Submitted:
02 October 2024
Posted:
02 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Test the base ionic liquid and the INF produced as heat carrier fluid in a commercial solar thermal-photovoltaic hybrid (PVT) collector to compare its performance with that of water and determine the suitability of current PVT collectors for the use of INFs.
- Study by numerical simulation by means of the HEATT application the thermal field inside the PVT collector tubes in order to optimize the tube length and the operating conditions of the collector based on the concept of characteristic length.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
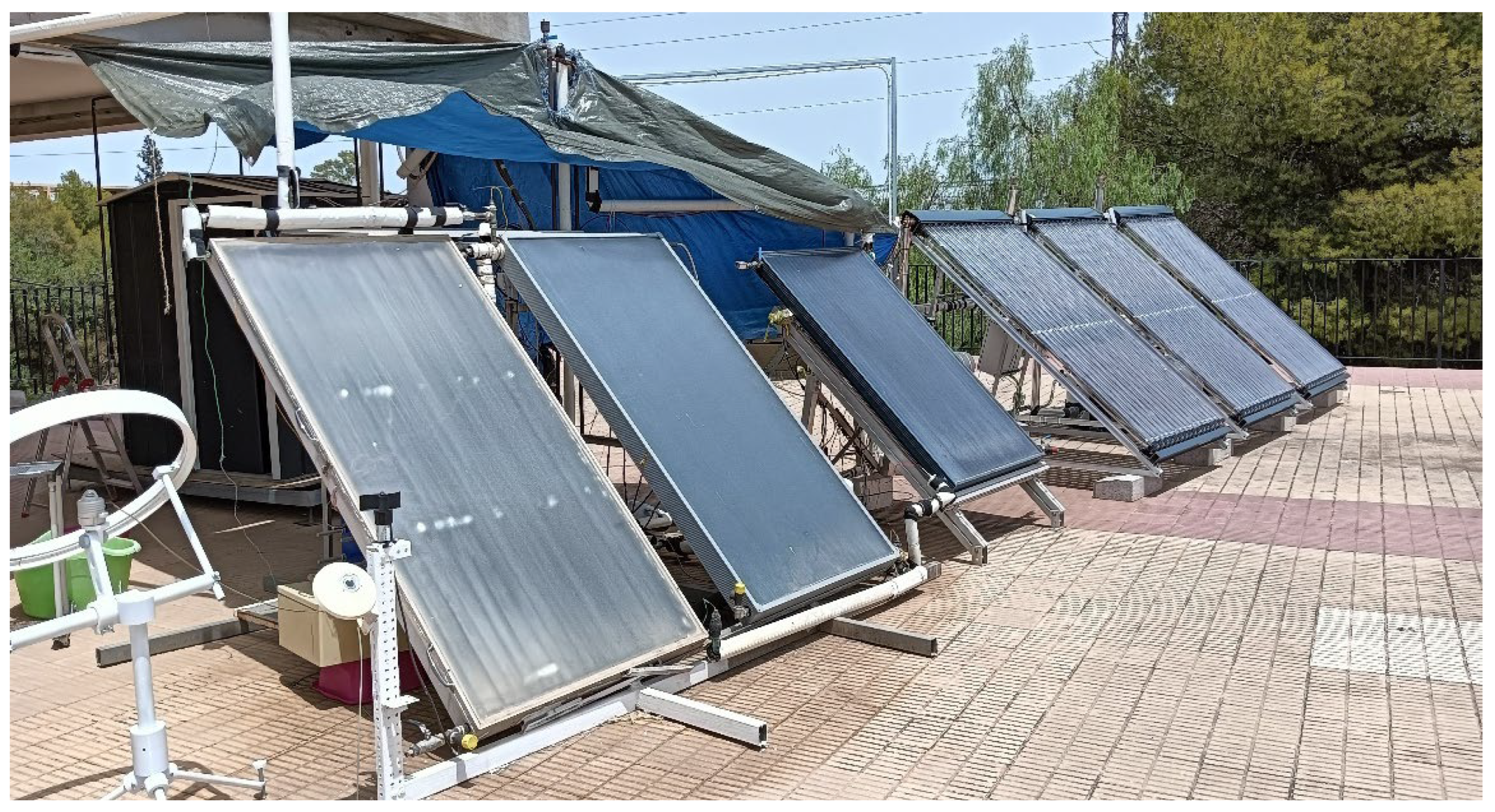
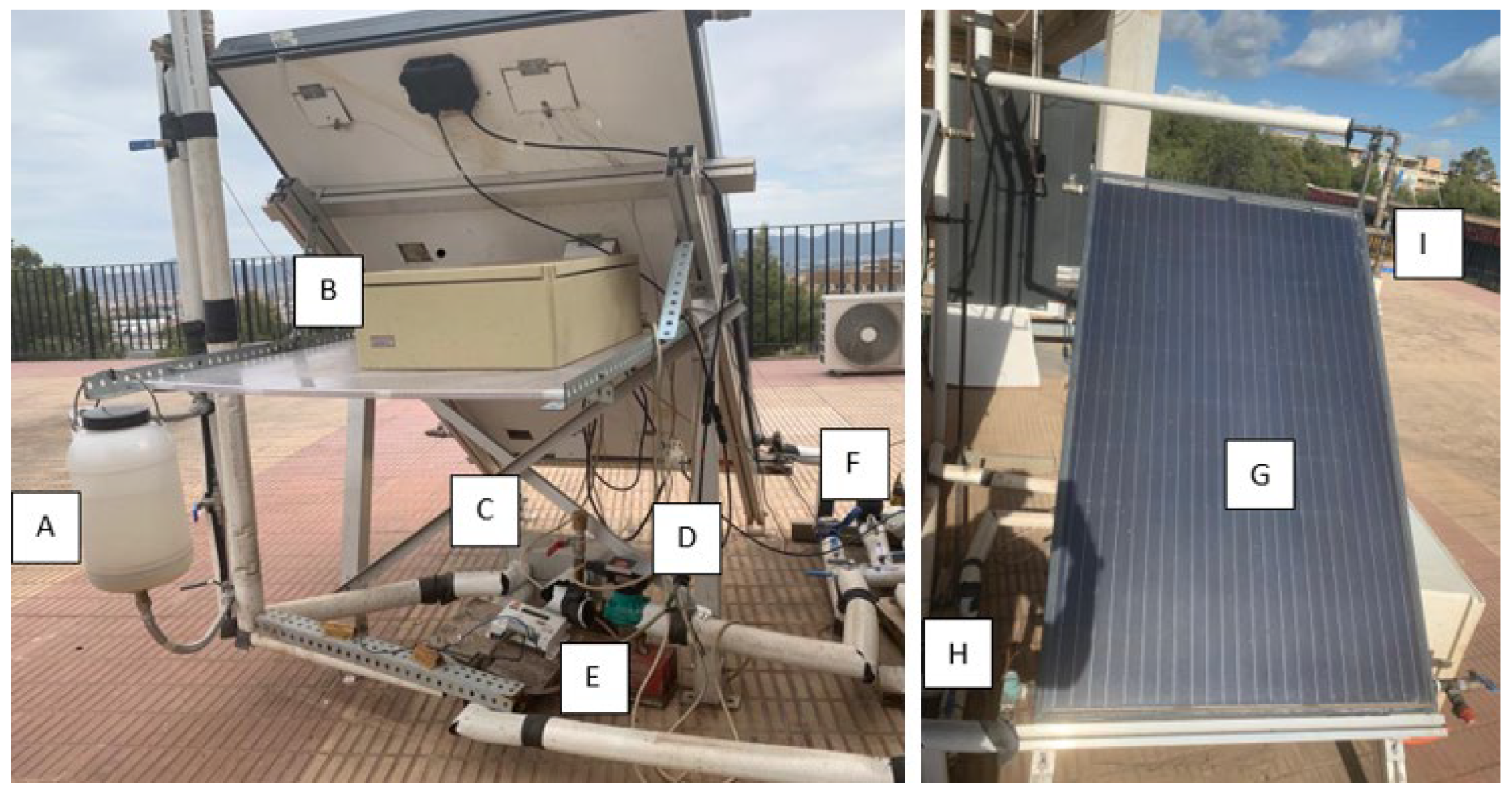
2.2. Solar collector tests

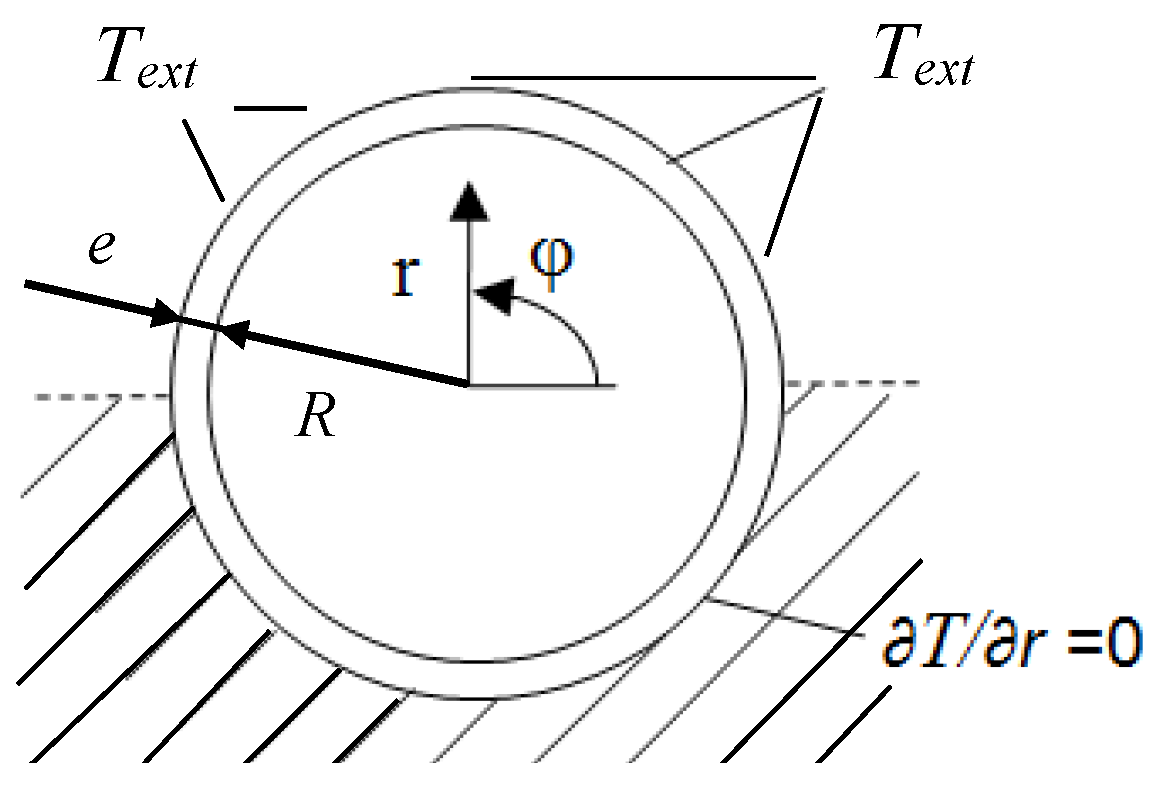
2.3. Numerical simulation: the HEATT® Platform

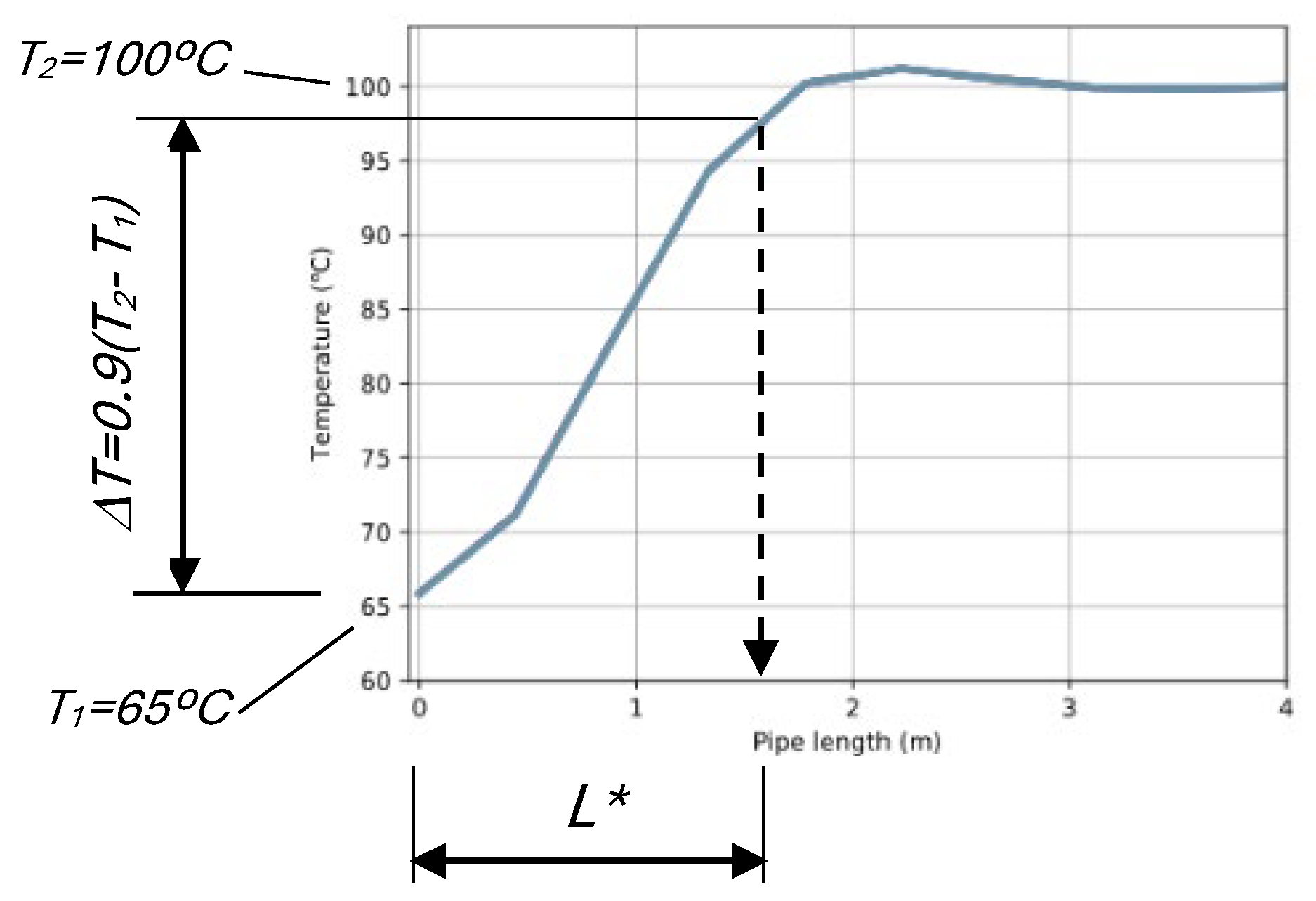
2.4. Characteristic length
3. Results
3.1. Experimental fluid temperatures
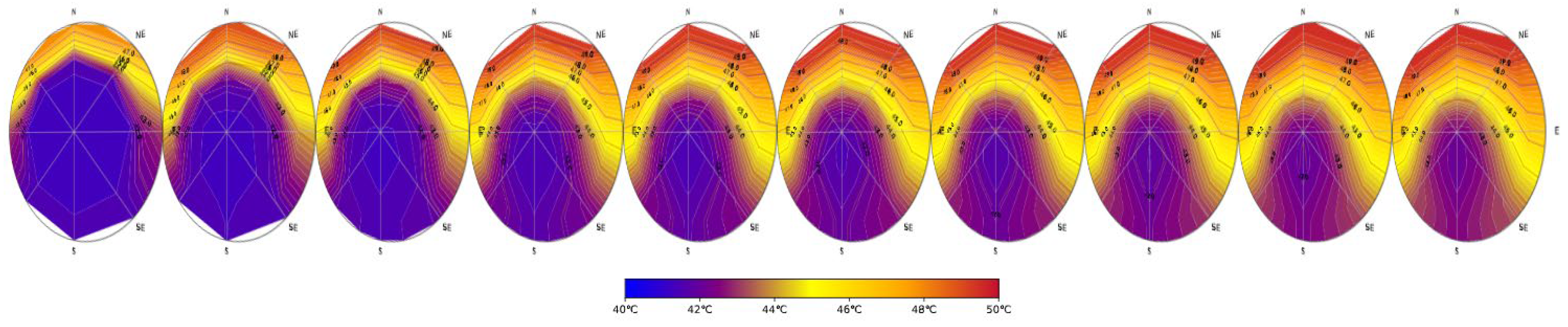
3.2. HEATT simulations
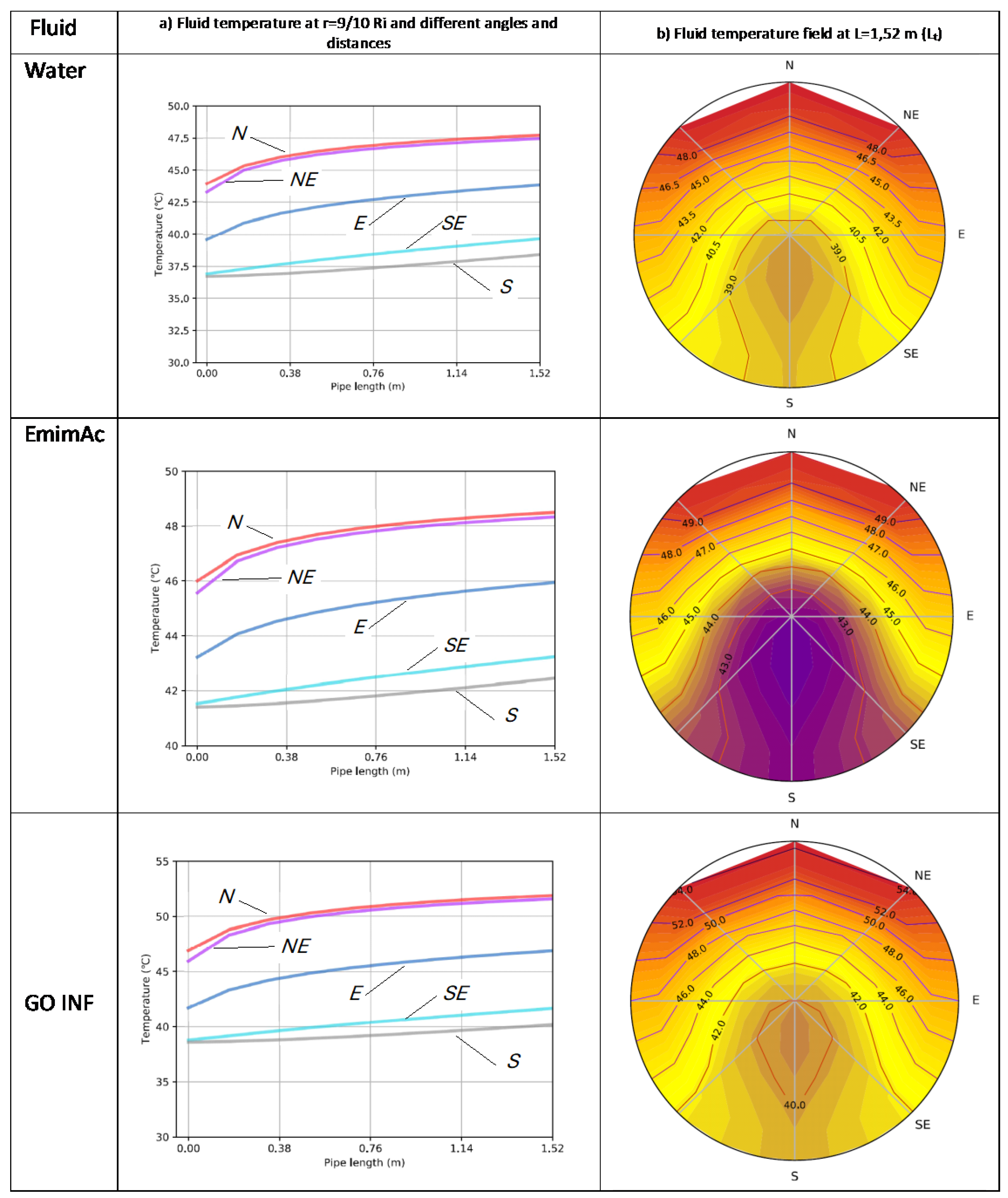
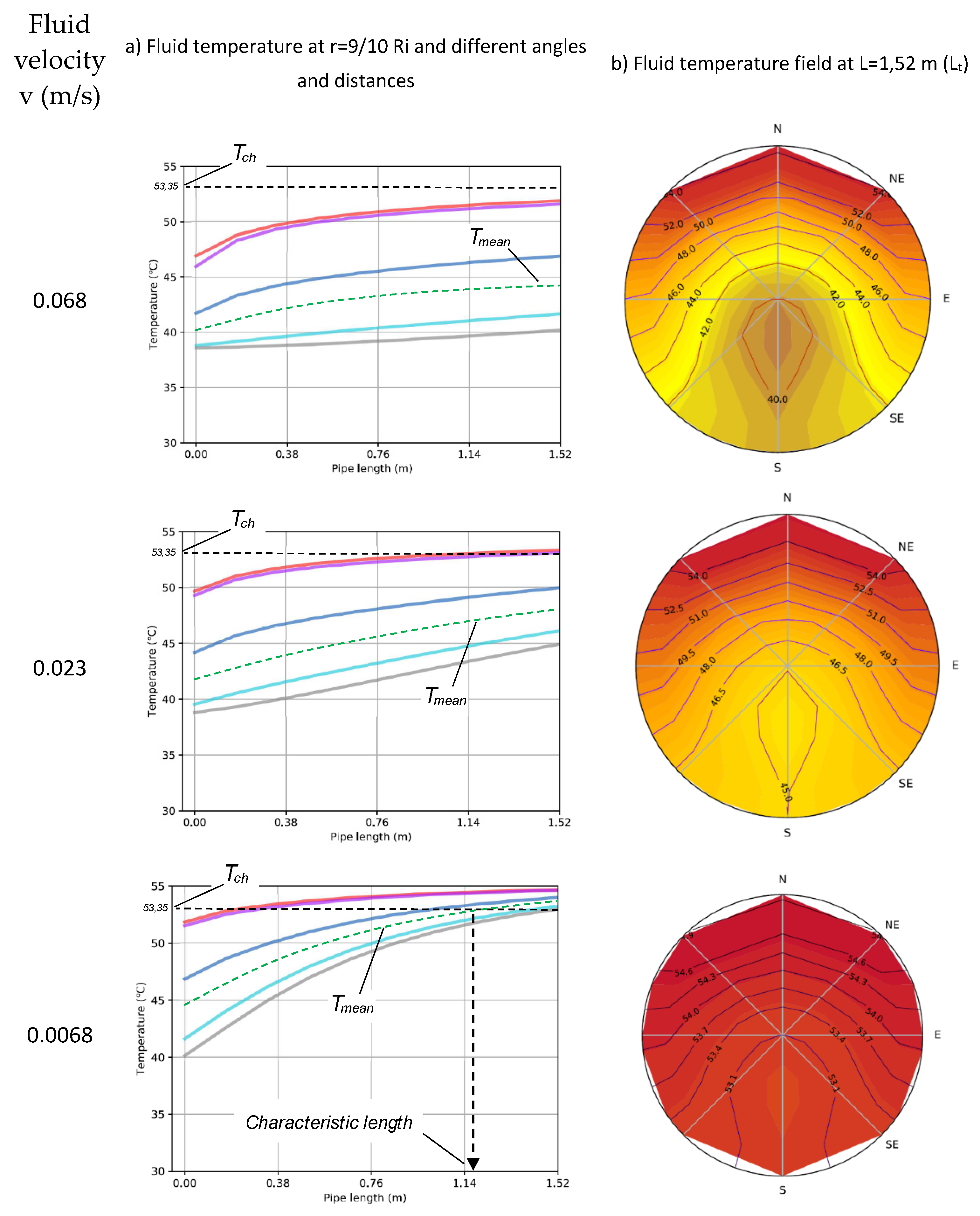
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Council of the European Uunion and the European Council, “European Green Deal. Fit for 55.” [Online]. Available: https://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/policies/green-deal/fit-for-55-the-eu-plan-for-a-green-transition/. (Accessed on 01 09 2024).
- D. Bogdanov, A. Gulagi, M. Fasihi, and C. Breyer, “Full energy sector transition towards 100% renewable energy supply: Integrating power, heat, transport and industry sectors including desalination,” Appl Energy, vol. 283, 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. Gul et al., “Transition toward net zero emissions - Integration and optimization of renewable energy sources: Solar, hydro, and biomass with the local grid station in central Italy,” Renew Energy, vol. 207, 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. Wehbi, “Powering the Future: An Integrated Framework for Clean Renewable Energy Transition,” Sustainability, vol. 16, no. 13, p. 5594, Jun. 2024. [CrossRef]
- D. Xu, X. Gu, and Y. Dai, “Concentrating solar assisted biomass-to-fuel conversion through gasification: A review,” 2023. [CrossRef]
- Dr. Sharad Kadam, Komal Dhole, Abhay Kumar, Nikhil Gupta, and Saurav Mishra, “Impact of International Solar Alliance on World,” International Journal of Advanced Research in Science, Communication and Technology, 2023. [CrossRef]
- P. G. Loutzenhiser and A. P. Muroyama, “A review of the state-of-the-art in solar-driven gasification processes with carbonaceous materials,” Solar Energy, vol. 156, pp. 93–100, Nov. 2017. [CrossRef]
- B. Tan, X. Ke, D. Tang, and S. Yin, “Improved perturb and observation method based on support vector regression,” Energies (Basel), vol. 12, no. 6, 2019. [CrossRef]
- I. Moulefera et al., “Novel application for graphene oxide-based ionanofluids in flat plate solar thermal collectors,” Sci Rep, vol. 14, no. 1, p. 17610, Jul. 2024. [CrossRef]
- J. A. Duffie and W. A. Beckman, Solar Engineering of Thermal Processes: Fourth Edition. 2013. [CrossRef]
- IEA (2022), “Renewables 2022,” https://www.iea.org/reports/renewables-2022. (Accessed on 01 09 2024).
- S. A. Kalogirou, Solar Energy Engineering: Processes and Systems. 2023. [CrossRef]
- A. Ramos et al., “Solar-Thermal and Hybrid Photovoltaic-Thermal Systems for Renewable Heating,” Grantham Institute, Briefing paper No 22. Imperial College London, no. 22, 2017. [CrossRef]
- J. Lee and J. Shin, “The Economic Value of New Sustainable Products: The Case of Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT) Hybrid Solar Collectors,” Energies (Basel), vol. 16, no. 14, 2023. [CrossRef]
- B. Emmanuel, Y. Yuan, B. maxime, N. Gaudence, and J. Zhou, “A review on the influence of the components on the performance of PVT modules,” Solar Energy, vol. 226, pp. 365–388, Sep. 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Khelifa, K. Touafek, H. Ben Moussa, I. Tabet, H. B. C. El Hocine, and H. Haloui, “Analysis of a Hybrid Solar Collector Photovoltaic Thermal (PVT),” Energy Procedia, vol. 74, pp. 835–843, Aug. 2015. [CrossRef]
- S. Dubey and G. N. Tiwari, “Analysis of PV/T flat plate water collectors connected in series,” Solar Energy, vol. 83, no. 9, 2009. [CrossRef]
- M. T. Ahmed, M. R. Rashel, M. Abdullah-Al-Wadud, T. T. Hoque, F. M. Janeiro, and M. Tlemcani, “Mathematical Modeling, Parameters Effect, and Sensitivity Analysis of a Hybrid PVT System,” Energies (Basel), vol. 17, no. 12, p. 2887, Jun. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Z. Wang, G. Hou, H. Taherian, and Y. Song, “Numerical Investigation of Innovative Photovoltaic–Thermal (PVT) Collector Designs for Electrical and Thermal Enhancement,” Energies (Basel), vol. 17, no. 10, p. 2429, May 2024. [CrossRef]
- S. Margoum, B. Hajji, S. Aneli, G. M. Tina, and A. Gagliano, “Optimizing Nanofluid Hybrid Solar Collectors through Artificial Intelligence Models,” Energies (Basel), vol. 17, no. 10, p. 2307, May 2024. [CrossRef]
- P. K. Nagarajan, J. Subramani, S. Suyambazhahan, and R. Sathyamurthy, “Nanofluids for solar collector applications: A review,” in Energy Procedia, 2014, pp. 2416–2434. [CrossRef]
- P. Jha, B. Das, R. Gupta, J. D. Mondol, and M. A. Ehyaei, “Review of recent research on photovoltaic thermal solar collectors,” Solar Energy, vol. 257, pp. 164–195, Jun. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Z. Said, R. Saidur, and N. A. Rahim, “Energy and exergy analysis of a flat plate solar collector using different sizes of aluminium oxide based nanofluid,” J Clean Prod, vol. 133, 2016. [CrossRef]
- R. Ganvir, P. Walke, and V. Kriplani, “Heat transfer characteristics in nanofluid—A review,” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 75, 2017.
- M. E. Zayed, J. Zhao, Y. Du, A. E. Kabeel, and S. M. Shalaby, “Factors affecting the thermal performance of the flat plate solar collector using nanofluids: A review,” Apr. 01, 2019, Elsevier Ltd. [CrossRef]
- W. Wang, Z. Wu, B. Li, and B. Sundén, “A review on molten-salt-based and ionic-liquid-based nanofluids for medium-to-high temperature heat transfer,” 2019. [CrossRef]
- Z. Said, A. A. Hachicha, S. Aberoumand, B. A. A. Yousef, E. T. Sayed, and E. Bellos, “Recent advances on nanofluids for low to medium temperature solar collectors: energy, exergy, economic analysis and environmental impact,” Prog Energy Combust Sci, vol. 84, p. 100898, May 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. S. Abdelrazik, K. H. Tan, N. Aslfattahi, A. Arifutzzaman, R. Saidur, and F. A. Al-Sulaiman, “Optical, stability and energy performance of water-based MXene nanofluids in hybrid PV/thermal solar systems,” Solar Energy, vol. 204, pp. 32–47, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- N. Aslfattahi, L. Samylingam, A. S. Abdelrazik, A. Arifutzzaman, and R. Saidur, “MXene based new class of silicone oil nanofluids for the performance improvement of concentrated photovoltaic thermal collector,” Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, vol. 211, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. Liu, F. Wang, L. Zhang, X. Fang, and Z. Zhang, “Thermodynamic properties and thermal stability of ionic liquid-based nanofluids containing graphene as advanced heat transfer fluids for medium-to-high-temperature applications,” Renew Energy, vol. 63, pp. 519–523, 2014. [CrossRef]
- C. A. Nieto de Castro et al., “Thermal Properties of Ionic Liquids and IoNanofluids of Imidazolium and Pyrrolidinium Liquids,” J Chem Eng Data, vol. 55, no. 2, pp. 653–661, Feb. 2010. [CrossRef]
- N. B. Shaik et al., “Artificial neural network modeling and optimization of thermophysical behavior of MXene Ionanofluids for hybrid solar photovoltaic and thermal systems,” Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, vol. 33, p. 101391, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- B. Jozwiak et al., “Remarkable Thermal Conductivity Enhancement in Carbon-Based Ionanofluids: Effect of Nanoparticle Morphology,” ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, vol. 12, no. 34, pp. 38113–38123, 2020. [CrossRef]
- F.-F. Zhang, F.-F. Zheng, X.-H. Wu, Y.-L. Yin, and G. Chen, “Variations of thermophysical properties and heat transfer performance of nanoparticle-enhanced ionic liquids,” R Soc Open Sci, vol. 6, no. 4, p. 182040, Apr. 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. Hasečić, J. H. Almutairi, S. Bikić, and E. Džaferović, “Numerical analysis of heat transfer performances of ionic liquid and ionanofluids with temperature-dependent thermophysical properties,” Energies (Basel), vol. 14, no. 24, 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. Das, K. Habib, R. Saidur, N. Aslfattahi, S. M. Yahya, and F. Rubbi, “Improved Thermophysical Properties and Energy Efficiency of Aqueous Ionic Liquid/MXene Nanofluid in a Hybrid PV/T Solar System,” Nanomaterials, vol. 10, no. 7, p. 1372, Jul. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Seco-Nicolás, M. Alarcón, and J. P. Luna-Abad, “3D numerical simulation of laminar forced-convection flow subjected to asymmetric thermal conditions. An application to solar thermal collectors,” Solar Energy, vol. 220, pp. 230–245, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Seco-Nicolás, M. Alarcón, and F. Alhama, “Thermal behavior of fluid within pipes based on discriminated dimensional analysis. An improved approach to universal curves,” Appl Therm Eng, vol. 131, 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Seco-Nicolás, M. Alarcón, A. P. Ramallo González, and J. P. Luna-Abad, “HEATT©. A free software for thermal design of liquid flows inside pipes,” Results in Engineering, p. 100983, Feb. 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Alarcón, M. Seco Nicolás, J. P. Luna-Abad, and A. P. Ramallo-González, “Forced Laminar Flow in Pipes Subjected to Asymmetric External Conditions: The HEATT© Platform for Online Simulations.,” in Pipeline Engineering - Design, Failure, and Management, S. Rushd, M. Ismail, and K. F. Adane, Eds., London (UK): IntechOpen, 2022, p. 20. [CrossRef]
- L. Bo et al., “An overview of the applications of ionic fluids and deep eutectic solvents enhanced by nanoparticles,” J Therm Anal Calorim, vol. 147, no. 14, pp. 7589–7601, Jul. 2022. [CrossRef]
- ABORA ENERGY S.L., “SHE: Solar Heat & Electricity,” https://abora-solar.com/en/she-project/.
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO), “ISO 9806:2017. Solar energy. Solar thermal collectors. Test methods.,” 2017, International Organization for Standardization (ISO), Geneva (Switzerland).
- E. C. for S. (CEN), EN 12975-2:2006. Thermal solar systems and components – Solar collectors –Part 2 Test methods. AENOR, 2006.
- A. Gagliano, G. M. Tina, S. Aneli, and S. Nižetić, “Comparative assessments of the performances of PV/T and conventional solar plants,” J Clean Prod, vol. 219, pp. 304–315, May 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Alarcón, M. Seco-Nicolás, J. P. Luna-Abad, and A. P. Ramallo-González, “HEATT.” [Online]. Available: https://heatt.inf.um.es/en/.
- Ş. Bilir, “NUMERICAL SOLUTION OF GRAETZ PROBLEM WITH AXIAL CONDUCTION,” Numeri Heat Transf A Appl, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 493–500, Jun. 1992. [CrossRef]
- F. P. Incropera, D. P. DeWitt, T. L. Bergman, and A. S. Lavine, Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 6th. 2007. [CrossRef]
- N. V. Suryanarayana, “Forced Convection - Internal Flows,” in The CRC Handbook of Thermal Engineering, F. Kreith, Ed., Boca Ratón, London, New York, Washington, D.C.: CRC Press LLC, 2000, ch. 3. Heat an, pp. 3-47 3-55.
- C. N. Madrid and F. Alhama, “Discrimination: A fundamental and necessary extension of classical dimensional analysis theory,” International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, vol. 33, no. 3, pp. 287–294, Mar. 2006. [CrossRef]
- M. Cánovas, I. Alhama, and F. Alhama, “Mathematical Characterization of Bénard-Type Geothermal Scenarios Using Discriminated Non-dimensionalization of the Governing Equations,” International Journal of Nonlinear Sciences and Numerical Simulation, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 23–34, Feb. 2015. [CrossRef]
- C. N. Madrid and F. Alhama, “Discriminated dimensional analysis of the energy equation: Application to laminar forced convection along a flat plate,” International Journal of Thermal Sciences, vol. 44, no. 4, pp. 333–341, Apr. 2005. [CrossRef]
| Water | [Emim]Ac | Gr-INF 1% | |
| Density, ρ (kg m-3) | 990 | 1088.7 | 1100 |
| Specific heat, cp (J kg-1 K-1) | 4210 | 1939.95 | 2025 |
| Thermal conductivity, k (W m-1K-1) | 0.66 | 0.19915 | 0.24 |
| Dynamic viscosity, μ (Pa s) | 4.27E-04 | 0.034 | 0.01 |
| External tube diameter, De (m) | 0.008 |
| Tube thickness, e (m) | 0.0004 |
| Tube length, L (m) | 1.52 |
| Dimensionless number | Equation | Condition | Title 1 | Title 2 | Title 3 |
| Reynods Nr, Re | 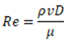 |
1E2<Re<2E3 | entry 1 | data | data |
| Prandtl Nr., Pr*D/L | 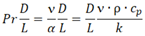 |
0,01<Pr*D/L<1 | entry 2 | data | data 1 |
| Rayleigh Nr, Ra | 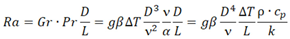 |
<1E3 |
| (kg s-1) | v (m s-1) | G (Wm-2) | Tin (ºC) | Tout (ºC) | ΔTcol (K) | Qcol (W) | Pel (W) | ηth (%) | ηov (%) | |
| Water | 0.0380 | 0.086 | 955.7 | 38.9 | 44.3 | 5.4 | 862.8 | 80.0 | 58.2 | 63.6 |
| EmimAc | 0.0287 | 0.059 | 900.0 | 41.7 | 46.2 | 4.5 | 250.3 | 72.9 | 17.9 | 23.2 |
| Gr-INF | 0.0334 | 0.068 | 845.8 | 38.6 | 50.3 | 11.7 | 790.9 | 74.7 | 60.3 | 66.0 |
| Case | Mass flow rate (kg s-1) | v (m s-1) | Tin (ºC) | Tout (ºC) | ΔTcol (K) | Qcol (W) | ηth (%) |
| 1 | 0.0334 | 0.0682 | 38.6 | 50.3 | 11.7 | 790.9 | 60.3 |
| 2 | 0.0113 | 0.0230 | 38.6 | 52.1 | 13.5 | 301.5 | 23.0 |
| 3 | 0.0033 | 0.0068 | 38.6 | 54.6 | 16.0 | 105.6 | 8.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





