Submitted:
03 October 2024
Posted:
07 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Review Methods
2. Basic Concepts
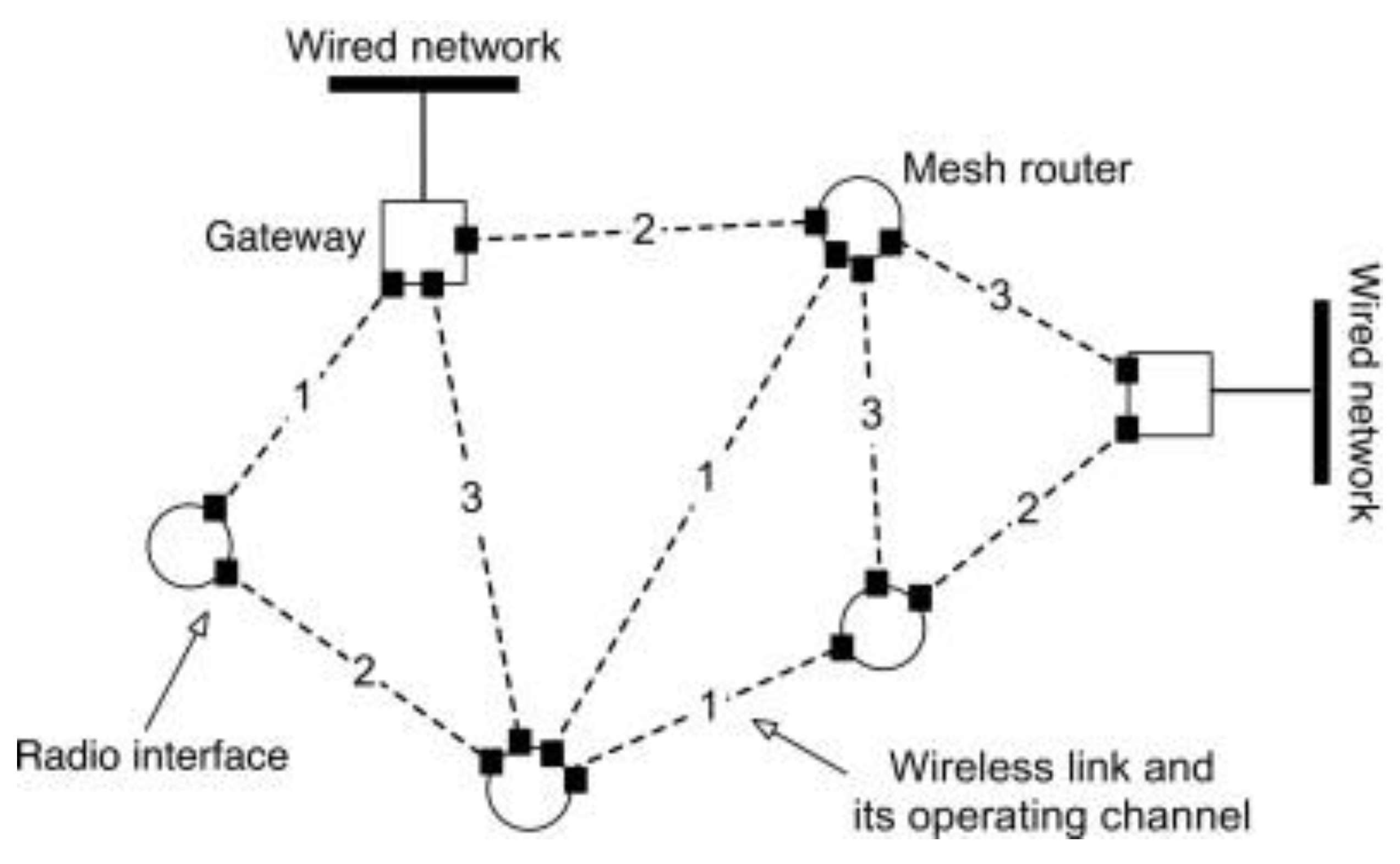
2.1. Definition of Wireless Mesh Networks
2.2. Introduction to Gateways and Their Role in Mesh Networks
2.3. Introduction to Gateway Selection Criteria
- Link Quality: The quality of the link between nodes and potential gateways is a crucial criterion. Factors such as signal strength, signal-to-noise ratio, packet loss rate, and link stability are evaluated. Gateways with stronger and more reliable links are preferred to ensure robust and stable connections.
-
Network Metrics: Several network-level metrics are considered during gateway selection:
- a.
- Network Congestion: The level of congestion in the network and at candidate gateways is assessed. Gateways with lower congestion levels are favored to avoid bottlenecks and ensure smooth data transmission.
- b.
- Available Bandwidth: The bandwidth capacity of candidate gateways is taken into account. Gateways with higher available bandwidth are preferred, especially for applications requiring high data rates.
- c.
- Hop Count: The number of hops required to reach a gateway is considered. Gateways with a lower hop count can minimize latency and reduce routing overhead.
- Quality of Service (QoS) Requirements: Specific applications or services may have unique QoS requirements, such as low latency, high throughput, or reliable connections. Gateways that can meet these requirements are prioritized during gateway selection. Differentiated QoS policies and mechanisms can be applied to ensure the desired level of service for different types of traffic.
- Network Topology and Coverage: The network topology and coverage area are crucial factors. Gateways should be strategically placed to ensure adequate coverage and connectivity to all parts of the network. The distribution of gateways should optimize network reachability, minimize transmission distances, and ensure efficient network operation.
- Security Considerations: The security aspects of gateways are taken into account during selection. Gateways should have robust security mechanisms, such as encryption, authentication, and access control, to protect the network from unauthorized access and ensure data confidentiality and integrity.
- Redundancy and Fault Tolerance: Redundant gateways can be deployed to enhance network reliability and fault tolerance. Selection criteria may consider the presence of backup gateways and their ability to seamlessly handle traffic in case of gateway failures. Redundancy helps ensure continuous network operation and reduces the impact of single points of failure.
- Energy Efficiency: The optimization of energy consumption is a crucial factor, particularly in wireless mesh networks that operate under limited resources. Gateways exhibiting lower energy consumption or higher energy efficiency are prioritized to extend the longevity of the network and reduce the energy consumption of individual nodes.
- Scalability and Manageability: Gateways should be scalable and manageable in large-scale mesh networks. The selection criteria may consider factors such as the scalability of gateway management, ease of configuration and maintenance, and compatibility with network management protocols.
- Gateway Capacity: The capacity of the gateway to handle the expected traffic load is an essential criterion. It considers factors such as processing power, memory, and storage capacity of the gateway. Gateways with higher capacity can effectively handle a larger volume of traffic without performance degradation.
- Cost and Deployment Constraints: The cost of deploying and maintaining gateways is a practical consideration. The selection criteria may take into account the cost of the gateway hardware, installation, configuration, and ongoing operational expenses. Additionally, physical constraints, such as the availability of power supply and suitable locations for gateway placement, can also influence gateway selection.
- Traffic Pattern Analysis: Analyzing the traffic patterns and characteristics of the wireless mesh network can be used as a criterion for gateway selection. By considering the traffic flow, volume, and communication patterns, gateways can be strategically selected to optimize routing efficiency and reduce network congestion.
- Application Requirements: Different applications within the wireless mesh network may have specific requirements that need to be considered during gateway selection. For example, real-time applications such as voice or video streaming may require low latency and high bandwidth, while data transfer applications may prioritize reliable connections and efficient throughput.
- Network Stability and Resilience: Gateway selection criteria can include evaluating the stability and resilience of potential gateways. Gateways that have a history of stable performance, minimal downtime, and resilience to network disruptions are preferred to ensure continuous network operation and minimize service interruptions.
- Policy-Based Selection: Gateway selection can be influenced by policy-based rules and preferences. Administrators can define policies based on factors such as cost, performance, security, or specific routing requirements. These policies guide the selection process, allowing gateways to be chosen based on predefined rules.
- Compatibility and Interoperability: The compatibility and interoperability of gateways with existing network infrastructure and protocols are important criteria. Gateways should support the necessary communication protocols, standards, and interfaces to seamlessly integrate with the wireless mesh network and external networks.
- Vendor Reliability and Support: The reliability and support provided by gateway vendors can be considered during selection. Reputation, track record, and vendor support capabilities can play a role in ensuring that the selected gateways are backed by reliable manufacturers and have access to timely technical assistance if needed.
3. Gateway Selection
3.1. Gateway Selection Algorithms
3.2. Multi-Criteria Determination Making (MCDM)
3.3. Load Balancing Algorithms
3.4. Game Theory
3.5. Reinforcement Learning Algorithms
3.6. Q-Learning
3.7. Genetic Algorithms
- Representation: The first step in applying genetic algorithms is to define the representation of the gateway selection problem. Each individual in the population represents a potential gateway selection policy. The chromosome of an individual can be encoded as a binary string, with each gene indicating the selection or non-selection of a particular gateway [121,122].
- Fitness Evaluation: The fitness of each individual in the population is evaluated based on predefined metrics, such as network throughput, latency, or load balancing. Fitness evaluation involves simulating the network and measuring the performance of the selected gateways based on the encoded policy [123,124].
- Genetic Operators: Genetic algorithms employ genetic operators, including selection, crossover, and mutation, to evolve the population and generate new generations of individuals. Selection biases the selection of individuals with higher fitness, crossover combines the genetic material of two individuals to produce offspring, and mutation introduces random changes to maintain diversity in the population [124,125].
3.8. Machine Learning-Based Algorithms
3.9. Supervised Learning
4. Statistical and Predictive-Based Gateway Selection Algorithms
4.1. Statistical Analysis:
4.2. Predictive Modeling
4.3. Issues and Challenges
- ➢
- Scalability: One of the primary challenges in gateway selection for WMNs is ensuring scalability. As the network grows and the number of mesh nodes increases, the gateway must have the capacity to handle the growing traffic and provide efficient routing between the mesh network and external networks. Selecting a gateway that can scale with the network's growth is crucial to avoid performance bottlenecks and ensure smooth operations.
- ➢
- Network Performance: Gateway selection plays a vital role in maintaining network performance in WMNs. The gateway should have sufficient processing power, memory, and bandwidth to handle the network's traffic demands. Inadequate gateway performance can lead to delays, packet loss, or degraded network performance, impacting the overall user experience.
- ➢
- Quality of Service (QoS): WMNs often support diverse applications with varying QoS requirements, such as real-time multimedia streaming, voice communication, or data transfer. Gateway selection should consider the ability to prioritize and manage different types of traffic to ensure appropriate QoS levels. The gateway must support QoS mechanisms that prioritize critical traffic and allocate network resources accordingly.
- ➢
- Interoperability: WMNs can comprise nodes from different vendors or operate on different wireless standards. Ensuring interoperability between the gateway and the mesh nodes is essential for seamless communication and network integration. The selected gateway should support the necessary wireless standards and protocols used by the mesh nodes to facilitate interoperability.
- ➢
- Security: Security is a critical concern in gateway selection for WMNs. Gateways serve as the entry points between the mesh network and external networks, making them potential targets for attacks. The selected gateway should have robust security features, such as strong authentication, encryption, intrusion detection, and secure routing protocols, to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, or network intrusions.
- ➢
- Power Consumption and Energy Efficiency: In WMNs, nodes may be powered by limited energy sources, such as batteries or solar panels. The gateway should be energy-efficient to minimize power consumption and maximize the network's overall lifespan. Selecting a gateway with low power requirements and power-saving features can contribute to the sustainability and longevity of the WMN.
- ➢
- Deployment and Management: Gateway selection should also consider factors related to deployment and management. The gateway should be easy to install, conFigure , and manage, as it plays a central role in network operations. Additionally, remote management capabilities, centralized monitoring, and configuration management tools are beneficial for efficient administration and maintenance of the gateway.
- ➢
- Cost: Cost is always a consideration in gateway selection. The selected gateway should provide a balance between cost and the required functionality. While it is important to invest in a reliable and secure gateway, organizations need to consider their budgetary constraints and evaluate the cost-effectiveness of the chosen solution.
4.4. Security Issues in Gateway Selection
- ➢
- Authentication and Authorization: Gateways in WMNs should enforce strong authentication and authorization mechanisms to ensure that only authorized nodes can connect to the network. Weak or compromised authentication can lead to unauthorized access and potential security breaches.
- ➢
- Secure Key Management: WMNs often use encryption to protect the confidentiality of data transmitted between nodes. Gateways play a crucial role in key management for secure communication. It is important to select gateways that implement robust key management protocols to ensure secure generation, distribution, and revocation of encryption keys.
- ➢
- Secure Routing: Gateways in WMNs are responsible for routing traffic between the mesh network and external networks or the internet. Secure routing protocols should be implemented to protect against attacks such as spoofing, tampering, or hijacking of routing information. Gateways should employ secure routing protocols, such as the Secure Hybrid Wireless Mesh Protocol (SHWMRP), to ensure the integrity and authenticity of routing information.
- ➢
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: Gateways in WMNs are potential targets for DoS attacks, which can disrupt network operations by overwhelming the gateway with excessive traffic or exploiting vulnerabilities. Gateways should have mechanisms in place to detect and mitigate DoS attacks, such as rate limiting, traffic shaping, or intrusion prevention systems (IPS).
- ➢
- Physical Security: Gateways in WMNs may be deployed in outdoor or publicly accessible areas, making them vulnerable to physical attacks. Physical security measures, such as tamper-resistant enclosures, video surveillance, or access control mechanisms, should be considered to protect the gateways from unauthorized access or tampering.
- ➢
- Firmware and Software Security: Gateways in WMNs run firmware or software that may have vulnerabilities. It is crucial to select gateways from trusted vendors that regularly release security patches and updates to address any identified vulnerabilities. Additionally, gateways should have secure update mechanisms to ensure that firmware or software updates are obtained from authenticated and trusted sources.
- ➢
- Monitoring and Intrusion Detection: Gateways should have monitoring and intrusion detection capabilities to detect and respond to security incidents promptly. This includes monitoring network traffic, detecting anomalies, and employing intrusion detection systems (IDS) or intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to identify and mitigate potential threats.
- ➢
- Compliance Considerations: Depending on the specific industry or regulatory requirements, gateways in WMNs may need to comply with specific security standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) guidelines. It is essential to select gateways that meet the required compliance standards.
- ➢
- Vendor Trustworthiness: The trustworthiness of gateway vendors is crucial in ensuring the security of WMNs. It is important to choose vendors with a strong reputation in security, timely security updates, and a commitment to addressing vulnerabilities promptly.
5. Conclusion and Recommendations
5.1. Key Points and Areas for Further Research
6. Recommendations for Future Research
Funding
References
- Marco Di Felice, Kaushik Roy Chowdhury, Andreas Kassler, Luciano Bononi (2011). Adaptive Sensing Scheduling and Spectrum Selection in Cognitive Wireless Mesh Networks. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Xuecai Bao, Wenqun Tan, Jugen Nie, Changlong Lu, Guanglang Jin(2014). Design of logical topology with K-connected constraints and channel assignment for multi-radio wireless mesh networks. Communication system. [CrossRef]
- Mohsen Jahanshahi, Mehdi Dehghan, Mohammad Reza Meybodi (2016). A cross-layer optimization framework for joint channel assignment and multicast routing in multi-channel multi-radio wireless mesh networks. International Journal of Computer Mathematics. [CrossRef]
- Carlos Ferreira, Susana Sargento, Arnaldo Oliveira (2017). An architecture for a learning-based autonomic decision system. Journal of Computational Science. [CrossRef]
- Majid Asadi Shahmirzadi, Mehdi Dehghan, Abdorasoul Ghasemi (2017). On the Load Balancing of Multicast Routing in Multi-Channel Multi-Radio Wireless Mesh Networks with Multiple Gateways. International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security.
- Arash Bozorgchenani, Mohsen Jahanshahi (2017). A Novel Reliability and Traffic Aware Gateway Selection Scheme in Wireless Mesh Networks. Wireless Personal Communications. [CrossRef]
- Yuan Chai, Wenxiao Shi, Tianhe Shi (2017). Load-aware cooperative hybrid routing protocol in hybrid wireless mesh networks. AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications. [CrossRef]
- N. N. Krishnaveni, K. Chitra (2017). CFTLB: a novel cross-layer fault tolerant and load balancing protocol for WMN. International Journal of Electronics. [CrossRef]
- Michael Rademacher, Karl Jonas, Florian Siebertz, Adam Rzyska, Moritz Schlebusch, Markus Kessel (2017). The Computer Journal, Volume 60, Issue 10, October 2017, Pages 1520–1535. [CrossRef]
- Yan Feng, Xingxing Wu, Yaoke Hu (2017). Forecasting Research on the Wireless Mesh Network Throughput Based on the Support Vector Machine. Wireless Personal Communications. [CrossRef]
- Mustapha Boushaba, Abdelhakim Hafid, Michel Gendreau (2017). Node stability-based routing in Wireless Mesh Networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications. [CrossRef]
- Khalid Mahmood, Babar Nazir, Iftikhar Ahmad Khan, Nadir Shah (2017). Search-based routing in wireless mesh network. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking. [CrossRef]
- G. Vijaya Kumar and C. Shoba Bindu (2017). Liberal method of access point selection in wireless mesh networks. International Journal of Communication Networks and Distributed Systems. [CrossRef]
- Jihong Wang, Wenxiao Shi (2017). Joint multicast routing and channel assignment for multi-radio multi-channel wireless mesh networks with hybrid traffic. Journal of Network and Computer Applications. [CrossRef]
- Kagan Gokbayrak, E. Alper Yıldırım(2017). Exact and heuristic approaches based on noninterfering transmissions for joint gateway selection, time slot allocation, routing and power control for wireless mesh networks. Computers & Operations Research. [CrossRef]
- Liang Zhao, Ahmed Al-Dubai, Xianwei Li, Guolong Chen, Geyong Min (2017). A new efficient cross-layer relay node selection model for Wireless Community Mesh Networks. Computers & Electrical Engineering. [CrossRef]
- Jinqiang Yu, Wai-Choong Wong (2017). A Network Resource Management Framework for Wireless Mesh Networks. Wireless Personal Communications. [CrossRef]
- Saleem Iqbal, Abdul Hanan Abdullah, Kashif Naseer Qureshi (2017). Channel quality and utilization metric for interference estimation in Wireless Mesh Networks. Computers, Electrical Engineering. [CrossRef]
- Jae-Wan Kim, Sang-Tae Kim & Yang-Ick Joo (2017). Distributed Channel Assignment Algorithm Based on Traffic Awareness in Wireless Mesh Networks. Wireless Personal Communications. [CrossRef]
- Dibakar Chakraborty, Khumbar Debbarma(2017). Q-CAR: an intelligent solution for joint QoS multicast routing and channel assignment in multichannel multiradio wireless mesh networks. Applied Intelligence. [CrossRef]
- Zhufang Kuang, Zhigang Chen (2017). A high reliability and low latency routing algorithm in cognitive wireless mesh networks. International Journal of Communication Networks and Distributed Systems. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Yong, Liu Han, Ma Wenjie, Liu Kai-ming, Li Nan (2017). D-LAJOA: DYNAMIC LOAD-AWARE JOINT OPTIMAL ALGORITHM IN MULTI-RADIO MULTI-CHANNEL WIRELESS MESH NETWORKS.
- Xiaojun Wang, Lingzhen Meng, Jiangfei Peng and Xiaoshu Chen (2017). A joint routing and channel assignment in multi-radio multi-channel wireless mesh networks. International Journal of Sensor Networks. [CrossRef]
- Yuan Chai, Wenxiao Shi, Tianhe Shi, Xiaoping Yang (2017). An efficient cooperative hybrid routing protocol for hybrid wireless mesh networks. Wireless Networks. [CrossRef]
- G. Audrito, A.A. G. Audrito, A.A. Bertossi, A. Navarra, C.M. Pinotti(2017). Maximizing the overall end-user satisfaction of data broadcast in wireless mesh networks. Journal of Discrete Algorithms. [CrossRef]
- Jamal, N. Al-Karaki, Ghada A. Al-Mashaqbeh, Sameer Bataineh(2017). Routing protocols in wireless mesh networks: a survey. International Journal of Information and Communication Technology. [CrossRef]
- L. M. Kola, M. Velempini (2018). The Design and Implementation of the XWCETT Routing Algorithm in Cognitive Radio Based Wireless Mesh Networks. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing. [CrossRef]
- Jingyang Lu, Xingyu Xiang, Dan Shen; Genshe Chen, Ning Chen, Erik Blasch, Khanh Pham, Yu ChenArtificial (2018). intelligence based directional mesh network design for spectrum efficiency. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Khulan Batbaya,Emmanouil Dimogerontakis,Roc Meseguer,Esunly Medina, Rodrigo M. Santos (2018). The RIMO Gateway Selection Approach for Mesh Networks: Towards a Global Internet Access for All †. Proceedings. [CrossRef]
- Majid Asadi Shahmirzadi, Mehdi Dehghan, Abdulrasoul Ghasemi(2018). An optimization framework for multicasting in MCMR wireless mesh network with partially overlapping channels. Wireless Networks. [CrossRef]
- Tran Anh Quang Pham, Kamal Deep Singh, Juan Antonio Rodríguez-Aguilar, Gauthier Picard, Kandaraj Piamrat, Jesús Cerquides, César Viho (2018). AD3-GLaM: A cooperative distributed QoE-based approach for SVC video streaming over wireless mesh networks. Ad Hoc Networks. [CrossRef]
- Wenxiao Shi, Shaobo Wang, Zhuo Wang, Endong Wang (2018). An efficient channel assignment algorithm for multicast wireless mesh networks. AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications. [CrossRef]
- Zeineb Lazrag, Monia Hamdi, Mourad Zaied (2018). Bi-objective GA for Cost-Effective and Delay-Aware Gateway Placement in Wireless Mesh Networks. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Tran Anh Quang Pham, Kamal Deep Singh, Juan Antonio Rodríguez-Aguilar, Gauthier Picard, Kandaraj Piamrat, Jesús Cerquides, César Viho (2018). AD3-GLaM: A cooperative distributed QoE-based approach for SVC video streaming over wireless mesh networks. Ad Hoc Networks. [CrossRef]
- Ilir Shinko, Vladi Kolici, Ryoichiro Obukata, Admir Barolli, Tetsuya Oda, Leonard Barolli (2018). Performance analysis of a genetic algorithm-based system for wireless mesh networks considering exponential and Weibull distributions, DCF and EDCA, and different number of flows. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing. [CrossRef]
- Leili Farzinvash (2018). A novel approach for multicast call acceptance in multi-channel multi-radio wireless mesh networks. Wireless Networks. [CrossRef]
- Maheen Islam, Md. Abdur Razzaque, Md. Mamun-Or-Rashid, Mohammad Mehedi Hassan, Abdulhameed Alelaiwi, Atif Alamri (2018). Traffic engineering in cognitive mesh networks: Joint link-channel selection and power allocation. Computer Communications. [CrossRef]
- Jilong Li, Bhagya Nathali Silva, Muhammad Diyan, Zhenbo Cao, Kijun Han (2018). A clustering-based routing algorithm in IoT aware Wireless Mesh Networks. Sustainable Cities and Society. [CrossRef]
- Kagan Gokbayrak(2018). Robust gateway placement in wireless mesh networks. Computers & Operations Research. [CrossRef]
- Y. Mallikarjuna Rao, M. V. Y. Mallikarjuna Rao, M. V. Subramanyam, K. Satya Prasad (2018). Cluster-based mobility management algorithms for wireless mesh networks. Communication system. [CrossRef]
- Fuad, A. Ghaleb, Maznah Kamat, Mazleena Salleh, Mohd. Foad Rohani, Shukor Abd Razak, Mohd Arief Shah (2018). Fairness of Channel Assignment Algorithm Based on Weighted Links Ranking Scheme for Wireless Mesh Network. Fairness of Channel Assignment Algorithm Based on Weighted Links Ranking Scheme for Wireless Mesh Network. [CrossRef]
- Y. Mallikarjuna Rao, M. V. Subramanyam, K. Satya Prasad (2018). Cluster Based Hybrid Routing Protocol for Wireless Mesh Networks. Wireless Personal Communications. [CrossRef]
- Wenxiao Shi, Shaobo Wang, Zhuo Wang, Ruidong Zhang (2018). An Efficient Multicast Routing Algorithm for Wireless Mesh Networks. An Efficient Multicast Routing Algorithm for Wireless Mesh Networks. [CrossRef]
- Cheng-Han Lin, Ce-Kuen Shieh, Wen-Shyang Hwang, Wei-Tsang Huang (2018). Proportional bandwidth allocation with consideration of delay constraint over IEEE 802.11e-based wireless mesh networks.
- Vinícius, N. Medeiros, Bruno Silvestre, Vinicius C. M. Borges (2019). Multi-objective routing aware of mixed IoT traffic for low-cost wireless Backhauls.
- G. P. Raja, S. Mangai (2019). Firefly load balancing based energy optimized routing for multimedia data delivery in wireless mesh network. Cluster Computing. [CrossRef]
- Feng Zeng, Nan Zhao, Wenjia Li (2019). Joint interference optimization and user satisfaction improvement for multicast routing and channel assignment in wireless mesh networks. Cluster Computing. [CrossRef]
- Samurdhi Karunaratne, Haris Galanin (2019). An Overview of Machine Learning Approaches in Wireless Mesh Networks. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- R. Parvanak, M. Jahanshahi, M. Dehghan(2019). A cross-layer learning automata-based gateway selection method in multi-radio multi-channel wireless mesh networks. Computing. [CrossRef]
- Amin Erfanian Araqi, Behrad Mahboobi (2019). Joint Channel Assignment and Multicast Routing in Multi-Channel Multi-Radio Wireless Mesh Networks Based on Q-Learning. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Robert singh, D. Devaraj, R. Narmatha Banu (2019). Genetic algorithm-based optimization of load-balanced routing for AMI with wireless mesh networks. Applied Soft Computing. [CrossRef]
- Nandini Balusu, Suresh Pabboju, G Narsimha (2019). An Intelligent Channel Assignment Approach for Minimum Interference in Wireless Mesh Networks Using Learning Automata and Genetic Algorithms. Wireless Personal Communications. [CrossRef]
- B. Prakash, S. Jayashri, T. S. Karthik (2019). An Intelligent Channel Assignment Approach for Minimum Interference in Wireless Mesh Networks Using Learning Automata and Genetic Algorithms A hybrid genetic artificial neural network (G-ANN) algorithm for optimization of energy component in a wireless mesh network toward green computing. Soft Computing. [CrossRef]
- Esmaeil Nik Maleki, Ghasem Mirjalily (2019). Cross layer resource allocation for fault-tolerant topology control in wireless mesh networks based on genetic algorithm. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking. [CrossRef]
- Lamri Sayad, Louiza Bouallouche-Medjkoune, Djamil Aissani (2019). An Electromagnetism-like mechanism algorithm for the router node placement in wireless mesh networks. Soft Computing. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad Usama, Junaid Qadir, Aunn Raza, Hunain Arif, Kok-lim Alvin Yau, Yehia Elkhatib, Amir Hussain (2019). Unsupervised Machine Learning for Networking: Techniques, Applications and Research Challenges. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Samurdhi Karunaratne, Ramy Atawia, Erma Perenda, Haris Gacanin (2019). Artificial Intelligence Driven Optimization of Channel and Location in Wireless Networks. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Antonio Cilfone, Luca Davoli,Laura Belli,Gianluigi Ferrari (2019). Wireless Mesh Networking: An IoT-Oriented Perspective Survey on Relevant Technologies. Future Internet. [CrossRef]
- Lu Yang, Yujie Li, Shiyan Wang, Haoyue Xiao (2019). Interference-Avoid Channel Assignment for Multi-Radio Multi-Channel Wireless Mesh Networks with Hybrid Traffic. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Anbu Ananth, C; Suresh, T; Prabakaran, G (2019). Efficient Load Balancing Techniques for Wireless Mesh Networks Based on Multi-Path Optimized Link State Routing Protocol. Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience. [CrossRef]
- Akram Hakiri, Aniruddha Gokhale, Pascal Berthou (2019). Software-defined wireless mesh networking for reliable and real-time smart city cyber physical applications. Software-defined wireless mesh networking for reliable and real-time smart city cyber physical applications. [CrossRef]
- Leili Farzinvash (2019). Online multicast tree construction with bandwidth and delay constraints in multi-channel multi-radio wireless mesh networks. Telecommunication Systems.
- Chun-Cheng Lin, Shu-Huai Chang, Chien-Liang Chen (2020). Link Scheduling for Wireless Mesh Networks Considering Gateway Feature. EAI Endorsed Transactions on Internet of Things. [CrossRef]
- Jianjun Jing, Kailing Yao, Yuhua Xu, Xin Liu, Yuli Zhang, Changhua Yao (2020). QoE-oriented partially overlapping channel access in wireless networks: a game-theoretic learning approach. Wireless Networks. [CrossRef]
- Syed Sherjeel, A. Gilani, Amir Qayyum, Rao Naveed Bin Rais, Mukhtiar Bano (2020). SDNMesh: An SDN Based Routing Architecture for Wireless Mesh Networks. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Mouna Naravani, Narayan D.G., Sumedha Shinde, Mohammed Moin Mulla (2020). A Cross-Layer Routing Metric with Link Prediction in Wireless Mesh Networks. Procedia Computer Science. [CrossRef]
- Admir Barolli, Kevin Bylykbashi, Ermioni Qafzezi, Shinji Sakamoto, Leonard Barolli.
- Jawad Manzoor, Llorenç Cerdà-Alabern, Ramin Sadre, Idilio Drago (2020). On the Performance of QUIC over Wireless Mesh Networks. Journal of Network and Systems Management. [CrossRef]
- Amar Singh, Shakti Kumar, Ajay Singh, Sukhbir S. (2020). Walia Parallel 3-Parent Genetic Algorithm with Application to Routing in Wireless Mesh Networks. Implementations and Applications of Machine Learning. [CrossRef]
- Syed Sherjeel, A. Gilani, Amir Qayyum, Rao Naveed Bin Rais, Mukhtiar Bano (2020). SDNMesh: An SDN Based Routing Architecture for Wireless Mesh Networks. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Lamri Sayad, Louiza Bouallouche-Medjkoune, Djamil Aissani (2020). A Chemical Reaction Algorithm to Solve the Router Node Placement in Wireless Mesh Networks. Mobile Networks and Applications volume. [CrossRef]
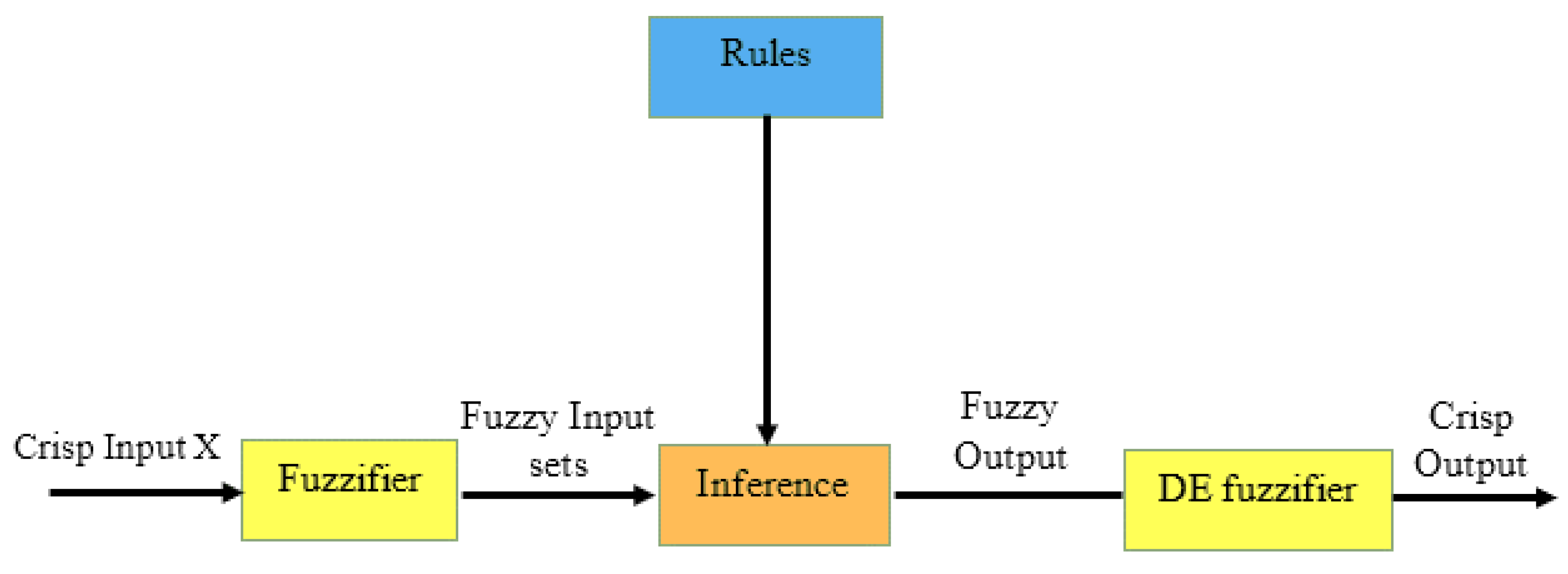
- Wajahat Maqbool, S. K. Syed-Yusof, N. M. Abdul Latiff, Bushra Naeem, Bilal Shabbir, N. N. Nik Abdul Malik (2020). Optimal End-to-End Path Selection Mechanism for CR-WMNs Based on Fuzzy Logic System. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Nandini Balusu (2020). Swarm Optimization Based Gravitational Search Approach for Channel Assignment in MCMR Wireless Mesh Network.
- Isaac Machorro-Cano,Giner Alor-Hernández,Mario Andrés Paredes-Valverde,Lisbeth Rodríguez-Mazahua,José Luis Sánchez-Cervantes, José Oscar Olmedo-Aguirre(2020). HEMS-IoT: A Big Data and Machine Learning-Based Smart Home System for Energy Saving. Energies. [CrossRef]
- G.P. Raja, S. Mangai (2020). Investigation on optimization, prioritizing and weight allocation techniques for load balancing and controlling multimedia traffic in wireless mesh network. International Journal of Business Information Systems. [CrossRef]
- Narayan, D.G. , Mouna Naravani, Sumedha Shinde (2020). Cross-layer Optimization for Video Transmission using MDC in Wireless Mesh Networks. Procedia Computer Science. [CrossRef]
- Fuad, A. Ghaleb, Bander Ali Saleh Al-Rimy, Wadii Boulila, Faisal Saeed,Maznah Kamat,Mohd. Foad Rohani,Shukor Abd Razak(2021). Fairness-Oriented Semichaotic Genetic Algorithm-Based Channel Assignment Technique for Node Starvation Problem in Wireless Mesh Networks. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience. [CrossRef]
- Satish BHOJANNAWAR, Shrinivas MANGALWEDE (2021). Interference, Traffic Load and Delay Aware Routing Metric for Wireless Mesh Network. Advances in Electrical and Computer Engineering. [CrossRef]
- Di Zhou, Min Sheng, Jiaxin Wu, Jiandong Li, Zhu Han, Kyung Hee (2021). Gateway Placement in Integrated Satellite–Terrestrial Networks: Supporting Communications and Internet of Remote Things. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Diana Jeba Jingle, P. Mano Paul (2021). A collaborative defense protocol against collaborative attacks in wireless mesh networks. International Journal of Enterprise Network Management. [CrossRef]
- Shasha Zhao, Gan Yu (2021). Channel allocation optimization algorithm for hybrid wireless mesh networks for information physical fusion system. Computer Communications. [CrossRef]
- Fuad, A. Ghaleb, Bander Ali Saleh Al-Rimy, Wadii Boulila, Faisal aeed,Maznah Kamat,Mohd. Foad Rohani, Shukor Abd Razak (2021). Fairness-Oriented Semichaotic Genetic Algorithm-Based Channel Assignment Technique for Node Starvation Problem in Wireless Mesh Networks. Networking and Internet Architecture. [CrossRef]
- Amel Faiza Tandjaoui, Mejdi Kaddour(2021). A Cross Layer Optimization Model for Investigating the Impact of Partially Overlapping Channels on Wireless Mesh Networks Capacity. International Journal of Wireless Information Networks. [CrossRef]
- Iyad Lahsen-Cherif, Lynda Zitoune, Véronique Vèque(2021). Energy Efficient Routing for Wireless Mesh Networks with Directional Antennas: When Q-learning meets Ant systems. Ad Hoc Networks. [CrossRef]
- Khamxay Leevangtou, Hideya Ochiai, Chaodit Aswakul (2021). Application of Q-Learning in Routing of Software-Defined Wireless Mesh Network. IEEJ. [CrossRef]
- Ankita Singh, Shiv Prakash, Sudhakar Singh (2021). Optimization of reinforcement routing for wireless mesh network using machine learning and high-performance computing. Concurrency and computation. [CrossRef]
- INTERFERENCE AND LOAD BALANCING ROUTING, METRICS USED IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORK: NEW, TREND AND CHALLENGES (2021). INTERFERENCE AND LOAD BALANCING ROUTING METRICS USED IN WIRELESS MESH NETWORK: NEW TREND AND CHALLENGES. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology.
- Fuad, A. Ghaleb, Bander Ali Saleh Al-Rimy,Wadii Boulila, Faisal Saeed,Maznah Kamat,Mohd. Foad Rohani, Shukor Abd Razak (2021). Fairness-Oriented Semichaotic Genetic Algorithm-Based Channel Assignment Technique for Node Starvation Problem in Wireless Mesh Networks. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience. [CrossRef]
- Mariusz Wzorek, Cyrille Berger, Patrick Doherty (2021). Router and gateway node placement in wireless mesh networks for emergency rescue scenarios. Autonomous Intelligent Systems. [CrossRef]
- Nabil Abdelkader Nouri, Zibouda Aliouat, Abdenacer Naouri,Soufiene Ali Hassak (2021). Accelerated PSO algorithm applied to client’s coverage and routers connectivity in wireless mesh networks. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing. [CrossRef]
- M Kiran Sastry, Arshad Ahmad Khan Mohammad, Arif Mohammad Abdul (2021). Optimized Energy-efficient Load Balance Routing Protocol for Wireless Mesh Networks. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications.
- Karunya Rathan, SusaiMichael Emalda Roslin, Easpin Brumancia (2021). MO-CSO-based load-balanced routing in MRMC WMN. IET communication. [CrossRef]
- Yanjun Yang, Aimin Liu, Hongwei Xin, Jianguo Wang, Xin Yu, Wen Zhang (2021). Deployment optimization of wireless mesh networks in wind turbine condition monitoring system. Wireless Networks.
- Rohit Kumar, Venkanna U., Vivek Tiwari (2021). Opt-ACM: An Optimized load balancing based Admission Control Mechanism for Software Defined Hybrid Wireless based IoT (SDHW-IoT) network. Computer Networks. [CrossRef]
- Ángeles Verdejo Espinosa, José Lopez Ruiz,Francisco Mata Mata, Macarena Espinilla Estevez (2021). Application of IoT in Healthcare: Keys to Implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals. Sensors. [CrossRef]
- Smita Mahajan, R. Harikrishnan, Ketan Kotecha (2022). Adaptive Routing in Wireless Mesh Networks Using Hybrid Reinforcement Learning Algorithm. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Saleem Iqbal, Kashif Naseer Qureshi, Saqib Majeed, Kayhan Zrar Ghafoor, Gwanggil Jeon (2022). Partially Overlapped Channel Assignment for Cloud-Based Heterogeneous Cellular and Mesh Networks. Wireless Personal Communications. [CrossRef]
- Satish, S. Bhojannawar, Shrinivas R. Managalwede (2022). Distributed and Dynamic Channel Assignment Schemes for Wireless Mesh Network. Computer Network and Information Security. [CrossRef]
- Fawaz, S. Al-Anzi (2022). Design and analysis of intrusion detection systems for wireless mesh networks. Digital Communications and Networks. [CrossRef]
- Thuy-Van, T. Duong, Le Huu Binh, Vuong M. Ngo (2022). Reinforcement learning for QoS-guaranteed intelligent routing in Wireless Mesh Networks with heavy traffic load. ICT Express. [CrossRef]
- Farid Bavifard, Mohammad Kheyrandish, Mohammad Mosleh(2022). A new approach based on game theory to reflect meta-cluster dependencies into VoIP attack detection using ensemble clustering. Cluster Computing. [CrossRef]
- Shabir Ali, Mayank Pandey, Neeraj Tyagi (2022). SDFog-Mesh: A software-defined fog computing architecture over wireless mesh networks for semi-permanent smart environments. Computer Networks. [CrossRef]
- Admir Barolli, Kevin Bylykbashi, Ermioni Qafzezi, Shinji Sakamoto, Leonard Barolli (2022). A comparison study of Weibull, normal and Boulevard distributions for wireless mesh networks considering different router replacement methods by a hybrid intelligent simulation system. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing. [CrossRef]
- Sylia Mekhmoukh Taleb, Yassine Meraihi, Asma Benmessaoud Gabis, Seyedali Mirjalili, Amar Ramdane-Cherif (2022). Nodes placement in wireless mesh networks using optimization approaches: a survey. Neural Computing and Applications. [CrossRef]
- Admir Barolli, Kevin Bylykbashi, Ermioni Qafzezi, Shinji Sakamoto, Leonard Barolli (2022). A hybrid intelligent system based on particle swarm optimization and distributed genetic algorithm for WMNs: a comparison study of boulevard and stadium distributions considering different router replacement methods and load balancing. Wireless Networks. [CrossRef]
- Admir Barolli,Shinji SakamotoKevin Bylykbashi, Leonard Barolli (2022). A Hybrid Intelligent Simulation System for Building IoT Networks: Performance Comparison of Different Router Replacement Methods for WMNs Considering Stadium Distribution of IoT Devices. Sensor. [CrossRef]
- Ohara Seiji, Barolli Admir, Ampririt Phudit, Sakamoto Shinji, Matsuo Keita d, Barolli Leonard (2022). A Hybrid Intelligent Simulation System for Constructing IoT Networks: Performance Evaluation of WMN-PSODGA Simulation System Considering Different Router Replacement Methods. Internet of Things. [CrossRef]
- Shubhangi Kharche, Sanjay Pawar (2022). Optimizing network lifetime and QoS in 6LoWPANs using deep neural networks. Computers & Electrical Engineering. [CrossRef]
- Md. Iftekhar Hussain, Nurzaman Ahmed, Md. Zaved Iqubal Ahmed, Nityananda Sarma (2022). QoS Provisioning in Wireless Mesh Networks: A Survey. Wireless Personal Communications. [CrossRef]
- C. S. Anita, R. Sasikumar (2022). Neighbor Coverage and Bandwidth Aware Multiple Disjoint Path Discovery in Wireless Mesh Networks. Wireless Personal Communications. [CrossRef]
- Niloofar Tahmasebi-Pouya, Mehdi-Agha Sarram, Seyed-Akbar Mostafavi (2022). Load Balancing in Mobile Edge Computing: A Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Ganesh Reddy Karri, A. V. Prabu, Sidheswar Routray, D. Sumathi, S. Rajasoundaran, Amrit Mukherjee, Pushpita Chatterjee, Waleed Alnumay (2022). Efficient Key Management Mechanism with Trusted Gateways for Wireless Mesh Networks. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing. [CrossRef]
- Admir Barolli, Kevin Bylykbashi, Ermioni Qafzezi, Shinji Sakamoto, Leonard Barolli(2022). Implementation of roulette wheel and random selection methods in a hybrid intelligent system: A comparison study for two Islands and Subway distributions considering different router replacement methods. Applied Soft Computing. [CrossRef]
- Jianwei Zhang, Chenwei Zhao, Zengwei Zheng, Jianping Cai (2022). SR-WMN: Online Network Throughput Optimization in Wireless Mesh Networks with Segment Routing. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Daud Abdul, Jiang Wenqi (2022). Evaluating appropriate communication technology for smart grid by using a comprehensive decision-making approach fuzzy TOPSIS. Soft Computing. [CrossRef]
- Maraj Uddin Ahmed Siddiqui, Faizan Qamar,Muhammad Tayyab,MHD Nour Hindia,Quang Ngoc Nguyen,Rosilah Hassan (2022). Mobility Management Issues and Solutions in 5G-and-Beyond Networks: A Comprehensive Review. Electronics. [CrossRef]
- Moses Effiong Ekpenyong, Daniel Ekpenyong Asuquo, Ifiok James Udo, Samuel Akpan Robinson, Francis Funebi Ijebu (2022). IPv6 Routing Protocol Enhancements over Low-power and Lossy Networks for IoT Applications: A Systematic Review. New Review of Information Networking. [CrossRef]
- Rashmi Kushwah (2023). A novel traffic aware reliable gateway selection in wireless mesh network. Cluster Computing. [CrossRef]
- Sylia Mekhmoukh Taleb, Yassine Meraihi, Seyedali Mirjalili, Dalila Acheli, Amar Ramdane-Cherif, Asma Benmessaoud Gabis (2023). Mesh Router Nodes Placement for Wireless Mesh Networks Based on an Enhanced Moth–Flame Optimization Algorithm. Mobile Networks and Applications. [CrossRef]
- Narayana Rao Appini, A. Rajasekhar Reddy (2023). Joint Channel Assignment and Bandwidth Reservation Using Improved FireFly Algorithm (IFA) in Wireless Mesh Networks (WMN). Wireless Personal Communications. [CrossRef]
- Tetsuya Oda (2023). A Delaunay Edges and Simulated Annealing-Based Integrated Approach for Mesh Router Placement Optimization in Wireless Mesh Networks. Sensors. [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz Salama, Achilleas Stergioulis, Ali M. Hayajneh, Syed Ali Raza Zaidi, Des McLernon, Ian Robertson (2023). Decentralized Federated Learning Over Slotted ALOHA Wireless Mesh Networking. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Nitasha Sahani Ruoxi Zhu Jin-Hee Cho Chen-Ching Liu (2023). Machine Learning-based Intrusion Detection for Smart Grid Computing: A Survey.ACM Transactions on Cyber-Physical Systems. [CrossRef]
- Ankita Singh, Sudhakar Singh, Shiv Prakash (2023). Critical Comparative Analysis and Recommendation in MAC Protocols for Wireless Mesh Networks Using Multi-Objective Optimization and Statistical Testing. Wireless Personal Communications volume. [CrossRef]
- Odongo Steven Eyobu, Kamwesigye Edwinah (2023). A Deep Learning-based Routing Approach for Wireless Mesh Backbone Networks. IEEE. [CrossRef]
| Title | Writers | Year | Research goal | Methodology | Result | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| logical topology design for K-connected channel allocation and multi-radio wireless mesh networks. | Xuecai Bao et al | 2014 | Determine the minimum and maximum numbers of channels that may be allocated after analyzing the factors impacting channel assignment performance. | k-connected logical topology | Numerical results confirm that our proposed channel assignment greatly improves network performance in the context of limited radio interfaces. | |
| Wireless Mesh Networks with a Distributed Channel Assignment Algorithm that Considers Traffic | Jae-Wan Kim, et al | 2017 | To improve performance, learn more about the multi-channel assignment system. | a new method of WMN channel allocation based on the use of many channels and interfaces | Results show that the proposed architecture improves network throughput in compared to the status quo. | |
| In MIMO WDM wireless mesh networks, intelligent QoS multicast routing and channel assignment are performed using Q-CAR. | Chakraborty, Debbarma | 2017 | uses sophisticated computational approaches to resolve the channel assignment and multicast tree building issues | Q-CAR | Finally, we compare Q-CAR to two alternative algorithms, Quality of Service Multicast Routing and Channel Assignment (QoS-MRCA) and intelligent Quality of Service Multicast Routing and Channel Assignment (i-QCA), for use in multichannel, multiradio wireless mesh networks. We performed comprehensive tests to prove that the proposed method is the best option. | |
| An efficient and quick routing technique for cognitive wireless mesh networks | Kuang , Chen | 2017 | HRL2A aims to be a reliable, low-latency route. | HRL2A | ||
| In multi-radio, multi-channel wireless mesh networks, channel assignment and routing are done simultaneously. | Xiaojun Wang, et al | 2017 | Choose the channel with the least amount of static. | MRMC-AODV | In simulations, the HRL2A algorithm achieved the desired result. The construction route is quicker and more trustworthy than the other. The production has increased. | |
| Highest end-user satisfaction wireless mesh networks for data transmission | G. Audrito , et al | 2017 | Our objective is to optimize total user satisfaction provided that no more than K times of the same common material can be retransmitted at various speeds by different access points. | Time by exploiting the convex Monge property of the satisfaction function | The simulation results show that this method has the potential to improve network performance, latency, and packet loss. | |
| An overview of wireless mesh network routing methods | Jamal N. Al-Karaki, et al | 2017 | Consider the routing metrics, operations, and design concerns of these protocols. | MANETs | Then, optimal strategies are devised for solving certain particular problems in polynomial time. | |
| Effective cooperative hybrid routing in hybrid node wireless mesh networks | Yuan Chai, et al | 2017 | Consider the channel, interference, and client power constraints while choosing a route. | CHRP | This publication offers a wide-ranging survey of relevant methodologies and many contrasts between diverse approaches. We also describe the most critical issues that affect the overall protocol and routing metric development for WMNs. The paper concludes with several recommendations for moving ahead in this crucial area. | |
| The D-LAJOA method is a dynamic load-aware joint optimum technique for wireless mesh networks with multiple radios and multiple channels. | Zhang Yong, et al | 2017 | Design optimizations for interference avoidance, load balancing, channel allocation, and routing | LAJOA | Using ns-3 simulations, we showed how the proposed CHRP improves upon state-of-the-art solutions in terms of packet loss rate, latency, network throughput, client energy consumption, and residual client energy. | |
| Algorithms for weighted links-based channel allocation and its fairness An Effective Multicast Routing Algorithm in Wireless Mesh Networks, and a Cluster-Based Method for Evaluating a Hybrid Routing Protocol | Fuad A. Ghaleb, et al | 2018 | Reduce interference to maximize network performance. | Algorithm based on weighted link ranking scheme | The average performance, network overhead, and packet loss are all much better for D-LAJOA in the simulations. | |
| Fair bandwidth distribution in IEEE 802.11e wireless mesh networks when there is a delay restriction | Rohani, et al | 2018 | connection load and connection quality between two nodes must be optimized for optimal resource use in order to provide a high level of service to end users. | Combination of intra cluster routing protocol (ICR) and inter cluster routing protocol | Numerical simulations have proven that the proposed channel assignment method is effective in decreasing interference, increasing network capacity, and guaranteeing fair channel allocation. | |
| Cluster-based mobility management algorithms for wireless mesh networks | Y. Mallikarjuna Rao, et al | 2018 | proposes a delay-aware proportional bandwidth allocation method | LLLQ | Throughput, end-to-end latency, packet delivery ratio, and jitter are all improved over baseline routing approaches, showing that the proposed protocol is the way to go. | |
| Design and Implementation of the XWCETT Routing Algorithm for Cognitive Radio-Based Wireless Mesh Networks. | Wenxiao Shi, et al | 2018 | Protocols for routing and clustering analysis | QoE | In simulations, we found that our method significantly improved WMN efficiency. | |
| Online multicast tree construction is used in multi-channel, multi-radio wireless mesh networks, however it is constrained by latency and bandwidth. | Cheng-Han Lin, et al | 2018 | Cognitive radio (CR) technology and other emerging wireless methods are being integrated into the existing wireless infrastructure. | Static clustering algorithm Dynamic clustering algorithm |
The results of the simulations show that the suggested technique improves over its forerunners in terms of throughput equity among WMN users and end-to-end transmission delay. | |
| Wireless networks with low costs that provide multi-objective routing and take into account mixed IoT traffic backhauls | Y. Mallikarjuna Rao, et al | 2018 | Each incoming session's latency and bandwidth needs may be accommodated by the proposed method. | xWCETT | Compared to the state-of-the-art baseline mobility management algorithms and routing protocols, the realized throughput, packet delivery ratio, and communication cost are all much greater. | |
| Multimedia data transfer in a wireless mesh network with energy-efficient load-balancing routing employing fireflies | Kola, Velempini | 2019 | uses three weighted criteria to determine how to route in a wide variety of wireless mesh networks | A mathematical model to satisfy bandwidth requirement in the second phase, which constructs the tree over the selected paths. | The results of the comparative evaluation demonstrate that the xWCETT has much greater average throughput, latency, and the normalized routing load. | |
| Using segment routing and gateway-aware link scheduling, wireless mesh networks may have their network throughput optimized in real-time. Wireless Mesh Networks | Leili Farzinvash | 2019 | Balancing the load | MAXI | Extensive simulations show that the proposed method works well. It increases the total acceptance rate from the previous systems by as much as 60%, for example. | |
| dynamic programming excels above genetic algorithms in performance. | Chun-Cheng Lin, et al | 2022 | Determine the minimum and maximum numbers of channels that may be allocated after analyzing the factors impacting channel assignment performance. | SR-WMN | The experimental results show that the proposed scheduling method not only preserves numerous wireless network characteristics, but also correctly simulates the results of dynamic programming and surpasses the genetic algorithm. |
| Title | Writers | Year | Research goal | Methodology | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sustainable Development Goals Implementation Drivers from IoT Healthcare Applications | Ángeles Verdejo et sl | 2021 | There is a close relationship between public health, energy efficiency, and sustainable development. | Methodology combining a literature research with an examination of how IoT and smart technologies might contribute to the UN's Sustainable Development Goals | Questions like the ones below are addressed with regards to these systems and applications as a consequence of the study of results: (a) Do Internet of Things (IoT) applications play a crucial role in bettering human health and the state of the planet? (b) Do any studies or case studies show that IoT applications improve public health and have been deployed in any cities or territories? What indicators and goals of sustainable development may be evaluated in the applications and projects under consideration (c)? |
| A Systematic Analysis of Mobility Management Challenges and Approaches for 5G and Beyond Networks | Maraj Uddin Ahmed Siddiqui et sl | 2022 | It is crucial to deal with traffic issues and eliminate any possibility of a network failure. | DMM | By outlining recent studies, we demonstrate the feasibility of a flat network architecture for mobility management in B5G and illustrate its potential and advantages for efficient and fast traffic routing. |
| Systematic Review of Improvements to the IPv6 Routing Protocol across Low-power and Lossy Networks for Internet-of-Things Applications | Moses Effiong Ekpenyong et sl | 2022 | Literature-adopted metrics are analyzed for their strengths and flaws, with recommendations for improving areas of weakness offered. | machine learning (ML) for RPL functionalities in IoT-based networks | Review results showed that ML approaches may help deploy several sought-after parameters to significantly boost LLNs' performance. |
| Using a Fuzzy Logic-based Method for Evaluating Smart Grid Communication Technologies TOPSIS | Daud Abdul, Jiang Wenqi | 2022 | The purpose of this research is to look at a viable means of SG communication. | F-TOPSIS | According to the case study's findings, wireless communication technology is better suited to the SG. Future SG communication technology infrastructure may benefit from this broader examination of SGs and telecommunications networks from the vantage point of power production, transmission, distribution, and pollution. |
| Title | Writers | Year | Research goal | Methodology | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Future Opportunities in Software-Defined Wireless Mesh Networking and the Current State of the Art | Michael Rademacher, Karl Jonas, Florian Siebertz, Adam Rzyska, Moritz Schlebusch, Markus Kessel | 2017 | Examines where we are now with regards to software-defined wireless meshed networks | SDN | On the control plane, it is necessary to represent and handle modulation and coding, routing and load balancing, client administration, and topology discovery. |
| Innovative CFTLB technology for wireless mesh networks, which can handle faults and distribute them evenly. | N. N. Krishnaveni, K. Chitra | 2017 | Fix WMN's problems. | CFTLB | The proposed CFTLB uses a hashing algorithm to check the packets' integrity and outperforms prior art in terms of throughput, latency, and overhead. |
| Multicast traffic in multi-radio, multi-channel wireless mesh networks is coordinated by channel allocation. | Jihong Wang, Wenxiao Shi | 2017 | From a traffic management standpoint, multicast routing and channel assignment issues are resolved by adding load balancing. | POCs | We present a heuristic method for multicast routing and channel assignment using a multicast weighted conflict graph to solve this problem. The simulation findings show that the service capacity of WMNs may be much enhanced by using this heuristic technique, while the computational cost of the problem is also greatly reduced. |
| The use of accurate and heuristic algorithms based on noninterfering transmissions to jointly choose gateways, allocate time slots, route data, and manage power in wireless mesh networks. | Kagan Gokbayrak, E. Alper Yıldırım | 2017 | Our mission is to distribute resources across nodes in accordance with their traffic loads in order to optimize the service level defined by the minimal capacity-to-demand ratio. | TDMA | Our computer results demonstrate the correctness of the inequality and the promise of our precise and heuristic methods. |
| In wireless community mesh networks, a new and more efficient method of choosing relay nodes across layers is needed. | Liang Zhao, Ahmed Al-Dubai, Xianwei Li, Guolong Chen, Geyong Min | 2017 | QoS Selects requires novel routing techniques to be developed in order to reduce interference on the selected channels. | PP-QoS | PP-QoS considers the busyness of the channel to further improve the efficacy of the route selection process. The simulation results show that the proposed model is superior than many alternative options. |
| A method for estimating interference in wireless meshed networks based on measurements of channel quality and utilization. | Saleem Iqbal, Abdul Hanan Abdullah, Kashif Naseer Qureshi | 2017 | improved use of WMN network resources | QUAM | Simulation findings verified the efficacy of QUAM by demonstrating a significant improvement in network throughput with a reduction in network latency and packet losses. |
| Management of Resources in Wireless Mesh Networks | Jinqiang Yu, Wai-Choong Wong | 2017 | routing specified gateway capabilities while accommodating for router and client quirks and taking load into account In multicast communication, the path-tracing technique is used to reduce the maximum channel use. | MAP–STA | It is possible to improve either network performance or user equity using the flexible MAPs for the backhaul and the utility-fair bandwidth distribution mechanism. We demonstrate the increased performance of the proposed approaches via simulations with various network topologies and scenarios. |
| Load-aware cooperative routing in wireless mesh networks that combine the best of both worlds | Yuan Chai, Wenxiao Shi, Tianhe Shi | 2017 | Algorithm for routing based on clustering | LA-CHRP | The results of the simulations indicate that LA-CHRP has the potential to decrease latency and packet loss in hybrid WMNs while keeping the throughput the same. |
| Incorporating Reliability and Traffic into Gateway Selection in Wireless Mesh Networks | Arash Bozorgchenani , Mohsen Jahanshahi | 2017 | To prevent wireless congestion, we implement the spatial reuse time division multiple access (TDMA) technique, which allocates time slots for wireless communications. | Internet Gateway (IGW) selection | The simulation findings demonstrate that our novel approach improves throughput, latency, and overall network energy consumption. |
| Balancing multicast traffic in densely connected wireless mesoscopic networks | Majid Asadi Shahmirzadi, Mehdi Dehghan, Abdorasoul Ghasemi | 2017 | the goal being a higher data rate achieved by the coordinated control of network interfaces and channels | Load-balanced Multicasting with Multiple Gateways (LMMG) framework |
The results of our simulations demonstrate the importance of channel optimization for network performance. |
| Secure gateway placement in clusters of wireless mesh networks, optimized for the Internet of Things | Jilong Li, Bhagya Nathali Silva, Muhammad Diyan, Zhenbo Cao, Kijun Han | 2018 | Learn how to get around the issues of unipath routing. | Minimizing the existing issues of networks | From the simulation results, it is clear that the proposed method outperforms the current state-of-the-art routing metrics. |
| Hybrid traffic channel allocation in multi-radio, multi-channel wireless meshed networks with interference mitigation | Kagan Gokbayrak | 2018 | Refactoring wireless protocols into control and forwarding choices provides a consolidated, real-time perspective on the whole network. | TDMA | In order to establish which of the suggested formulations, with or without valid inequalities, produces the best results in terms of accurate solution performance and linear programming (LP) relaxations in light of demand forecasting errors, a local search approach is introduced. prove, using these examples, that our local search method can fortify networks against inaccurate predicting. |
| Load balancing strategies for wireless mesh networks based on a multi-path optimal link state routing protocol; software-defined wireless mesh networking for reliable and real-time cyber physical applications in smart cities. | Lu Yang, Yujie Li, Shiyan Wang, Haoyue Xiao | 2019 | Enhancing the Quality of Service for Multi-Radio Video Streaming Mesh Networks, or Wireless, | LBIA-POCA | The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed system achieves an acceptable performance and packet loss rate in hybrid traffic WMNs. |
| Improving Media Flow Management in Wireless Mesh Networked Video Applications | Anbu Ananth, C; Suresh, T; Prabakaran, G | 2019 | Routing metrics help determine the optimal path for data to go from one node to another. | MP-OLSR | Dijkstra's initial method for finding the quickest route across a network has been improved upon to allow for quicker route computations. The method was designed to effectively get the alternative routes and to aid the cost function. |
| Load-balanced routing using MO-CSOs in the MRMC WMN Wind turbine condition monitoring system deployment optimization using wireless mesh networks Energy-efficient load-balance routing protocol for wireless mesh networks: research on optimization, prioritization, and weight allocation techniques for balancing and controlling multimedia traffic | Akram Hakiri, Aniruddha Gokhale, Pascal Berthou | 2019 | Attempts to solve the shortcomings of standard approaches by proposing an energy-efficient load balancing routing measure. | SDN | Network virtualization, routing, and traffic engineering may improve the stability, flexibility, and predictability of a communication network. |
| Opt-ACM is an improved load balancing Admission Control Mechanism for SDHW-IoT networks. | Narayan D.G., Mouna Naravani, Sumedha Shinde | 2020 | Congestion and collisions in networks are exacerbated by the use of shortest-path and GW routing algorithms. | Multiple Description Coding (MDC) | The results show that the proposed approach with MDC is superior to the status quo with respect to PSNR, frame delay, and frame loss. |
| Future Opportunities in Software-Defined Wireless Mesh Networking and the Current State of the Art | G.P. Raja, S. Mangai | 2020 | By delivering a scalable, cost-effective, and simple-to-implement network infrastructure, we can ensure that the newly installed CMS will not disrupt the SCADA system's communication network in extreme conditions. | WSN | Developing a methodology for load-balancing and energy efficiency in WMN routing. |
| Innovative CFTLB technology for wireless mesh networks, which can handle faults and distribute them evenly. | M Kiran Sastry, Arshad Ahmad Khan Mohammad, Arif Mohammad Abdul | 2021 | Congestion in the network should be reduced or avoided. | QoS in the WMN by load balancing, and energy efficiency | Results showed that the proposed routing protocols worked better than the two existing ones, Buffer-based load balancing and energy-delay-based load balancing. |
| Future Opportunities in Software-Defined Wireless Mesh Networking and the Current State of the Art | Karunya Rathan, SusaiMichael Emalda Roslin, Easpin Brumancia | 2021 | Examines where we are now with regards to software-defined wireless meshed networks | MO-CSOAHP | The simulation results show that the proposed MO-CSO achieves higher network performance than the state-of-the-art routing techniques such as SBR, ETX, LG, NG, and IR. |
| Innovative CFTLB technology for wireless mesh networks, which can handle faults and distribute them evenly. | Yanjun Yang, Aimin Liu, Hongwei Xin, Jianguo Wang, Xin Yu, Wen Zhang | 2021 | Fix WMN's problems. | K-medoids clustering algorithm | The results show that the proposed approach has the potential to reduce network operating costs, meet the capacity requirements of MC, and mitigate the effects of link losses. |
| Multicast traffic in multi-radio, multi-channel wireless mesh networks is coordinated by channel allocation. | Rohit Kumar, Venkanna U., Vivek Tiwari | 2021 | From a traffic management standpoint, multicast routing and channel assignment issues are resolved by adding load balancing. | Opt-ACM | Mininet-Wifi can also simulate Opt-ACM in different network topologies, allowing comparisons to be made with both time-tested routing protocols like OLSR and OSPF and state-of-the-art alternatives like FACOR and EASDN. The Packet Delivery Ratio (PDR) and Packet Loss Ratio (PLR) achieved by Opt-ACM are superior than those achieved by competing techniques by an average of 9.47% and 12.32%, respectively. Improvements in Average Delay (AD) and Average Jitter (AJ) are similar in size, coming in at 26.77% and 33.10%, respectively. |
| Title | Writers | Year | Research goal | Methodology | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| More liberal techniques for access point selection in wireless mesh networks | G. Vijaya Kumar and C. Shoba Bindu | 2017 | In WMNs, the system throughput is enhanced more so than with the RSS-based AP selection method. | Vovel method of AP selection | In order to connect to the internet using a WMN that has already been set up, users just need to pair their devices with one of the APs in the network. |
| Artificial intelligence-guided mesh network design for spectral efficiency | Jingyang Lu, Xingyu Xiang, Dan Shen; Genshe Chen, Ning Chen , Erik Blasch, Khanh Pham, Yu Chen |
2018 | A DMN might make greater use of its radio spectrum by using ML strategies from the field of artificial intelligence. | DMN | It enhances system security by reducing network congestion. |
| An efficient channel assignment method is necessary in multicast wireless mesh networks. | Wenxiao Shi, Shaobo Wang, Zhuo Wang, Endong Wang | 2018 | We present the concept of local multicast and a channel assignment technique for multicast WMNs that accounts for interference and forwarding weight at the local level. | Algorithm considering the interference of local multicast and forwarding weight of each node (LMFW). | Simulations have demonstrated that the proposed method may increase WMN network capacity while decreasing interference. |
| Using a cooperative distributed QoE-based technique called AD3-GLaM, SVC video may be streamed through wireless mesh networks. | Tran Anh Quang Pham, Kamal Deep Singh, Juan Antonio Rodríguez-Aguilar, Gauthier Picard, Kandaraj Piamrat , Jesús Cerquides , César Viho | 2018 | The ultimate objective is to improve everyone's time spent online. | OLSR and AD3 | AD3-GLaM makes use of OLSR, a common routing protocol used by the great majority of modern ad hoc-capable devices. |
| An optimization framework for multicasting across partly overlapping channels in a multihop, multiradio (MCMR) wireless mesh network | Majid Asadi Shahmirzadi, Mehdi Dehghan, Abdulrasoul Ghasemi | 2018 | In particular, it tackles the problem of how to improve multi-channel multicast routing's performance. | MG-POC | Reducing network interference by using numerous gateways and channels that only partly overlap significantly increases network performance. |
| Gateways in Mesh Networks The RIMO Algorithm for Throughput Prediction Research in Wireless Mesh Networks: Towards Universal Internet Access Building on support vector machines | Khulan Batbaya ,Emmanouil Dimogerontakis,Roc Meseguer,Esunly Medina, Rodrigo M. Santos | 2018 | With this best-effort method, each client node may choose its own gateway independently of the others. | RIMO algorithm | As a consequence, underprivileged people may access the Internet using a simple, robust, and cost-effective approach that does not rely on expensive network capacity planning and traffic management. As a result of RIMO's optimization, even a little increase in network traffic doesn't compromise performance. Through the employment of gateways, RIMO achieves a balance between client nodes, which boosts the network's resilience and the user's perception of the Internet's speed. |
| The application of learning-based game theory to the problem of partial overlap channel access in wireless networks with an emphasis on user experience quality | Feng Zeng, Nan Zhao, Wenjia Li | 2019 | By building and allocating multicast trees at the same time, we may reduce co-channel interference in multicast transmission, which is the focus of this study. | CIOMT | The recommended multicast routing approach has been shown to be successful in simulation. In comparison to the two conventional algorithms, the new technique significantly improves customer satisfaction. |
| A novel method for edge computing based on multi-strategy channel allocation | Jianjun Jing, Kailing Yao, Yuhua Xu, Xin Liu, Yuli Zhang, Changhua Yao | 2020 | Our major optimization goal is not throughput or interference reduction, but rather QoE enhancement for end users. | Using a rough correlation between interference and quality of experience | Using an approximation of the relationship between interference and quality of experience, it was shown that the proposed game had at least one pure NE with ordinal potential. However, the best NE point for a purely theoretical strategy was quite near to the worldwide optimum for QoE maximization in the network. To find the NE of the game, a decentralized approach was proposed; this method may asymptotically maximize the QoE of the network given a sufficiently large learning parameter. |
| Channel allocation optimization algorithm for I/O-centric physical-data fusion in hybrid wireless mesh networks | Degan Zhang, Mingjie Piao, Ting Zhang, Chen Chen , Haoli Zhu | 2020 | When transmitting data via WMNs, it is important to look at issues such radio interference and time slot multi-user collisions. | A multi-strategy channel allocation technique for edge computing is built using a node data cache model and step-by-step calculations of node channel separation. | Reduce channel interference and overall network energy consumption while maximizing throughput and decreasing delay from beginning to end. |
| To investigate the impact of interleaved channels, we provide a model for cross-layer optimization in wireless mesh networks. Channel allocation in wireless meshed networks that prioritizes capacity fairness using a semi-chaotic genetic algorithm | Shasha Zhao, Gan Yu | 2021 | Think of a reasonable way to distribute traffic. | Algorithm for hybrid wireless mesh network optimization | Despite being arbitrarily divided into distinct sub-time periods, it is difficult to guarantee that inter-node communication will be present at any given instant. By using the shortest route as a sorting criterion, the communication paths between nodes may be determined and the issue can be avoided. |
| Incorporating Interference, Traffic Load, and Delay into Wireless Mesh Network Gateway Positions as a Communication and Internet of Things Support Metric | Amel Faiza Tandjaoui , Mejdi Kaddour | 2021 | In contrast to traditional operations, which are limited to orthogonal channels, a cross-layer optimization model based on the physical interference model may predict the potential increase of network capacity that may be obtained by using all channels in the radio spectrum. | Algorithm-Based Channel Assignment Technique (FASCGA-CAA) is a cross-layer optimization technique that uses the physical interference model to address the issue of node hunger in wireless mesh networks. Using a unique nonlinear fairness-oriented fitness function, FA-SCGA-CAA optimizes link fairness while reducing link interference. | It's possible that the capacity gains from using a dynamic channel assignment won't amount to much of an upgrade if an efficient static assignment is expected. |
| For wireless mesh networks, an anti-collaborative attack technique | Fuad A. Ghaleb , , Bander Ali Saleh Al-Rimy, Wadii Boulila , Faisal Saeed, Maznah Kamat,Mohd. Foad Rohani, ,Shukor Abd Razak |
2021 | Utilization of all available channels across the mesh's nodes. | Using a rough correlation between interference and quality of experience | The proposed FA-SCGA-CAA is reliable for achieving the ultimate goal of many wireless networks, which is to increase resource consumption without sacrificing good node-level fairness. |
| Adaptive Routing in Wireless Mesh Networks Utilizing a Hybrid Reinforcement Learning Algorithm | Satish BHOJANNAWAR, Shrinivas MANGALWEDE | 2021 | Add together the wait times for each step of the route (contention, transmission, and queuing) to get the whole route delay. | ITLDA | Simulation results suggest that ITLDA performs better than traditional routing metrics. |
| A strategy for detecting VoIP threats using ensemble clustering that is influenced by game theory. | Di Zhou, Min Sheng, Jiaxin Wu, Jiandong Li, Zhu Han , Kyung Hee |
2021 | Placement of gateways in ISoLS-TNs may be seen as a multi-objective optimization issue with objectives including maximization of total revenue of service data demand within coverage, minimization of average access distance, and maximization of the number of installed gateways. | To determine the total income of service data demand within coverage, an algorithm using the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) was developed as part of a distributed resource allocation (DRA) mechanism. | The results also provide insight on the distribution of service data demand and how users' choices for gateway sites stack up against one another. |
| Cloud-based heterogeneous cellular and mesh networks: designing and analyzing an intrusion detection system for networks with partially overlapping channel assignments Channel assignments in wireless mesh networks may be dynamic and spread. | I. Diana Jeba Jingle, P. Mano Paul | 2021 | Compare the outcomes of basic routing algorithms like Ad hoc On-Demand Distance-Vector routing with those of more complex ones like Optimized-Link-State Routing, Destination-Sequenced Distance-Vector routing, and Distance Source routing to identify the nature of the attack before it does significant damage. | Collaborative defense protocol (CDP) | CDP is reliable and efficient, and it can identify an attack before major damage is done. |
| More liberal techniques for access point selection in wireless mesh networks | Smita Mahajan, R. Harikrishnan, Ketan Kotecha All Authors |
2022 | As a means of effectively considering complex relationships between attributes. To address this shortcoming, ensemble clustering may be used to synthesize the verdicts of many base clustering components into a single judgment. | Routing algorithm (QFFR) | The top results for the Ad hoc On-Demand Distance Vector Algorithm are a throughput of 723.13 Kbps and a latency of 343.73 ns. Q-learning agent in non-grid architecture can determine the optimal route to the goal and reach it in an average of 3.7 seconds. The Q-learning agent needs just 0.49 seconds to do its work on a 10x10 grid, but it takes 0.53 seconds on a 3x4 grid. The suggested QFFR consistently and reliably maintains a score-over-time of 7.62s. |
| Artificial intelligence-driven directed mesh network architecture for optimum spectrum efficiency in multicast wireless mesh networks. | Farid Bavifard, Mohammad Kheyrandish, Mohammad Mosleh | 2022 | Learning how these systems flag security breaches across several OSI layers was the key focus. | The proposed intrusion detection on VoIP traffics is implemented in MATLAB, then trained and evaluated on NSL-KDD and a real dataset, containing traffics on a VoIP framework. | Increases of 7.15 percent in Accuracy, 23.43 percent in Detection Rate, and 29.83 percent in F-Measure are typical. |
| More liberal techniques for access point selection in wireless mesh networks | Fawaz S. Al-Anzi | 2022 | The proposed INCACG system aims to assign the available non-overlapping channels to the WMN backbone routers in a way that ensures low interference and sufficient network connectivity. | IDS | If an effective static assignment is anticipated, the capacity improvements from using a dynamic channel assignment may not amount to much of an increase. |
| Artificial intelligence-guided mesh network design for spectral efficiency | Satish S. Bhojannawar, Shrinivas R. Managalwede | 2022 | Centralized Interference Aware Partially Overlapped Channel Assignment is offered to take into consideration both external and internal interference, as well as the degree of overlap between nearby channels. | INCACG FLADCA |
The simulation results demonstrate that the INCACG scheme quickly converges and effectively distributes channels among the routers. |
| An efficient channel assignment method is necessary in multicast wireless mesh networks. | Saleem Iqbal, Kashif Naseer Qureshi, Saqib Majeed, Kayhan Zrar Ghafoor, Gwanggil Jeon | 2022 | In WMNs, the system throughput is enhanced more so than with the RSS-based AP selection method. | POCs | Simulations showed considerable improvements in throughput, packet loss ratio, and end-to-end latency compared to the current state of affairs. |
| Title | Writers | Year | Research goal | Methodology | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A cross-layer optimization method for allocating channels and routing multicast traffic in wireless mesh networks with numerous channels and radios is presented. | Mohsen Jahanshahi , Mehdi Dehghan , Mohammad Reza Meybodi | 2016 | Develop network coding strategies that maximize throughput while reducing error rates and allowing optimal routing to be determined in polynomial time. | Maximizing multicast performance and assigning channels simultaneously in MCMR wireless mesh networks QoS routing using a cross-layer convex optimization framework NSR, or "Node Stability-based Routing," is a routing technique that prioritizes connections based on the stability of individual nodes. | We have conducted thorough tests to determine how well our strategy works in comparison to other available choices. |
| A machine-learning-based framework for fully autonomous decision making | Carlos Ferreira, Susana Sargento, Arnaldo Oliveira | 2017 | It was crucial to assign certain pieces of network gear with administrative responsibilities. | The Using Genetic Algorithms Technique | The results show that even without perfect knowledge of the network state, agents in the surrounding area can work together to establish bandwidth-aware communication paths that are just as optimal as those obtained with a concentrated decision approach that contains full network information, and that these paths can react to changes in the network with rapid convergence. |
| Stability-Based Routing in Wireless Mesh Networks | Mustapha Boushaba, Abdelhakim Hafid, Michel Gendreau | 2017 | Network stability is a crucial performance indicator for real-time wireless communication. | COTE | Simulation results show that NSR can significantly improve the overall network performance compared to other routing methods such as interference and channel switching (MIC), Expected Transmission count (ETX) or load at entrances as a routing metric, Reinforcement learning-based best path to best gateway (RLBDR), and nearest gateway (i.e. shortest path to gateway). |
| Search-based routing in a wireless mesh network | Khalid Mahmood, Babar Nazir, Iftikhar Ahmad Khan, Nadir Shah | 2017 | Data transmission networks may be made more economically viable by the development of a suitable cost metric for use by routing protocols. | A less-than-ideal mathematical model for constructing trees has been built over the generated mesh. | Our results show that evolutionary algorithms perform better than the more common hop count measure when used to WMN routing. Finally, we go into the numbers to learn more about the potential of the genetic algorithm for routing in WMN. |
| Cognitive mesh networks for traffic engineering: power management and link-channel selection | Maheen Islam, Md. Abdur Razzaque, Md. Mamun-Or-Rashid, Mohammad Mehedi Hassan, Abdulhameed Alelaiwi, Atif Alamri | 2018 | Our goal is to increase the network's total throughput by picking the best possible link-channel combinations, sharing the load among them, and dividing the traffic fairly. | We evaluate the performance of conventional and hybrid wireless mesh networks (WMNs). | We provide thorough simulation results to demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed TE mechanisms compared to the existing gold standard. |
| A novel method has been developed for multicast call acceptance in wireless mesh networks that make use of many channels and radios. | Leili Farzinvash | 2018 | enabling Multimedia Content | Describe the current developments in unsupervised learning and the range of learning problems that could benefit from it. | The results show that, in comparison to conventional methods, the proposed strategy increases the acceptance rate of multicast calls by an average of 40%. |
| This paper analyzes the efficiency of a genetic algorithm–based system for wireless mesh networks, considering several flow rates and distributions (Weibull, exponential, DCF, EDCA), as well as the potential impact of each. | Ilir Shinko, Vladi Kolici, Ryoichiro Obukata, Admir Barolli, Tetsuya Oda, Leonard Barolli | 2018 | Simulations of the connection state optimized for ns-3 time steps | For an NP-hard task, consider wireless mesh networks' access points (APs). | In the instance of Hybrid WMN, the simulation results show that the throughput of both MAC protocols is more than I/B for exponential distribution. The WMN has contributed to the development of machine learning that is more flexible, universal, and autonomous. |
| Wireless mesh network router node placement using an electromagnetic algorithm: techniques, applications, and future research challenges in unsupervised machine learning for networking. | Muhammad Usama, Junaid Qadir, Aunn Raza, Hunain Arif, Kok-lim Alvin Yau, Yehia Elkhatib, Amir Hussain | 2019 | We want to advance the state of the art by synthesizing the results of previous survey studies and providing comprehensive coverage of the most recent developments and improvements. | The collected findings demonstrate that the proposed EM algorithm outperforms the present particle swarm intelligence algorithm and genetic algorithm in designing almost optimal locations for mesh routers with regard to coverage and connection. | |
| Optimization of Wireless Network Channels and Locations using Deep Learning | Lamri Sayad, Louiza Bouallouche-Medjkoune , Djamil Aissani | 2019 | Optimisation of Mesh Routers | Self-X (self-improvement via learning) | To ensure its fast convergence, enhanced throughput, and resistance to dynamic interference, we run comprehensive simulations. |
| Using a genetic approach for cross-layer resource allocation, wireless mesh networks may maintain fault-tolerant topologies. | Samurdhi Karunaratne, Ramy Atawia, Erma Perenda, Haris Gacanin | 2019 | Channel configuration for wireless repeaters and access points (APs) in a Wireless Mesh Network. | Using a heuristic strategy based on problem decomposition, the computational complexity may be reduced by a factor of four. | We propose an approach for topology control in wireless mesh networks, and numerical validation demonstrates its efficacy. |
| Analyzing Wireless Mesh Networking Technologies from an Internet of Things-Focused Perspective | Esmaeil Nik Maleki, Ghasem Mirjalily | 2019 | There must be a way to solve the NP-complete issue. | Using technologies like sub-GHz radio, Bluetooth, and IEEE 802.15.4, LoRa | Please provide concrete illustrations of the applications of the mesh-oriented technologies you researched. |
| Using Learning Automata and Genetic Algorithms for Efficient Channel Assignment in Wireless Mesh Networks | Antonio Cilfone, Luca Davoli, Laura Belli, Gianluigi Ferrari | 2019 | Our goal is to bring attention to the fact that many different kinds of communication protocols may either natively support mesh networks or be adapted to do so. | The genetic algorithm's robust search capabilities and the learning automata methodology of adaptive decision making are used in this approach. | Experiments are run in NS2, and a high-performance proposal is made based on comparisons of packet delivery ratio, end-to-end latency, throughput, and total cost to those of LAMR, LCA, and GA based multicast channel assignment methods. |
| Using a genetic algorithm, we optimize load-balanced routing in a wireless mesh network for AMI. | Nandini Balusu, Suresh Pabboju, G Narsimha | 2019 | There must be a way to drastically improve throughput while lowering the amount of noise in the network. | Load aware-HWMP (LA-HWMP) is a kind of hybrid wireless mesh routing protocol (HWMP) used in WMNs to decide which paths to use. | The proposed method finds a route with better latency and throughput than the alternatives, as shown by the results. |
| Maximizing 6LoWPANs' service life and quality of life with the use of deep neural networks. | A. Robert singh , D. Devaraj , R. Narmatha Banu | 2019 | Avoid doing so because of the frequent need for packet retransmissions. | P3PGA uses deep neural networks to solve routing problems that are NP-hard. | The proposed routing method improves upon the basic 6LoWPAN routing protocol by increasing network lifetime by 50%, decreasing latency by 40%, and decreasing jitter by 25%. An 18 dB improvement in signal-to-interference and noise ratio is achieved on average. |
| Parallel Routing Protocol for Wireless Mesh Networks The Genetic Algorithm with 3 Parents | Shubhangi Kharche, Sanjay Pawar | 2020 | offers a variety of solutions for eliminating the interference, from which the best may be selected. | Both a Particle Swarm Optimization (WMN-PSO) and a Genetic Algorithm (WMN-GA) based simulation system may be used to tackle the node placement issue in WMNs. | We compared it to eight other algorithms—including genetic algorithms, biogeographic optimization, ant colony optimization, the BAT algorithm, and the big bang big crunch algorithm—to see how well they performed on this challenge. P3PGA outperformed all other approaches for networks with 1000+ nodes. |
| Chemical-reaction-based method for routing-node placement in wireless mesh networks | Amar Singh, Shakti Kumar, Ajay Singh, Sukhbir S. Walia | 2020 | Minimal-effort route routing in wireless mesh networks. | Using fuzzy logic | Compared to the GA technique and the SA algorithm, our proposed strategy may improve client coverage by 4.5-18% and network connectivity by 4.5-61%, as shown by the simulation results. |
| Performance Evaluation of the WMN-PSODGA Simulation Environment Regarding Alternative Router Replacement Strategies for IoT Network Construction Using a Hybrid Intelligent Simulation Environment | Lamri Sayad, Louiza Bouallouche-Medjkoune , Djamil Aissani | 2020 | Wireless Internet that is both cheap and fast increasing; a solution to the challenge of wireless mesh network router node placement (WMN-RNP). | Effective strategies for allocating channels | The results of the simulations show that the CM and LDVM alternatives for replacing routers work better. It's obvious that LDVM behaves better than CM when the two are compared. |
| An Optimal End-to-End Path Selection Mechanism for CR-WiMAX Networks Utilizing Fuzzy Logic | Ohara Seiji, Barolli Admir, Ampririt Phudit, Sakamoto Shinji, Matsuo Keita d, Barolli Leonard | 2020 | A cognitive user may make the best use of the network's resources by figuring out the quickest path between any two sets of nodes. | The HEMS-IoT Approach (FA-SCGA-CAA): SDNMesh, a Software-Defined Network (SDN)-based Routing Architecture for Wireless Mesh Networks. | Most of the information gathered pertained to improving the processes of route analysis and path selection. The proposed method is modeled in Matlab. The results of the simulations demonstrate the efficacy of the fuzzy system. |
| A Gravitational Search Algorithm Based on Adaptive Swarm Theory for MCMR Channel Assignment in a Wireless Mesh Network | Wajahat Maqbool, S. K. Syed-Yusof, N. M. Abdul Latiff, Bushra Naeem, Bilal Shabbir, N. N. Nik Abdul Malik | 2020 | The inability to scale with increasing bandwidth demands is one of the disadvantages of single-radio networks that might be mitigated by combining many radio nodes into a mesh structure. | RRT-WMN APSO Algorithm | This approach is put through its paces in NS2 and compared to a number of other heuristic optimization tactics, such as the Learning Automated and Genetic Algorithm Approach, the Improved Gravitational Search Approach, and the Dynamic Particle Swarm Optimization Approach, to determine its effectiveness. The simulation results showed that the suggested solution performed better than the current best practices. |
| A Smart Home Energy Management System with Internet of Things for Big Data and Machine Learning | Nandini Balusu | 2020 | An intelligent energy management system for homes that leverages big data and machine learning to improve occupants' well-being, security, and productivity. | Combinations of precise and heuristic or meta-heuristic approaches are also possible. | RuleML and Apache Mahout are used to provide energy-saving recommendations, ensuring the smart home's comfort and safety. |
| Software-Defined Routing in a Wireless Mesh Network (SDNMesh) | Isaac Machorro-Cano,Giner Alor-Hernández,Mario Andrés Paredes-Valverde,Lisbeth Rodríguez-Mazahua,José Luis Sánchez-Cervantes, José Oscar Olmedo-Aguirre | 2020 | When software-defined networking (SDN) is combined with wireless mesh networking (WMN), mesh networks may meet the needs of current users for resources, coverage, and scalable high bandwidth. | This strategy combines the efficient decision-making of learning automata with the extensive search capabilities of a genetic algorithm. | We show that our SDNMesh routing solution outperforms OLSR, BATMAN, and an SDN based Three-Stage routing protocol in simulated networks with regards to throughput, packet loss ratio, and latency. According to experimental results, SDNMesh also excels in these efficiency areas. |
| Fairness-Driven Semi-Chaotic Genetic Algorithm-Based Channel Allocation to Solve the "Node Starvation" Issue in Wireless Mesh Networks Approach | Syed Sherjeel A. Gilani, Amir Qayyum, Rao Naveed Bin Rais, Mukhtiar Bano | 2020 | The distribution of channels in a mesh network so that users may share the available bandwidth equitably. | WMN-PSODGA | Trustworthy preservation of high node-level fairness while increasing resource consumption is the ultimate goal of many wireless networks, and this is exactly what the proposed FA-SCGA-CAA does. |
| Routing and access point deployment in a wireless mesh network for use in search and rescue | Fuad A. Ghaleb , Bander Ali Saleh Al-Rimy ,Wadii Boulila , Faisal Saeed,Maznah Kamat,Mohd. Foad Rohani, Shukor Abd Razak |
2021 | The fundamental capabilities of UAVs need at the outset of rescue operations to immediately establish an ad hoc communication infrastructure | Techniques such as Vmax constriction (VC), RIWM, and reasonable decrement of Vmax (RDVM). | Strategies that cut the required number of routers by between 73% and 92% while maintaining the same service quality. |
| To maximize client coverage and router connection, the PSO algorithm is sped up in wireless mesh networks. | Mariusz Wzorek, Cyrille Berger, Patrick Doherty | 2021 | Keep users connected and online at all times. | Multiple Wireless Mesh Network Quality of Service Issues, and Reported Solutions | The results of these experiments show that the APSO approach is much more effective than the linearly decreasing weight particle swarm optimizer (LDWPSO). |
| A survey of the literature on methods for optimally positioning nodes in wireless mesh networks. | Nabil Abdelkader Nouri, Zibouda Aliouat, Abdenacer Naouri ,Soufiene Ali Hassak | 2021 | Locating nodes in WMNs is a problem that has to be addressed. | Method for Identifying a Collection of Distinct Courses (MDPD) | Objectives, constraints, node placement (Mesh Router vs. Mesh Gateway), node distribution (discrete vs. continuous), and category context (static vs. dynamic) all go into a critical assessment of each class. |
| The use of a genetic artificial neural network (G-ANN) hybrid strategy for eco-friendly computing in mobile ad hoc networks | Sylia Mekhmoukh Taleb, Yassine Meraihi, Asma Benmessaoud Gabis, Seyedali Mirjalili, Amar Ramdane-Cherif | 2022 | There must be a way to drastically improve throughput without significantly impacting the stability of the network. | Methods for maximizing expected utility in a Markov decision-making process (MDP) based on the MEC model, include Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) and Distributed Genetic Algorithm (DGA). | Experiments are run in NS2, and a high-performance proposal is made based on comparisons of packet delivery ratio, end-to-end latency, throughput, and total cost to those of LAMR, LCA, and GA based multicast channel assignment methods. |
| Study of wireless mesh networks (WMNs) using particle swarm optimization and a distributed genetic algorithm, comparing boulevard and stadium distributions with an eye on router replacement techniques and load balancing. | B. Prakash, S. Jayashri , T. S. Karthik | Use the fewest possible mesh routers that are nevertheless totally interconnected and can cover all mesh clients if you wish to install a powerful, well-connected WMN on a small budget. | The FireFly Algorithm (JCABR-IFA) is used in the WMN Coverage Construction Method (CCM). | Our simulation results show that the best client coverage, router connectivity, and load balancing can be achieved by combining the Stadium distribution with the Rational Decrement of Vmax approach as the router replacement technique. | |
| Performance Comparison of Router Replacement Techniques for Wireless Mesh Networks Using a Hybrid Intelligent Simulation System for Building Internet of Things Networks | Admir Barolli, Kevin Bylykbashi, Ermioni Qafzezi, Shinji Sakamoto, Leonard Barolli | 2022 | Identifying the best spots to put nodes | Using stochastic geometry, we model these dynamics explicitly and determine how well the DFL ML-based IDS performs in smart grids. | Simulation findings reveal that RIWM offers greater performance over CM and RDVM because it gives the highest connection while covering more customers. |
| Quantitative study of wireless mesh network neighbor coverage and bandwidth-aware QoS provisioning Multiple, Independent Path Discovery in Wireless Mesh Networks | Admir Barolli,Shinji SakamotoKevin Bylykbashi , Leonard Barolli | 2022 | Offers a comprehensive analysis of service quality enhancement strategies discussed in the academic literature. | Channel parameters, AP load, and the wireless mesh backhaul methodology are all considered in this novel approach of selecting access points. | provides a glimpse into the benefits and drawbacks of the researched protocols while highlighting the outstanding research topics for the future generation of networking. |
| Load Balancing using Reinforcement Learning for Mobile Edge Computing | Md. Iftekhar Hussain, Nurzaman Ahmed, Md. Zaved Iqubal Ahmed, Nityananda Sarma | 2022 | Combining the WMN with the Internet of Things | Optimization of both channel allocation and multicast performance in MCMR WMNs QoS routing using a cross-layer convex optimization framework NSR, or "Node Stability-based Routing," is a routing technique that prioritizes connections based on the stability of individual nodes. | The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed MDPD mechanism over WMN may efficiently identify a large number of distinct paths and optimize data flow along those paths. |
| Wireless mesh networks benefit from a reliable key management system made possible by trusted gateways. | C. S. Anita, R. Sasikumar | 2022 | Uniformly distributing user requests among edge servers may minimize wait times and increase response times, which is particularly important in healthcare. | The Using Genetic Algorithms Technique | The simulation findings demonstrate the effectiveness of the suggested load balancing methodology in both healthcare and emergency settings, with improvements over prior approaches in terms of average execution latency, load balancing, and response time. |
| Improved FireFly Algorithm (IFA) for Joint Channel Assignment and Bandwidth Reservation in Wireless Mesh Networks (WMN) A study comparing two Island and Subway distributions utilizing a roulette wheel and random selection procedures, taking into consideration router replacement strategies. | Niloofar Tahmasebi-Pouya, Mehdi-Agha Sarram, Seyed-Akbar Mostafavi | 2022 | It has become clear that the present protocols are not adequate to safeguard the backbone network on a number of fronts. | COTE | Our research and experimental results show that the suggested approach mitigates the impact of malicious nodes and improves security compared to previous centralized solutions such digital signature authentication (DSA-Mesh, MENSA, Mobisec, and AHKM). The significance of the proposed work is illustrated by experimental solutions that boost performance by 10% to 12% above state-of-the-art approaches. |
| An Integrated Approach to Mesh Router Placement Optimization Through Distributed Federated Learning Over Slotted ALOHA Wireless Networking with Delaunay Edges and Simulated Annealing | Ganesh Reddy Karri, A. V. Prabu, Sidheswar Routray, D. Sumathi, S. Rajasoundaran, Amrit Mukherjee, Pushpita Chatterjee, Waleed Alnumay | 2022 | By improving communication between mesh routers and the clients they serve, we can deploy WMNs with high availability and low latency at a cheap cost. | A less-than-ideal mathematical model for constructing trees has been built over the generated mesh. | By simulating different selection and router replacement strategies and comparing their outcomes, we are able to determine which configurations provide the best coverage, connectivity, and load balancing. The random selection method, in conjunction with the Constriction Method (CM) and the Random Inertia Weight Method (RIWM), can produce full network connectivity and client coverage, but the Two Islands and Subway distributions provide the best load balancing. |
| Admir Barolli, Kevin Bylykbashi, Ermioni Qafzezi, Shinji Sakamoto, Leonard Barolli | 2022 | Frequency and Channel Assignment Coordination | We evaluate the performance of conventional and hybrid wireless mesh networks (WMNs). | Through simulation, we show that our proposed approach successfully decreases traffic while simultaneously raising channel efficiency. | |
| Multi-objective optimization and statistical testing are used to critically compare and select MAC protocols for wireless mesh networks. Smart grid computing with machine learning-based intrusion detection: a literature review | Narayana Rao Appini, A. Rajasekhar Reddy | 2023 | Improving network performance by strategically placing mesh routers. | Maximizing multicast performance and assigning channels simultaneously in MCMR wireless mesh networks QoS routing using a cross-layer convex optimization framework NSR, or "Node Stability-based Routing," is a routing technique that prioritizes connections based on the stability of individual nodes. | The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed strategy may optimize mesh router placement to guarantee service to all mesh clients in the evacuation zone. In addition, the DECCM-based SA technique helps improve network connectivity in WMNs since it often encompasses a greater number of mesh clients. |
| A cross-layer optimization method for allocating channels and routing multicast traffic in wireless mesh networks with numerous channels and radios is presented. | Tetsuya Oda | 2023 | This study's goal is to do away with the necessity for a central server by using Decentralized Federated Learning (DFL) via one-hop neighbors. | The Using Genetic Algorithms Technique | Due to the random nature of communication, these actors interact with a non-zero percentage of the nodes in the neighborhood, exchanging model parameters that are subsequently utilized to fine-tune their own models. These folks made friendships with a diverse set of neighbors. |
| A machine-learning-based framework for fully autonomous decision making | Abdelaziz Salama, Achilleas Stergioulis, Ali M. Hayajneh, Syed Ali Raza Zaidi, Des McLernon, Ian Robertson | 2023 | The CPS as a whole works as a unified unit. | COTE | |
| Stability-Based Routing in Wireless Mesh Networks | Nitasha Sahani Ruoxi Zhu Jin-Hee Cho Chen-Ching Liu | 2023 | Associating with lower-rate users may cause a performance drop for higher-rate users who are already connected to the same AP, but our method aims to alleviate this problem. | A less-than-ideal mathematical model for constructing trees has been built over the generated mesh. | We have conducted thorough tests to determine how well our strategy works in comparison to other available choices. |
| A cross-layer optimization method for allocating channels and routing multicast traffic in wireless mesh networks with numerous channels and radios is presented. | Ankita Singh, Sudhakar Singh, Shiv Prakash | 2023 | Develop network coding strategies that maximize throughput while reducing error rates and allowing optimal routing to be determined in polynomial time. | We evaluate the performance of conventional and hybrid wireless mesh networks (WMNs). | The strategy, as opposed to the RSS-based AP selection method, increases system throughput in WMNs. |
| Title | Writers | Year | goals of the research | Methodology | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Using a Support Vector Machine with Adaptive Sensing, Scheduling, and Spectrum Selection in Cognitive Networks to Predict Throughput in Wireless Mesh Networks. | Marco Di Felice, Kaushik Roy Chowdhury, Andreas Kassler, Luciano Bononi | 2011 | Each MR in a CR-WMN must be able to determine the spectrum's current condition, choose a channel free of PUs, and then switch to a new channel if a PU is discovered on the first channel. | An MR may find its own sweet spot between detecting, exploiting, and exploring the spectrum by using network feedbacks from the simulated MCs in a network simulator (NS2). | Long-running simulations confirm that our strategy scales well and outperforms non-learning-based approaches to CR-WMNs in terms of throughput improvement. |
| Using a cooperative distributed QoE-based strategy for SVC video streaming via wireless mesh networks: AD3-GLaM. | Yan Feng, Xingxing Wu, Yaoke Hu | 2017 | Experimental research and machine learning approaches were used to create a model that can accurately forecast IEEE 802.11 WMN throughput. | Quality-of-experience-based cooperative distributed routing | The experimental results show that the suggested SVR-based model has better prediction accuracy than the BPNN model. The WMN's throughput prediction models are now in place, laying the groundwork for efficient network architecture planning, management, and design. |
| Cost and delay are taken into account in a bi-objective GA for determining where to put gateways in wireless meshed networks. | Tran Anh Quang Pham, Kamal Deep Singh, Juan Antonio Rodríguez-Aguilar, Gauthier Picard, Kandaraj Piamrat, Jesús Cerquides, César Viho | 2018 | The final result should be a better network experience for everyone using it. | AD3 is one of the best distributed cooperative optimization algorithms because of its fast convergence. | |
| Selected Gateways in Multi-Radio, Multi-Channel Wireless Mesh Networks Employing Cross-Layer Learning Automata | Zeineb Lazrag, Monia Hamdi, Mourad Zaied | 2018 | We seek to determine the best placement for gateways by reducing the range of hop counts in the MR-IG and the total number of gates in use. | Multi-objective optimization using genetic algorithms | The simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach with respect to both operational expenditures and communication latencies. |
| Using QUIC Effectively in Wireless Mesh Networks: A Predictive Metric for Cross-Layer Routing | Amin Erfanian Araqi, Behrad Mahboobi | 2019 | Multicast routing distributes data more efficiently across a group of nodes than traditional unicast routing systems. | The multicast channel assignment issue in MCMR wireless mesh networks | Throughput, end-to-end latency, packet delivery ratio, and other metrics are all improved upon by QLMR, as shown by modeling and experimental results. The proposed method will be evaluated for its efficacy. |
| Software-Defined Networking (SDNMesh) for Wireless Mesh Network Routing | Samurdhi Karunaratne, Haris Gacanin | 2019 | The optimal use of the network capacity and minimized congestion consequences are two aims of WMNs, making gateway selection one of the main research issues. | Tools of the Trade for ML | |
| Using directional antennas, a wireless mesh network's routing may save power. Combining Q-learning with Ant-based systems | A. R. Parvanak, M. Jahanshahi, M. Dehghan | 2019 | An ingenious method of diagnosing and fixing weak wireless connections. | RLBPR Algorithms | Better use of network capacity is achieved with this strategy as opposed to the closest gateway, minimum load index, projected transmission count, best route to best gateway, and RLBPR algorithms. |
| Machine learning and HPC are used to optimize reinforcement routing in wireless mesh networks. The use of Q-learning to SD-WiMesh networks | Mouna Naravani , Narayan D.G. , Sumedha Shinde , Mohammed Moin Mulla | 2020 | Compare the QUIC protocol's file-download rates to those of the TCP protocol. | Prediction techniques include multiple linear regression, support vector regression, and the Gaussian process. | NS-2 simulation results demonstrate that the multiple linear regression method is superior for predicting throughput, average delay, and packet loss. |
| Emerging Trends and Challenges in Wireless MemBrain Network Interference and Load Balancing Routing Metrics | Jawad Manzoor, Llorenç Cerdà-Alabern, Ramin Sadre, Idilio Drago | 2020 | The end objective is to make it easier to control and administer both wired and wireless networks. | The Effectiveness of QUIC in Wireless Mesh Networks | Our results show that although QUIC outperforms TCP on wired networks, it is much slower on the WMN. |
| Semi-permanent smart settings may take use of a software-defined fog computing architecture that is built on wireless mesh networks. | Syed Sherjeel A. Gilani, Amir Qayyum, Rao Naveed Bin Rais, Mukhtiar Bano | 2020 | Develop a novel technique for optimizing backhaul throughput and energy consumption. DAs in wireless network topologies | Take advantage of an SDN by using the WMN MILP Ant-Q algorithm | We show that our SDNMesh routing solution outperforms OLSR, BATMAN, and an SDN based Three-Stage routing protocol in simulated networks with regards to throughput, packet loss ratio, and latency. According to experimental results, SDNMesh also excels in these efficiency areas. |
| Reinforcement learning for quality-of-service-assured intelligent routing in crowded wireless mesh networks | Iyad Lahsen-Cherif, Lynda Zitoune, Véronique Vèque | 2021 | The purpose of this project is to optimize network routing using a reinforcement-learning framework. | The purpose of this project is to optimize network routing using a reinforcement-learning framework. The purpose of this project is to optimize network routing using a reinforcement-learning framework. | We look at the optimization weight factor, gateway location, network design, and beamwidth to see how these affect the overall tradeoff. |
| Weibull, normal, and Boulevard distributions are compared for mesh networks with router replacement choices using a hybrid intelligent simulation system. | 26. Khamxay Leevangtou, Hideya Ochiai, Chaodit Aswakul | 2021 | The fundamental objective of this research is to develop an adaptive routing system that may simultaneously decrease delivery times and prevent networks from becoming saturated. | Adaptive Routing Algorithm | When compared to the suggested method, the Dijkstra algorithm uses static or instantaneous changes to connection costs. The per-hop latency measurement from a real-world outdoor testbed is utilized to calibrate the simulation and provide the resultant end-to-end route delay. |
| Positional Improvements for Mesh Router Nodes In Wireless Mesh Networks, an Enhanced Moth-Flame Algorithm is Used. | Ankita Singh, Shiv Prakash, Sudhakar Singh | 2021 | An effective routing metric is necessary for a productive routing mechanism. | Data must be routed using unique and intelligent routing protocols based on routing metrics to improve the performance of these networks. | The outcomes significantly outperform the reference routing algorithms in an experimental evaluation. Using the NS-3 simulator, we assess how well the proposed approach performs in terms of QoS measures including packet delivery ratio (PDR), latency, and throughput. |
| Selecting Gateways in Wireless Mesh Networks that Can Handle Heavy Traffic Loads Using a Deep Learning-based Routing Strategy. | BAHAA MUNEER ISMAEL , ASRI BIN NGADI , JOHAN BIN MOHAMAD SHARIF |
2021 | Wireless mesh networks (WMN) offer a streamlined underlying communication substrate for constructing Internet of Things (IoT)-based smart infrastructures when a cable network is not an option owing to expense. | Algorithm for Learning Meshes in Stochastic Environments (SDFog-Mesh) | With the information gleaned from this literature review, the researcher will be better equipped to develop and test new, more effective routing methods. |
| Wireless mesh network throughput forecasting Adaptive sensing, scheduling, and spectrum selection using a support vector machine in cognitive networks | Shabir Ali, Mayank Pandey, Neeraj Tyagi | 2022 | choosing a route with the greatest packet delivery rate prediction. | Combines particle swarm optimization (PSO) with a distributed genetic algorithm (DGA) in a hybrid intelligence architecture (WMN-PSODGA ECLO-MFO LSTM). | Consideration has been given to the time required for setup, the time required to construct flows in data route devices, the time required to deliver microservices, the quality of service constraints, and the expenses associated with maintenance. |
| Thuy-Van T. Duong, Le Huu Binh, Vuong M. Ngo | 2022 | Overhead, mesh routers are set up to cover the desired area. | Traffic aware reliable gateway selection (TARGS) is a novel approach created to improve WMN service quality. | Our experiments show that the proposed method outperforms several widely used routing techniques. | |
| Title | Admir Barolli, Kevin Bylykbashi, Ermioni Qafzezi, Shinji Sakamoto, Leonard Barolli | 2022 | Wireless mesh network node placement difficulties for mesh routers (WMN-MRNP) need to be resolved. | Methodology | Our simulation results show that normal distribution with LDIWM as a replacement method for routers offers the best performance in terms of coverage and load balancing. |
| Using a Support Vector Machine with Adaptive Sensing, Scheduling, and Spectrum Selection in Cognitive Networks to Predict Throughput in Wireless Mesh Networks. | Sylia Mekhmoukh Taleb, Yassine Meraihi, Seyedali Mirjalili, Dalila Acheli, Amar Ramdane-Cherif , Asma Benmessaoud Gabis | 2023 | To forecast the route with the greatest Quality of Service (QoS), we use data from a simulated wireless mesh network to train a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)-based deep learning model. | An MR may find its own sweet spot between detecting, exploiting, and exploring the spectrum by using network feedbacks from the simulated MCs in a network simulator (NS2). | The superiority and precision of ECLO-MFO in locating mesh routers is proved by simulated results produced in MATLAB 2020a. Here, we evaluate ECLO-MFO against not only the original MFO but also eleven additional optimization methods, such as the Genetic Algorithm (GA), Simulated Annealing (SA), Harmony Search (HS), Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), Artificial Bee Colony (ABC), Cuckoo Search Algorithm (CS), and Bat Algorithm (BA). |
| Using a cooperative distributed QoE-based strategy for SVC video streaming via wireless mesh networks: AD3-GLaM. | Odongo Steven Eyobu, Kamwesigye Edwinah | 2023 | A novel method known as traffic aware reliable gateway selection (TARGS) was developed to improve WMNs' QoS. | Quality-of-experience-based cooperative distributed routing | Our results show that the LSTM-based model achieves the best PDR and throughput with its route selection. We also discover that the PDR and throughput of the learning models (MLP, LR, RF) are higher than those of the traditional Ad-hoc On-demand Distance Vector (AODV) routing protocol. |
| Cost and delay are taken into account in a bi-objective GA for determining where to put gateways in wireless meshed networks. | Rashmi Kushwah | 2023 | Each MR in a CR-WMN must be able to determine the spectrum's current condition, choose a channel free of PUs, and then switch to a new channel if a PU is discovered on the first channel. | Multi-objective optimization using genetic algorithms | Simulation findings show that the proposed strategy achieves lower average latency and traffic load and greater throughput than two other techniques available in the literature. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




