altered gene expression and contributes to cancer development (Jamieson et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2020). They are also present in a smaller percentage of non-endometrioid subtypes (Jamieson et al., 2024; Espinosa et al., 2024; Church and Workman, 2024). These mutations are often characterized by frameshift and nonsense mutations, leading to a truncated, non-functional protein. Such loss-of-function mutations result in the inactivation of the SWI/SNF complex, thereby affecting chromatin remodeling and transcriptional regulation (Church and Workman, 2024). The ARID1A gene plays a pivotal role in various cellular processes, including DNA repair, cell cycle regulation, and apoptosis. The inactivation of ARID1A impairs these critical functions, promoting genomic instability and oncogenic transformation (Jamieson et al., 2024). Specifically, ARID1A mutations are associated with defects in the homologous recombination repair pathway, leading to the accumulation of DNA damage and increased mutation rates (Church and Workman, 2024).
In EC, ARID1A mutations often co-occur with mutations in other genes such as PIK3CA and PTEN, suggesting a collaborative role in driving tumorigenesis. The interplay between these mutations exacerbates oncogenic signaling pathways, particularly the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, further promoting cancer cell proliferation and survival (shown in
Figure 4) (Devi et al., 2024). The presence of ARID1A mutations in EC has several clinical implications. Studies have shown that ARID1A mutations are associated with favorable prognostic outcomes in endometrioid EC, although this association is not universally observed across all studies (Church and Workman, 2024). The prognostic impact may be influenced by the molecular context and co-occurring genetic alterations. The loss of ARID1A function presents potential therapeutic opportunities. For instance, tumors with ARID1A mutations exhibit increased sensitivity to inhibitors of the ATR and PARP pathways, which are involved in DNA damage response and repair (Zhou et al., 2024). This synthetic lethality approach exploits the DNA repair deficiencies in ARID1A-mutant cancers, offering a targeted treatment strategy. ARID1A mutations may serve as predictive biomarkers for response to certain therapies (Onoprienko et al., 2024; Yamashita et al., 2024). For example, immune checkpoint inhibitors have shown efficacy in ARID1A-mutant tumors, potentially due to the increased mutational burden and neoantigen load associated with these mutations (Onoprienko et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2024).
Recent genomic studies have provided deeper insights into the functional consequences of ARID1A mutations and their role in EC. Comprehensive analyses, such as those by The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), have elucidated the molecular subtypes of EC, highlighting the distinct genetic and epigenetic landscapes driven by ARID1A alterations (Bostan et al., 2024; Paleari et al., 2021; Yamashita et al., 2024). Additionally, emerging research is exploring the combination of ARID1A-targeted therapies with other treatment modalities. For instance, combining ATR inhibitors with immune checkpoint blockade is being investigated in preclinical models, showing promising synergistic effects in ARID1A-mutant cancers (Toumpeki et al., 2019). Thus, ARID1A mutations are a significant driver of EC, particularly in the endometrioid subtype. These mutations disrupt chromatin remodeling and DNA repair processes, contributing to tumorigenesis. Understanding the prevalence, mechanisms, and clinical implications of ARID1A mutations is essential for developing targeted therapies and improving patient outcomes in EC (Paleari et al., 2021; Yamashita et al., 2024).
Chromosomal abnormalities in EC include a wide range of genetic alterations such as copy number variations (CNVs), loss of heterozygosity (LOH), and specific chromosomal rearrangements (Paleari et al., 2021; Chukkalore et al., 2023). These abnormalities result in gains and losses of whole chromosomes or large chromosomal regions, and structural rearrangements. The common abnormalities include chromosome 1q gains and 16q losses, and structural rearrangements (Toumpeki et al., 2019). Frequently observed in ECs, these chromosomal alterations are thought to harbor key oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes that drive tumorigenesis (Chukkalore et al., 2023). Structural rearrangements include translocations, inversions, and complex rearrangements that can lead to oncogene activation or tumor suppressor gene inactivation. These abnormalities contribute to the pathogenesis and progression of EC by disrupting critical regulatory pathways involved in cell cycle control, apoptosis, and DNA repair mechanisms (Paleari et al., 2021).
Copy number variations (CNVs) including amplifications and deletions of specific chromosomal regions, are frequently observed in EC (Richenberg et al., 2023). For instance, amplifications of chromosomal regions 1q, 8q, and 10q have been associated with aggressive tumor behavior and poor prognosis (Gotoh et al., 2024; Dugo et al., 2024). Deletions in regions such as 1p, 3p, and 9p are also common and are linked to the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes (Richenberg et al., 2023). Loss of heterozygosity (LOH) is another critical chromosomal alteration observed in EC. LOH at chromosomal regions harboring tumor suppressor genes can lead to the complete inactivation of these genes (Dugo et al., 2024). Notably, LOH at 10q23, the locus of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene, is frequently reported in endometrial carcinomas and is associated with the development of endometrioid subtype of EC (Dugo et al., 2024). Specific chromosomal rearrangements, although less common than CNVs and LOH, also play a role in the pathogenesis of EC (Richenberg et al., 2023). For example, translocations involving the chromosomal region 17q21 have been identified in a subset of ECs and are associated with alterations in the expression of the HER2/neu oncogene (Canoy et al., 2023).
The identification of chromosomal abnormalities in EC has significant implications for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment (Richenberg et al., 2023). Genomic profiling of tumors can help identify patients at higher risk for aggressive disease and guide personalized treatment strategies (Yamashita et al., 2024). Targeted therapies aimed at specific genetic alterations, such as HER2/neu amplification, have shown promise in clinical trials (Fader et al., 2020). Hence, chromosomal abnormalities play a crucial role in the development and progression of EC. Understanding these genetic alterations is essential for improving the diagnosis, prognostication, and treatment of EC. Ongoing research and advancements in genomic technologies continue to enhance our knowledge of these abnormalities, offering hope for more effective and personalized therapeutic approaches.
4. Classification of Endometrial Cancers into Distinct Molecular Subtypes
Traditionally, EC has been classified based on histopathological criteria into two main types: Type I (endometrioid) and Type II (non-endometrioid) carcinomas. Type I cancers are typically estrogen-dependent and associated with a better prognosis, while Type II cancers are more aggressive and often present with a poorer prognosis (Bostan et al., 2024). However, this histological classification does not fully capture the underlying molecular heterogeneity of the disease, leading to variable responses to therapy and outcomes among patients with similar histopathological diagnoses (Hong et al., 2022). Advances in genomic technologies have revolutionized our understanding of the molecular landscape of EC. Comprehensive genomic analyses by The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) project have identified four distinct molecular subtypes of EC that provide a more accurate and prognostically relevant classification system: POLE ultramutated, microsatellite instability hypermutated (MSI-H), copy number low, and copy number high (shown in
Figure 5) (Hong et al., 2022). These molecular subtypes are defined by specific genetic, epigenetic, and transcriptomic alterations, offering insights into the mechanisms driving tumorigenesis and potential therapeutic targets. Each subtype has different mutation profiles and clinical outcomes, guiding personalized treatment strategies (Paleari et al., 2021; Bostan et al., 2024).
4.1. POLE-Ultramutated Subtype
POLE-ultramutated EC has garnered significant attention due to its unique genetic profile and clinical behavior. This subtype is characterized by an exceptionally high mutational burden and distinct prognostic implications due to mutations in the exonuclease domain of the DNA Polymerase Epsilon (POLE) gene, which encodes the DNA polymerase epsilon catalytic subunit. These tumors are often associated with a high number of neoantigens, which may enhance immune response (Espinosa et al., 2024). POLE is a key enzyme involved in DNA replication and repair, possessing a proofreading function that corrects replication errors. Mutations in the exonuclease domain of the POLE gene (most frequently occurring in the exonuclease domain hot spots) disrupt this proofreading ability, leading to an ultramutated phenotype with a high number of single nucleotide substitutions (Alexandrov et al., 2020). These mutations result in a hypermutator phenotype with a significant neoantigen load, which is hypothesized to enhance the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack the tumor cells (Keyhanian et al., 2024).
POLE-ultramutated ECs are predominantly endometrioid adenocarcinomas and are often of high grade. Despite their aggressive histopathological appearance, these tumors are associated with a favorable prognosis. The high mutation burden is thought to provoke a robust anti-tumor immune response, contributing to the lower recurrence rates and better overall survival observed in patients with POLE-ultramutated tumors compared to other subtypes (Espinosa et al., 2024; León-Castillo et al., 2020). The identification of POLE-ultramutated EC requires molecular testing. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) is the standard method for detecting POLE mutations and differentiating this subtype from other molecular variants of EC. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) alone is insufficient for diagnosing POLE mutations, making NGS an essential tool for accurate classification and personalized treatment planning (Espinosa et al., 2024).
Standard treatment for EC typically involves surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. However, the favorable prognosis of POLE-ultramutated tumors suggests that some patients may benefit from less aggressive treatment strategies. Additionally, the high mutational burden and increased neoantigen presentation in these tumors make them promising candidates for immunotherapy. Early clinical evidence suggests that immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as pembrolizumab, may be particularly effective in treating POLE-ultramutated ECs (Ott et al., 2019; Makker et al., 2022). Ongoing research aims to elucidate the biological mechanisms underlying the favorable outcomes of POLE-ultramutated ECs. Studies are also exploring the potential of combining immunotherapy with other treatments to enhance efficacy. Moreover, efforts are being made to develop reliable biomarkers for early detection and monitoring treatment response, which could further improve patient management (Southworth et al., 2024; Galant et al., 2024). Thus, POLE-ultramutated EC is a unique molecular subtype with distinct genetic and clinical characteristics. The presence of POLE mutations confers a high mutational burden, which is associated with improved prognosis and potential responsiveness to immunotherapy. Accurate molecular diagnosis is crucial for appropriate patient management and optimizing treatment outcomes. As research progresses, there is hope for more targeted and effective therapies that will continue to improve the outlook for patients with this and other subtypes of EC.
4.2. Microsatellite Instability (MSI)
Microsatellite instability (MSI) is a form of genetic hypermutability that results from impaired DNA mismatch repair (MMR) system, leading to high mutation rates (Riedinger et al., 2024). This condition has significant implications in EC, where MSI is an important biomarker for prognosis and therapeutic decision-making. MSI tumors are characterized by a distinct mutational signature and are responsive to immunotherapy (Jamieson et al., 2024). Recent advances in molecular diagnostics and targeted therapies have highlighted the role of MSI in the personalized treatment of EC (Lu and Broaddus, 2020). Microsatellites are short, repetitive sequences of DNA that are particularly prone to replication errors (Riedinger et al., 2024). The DNA MMR system, which includes proteins such as MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2, is responsible for correcting these errors. When this repair system is defective, replication errors accumulate, leading to MSI (Riedinger et al., 2024). In EC, MSI commonly results from epigenetic silencing of the MLH1 gene through promoter hypermethylation, although germline mutations in MMR genes can also contribute, especially in the context of Lynch syndrome (Lu and Broaddus, 2020; Riedinger et al., 2024).
MSI is present in approximately 20-30% of all ECs. Tumors with MSI, referred to as MSI-high (MSI-H), often exhibit distinct pathological and clinical features (Riedinger et al., 2024). MSI-H ECs tend to be of the endometrioid subtype, with a high grade and early-stage presentation (Lu and Broaddus, 2020). Importantly, MSI-H status is associated with a better overall prognosis compared to microsatellite stable (MSS) tumors, although they may also have a higher likelihood of concurrent Lynch syndrome (Kelkar et al., 2024). The identification of MSI in EC is crucial for guiding treatment and identifying potential Lynch syndrome cases (Le et al., 2017; Bostan et al., 2024). Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is a commonly used screening tool for MMR proteins. Loss of expression of one or more MMR proteins suggests MSI and warrants further genetic testing (Lu and Broaddus, 2020). Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)-based assays are also used to detect MSI by comparing the length of microsatellite sequences in tumor DNA to normal DNA (Chukkalore et al., 2023). Alternatively, next-generation sequencing (NGS) is used to offer a comprehensive approach to identify MSI and other genetic alterations, providing valuable information for personalized treatment strategies (Le et al., 2017; Bostan et al., 2024).
According to Chukkalore et al., 2023, MSI status has significant therapeutic implications in EC. In immunotherapy MSI-H tumors are characterized by a high mutational burden and increased neoantigen load, making them particularly responsive to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Pembrolizumab, an anti-PD-1 antibody, has shown efficacy in treating MSI-H EC, leading to its FDA approval for this indication (Makker et al., 2021). Moreso, the role of MSI in predicting chemotherapy response is complex and still under investigation. Some studies suggest that MSI-H tumors may be less responsive to traditional chemotherapeutics, highlighting the need for alternative treatment strategies (Chukkalore et al., 2023). The role of MSI in EC is still under research to improve diagnostic and further elucidate therapeutic approaches. The key research focus areas include identifying additional biomarkers that can predict response to immunotherapy and other treatments, investigating the efficacy of combining immunotherapy with other treatments, such as targeted therapies and radiation, and enhancing genetic counseling and testing for Lynch syndrome in patients with MSI-H tumors and improve early detection and prevention strategies (Corr et al., 2022). Thus, MSI is a critical biomarker in EC, influencing prognosis, treatment decisions, and genetic counseling. Advances in molecular diagnostics and targeted therapies continue to improve the management of MSI-H EC, offering hope for better patient outcomes.
4.3. Copy-Number Low Subtype
This subtype, also known as the endometrioid subtype, typically has few copy number alterations and specific molecular features that distinguish it from other EC subtypes. It is often associated with mutations in genes such as PTEN, PIK3CA, and CTNNB1. These tumors have a favorable prognosis and are typically low-grade and early-stage at diagnosis (Espinosa et al., 2024). The CNL subtype of EC exhibits fewer genomic alterations compared to the copy-number high (CNH) subtype. It is often associated with a lower mutation burden and a more stable genome. This subtype typically includes endometrioid endometrial carcinomas, which are often hormone receptor-positive and exhibit a relatively favorable prognosis (Bostan et al., 2024). The CNL subtype is frequently characterized by low frequency of somatic copy-number alterations, mutations in PTEN, PIK3CA, and ARID1A, and microsatellite stability (MSS). Unlike CNH tumors that exhibit numerous chromosomal amplifications and deletions, CNL tumors maintain a relatively stable genome. The mutations in PTEN, PIK3CA, and ARID1A are common but are not associated with extensive chromosomal instability. CNL tumors typically do not exhibit the high mutation rates associated with microsatellite instability (MSI) (Espinosa et al., 2024).
The molecular stability of CNL ECs translates into distinct clinical characteristics that include prognosis, hormone receptor status and therapeutic strategies. CNL tumors generally have a better prognosis compared to CNH tumors, with lower recurrence rates and higher overall survival (Makker et al., 2021). Many CNL tumors are estrogen and progesterone receptor-positive, which may make them more responsive to hormonal therapies (Makker et al., 2021). The stable genome of CNL tumors suggests they may respond well to conventional treatments such as surgery and radiation. Hormonal therapies are also a viable option due to the frequent hormone receptor positivity. Targeted therapies directed at the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, given the common mutations in PTEN and PIK3CA, are also being explored (Lu and Broaddus, 2020).
Accurate classification of EC subtypes, including CNL, is crucial for tailoring treatment strategies. Genomic sequencing and Immunohistochemistry (IHC) are the two most common diagnostic approaches currently in use. Whole-exome or targeted sequencing is used to identify specific mutations and copy-number alterations characteristic of CNL tumors. IHC for hormone receptors and mismatch repair proteins provide insights into the tumor’s molecular profile and potential subtype (Espinosa et al., 2024). The understanding of the CNL subtype has implications for patient care which include biomarker discovery, clinical trials and long-term outcomes. Identifying novel biomarkers specific to CNL tumors could enhance diagnostic accuracy and treatment personalization. Investigating the efficacy of targeted therapies and novel agents in CNL EC could expand therapeutic options. Further studies on the long-term outcomes of patients with CNL tumors will help to validate prognostic predictions and inform follow-up strategies (Bostan et al., 2024). Hence, the CNL subtype of EC represents a distinct molecular and clinical entity with relatively favorable outcomes. Understanding the unique characteristics of CNL tumors can guide more effective and personalized treatment approaches, improving patient prognosis and quality of life.
4.4. Copy-Number High (CNH) Subtype
The copy-number high (CNH) subtype, also referred to as the serous-like subtype, is marked by a high frequency of copy-number alterations, frequent TP53 mutations and distinct molecular features that differentiate it from other subtypes, contributing to its aggressive clinical behavior (Espinosa et al., 2024). They are often high-grade, aggressive, and associated with poor prognosis. This subtype includes serous and mixed histologies (Espinosa et al., 2024). The CNH subtype of EC is notable for its extensive genomic instability. It is often associated with serous histology but can also be found in high-grade endometrioid carcinomas. The key molecular features of CNH EC include high frequency of somatic copy-number alterations (SCNAs), mutations in TP53, low frequency of mutations in PTEN, PIK3CA, and ARID1A, and microsatellite stability (MSS). CNH tumors exhibit numerous chromosomal amplifications and deletions, indicating a highly unstable genome (Bostan et al., 2024). Mutations in the tumor suppressor gene TP53 are prevalent in CNH tumors, contributing to their aggressive nature and poor prognosis (Bostan et al., 2024). Unlike the copy-number low (CNL) subtype, these mutations are less common in CNH tumors. CNH tumors typically do not exhibit microsatellite instability, distinguishing them from the MSI subtype (Bostan et al., 2024). The molecular instability of CNH ECs translates into distinct clinical characteristics. CNH tumors generally have a poorer prognosis compared to other subtypes, with higher recurrence rates and lower overall survival (Makker et al., 2021). Due to the aggressive nature of CNH tumors, treatment often involves a combination of surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. The efficacy of targeted therapies and immunotherapies is an area of active research (Bostan et al., 2024; Paleari et al., 2021).
Accurate classification of EC is crucial for guiding treatment strategies. Whole-exome or targeted sequencing can identify specific mutations and extensive SCNAs characteristic of CNH tumors. IHC for p53 protein expression can help identify TP53 mutations and assess tumor subtype (Espinosa et al., 2024). Identifying novel biomarkers specific to CNH tumors could enhance diagnostic accuracy and treatment personalization. Investigating the efficacy of novel therapies, including targeted agents and immunotherapies, in CNH EC could expand therapeutic options. Further studies on the long-term outcomes of patients with CNH tumors will help validate prognostic predictions and inform follow-up strategies (Bostan et al., 2024). Thus, the CNH subtype of EC represents a distinct molecular and clinical entity characterized by extensive genomic instability and poor prognosis. Understanding the unique characteristics of CNH tumors can guide more effective and personalized treatment approaches, improving patient outcomes.
5. Epigenetic Modifications
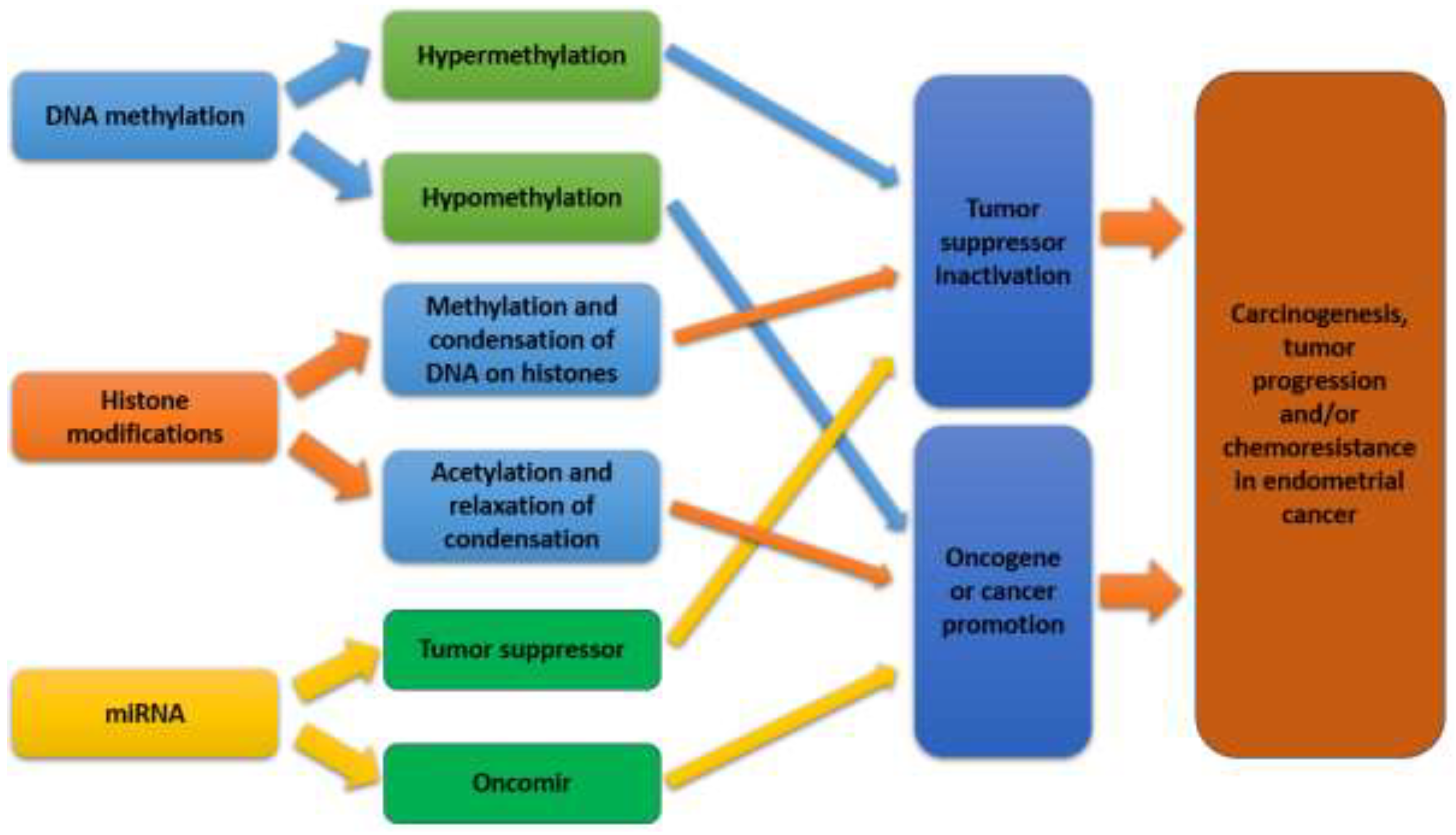
EC is increasingly recognized as a disease influenced not only by genetic mutations but also by epigenetic modifications. Epigenetic alterations play a critical role in the regulation of gene expression and cancer progression in EC (Inoue et al., 2021). The modifications which include DNA methylation, histone modifications, and non-coding RNA expression (shown in
Figure 6), play a crucial role in the regulation of gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence (Gotoh et al., 2024). Epigenetic changes can drive carcinogenesis by silencing tumor suppressor genes or activating oncogenes, thereby contributing to the development and progression of EC (Jamieson et al., 2024).
Recent advances in epigenomic technologies have facilitated the comprehensive mapping of epigenetic changes in EC, revealing distinct epigenetic profiles associated with different molecular subtypes of the disease (Xu et al., 2022). These findings have not only enhanced our understanding of the molecular underpinnings of EC but also opened new avenues for targeted therapeutic strategies aimed at reversing aberrant epigenetic modifications (Bostan et al., 2024). The integration of epigenetic biomarkers into clinical practice holds promise for improving the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of EC. Drugs targeting epigenetic modifications are being explored as potential treatments for EC (Inoue et al., 2021).
5.1. DNA Methylation in Endometrial Cancer
DNA methylation is a crucial epigenetic modification that plays a significant role in gene regulation. In the context of EC, aberrant DNA methylation patterns are common and contribute to the initiation and progression of the disease. This includes hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes, hypomethylation of oncogenes, and global changes in methylation that affect genomic stability (shown in
Figure 7). DNA methylation typically occurs at the 5-carbon position of cytosine residues within CpG dinucleotides, leading to the formation of 5-methylcytosine. This modification generally acts to repress gene expression by preventing the binding of transcription factors to DNA or by recruiting proteins that mediate gene silencing (Jamieson et al., 2024). In cancer, dysregulation of DNA methylation is a common phenomenon, often resulting in the silencing of key regulatory genes that control cell growth and apoptosis.
In EC, one of the most notable epigenetic changes is the hypermethylation of promoter regions of tumor suppressor genes, leading to their silencing. For example, the PTEN gene, which is frequently mutated in EC, is also commonly inactivated through promoter hypermethylation (Gotoh et al., 2024). This loss of PTEN function contributes to the uncontrolled cell proliferation characteristic of cancer. Similarly, the MLH1 gene, a critical component of the DNA mismatch repair (MMR) system, is often silenced by promoter hypermethylation in microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) ECs (Jamieson et al., 2024). The loss of MLH1 expression leads to the accumulation of DNA errors, further driving tumorigenesis. While hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes is a well-recognized phenomenon in EC, global DNA hypomethylation also plays a significant role (Besselink et al., 2023). Hypomethylation can lead to the activation of oncogenes, such as the insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) gene, which is often overexpressed in EC due to loss of imprinting caused by hypomethylation (Jamieson et al., 2024). Furthermore, hypomethylation of repetitive DNA elements, such as LINE-1, is frequently observed in EC. This can result in chromosomal instability, contributing to the progression of the disease (Besselink et al., 2023).
The alterations in DNA methylation patterns in EC have potential utility as biomarkers for early detection, prognosis, and treatment stratification (Bostan et al., 2024). For example, the methylation status of the MLH1 promoter is used to identify patients with MSI-H tumors, which have distinct clinical behaviors and may respond differently to immunotherapy (Le et al., 2017). Additionally, global methylation patterns could potentially distinguish between different subtypes of EC, aiding in personalized treatment approaches (Espinosa et al., 2024). The reversible nature of DNA methylation makes it an attractive target for therapeutic intervention. Agents that inhibit DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), such as 5-azacytidine and decitabine, have shown promise in preclinical models of EC by reactivating silenced tumor suppressor genes and reducing tumor growth (Brasseur et al., 2017). These epigenetic therapies, alone or in combination with other treatments, could offer new avenues for treating EC, particularly in patients with hypermethylated tumors. Thus, DNA methylation plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of EC by modulating the expression of key genes involved in cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, and DNA repair. The aberrant methylation patterns observed in EC not only provide insights into the molecular mechanisms driving the disease but also offer potential biomarkers for diagnosis and targets for therapy. Continued research in this area is likely to yield further advances in our understanding and treatment of EC.
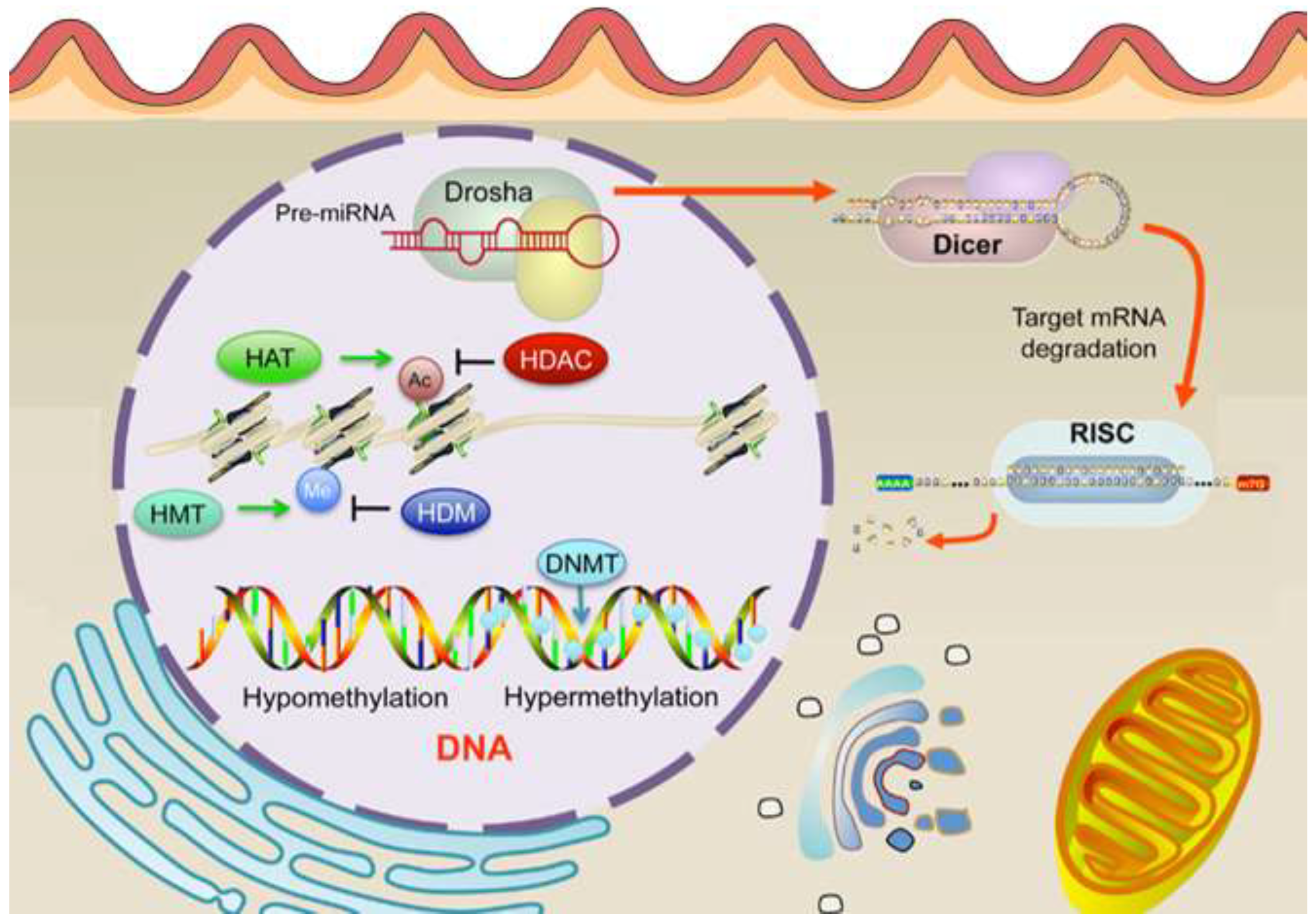
5.2. Histone Modifications in Endometrial Cancer
Histone modifications are critical epigenetic regulators that influence chromatin structure and gene expression, playing a significant role in the development and progression of EC (Inoue et al., 2024). These modifications, which include acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and sumoylation of histone tails (shown in
Figure 8), can either activate or repress transcriptional activity depending on the specific residues modified and the type of modification (Bostan et al., 2024). In the context of EC, aberrant histone modifications have been increasingly recognized as key factors contributing to tumorigenesis. One of the most studied histone modifications in EC is histone methylation. Methylation of histone H3 on lysine residues 4 (H3K4), 9 (H3K9), and 27 (H3K27) is particularly relevant, as these marks are associated with either active or repressive chromatin states (Bostan et al., 2024). For instance, H3K4 methylation is typically linked with transcriptional activation, while H3K27 methylation is associated with gene repression. Studies have shown that alterations in the enzymes responsible for adding or removing these methyl marks, such as the H3K27 methyltransferase EZH2, are often dysregulated in EC (Inoue et al., 2024). Overexpression of EZH2, leading to increased H3K27 trimethylation (H3K27me3), has been correlated with poor prognosis and aggressive tumor behavior (Inoue et al., 2021; Inoue et al., 2021; Keller et al., 2024).
Histone acetylation, another important modification, is generally associated with transcriptional activation due to the relaxation of chromatin structure, allowing transcription factors access to DNA (Inoue et al., 2024). Dysregulation of histone acetyltransferases (HATs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs) has been implicated in EC, with alterations in these enzymes leading to an imbalance in acetylation patterns that can either promote or inhibit tumor growth (Bostan et al., 2024; Inoue et al., 2024). HDAC inhibitors, which restore normal acetylation levels, have shown promise in preclinical models of EC by reactivating tumor suppressor genes and inducing cancer cell death (Psilopatis et al., 2021). Moreover, recent research has identified the interplay between histone modifications and other epigenetic mechanisms, such as DNA methylation and non-coding RNAs, in the regulation of gene expression in EC (Bostan et al., 2024). This crosstalk contributes to the complex epigenetic landscape of the disease and underscores the potential for therapeutic interventions targeting multiple epigenetic pathways (Inoue et al., 2021). Thus, histone modifications play a crucial role in the epigenetic regulation of EC. Understanding these modifications provides insights into the molecular mechanisms driving the disease and highlights potential targets for novel therapeutic strategies aimed at reversing aberrant epigenetic changes.
6. Genomic Techniques and Approaches
The exploration of the genomic landscape of EC has been significantly advanced by the development and application of various genomic techniques. These techniques have enabled a deeper understanding of the molecular underpinnings of EC, leading to more precise diagnostic tools, the identification of novel therapeutic targets, and the development of personalized treatment strategies (Chukkalore et al., 2023). The implementation of genomic techniques such high-throughput sequencing (HTS) technologies, bioinformatics and computational tools has not only facilitated the molecular subtyping of EC but also revealed the complex interplay of genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors contributing to tumor development and progression (Liu, et al., 2023; Bostan et al., 2024).
6.1. High-Throughput Sequencing Technologies
High-throughput sequencing (HTS) technologies have revolutionized cancer genomics, offering unprecedented insights into the molecular landscape of various malignancies, including EC (Paleari et al., 2021; Bostan et al., 2024). HTS technologies, including whole-genome sequencing (WGS), whole-exome sequencing (WES), and RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), have been pivotal in uncovering these alterations, leading to the identification of distinct molecular subtypes of EC with differing prognoses and therapeutic responses. The application of HTS has also facilitated the discovery of novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets, paving the way for more personalized and effective treatment strategies (Liu, et al., 2023).
6.2. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) has emerged as a transformative tool in the study of EC, significantly advancing our understanding of its molecular underpinnings (Talhouk et al., 2019). NGS technologies have been pivotal in identifying mutations, copy number variations, and other genetic alterations in EC. It offers high sensitivity, speed, and the ability to detect a wide range of genetic alterations, including single nucleotide variants (SNVs), insertions, deletions, and structural variants (Bostan et al., 2024). NGS allows for comprehensive profiling of these alterations, providing insights that are crucial for diagnosis, prognosis, and the development of targeted therapies. It has been instrumental in identifying key mutations, gene expression changes, and structural variations in EC. For example, studies utilizing Whole-exome sequencing (WES) have uncovered frequent mutations in genes such as PTEN, PIK3CA, ARID1A, and CTNNB1, which are involved in critical signaling pathways regulating cell growth and apoptosis (Talhouk et al., 2019). NGS has facilitated the classification of EC into distinct molecular subtypes, such as the POLE ultramutated, microsatellite instability (MSI), copy-number low, and copy-number high subtypes. These molecular subtypes have been shown to have significant prognostic and therapeutic implications (Lu and Broaddus, 2020).
Furthermore, NGS has enabled the identification of potential biomarkers for targeted therapies. For instance, the detection of ERBB2 amplifications and PIK3CA mutations through NGS has led to the exploration of targeted inhibitors in clinical trials (Bostan et al., 2024). NGS is also pivotal in understanding the mechanisms of resistance to therapies, allowing for the adaptation of treatment strategies based on the evolving molecular landscape of the tumor (Talhouk et al., 2019). The use of NGS in EC research continues to evolve, with ongoing studies aiming to integrate genomic data with other omics approaches, such as proteomics and metabolomics, to provide a more comprehensive understanding of tumor biology. As NGS technologies become more accessible and cost-effective, their integration into clinical practice is expected to further personalize the management of EC, improving outcomes for patients (Lu and Broaddus, 2020).
6.3. Whole-Exome and Whole-Genome Sequencing
Whole-exome sequencing (WES) and whole-genome sequencing (WGS) have significantly contributed to the understanding of the genetic landscape of EC. These high-throughput sequencing technologies enable comprehensive analysis of genetic alterations, offering insights into the mutational profiles and potential therapeutic targets in EC (Jamieson et al., 2024; Talhouk et al., 2019). WES focuses on sequencing the protein-coding regions of the genome, which constitute about 1-2% of the human genome but harbor approximately 85% of disease-related variants (Southworth et al., 2024). In EC, WES has been instrumental in identifying recurrent mutations in key driver genes. For instance, studies have consistently found mutations in genes such as PTEN, PIK3CA, ARID1A, CTNNB1, and TP53 in various subtypes of EC. These genes are involved in critical pathways like the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, WNT/β-catenin signaling, and chromatin remodeling, which are crucial for cell proliferation and survival (Lu and Broaddus, 2020). WES has also been pivotal in the molecular classification of EC, as demonstrated by the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) project. This large-scale study classified ECs into four distinct molecular subtypes: POLE ultramutated, microsatellite instability (MSI) hypermutated, copy-number low, and copy-number high (serous-like). Each subtype is associated with unique genetic alterations and clinical outcomes, highlighting the heterogeneity of the disease and guiding personalized treatment approaches (Paleari et al., 2021).
WGS, which sequences the entire genome, provides a more comprehensive analysis by capturing not only coding but also non-coding regions, structural variants, and other regulatory elements (Southworth et al., 2024). This approach has revealed novel insights into the genomic architecture of EC, including the identification of non-coding mutations and structural rearrangements that may play a role in tumorigenesis (Lu and Broaddus, 2020). One significant finding from WGS studies is the identification of structural variations such as copy number alterations and gene fusions that are not typically detected by WES. For example, ERBB2 amplifications, which are more common in serous endometrial carcinomas, have been detected through WGS and are associated with poor prognosis and potential responsiveness to HER2-targeted therapies (Paleari et al., 2021). Additionally, WGS has uncovered complex rearrangements and non-coding region mutations that may contribute to gene dysregulation in EC. Furthermore, WGS has been useful in identifying mutational signatures associated with specific DNA repair defects, such as those resulting from defects in the mismatch repair (MMR) system, which are prevalent in MSI-high ECs. Understanding these signatures can inform the use of targeted therapies, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, which have shown efficacy in MSI-high tumors (Southworth et al., 2024).
The integration of WES and WGS into clinical practice has the potential to revolutionize the management of EC. These technologies provide a more detailed molecular profile of tumors, enabling the identification of actionable mutations and the development of targeted therapies. For instance, the identification of PIK3CA mutations has led to the exploration of PI3K inhibitors in clinical trials. Moreover, the ability of WGS to detect structural variants and non-coding mutations may uncover new therapeutic targets and biomarkers for patient stratification. As sequencing technologies continue to advance, the cost of WES and WGS is expected to decrease, making these approaches more accessible in clinical settings. Future research will likely focus on integrating genomic data with other omics approaches, such as transcriptomics and proteomics, to gain a more holistic understanding of EC and to refine therapeutic strategies.
6.4. RNA Sequencing (RNA-seq)
RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) has emerged as a powerful tool for transcriptome analysis, enabling a comprehensive understanding of gene expression profiles, alternative splicing events, and non-coding RNA activity in various cancers, including EC (Jia et al., 2022). This technology provides insights into the molecular mechanisms driving EC pathogenesis, progression, and treatment resistance, offering opportunities for the development of novel therapeutic strategies and biomarkers. RNA-seq has been instrumental in delineating the molecular subtypes of EC, which have distinct gene expression profiles and clinical outcomes (Jia et al., 2022). The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) initially identified four molecular subtypes of EC: POLE ultramutated, microsatellite instability (MSI) hypermutated, copy-number low (endometrioid), and copy-number high (serous-like) using a combination of RNA-seq and other genomic techniques (Xu et al., 2024). These subtypes have since been validated and refined through RNA-seq studies, which have provided deeper insights into the transcriptional landscapes associated with each subtype. For example, the POLE ultramutated subtype is characterized by high expression of immune-related genes, reflecting an immune-rich tumor microenvironment that may be amenable to immunotherapy (Jia et al., 2022).
Conversely, the serous-like subtype shows high expression of genes involved in cell cycle regulation and DNA damage response, highlighting potential targets for therapeutic intervention, such as PARP inhibitors (Galant et al., 2024). RNA-seq has also uncovered the complexity of alternative splicing events in EC, revealing novel isoforms that may contribute to tumorigenesis and drug resistance. For instance, a recent study by Li et al. (2021) identified a set of differentially spliced genes in EC that are associated with key oncogenic pathways, including the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and Wnt/β-catenin pathways. These splicing events could serve as potential biomarkers for disease progression and treatment response. In addition to mRNA transcripts, RNA-seq has shed light on the role of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), such as microRNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), in EC. For example, Zhang et al. (2022) reported the upregulation of the lncRNA HOTAIR in EC tissues, which was associated with poor prognosis and enhanced metastatic potential. Similarly, miRNA profiling through RNA-seq has identified miRNAs, such as miR-200c and miR-205, that are differentially expressed in EC and may regulate epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and other critical processes (Iavarone et al., 2024).
RNA-seq has provided significant insights into the tumor microenvironment (TME) of EC, particularly in understanding the immune landscape. Recent RNA-seq studies have identified distinct immune-related gene expression signatures that correlate with patient outcomes and response to immunotherapy (Guo et al., 2024). For instance, tumors with high expression of PD-L1 and other immune checkpoint molecules have been shown to respond better to checkpoint inhibitors, underscoring the potential of RNA-seq in guiding personalized immunotherapy strategies (Song et al., 2023). Moreover, RNA-seq has been used to profile the TME, revealing the presence of various immune cell subsets, such as tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and macrophages, which play critical roles in tumor progression and immune evasion (Chen et al., 2024). Understanding the transcriptional profiles of these immune cells through RNA-seq can inform the development of combination therapies that target both the tumor cells and the immune components of the TME (Southworth et al., 2024).
The insights gained from RNA-seq studies in EC have significant clinical implications. By identifying distinct molecular subtypes, alternative splicing events, and non-coding RNAs, RNA-seq has the potential to improve patient stratification, guide therapeutic decisions, and identify novel targets for drug development. For example, the identification of immune-related gene expression signatures through RNA-seq can inform the use of immunotherapies in patients with specific molecular subtypes of EC (Jia et al., 2022). Looking forward, the integration of RNA-seq with other omics technologies, such as proteomics and single-cell RNA-seq, will provide a more comprehensive understanding of the molecular and cellular heterogeneity in EC. This multi-omics approach is expected to uncover novel therapeutic targets and biomarkers, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
6.5. Bioinformatics and Computational Tools
The integration of bioinformatics and computational tools in EC research has significantly advanced our understanding of the disease’s molecular underpinnings (Madabhushi et al., 2023). These tools have enabled the discovery of novel biomarkers, molecular subtypes, and therapeutic targets, paving the way for personalized medicine (Mustea et al., 2024). As bioinformatics continues to evolve, it holds great potential for further breakthroughs in EC research, ultimately improving patient outcomes and guiding clinical decision-making (Madabhushi et al., 2023).
6.6. Algorithms for Mutation Detection and Interpretation
The analysis of NGS data requires sophisticated bioinformatics tools to accurately detect and interpret genetic mutations (Dellino et al., 2023). Detecting and interpreting these mutations are critical steps in understanding the molecular basis of EC and in the development of personalized treatment strategies (Stan et al., 2024). Advances in sequencing technologies have led to the generation of vast amounts of genomic data, necessitating the use of sophisticated algorithms for the accurate detection and interpretation of mutations (Streel et al., 2023). These algorithms help in identifying driver mutations, predicting their functional impacts, and linking them to therapeutic options, thereby enhancing the precision of cancer management (Dellino et al., 2023). The raw data generated through genomic profiling using the high-throughput sequencing technologies require rigorous processing and analysis to identify mutations accurately. Algorithms such as MuTect, VarScan, and GATK are widely used for calling somatic mutations from sequencing data (Corr et al., 2022). Algorithms for mutation detection typically involve several steps: read alignment, variant calling, and post-processing to filter out false positives (Dellino et al., 2023). Tools like ANNOVAR and SnpEff help annotate and predict the functional impact of identified mutations, aiding in the understanding of their potential role in cancer (Streel et al., 2023).
GATK (Genome Analysis Toolkit) is one of the most widely used tools for variant calling in cancer genomics. It incorporates a series of best practices for read alignment, base quality score recalibration, and variant calling, which are essential for identifying somatic mutations in tumor samples (Wang et al., 2023). GATK has been successfully applied in various studies on EC, enabling the identification of both common and rare mutations associated with the disease (Dellino et al., 2023). Another powerful tool is MuTect2, which is specifically designed to detect somatic point mutations in paired tumor-normal samples. This tool is particularly effective in identifying low-frequency mutations that might be overlooked by other methods (Streel et al., 2023). In the context of EC, MuTect2 has been instrumental in uncovering mutations in key genes such as PTEN, PIK3CA, and ARID1A, which are frequently altered in this cancer type (Pandya et al., 2024). Strelka2 is another mutation caller that has gained prominence for its sensitivity and accuracy in detecting both single nucleotide variants (SNVs) and small insertions/deletions (indels) (Kim et al., 2018). Strelka2’s efficiency in handling high-depth sequencing data makes it a valuable tool for analyzing complex tumor genomes, including those of EC (Streel et al., 2023).
Once mutations are detected, the next challenge is to interpret their potential impact on protein function and their role in cancer. This interpretation is crucial for distinguishing between driver mutations, which contribute to cancer progression, and passenger mutations, which are biologically neutral (Streel et al., 2023). OncoKB is a precision oncology knowledge base that provides curated information about the oncogenic effects and treatment implications of specific mutations (Corr et al., 2022). By integrating genomic data with OncoKB, researchers and clinicians can classify mutations in EC into categories such as likely oncogenic, tumor suppressor, or unknown significance, thereby aiding in clinical decision-making (Chakravarty et al., 2017; Corr et al., 2022). CHASM (Cancer-Specific High-Throughput Annotation of Somatic Mutations) is an algorithm designed to predict the likelihood that a given mutation is a driver mutation. It uses machine learning models trained on large datasets of known cancer mutations and can accurately prioritize mutations in EC for further functional validation (Stan et al., 2024; Streel et al., 2023).
Polymorphism Phenotyping v2 (PolyPhen-2) is another widely used tool that predicts the potential impact of an amino acid substitution on the structure and function of a protein. While not cancer-specific, PolyPhen-2 has been applied to the interpretation of mutations in EC, particularly in the context of identifying deleterious variants in tumor suppressor genes (Alessandro et al., 2022). Rare Exome Variant Ensemble Learner (REVEL) is a meta-predictor that combines multiple algorithms to predict the pathogenicity of rare variants (Nousiainen et al., 2023). REVEL’s application in EC has been useful for assessing the clinical significance of novel or rare mutations, providing insights into their potential role in cancer development (Ioannidis et al., 2016; Nousiainen et al., 2023). The integration of these mutation detection and interpretation algorithms into clinical workflows is critical for the advancement of personalized medicine in EC (Nousiainen et al., 2023). Emerging tools that combine the strengths of multiple algorithms and incorporate additional data types, such as epigenetic marks and transcriptomic profiles, are likely to improve the accuracy and clinical utility of mutation analysis. Additionally, the development of cloud-based platforms that facilitate the sharing and analysis of genomic data across institutions is expected to enhance collaborative efforts in EC research. Such platforms will enable the continuous refinement of existing algorithms, and the creation of new tools tailored to the unique genomic landscapes of different cancer types, including EC.
6.7. Databases and Resources for Genomic Data
The integration and interpretation of genomic data are facilitated by various databases and resources. The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) provides a comprehensive dataset of genomic, epigenomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic data across various cancer types, including EC (Espinosa et al., 2024). Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer (COSMIC) is a database that catalogs somatic mutations in human cancers, providing valuable information for the study of EC (Forbes et al., 2017; Nousiainen et al., 2023). The vast amount of data generated by NGS requires significant computational resources and expertise to process, analyze, and interpret (Southworth et al., 2024). Distinguishing between driver mutations and passenger mutations remains a challenge, requiring robust functional assays and validation studies (Nousiainen et al., 2023). The quality and purity of tumor samples can affect the accuracy of sequencing results, with tumor heterogeneity and contamination by normal tissue posing additional challenges (Schwarze et al., 2018). Despite advances in sequencing technologies, certain regions of the genome remain difficult to sequence and interpret accurately (Nousiainen et al., 2023). Understanding the biological significance of many genetic alterations, especially those in non-coding regions, remains limited, necessitating further functional studies (Streel et al., 2023). The translation of genomic findings into clinical practice is still in its infancy, with challenges in integrating genomic data into standard care protocols and ensuring accessibility to precision medicine (Southworth et al., 2024).
7. Clinical Implications of Genomic Findings
The genomic landscape of EC has provided valuable insights that have significant clinical implications (Dobrzycka et al., 2024). The translation of these genomic discoveries into clinical practice has the potential to revolutionize the management of EC through personalized medicine, the development of targeted therapies, and the identification of prognostic and predictive biomarkers (Chukkalore et al., 2023). Advances in genomic research have identified various genetic alterations in EC that can be targeted by specific therapies. For instance, mutations in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, which are prevalent in EC, have led to the development of targeted inhibitors for this pathway. Targeted therapies aimed at the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway have shown promise in treating EC (Makker et al., 2021). The presence of mutations in genes such as PTEN, PIK3CA, and ARID1A makes this pathway a critical target for intervention (Bell and Ellenson, 2019). Several targeted therapies have been developed based on the genomic alterations identified in EC, leading to more personalized treatment approaches. Alpelisib, a PI3K inhibitor, has shown efficacy in treating patients with PIK3CA-mutated cancers, including EC (Miller et al., 2020). Everolimus, an mTOR inhibitor, has demonstrated activity in EC, particularly in tumors with PTEN mutations (Slomovitz et al., 2020).
The identification of genomic biomarkers is crucial for predicting disease prognosis and treatment responses in EC. Microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) and deficient mismatch repair (dMMR) are biomarkers associated with better responses to immunotherapy in EC (Dobrzycka et al., 2024). Pembrolizumab, an immune checkpoint inhibitor, has been approved for MSI-H/dMMR ECs (Makker et al., 2022). TP53 mutations are indicative of high-grade, aggressive EC and are associated with poor prognosis, helping stratify patients for more aggressive treatment regimens (Hong et al., 2022). Several clinical trials are ongoing to evaluate the efficacy of targeted therapies and the use of biomarkers in EC. A phase II trial (NCT03367741) is investigating the combination of PI3K inhibitors with standard chemotherapy in PIK3CA-mutated EC (Makker et al., 2021). The NCT02725268 trial is evaluating the efficacy of pembrolizumab in MSI-H/dMMR EC patients, showing promising results in terms of response rates and progression-free survival (Hong et al., 2022).
One of the significant challenges in translating genomic data into clinical practice is the variability in patient responses to targeted therapies (Dobrzycka et al., 2024). EC exhibits significant intra-tumoral and inter-tumoral heterogeneity, leading to variable responses to the same targeted therapies (Bell and Ellenson, 2019). The development of resistance to targeted therapies poses a challenge, necessitating combination therapies or the development of next-generation inhibitors (Slomovitz et al., 2020). The integration of genomic data into routine clinical workflows involves several logistical and practical challenges. Implementing comprehensive genomic profiling in clinical practice requires significant resources, including access to advanced sequencing technologies and bioinformatics support (Hong et al., 2022). Effective integration of genomic data necessitates collaboration among oncologists, geneticists, pathologists, and bioinformaticians to interpret the data and make informed treatment decisions (Miller et al., 2020).
8. Future Directions in Genomic Research and Clinical Applications
CRISPR-Cas9 technology has revolutionized genomic research by enabling precise, targeted modifications to the DNA of living organisms (Devi et al., 2024). In the context of EC, CRISPR offers the potential to create specific gene knockouts or modifications to study the function of genes involved in cancer development and progression (Zhang et al., 2020). For instance, CRISPR can be used to disrupt oncogenes or repair tumor suppressor genes in cellular models, providing insights into their roles and offering pathways for therapeutic intervention (Devi et al., 2024). Moreover, advancements in CRISPR technology, such as CRISPR-Cas12 and CRISPR-Cas13, have expanded the toolkit for genomic editing and RNA targeting, respectively, broadening the scope of cancer research (Zhang et al., 2020; Devi et al., 2024). Single-cell genomics has emerged as a powerful tool to dissect the heterogeneity of tumor cells at an unprecedented resolution (Zhang et al., 2020). By analyzing the genetic and transcriptomic profiles of individual cells within a tumor, researchers can uncover subpopulations of cancer cells that contribute to treatment resistance and disease recurrence (Papalexi & Satija, 2018). Spatial transcriptomics further complements this by mapping gene expression within the tissue context, preserving spatial information that is lost in traditional bulk sequencing approaches (Chen et al., 2024). These technologies enable a more comprehensive understanding of the tumor microenvironment and the interactions between cancer cells and their surrounding stromal and immune cells, which is crucial for developing targeted therapies.
The integration of multi-omics data is a burgeoning field that seeks to combine different layers of biological information to provide a holistic view of disease mechanisms. In EC, combining genomic data (e.g., DNA mutations, copy number variations) with transcriptomic (mRNA expression), proteomic (protein expression and modifications), and metabolomic (metabolic pathways) data can reveal complex regulatory networks and identify key drivers of cancer progression (Hasin et al., 2017). For example, proteogenomics integrates proteomic and genomic data to connect genomic alterations to protein expression changes, which can be more directly linked to phenotypic outcomes (Streel et al., 2023). A multi-omics approach enables the identification of biomarkers that might not be apparent when examining a single omic layer. For instance, post-translational modifications of proteins, which are critical in cancer signaling pathways, can be missed by genomic or transcriptomic analyses alone (Mustea et al., 2024). Integrating these data types enhances the understanding of the molecular underpinnings of EC and aids in the identification of novel therapeutic targets. Additionally, it can improve patient stratification for personalized treatments by considering a more comprehensive molecular profile (Hoadley et al., 2018).
The ultimate goal of genomic research in EC is to facilitate the development of personalized treatment plans. Precision oncology aims to tailor treatments based on the specific genetic and molecular profile of a patient’s tumor. This approach can lead to the selection of therapies that are more effective and have fewer side effects compared to traditional one-size-fits-all treatments (Chen et al., 2024). Advances in high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics have enabled the identification of actionable mutations and the development of targeted therapies, such as PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors for patients with relevant pathway alterations (Bostan et al., 2024). Despite the promise of personalized medicine, there are significant ethical and practical challenges to its widespread implementation. One major concern is the equitable access to genomic testing and targeted therapies, which can be expensive and limited to specialized centers (Chen et al., 2024). Additionally, the interpretation of genomic data requires sophisticated bioinformatics tools and expertise, which may not be readily available in all healthcare settings. Ethical issues also arise regarding genetic privacy and the potential for genetic discrimination. Ensuring that patients understand the implications of genomic testing and maintaining confidentiality are paramount (Southworth et al., 2024).
9. Conclusion
The intricate genomic landscape of EC and its profound implications for clinical practice form the foundation of our understanding of this malignancy. The key genetic alterations, such as mutations in PTEN, PIK3CA, and ARID1A, as well as chromosomal abnormalities are a tremendously important therapeutic arsenal that may extrapolate to highly protracted remissions and curative therapies for EC. The identification of distinct molecular subtypes, including POLE-ultramutated, MSI, Copy-number low, and Copy-number high, underscores the heterogeneity of EC and highlights the necessity of tailored therapeutic approaches. Emerging technologies, such as CRISPR gene editing, single-cell genomics, and spatial transcriptomics, have significantly advanced our ability to study cancer at an unprecedented resolution. These innovations, coupled with the integration of multi-omics data - encompassing genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics - offer a holistic view of the disease, enhancing our ability to identify novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
The translation of genomic findings into personalized medicine and precision oncology is increasingly becoming a reality in clinical practice. The development of targeted therapies based on specific genetic alterations, such as PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors, exemplifies the potential for improved treatment efficacy and reduced side effects. However, the journey from bench to bedside is fraught with challenges, including the variability in patient responses, the integration of genomic data into clinical workflows, and the ethical considerations surrounding genetic testing and personalized treatments. Looking ahead, the ongoing need for research and collaboration remains paramount. The complexities of EC demand a multidisciplinary approach, leveraging expertise from genetics, bioinformatics, clinical medicine, and beyond. By fostering collaboration and continuing to push the boundaries of genomic research, we can look forward to future breakthroughs in the diagnosis and treatment of EC. There is optimism that with sustained effort, we can achieve more precise, effective, and personalized care for patients, ultimately improving outcomes and quality of life for those affected by this disease.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Alessandro, L.; Low, K.-J.E.; Abushelaibi, A.; Lim, S.-H.E.; Cheng, W.-H.; Chang, S.-K.; Lai, K.-S.; Sum, Y.W.; Maran, S. Identification of NRAS Diagnostic Biomarkers and Drug Targets for Endometrial Cancer—An Integrated in Silico Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, L. B. , Kim, J., Haradhvala, N. J., Huang, M. N., Tian Ng, A. W., Wu, Y., … & Stratton, M. R., et al. The repertoire of mutational signatures in human cancer. Nature 2020, 578, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amant, F. , Mirza, M. R., Koskas, M., & Creutzberg, C. L. Cancer of the corpus uteri. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2018, 143 (Suppl 2), 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, D.W.; Ellenson, L.H. Molecular Genetics of Endometrial Carcinoma. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2019, 14, 339–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besselink, N.; Keijer, J.; Vermeulen, C.; Boymans, S.; de Ridder, J.; van Hoeck, A.; Cuppen, E.; Kuijk, E. The genome-wide mutational consequences of DNA hypomethylation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostan, I.-S.; Mihaila, M.; Roman, V.; Radu, N.; Neagu, M.T.; Bostan, M.; Mehedintu, C. Landscape of Endometrial Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Target Therapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostan, I.-S.; Mihaila, M.; Roman, V.; Radu, N.; Neagu, M.T.; Bostan, M.; Mehedintu, C. Landscape of Endometrial Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Target Therapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasseur, K.; Gévry, N.; Asselin, E. Chemoresistance and targeted therapies in ovarian and endometrial cancers. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 4008–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredin, H.K.; Krakstad, C.; Hoivik, E.A. PIK3CA mutations and their impact on survival outcomes of patients with endometrial cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLOS ONE 2023, 18, e0283203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredin, H.K.; Krakstad, C.; Hoivik, E.A. PIK3CA mutations and their impact on survival outcomes of patients with endometrial cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLOS ONE 2023, 18, e0283203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canoy, R.J.; Shmakova, A.; Karpukhina, A.; Lomov, N.; Tiukacheva, E.; Kozhevnikova, Y.; André, F.; Germini, D.; Vassetzky, Y. Specificity of cancer-related chromosomal translocations is linked to proximity after the DNA double-strand break and subsequent selection. NAR Cancer 2023, 5, zcad049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarty, D.; Gao, J.; Phillips, S.; Kundra, R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Rudolph, J.E.; Yaeger, R.; Soumerai, T.; Nissan, M.H.; et al. OncoKB: A Precision Oncology Knowledge Base. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017, 2017, PO–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Song, Y.; Huang, J.; Wan, X.; Li, Y. Integrated single-cell RNA sequencing and spatial transcriptomics analysis reveals the tumour microenvironment in patients with endometrial cancer responding to anti-PD-1 treatment. Clin. Transl. Med. 2024, 14, e1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukkalore, D.; Rajavel, A.; Asti, D.; Dhar, M. Genomic determinants in advanced endometrial cancer patients with sustained response to hormonal therapy- case series and review of literature. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1188028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, M.C.; Workman, J.L. The SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex: a critical regulator of metabolism. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2024, 52, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corr, B. , Cosgrove, C., Spinosa, D., Guntupalli, S. (2022). Endometrial cancer: molecular classification and future treatments. BMJ Med, 1(1), e000152. [CrossRef]
- Corr, B. , Cosgrove, C., Spinosa, D., Guntupalli, S. (2022). Endometrial cancer: molecular classification and future treatments. BMJ Med, 1(1), e000152. [CrossRef]
- Dellino, M. , Cerbone, M., Laganà, A. S., Vitagliano, A., Vimercati, A., Marinaccio, M., Baldini, G. M., Malvasi, A., Cicinelli, E., Damiani, G. R., Cazzato, G., Cascardi, E. (2023). Upgrading Treatment and Molecular Diagnosis in Endometrial Cancer-Driving New Tools for Endometrial Preservation? Int J Mol Sci, 24(11), 9780. [CrossRef]
- Shamjetsabam, N.D.; Rana, R.; Malik, P.; Ganguly, N.K. CRISPR/Cas9: an overview of recent developments and applications in cancer research. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 6198–6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, G.; Gonzalez-Bosquet, J.; Skurski, J.; Devor, E.J.; Dickerson, E.B.; Nothnick, W.B.; Issuree, P.D.; Leslie, K.K.; Maretzky, T. FGFR2 mutations promote endometrial cancer progression through dual engagement of EGFR and Notch signalling pathways. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzycka, B.; Terlikowska, K.M.; Kowalczuk, O.; Niklinski, J.; Kinalski, M.; Terlikowski, S.J. Prognosis of Stage I Endometrial Cancer According to the FIGO 2023 Classification Taking into Account Molecular Changes. Cancers 2024, 16, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugo, E.; Piva, F.; Giulietti, M.; Giannella, L.; Ciavattini, A. Copy number variations in endometrial cancer: from biological significance to clinical utility. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2024, 34, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, I.; D’Angelo, E.; Prat, J. Endometrial carcinoma: 10 years of TCGA (the cancer genome atlas): A critical reappraisal with comments on FIGO 2023 staging. Gynecol. Oncol. 2024, 186, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Factor, P.A.A.; Pasamba, K.C. Metformin as an Adjunct to Progestin Therapy in Endometrial Hyperplasia and Early-Stage Endometrial Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Acta Medica Philipp. 2024, 58, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fader, A. N. , Roque, D. M., Siegel, E., Buza, N., Hui, P., Abdelghany, O.,... & Santin, A. D. (2020). Randomized Phase II Trial of Carboplatin-Paclitaxel Compared with Carboplatin-Paclitaxel-Trastuzumab in Advanced (Stage III-IV) or Recurrent Uterine Serous Carcinomas that Overexpress Her2/Neu (NCT01367002): Updated Overall Survival Analysis. Clin Cancer Res, 26(15):3928-3935. [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, S.A.; Beare, D.; Boutselakis, H.; Bamford, S.; Bindal, N.; Tate, J.; Cole, C.G.; Ward, S.; Dawson, E.; Ponting, L.; et al. COSMIC: Somatic cancer genetics at high-resolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D777–D783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galant, N., Krawczyk, P., Monist, M., Obara, A., Gajek, Ł., Grenda, A., … & Milanowski, .J. (2024). Molecular Classification of Endometrial Cancer and Its Impact on Therapy Selection. Int J Mol Sci, 25(11), 5893.
- Gordhandas, S.; Zammarrelli, W.A.; Rios-Doria, E.V.; Green, A.K.; Makker, V. Current Evidence-Based Systemic Therapy for Advanced and Recurrent Endometrial Cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2023, 21, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, O.; Sugiyama, Y.; Tonooka, A.; Kosugi, M.; Kitaura, S.; Minegishi, R.; Sano, M.; Amino, S.; Furuya, R.; Tanaka, N.; et al. Genetic and epigenetic alterations in precursor lesions of endometrial endometrioid carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2024, 263, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Tang, B.; Fu, J.; Zhu, X.; Xie, W.; Wang, N.; Ding, Z.; Song, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, G.; et al. High-plex spatial transcriptomic profiling reveals distinct immune components and the HLA class I/DNMT3A/CD8 modulatory axis in mismatch repair-deficient endometrial cancer. Cell. Oncol. 2023, 47, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasin, Y.; Seldin, M.; Lusis, A. Multi-omics approaches to disease. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoadley, K.A.; Yau, C.; Hinoue, T.; Wolf, D.M.; Lazar, A.J.; Drill, E.; Shen, R.; Taylor, A.M.; Cherniack, A.D.; Thorsson, V.; et al. Cell-of-Origin Patterns Dominate the Molecular Classification of 10,000 Tumors from 33 Types of Cancer. Cell 2018, 173, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.H.; Cho, H.W.; Ouh, Y.-T.; Lee, J.K.; Chun, Y.; Gim, J.-A. Genomic landscape of advanced endometrial cancer analyzed by targeted next-generation sequencing and the cancer genome atlas (TCGA) dataset. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2022, 33, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iavarone, I.; Molitierno, R.; Fumiento, P.; Vastarella, M.G.; Napolitano, S.; Vietri, M.T.; De Franciscis, P.; Ronsini, C. MicroRNA Expression in Endometrial Cancer: Current Knowledge and Therapeutic Implications. Medicina 2024, 60, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatov, A.; Ortmann, O. Endocrine Risk Factors of Endometrial Cancer: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, Oral Contraceptives, Infertility, Tamoxifen. Cancers 2020, 12, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, F.; Sone, K.; Kumegawa, K.; Hachijo, R.; Suzuki, E.; Tanimoto, S.; Tsuboyama, N.; Kato, K.; Toyohara, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; et al. Inhibition of protein arginine methyltransferase 6 activates interferon signaling and induces the apoptosis of endometrial cancer cells via histone modification. Int. J. Oncol. 2024, 64, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, N.M.; Rothstein, J.H.; Pejaver, V.; Middha, S.; McDonnell, S.K.; Baheti, S.; Musolf, A.; Li, Q.; Holzinger, E.; Karyadi, D.; et al. REVEL: An Ensemble Method for Predicting the Pathogenicity of Rare Missense Variants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, A.; de Barros, J.S.; Cochrane, D.R.; Douglas, J.M.; Shankar, S.; Lynch, B.J.; Leung, S.; Martin, S.; Senz, J.; Lum, A.; et al. Targeted and Shallow Whole-Genome Sequencing Identifies Therapeutic Opportunities in p53abn Endometrial Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 2461–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Q. , Chu, H., Jin, Z., Long, H., Zhu, B. (2022). High-throughput single-cell sequencing in cancer research. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 7(1), 145.
- Kelkar, S.S.; Prabhu, V.S.; Zhang, J.; Ogando, Y.M.; Roney, K.; Verma, R.P.; Miles, N.; Marth, C. Real-world prevalence of microsatellite instability testing and related status in women with advanced endometrial cancer in Europe. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2024, 309, 2833–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, P.J.; Adams, E.J.; Wu, R.; Côté, A.; Arora, S.; Cantone, N.; Meyer, R.; Mertz, J.A.; Gehling, V.; Cui, J.; et al. Comprehensive Target Engagement by the EZH2 Inhibitor Tulmimetostat Allows for Targeting of ARID1A Mutant Cancers. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 2501–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyhanian, K.M.; Han, L.; Howitt, B.E.; Longacre, T. Specific Pathology Features Enrich Selection of Endometrial Carcinomas for POLE Testing. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2023, 48, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. , Scheffler, K., Halpern, A. L., Källberg, M., Kim, J., Chinchilla, F.,... & Feldman, A. (2018). Strelka2: Fast and accurate calling of germline and somatic variants. Nature Methods, 15(8), 591-594. [CrossRef]
- Le, D.T.; Durham, J.N.; Smith, K.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Aulakh, L.K.; Lu, S.; Kemberling, H.; Wilt, C.; Luber, B.S.; et al. Mismatch repair deficiency predicts response of solid tumors to PD-1 blockade. Science 2017, 357, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León-Castillo, A.; de Boer, S.M.; Powell, M.E.; Mileshkin, L.R.; Mackay, H.J.; Leary, A.; Nijman, H.W.; Singh, N.; Pollock, P.M.; Bessette, P.; et al. Molecular Classification of the PORTEC-3 Trial for High-Risk Endometrial Cancer: Impact on Prognosis and Benefit From Adjuvant Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3388–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.H.; Broaddus, R.R. Endometrial Cancer. N Engl J Med 2020, 383(21), 2053–2064. [Google Scholar]
- Madabhushi, A. , Azarianpour-Esfahani, S., Khalighi, S., Aggarwal, A., Viswanathan, V., Fu, P., Avril, S. (2023). Computational Image and Molecular Analysis Reveal Unique Prognostic Features of Immune Architecture in African Versus European American Women with Endometrial Cancer. Res Sq [Preprint], rs.3.rs-3622429.
- Mahdy, H. , Casey, M. J., Vadakekut, E. S., Crotzer, D. (2024). Endometrial Cancer. 2024 Apr 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan–. [PubMed]
- Makker, V.; Colombo, N.; Herráez, A.C.; Santin, A.D.; Colomba, E.; Miller, D.S.; Fujiwara, K.; Pignata, S.; Baron-Hay, S.; Ray-Coquard, I.; et al. Lenvatinib plus Pembrolizumab for Advanced Endometrial Cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makker, V.; MacKay, H.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Levine, D.A.; Westin, S.N.; Aoki, D.; Oaknin, A. Endometrial cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021, 7(1), 88. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D.S.; Filiaci, V.L.; Mannel, R.S.; Cohn, D.E.; Matsumoto, T.; Tewari, K.S.; DiSilvestro, P.; Pearl, M.L.; Argenta, P.A.; Powell, M.A.; et al. Carboplatin and Paclitaxel for Advanced Endometrial Cancer: Final Overall Survival and Adverse Event Analysis of a Phase III Trial (NRG Oncology/GOG0209). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3841–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Ahmed, R.; Das, D.K.; Das Pramanik, D.; Dash, S.K.; Pramanik, A. Recent Advancements in the Application of Circulating Tumor DNA as Biomarkers for Early Detection of Cancers. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 4740–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, R.B.; Homayouni, T.S.; Baluch, N.; Morgatskaya, E.; Kumar, S.; Das, B.; Yeger, H. Combination therapy in combating cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38022–38043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, I.; Bartosch, C.; Teixeira, M.; Ferreira, M. Molecular Classification of Endometrial Carcinoma: Protocol for a Cohort Study. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2022, 11, e34461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustea, A.; Ralser, D.J.; Egger, E.K.; Ziehm, U.; Vivas, S.; Brock, S.; Jackson, D.; Condic, M.; Rauschendorf, M.-A.; Würfel, P.; et al. Determination of endometrial cancer molecular subtypes using a whole exome-sequencing based single-method approach. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nousiainen, S.; Kuismin, O.; Reinikka, S.; Manninen, R.; Khamaiseh, S.; Kuivalainen, M.; Terho, A.; Koivurova, S.; Niinimäki, M.; Salokas, K.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing reveals candidate high-risk susceptibility genes for endometriosis. Hum. Genom. 2023, 17, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoprienko, A.; Hofstetter, G.; Muellauer, L.; Dorittke, T.; Polterauer, S.; Grimm, C.; Bartl, T. Prognostic role of transcription factorARID1Ain patients with endometrial cancer of no specific molecular profile (NSMP) subtype. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2024, 34, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Openshaw, M.R.; McVeigh, T.P. Non-invasive Technology Advances in Cancer—A Review of the Advances in the Liquid Biopsy for Endometrial and Ovarian Cancers. Front. Digit. Heal. 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, P.A.; Bang, Y.-J.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Razak, A.R.A.; Bennouna, J.; Soria, J.-C.; Rugo, H.S.; Cohen, R.B.; O’Neil, B.H.; Mehnert, J.M.; et al. T-Cell–Inflamed Gene-Expression Profile, Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression, and Tumor Mutational Burden Predict Efficacy in Patients Treated With Pembrolizumab Across 20 Cancers: KEYNOTE-028. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleari, L.; Pesce, S.; Rutigliani, M.; Greppi, M.; Obino, V.; Gorlero, F.; Vellone, V.G.; Marcenaro, E. New Insights into Endometrial Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, D.; Tomita, S.; Rhenals, M.P.; Swierczek, S.; Reid, K.; Camacho-Vanegas, O.; Camacho, C.; Engelman, K.; Polukort, S.; RoseFigura, J.; et al. Mutations in cancer-relevant genes are ubiquitous in histologically normal endometrial tissue. Gynecol. Oncol. 2024, 185, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papalexi, E.; Satija, R. Single-cell RNA sequencing to explore immune cell heterogeneity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 18, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passarelli, A.; Ventriglia, J.; Pisano, C.; Cecere, S.C.; Di Napoli, M.; Rossetti, S.; Tambaro, R.; Tarotto, L.; Fiore, F.; Farolfi, A.; et al. The way to precision medicine in gynecologic cancers: The first case report of an exceptional response to alpelisib in a PIK3CA-mutated endometrial cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 12, 1088962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psilopatis, I.; Pergaris, A.; Giaginis, C.; Theocharis, S. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: A Promising Therapeutic Alternative for Endometrial Carcinoma. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 7850688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richenberg, G. , Francis, A., Owen, C. N., Gray, V., Robinson, T., Gabriel, A. A., et al., … & Kar, S. P. (2023). The tumor multi-omic landscape of endometrial cancers developed on a germline genetic background of adiposity. [CrossRef]
- Riedinger, C.J.; Esnakula, A.; Haight, P.J.; Suarez, A.A.; Chen, W.; Gillespie, J.; Villacres, A.; Chassen, A.; Cohn, D.E.; Goodfellow, P.J.; et al. Characterization of mismatch-repair/microsatellite instability-discordant endometrial cancers. Cancer 2023, 130, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyn, J.; Roncolato, F.; Willson, M.L.; Lindemann, K.; Mileshkin, L. PI3K/AKT/mTOR inhibitors for advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 10, CD012160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, C.; Veneruso, I.; De Simone, R.R.; Di Bonito, G.; Secondino, A.; D’argenio, V. The Third-Generation Sequencing Challenge: Novel Insights for the Omic Sciences. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarze, K.; Buchanan, J.; Taylor, J.C.; Wordsworth, S. Are whole-exome and whole-genome sequencing approaches cost-effective? A systematic review of the literature. Anesthesia Analg. 2018, 20, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R. L. , Miller, K. D., & Jemal, A. (2020). Cancer statistics, 2020. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 70(1), 7-30.
- Slomovitz, B.M.; Filiaci, V.L.; Walker, J.L.; Taub, M.C.; Finkelstein, K.A.; Moroney, J.W.; Fleury, A.C.; Muller, C.Y.; Holman, L.L.; Copeland, L.J.; et al. A randomized phase II trial of everolimus and letrozole or hormonal therapy in women with advanced, persistent or recurrent endometrial carcinoma: A GOG Foundation study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2022, 164, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Gu, H.; Li, J.; Yang, P.; Qi, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Shu, P. Identification of immune-related gene signature for predicting prognosis in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southworth, E.; Thomson, J.P.; Croy, I.; Churchman, M.; Arends, M.J.; Hollis, R.L.; Gourley, C.; Herrington, C.S. Whole exome sequencing reveals diverse genomic relatedness between paired concurrent endometrial and ovarian carcinomas. Eur. J. Cancer 2024, 208, 114205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stan, A.; Bosart, K.; Kaur, M.; Vo, M.; Escorcia, W.; Yoder, R.J.; Bouley, R.A.; Petreaca, R.C. Detection of driver mutations and genomic signatures in endometrial cancers using artificial intelligence algorithms. PLOS ONE 2024, 19, e0299114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streel, S.; Salmon, A.; Dheur, A.; Bours, V.; Leroi, N.; Habran, L.; Delbecque, K.; Goffin, F.; Pleyers, C.; Kakkos, A.; et al. Diagnostic Performance of Immunohistochemistry Compared to Molecular Techniques for Microsatellite Instability and p53 Mutation Detection in Endometrial Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhouk, A.; Derocher, H.; Schmidt, P.; Leung, S.; Milne, K.; Gilks, C.B.; Anglesio, M.S.; Nelson, B.H.; McAlpine, J.N. Molecular Subtype Not Immune Response Drives Outcomes in Endometrial Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 2537–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toumpeki, C.; Liberis, A.; Tsirkas, I.; Tsirka, T.; Kalagasidou, S.; Inagamova, L.; Anthoulaki, X.; Tsatsaris, G.; Kontomanolis, E.N. The Role of ARID1A in Endometrial Cancer and the Molecular Pathways Associated With Pathogenesis and Cancer Progression. Vivo 2019, 33, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Du, H.; Dai, W.; Bao, C.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.; et al. Diagnostic Potential of Endometrial Cancer DNA from Pipelle, Pap-Brush, and Swab Sampling. Cancers 2023, 15, 3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Hoang, L.; Ji, J.X.; Huntsman, D.G. SWI/SNF Complex Mutations in Gynecologic Cancers: Molecular Mechanisms and Models. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2020, 15, 467–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.R.; Reske, J.J.; Holladay, J.; Neupane, S.; Ngo, J.; Cuthrell, N.; Wegener, M.; Rhodes, M.; Adams, M.; Sheridan, R.; et al. ARID1A Mutations Promote P300-Dependent Endometrial Invasion through Super-Enhancer Hyperacetylation. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Cancer. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- Xu, T.; Ding, H.; Chen, J.; Lei, J.; Zhao, M.; Ji, B.; Chen, Y.; Qin, S.; Gao, Q. Research Progress of DNA Methylation in Endometrial Cancer. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Pan, T.; Li, S.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Chen, R.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y. Mapping Single-Cell Transcriptomes of Endometrium Reveals Potential Biomarkers in Endometrial Cancer. ImmunoTargets Ther. 2024, 13, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, H.; Nakayama, K.; Kanno, K.; Ishibashi, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Iida, K.; Razia, S.; Kiyono, T.; Kyo, S. Evaluation of ARID1A as a Potential Biomarker for Predicting Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients with Endometrial Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-H.; Hu, P.; Xie, Y.-Q.; Kang, Y.-J.; Li, M. Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR Promotes Endometrial Carcinoma Cell Proliferation by Binding to PTEN via the Activating Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt Signaling Pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2019, 39, e00251-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Sun, D.; Song, S.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, H.; Cui, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, N.; Hou, H. Efficacy of immunotherapy in ARID1A-mutant solid tumors: a single-center retrospective study. Discov. Oncol. 2024, 15, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
The genomic underpinnings of endometrial cancer. The pathogenesis of EC is a complex process of molecular mechanisms involved in the manifestation of genetic mutations, activation of oncogenes and inactivation of tumor suppressor genes, defects in the DNA MMR pathway, imbalance in hormonal signaling pathways, epigenetic changes, disorders in angiogenesis, and others. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play significant roles in the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression and their dysregulation has been linked to various aspects of EC progression. Figure adopted from Bostan et al., 2024.
Figure 1.
The genomic underpinnings of endometrial cancer. The pathogenesis of EC is a complex process of molecular mechanisms involved in the manifestation of genetic mutations, activation of oncogenes and inactivation of tumor suppressor genes, defects in the DNA MMR pathway, imbalance in hormonal signaling pathways, epigenetic changes, disorders in angiogenesis, and others. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play significant roles in the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression and their dysregulation has been linked to various aspects of EC progression. Figure adopted from Bostan et al., 2024.
Figure 2.
The PI3K-AKT-mTORc1 pathway is extensively involved in endometrial serous carcinoma carcinogenesis. PTEN mutations lead to the activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway thereby promoting loss of function and contributing to uncontrolled cell proliferation and survival, which are hallmarks of cancer. Abbreviations: HER, human epidermal growth fac-tor receptor; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol3 kinase; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten; PP2A, protein phosphatase 2, regulatory subunit A, alpha; AKT, v-akt murine thymo-ma viral oncogene homolog 1; mTORc, mammalian target of rapamycin complex. Figure adopted from Roncolato et al., 2019.
Figure 2.
The PI3K-AKT-mTORc1 pathway is extensively involved in endometrial serous carcinoma carcinogenesis. PTEN mutations lead to the activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway thereby promoting loss of function and contributing to uncontrolled cell proliferation and survival, which are hallmarks of cancer. Abbreviations: HER, human epidermal growth fac-tor receptor; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol3 kinase; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten; PP2A, protein phosphatase 2, regulatory subunit A, alpha; AKT, v-akt murine thymo-ma viral oncogene homolog 1; mTORc, mammalian target of rapamycin complex. Figure adopted from Roncolato et al., 2019.
Figure 3.
PIK3CA mutations in endometriosis. PI3K is activated by the PIK3CA mutation, which results in phosphorylation of PIP2 to PIP3 and activates AKT and mTOR. MAPK/ERK and mTOR have common effects on RhoA activity, which regulates the serum response elements (SRF) with the help of TNF-α. SRF is a transcription factor that has downstream effects on LOX and PTX3 leading to cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Figure adopted from Bredin et al., 2023.
Figure 3.
PIK3CA mutations in endometriosis. PI3K is activated by the PIK3CA mutation, which results in phosphorylation of PIP2 to PIP3 and activates AKT and mTOR. MAPK/ERK and mTOR have common effects on RhoA activity, which regulates the serum response elements (SRF) with the help of TNF-α. SRF is a transcription factor that has downstream effects on LOX and PTX3 leading to cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Figure adopted from Bredin et al., 2023.
Figure 4.
ARID1A mutations in endometrial cancer. ARID1A is a crucial component of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, which plays a vital role in regulating gene expression and maintaining genomic stability. The loss or mutation of ARID1A disrupts these processes, contributing to the pathogenesis of EC. Figure adopted from Wilson et al., 2020.
Figure 4.
ARID1A mutations in endometrial cancer. ARID1A is a crucial component of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex, which plays a vital role in regulating gene expression and maintaining genomic stability. The loss or mutation of ARID1A disrupts these processes, contributing to the pathogenesis of EC. Figure adopted from Wilson et al., 2020.
Figure 5.
Molecular subtypes of endometrial cancer. The classification of EC into distinct molecular subtypes represents a paradigm shift in the management of this disease. By moving beyond traditional histopathological criteria, this approach offers a more nuanced understanding of the biological diversity of EC, paving the way for more effective, personalized treatment strategies and ultimately improving patient outcomes. POLE-mutated is characterized by high mutational burden and distinct prognostic implications due to mutations in the exonuclease domain of the DNA Polymerase Epsilon (POLE) gene. MSI-High is a form of genetic hypermutability that results from impaired DNA mismatch repair (MMR) system, leading to high mutation rates. MSS CN Low is characterized by few copy number alterations and specific molecular features that distinguish it from other EC subtypes. CN High is marked by a high frequency of copy-number alterations, frequent TP53 mutations and distinct molecular features that contribute to its aggressive clinical behavior. Abbreviations: CN - Copy number; MSS - Microsatellite stable; and MSI - Microsatellite instability. Figure adopted from Openshaw and McVeigh (2020).
Figure 5.
Molecular subtypes of endometrial cancer. The classification of EC into distinct molecular subtypes represents a paradigm shift in the management of this disease. By moving beyond traditional histopathological criteria, this approach offers a more nuanced understanding of the biological diversity of EC, paving the way for more effective, personalized treatment strategies and ultimately improving patient outcomes. POLE-mutated is characterized by high mutational burden and distinct prognostic implications due to mutations in the exonuclease domain of the DNA Polymerase Epsilon (POLE) gene. MSI-High is a form of genetic hypermutability that results from impaired DNA mismatch repair (MMR) system, leading to high mutation rates. MSS CN Low is characterized by few copy number alterations and specific molecular features that distinguish it from other EC subtypes. CN High is marked by a high frequency of copy-number alterations, frequent TP53 mutations and distinct molecular features that contribute to its aggressive clinical behavior. Abbreviations: CN - Copy number; MSS - Microsatellite stable; and MSI - Microsatellite instability. Figure adopted from Openshaw and McVeigh (2020).
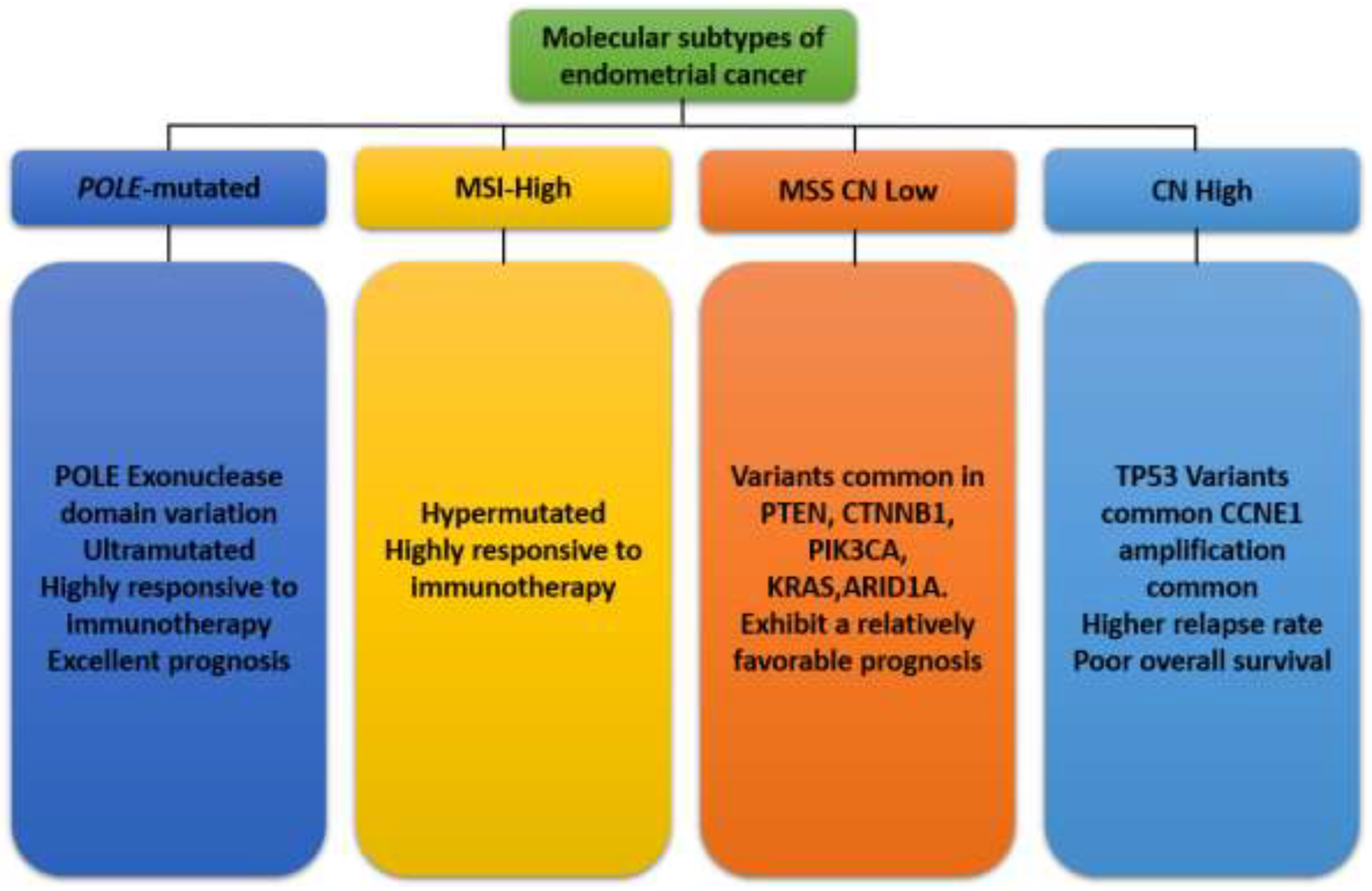
Figure 6.
Epigenetic modifications in endometrial cancer. Aberrant DNA methylation patterns, such as hypermethylation of tumor suppressor gene promoters, lead to gene silencing and contribute to carcinogenesis. Hypomethylation of oncogenes can also promote tumor development. Alterations in histone modifications, including methylation, acetylation, and phosphorylation, affect chromatin structure and gene expression. Dysregulation of histone-modifying enzymes has been implicated in EC. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play significant roles in the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Dysregulation of miRNAs and lncRNAs has been linked to various aspects of EC progression, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, and metastasis. Figure adopted from Bostan et al., 2024.
Figure 6.
Epigenetic modifications in endometrial cancer. Aberrant DNA methylation patterns, such as hypermethylation of tumor suppressor gene promoters, lead to gene silencing and contribute to carcinogenesis. Hypomethylation of oncogenes can also promote tumor development. Alterations in histone modifications, including methylation, acetylation, and phosphorylation, affect chromatin structure and gene expression. Dysregulation of histone-modifying enzymes has been implicated in EC. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play significant roles in the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. Dysregulation of miRNAs and lncRNAs has been linked to various aspects of EC progression, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, and metastasis. Figure adopted from Bostan et al., 2024.
Figure 7.
Molecular epigenetic mechanisms of DNA methylation in endometrial cancer. DNA hyper-methylation often leads to silencing at CpG islands. The hypermethylated CpG islands normally silence crucial tumor suppressor genes that wreaked havoc on the cell’s ability to repair DNA damage, thus hindering its growth and proliferation controls. On the other hand, DNA hypo-methylation is linked to active genes in cancerous cells. It promotes oncogenesis by transcriptional activation of previously silenced oncogenes. It reactivates dormant transposons and induces chromosomal instability at particular pericentromeric satellite regions. Figure adopted from Bostan et al., 2024.
Figure 7.
Molecular epigenetic mechanisms of DNA methylation in endometrial cancer. DNA hyper-methylation often leads to silencing at CpG islands. The hypermethylated CpG islands normally silence crucial tumor suppressor genes that wreaked havoc on the cell’s ability to repair DNA damage, thus hindering its growth and proliferation controls. On the other hand, DNA hypo-methylation is linked to active genes in cancerous cells. It promotes oncogenesis by transcriptional activation of previously silenced oncogenes. It reactivates dormant transposons and induces chromosomal instability at particular pericentromeric satellite regions. Figure adopted from Bostan et al., 2024.
Figure 8.
Histone modification in endometrial cancers. Hypoacetylations on tumor suppressor gene sequences or hyperacetylations on oncogene areas are among the common aberrant histone modifications in endometrial carcinogenesis. Enzymatic inhibitors can biochemically rectify these processes. Tumor suppressor gene deacetylation and reactivation can be prevented by employing histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi). Similar to this, acetyltransferase inhibitors (HACi) are potential drugs for EC treatments since they can prevent oncogenes from being acetylated and inactivated. Figure adopted from Inoue et al., 2024.
Figure 8.
Histone modification in endometrial cancers. Hypoacetylations on tumor suppressor gene sequences or hyperacetylations on oncogene areas are among the common aberrant histone modifications in endometrial carcinogenesis. Enzymatic inhibitors can biochemically rectify these processes. Tumor suppressor gene deacetylation and reactivation can be prevented by employing histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi). Similar to this, acetyltransferase inhibitors (HACi) are potential drugs for EC treatments since they can prevent oncogenes from being acetylated and inactivated. Figure adopted from Inoue et al., 2024.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).