Submitted:
11 October 2024
Posted:
12 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
The gut, often referred to as the "second brain," has significant contributions in the maintaining of the good bacteria contribute enormous role such as digestion, produce essential vitamins, support the immune system, and protect against harmful bacteria. The beneficial flora including Akkermansia muciniphila, Adlercreutzia equolifasciens, Barnesiella, Christensenella minuta, and Oxalobacter formigenes, along with their derived bioactive metabolites emerged as a key player in maintaining host metabolic and immune health. Dietary choices such as blending of prebiotic, fermented, symbiotic, anti-inflammatory foods, and secondary metabolites from a wide variety of plants and fruits promotes the diversity, composition, and stability of beneficial intestinal microbes. The colourful plant foods rich in phytochemicals bioactive compounds such as carotenoids, flavonoids, polyphenols, alkaloids, anthocyanins, and capsaicin offer a wide array of unique properties such as analgesics, antioxidants, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobials effect and promoting the abundance of beneficial gut bacteria and their bioactive metabolites confer numerous health-promoting effects. Here, we present knowledge about most beneficial gut bacteria and their derived metabolites in terms of their sources and health benefits. Finally, we discuss best foods that skew towards promoting healthy intestinal microbes.
Keywords:
Introduction
Impact of Microbiota on Human Health
Role of Microbiota in Disease Induction
Essential Gut-Friendly Bacteria and their Byproducts
A. muciniphila
Adlercreutzia Equolifasciens
Barnesiella
Christensenella Minuta
Oxalobacter Formigenes
Optimal Foods for Nurturing the Growth of Gut-Friendly Bacteria
Carotenoids
Flavonoids
Anthocyanins
Polyphenols
Alkaloids
Capsaicin
Prebiotic-Rich Foods
Fermented Foods
Synbiotic Foods
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
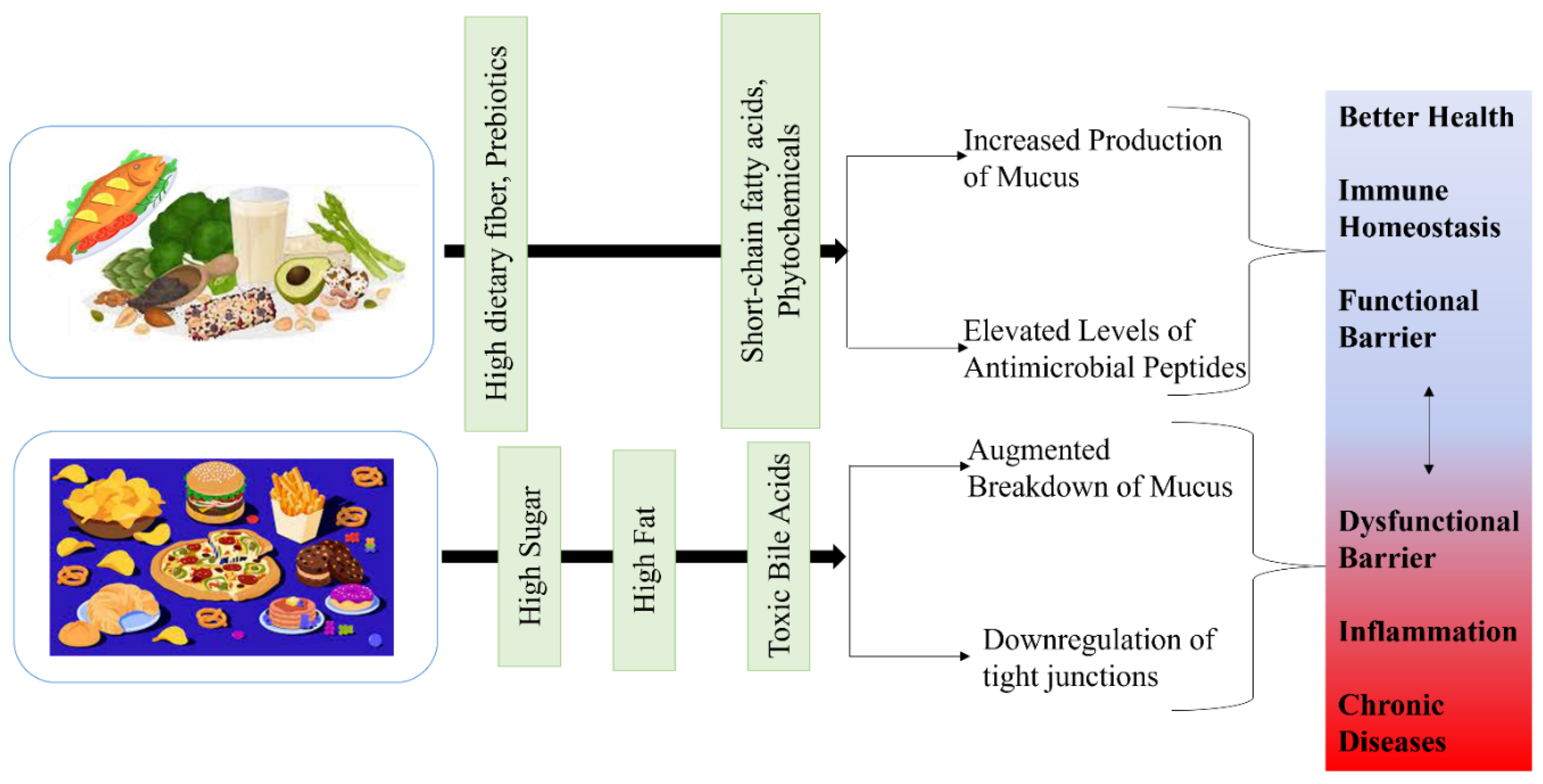
Impact of Diet on Microbial Ecology in the Gut
Conclusion
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication
Availability of data and material
Competing interests
Funding
Acknowledgement
References
- Afzaal, M. , Saeed, F., Shah, Y. A., Hussain, M., Rabail, R., Socol, C. T., Hassoun, A., Domínguez, R., Lorenzo, J. M., Rusu, A. V., & Aadil, R. M. (2022). Human gut microbiota in health and disease: Unveiling the relationship. Frontiers in Microbiology. [CrossRef]
- AGA does not recommend the use of probiotics for most digestive conditions. American Gastroenterological Association. Accessed 03/17/2021.
- Aindelis, G. , & Chlichlia, K. (2020). Modulation of Anti-Tumour Immune Responses by Probiotic Bacteria. Vaccines. [CrossRef]
- Ang, W. S. , Law, J. W., Letchumanan, V., Hong, K. W., Wong, S. H., Ab Mutalib, N. S., Chan, K. G., Lee, L. H., & Tan, L. T. (2023). A Keystone Gut Bacterium Christensenella minuta-A Potential Biotherapeutic Agent for Obesity and Associated Metabolic Diseases. Foods (Basel, Switzerland). [CrossRef]
- Anhê, F. F. , Pilon, G., Roy, D., Desjardins, Y., Levy, E., & Marette, A. (2016). Triggering Akkermansia with dietary polyphenols: A new weapon to combat the metabolic syndrome?. Gut microbes, 7(2), 146–153. [CrossRef]
- Arora, T. , Rudenko, O., Egerod, K. L., Husted, A. S., Kovatcheva-Datchary, P., Akrami, R., Kristensen, M., Schwartz, T. W., & Bäckhed, F. (2019). Microbial fermentation of flaxseed fibers modulates the transcriptome of GPR41-expressing enteroendocrine cells and protects mice against diet-induced obesity. American journal of physiology. Endocrinology and metabolism. [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, S. , Zolghadri, S., & Stanek, A. (2022). Beneficial Effects of Anti-Inflammatory Diet in Modulating Gut Microbiota and Controlling Obesity. Nutrients. [CrossRef]
- Bahare, S. , Javad, S., Francesca, C., et al. (2020). The Therapeutic Potential of Anthocyanins: Current Approaches Based on Their Molecular Mechanism of Action. Front. Pharmacol,. [CrossRef]
- Baky, M. H. , Elshahed, M., Wessjohann, L., & Farag, M. A. (2022). Interactions between dietary flavonoids and the gut microbiome: a comprehensive review. The British journal of nutrition. [CrossRef]
- Bertelli, A. , Biagi, M., Corsini, M., Baini, G., Cappellucci, G., & Miraldi, E. (2021). Polyphenols: From Theory to Practice. Foods (Basel, Switzerland). [CrossRef]
- Bull, M. J. , & Plummer, N. T. (2014). Part 1: The Human Gut Microbiome in Health and Disease. Integrative medicine (Encinitas, Calif.), 13(6), 17–22.
- Carlson, J. L. , Erickson, J. M., Lloyd, B. B., & Slavin, J. L. (2018). Health Effects and Sources of Prebiotic Dietary Fiber. L. ( 2(3), nzy005. [CrossRef]
- Carlson JL, Erickson JM, Lloyd BB, Slavin JL. Health effects and sources of prebiotic dietary fiber. Curr Dev Nutr.
- Chandra P, Enespa, Singh R, Arora PK. Microbial lipases and their industrial applications: a comprehensive review. Microb Cell Fact, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Chenbo, Y. , Chuanqi, C. ( a focus on the effect of plant extracts. Journal of Functional Foods.93, 105093. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H. , Liu, J., Tan, Y., Feng, W., & Peng, C. (2022). Interactions between gut microbiota and berberine, a necessary procedure to understand the mechanisms of berberine. ( 12(4), 541–555. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L. , Wang, X. J., Chen, J. X., Yang, J. C., Ling Lin, Cai, X. B., & Chen, Y. S. (2023). Caffeine ameliorates the metabolic syndrome in diet-induced obese mice through regulating the gut microbiota and serum metabolism. Diabetology & metabolic syndrome. [CrossRef]
- Chmiel, J. A. , Carr, C., Stuivenberg, G. A., Venema, R., Chanyi, R. M., Al, K. F., Giguere, D., Say, H., Akouris, P. P., Domínguez Romero, S. A., Kwong, A., Tai, V., Koval, S. F., Razvi, H., Bjazevic, J., & Burton, J. P. (2022). New perspectives on an old grouping: The genomic and phenotypic variability of Oxalobacter formigenes and the implications for calcium oxalate stone prevention. Frontiers in microbiology. [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, T. A. F. , Rogero, M. M., Hassimotto, N. M. A., & Lajolo, F. M. (2019). The Two-Way Polyphenols-Microbiota Interactions and Their Effects on Obesity and Related Metabolic Diseases. Frontiers in nutrition. [CrossRef]
- Costantini, L. , Molinari, R., Farinon, B., & Merendino, N. (2017). Impact of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on the Gut Microbiota. International journal of molecular sciences. [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, G. M. , da Silva, M. C., Nascimento, D. V. G., Lima Silva, E. M., Gouvêa, F. F. F., de França Lopes, L. G., Araújo, A. V., Ferraz Pereira, K. N., & de Queiroz, T. M. (2021). Nitric Oxide as a Central Molecule in Hypertension: Focus on the Vasorelaxant Activity of New Nitric Oxide Donors. Biology. [CrossRef]
- Daillère, R. , Vétizou, M., Waldschmitt, N., Yamazaki, T., Isnard, C., Poirier-Colame, V., Duong, C. P. M., Flament, C., Lepage, P., Roberti, M. P., Routy, B., Jacquelot, N., Apetoh, L., Becharef, S., Rusakiewicz, S., Langella, P., Sokol, H., Kroemer, G., Enot, D., Roux, A., … Zitvogel, L. (2016). Enterococcus hirae and Barnesiella intestinihominis Facilitate Cyclophosphamide-Induced Therapeutic Immunomodulatory Effects. Immunity. [CrossRef]
- Davani-Davari, D. , Negahdaripour, M., Karimzadeh, I., Seifan, M., Mohkam, M., Masoumi, S. J., Berenjian, A., & Ghasemi, Y. (2019). Prebiotics: Definition, Types, Sources, Mechanisms, and Clinical Applications. Foods (Basel, Switzerland). [CrossRef]
- De Filippo, C. , Cavalieri, D. ( 2010). Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 14691–14696.
- Dehau, T. , Cherlet, M., Croubels, S., van Immerseel, F., & Goossens, E. (2023). A High Dose of Dietary Berberine Improves Gut Wall Morphology, Despite an Expansion of Enterobacteriaceae and a Reduction in Beneficial Microbiota in Broiler Chickens. mSystems. [CrossRef]
- Duncan, S. H. , Richardson, A. J., Kaul, P., Holmes, R. P., Allison, M. J., & Stewart, C. S. (2002). Oxalobacter formigenes and its potential role in human health. Applied and environmental microbiology, 3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, S. L. , Moradi, L., Paiste, H., Wood, K. D., Assimos, D. G., Holmes, R. P., Nazzal, L., Hatch, M., & Knight, J. (2021). Forty Years of Oxalobacter formigenes, a Gutsy Oxalate-Degrading Specialist. Applied and environmental microbiology, 0054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinsmoor, A. , Thompson, S., Edwards, C., Burd, N., Khan, N., Erdman, J., Jr, & Holscher, H. (2019). Associations Between Serum Lutein and Human Gut Microbiota (P02-004-19). Current Developments in Nutrition. [CrossRef]
- Englyst HN, Cummings JH. Digestion of the carbohydrates of banana (Musa paradisiaca sapientum) in the human small intestine. Am J Clin Nutr. [CrossRef]
- Emran, T. B. , & Uddin, M. S. (2021). Role of Phenolic Compounds in Human Disease: Current Knowledge and Future Prospects. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). [CrossRef]
- Eroglu A, Al'Abri IS, Kopec RE, Crook N, Bohn T. Carotenoids and Their Health Benefits as Derived via Their Interactions with Gut Microbiota. Adv Nutr. [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, D. W. , Kelly, J. P., Curhan, G. C., Anderson, T. E., Dretler, S. P., Preminger, G. M., & Cave, D. R. (2008). Oxalobacter formigenes may reduce the risk of calcium oxalate kidney stones. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology : JASN, 19(6), 1197–1203. [CrossRef]
- Feng, W. , Ao, H., & Peng, C. (2018). Gut Microbiota, Short-Chain Fatty Acids, and Herbal Medicines. Frontiers in pharmacology. [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, I.; et al. (2019). Anthocyanins: Nutrition and Health. In: Mérillon, JM., Ramawat, K. (eds) Bioactive Molecules in Food. Reference Series in Phytochemistry. Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, M. A. , & Marette, A. (2017). Potential Health Benefits of Combining Yogurt and Fruits Based on Their Probiotic and Prebiotic Properties. ( 8(1), 155S–164S. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotschki, B. , Juśkiewicz, J., Sójka, M., Jurgoński, A., & Zduńczyk, Z. (2015). Ellagitannins and Flavan-3-ols from Raspberry Pomace Modulate Caecal Fermentation Processes and Plasma Lipid Parameters in Rats. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frati F, Salvatori C, Incorvaia C. The role of the microbiome in asthma: The gut-lung axis. Int J Mol Sci.
- Geum, H.L. , et al. (2020). Anthocyanins attenuate endothelial dysfunction through regulation of uncoupling of nitric oxide synthase in aged rats. Aging Cell,. [CrossRef]
- Geerlings, S. Y. , Kostopoulos, I., de Vos, W. M., & Belzer, C. (2018). Akkermansia muciniphila in the Human Gastrointestinal Tract: When, Where, and How? Microorganisms. [CrossRef]
- Gizem, C. , Koen, V., Luigi, L. et al. (2020). Interaction of dietary polyphenols and gut microbiota: Microbial metabolism of polyphenols, influence on the gut microbiota, and implications on host health. Food Frontiers, 1(2), 109-133. [CrossRef]
- González-Regueiro, J. A. , Moreno-Castañeda, L., Uribe, M., & Chávez-Tapia, N. C. (2017). The Role of Bile Acids in Glucose Metabolism and Their Relation with Diabetes. Annals of hepatology, s: 1. [CrossRef]
- Guillamón, E. , Andreo-Martínez, P., Mut-Salud, N., Fonollá, J., & Baños, A. (2021). Beneficial Effects of Organosulfur Compounds from Allium cepa on Gut Health: A Systematic Review. Foods (Basel, Switzerland). [CrossRef]
- Gu, J. , Thomas-Ahner, J. M., Riedl, K. M., Bailey, M. T., Vodovotz, Y., Schwartz, S. J., & Clinton, S. K. (2019). Dietary black raspberries impact the colonic microbiome and phytochemical metabolites in mice. Molecular nutrition & food research, 63(8), 1800636.
- Heinrich, M. , Mah, J., & Amirkia, V. (2021). Alkaloids Used as Medicines: Structural Phytochemistry Meets Biodiversity-An Update and Forward Look. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). [CrossRef]
- Hou, K. , Wu, Z., Chen, X., Wang, J., Zhang, D., Xiao, C., Zhu, D., Koya, J., Wei, L., Li, J., & Chen, Z. (2022). Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. [CrossRef]
- Hills RD Jr, Pontefract BA, Mishcon HR, Black CA, Sutton SC, Theberge CR. Gut microbiome: Profound implications for diet and disease. Nutrients. 1613.
- Illescas, O. , Rodríguez-Sosa, M., & Gariboldi, M. (2021). Mediterranean Diet to Prevent the Development of Colon Diseases: A Meta-Analysis of Gut Microbiota Studies. Nutrients. [CrossRef]
- Iriondo-DeHond, A. , Uranga, J. A., Del Castillo, M. D., & Abalo, R. (2020). Effects of Coffee and Its Components on the Gastrointestinal Tract and the Brain-Gut Axis. Nutrients. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H. , Cai, M., Shen, B., Wang, Q., Zhang, T., & Zhou, X. (2022). Synbiotics and Gut Microbiota: New Perspectives in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Foods (Basel, Switzerland). [CrossRef]
- Jandhyala, S. M. , Talukdar, R. ( 21(29), 8787–8803. [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S. N. , Cady, N. M., Shahi, S. K., Peterson, S. R., Gupta, A., Gibson-Corley, K. N., & Mangalam, A. K. (2021). Isoflavone diet ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through modulation of gut bacteria depleted in patients with multiple sclerosis. Science advances, 7(28), eabd4595. [CrossRef]
- Joaquim, B. , Bruno, S., Pedro, C., Maria, H. (2023). Polyphenols in Health and Disease: Gut Microbiota, Bioaccessibility, and Bioavailability. Compounds, -72. [CrossRef]
- Kadyan, S. , Sharma, A., Arjmandi, B. H., Singh, P., & Nagpal, R. (2022). Prebiotic Potential of Dietary Beans and Pulses and Their Resistant Starch for Aging-Associated Gut and Metabolic Health. Nutrients. [CrossRef]
- Kajla, P. , Sharma, A., & Sood, D. R. (2015). Flaxseed-a potential functional food source. Journal of food science and technology, 1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C. , Wang, B., Kaliannan, K., Wang, X., Lang, H., Hui, S., Huang, L., Zhang, Y., Zhou, M., Chen, M., & Mi, M. (2017). Gut Microbiota Mediates the Protective Effects of Dietary Capsaicin against Chronic Low-Grade Inflammation and Associated Obesity Induced by High-Fat Diet. mBio. [CrossRef]
- Khoo, H. E. , Azlan, A., Tang, S. T., & Lim, S. M. (2017). Anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: colored pigments as food, pharmaceutical ingredients, and the potential health benefits. Food & nutrition research. [CrossRef]
- Kitwetcharoen, H. , Phung, L.T., Klanrit, P., Thanonkeo, S., Tippayawat P, Yamada, M., Thanonkeo, P. (2023). Kombucha Healthy Drink—Recent Advances in Production, Chemical Composition and Health Benefits. Fermentation, 9(1):48. Nutrients, 11(8), 1806. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9010048. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081806.
- Kumar, S. , Perumal, N., Yadav, P. K., Pandey, R. P., Chang, C. M., & Raj, V. S. (2022). Amoxicillin impact on pathophysiology induced by short term high salt diet in mice. S. ( 12(1), 19351. [CrossRef]
- Kumar Singh, A. , Cabral, C., Kumar, R., Ganguly, R., Kumar Rana, H., Gupta, A., Rosaria Lauro, M., Carbone, C., Reis, F., & Pandey, A. K. (2019). Beneficial Effects of Dietary Polyphenols on Gut Microbiota and Strategies to Improve Delivery Efficiency. Nutrients. [CrossRef]
- Karamad, D. , Khosravi-Darani, K., Khaneghah, A. M., & Miller, A. W. (2022). Probiotic Oxalate-Degrading Bacteria: New Insight of Environmental Variables and Expression of the oxc and frc Genes on Oxalate Degradation Activity. Foods (Basel, Switzerland). [CrossRef]
- Kropp, C. , Le Corf, K., Relizani, K., Tambosco, K., Martinez, C., Chain, F., Rawadi, G., Langella, P., Claus, S. P., & Martin, R. (2021). The Keystone commensal bacterium Christensenella minuta DSM 22607 displays anti-inflammatory properties both in vitro and in vivo. Scientific reports. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. , Shin, Y. C., Kim, T. Y., Kim, Y., Lee, Y. S., Lee, S. H., Kim, M. N., O, E., Kim, K. S., & Kweon, M. N. (2021). Mucin degrader Akkermansia muciniphila accelerates intestinal stem cell-mediated epithelial development. Gut microbes. [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, A. , & Sokol, H. (2020). Gut microbiota-derived metabolites as key actors in inflammatory bowel disease. Nature reviews. Gastroenterology & hepatology. [CrossRef]
- Leeuwendaal, N. K. , Stanton, C., O'Toole, P. W., & Beresford, T. P. (2022). Fermented Foods, Health and the Gut Microbiome. P. ( 14(7), 1527. [CrossRef]
- Leonel AJ, Alvarez-Leite JI. Butyrate: implications for intestinal function. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. [CrossRef]
- Lisko, D. J. , Johnston, G. P., & Johnston, C. G. (2017). Effects of Dietary Yogurt on the Healthy Human Gastrointestinal (GI) Microbiome. G. ( 5(1), 6. [CrossRef]
- Li, J. , Liao, X., Yin, X., Deng, Z., Hu, G., Zhang, W., Jiang, F., & Zhao, L. (2022). Gut Microbiome and Serum Metabolome Profiles of Capsaicin with Cognitive Benefits in APP/PS1 Mice. Nutrients. [CrossRef]
- Lockyer, S. , Stanner, S (2019). Prebiotics – an added benefit of some fibre types. Nutrition Bulletin, 44(1), 74-91. [CrossRef]
- Lippolis, T. , Cofano, M., Caponio, G. R., De Nunzio, V., & Notarnicola, M. (2023). Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability of Diet Polyphenols and Their Modulation of Gut Microbiota. ( 24(4), 3813. [CrossRef]
- Liang, A. , Leonard, W., Beasley, J. T., Fang, Z., Zhang, P., & Ranadheera, C. S. (2023). Anthocyanins-gut microbiota-health axis: A review. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition. [CrossRef]
- Li, J. , Liao, X., Yin, X., Deng, Z., Hu, G., Zhang, W., Jiang, F., & Zhao, L. (2022). Gut Microbiome and Serum Metabolome Profiles of Capsaicin with Cognitive Benefits in APP/PS1 Mice. Nutrients. [CrossRef]
- Lobo, V. , Patil, A., Phatak, A., & Chandra, N. (2010). Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacognosy reviews. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. J. , Wang, J., He, T. F., Liu, H. S., & Piao, X. S. (2021). Effects of natural capsicum extract on growth performance, nutrient utilization, antioxidant status, immune function, and meat quality in broilers. Poultry science, /: https, 0130. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M. J. , Yang, J. Y., Yan, Z. H., Hu, S., Li, J. Q., Xu, Z. X., & Jian, Y. P. (2022). Recent findings in Akkermansia muciniphila-regulated metabolism and its role in intestinal diseases. Clinical nutrition (Edinburgh, Scotland), 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manach, C. , Scalbert, A., Morand, C., Rémésy, C., & Jiménez, L. (2004). Polyphenols: food sources and bioavailability. The American journal of clinical nutrition. [CrossRef]
- Markowiak, P. , & Śliżewska, K. (2017). Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics on Human Health. ( 9(9), 1021. [CrossRef]
- Menden A, Hall D, Hahn-Townsend C, et al. Exogenous lipase administration alters gut microbiota composition and ameliorates Alzheimer's disease-like pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Sci Rep, 4797. [CrossRef]
- Min, W. , Renzhe, T., Rui, Z., Yongxiang, Q., Dongmei, D. (2023). The protective effect of serum carotenoids on cardiovascular disease: a cross-sectional study from the general US adult population, 10. [CrossRef]
- Mueed, A. , Shibli, S., Korma, S. A., Madjirebaye, P., Esatbeyoglu, T., & Deng, Z. (2022). Flaxseed Bioactive Compounds: Chemical Composition, Functional Properties, Food Applications and Health Benefits-Related Gut Microbes. Foods (Basel, Switzerland). [CrossRef]
- Maruo, T. , Sakamoto, M., Ito, C., Toda, T., & Benno, Y. (2008). Adlercreutzia equolifaciens gen. nov., sp. nov., an equol-producing bacterium isolated from human faeces, and emended description of the genus Eggerthella. International journal of systematic and evolutionary microbiology, 58(Pt 5), 1221–1227. [CrossRef]
- Makki, K. , Deehan, E. C., Walter, J., & Bäckhed, F. (2018). The impact of dietary fiber on gut microbiota in host health and disease. Cell Host & Microbe. [CrossRef]
- Mazier, W. , Le Corf, K., Martinez, C., Tudela, H., Kissi, D., Kropp, C., Coubard, C., Soto, M., Elustondo, F., Rawadi, G., & Claus, S. P. (2021). A New Strain of Christensenella minuta as a Potential Biotherapy for Obesity and Associated Metabolic Diseases. P. ( 10(4), 823. [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G. , Balercia, G., Barrea, L., Cignarelli, A., Giorgino, F., Holst, J. J., Laudisio, D., Orio, F., Tirabassi, G., & Colao, A. (2017). Gut: A key player in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes? Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miaoyu, L. , Leilei, Y., Jianxin, Z et al. (2021). Role of dietary edible mushrooms in the modulation of gut microbiota. ( 2021). Role of dietary edible mushrooms in the modulation of gut microbiota. Journal of Functional Foods. 83, 104538. [CrossRef]
- Mayo, B. , Vázquez, L., & Flórez, A. B. (2019). Equol: A Bacterial Metabolite from The Daidzein Isoflavone and Its Presumed Beneficial Health Effects. Nutrients. [CrossRef]
- Monda V, Villano I, Messina A, et al. Exercise modifies the gut microbiota with positive health effects. Exercise modifies the gut microbiota with positive health effects. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017.
- Nambiar, R. B. , Perumal, A. B., Shittu, T., Sadiku, E. R., & Sellamuthu, P. S. (2023). Editorial: Probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, postbiotics, & paraprobiotics - New perspective for functional foods and nutraceuticals. Frontiers in nutrition. [CrossRef]
- Othman, L. , Sleiman, A. M. ( 10, 911. [CrossRef]
- Parekh, P. J. , Balart, L. A., & Johnson, D. A. (2015). The influence of the gut microbiome on obesity, metabolic syndrome and gastrointestinal disease. A. ( 6(6), e91. [CrossRef]
- Probiotics for the treatment of adult gastrointestinal disorders. American College of Gastroenterology. Accessed 03/17/2021.
- Pelaseyed, T. , Bergström, J. H., Gustafsson, J. K., Ermund, A., Birchenough, G. M., Schütte, A., van der Post, S., Svensson, F., Rodríguez-Piñeiro, A. M., Nyström, E. E., Wising, C., Johansson, M. E., & Hansson, G. C. (2014). The mucus and mucins of the goblet cells and enterocytes provide the first defense line of the gastrointestinal tract and interact with the immune system. Immunological reviews, 260(1), 8–20. [CrossRef]
- Portincasa, P. , Bonfrate, L., Vacca, M., De Angelis, M., Farella, I., Lanza, E., Khalil, M., Wang, D. Q., Sperandio, M., & Di Ciaula, A. (2022). Gut Microbiota and Short Chain Fatty Acids: Implications in Glucose Homeostasis. International journal of molecular sciences, 23(3), 1105. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, K. R. , Naik, S. R., & Vakil, B. V. (2015). Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics- a review. Journal of food science and technology, 7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J. , Zheng, T. T., Li, X., Liang, Y., Wang, L. J., Huang, Y. C., & Xiao, H. T. (2019). Plant-Derived Alkaloids: The Promising Disease-Modifying Agents for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Frontiers in pharmacology. [CrossRef]
- Pan, L. , Ye, H., Pi, X., Liu, W., Wang, Z., Zhang, Y., & Zheng, J. (2023). Effects of several flavonoids on human gut microbiota and its metabolism by in vitro simulated fermentation. ( 14, 1092729. [CrossRef]
- Parada Venegas, D. , De la Fuente, M. K., Landskron, G., González, M. J., Quera, R., Dijkstra, G., Harmsen, H. J. M., Faber, K. N., & Hermoso, M. A. (2019). Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)-Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Frontiers in immunology. [CrossRef]
- Roopchand, D.; et al. , (2015). Dietary Polyphenols Promote Growth of the Gut BacteriumAkkermansia muciniphila and Attenuate High-Fat Diet–Induced Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes, 64(8), 2847-2858.
- Rodrigues, V. F. , Elias-Oliveira, J., Pereira, Í. S., Pereira, J. A., Barbosa, S. C., Machado, M. S. G., & Carlos, D. (2022). Akkermansia muciniphila and Gut Immune System: A Good Friendship That Attenuates Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Obesity, and Diabetes. Frontiers in immunology. [CrossRef]
- Roberfroid, M. , Bornet, F., Bouley, C., & Cummings, J. (2009). Colonic Microflora: Nutrition and Health0. Summary and Conclusions of an International Life Sciences Institute (ILSI) [Europe] Workshop held in Barcelona, Spain. Nutrition Reviews. [CrossRef]
- Reynolds A, Mann J, Cummings J, Winter N, Mete E, Te Morenga L. Carbohydrate quality and human health: a series of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Lancet. 1017.
- Rocha, H. R. , Coelho, M. C., Gomes, A. M., & Pintado, M. E. (2023). Carotenoids Diet: Digestion, Gut Microbiota Modulation, and Inflammatory Diseases. Nutrients. [CrossRef]
- Rowles, J. L. , 3rd, & Erdman, J. W., Jr (2020). Carotenoids and their role in cancer prevention. Biochimica et biophysica acta. Molecular and cell biology of lipids, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E. , Cintoni, M., Raoul, P., Lopetuso, L. R., Scaldaferri, F., Pulcini, G., Miggiano, G. A. D., Gasbarrini, A., & Mele, M. C. (2019). Food Components and Dietary Habits: Keys for a Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition. Nutrients. [CrossRef]
- Stephanie, Ratih, N.K., Soka, S. and Suwanto, A. (2017). Effect of tempeh supplementation on the profiles of human intestinal immune system and gut microbiota. Microbiology Indonesia. [CrossRef]
- Slavin, J. (2013). Fiber and prebiotics: mechanisms and health benefits. Nutrients, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. K. , Chang, H. W., Yan, D., Lee, K. M., Ucmak, D., Wong, K., Abrouk, M., Farahnik, B., Nakamura, M., Zhu, T. H., Bhutani, T., & Liao, W. (2017). Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health. ( 15(1), 73. [CrossRef]
- Su, Q. , & Liu, Q. (2021). Factors Affecting Gut Microbiome in Daily Diet. ( 8, 644138. [CrossRef]
- Samtiya, M. , Aluko, R. E., Dhewa, T., & Moreno-Rojas, J. M. (2021). Potential Health Benefits of Plant Food-Derived Bioactive Components: An Overview. Foods (Basel, Switzerland), 10(4), 839. [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. , Chandrashekharappa, S., Bodduluri, S. R., Baby, B. V., Hegde, B., et al (2019). Enhancement of the gut barrier integrity by a microbial metabolite through the Nrf2 pathway. Nature communications. [CrossRef]
- Song, J. X. , Ren, H., Gao, Y. F., Lee, C. Y., Li, S. F., Zhang, F., Li, L., & Chen, H. (2017). Dietary Capsaicin Improves Glucose Homeostasis and Alters the Gut Microbiota in Obese Diabetic ob/ob Mice. Frontiers in physiology. [CrossRef]
- Singh RK, Chang HW, Yan D. Influence of diet on the gut microbiome and implications for human health. J Transl Med.
- Tao, F. , Xing, X., Wu, J., & Jiang, R. (2021). Enteral nutrition modulation with n-3 PUFAs directs microbiome and lipid metabolism in mice. PloS one, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuli, H. S. , Kumar, A., Sak, K., Aggarwal, D., Gupta, D. S., Kaur, G., Vashishth, K., Dhama, K., Kaur, J., Saini, A. K., Varol, M., Capanoglu, E., & Haque, S. (2022). Gut Microbiota-Assisted Synthesis, Cellular Interactions and Synergistic Perspectives of Equol as a Potent Anticancer Isoflavone. Pharmaceuticals (Basel, Switzerland), 15(11), 1418. [CrossRef]
- Ubeda, C. , Bucci, V., Caballero, S., Djukovic, A., Toussaint, N. C., Equinda, M., Lipuma, L., Ling, L., Gobourne, A., No, D., Taur, Y., Jenq, R. R., van den Brink, M. R., Xavier, J. B., & Pamer, E. G. (2013). Intestinal microbiota containing Barnesiella species cures vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium colonization. Infection and immunity, 81(3), 965–973. [CrossRef]
- Visioli, F. , Risé, P., Barassi, M. C., Marangoni, F., & Galli, C. (2003). Dietary intake of fish vs. formulations leads to higher plasma concentrations of n-3 fatty acids. Lipids. [CrossRef]
- Pandey RP, Mukherjee R, Priyadarshini A, Gupta A, Vibhuti A, Leal E, Sengupta U, Katoch VM, Sharma P, Moore CE, Raj VS, Lyu X. Potential of nanoparticles encapsulated drugs for possible inhibition of the antimicrobial resistance development. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Sep;141:111943. [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury NK, Choudhury R, Gogoi B, Chang CM, Pandey RP. Microbial Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles and their Application. Curr Drug Targets. 2022;23(7):752-760. [CrossRef]
- Dutt, Y.; Pandey, R.P.; Dutt, M.; Gupta, A.; Vibhuti, A.; Raj, V.S.; Chang, C.; Priyadarshini, A. Liposomes and phytosomes: Nanocarrier systems and their applications for the delivery of phytoconstituents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 491, 0010–8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar S, Dhiman R, Prudencio CR, da Costa AC, Vibhuti A, Leal E, Chang CM, Raj VS, Pandey RP. Chitosan: Applications in Drug Delivery System. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2023;23(2):187-191. [CrossRef]
- Gunjan, Vidic J, Manzano M, Raj VS, Pandey RP, Chang CM. Comparative meta-analysis of antimicrobial resistance from different food sources along with one health approach in Italy and Thailand. One Health. 2022 Dec 22;16:100477. [CrossRef]
- Khatri P, Rani A, Hameed S, Chandra S, Chang CM, Pandey RP. Current Understanding of the Molecular Basis of Spices for the Development of Potential Antimicrobial Medicine. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Jan 29;12(2):270. [CrossRef]
- Pandey RP, Nascimento MS, Franco CH, Bortoluci K, Silva MN, Zingales B, Gibaldi D, Castaño Barrios L, Lannes-Vieira J, Cariste LM, Vasconcelos JR, Moraes CB, Freitas-Junior LH, Kalil J, Alcântara L, Cunha-Neto E. Drug Repurposing in Chagas Disease: Chloroquine Potentiates Benznidazole Activity against Trypanosoma cruzi In Vitro and In Vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Nov 15;66(11):e0028422. [CrossRef]
- do Socorro Fôro Ramos E, de Oliveira Ribeiro G, Villanova F, de Padua Milagres FA, Brustulin R, Araújo ELL, Pandey RP, Raj VS, Deng X, Delwart E, Luchs A, da Costa AC, Leal É. Composition of Eukaryotic Viruses and Bacteriophages in Individuals with Acute Gastroenteritis. Viruses. 2021 Nov 25;13(12):2365. [CrossRef]
- Verediano, T. A. , Stampini Duarte Martino, H., Dias Paes, M. C., & Tako, E. (2021). Effects of Anthocyanin on Intestinal Health: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. , Yu, F., Zhang, Y., Chang, W., & Zhou, M. (2022). The Effects and Mechanisms of Flavonoids on Cancer Prevention and Therapy: Focus on Gut Microbiota. International journal of biological sciences, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; et al. , (2019). The human gut bacteria Christensenellaceae are widespread, heritable, and associated with health. BMC Biol 17(83).
- Wang, X. , Qi, Y., & Zheng, H. (2022). Dietary Polyphenol, Gut Microbiota, and Health Benefits. ( 11(6), 1212. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. , Zhang, Y., Li, C., Chang, W., & Zhang, L. (2023). The relationship between gut microbiota and COVID-19 progression: new insights into immunopathogenesis and treatment. Frontiers in Immunology. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M. K. , Kumari, I., Singh, B., Sharma, K. K., & Tiwari, S. K. (2022). Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics: Safe options for next-generation therapeutics. Applied microbiology and biotechnology. [CrossRef]
- York, A. Your microbiome is what you eat. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N. , Huang, X., Zeng, Y., Wu, X., & Peng, X. (2013). Study on prebiotic effectiveness of neutral garlic fructan in vitro. Food Science and Human Wellness,. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M. , Li, A., Yang, Q., Li, J., Wang, L., Liu, X., Huang, Y., & Liu, L. (2021). Beneficial Effect of Alkaloids From Sophora alopecuroides L. on CUMS-Induced Depression Model Mice via Modulating Gut Microbiota. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H. , Xu, J., Yang, M., Hussain, M., Liu, X., Feng, F., & Guan, R. (2023). Protective Effect of Anthocyanins against Neurodegenerative Diseases through the Microbial-Intestinal-Brain Axis: A Critical Review. Nutrients. [CrossRef]
- Zhiguo, Z. , Buyu, L., Xingquan, L., Weiwei, H et al. (2023). Effects of Steaming on Sweet Potato Soluble Dietary Fiber: Content, Structure, and Lactobacillus Proliferation In Vitro. Foods, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhixian, L. , Zhuqing, D., Enjuan, S. et al. (2023). Study on the interaction between β-carotene and gut microflora using an in vitro fermentation model. Food Science and Human Wellness,. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K. (2017). Strategies to promote abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila, an emerging probiotics in the gut, evidence from dietary intervention studies. Journal of functional foods, 33, 194–201. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. , Singh, M. P., Bharti, V. K., & Pandey, R. P. (2018). Quality control of vaccines-A journey from classical approach to 3Rs. Microbiology: Current Research.
- Pandey RP, Mukherjee R, Chang CM. Emerging Concern with Imminent Therapeutic Strategies for Treating Resistance in Biofilm. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Apr 2;11(4):476. [CrossRef]
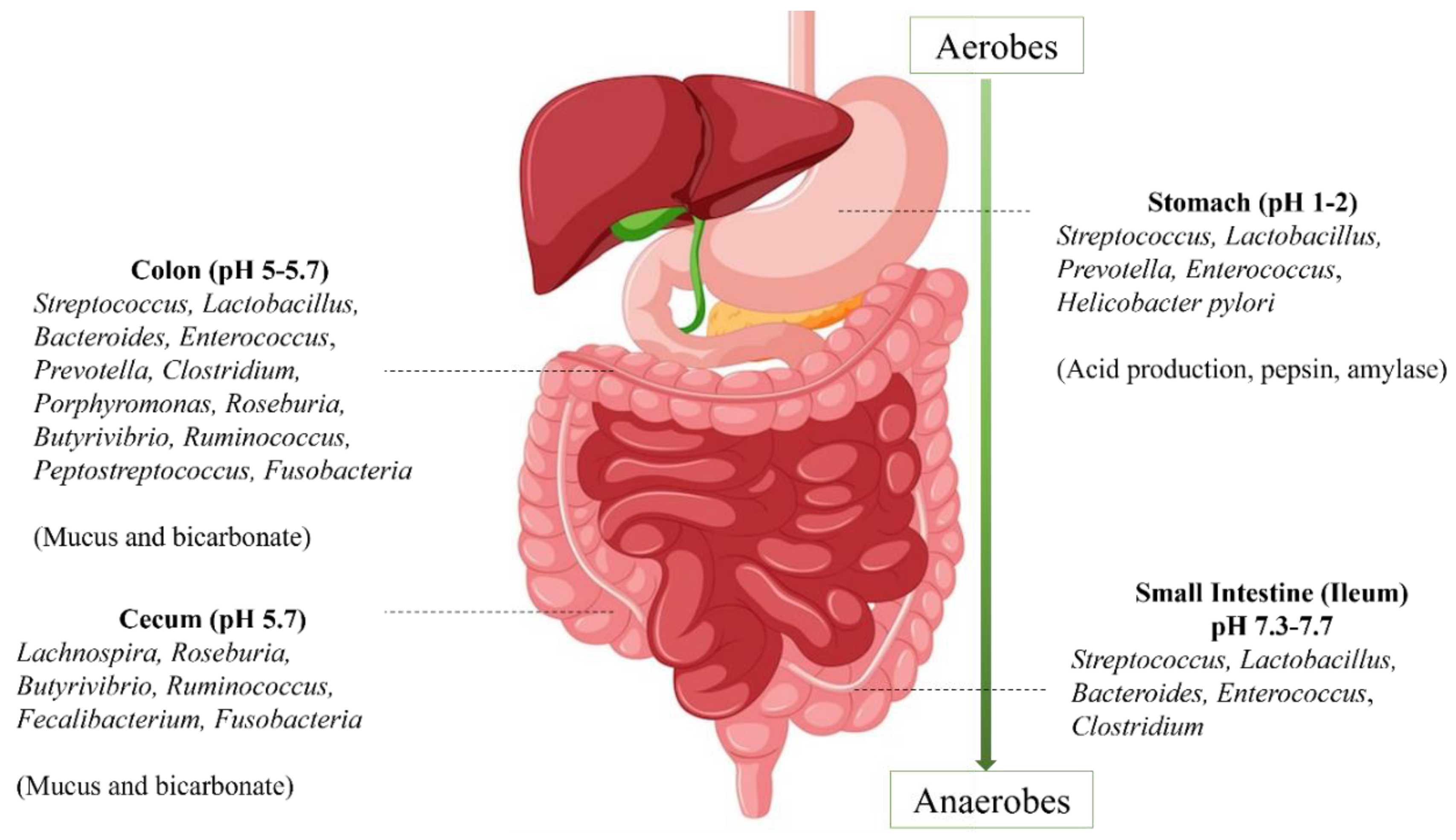

| S. No. | Beneficial bacteria | Substances | Sources | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 1. |
Akkermansia muciniphila | Polyphenols | Caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, salvianolic acid A, ferulic, Concord grape polyphenols, puerarin, resveratrol, epigallocatechin gallate, black tea, red wine, grape juice, aronia juice, canarium album extract, arctic berries, flavonoids | Zhou et al 2017 Visioli et al 2003 Anhe et al 2014 Roopchand et al 2015 Kajla et al. 2015 Chenbo et al 2022 |
| Alkaloids | Berberine, curcumin caffeine, chlorogenic acid and betaine | |||
| Capsaicin | Chili peppers | |||
| Plant-derived carbohydrates | Nonfermentable fiber, wheat dietary fiber, konjac glucomannan, bran, fiber-rich common beans, oligofructose, Inulin-type fructan, stachyose, polysaccharides from spirulina platensis, lycium barbarum polysaccharide and fucoidan | |||
| Others | Oily fish, walnuts bamboo shoots, rhubarb extract and flaxseed | |||
| 2. | Adlercreutzia equolifasciens | Isoflavone diet | Tofu, tempeh, and soy milk | Jensen et al 2021 |
| 3. | Barnesiella | Polyphenols | Cherry juices Black raspberry-rich diet Ganoderma lucidum mushroom |
Ubeda et al, 2013 Daillère et al, 2016 Gu et al, 2019 Miaoyu et al, 2021 |
| Prebiotics | ||||
| 4. | Christensenella minuta | Polyphenols | Red grapes, cranberries, strawberries and blueberries | Mazier et al, 2021 Ang et al, 2023 Waters et al 2019 |
| 5. | Oxalobacter formigenes | Prebiotic foods | Prebiotic foods like kimchi, sauerkraut, kefi, spinach, legumes, tea and celery | Kaufman et al, 2008 Chmiel et al, 2022 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





