Submitted:
10 October 2024
Posted:
11 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods
| Treatment | Forage type | No. |
| Fert. | El. N | Ⅰ. |
| El. T | Ⅱ. | |
| Po. L | Ⅲ. | |
| El. N + El. T | Ⅰ. + Ⅱ. | |
| El. N + Po. L | Ⅰ. + Ⅲ. | |
| El. T + Po. L | Ⅱ. + Ⅲ. | |
| El. N + El. T + Po. L | Ⅰ. + Ⅱ. + Ⅲ. | |
| No-Fert. | El. N | Ⅰ. |
| El. T | Ⅱ. | |
| Po. L | Ⅲ. | |
| El. N + El. T | Ⅰ. + Ⅱ. | |
| El. N + Po. L | Ⅰ. + Ⅲ. | |
| El. T + Po. L | Ⅱ. + Ⅲ. | |
| El. N + El. T + Po. L | Ⅰ. + Ⅱ. + Ⅲ. |
2.3. Measurement Methods
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. The Competitiveness of Inter-Species
2.4.2. The Effect of Super-Production
3. Results
3.1. Dynamic Change of Aboveground Biomass Indicators under Different Sowing Combinations
3.1.1. Forage Yield
3.1.2. RYT and OY
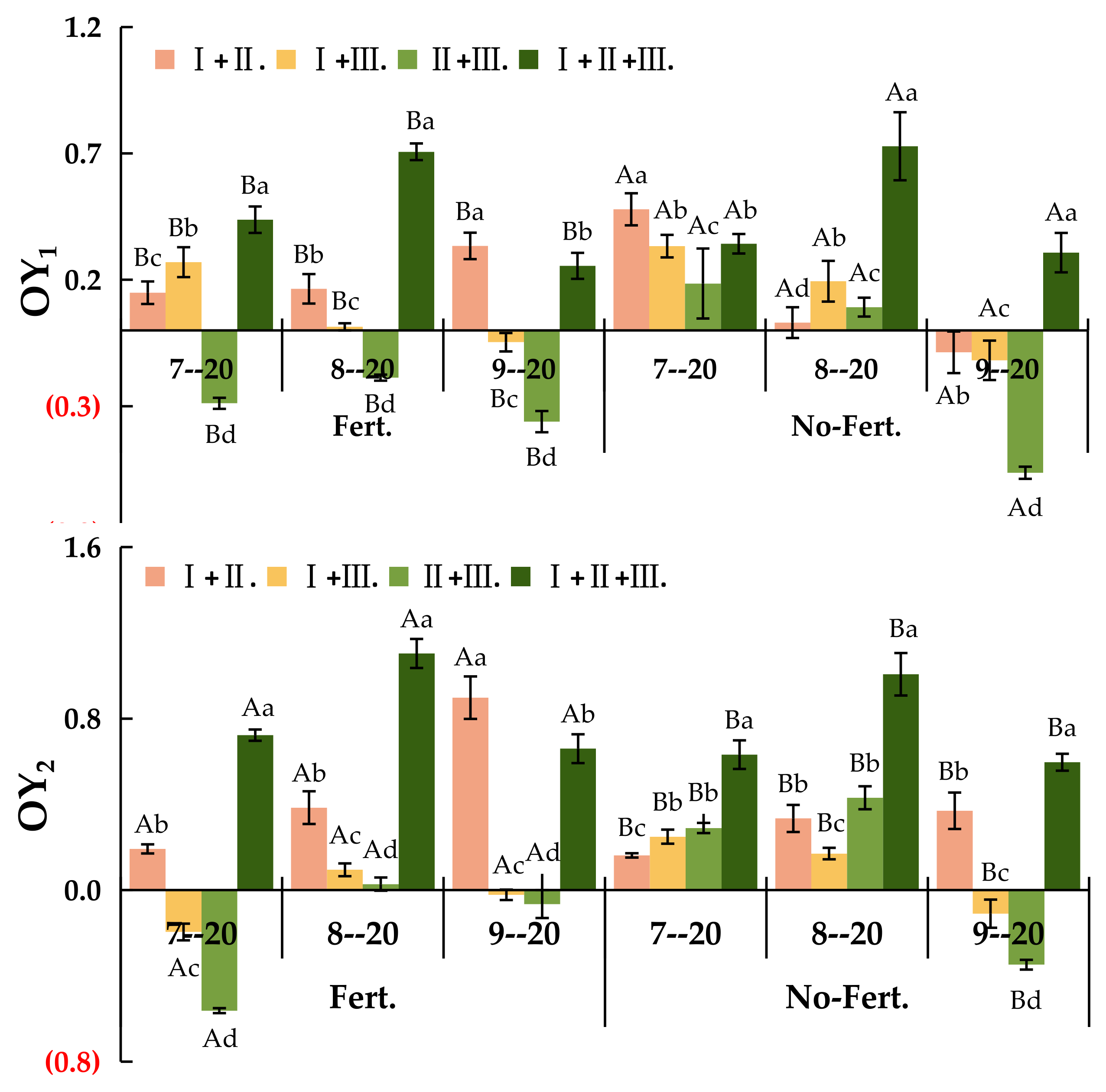
3.1.3. OY1 and OY2
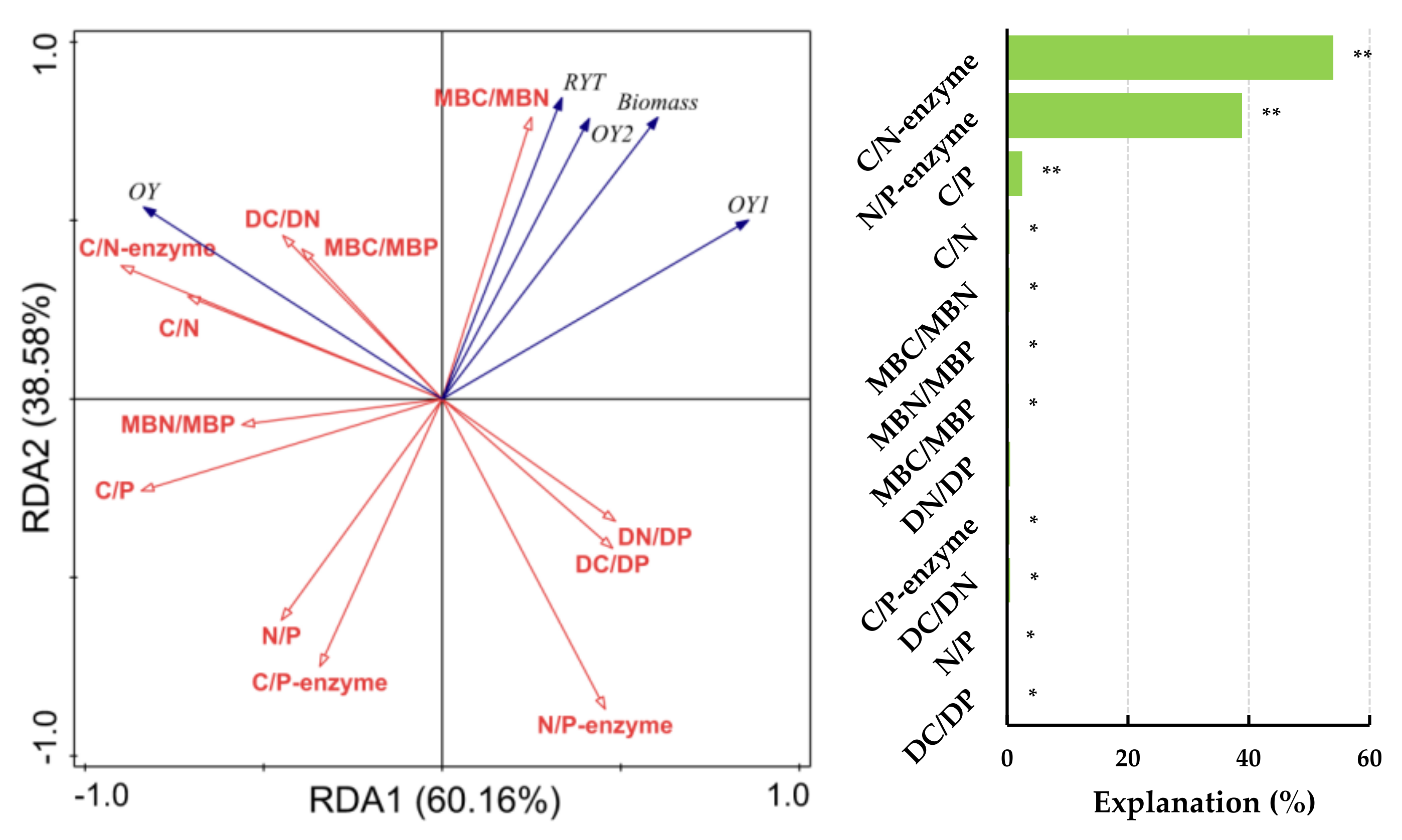
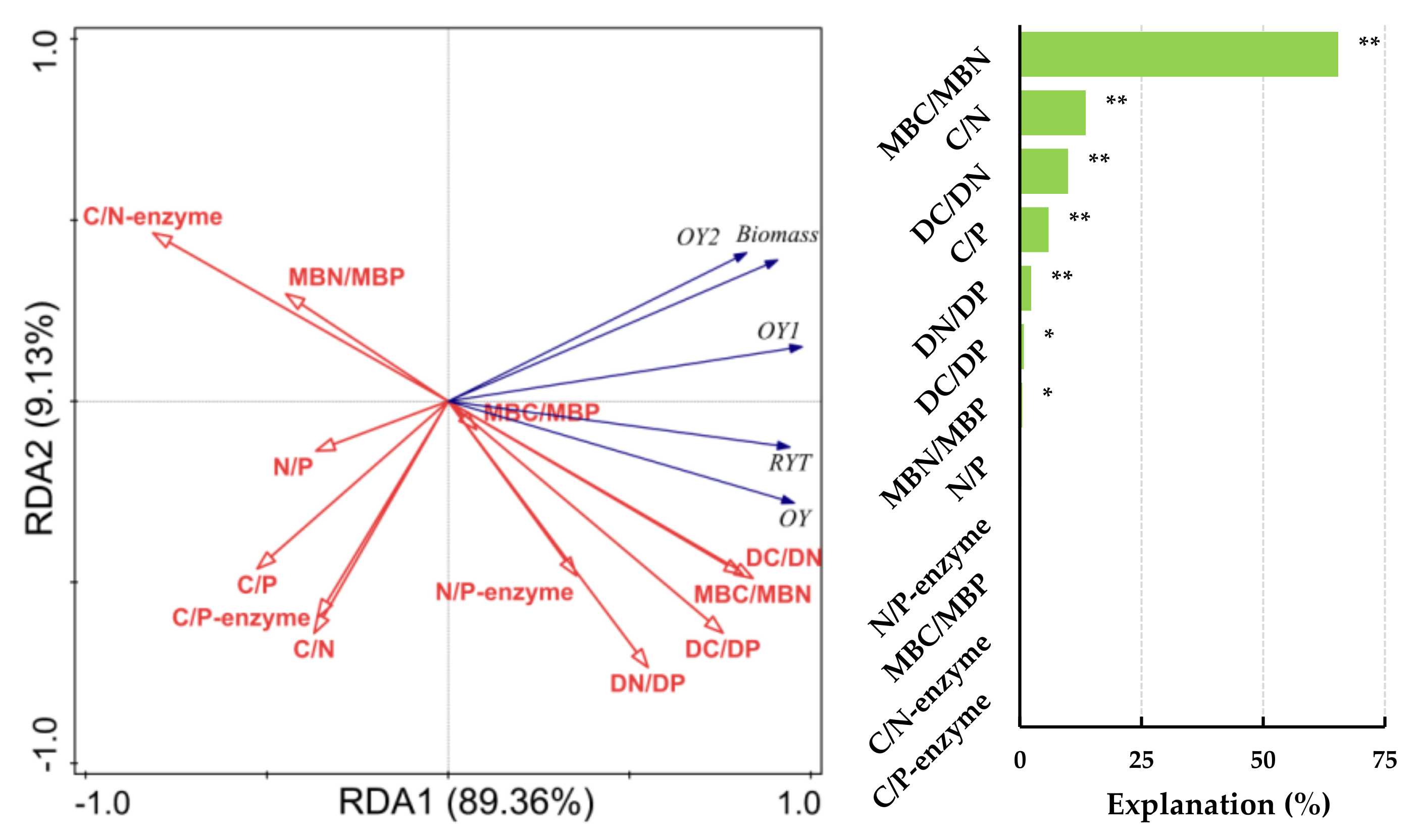
3.2. Influential Factors of Forage Yield Indicators
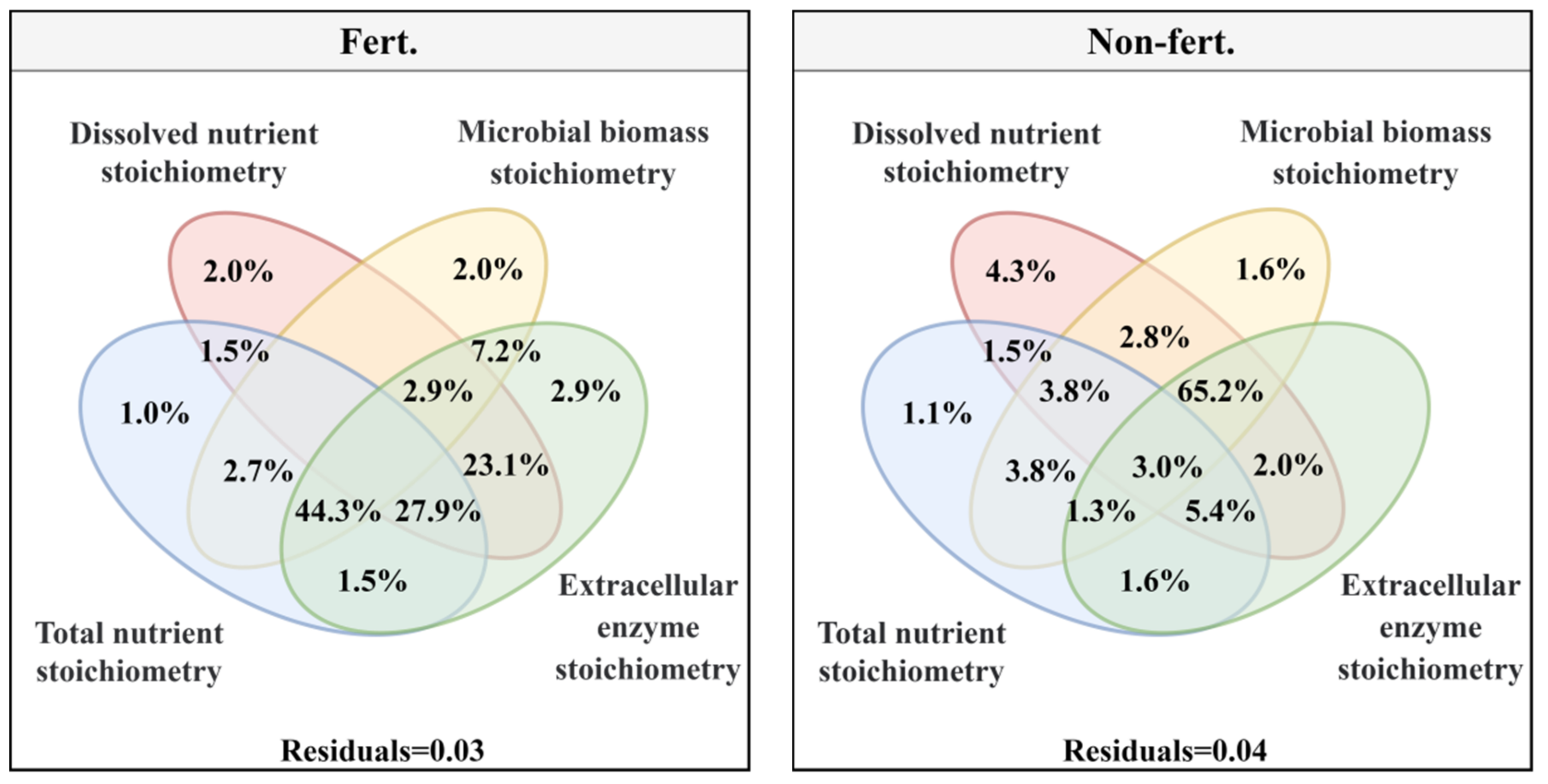
3.3. The Relationship between Soil Ecological Stoichiometry Characteristics and Forage Yield
4. Discussion
4.1. The Effect of Mixed-Sowing on Aboveground Biomass
4.2. The Effect of Fertilizer Application on Aboveground Biomass and Con-Existence of Species in Mixed Combinations
4.3. The Response Strategies of Soil Ecological Stoichiometry Characteristics to Mixed Combinations and Fertilizer Application
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, L.; Han, X.G.; Zhang, Z.B.; Sun, O.J. Grassland ecosystems in China: review of current knowledge and research advancement. Philos T R Soc B 2007, 362, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.S.; Xie, W.G. Anatomical and Physiological Characteristics of Awn Development in Elymus nutans, an Important Forage Grass in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Agronomy 2023, 13(3), 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.H.; Dong, S.K.; Wang, T.; Xie, Z.K. Interspecific interactions under fertilization among Elymus nutans, Festuca sinensis and Festuca ovina on the eastern Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Plant Spec Biol 2012, 27, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.H.; Dong, Q.M.; Shi, J.J.; Zhou, H.K.; Dong, S.K.; Shao, X.Q.; Li, S.X.; Wang, Y.L.; Ma, Y.S.; Ding, L.M.; et al. Research progress in recent ten years of ecological restoration for “black soil land” degraded grassland on Tibetan Plateau concurrently discuss of ecological restoration in San jiang yuan region. Acta Agrestia Sinica 2018, 26(1): 1-21. [CrossRef]
- Littlejohn, C.P.; Hofmann, R.W.; Wratten, S.D. Delivery of multiple ecosystem services in pasture by shelter created from the hybrid sterile bioenergy grass Miscanthus x giganteus. Sci. Rep 2019, 9, 5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Z.C.; Dong, S.K. Adaptive management of alpine grassland ecosystems over Tibetan Plateau. Pratacultural Science 2019, 36(4): 933-938. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, J.C.; Bai, Y.P.; Wang, P. Assessing the sustainability of grass-based livestock husbandry in Hulun Buir, China. Phys Chem Earth, Parts A/B/C 2020, 120, 102907. [CrossRef]
- Soleymani, A.; Shahrajabian, M.H.; Khoshkharam, M. Effect of different fertility systems on fresh forage yield and qualitative traits of forage corn. Res. Crop 2012, 13, 861–865. [Google Scholar]
- Crotty, F.V.; Fychan, R.; Sanderson, R.; Marley, C.L. ncreasing legume forage productivity through slurry application-A way to intensify sustainable agriculture?. Food Energy Secur 2018, 7(4), e00144. [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.K.; Shang, Z.H.; Gao, J.X.; Boone, R.B. Enhancing sustainability of grassland ecosystems through ecological restoration and grazing management in an era of climate change on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 2020,287,106684. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Li, W.Q.; Zhou, H.K.; Kang, Q.; Ma, X.L.; Liu, P.; Wang, Z. Dynamics of soil dissolved organic nitrogen and inorganic nitrogen pool in alpine artificial grasslands. Ecol. Environ Sci 2016, 25(1): 30-35. [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, H.K.; Lu, B.B.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.W.; Li, Y.Z.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.J.; et al. Single-species artificial grasslands decrease soil multifunctionality in a temperate steppe on the Qinghai–Tibet plateau. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.W.; Li, H.Y.; Sun, T. An Experimental Study of Variety Screening, Sequential Cropping, Compaction and Mixed Cropping Techniques for the Cultivation of Annual Forage Crops in Agro-pastoral Area of Tibet, China. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2014, 16(1).
- Poltoretskyi, S.; Prykhodko, V.; Poltoretska, N. Agro-ecological and biological aspects of the components selection for mixed sowings of forage crops. Ukr J. Ecol 2019, 9(3): 31-36.
- Zhang, Q.G.; Zhang, D.Y. Competitive hierarchies inferred from pair-wise and multi-species competition experiments. Acta oecologica 2012, 38, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayal, M.; Lenihan, H.S.; Brooks, A.J.; Holbrook, S.J.; Schmitt, R.J.; Kendall, B.E. Predicting coral community recovery using multi-species population dynamics models. Ecol. Lett 2018, 21, 1790–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, E.G.; Kennedy, N.; Siciliano, S.D. Effects of plant species richness and evenness on soil microbial community diversity and function. Plant Soil 2011, 338, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.U.; Chapin, F.S.; Ewel, J.J.; Hector, A.; Inchausti, P.; Lavorel, S.; Lawton, J.H.; Lodge, D.M.; Loreau, M.; Naeem, S.; et al. Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: A consensus of current knowledge. Ecol. Monogr 2005, 75, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loreau, M.; Naeem, S.; Inchausti, P.; Bengtsson, J.; Grime, J.P.; Hector, A.; Hooper, D.U.; Huston, M.A.; Raffaelli, D.; Schmid, B.; et al. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: Current knowledge and future challenges. Science 2001, 294, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Waal, D.B.; Elser, J.J.; Martiny, A.C.; Sterner, R.W.; Cotner, J.B. Editorial: Progress in ecological stoichiometry. Front Microbiol 2018, 9: 1957. [CrossRef]
- Ott, D.; Digel, C.; Rall, B.C.; Maraun, M.; Scheu, S.; Brose, U. Unifying elemental stoichiometry and metabolic theory in predicting species abundances. Ecol. Lett 2014, 17, 17(10),1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, A.J.; Taylor, B.W. Using ecological stoichiometry to understand and predict infectious diseases. Oikos 2018, 127(10), 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockmann, U.; Adams, M.A.; Crawford, J.W.; Field, D.J.; Henakaarchchi, N.; Jenkins, M.; Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B.; Vivien de Remy de Courcelles, V.R.; Singh, K.; et al. The knowns, known unknowns and unknowns of sequestration of soil organic carbon. Agr Ecosyst Environ 2013, 164, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, J.P.; Hart, S.C. Competition for nitrogen between plants and soil microorganisms. Trends Ecol. Evol 1997, 12(4), 139-143. [CrossRef]
- Güsewell, S.; Bollens, U. Composition of plant species mixtures grown at various N: P ratios and levels of nutrient supply. Basic Appl Ecol. 2003, 4, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Lauber, C.L.; Weintraub, M.N.; Ahmed, B.; Allison, S.D.; Crenshaw, C.; Contosta, A.R.; Cusack, D.; Frey, S.; Gallo, M.E.; et al. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol. Lett 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Weintraub, M.N. Vector analysis of ecoenzyme activities reveal constraints on coupled C, N and P dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem 2016, 93, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Liptzin, D. C: N: P stoichiometry in soil: is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass?. Biogeochemistry 2007, 85,235-252.
- Manzoni, S.; Čapek, P.; Mooshammer, M.; Lindahl, B.D.; Richter, A.; Šantrůčková, H. Optimal metabolic regulation along resource stoichiometry gradients. Ecol. Lett 2017, 20, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G.; DeForest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Weintraub, M.N.; Zoppini, A. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol Biochem 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.X.; Moorhead, D.L.; Guo, X.B.; Peng, S.S.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.C.; Fang, L.C. Stoichiometric models of microbial metabolic limitation in soil systems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr 2021, 30, 2297–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.M.; Liu, C.H.; Zhou, Z.C.; Wanek, W. Extracellular enzyme stoichiometry reflects the metabolic C-and P-limitations along a grassland succession on the Loess Plateau in China. Appl Soil Ecol. 2022, 179, 104594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Wang, B.R.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Qu, T.T.; Xue, Z.J.; Li, X.Y.; Zhou, Z.C.; An, S.S. Eco-enzymatic stoichiometry and microbial non-homeostatic regulation depend on relative resource availability during litter decomposition. Ecol. Indic 2022, 145: 109729. [CrossRef]
- Farrer, E.C.; Suding, K.N. Teasing apart plant community responses to N enrichment: the roles of resource limitation, competition and soil microbes. Ecol. Lett 2016, 19, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.S.; Wolfe-Bellin, K.S.; Schmid, B.; Bazzaz, F.A. Density may alter diversity-productivity relationships in experimental plant communities. Basic Appl Ecol. 2005, 6(6), 505-517. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.X.; Lu, J.W.; Yang, J. Effect of fertilization on the grass yield, water utilizing and nutrition uptake of Sudan grass and Ryegrass rotation regime. Acta Prataculturae Sinica 2009, 18, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaja, N.; Codling, E.E.; Rutto, L.K.; Timlin, D.; Reddy, V.R. Poultry litter and inorganic fertilization: effects on biomass yield, metal and nutrient concentration of three mixed-season perennial forages. Agronomy 2022, 12, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guretzky, J.; Kering, M.; Mosali, J.; Funderburg, E.; Biermacher, J. Fertilizer rate effects on forage yield stability and nutrient uptake of midland bermudagrass. J. Plant Nutr 2010, 33, 1819–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. Methods of Soil Analysis Parts 3-Chemical Methods Ⅱ 1996. [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Analysis on soil and agricultural chemistry. China Agri-cultural Press 2005, Beijing.
- Vance, E.D.; Brookess, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Landman, A.; Pruden, G.; Jenkinson, D.S. Chloro-form fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: a rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 1985, 17, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Powlson, D.S.; Jenkinson, D.S. Measurement of microbial biomass phosphorus in soil. Soil Bio Biochem 1982, 14(4): 319-329. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lu, Y.H.; Liu, C.K.; Shang, P.; Liu, J.; Zheng, C.M. Sources and Dynamics of Dissolved Inorganic Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus in a Large Agricultural River Basin in Arid Northwestern China. Water 2017, 9, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cesare, D.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Transcriptional regulation by cyclic AMP-responsive factors. Prog Nucleic Acid Re 2000, 64, 343–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandy, A.S.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Neff, J.C. Nitrogen deposition effects on soil organic matter chemistry are linked to variation in enzymes, ecosystems and size fractions. Biogeochemistry 2008, 91(1): 37-49. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Wu, Z.J.; Chen, L.J.; Li, D.P.; Ma, X.Z.; Shi, Y.F. A microplate fluorimetric assay for sacchariase activity measurement. Spectrosc Spect Anal 2009, 29, 1341–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.T.; Yuan, G.Y.; Shen, Y.Y.; Yang, X.L. Effects of temperature and mixed sowing ratio on growth and interspecific competition of Onobrychis viciaefolia and Elymus nutans community. Chinese Journal of Grassland 2021, 43, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebenkäs, A.; Schumacher, J.; Roscher, C. Resource availability alters biodiversity effects in experimental grass-forb mixtures. PLOS One 2016, 11(6): 1-21. [CrossRef]
- Pantel, A.; Romo, J.T.; Bai, Y. Above-ground net primary production for Elymus lanceolatus and Hesperostipa curtiseta after a single defoliation event. Rangeland Ecol Manag 2011, 64(3), 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, K.; Hebda, R.J. A morphometric analysis of variation between Elymus alaskanus and Elymus violaceus (Poaceae): implications for recognition of taxa. Madroño 2011, 58(1), 32-49. [CrossRef]
- Soe Htet, M.N.; Wang, H.L.; Yadav, V.; Sompouviseth, T.; Feng, B. Legume Integration Augments the Forage Productivity and Quality in Maize-Based System in the Loess Plateau Region. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bork, E.W.; Gabruck, D.T.; McLeod, E.M.; Hall, L.M. Five-year forage dynamics arising from four legume-grass seed mixes. Agron. J 2017, 109, 2789–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.F.; Peng, L.X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Cheng, Y.X.; Hou, F.J. Multi-cutting improves forage yield and nutritional value and maintains the soil nutrient balance in a rainfed agroecosystem. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginwal, D.S.; Kumar, R., Ram, H.; Meena, R.K.; Kumar, U. Quality characteristics and nutrient yields of maize and legume forages under changing intercropping row ratios. Indian J. Anim. Sci 2019, 89(3),281-286. [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Akbar, N.; Khan, H.Z. Productivity of summer legume forages intercropped with maize as affected by mixed cropping in different sowing techniques. J. Anim. Plant Sci 2012, 22, 758–763. [Google Scholar]
- Bork, E.W.; Gabruck, D.T.; McLeod, E.M.; Hall, L.M. Five-year forage dynamics arising from four legume-grass seed mixes. Agron. J 2017, 109, 2789–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocheville, A. The ecological niche: history and recent controversies. Handbook of evolutionary thinking in the sciences 2015, 547-586.
- White, A.; Darby, H.; Ruh, L.; Sands, B. Long term influence of alternative corn cropping practices and corn-hay rotations on soil health, yields and forage quality. Front. Environ. Sci 2023, 11: 243. [CrossRef]
- Letten, A.D.; Ke, P.J.; Fukami, T. Linking modern coexistence theory and contemporary niche theory. Ecol. Monogr 2017, 87(2): 161-177. [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Reich, P.B.; Knops, J.; Wedin, D.; Mielke, T.; Lehman, C. Diversity and productivity in a long-term grassland experiment. Science 2001, 294, 843–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tilman, D.; Lambers, H.; Zhang, F.S. Plant diversity and overyielding: insights from belowground facilitation of intercropping in agriculture. New Phytol 2014, 203, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziadi, N.; Simard, R.R.; Allard, G.; Parent, G. Yield response of forage grasses to N fertilizer as related to spring soil nitrate sorbed on anionic exchange membranes. Can. J. Soil Sci 2000, 80, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buche, L.; Spaak, J.W.; Jarillo, J. Niche differences, not fitness differences, explain predicted coexistence across ecological groups. J. Ecol. 2022, 110(11): 2785-2796. [CrossRef]
- Spaak, J.W.; Carpentier, C.; De Laender, F. Species richness increases fitness differences, but does not affect niche differences. Ecol. Lett 2021, 24, 2611–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaub, S.; Finger, R.; Leiber, F.; Probst, S.; Kreuzer, M.; Weigelt, A.; Buchmann, N.; Scherer-Lorenzen, M. Plant diversity effects on forage quality, yield and revenues of semi-natural grasslands. Nat. Commun 2020, 11, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, P.B.; Smull, D.; Beard, K.H.; Choi, R.T.; Furniss, T.; Kulmatiski, A.; Meiners, J.M.; Tredennick, A.T.; Veblen, K.E. Competition and coexistence in plant communities: intraspecific competition is stronger than interspecific competition. Ecol. Lett 2018, 21, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.J.; Gao, S.; Zhou, D.H.; Liu, M.X.; Wang, J.F.; Knops, J.M.H.; Mu, C.S. Fall nitrogen application increases seed yield, forage yield and nitrogen use efficiency more than spring nitrogen application in Leymus chinensis, a perennial grass. Field Crop Res 2017, 214, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loreau, M.; de Mazancourt, C. Species synchrony and its drivers: neutral and nonneutral community dynamics in fluctuating environments. Am. Nat 2008, 172, E48–E66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreyling, J.; Beierkuhnlein, C.; Ellis, L.; Jentsch, A. Invasibility of grassland and heath communities exposed to extreme weather events–additive effects of diversity resistance and fluctuating physical environment. Oikos 2008, 117, 1542–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 71bPetersen, U.; Isselstein, J. Nitrogen addition and harvest frequency rather than initial plant species composition determine vertical structure and light interception in grasslands. AoB Plants 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin Iii, F.S.; Zavaleta, E.S.; Eviner, V.T.; Naylor, R.L.; Vitousek, P.M.; Reynolds, H.L.; Hooper, D.U.; Lavorel, S.; Sala, O.E.; Hobbie, S.E. Consequences of changing biodiversity. Nature 2000, 405, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungers, J.M.; DeHaan, L.R.; Betts, K.J.; Sheaffer, C.C.; Wyse, D.L. Intermediate wheatgrass grain and forage yield responses to nitrogen fertilization. Agron J. 2017, 109, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Keiblinger, K.M.; Mooshammer, M.; Peñuelas, J.; Richter, A.; Sardans, J.; Wanek, W. The application of ecological stoichiometry to plant–microbial–soil organic matter transformations. Ecol. Monogr 2015, 85(2), 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.J.; Dippold, M.A.; An, S.; Wang, B.R.; Zhang, H.X.; Sebastian, L. Extracellular enzyme activity and stoichiometry: The effect of soil microbial element limitation during leaf litter decomposition. Ecol. Indic 2021, 121, 107200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.P.; Weintraub, M.N. The implications of exoenzyme activity on microbial carbon and nitrogen limitation in soil: a theoretical model. Soil Biol. Biochem 2003, 35, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.W.; Elser, J.J. Stoichiometry and homeostasis. In: Sterner, R.W., Elser, J.J. (Eds.), Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Bio-Sphere. Princeton University Press 2017, Princeton, NJ, USA, 1–43.
- Tessier, J.T.; Raynal, D.J. Use of nitrogen to phosphorus ratios in plant tissue as an indicator of nutrient limitation and nitrogen saturation. J. Appl. Ecol 2003, 40, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Acharya, K.; Kyle, M.; Cotner, J.; Makino, W.; Markow, T.; Watts, T.; Hobbie, S.; Fagan, W.; Schade, J.; et al. Growth rate–stoichiometry couplings in diverse biota. Ecol. Lett 2003, 6, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; de Ruiter, P.C.; Wassen, M.J.; Heil, G.W. Time-dependent, species-specific effects of N: P stoichiometry on grassland plant growth. Plant Soil 2010, 334: ,99-112. [CrossRef]
- Feldhaar, H. Ant nutritional ecology: linking the nutritional niche plasticity on individual and colony-level to community ecology. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2014, 5, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kering, M.K.; Guretzky, J.; Funderburg, E.; Mosali, J. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer rate and harvest season on forage yield, quality, and macronutrient concentrations in midland Bermuda grass. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal 2011, 42, 1958–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Weil, R.R.; Nan, X.X. Total and permanganate-oxidizable organic carbon in the corn rooting zone of US Coastal Plain soils as affected by forage radish cover crops and N fertilizer. Soil Till Res 2017, 165, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, S.S.; Nyborg, M.; Soon, Y.K. Long-term effects of balanced fertilization on grass forage yield, quality and nutrient uptake, soil organic C and N, and some soil quality characteristics. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 2010, 86, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Y.; Tian, H.; Zhang, H.S.; Xiong, J.B.; Yang, H.M.; Liu, Y. Shoot-soil ecological stoichiometry of alfalfa under nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization in the Loess Plateau. Sci. Rep 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, H.W.; Yi, H.J. Impact of fertilizer on crop yield and C: N: P stoichiometry in arid and semi-arid soil. Int. J. Environ 2021, 18, 4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokol, N.W.; Sanderman, J.; Bradford, M.A. Pathways of mineral-associated soil organic matter formation: Integrating the role of plant carbon source, chemistry, and point of entry. Glob Chang Biol 2019, 25, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L. Phenol oxidase, peroxidase and organic matter dynamics of soil. Soil BiolBiochem 2010, 42, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Jia, J.; Chen, L.T.; Chu, H.Y.; He, J.S.; Zhang, Y.J.; Feng, X.J. Aridity and NPP constrain contribution of microbial necromass to soil organic carbon in the Qinghai-Tibet alpine grasslands. Soil Biol Biochem 2021, 156, 108213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sowing combinations | Component | Sampling time (Month-day) | |||||
| Fert. | No-Fert. | ||||||
| 7-20 | 8-20 | 9-20 | 7-20 | 8-20 | 9-20 | ||
| Ⅰ., Ⅱ., Ⅲ. | Ⅰ. -- El. N | 361.51 | 1003.47 | 1972.35 | 91.49 | 620.59 | 91.49 |
| Ⅱ. -- El. T | 334.29 | 702.02 | 801.46 | 32.14 | 337.65 | 39.64 | |
| Ⅲ. -- Po. L | 208.58 | 1177.15 | 2188.39 | 36.16 | 634.82 | 36.16 | |
| Ⅰ. + Ⅱ. | Ⅰ. | 378.50 | 775.79 | 1848.49 | 54.98 | 368.69 | 812.92 |
| Ⅱ. | 38.51 | 375.08 | 778.99 | 21.75 | 273.33 | 169.60 | |
| Total | 417.01 | 1150.87 | 2627.48 | 76.73 | 642.02 | 982.52 | |
| Ⅱ. + Ⅲ . | Ⅱ. | 354.55 | 841.55 | 1755.33 | 87.47 | 464.21 | 792.9 |
| Ⅲ. | 107.82 | 348.57 | 336.59 | 24.97 | 278.80 | 128.28 | |
| Total | 462.37 | 1190.13 | 2091.91 | 112.43 | 743.02 | 921.07 | |
| Ⅰ. +Ⅲ. | Ⅰ. | 165.06 | 588.58 | 1074.38 | 53.15 | 365.41 | 314.18 |
| Ⅲ. | 70.91 | 355.11 | 329.16 | 33.72 | 332.90 | 141.25 | |
| Total | 235.98 | 943.69 | 1403.54 | 86.87 | 698.31 | 455.43 | |
| Ⅰ. + Ⅱ. + Ⅲ. | Ⅰ. | 434.00 | 958.97 | 2280.90 | 128.17 | 489.80 | 1019.95 |
| Ⅱ. | 22.29 | 557.55 | 268.95 | 45.10 | 310.07 | 174.60 | |
| Ⅲ. | 19.06 | 480.08 | 243.19 | 36.73 | 267.79 | 168.54 | |
| Total | 475.35 | 1996.60 | 2793.04 | 209.99 | 1067.67 | 1363.09 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




