Submitted:
03 October 2024
Posted:
04 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Objective
- Automated faut diagnosis: the identification of incipient faults during regular machine operation is of significant importance, as it contributes to overall cost reduction, higher safety and reliability.
- Sensors fusion: combining data from multiple sensors provides more accurate, reliable, or comprehensive information than could be achieved by using any single sensor alone. It helps FD algorithms make safer and more informed decisions.
- Operating conditions: methodologies capable of working under non-stationary conditions should be preferred, although approaches which require steady-state conditions will also be evaluated.
- Machine topology: in industrial applications, induction machines (IMs) have been the most extensively studied [1,2,4,5,6]. Electric vehicles (EVs), on the other hand, can utilize a large variety of topologies, including IMs, permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs), synchronous reluctance machines (SyRMs), and wound field synchronous machines (WFSMs). Typically, these machines feature three-phase windings and operate with radial flux. However, the interest towards the adoption of multiphase configurations as well as axial flux machines (AFMs) is gradually increasing.
2. Overview of the Key Physical Quantities in the Analysis
- Currents: Among the various parameters examined in extensive research, phase currents are particularly prominent, as current sensors are essential for safety and control purposes. Furthermore, their integration is relatively straightforward. Consequently, FD analysis utilizing Motor Current Signature Analysis (MCSA) remains a beneficial approach for traction applications, leveraging the existing current sensors employed for drive control [5,7,8,9]. However, a significant limitation of current-based FD arises in scenarios involving low loads or minor faults, where inherent measurement noise can hinder the accurate assessment of the machine’s condition.
- Voltages: Although voltage sensors are less frequently utilized in many industrial applications, they are essential in electric vehicles (EVs), where their presence is critical not only for proper drive control [10], but also for safety reasons. Their implementation is also straightforward, making them viable candidates for FD in EVs.
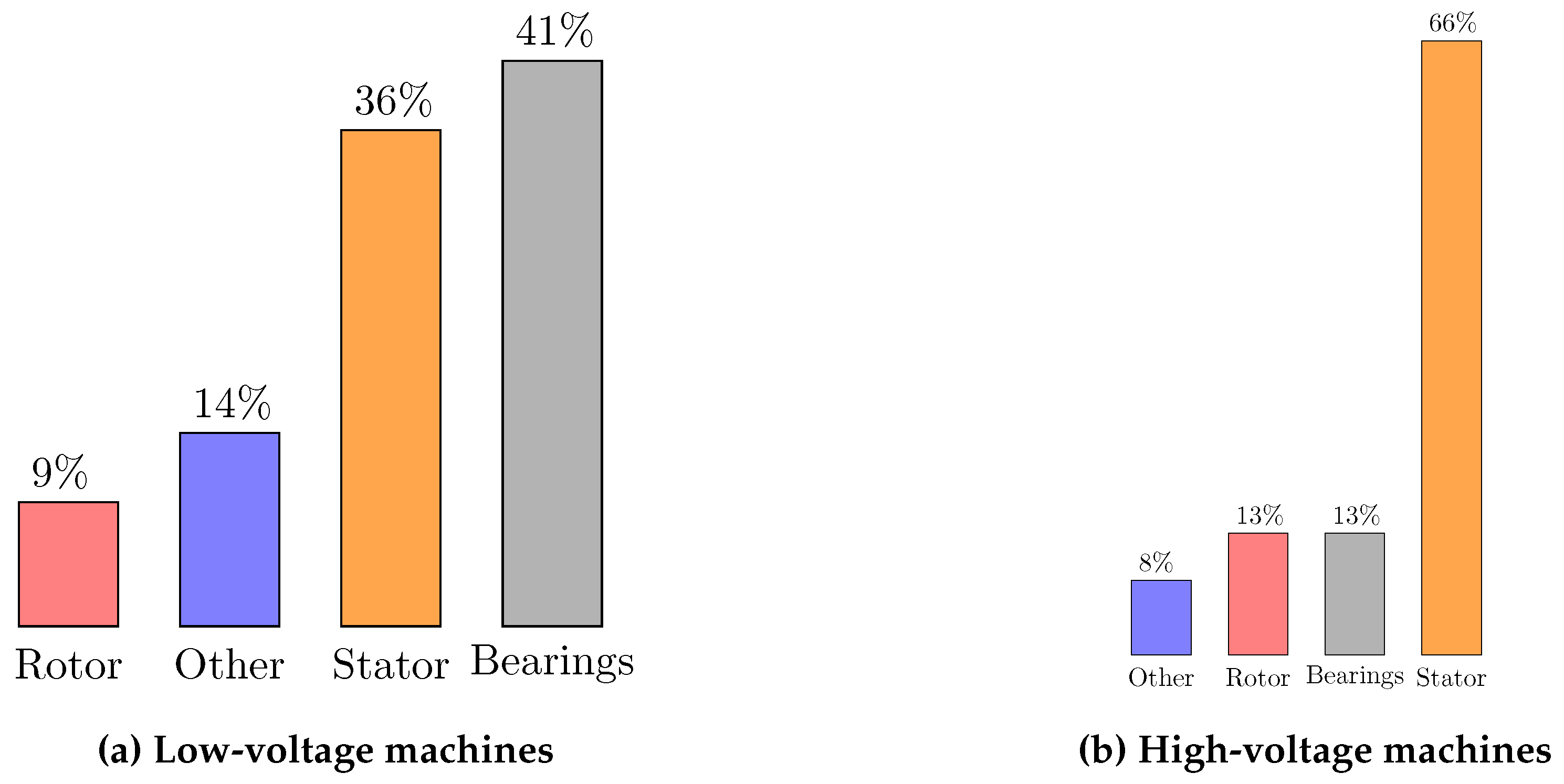
- Vibrations: Numerous investigations have been conducted on FD for industry application through vibration measurements, particularly for identifying bearing faults [9,11,12,13], which constitute the largest proportion of total failure in low-voltage (LV) machines and more than one tenth in high-voltage (HV) ones, where stator insulation failure become predominant, as illustrated in Figure 1 [7]. While promising results have been obtained, several limitations are present. Specifically, the need for additional sensors and the complexities associated with their installation present challenges for accurate assessments. Furthermore, the significant mechanical noise prevalent in EV environments introduces additional obstacles.
- Fluxes: Some research has explored the use of flux measurements as potential indicators of faults, similar to current analysis [9,11,14,15]. However, their application is limited due to the necessity for additional sensors. Most research make use of stray flux measurement [16,17], although the available data from previous studies is currently more limited compared to that of MCSA. Another option is represented by search coils. However, in EV applications, where the air gap is typically small, their incorporation may not be practical.
- Temperature: In terms of temperature-based methodologies, infrared thermography has been employed for FD purposes. This technique can map the thermal distribution across machine components, facilitating the identification of faults that induce excessive or uneven losses [18,19]. While this approach is still in its nascent stages and has predominantly been tested in industrial contexts, it holds potential as a viable alternative for future applications.
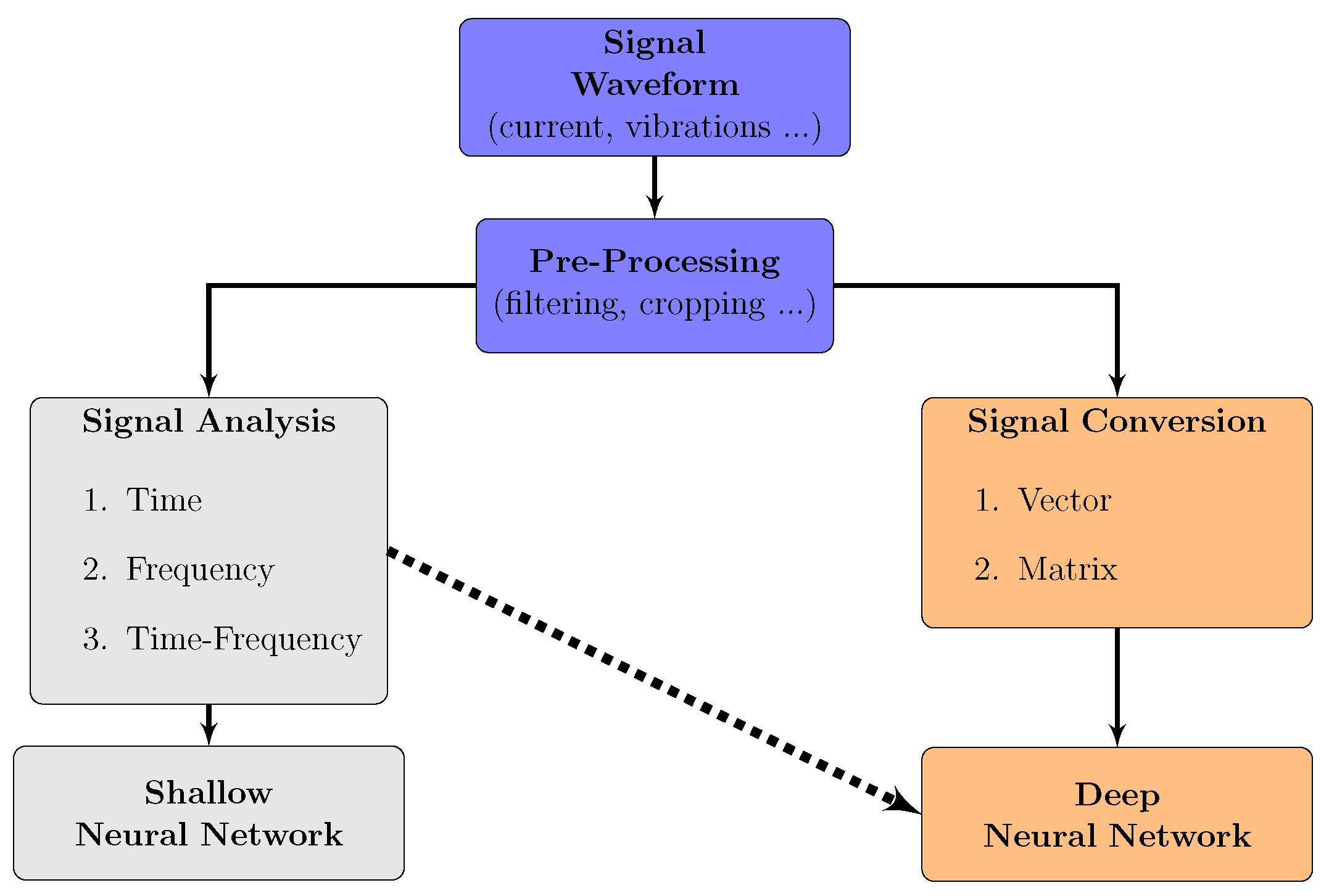
2.1. Signal Pre-Processing
3. Methods for Automatic Fault Detection
3.1. Model Based Methods
3.2. Artificial Intelligence Based Methods
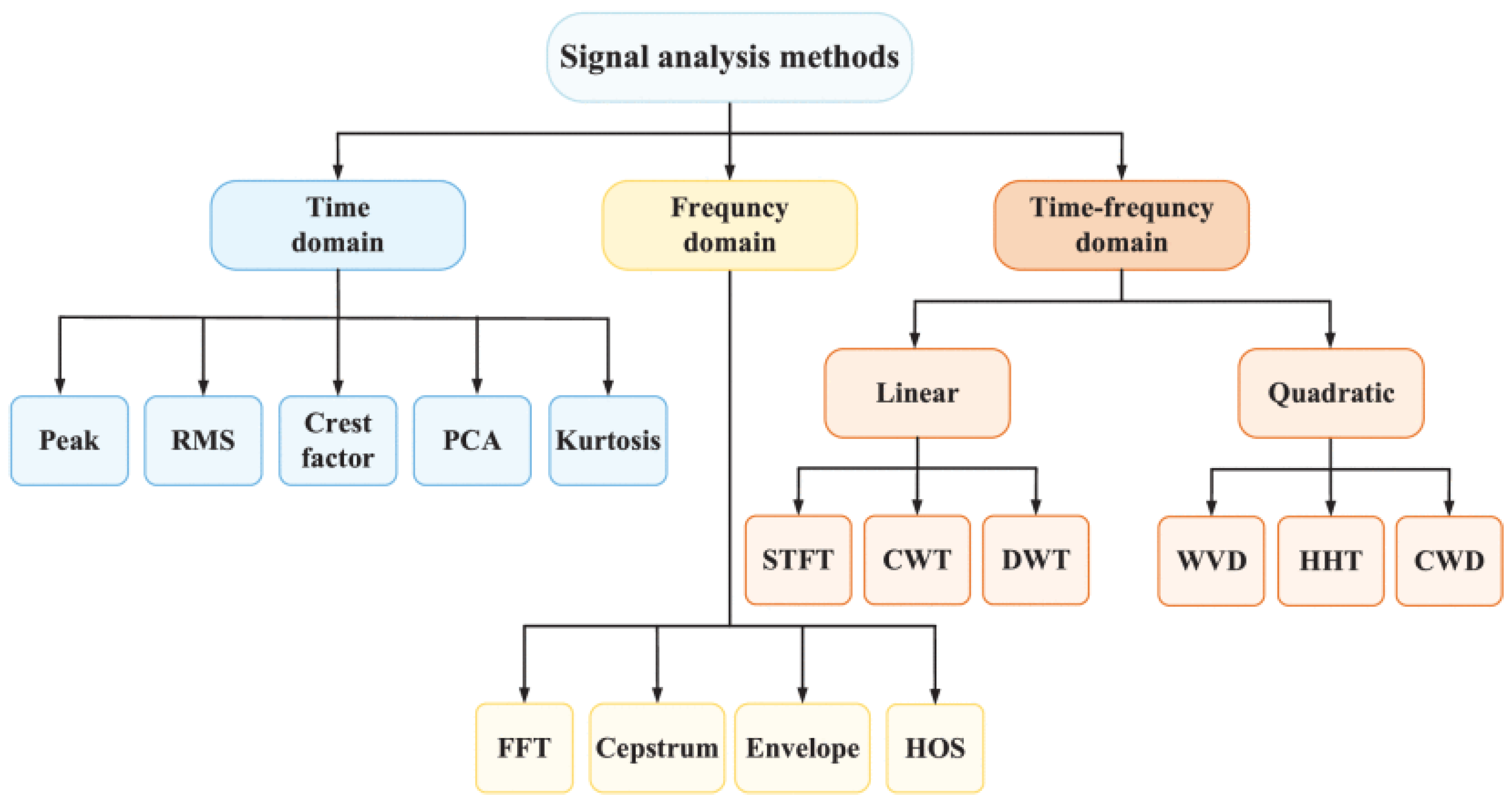
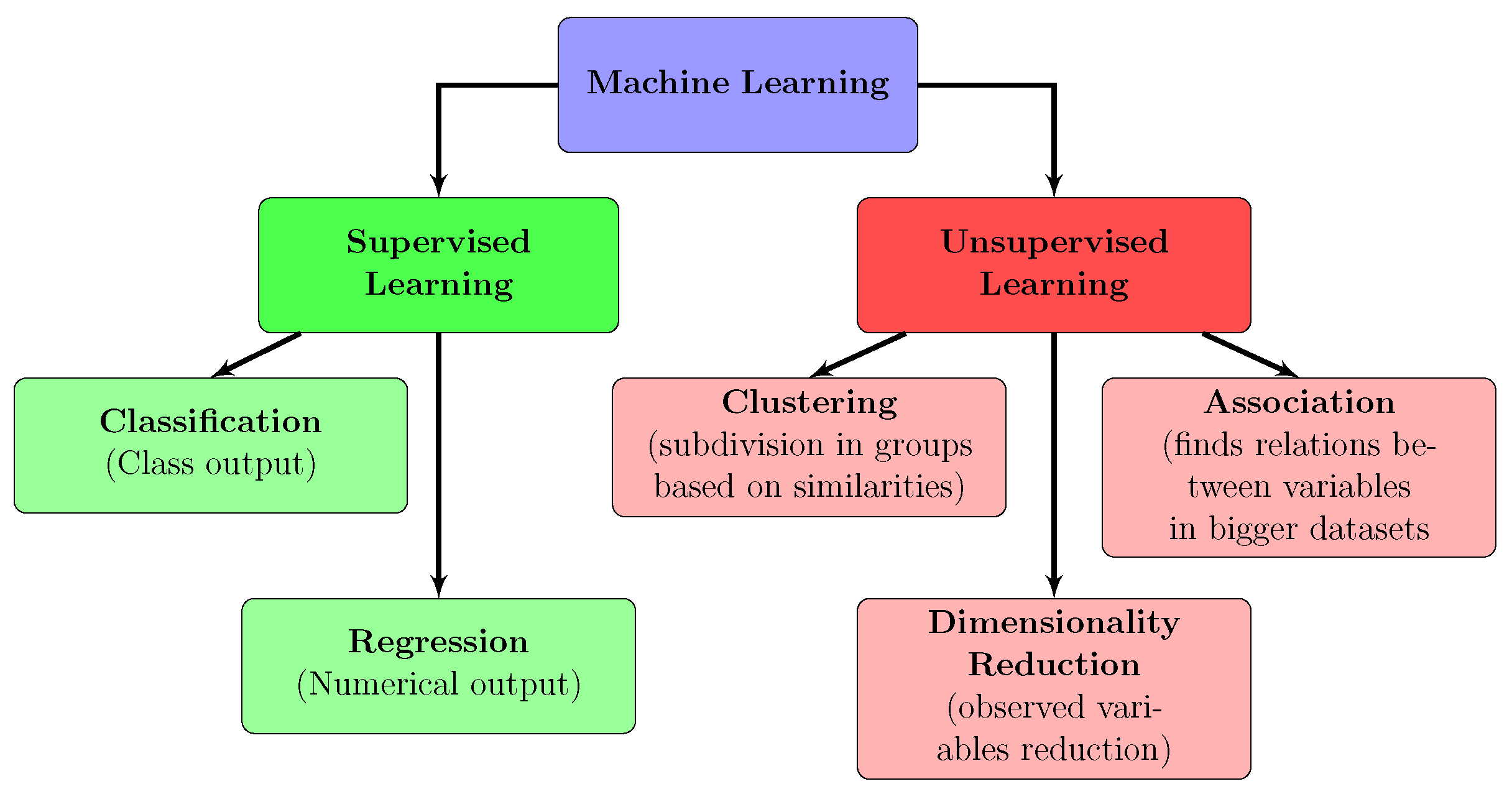
- Supervised Learning: they are by far the most adopted for electrical machine FD. Their main feature is the training based on labeled data. This means that the training dataset includes input-output pairs, where the input is the data which needs to be classified and output is the corresponding value or class. The goal of the algorithm is to learn a mapping from inputs to outputs so that it can predict the labels for new, unseen data accurately. For example, in a supervised learning task for fault classification based on current waveform measurement, the algorithm would be trained on a dataset of currents (inputs) with corresponding labels (outputs stating if the currents belongs to a healthy machine or not, or even the type of fault, if present). NNs have been widely adopted in supervised learning. Among them, deep neural networks (DNNs) have demonstrated greater potential in FD due to their enhanced flexibility and superior classification capability. Indeed, DNNs have the capacity to process both raw data and preprocessed data using various transforms [8,26]. Moreover, they exhibit great efficiency with larger datasets. NNs with a lower number of layers, called also shallow NNs (SNNs) can be also used for FD purposes. SNNs typically require extensive preprocessing of signals to emphasize features related to specific faults and are more suitable for smaller datasets [26]. Figure 3 resumes the FD methodologies utilizing neural networks. Other types of supervised learning methods which have been also utilized are support vector machines (SVM), k-Nearest-Neighbors (k-NN), linear regression (LR) and decision tree (DT) but there may be also other examples [28].
- Unsupervised Learning: it is a type of machine learning where the model is trained on data without labeled responses. The goal is to identify patterns and structures within the data. Common techniques include clustering (grouping similar data points) and dimensionality reduction (simplifying data while retaining important information). Unsupervised learning is generally less adopted for FD purposes, due to the complexity of the problem, especially if the aim is to identify incipient faults. However, some example of FD with unsupervised learning approaches are present, especially with autoencoders [29,30,31], which can be classified as dimensionality reduction unsupervised learning method.
4. Induction Machines Faults
4.1. Broken Rotor Bar Fault
4.2. Bearing Faults
| Type of fault | |
| bearing cage | |
| outer race | |
| inner race | |
| rolling element |
4.3. Rotor Eccentricity
4.4. Stator Inter-Turn Short Circuit
5. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Faults
5.1. Demagnetization faults
5.2. Rotor Mechanical Faults
5.3. Stator Inter-Turn Short Circuit
6. Other Electrical Machines
6.1. Synchronous Reluctance Machines
6.2. Wound Field Synchronous Machines
6.3. Axial Flux Machines
6.4. Multiphase Machines
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFM | Axial Flux Machines |
| BEMF | Back Electromotive Force |
| BRB | Broken Rotor Bar |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| CWT | Continuous Wavelet Transform |
| DTC | Direct Torque Control |
| DWT | Discrete Wavelet Transform |
| EV | Electric Vehicle |
| FOC | Field oriented Control |
| FHC | Fault Harmonic Component |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| IM | Induction Machine |
| ITSC | Interturn Short Circuit |
| KF | Kalman Filter |
| KLD | Kullback-Leibler Divergence |
| k-NN | k-Nearest Neighbor (algorithm) |
| LBP | Linear Binary Pattern |
| LSM | Least Square Method |
| MCSA | Motor Current Signature Analysis |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MVSA | Motor Vibration Signature Analysis |
| PMSM | Permanent Magnet Synchoronous Machine |
| SNN | Shallow Neural Network |
| SynRMs | Synchronous Reluctance Machine |
| THD | Total harmonic distortion |
| WFSM | Wound Field Synchronous Machine |
8.
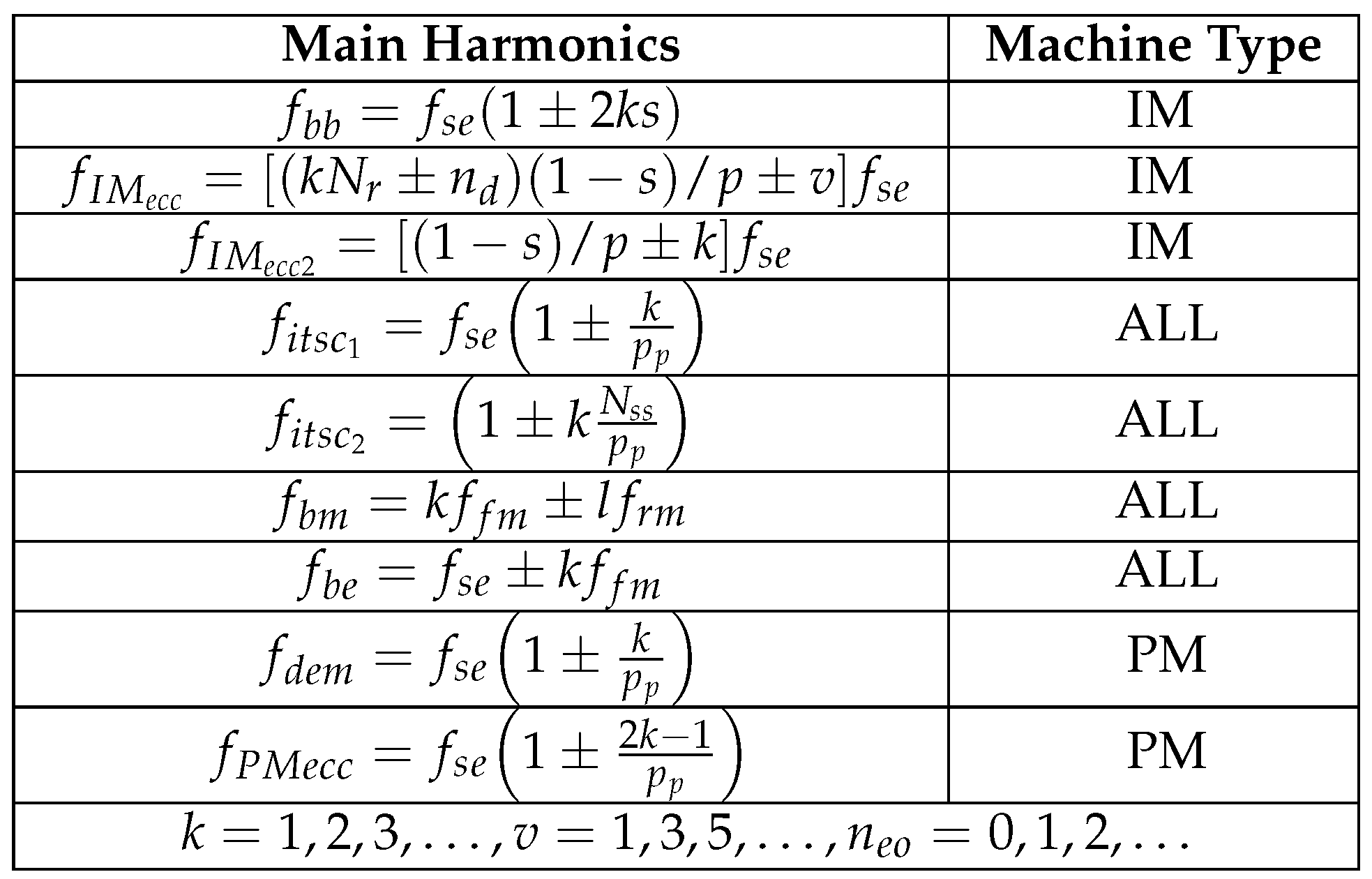
References
- Henao, H.; Capolino, G.A.; Fernandez-Cabanas, M.; Filippetti, F.; Bruzzese, C.; Strangas, E.; Pusca, R.; Estima, J.; Riera-Guasp, M.; Hedayati-Kia, S. Trends in Fault Diagnosis for Electrical Machines: A Review of Diagnostic Techniques. IEEE Industrial Electronics Magazine 2014, 8, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riera-Guasp, M.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A.; Capolino, G.A. Advances in Electrical Machine, Power Electronic, and Drive Condition Monitoring and Fault Detection: State of the Art. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2015, 62, 1746–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastura, M.; Zigliotto, M. Overview and Challenges of Fault Detection Methods in Electrical Motors for EV Applications. 26th Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM 2024), 2024.
- Nandi, S.; Toliyat, H.; Li, X. Condition Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis of Electrical Motors—A Review. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2005, 20, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhole, N.; Ghodke, S. Motor Current Signature Analysis for Fault Detection of Induction Machine–A Review. 2021 4th Biennial International Conference on Nascent Technologies in Engineering (ICNTE), 2021, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Bessous, N. Reliability Surveys of Fault Distributions in Rotating Electrical Machines : – Case Study of Fault Detections in IMs –. 2020 1st International Conference on Communications, Control Systems and Signal Processing (CCSSP), 2020, pp. 535–543. [CrossRef]
- Orlowska-Kowalska, T.; Wolkiewicz, M.; Pietrzak, P.; Skowron, M.; Ewert, P.; Tarchala, G.; Krzysztofiak, M.; Kowalski, C.T. Fault Diagnosis and Fault-Tolerant Control of PMSM Drives–State of the Art and Future Challenges. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 59979–60024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y. Motor Fault Diagnostics Based on Current Signatures: A Review. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2023, 72, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, D.V.; Baskar, S. Diverse fault detection techniques of three-phase induction motor — A review. 2016 International Conference on Emerging Technological Trends (ICETT), 2016, pp. 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Haje Obeid, N.; Battiston, A.; Boileau, T.; Nahid-Mobarakeh, B. Early Intermittent Interturn Fault Detection and Localization for a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor of Electrical Vehicles Using Wavelet Transform. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification 2017, 3, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Hang, J.; Zhang, J. Overview of fault diagnosis theory and method for permanent magnet machine. Chinese Journal of Electrical Engineering 2015, 1, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, F.B.; Sallem, M.; Braham, A. Optimized SWPT and Decision Tree for Incipient Bearing Fault Diagnosis. 2019 19th International Conference on Sciences and Techniques of Automatic Control and Computer Engineering (STA), 2019, pp. 231–236. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, S.; Li, W.; Song, K. Fault Diagnosis of Bearings Based on Multi-Sensor Information Fusion and 2D Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 23717–23725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaeva, G.; Saad, K.I.; Jahromi, M.G. Comprehensive Diagnostics of Induction Motor Faults Based on Measurement of Space and Time Dependencies of Air Gap Flux. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2017, 53, 2657–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.E.I.; Carmenate, J.G.; Antonino-Daviu, J.; Dunai, L.; Platero, C.A.; Conejero, J.A.; de Córdoba, P.F. Automatic Classification of Field Winding Faults in Synchronous Motors Based on Bicoherence Image Segmentation and Higher Order Statistics of Stray Flux Signals. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2023, 59, 3945–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minervini, M.; Mognaschi, M.E.; Di Barba, P.; Frosini, L. Convolutional Neural Networks for Automated Rolling Bearing Diagnostics in Induction Motors Based on Electromagnetic Signals. Applied Sciences 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frosini, L.; Minervini, M.; Ciceri, L.; Albini, A. Multiple faults detection in low voltage inverter-fed induction motors. 2019 IEEE 12th International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives (SDEMPED), 2019, pp. 323–329. [CrossRef]
- Alfredo Osornio-Rios, R.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A.; de Jesus Romero-Troncoso, R. Recent Industrial Applications of Infrared Thermography: A Review. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2019, 15, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Nunez, J.A.; Morales-Hernandez, L.A.; Osornio-Rios, R.A.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A.; Romero-Troncoso, R.J. Self-adjustment methodology of a thermal camera for detecting faults in industrial machinery. IECON 2016 - 42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, 2016, pp. 7119–7124. [CrossRef]
- Pons-Llinares, J.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A.; Riera-Guasp, M.; Bin Lee, S.; Kang, T.j.; Yang, C. Advanced Induction Motor Rotor Fault Diagnosis Via Continuous and Discrete Time–Frequency Tools. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2015, 62, 1791–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowsky, J.S. The continuous wavelet transform: a tool for signal investigation and understanding. 1994.
- A robust stator inter-turn fault detection in induction motor utilizing Kalman filter-based algorithm. Measurement 2022, 187, 110181. [CrossRef]
- Zarei, J.; Kowsari, E.; Razavi-Far, R. Induction Motors Fault Detection Using Square-Root Transformed Cubature Quadrature Kalman Filter. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2019, 34, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urresty, J.C.; Riba, J.R.; Romeral, L. Diagnosis of Interturn Faults in PMSMs Operating Under Nonstationary Conditions by Applying Order Tracking Filtering. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2013, 28, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, W.; Abd El Geliel, M.; Lotfy, A. Fault Diagnosis of PMSG Stator Inter-Turn Fault Using Extended Kalman Filter and Unscented Kalman Filter. Energies 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, W.; Hu, Y.; Gong, C.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Deng, J. Artificial Intelligence-Based Technique for Fault Detection and Diagnosis of EV Motors: A Review. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification 2022, 8, 384–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnavas, Y.L.; Chasiotis, I.D.; Drakaki, M.; Tziafettas, I.A. Recent Advances of Neural Network based Methods in Induction Motor Fault Diagnosis. 2020 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), 2020, Vol. 1, pp. 1411–1417. [CrossRef]
- F.Y, O.; J.E.T, A.; O., A.; O, H.J.; O, O.; J, A. Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms: Classification and Comparison. International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology 2017, 48, 128–138. [CrossRef]
- Amarbayasgalan, T.; Ryu, K.H. Unsupervised Feature-Construction-Based Motor Fault Diagnosis. Sensors 2024, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principi, E.; Rossetti, D.; Squartini, S.; Piazza, F. Unsupervised electric motor fault detection by using deep autoencoders. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica 2019, 6, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, S.; Aissa, C.; Hamou, A.A.; Chawki, S.; Oussama, B.S. A Deep Learning Based on Sparse Auto-Encoder with MCSA for Broken Rotor Bar Fault Detection and Diagnosis. 2018 International Conference on Electrical Sciences and Technologies in Maghreb (CISTEM), 2018, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Shanthamallu, U.; Spanias, A. Machine and Deep Learning Algorithms and Applications; Synthesis Lectures on Signal Processing, Springer International Publishing, 2022.
- López, C. MACHINE LEARNING WITH MATLAB. SUPERVISED LEARNING AND CLASSIFICATION; SCIENTIFIC BOOKS.
- LOPEZ, C. MACHINE LEARNING WITH MATLAB. UNSUPERVISED LEARNING TECHNIQUES: CLASSIFICATION; Lulu.com, 2020.
- Culbert, I.; Rhodes, W. Using current signature analysis technology to reliably detect cage winding defects in squirrel cage induction motors. Record of Conference Papers Industry Applications Society 52nd Annual Petroleum and Chemical Industry Conference, 2005, pp. 95–101. [CrossRef]
- Puche-Panadero, R.; Martinez-Roman, J.; Sapena-Bano, A.; Burriel-Valencia, J. Diagnosis of Rotor Asymmetries Faults in Induction Machines Using the Rectified Stator Current. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2020, 35, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Sun, L.; Xu, L.; Xu, G. Improvement of the Hilbert Method via ESPRIT for Detecting Rotor Fault in Induction Motors at Low Slip. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2013, 28, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Du, Y.; Habetler, T.G.; Lu, B. A Survey of Condition Monitoring and Protection Methods for Medium-Voltage Induction Motors. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2011, 47, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ramirez, M.; Rodriguez-Donate, C.; Ledesma-Carrillo, L.M.; Villalobos-Pina, F.J.; Munoz-Minjares, J.U.; Cabal-Yepez, E. Walsh–Hadamard Domain-Based Intelligent Online Fault Diagnosis of Broken Rotor Bars in Induction Motors. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2022, 71, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.B. Flux-Based Detection and Classification of Induction Motor Eccentricity, Rotor Cage, and Load Defects. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2021, 57, 2471–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puche-Panadero, R.; Martinez-Roman, J.; Sapena-Bano, A.; Burriel-Valencia, J.; Pineda-Sanchez, M.; Perez-Cruz, J.; Riera-Guasp, M. New Method for Spectral Leakage Reduction in the FFT of Stator Currents: Application to the Diagnosis of Bar Breakages in Cage Motors Working at Very Low Slip. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2021, 70, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, C.G.; Silva, L.C.d. Induction Motor Speed Estimation Based on Airgap Flux Measurement Using Hilbert Transform and Fast Fourier Transform. IEEE Sensors Journal 2022, 22, 12690–12699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualotto, D.; Zigliotto, M. Increasing Feasibility of Neural Network-Based Early Fault Detection in Induction Motor Drives. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics 2022, 10, 2042–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, H.; Ouassaid, M.; Ngote, N. An experimental method for diagnostic of incipient broken rotor bar fault in induction machines. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotou, P.A.; Arvanitakis, I.; Lophitis, N.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A.; Gyftakis, K.N. A New Approach for Broken Rotor Bar Detection in Induction Motors Using Frequency Extraction in Stray Flux Signals. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2019, 55, 3501–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.; Bhat, S.; Zychma, D.; Sowa, P. Broken Rotor Bar Fault Diagnosis Techniques Based on Motor Current Signature Analysis for Induction Motor—A Review. Energies 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, M.E.E.D.; Ibrahim, D.K.; Gilany, M.I. Broken Bar Fault Detection and Diagnosis Techniques for Induction Motors and Drives: State of the Art. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 88504–88526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, P.; Long, Z.; Yang, J.; Huang, S. A Novel Data-Driven Mechanical Fault Diagnosis Method for Induction Motors Using Stator Current Signals. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification 2023, 9, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviña-Corral, V.; de Jesus Rangel-Magdaleno, J.; Peregrina-Barreto, H.; Ramirez-Cortes, J.M. Bearing Fault Detection in ASD-Powered Induction Machine Using MODWT and Image Edge Detection. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 24181–24193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsugi, K.; Pandarakone, S.E.; Mizuno, Y.; Nakamura, H. Common Diagnosis Approach to Three-Class Induction Motor Faults Using Stator Current Feature and Support Vector Machine. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 24945–24952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusamarello, B.; Cardozo da Silva, J.C.; de Morais Sousa, K.; Guarneri, G.A. Bearing Fault Detection in Three-Phase Induction Motors Using Support Vector Machine and Fiber Bragg Grating. IEEE Sensors Journal 2023, 23, 4413–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Ray, S.; Dey, D.; Munshi, S. Detection of Simultaneous Bearing Faults Fusing Cross Correlation With Multikernel SVM. IEEE Sensors Journal 2023, 23, 14418–14427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusamarello, B.; Cardozo da Silva, J.C.; de Morais Sousa, K.; Guarneri, G.A. Bearing Fault Detection in Three-Phase Induction Motors Using Support Vector Machine and Fiber Bragg Grating. IEEE Sensors Journal 2023, 23, 4413–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DEHINA, W.; BOUMEHRAZ, M.; KRATZ, F.; FANTINI, J. Diagnosis and Comparison between Stator Current Analysis and Vibration Analysis of Static Eccentricity Faults in The Induction Motor. 2019 4th International Conference on Power Electronics and their Applications (ICPEA), 2019, pp. 1–4. [CrossRef]
- Alimardani, R.; Rahideh, A.; Hedayati Kia, S. Mixed Eccentricity Fault Detection for Induction Motors Based on Time Synchronous Averaging of Vibration Signals. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2024, 71, 3173–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agah, G.R.; Rahideh, A.; Khodadadzadeh, H.; Khoshnazar, S.M.; Hedayatikia, S. Broken Rotor Bar and Rotor Eccentricity Fault Detection in Induction Motors Using a Combination of Discrete Wavelet Transform and Teager–Kaiser Energy Operator. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2022, 37, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes, A.G.; Fonseca, D.S.B.; Antunes, H.R.P.; López, O.; Marques Cardoso, A.J.; Doval-Gandoy, J. Discrimination Between Eccentricity and Interturn Faults Using Current or Voltage-Reference Signature Analysis in Symmetrical Six-Phase Induction Machines. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2023, 38, 2421–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lin, C.; Inoue, H.; Kanemaru, M. Induction Motor Eccentricity Fault Detection and Quantification Using Topological Data Analysis. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 37891–37902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrhonen, J.; Jokinen, T.; Hrabovcova, V. Design of Rotating Electrical Machines; Wiley, 2013.
- Elbouchikhi, E.; Amirat, Y.; Feld, G.; Benbouzid, M. Generalized Likelihood Ratio Test Based Approach for Stator-Fault Detection in a PWM Inverter-Fed Induction Motor Drive. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2019, 66, 6343–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.K.; Radhika, S.; Padmanabhan, S.V. Wavelet Based Fault Detection and Diagnosis Using Online MCSA of Stator Winding Faults Due to Insulation Failure in Industrial Induction Machine. 2018 IEEE Recent Advances in Intelligent Computational Systems (RAICS), 2018, pp. 204–208. [CrossRef]
- Yagami, Y.; Araki, C.; Mizuno, Y.; Nakamura, H. Turn-to-turn insulation failure diagnosis of stator winding of low voltage induction motor with the aid of support vector machine. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation 2015, 22, 3099–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolkiewicz, M.; Tarchała, G.; Orłowska-Kowalska, T.; Kowalski, C.T. Online Stator Interturn Short Circuits Monitoring in the DFOC Induction-Motor Drive. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2016, 63, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengifo, J.; Moreira, J.; Vaca-Urbano, F.; Alvarez-Alvarado, M.S. Detection of Inter-Turn Short Circuits in Induction Motors Using the Current Space Vector and Machine Learning Classifiers. Energies 2024, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzoy, A.; Mohammed, O.A.; Restrepo, J. Analysis of the Impact of Stator Interturn Short-Circuit Faults on Induction Machines Driven by Direct Torque Control. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2018, 33, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, R.Z.; Strangas, E.G. On the Accuracy of Fault Detection and Separation in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines Using MCSA/MVSA and LDA. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2016, 31, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhang, X.; Qin, G.; Xie, J.; Peng, J.; Huang, S.; Long, Z.; Tang, Y. Demagnetization Fault Diagnosis of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Using Magnetic Leakage Signals. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 2023, 19, 6105–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzak, P.; Wolkiewicz, M. Demagnetization Fault Diagnosis of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on Stator Current Signal Processing and Machine Learning Algorithms. Sensors 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Gui, W.; Yang, C.; Peng, T.; Luo, J.; Han, Y. Multiple Observers-Based Demagnetization Fault Detection With Inductance Mismatch Impacts Eliminated for PMSMs. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2023, 38, 8016–8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Lee, S.T.; Hur, J. A Novel Fault Diagnosis Technique for IPMSM Using Voltage Angle. 2018 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), 2018, pp. 3236–3243. [CrossRef]
- Vancini, L.; Mengoni, M.; Rizzoli, G.; Zarri, L.; Tani, A. Local Demagnetization Detection in Six-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2024, 71, 5508–5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualotto, D.; Zigliotto, M. A comprehensive approach to convolutional neural networks-based condition monitoring of permanent magnet synchronous motor drives. IET ELECTRIC POWER APPLICATIONS 2021, pp. 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Mbo’o, C.P.; Hameyer, K. Bearing damage diagnosis by means of the linear discriminant analysis of stator current feature. 2015 IEEE 10th International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power Electronics and Drives (SDEMPED), 2015, pp. 296–302. [CrossRef]
- Mazzoletti, M.A.; Bossio, G.R.; Bossio, J.M.; Leidhold, R. Fault Diagnosis in PMSM with Partitioned Stator Windings - Part I: Experimental Validation with Static Eccentricity. 2020 IEEE Congreso Bienal de Argentina (ARGENCON), 2020, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Rosero, J.; Romeral, L.; Rosero, E.; Urresty, J. Fault Detection in dynamic conditions by means of Discrete Wavelet Decomposition for PMSM running under Bearing Damage. 2009 Twenty-Fourth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, 2009, pp. 951–956. [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Yin, Z.; Yuan, D.; Gao, F.; Liu, J. An Intelligent Method for Early Motor Bearing Fault Diagnosis Based on Wasserstein Distance Generative Adversarial Networks Meta Learning. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2023, 72, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, M.E.E.D.; Ibrahim, D.K.; Gilany, M.I. Detection and Diagnosis of Bearing Faults Under Fixed and Time-Varying Speed Conditions Using Persistence Spectrum and Multi-Scale Structural Similarity Index. IEEE Sensors Journal 2022, 22, 2637–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Jeong, H.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.W. Interturn Short Fault Diagnosis in a PMSM by Voltage and Current Residual Analysis With the Faulty Winding Model. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2018, 33, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Wang, J.; Mills, A.R.; Chong, E.; Sun, Z. High-Frequency Voltage Injection Based Stator Interturn Fault Detection in Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2021, 36, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Feng, X.; Zeng, J.; Wang, Z. A Novel Turn Fault Detection Strategy Based on High-Frequency Neutral-to-Ground Voltages. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2023, 38, 15945–15955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, Z.; Tetik, K. Diagnosis of Inter-Turn Faults Based on Fault Harmonic Component Tracking in LSPMSMs Working Under Nonstationary Conditions. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 92101–92112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Wang, J.; Sen, B.; Mills, A.R.; Chong, E.; Sun, Z. PWM Ripple Currents Based Turn Fault Detection for Multiphase Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2017, 53, 2740–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Wang, J.; Mills, A.R.; Chong, E.; Sun, Z. Current-Residual-Based Stator Interturn Fault Detection in Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2021, 68, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Xie, L.; Halick, M.S.M.; Vaiyapuri, V. Stator End-Winding Thermal and Magnetic Sensor Arrays for Online Stator Inter-Turn Fault Detection. IEEE Sensors Journal 2021, 21, 5312–5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Hur, J. Analysis of Inter-Turn-Short Fault in an FSCW IPM Type Brushless Motor Considering Effect of Control Drive. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2020, 56, 1356–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martin, I.D.; Brosch, A.; Tinazzi, F.; Zigliotto, M. Continuous Control Set Model Predictive Torque Control With Minimum Current Magnitude Criterion for Synchronous Motor Drives. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2024, 71, 6787–6796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama Krishna, M.S.; Seshadrinath, J. Stator Interturn Fault Modeling and Diagnosis for Synchronous Reluctance Motor Drive. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Drives and Energy Systems (PEDES), 2022, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Laadjal, K.; Bento, F.; Henriques, K.; Cardoso, A.J.M.; Sahraoui, M. A Novel Indicator-Based Online Diagnostics Technique of Interturn Short-Circuit Faults in Synchronous Reluctance Machines. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics 2023, 11, 3492–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, K.; Laadjal, K.; Cardoso, A.J.M. Inter-Turn Short-Circuit Fault Detection in Synchronous Reluctance Machines, Based on Current Analysis. Engineering Proceedings 2022, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, C.E.G.; de Porras Cosano, A.M.; Tian, P.; Diaz, J.C.; Zarzo, A.; Platero, C.A. Synchronous Machines Field Winding Turn-to-Turn Fault Severity Estimation Through Machine Learning Regression Algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2022, 37, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, R.; Mahtani, K.; Rivero, E.; Platero, C.A. Brushless Synchronous Machine Field Winding Interturn Fault Severity Estimation Through Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2024, 39, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, M.F.; Kim, H.j.; Battulga, B.; Lee, S.B. Insight to Enhancing the Performance of the Pole Drop Test for Detecting Field Winding Turn Faults in Salient Pole Synchronous Motors. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2021, 36, 3582–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrandideh, S.; Milasi, M.E.; Haghjoo, F.; Cruz, S.M.A. Turn to Turn Fault Detection, Discrimination, and Faulty Region Identification in the Stator and Rotor Windings of Synchronous Machines Based on the Rotational Magnetic Field Distortion. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2020, 35, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, W.; Jiao, N.; Sun, C.; Mao, S. Fault Diagnosis of Rotating Rectifier in Aircraft Wound-Rotor Synchronous Starter–Generator Based on Stator Currents Under all Operational Processes. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2023, 38, 16072–16084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, M.F.; Park, J.; Park, Y.; Lee, S.B.; Antonino-Daviu, J.A. Electrical Testing for Detection and Classification of Open Damper Bar and Shorted Field Winding Failures in Wound Field Synchronous Motors. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2022, 58, 4532–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bisschop, J.; Vansompel, H.; Sergeant, P.; Dupre, L. Demagnetization Fault Detection in Axial Flux PM Machines by Using Sensing Coils and an Analytical Model. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics 2017, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mínaz, M.R.; Akcan, E. An Effective Method for Detection of Demagnetization Fault in Axial Flux Coreless PMSG With Texture-Based Analysis. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 17438–17449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamprokostopoulos, A.; Mitronikas, E.; Barmpatza, A. Detection of Demagnetization Faults in Axial Flux Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Wind Generators. Energies 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirimani, S.M.; Vahedi, A.; Marignetti, F.; Di Stefano, R. An Online Method for Static Eccentricity Fault Detection in Axial Flux Machines. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2015, 62, 1931–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogidi, O.O.; Barendse, P.S.; Khan, M.A. Detection of Static Eccentricities in Axial-Flux Permanent-Magnet Machines With Concentrated Windings Using Vibration Analysis. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2015, 51, 4425–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, E. Advances in Converter Control and Innovative Exploitation of Additional Degrees of Freedom for Multiphase Machines. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2016, 63, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, C.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, Y. A Generalized, Fast and Robust Open-Circuit Fault Diagnosis Technique for Star-Connected Symmetrical Multiphase Drives. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2022, 37, 1921–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Fang, L.; Jiang, D.; Qu, R. A Machine-Learning-Based Fault Diagnosis Method With Adaptive Secondary Sampling for Multiphase Drive Systems. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2022, 37, 8767–8772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Gu, M.; Xiao, D.; He, J.; Emadi, A. Diagnosis-Free Self-Healing Scheme for Open-Circuit Faults in Dual Three-Phase PMSM Drives. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2020, 35, 12053–12071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, P.F.C.; Cruz, S.M.A.; Mendes, A.M.S. Online Diagnostic Method for the Detection of High-Resistance Connections and Open-Phase Faults in Six-Phase PMSM Drives. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications 2022, 58, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesai-Ahmed, H.; Jlassi, I.; Cardoso, A.J.M.; Bentaallah, A. Multiple Open-Circuit Faults Diagnosis in Six-Phase Induction Motor Drives Using Stator Current Analysis. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2022, 37, 7275–7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, A.; Lefley, P. Research on torque ripple under healthy and open-circuit fault-tolerant conditions in a PM multiphase machine. CES Transactions on Electrical Machines and Systems 2020, 4, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, M.J.; Gonzalez-Prieto, I.; Rios-Garcia, N.; Barrero, F. A Simple, Fast, and Robust Open-Phase Fault Detection Technique for Six-Phase Induction Motor Drives. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2018, 33, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Prieto, I.; Duran, M.J.; Rios-Garcia, N.; Barrero, F.; Martín, C. Open-Switch Fault Detection in Five-Phase Induction Motor Drives Using Model Predictive Control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 2018, 65, 3045–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Liu, Z.; Tasiu, I.A.; Chen, T. Fault Diagnosis and Tolerance With Low Torque Ripple for Open-Switch Fault of IM Drives. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification 2021, 7, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesai-Ahmed, H.; Jlassi, I.; Cardoso, A.J.M.; Bentaallah, A. Multiple Open-Circuit Faults Diagnosis in Six-Phase Induction Motor Drives Using Stator Current Analysis. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2022, 37, 7275–7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Olson, G.F.; Henriksson, C.; Peretti, L. Open Fault Detection in Variable Phase-Pole Machines Based on Harmonic Plane Decomposition. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2024, 39, 4557–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Cheng, M.; Wang, W.; Hu, Y. Comprehensive Diagnosis and Tolerance Strategies for Electrical Faults and Sensor Faults in Dual Three-Phase PMSM Drives. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2019, 34, 6669–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Femia, A.; Sala, G.; Vancini, L.; Rizzoli, G.; Mengoni, M.; Zarri, L.; Tani, A. A Machine-Learning-Based Interturn Short-Circuit Diagnosis for Multi-Three-Phase Brushless Motors. IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Industrial Electronics 2023, 4, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





