Submitted:
11 October 2024
Posted:
12 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Participants, Design and Interventions
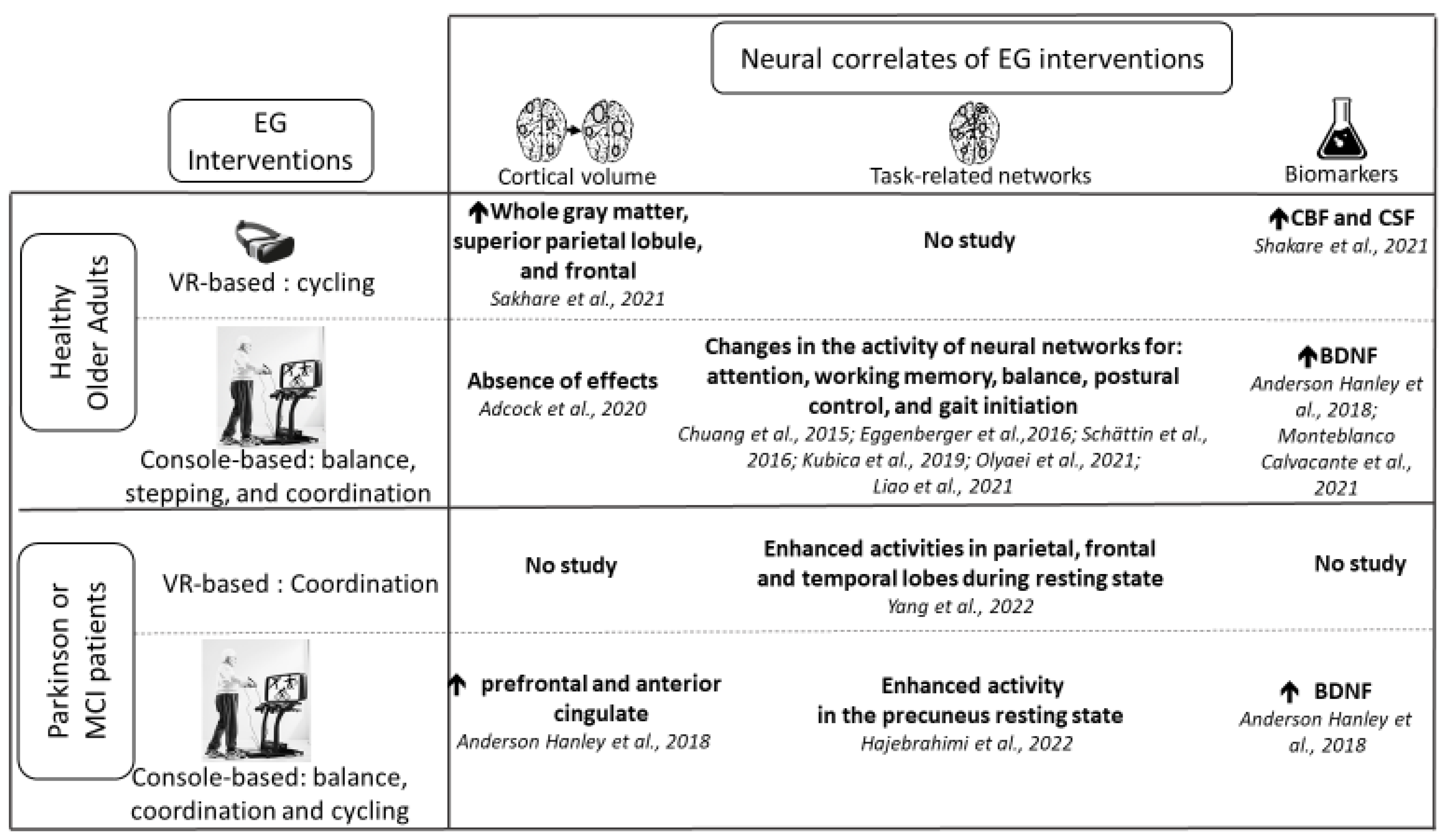
3.3. Neural Correlates of Exergame Interventions
3.3.1. Healthy Older Adults
3.3.2. Older Adults with a Neurocognitive Disorder
3.3.3. EG vs Conventional Interventions
3.4. Quality Assesment
4. Discussion
4.1. Neural Correlates of EG Interventions in Healthy Older Adults
4.2. Neural Correlates of EG Interventions in Older Adults with a Neurocognitive Disorder
4.3. Moderators of the Effects of EG Interventions on Brain Functions
4.4. Real-Time Neural Responses to the Execution of EG
4.5. Future Directions
5. Conclusion
References
- McPhee JS, French DP, Jackson D, Nazroo J, Pendleton N, Degens H. Physical activity in older age: perspectives for healthy ageing and frailty. Biogerontology. 2016 Jun;17(3):567–80. [CrossRef]
- Eckstrom E, Neukam S, Kalin L, Wright J. Physical Activity and Healthy Aging. Clin Geriatr Med. 2020 Nov;36(4):671–83. [CrossRef]
- Clemente Remón ÁL, Jiménez Díaz-Benito V, Jiménez Beatty JE, Santacruz Lozano JA. Levels of Physical Activity Among Older Adults in the European Union. J Aging Phys Act. 2021 Apr 1;29(2):242–9.
- Bethancourt HJ, Rosenberg DE, Beatty T, Arterburn DE. Barriers to and Facilitators of Physical Activity Program Use Among Older Adults. Clin Med Res. 2014 Sep;12(1–2):10–20. [CrossRef]
- Rúa-Alonso M, Bovolini A, Costa-Brito AR, Vaz C, Marques E, Serra N, et al. Exploring Perceived Barriers to Physical Activity among Older Adults Living in Low-Population Density Regions: Gender Differences and Associations with Activity Dimensions. Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Nov 11;11(22):2948. [CrossRef]
- Mazeas A, Duclos M, Pereira B, Chalabaev A. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Gamification on Physical Activity: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Med Internet Res. 2022 Jan 4;24(1):e26779.
- Vázquez FL, Otero P, García-Casal JA, Blanco V, Torres ÁJ, Arrojo M. Efficacy of video game-based interventions for active aging. A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. PLOS ONE. 2018 Dec 11;13(12):e0208192. [CrossRef]
- Baranowski T, Buday R, Thompson DI, Baranowski J. Playing for Real: Video Games and Stories for Health-Related Behavior Change. Am J Prev Med. 2008 Jan;34(1):74-82.e10.
- Sardi L, Idri A, Fernández-Alemán JL. A systematic review of gamification in e-Health. J Biomed Inform. 2017 Jul;71:31–48. [CrossRef]
- Altorfer P, Adcock M, de Bruin ED, Graf F, Giannouli E. Feasibility of Cognitive-Motor Exergames in Geriatric Inpatient Rehabilitation: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Study. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:739948. [CrossRef]
- Gallou-Guyot M, Mandigout S, Marie R, Robin L, Daviet JC, Perrochon A. Feasibility and potential cognitive impact of a cognitive-motor dual-task training program using a custom exergame in older adults: A pilot study. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023;15:1046676. [CrossRef]
- Sturnieks DL, Hicks C, Smith N, Ratanapongleka M, Menant J, Turner J, et al. Exergame and cognitive training for preventing falls in community-dwelling older people: a randomized controlled trial. Nat Med. 2024 Jan;30(1):98–105. [CrossRef]
- Levac DE, Huber ME, Sternad D. Learning and transfer of complex motor skills in virtual reality: a perspective review. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2019 Oct 18;16(1):121. [CrossRef]
- Béraud-Peigné N, Maillot P, Perrot A. The User Experience of an Immersive and Interactive Wall Exergame in Older Adults. Games Health J. 2023 Jun;12(3):220–7. [CrossRef]
- Campo-Prieto P, Cancela-Carral JM, Rodríguez-Fuentes G. Feasibility and Effects of an Immersive Virtual Reality Exergame Program on Physical Functions in Institutionalized Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Sensors (Basel). 2022 Sep 6;22(18):6742. [CrossRef]
- Drazich BF, Anokye D, Zhu S, Teleb J, Galik E, Colloca L, et al. Motivating older adults through immersive virtual exercise (MOTIVE): A randomized pilot study. Geriatr Nurs. 2023;54:229–36. [CrossRef]
- Gallou-Guyot M, Mandigout S, Bherer L, Perrochon A. Effects of exergames and cognitive-motor dual-task training on cognitive, physical and dual-task functions in cognitively healthy older adults: An overview. Ageing Res Rev. 2020 Nov;63:101135. [CrossRef]
- Sokolov AA, Collignon A, Bieler-Aeschlimann M. Serious video games and virtual reality for prevention and neurorehabilitation of cognitive decline because of aging and neurodegeneration. Curr Opin Neurol. 2020 Apr;33(2):239–48. [CrossRef]
- Chen M, Tang Q, Xu S, Leng P, Pan Z. Design and Evaluation of an Augmented Reality-Based Exergame System to Reduce Fall Risk in the Elderly. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Oct 1;17(19):7208. [CrossRef]
- Chao YY, Scherer YK, Montgomery CA. Effects of using Nintendo WiiTM exergames in older adults: a review of the literature. J Aging Health. 2015 Apr;27(3):379–402.
- Yen HY, Chiu HL. Virtual Reality Exergames for Improving Older Adults’ Cognition and Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Control Trials. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2021 May;22(5):995–1002. [CrossRef]
- Fernandes CS, Magalhães B, Lima A, Nóbrega P, Silva M, Santos C. Impact of Exergames on the Mental Health of Older Adults: A Systematic Review and GRADE Evidence Synthesis. Games Health J. 2022 Jul 11; [CrossRef]
- Chen Y, Zhang Y, Guo Z, Bao D, Zhou J. Comparison between the effects of exergame intervention and traditional physical training on improving balance and fall prevention in healthy older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2021 Nov 24;18(1):164. [CrossRef]
- Chan JKY, Klainin-Yobas P, Chi Y, Gan JKE, Chow G, Wu XV. The effectiveness of e-interventions on fall, neuromuscular functions and quality of life in community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Nurs Stud. 2021 Jan;113:103784. [CrossRef]
- Abd-Alrazaq A, Alajlani M, Alhuwail D, Toro CT, Giannicchi A, Ahmed A, et al. The Effectiveness and Safety of Serious Games for Improving Cognitive Abilities Among Elderly People With Cognitive Impairment: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JMIR Serious Games. 2022 Mar 10;10(1):e34592. [CrossRef]
- Ogawa EF, You T, Leveille SG. Potential Benefits of Exergaming for Cognition and Dual-Task Function in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. J Aging Phys Act. 2016 Apr;24(2):332–6. [CrossRef]
- van der Willik KD, Licher S, Vinke EJ, Knol MJ, Darweesh SKL, van der Geest JN, et al. Trajectories of Cognitive and Motor Function Between Ages 45 and 90 Years: A Population-Based Study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2021 Jan 18;76(2):297–306.
- Attoh-Mensah E, Pothier K, Loggia G, Morello R, Chavoix C, Marcelli C. Involvement of cognitive abilities in the occurrence of fractures in fallers aged 55 years or older: a cross-sectional study. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024 Aug 30;36(1):180. [CrossRef]
- Gavelin HM, Dong C, Minkov R, Bahar-Fuchs A, Ellis KA, Lautenschlager NT, et al. Combined physical and cognitive training for older adults with and without cognitive impairment: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ageing Res Rev. 2021 Mar;66:101232. [CrossRef]
- Manser P, Herold F, de Bruin ED. Components of effective exergame-based training to improve cognitive functioning in middle-aged to older adults – A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Research Reviews. 2024 Aug 1;99:102385. [CrossRef]
- Wollesen B, Wildbredt A, van Schooten KS, Lim ML, Delbaere K. The effects of cognitive-motor training interventions on executive functions in older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2020 Dec;17(1):9. [CrossRef]
- Abd-Alrazaq A, Alhuwail D, Ahmed A, Househ M. Effectiveness of Serious Games for Improving Executive Functions Among Older Adults With Cognitive Impairment: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JMIR Serious Games. 2022 Jul 25;10(3):e36123. [CrossRef]
- Abd-Alrazaq A, Alhuwail D, Al-Jafar E, Ahmed A, Shuweihdi F, Reagu SM, et al. The Effectiveness of Serious Games in Improving Memory Among Older Adults With Cognitive Impairment: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JMIR Serious Games. 2022 Aug 9;10(3):e35202. [CrossRef]
- Torre MM, Temprado JJ. A Review of Combined Training Studies in Older Adults According to a New Categorization of Conventional Interventions. Front Aging Neurosci [Internet]. 2022 Feb 1 [cited 2024 Oct 3];13. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/aging-neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2021.808539/full. [CrossRef]
- Suleiman-Martos N, García-Lara R, Albendín-García L, Romero-Béjar JL, Cañadas-De La Fuente GA, Monsalve-Reyes C, et al. Effects of active video games on physical function in independent community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Adv Nurs. 2022 May;78(5):1228–44. [CrossRef]
- Leal JC, Belo VS, Santos IM, Ferreira RV, de Melo SN, da Silva ES. Exergames in Older Adult Community Centers and Nursing Homes to Improve Balance and Minimize the Risk of Falls in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jun 28;11(13):1872. [CrossRef]
- Stillman CM, Esteban-Cornejo I, Brown B, Bender CM, Erickson KI. Effects of Exercise on Brain and Cognition Across Age Groups and Health States. Trends Neurosci. 2020 Jul;43(7):533–43. [CrossRef]
- Boa Sorte Silva NC, Barha CK, Erickson KI, Kramer AF, Liu-Ambrose T. Physical exercise, cognition, and brain health in aging. Trends Neurosci. 2024 Jun;47(6):402–17. [CrossRef]
- Erickson KI, Voss MW, Prakash RS, Basak C, Szabo A, Chaddock L, et al. Exercise training increases size of hippocampus and improves memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Feb 15;108(7):3017–22. [CrossRef]
- Erickson KI, Leckie RL, Weinstein AM. Physical activity, fitness, and gray matter volume. Neurobiol Aging. 2014 Sep;35 Suppl 2:S20-28.
- Hötting K, Röder B. Beneficial effects of physical exercise on neuroplasticity and cognition. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2013 Nov;37(9 Pt B):2243–57. [CrossRef]
- Cassilhas RC, Tufik S, de Mello MT. Physical exercise, neuroplasticity, spatial learning and memory. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Mar;73(5):975–83.
- Monteiro-Junior RS, da Silva Figueiredo LF, Maciel-Pinheiro P de T, Abud ELR, Braga AEMM, Barca ML, et al. Acute effects of exergames on cognitive function of institutionalized older persons: a single-blinded, randomized and controlled pilot study. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2017 Jun;29(3):387–94. [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini-Laplagne M, Dupuy O, Sosner P, Bosquet L. Acute Effect of a Simultaneous Exercise and Cognitive Task on Executive Functions and Prefrontal Cortex Oxygenation in Healthy Older Adults. Brain Sci. 2022 Mar 28;12(4):455. [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini-Laplagne M, Dupuy O, Sosner P, Bosquet L. Effect of simultaneous exercise and cognitive training on executive functions, baroreflex sensitivity, and pre-frontal cortex oxygenation in healthy older adults: a pilot study. Geroscience. 2023 Feb;45(1):119–40. [CrossRef]
- Torre MM, Temprado JJ. Effects of Exergames on Brain and Cognition in Older Adults: A Review Based on a New Categorization of Combined Training Intervention. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Mar 30;14:859715. [CrossRef]
- Yang Y, Wang K, Liu S, Liu H, Zhang T, Luo J. Exergames improve cognitive function in older adults and their possible mechanisms: A systematic review. J Glob Health. 13:04177. [CrossRef]
- Stojan R, Voelcker-Rehage C. A Systematic Review on the Cognitive Benefits and Neurophysiological Correlates of Exergaming in Healthy Older Adults. J Clin Med. 2019 May 23;8(5):734. [CrossRef]
- Reuter-Lorenz PA, Park DC. How Does it STAC Up? Revisiting the Scaffolding Theory of Aging and Cognition. Neuropsychol Rev. 2014 Sep;24(3):355–70. [CrossRef]
- Reuter-Lorenz PA, Lustig C. Brain aging: reorganizing discoveries about the aging mind. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 2005 Apr 1;15(2):245–51. [CrossRef]
- Festini SB, Zahodne L, Reuter-Lorenz PA. Theoretical Perspectives on Age Differences in Brain Activation: HAROLD, PASA, CRUNCH—How Do They STAC Up? In: Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Psychology [Internet]. Oxford University Press; 2018 [cited 2024 Jun 7]. Available from: https://oxfordre.com/psychology/view/10.1093/acrefore/9780190236557.001.0001/acrefore-9780190236557-e-400.
- Zhao Y, Feng H, Wu X, Du Y, Yang X, Hu M, et al. Effectiveness of Exergaming in Improving Cognitive and Physical Function in People With Mild Cognitive Impairment or Dementia: Systematic Review. JMIR Serious Games. 2020 Jun 30;8(2):e16841. [CrossRef]
- Manser P, Michels L, Schmidt A, Barinka F, de Bruin ED. Effectiveness of an Individualized Exergame-Based Motor-Cognitive Training Concept Targeted to Improve Cognitive Functioning in Older Adults With Mild Neurocognitive Disorder: Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Res Protoc. 2023 Feb 6;12:e41173. [CrossRef]
- Adcock M, Fankhauser M, Post J, Lutz K, Zizlsperger L, Luft AR, et al. Effects of an In-home Multicomponent Exergame Training on Physical Functions, Cognition, and Brain Volume of Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front Med [Internet]. 2020 Jan 28 [cited 2024 Jul 19];6. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/medicine/articles/10.3389/fmed.2019.00321/full. [CrossRef]
- Sakhare A, Stradford J, Ravichandran R, Deng R, Ruiz J, Subramanian K, et al. Simultaneous Exercise and Cognitive Training in Virtual Reality Phase 2 Pilot Study: Impact on Brain Health and Cognition in Older Adults. Brain Plast. 2021;7(2):111–30. [CrossRef]
- Olyaei G, Khanmohammadi R, Talebian S, Hadian MR, Bagheri H, Najafi M. The effect of exergaming on cognition and brain activity in older adults: A motor- related cortical potential study. Physiol Behav. 2022 Oct 15;255:113941. [CrossRef]
- Liao YY, Chen IH, Hsu WC, Tseng HY, Wang RY. Effect of exergaming versus combined exercise on cognitive function and brain activation in frail older adults: A randomised controlled trial. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2021 Sep;64(5):101492. [CrossRef]
- Eggenberger P, Wolf M, Schumann M, de Bruin ED. Exergame and Balance Training Modulate Prefrontal Brain Activity during Walking and Enhance Executive Function in Older Adults. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016;8:66. [CrossRef]
- Kubica J, Szymura J, Domagalik A, Golda S, Wiecek M, Fafrowicz M, et al. Systematic Balance Exercises Influence Cortical Activation and Serum BDNF Levels in Older Adults. J Clin Med. 2019 Nov 7;8(11). [CrossRef]
- Chuang LY, Hung HY, Huang CJ, Chang YK, Hung TM. A 3-month intervention of Dance Dance Revolution improves interference control in elderly females: a preliminary investigation. Exp Brain Res. 2015 Apr;233(4):1181–8. [CrossRef]
- Schättin A, Arner R, Gennaro F, de Bruin ED. Adaptations of Prefrontal Brain Activity, Executive Functions, and Gait in Healthy Elderly Following Exergame and Balance Training: A Randomized-Controlled Study. Front Aging Neurosci. 2016;8:278.
- Monteblanco Cavalcante M, Fraga I, Dalbosco B, De Marchi P, Iraci L, Baechtold da Silva ME, et al. Exergame training-induced neuroplasticity and cognitive improvement in institutionalized older adults: A preliminary investigation. Physiol Behav. 2021 Nov 1;241:113589. [CrossRef]
- Anderson-Hanley C, Arciero PJ, Brickman AM, Nimon JP, Okuma N, Westen SC, et al. Exergaming and older adult cognition: a cluster randomized clinical trial. Am J Prev Med. 2012 Feb;42(2):109–19.
- Anderson-Hanley C, Barcelos NM, Zimmerman EA, Gillen RW, Dunnam M, Cohen BD, et al. The Aerobic and Cognitive Exercise Study (ACES) for Community-Dwelling Older Adults With or At-Risk for Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI): Neuropsychological, Neurobiological and Neuroimaging Outcomes of a Randomized Clinical Trial. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:76. [CrossRef]
- Hajebrahimi F, Velioglu HA, Bayraktaroglu Z, Helvaci Yilmaz N, Hanoglu L. Clinical evaluation and resting state fMRI analysis of virtual reality based training in Parkinson’s disease through a randomized controlled trial. Sci Rep. 2022 May 16;12(1):8024. [CrossRef]
- Yang JG, Thapa N, Park HJ, Bae S, Park KW, Park JH, et al. Virtual Reality and Exercise Training Enhance Brain, Cognitive, and Physical Health in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 15;19(20). [CrossRef]
- van der Kleij LA, Petersen ET, Siebner HR, Hendrikse J, Frederiksen KS, Sobol NA, et al. The effect of physical exercise on cerebral blood flow in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage Clin. 2018;20:650–4. [CrossRef]
- Frederiksen KS, Gjerum L, Waldemar G, Hasselbalch SG. Effects of Physical Exercise on Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers: A Systematic Review of Intervention Studies. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;61(1):359–72. [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki M, Malis V, Yamamoto A, Kungsamutr J, McEvoy LK, McDonald MA, et al. Physical Exercise Alters Egress Pathways for Intrinsic CSF Outflow: An Investigation Performed with Spin-labeling MR Imaging. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2024 Apr 1;23(2):171–83. [CrossRef]
- Xiao Y, Yang T, Shang H. The Impact of Motor-Cognitive Dual-Task Training on Physical and Cognitive Functions in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2023 Mar 3;13(3):437. [CrossRef]
- Grosboillot N, Gallou-Guyot M, Lamontagne A, Bonnyaud C, Perrot A, Allali G, et al. Towards a Comprehensive Framework for Complex Walking tasks: Characterization, Behavioral Adaptations, and Clinical Implications in Ageing and Neurological Populations. Ageing Research Reviews. 2024 Aug 15;102458. [CrossRef]
- Attoh-Mensah E, Huret A, Leger M, Loggia G, Nee G, Largilliere S, et al. A Dual-Task Paradigm Combining Physical and Cognitive Training in Mice: Application to Aging. Aging Dis. 2024 Feb 14; [CrossRef]
- Schwarzkopf DS, Huang Z. A simple statistical framework for small sample studies [Internet]. bioRxiv; 2023 [cited 2024 Sep 25]. p. 2023.09.19.558509. Available from: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.09.19.558509v1.
- Massar S a. A, Rossi V, Schutter DJLG, Kenemans JL. Baseline EEG theta/beta ratio and punishment sensitivity as biomarkers for feedback-related negativity (FRN) and risk-taking. Clin Neurophysiol. 2012 Oct;123(10):1958–65. [CrossRef]
- Fransson P, Marrelec G. The precuneus/posterior cingulate cortex plays a pivotal role in the default mode network: Evidence from a partial correlation network analysis. Neuroimage. 2008 Sep 1;42(3):1178–84. [CrossRef]
- Thibes RB, Novaes NP, Lucato LT, Campanholo KR, Melo LM, Leite CC, et al. Altered Functional Connectivity Between Precuneus and Motor Systems in Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Brain Connect. 2017 Dec;7(10):643–7. [CrossRef]
- Tessitore A, Cirillo M, De Micco R. Functional Connectivity Signatures of Parkinson’s Disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 2019;9(4):637–52. [CrossRef]
- Malotaux V, Dricot L, Quenon L, Lhommel R, Ivanoiu A, Hanseeuw B. Default-Mode Network Connectivity Changes During the Progression Toward Alzheimer’s Dementia: A Longitudinal Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Brain Connect. 2023 Jun;13(5):287–96. [CrossRef]
- Lier EJ, Oosterman JM, Assmann R, de Vries M, van Goor H. The effect of Virtual Reality on evoked potentials following painful electrical stimuli and subjective pain. Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 3;10(1):9067. [CrossRef]
- van Balkom TD, van den Heuvel OA, Berendse HW, van der Werf YD, Vriend C. The Effects of Cognitive Training on Brain Network Activity and Connectivity in Aging and Neurodegenerative Diseases: a Systematic Review. Neuropsychol Rev. 2020 Jun;30(2):267–86. [CrossRef]
- Müller H, Baumeister J, Bardal EM, Vereijken B, Skjæret-Maroni N. Exergaming in older adults: the effects of game characteristics on brain activity and physical activity. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023;15:1143859. [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh JF, Frank MJ. Frontal theta as a mechanism for cognitive control. Trends Cogn Sci. 2014 Aug;18(8):414–21. [CrossRef]
- Büchel D, Lehmann T, Ullrich S, Cockcroft J, Louw Q, Baumeister J. Stance leg and surface stability modulate cortical activity during human single leg stance. Exp Brain Res. 2021 Apr;239(4):1193–202. [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen NSJ, Blum S, Witt K, Debener S. A walk in the park? Characterizing gait-related artifacts in mobile EEG recordings. Eur J Neurosci. 2021 Dec;54(12):8421–40. [CrossRef]
- Bohle H, Rimpel J, Schauenburg G, Gebel A, Stelzel C, Heinzel S, et al. Behavioral and Neural Correlates of Cognitive-Motor Interference during Multitasking in Young and Old Adults. Neural Plast. 2019;2019:9478656. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz D, Barria P, Cifuentes CA, Aguilar R, Baleta K, Azorín JM, et al. EEG Evaluation in a Neuropsychological Intervention Program Based on Virtual Reality in Adults with Parkinson’s Disease. Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Sep 12;12(9). [CrossRef]
- Sauseng P, Klimesch W. What does phase information of oscillatory brain activity tell us about cognitive processes? Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2008 Jul;32(5):1001–13.
- Magosso E, De Crescenzio F, Ricci G, Piastra S, Ursino M. EEG Alpha Power Is Modulated by Attentional Changes during Cognitive Tasks and Virtual Reality Immersion. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience. 2019;2019(1):7051079. [CrossRef]
- Shamsi F, Haddad A, Najafizadeh L. Early classification of motor tasks using dynamic functional connectivity graphs from EEG. J Neural Eng. 2021 Feb 22;18(1). [CrossRef]
- Gérard M, Bayot M, Derambure P, Dujardin K, Defebvre L, Betrouni N, et al. EEG-based functional connectivity and executive control in patients with Parkinson’s disease and freezing of gait. Clin Neurophysiol. 2022 May;137:207–15. [CrossRef]
- Hatlestad-Hall C, Bruña R, Liljeström M, Renvall H, Heuser K, Taubøll E, et al. Reliable evaluation of functional connectivity and graph theory measures in source-level EEG: How many electrodes are enough? Clin Neurophysiol. 2023 Jun;150:1–16.
- Kalashami MP, Pedram MM, Sadr H. EEG Feature Extraction and Data Augmentation in Emotion Recognition. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022;2022:7028517. [CrossRef]
- Hu W, Zhang Z, Zhao H, Zhang L, Li L, Huang G, et al. EEG microstate correlates of emotion dynamics and stimulation content during video watching. Cereb Cortex. 2023 Jan 5;33(3):523–42. [CrossRef]
- Ramanoël S, Durteste M, Delaux A, de Saint Aubert JB, Arleo A. Future trends in brain aging research: Visuo-cognitive functions at stake during mobility and spatial navigation. Aging Brain. 2022 Jan 1;2:100034. [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




