Submitted:
01 October 2024
Posted:
02 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of the ZnONPs
2.3. Exfoliation of MoS2
2.4. Synthesis of Composites
2.5. Characterization of Composites
2.6. Photocatalytic Experiments
2.7. Fabrication of Free-Standing SiNWs-SWNTs-MoS2 Electrodes
2.8. Post-Mortem Characterization of Li-Ion Coin Cells
3. Results
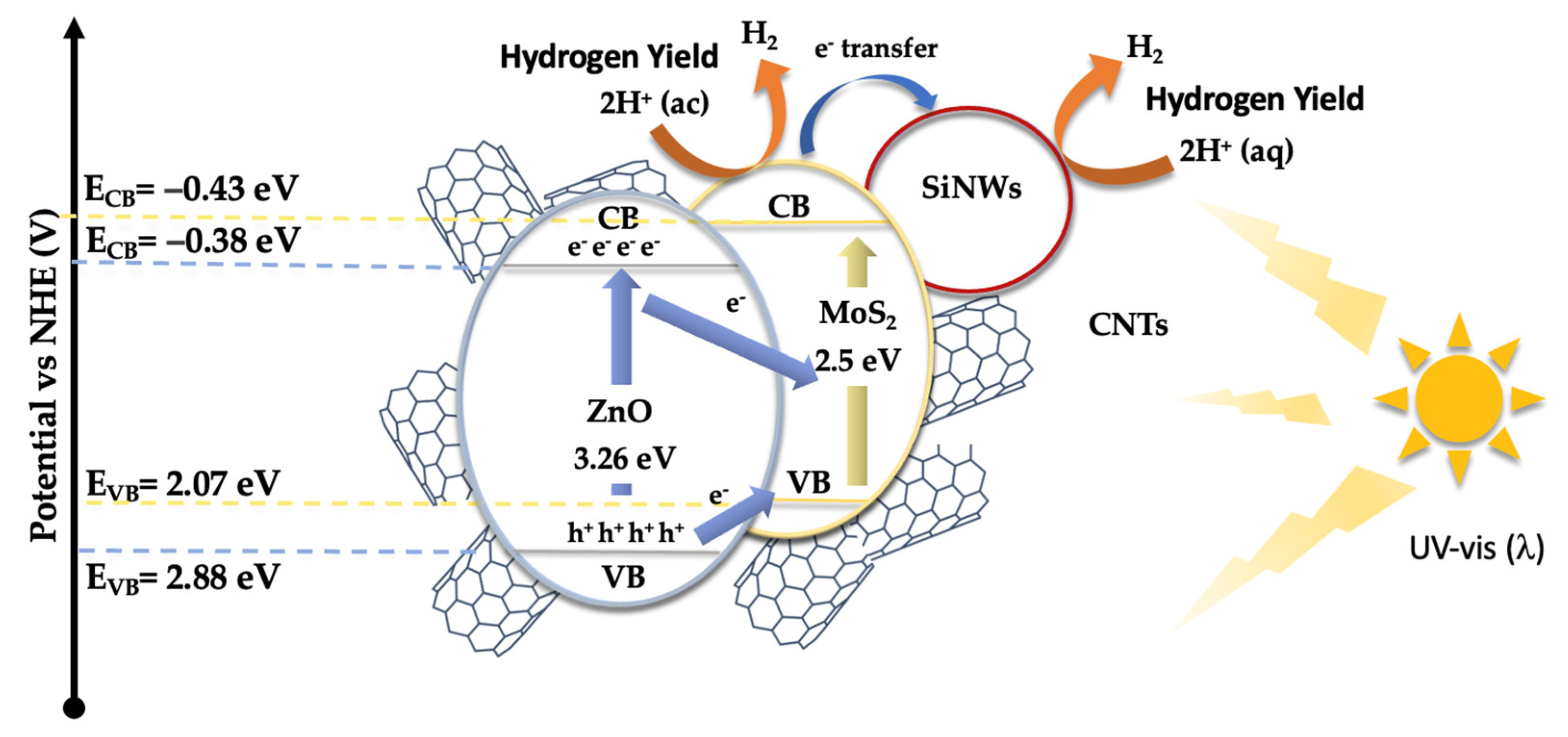
3.1. Hydrogen Evolution Reaction (HER)
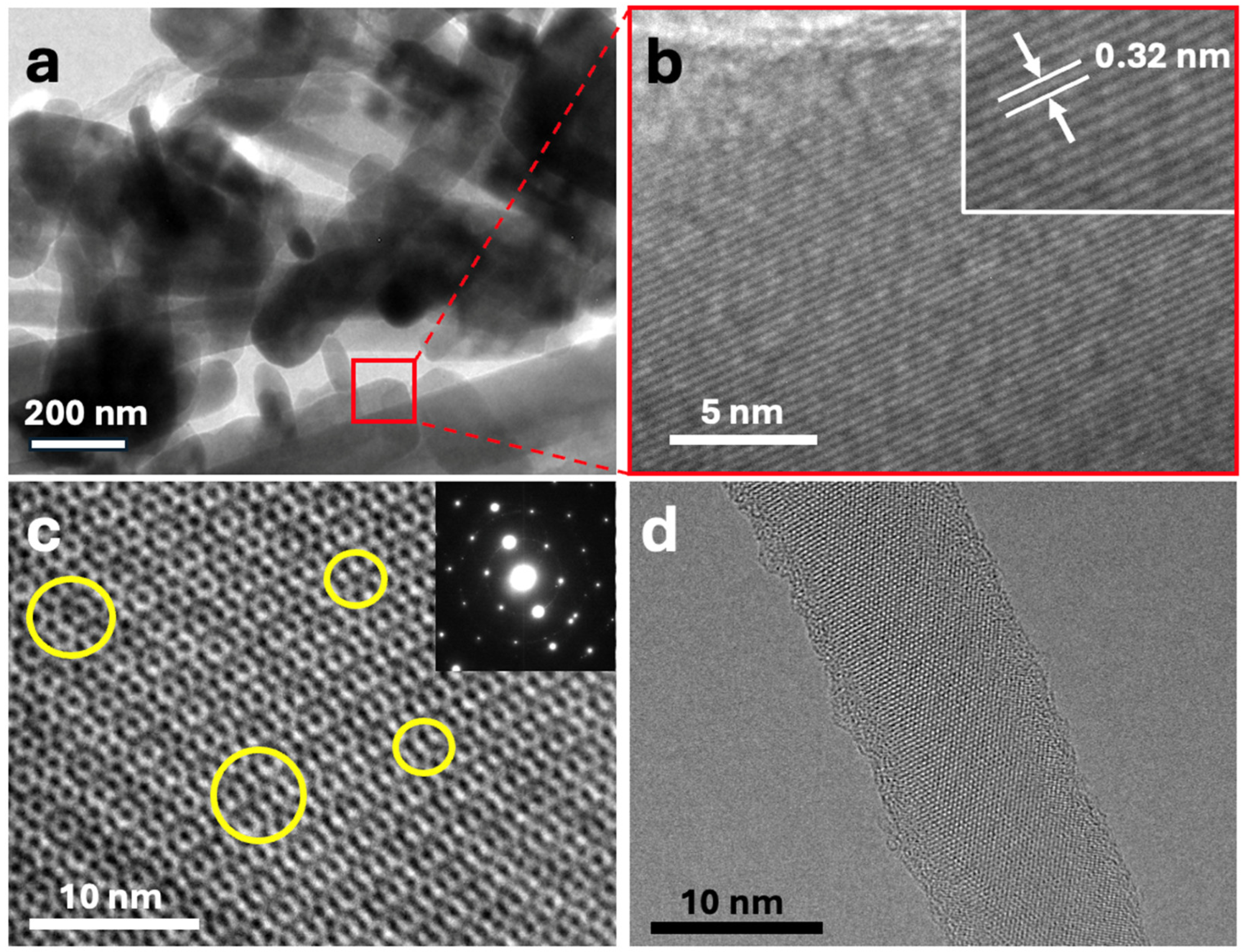
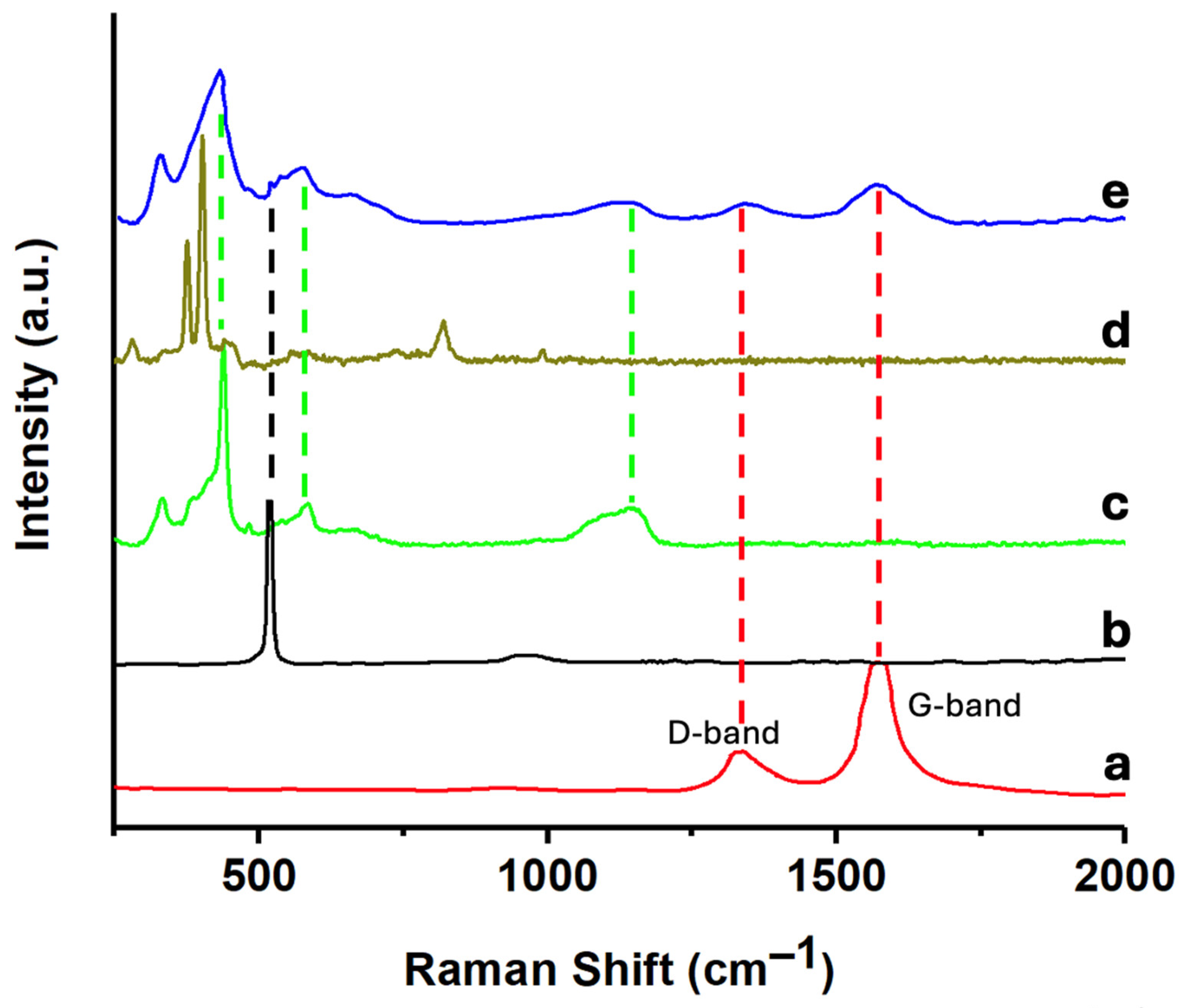
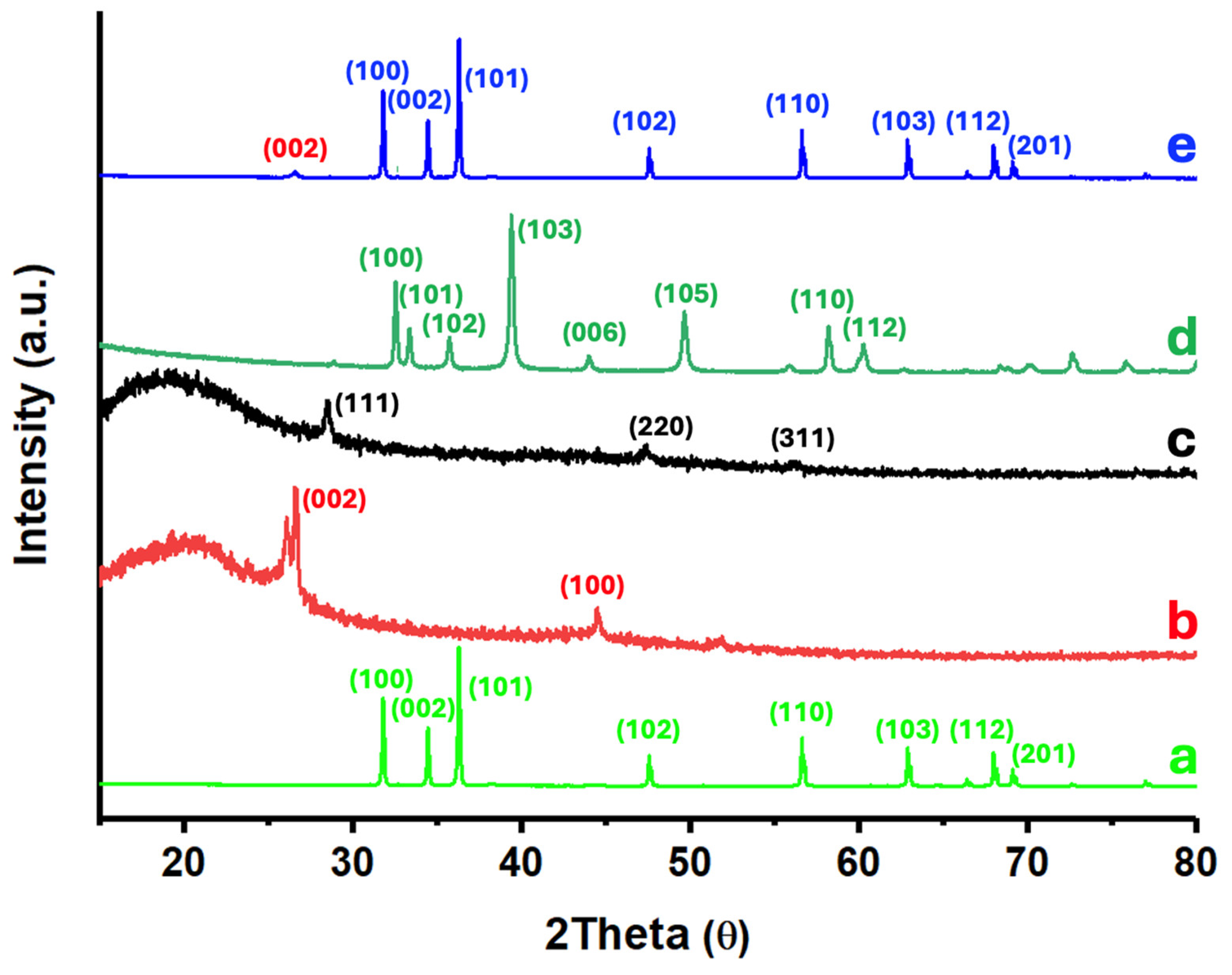
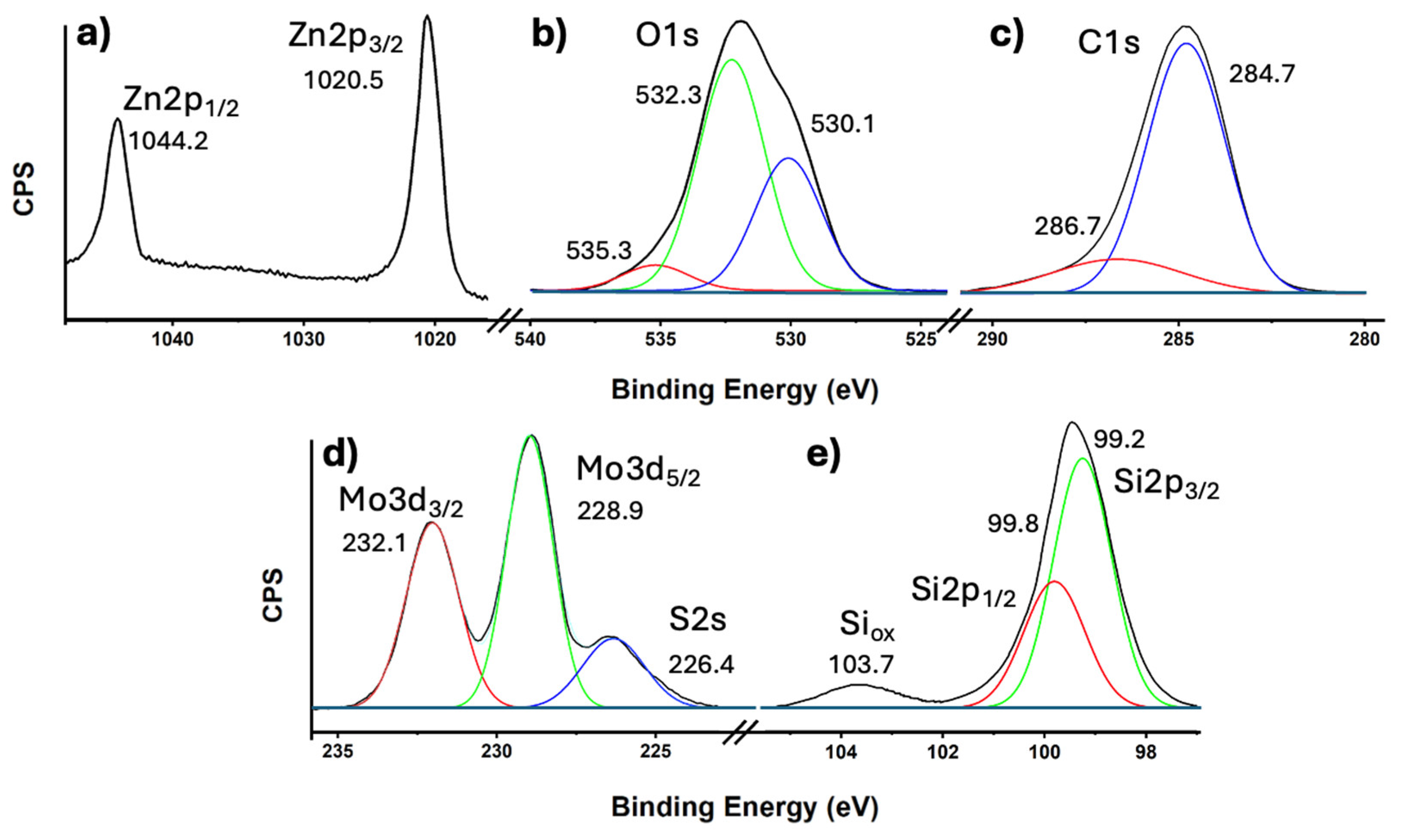
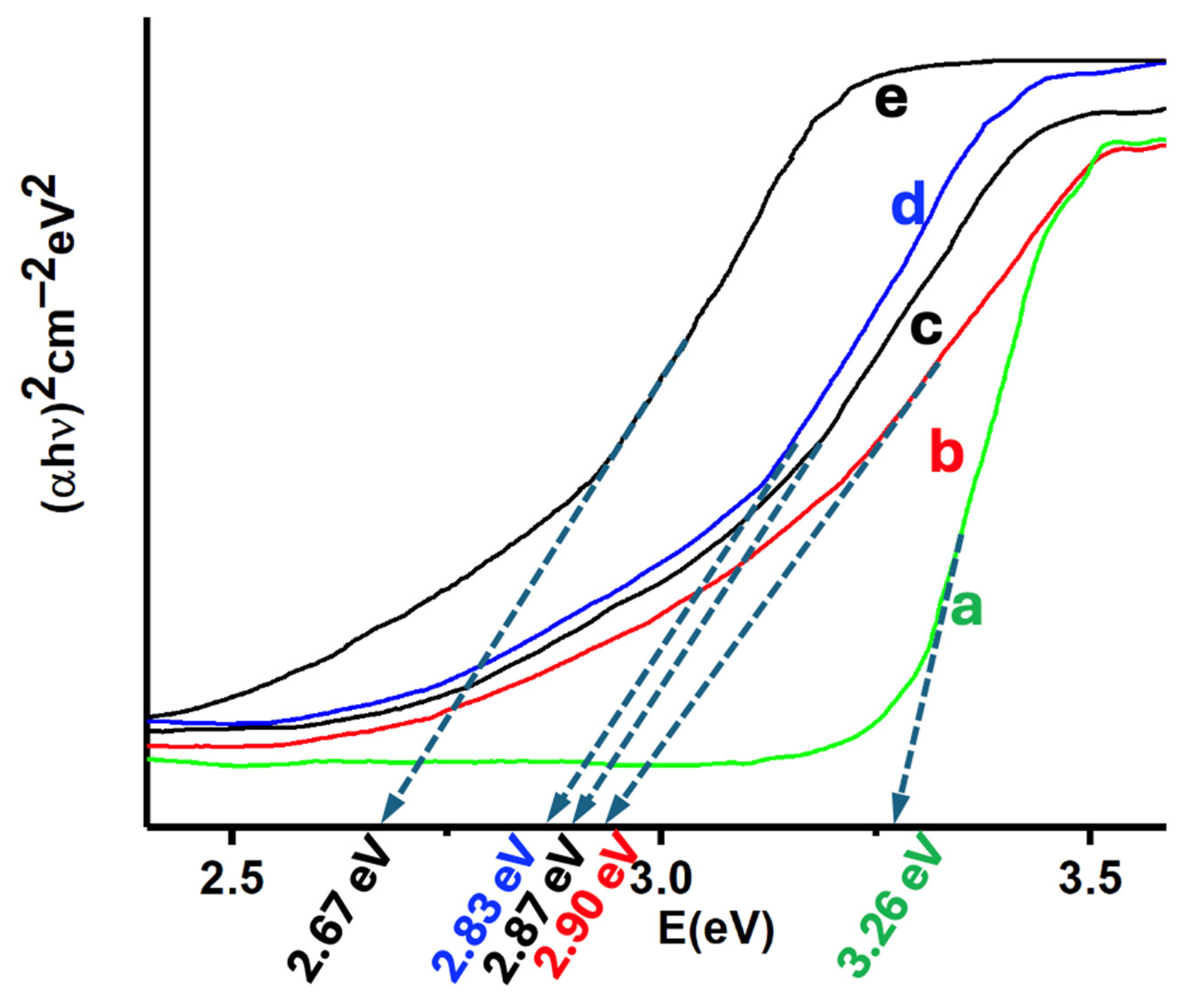
3.1.1. Characterization of Composites
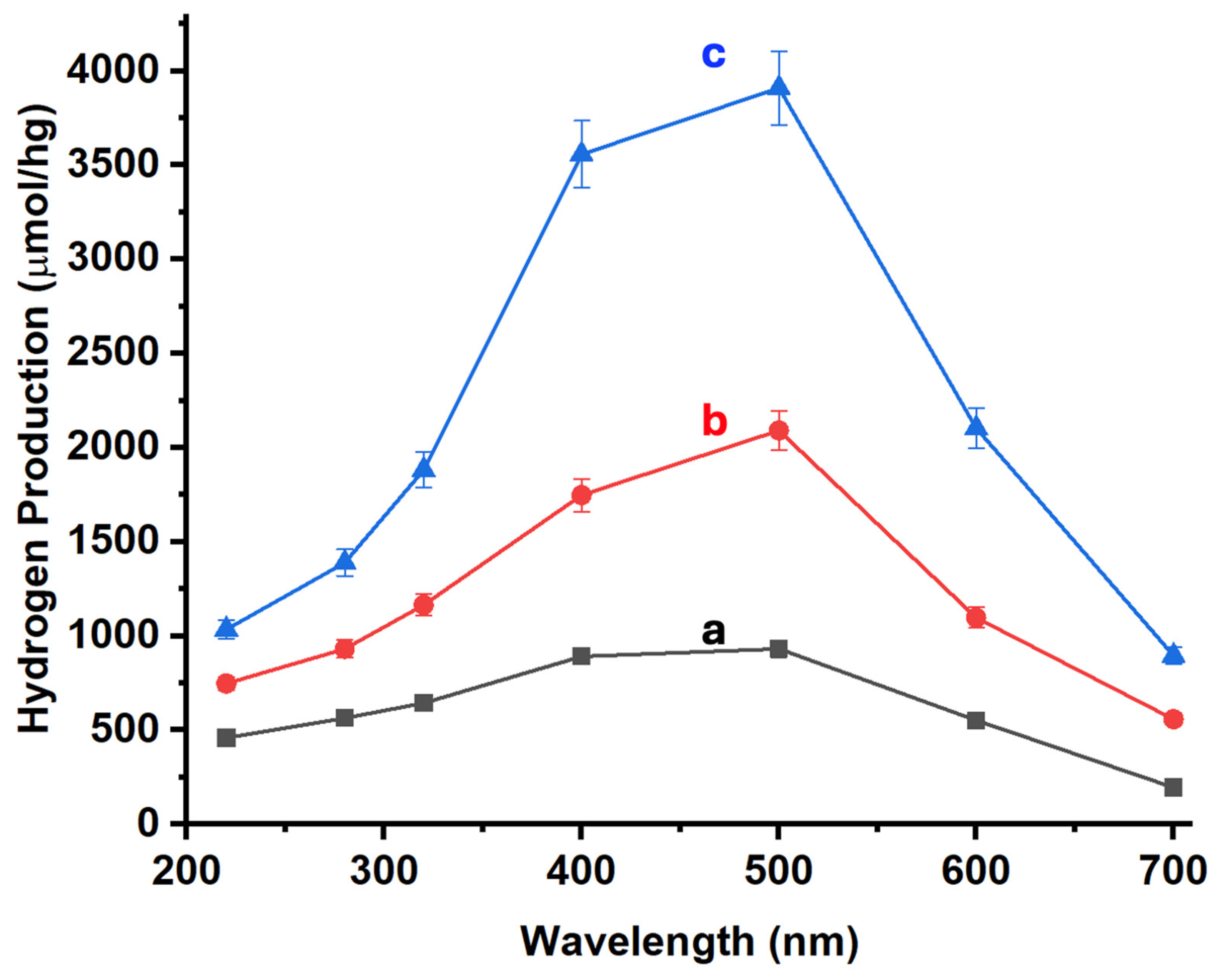
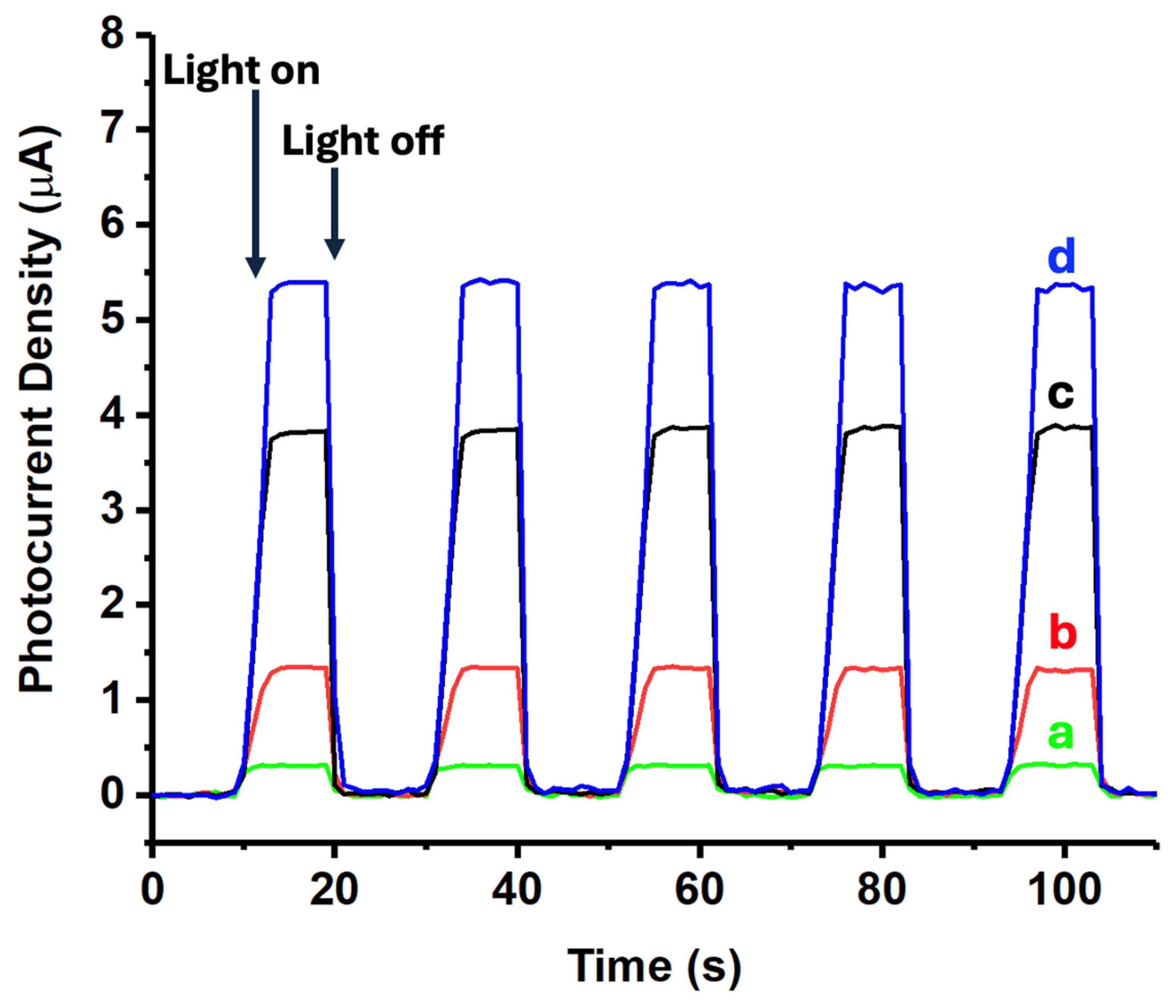
3.1.2. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production
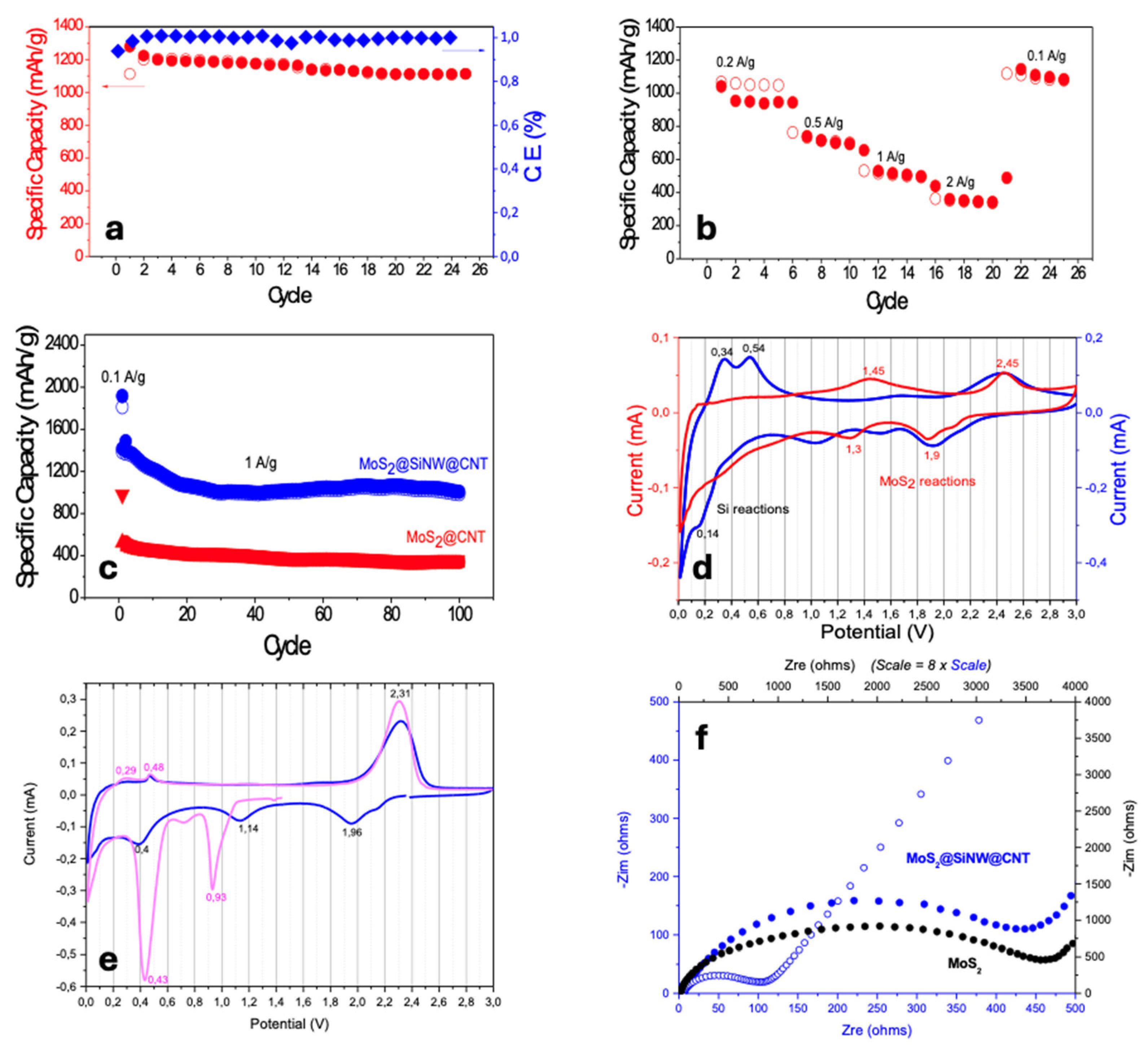
3.2. Li-Ion Batteries
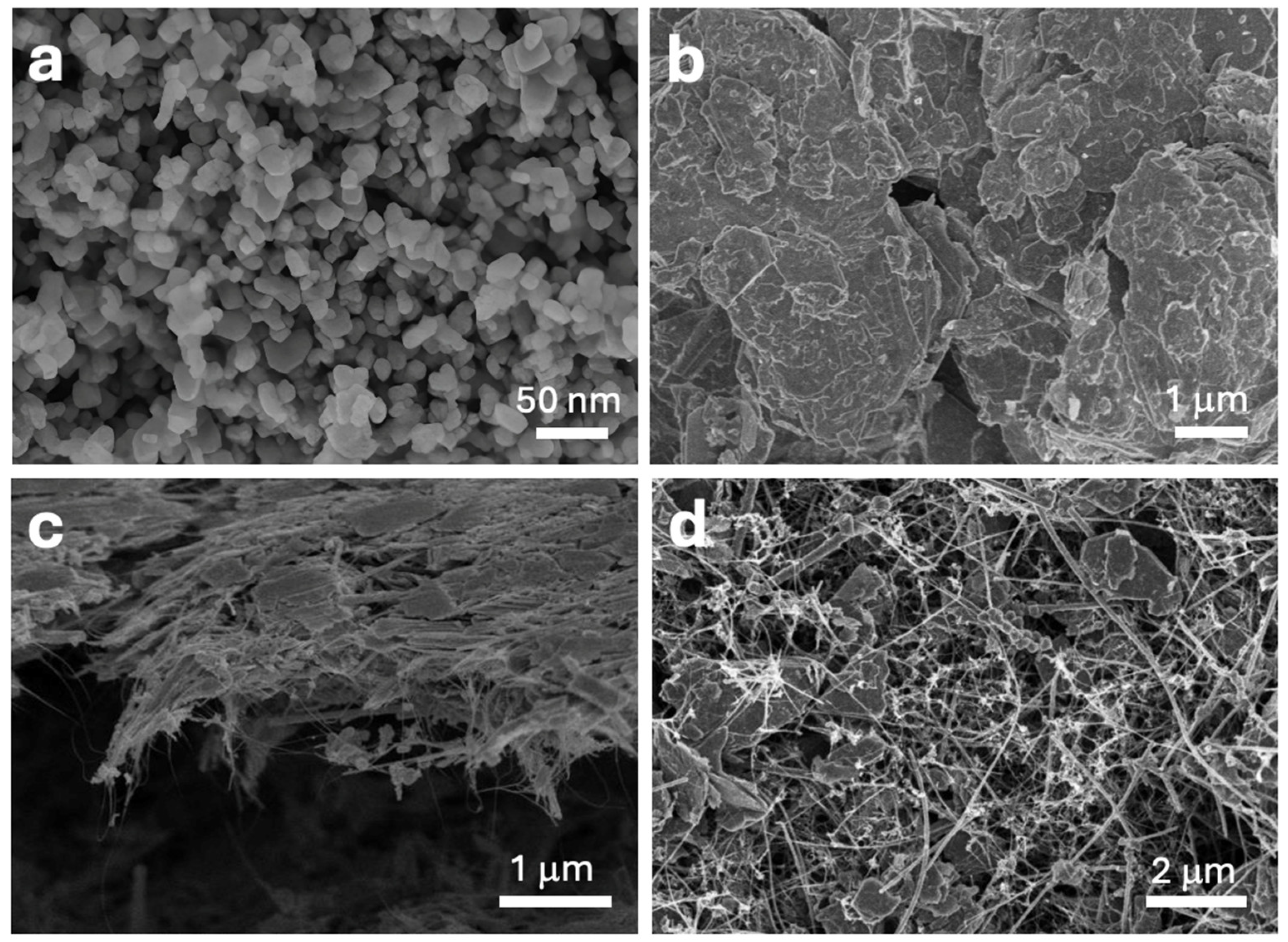
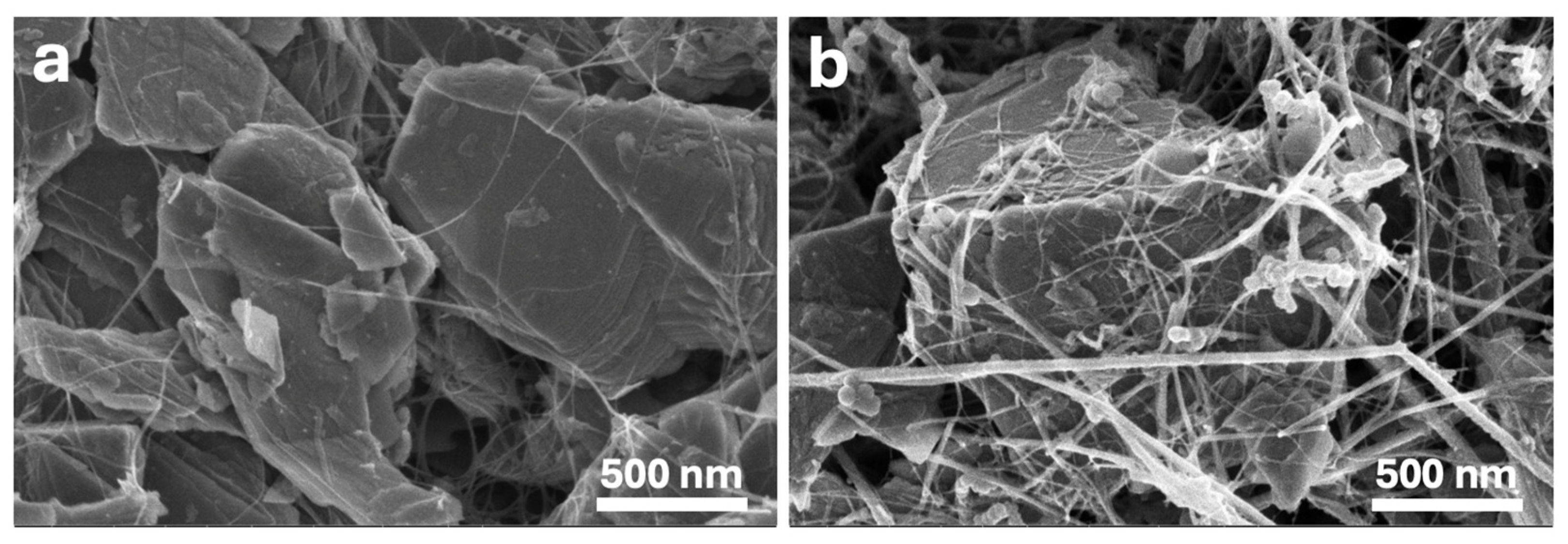
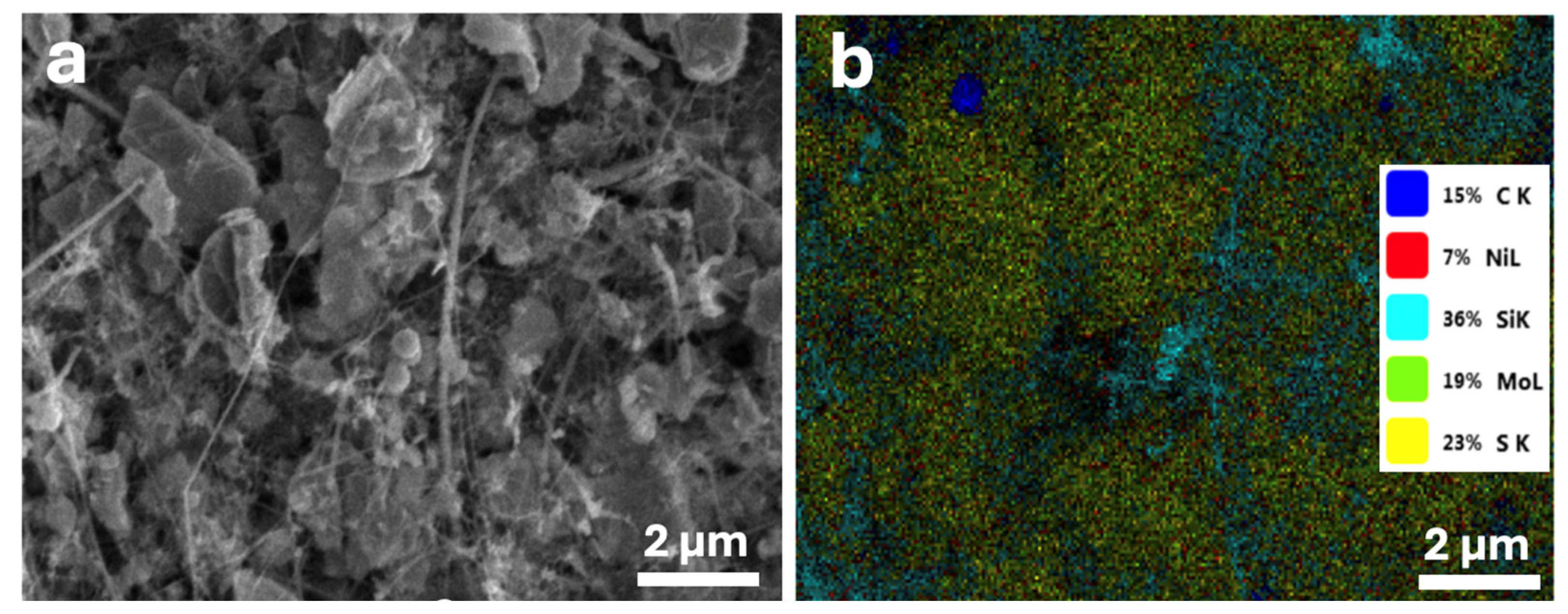
3.2.1. Morphology of Electrodes
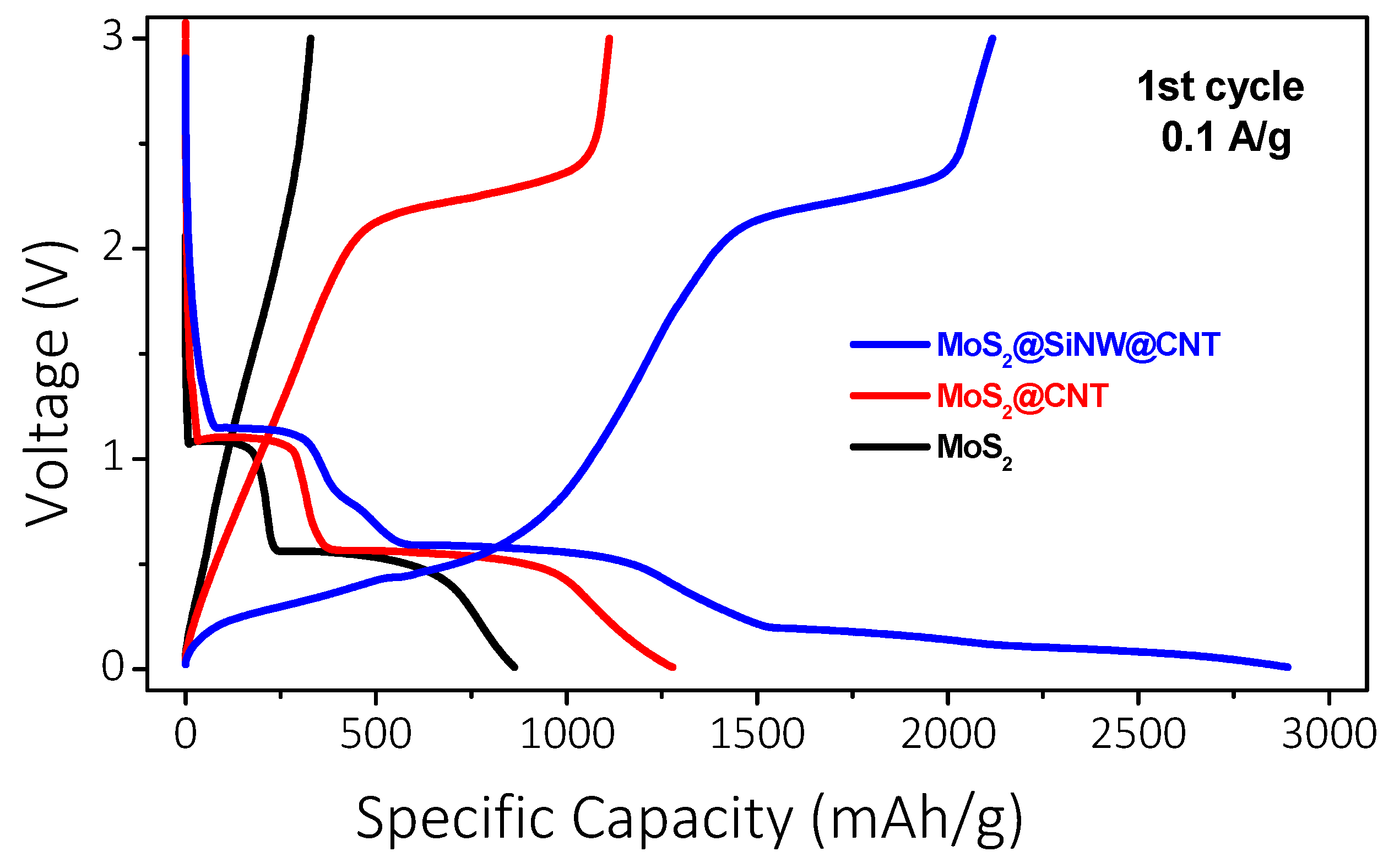
3.2.2. Electrochemical Study
- (1) xLi+ + xe- + MoS2 → Li xMoS2
- (1b) Li xMoS2 + (4 - x) Li++ (4 - x)e- → Mo + 2Li2S
- (2) xLi+ + xe- + Si (crystalline) → LixSi (amorphous)
- (3) LixSi (amorphous) + (3.75-x)Li+ +(3.75 - x)e- → Li15Si4 (crystalline)
- (4) Li15Si4 (crystalline) → 4Si (amorphous) + 15Li+ + 15e-
- (5) Li2MoS2 → MoS2 + 2Li+ + 2e-
- (6) Mo + 2Li2S → MoS2 + 4Li+ + 4e-
- Reduction (Cathodic sweep)
- (1) Reduction Peak at 1.9 V: This peak corresponds to the initial insertion of lithium ions into the MoS₂ structure. During this stage, MoS₂ undergoes a phase transformation, where Li ions intercalate into the MoS₂ layers, leading to the formation of LixMoS₂. This process is reversible and is characteristic of the layered structure of MoS₂.
- (1b) Reduction Peak at 1.3 V: This peak is associated with the further reduction of MoS₂ to form lithium sulfide (Li₂S) and metallic molybdenum (Mo).
- (2,3) Small reduction peak at 0.14 V: The reactions of Si and Li occur at low voltages [90] and may not be clearly detected in CV reduction curves recorded at 0.2 mV/s. The lithiation of silicon nanowires follows reaction (2) and is observed only in the first cycle. Subsequently, more Li is incorporated into the amorphous alloy LixSi, following reaction (3). These transformations are evident in the oxidation curves, where corresponding peaks are observed, and are clearly seen in the dQ/dV derivative curves from GCD (see Figure S7). These dQ/dV curves are essential for detecting redox transitions in electrochemical systems, revealing subtle voltage changes linked to oxidation and reduction processes and providing insights into the material’s redox behavior and stability during cycling. Therefore, the small peak at 0.14 V is attributed to reaction (3), representing the lithiation of silicon nanowires.
- Oxidation (Anodic sweep)
- (4) Oxidation peaks at low voltages (0.34 and 0.52 V): These peaks indicate the initial delithiation of lithium silicide (LixSi) and are observed exclusively in the MoS₂@SiNW@CNT composite (blue curve in Figure 13d). The peak at 0.34 V is likely associated with the delithiation of LiSi, where lithium is extracted from the silicon component, leading to the formation of silicon (Si) and the corresponding release of lithium ions (reaction 4). Similarly, the peak at 0.52 V may reflect the delithiation of intermediate phases or lithium silicide compounds, suggesting that multiple stages of lithiation and delithiation occur. These processes are characteristic of the interactions between lithium and silicon nanowires within the composite, highlighting the active role of Si in the electrochemical behavior of the MoS₂@SiNW@CNT composite. The observation of these peaks only in the composite indicates that the presence of SiNWs significantly impacts the electrochemical response, distinguishing it from other materials like MoS₂ alone.
- (5, 6) Oxidation peaks at higher voltages (1.45 and 2.45 V): The peak at 1.45 V corresponds to the initial delithiation of the LixMoS2 phase, where lithium ions are extracted (reaction 5), reversing the intercalation process. This process may not completely revert to the original MoS₂ structure, leading to partial reformation of the MoS2 phase. The peak at 2.45 V is associated with the re-oxidation of molybdenum and lithium sulfide back to MoS₂ (reaction 6), indicating the regeneration of the MoS₂ structure from Mo and Li₂S. This peak represents the final oxidation step, completing the delithiation process and restoring the electrode to its original state.
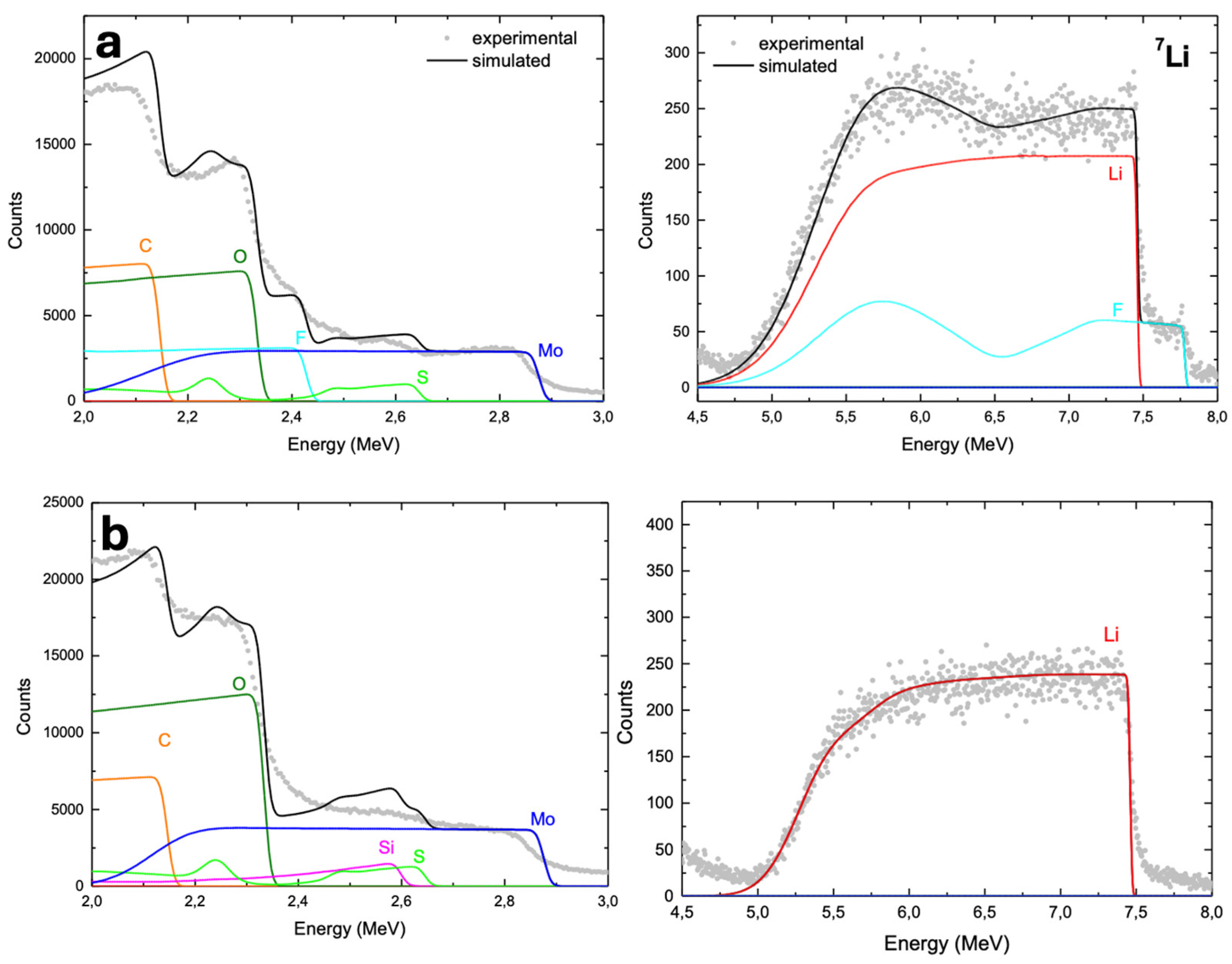
3.3. Postmortem Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hassan, Q.; Viktor, P.; J. Al-Musawi, T.; Mahmood Ali, B.; Algburi, S.; Alzoubi, H.M.; Khudhair Al-Jiboory, A.; Zuhair Sameen, A.; Salman, H.M.; Jaszczur, M. The Renewable Energy Role in the Global Energy Transformations. Renewable Energy Focus 2024, 48, 100545. [CrossRef]
- World Economic Forum Fostering Effective Energy Transition 2024.
- Peter Simpa; Nko Okina Solomon; Olubunmi Adeolu Adenekan; Scholar Chinenye Obasi Nanotechnology’s Potential in Advancing Renewable Energy Solutions. Eng. Sci. Technol. J. 2024, 5, 1695–1710. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Dong, Q.; Gao, C.; Bai, W.; Chu, D.; He, Y. A Comprehensive Review of Carbon Nanotubes: Growth Mechanisms, Preparation and Applications. Fullerenes, Nanotubes and Carbon Nanostructures 2024, 32, 415–429. [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.J.; Iyer, K.A.; Bird, R.E.; Ivanov, J.; Banerjee, S.; Georges, G.; Zhou, Q.A. Review of Carbon Nanotube Research and Development: Materials and Emerging Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 18695–18713. [CrossRef]
- Raman, S.; Sankar, R.; M, S. Advances in Silicon Nanowire Applications in Energy Generation, Storage, Sensing, and Electronics: A Review. Nanotechnology 2023, 34, 182001. [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, T.; Shrivastav, A.M.; Sinha, S.; Polley, D.; Alee, K.S.; Sujatha, R.A.; Mishra, A.; Saxena, S.K. Silicon Nanowire: From Fabrication to Its Application. In Materials for Electronic, Magnetic, and Spintronic Technologies; Mishra, A., Dixit, V., Somvanshi, D., Singh, A., Mishra, A., Eds.; Engineering Materials; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, 2024; pp. 41–63 ISBN 978-3-031-64541-9. [CrossRef]
- Ingsel, T.; Gupta, R.K. Nanostructured Silicon for Energy Applications. In Silicon-Based Hybrid Nanoparticles; Elsevier, 2022; pp. 169–197 ISBN 978-0-12-824007-6. [CrossRef]
- Samy, O.; El Moutaouakil, A. A Review on MoS2 Energy Applications: Recent Developments and Challenges. Energies 2021, 14, 4586. [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Toe, C.Y.; Scott, J.; Antonietti, M.; Guo, J.; Amal, R. Materials Advances in Photocatalytic Solar Hydrogen Production: Integrating Systems and Economics for a Sustainable Future. Advanced Materials 2024, 2404618. [CrossRef]
- Singla, S.; Sharma, S.; Basu, S.; Shetti, N.P.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Photocatalytic Water Splitting Hydrogen Production via Environmental Benign Carbon Based Nanomaterials. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 33696–33717. [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, P.; Harb, M.; Cao, Z.; Cavallo, L.; Breen, A.; Dervin, S.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Pillai, S.C. 2D Nanomaterials for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production. ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 1687–1709. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Likozar, B.; Jana, R.; Chanu, W.C.; Singh, M.K. A Review of Hydrogen Production Processes by Photocatalytic Water Splitting – From Atomistic Catalysis Design to Optimal Reactor Engineering. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 33282–33307. [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Sathish, C.I.; Yang, J.; Guan, X.; Zhang, X.; Qiao, L.; Domen, K.; Wang, S.; Vinu, A.; Yi, J. Strategies for Improving the Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction of Carbon Nitride-Based Catalysts. Small 2023, 19, 2302875. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Heo, Y.-J.; Lee, J.-W.; Lee, J.-H.; Bajgai, J.; Lee, K.-J.; Park, S.-J. Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution via Water Splitting: A Short Review. Catalysts 2018, 8, 655. [CrossRef]
- Molaei, M.J. Recent Advances in Hydrogen Production through Photocatalytic Water Splitting: A Review. Fuel 2024, 365, 131159. [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.A.; Najam, T.; Altaf, M.; Ahmad, K.; Hossain, I.; Assiri, M.A.; Javed, M.S.; Rehman, A.U.; Shah, S.S.A. Tuning the Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production via Co-Catalyst Engineering. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2024, 990, 174378. [CrossRef]
- Suman, N.; Irfan, H.; Shanmugharaj, A.M.; Mohamed Riyaz, A.K.; Pai, R.K. Layered Transition Metal Dichalcogenide-Based Nanomaterials for Lithium-Ion Batteries. In Nanostructured Materials for Energy Storage; Deshmukh, K., Pandey, M., Eds.; Wiley, 2024; pp. 319–370 ISBN 978-3-527-35067-4. [CrossRef]
- Hossain, Md.H.; Chowdhury, M.A.; Hossain, N.; Islam, Md.A.; Mobarak, M.H. Advances of Lithium-Ion Batteries Anode Materials—A Review. Chemical Engineering Journal Advances 2023, 16, 100569. [CrossRef]
- Dang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, R.; Fu, A.; Liu, X.; Li, H. Carbon Nanofibers Decorated by MoS2 Nanosheets with Tunable Quantity as Self-Supporting Anode for High-Performance Lithium Ion Batteries. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2689. [CrossRef]
- Poorshakoor, E.; Darab, M. Advancements in the Development of Nanomaterials for Lithium-Ion Batteries: A Scientometric Review. Journal of Energy Storage 2024, 75, 109638. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Qian, X.; Hou, S.; Xia, X.; He, D.; Xia, J.; He, G.; Chen, H. Recent Progress of Self-Supported Anode Materials for Li-Ion Batteries. Journal of Energy Storage 2024, 99, 113188. [CrossRef]
- Department of Physics, Noorul Islam Center for Higher Education, Kumaracoil, Thuckalay, Kanyakumari district, Tamilnadu, 629180, India.; Shams, S.; Bindhu, B.; Department of Physics, Noorul Islam Center for Higher Education, Kumaracoil, Thuckalay, Kanyakumari district, Tamilnadu, 629180, India. Recent Advancements in Hybrid Two Dimensional Materials for Energy Applications. ES Energy Environ. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Guo, F.; Ai, X.; Tian, Y.; Yang, J.; Zou, X.; Zhu, G. Constructing Heterogeneous Interface by Growth of Carbon Nanotubes on the Surface of MoB2 for Boosting Hydrogen Evolution Reaction in a Wide pH Range. Small 2024, 20, 2304573. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.; Han, J.H.; Seo, S.B.; Choi, Y.R.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.A. Perspective on Carbon Nanotubes as Conducting Agent in Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Status and Future Challenges. Carbon Lett. 2023, 33, 325–333. [CrossRef]
- Sehrawat, P.; Julien, C.; Islam, S.S. Carbon Nanotubes in Li-Ion Batteries: A Review. Materials Science and Engineering: B 2016, 213, 12–40. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Bi, Q.; Sajjad, M.; Wang, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, Z. One-Dimensional Porous Silicon Nanowires with Large Surface Area for Fast Charge–Discharge Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 285. [CrossRef]
- Ray, U.; Sarkar, S.; Banerjee, D. Silicon Nanowires as an Efficient Material for Hydrogen Evolution through Catalysis: A Review. Catalysis Today 2023, 423, 113964. [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Chandran, K.S.R. A Critical Review of Silicon Nanowire Electrodes and Their Energy Storage Capacities in Li-Ion Cells. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 3947–3957. [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, D.; Qiao, Q.; Yu, Y.; Peterson, D.; Zafar, A.; Kumar, R.; Curtarolo, S.; Hunte, F.; Shannon, S.; et al. All The Catalytic Active Sites of MoS 2 for Hydrogen Evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 16632–16638. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, L.; Lotya, M.; Coleman, J.N.; Chou, S.; Liu, H.; Minett, A.I.; Chen, J. Development of MoS2 –CNT Composite Thin Film from Layered MoS2 for Lithium Batteries. Advanced Energy Materials 2013, 3, 798–805. [CrossRef]
- Machín, A.; Cotto, M.; Duconge, J.; Arango, J.C.; Morant, C.; Pinilla, S.; Soto-Vázquez, L.; Resto, E.; Márquez, F. Hydrogen Production via Water Splitting Using Different Au@ZnO Catalysts under UV–Vis Irradiation. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry 2018, 353, 385–394. [CrossRef]
- Ghorai, A.; Ray, S.K.; Midya, A. Ethylenediamine-Assisted High Yield Exfoliation of MoS2 for Flexible Solid-State Supercapacitor Application. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1170–1177. [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Cubero, A.; Borge, M.J.G.; Gordillo, N.; Gutiérrez, P.C.; Olivares, J.; Pérez Casero, R.; Ynsa, M.D. Current Status and Future Developments of the Ion Beam Facility at the Centre of Micro-Analysis of Materials in Madrid. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 175. [CrossRef]
- Mathayan, V.; Moro, M.V.; Morita, K.; Tsuchiya, B.; Ye, R.; Baba, M.; Primetzhofer, D. In-Operando Observation of Li Depth Distribution and Li Transport in Thin Film Li Ion Batteries. Applied Physics Letters 2020, 117, 023902. [CrossRef]
- Mathayan, V.; Morita, K.; Tsuchiya, B.; Ye, R.; Baba, M.; Moro, M.V.; Primetzhofer, D. Assessing the Potential of Ion Beam Analytical Techniques for Depth Profiling Li in Thin Film Li Ion Batteries. Journal of Applied Physics 2021, 130, 125306. [CrossRef]
- Paneta, V.; Kafkarkou, A.; Kokkoris, M.; Lagoyannis, A. Differential Cross-Section Measurements for the 7Li(p,p0)7Li, 7Li(p,p1)7Li, 7Li(p,α0)4He, 19F(p,p0)19F, 19F(p,α0)16O and 19F(p,α1,2)16O Reactions. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms 2012, 288, 53–59. [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M. SIMNRA User’s Guide.; Max-Planck-Institut fur Plasmaphysik, Garching, 1997.
- Mayer, M. Ion Beam Analysis of Rough Thin Films. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms 2002, 194, 177–186. [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M. SIMNRA, a Simulation Program for the Analysis of NRA, RBS and ERDA. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP: Denton, Texas (USA), 1999; pp. 541–544. [CrossRef]
- Baruah, S.; Thanachayanont, C.; Dutta, J. Growth of ZnO Nanowires on Nonwoven Polyethylene Fibers. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials 2008, 9, 025009. [CrossRef]
- Miralrio, A.; Rangel Cortes, E.; Castro, M. Electronic Properties and Enhanced Reactivity of MoS2 Monolayers with Substitutional Gold Atoms Embedded into Sulfur Vacancies. Applied Surface Science 2018, 455, 758–770. [CrossRef]
- Dresselhaus, M.S.; Jorio, A.; Hofmann, M.; Dresselhaus, G.; Saito, R. Perspectives on Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Raman Spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 751–758. [CrossRef]
- Iatsunskyi, I.; Nowaczyk, G.; Jurga, S.; Fedorenko, V.; Pavlenko, M.; Smyntyna, V. One and Two-Phonon Raman Scattering from Nanostructured Silicon. Optik 2015, 126, 1650–1655. [CrossRef]
- Mottola, S.; Mancuso, A.; Sacco, O.; Vaiano, V.; De Marco, I. Photocatalytic Systems Based on ZnO Produced by Supercritical Antisolvent for Ceftriaxone Degradation. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1173. [CrossRef]
- Cuscó, R.; Alarcón-Lladó, E.; Ibáñez, J.; Artús, L.; Jiménez, J.; Wang, B.; Callahan, M.J. Temperature Dependence of Raman Scattering in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 165202. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Singh, B.P.; Dhar, S.; Gondorf, A.; Spasova, M. Effect of Surface Groups on the Luminescence Property of ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesized by Sol–Gel Route. Surface Science 2012, 606, L13–L17. [CrossRef]
- Fontánez, K.; García, D.; Ortiz, D.; Sampayo, P.; Hernández, L.; Cotto, M.; Ducongé, J.; Díaz, F.; Morant, C.; Petrescu, F.; et al. Biomimetic Catalysts Based on Au@TiO2-MoS2-CeO2 Composites for the Production of Hydrogen by Water Splitting. IJMS 2022, 24, 363. [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-Gomez, A.; Quereda, J.; van der Meulen, H.P.; Agraït, N.; Rubio-Bollinger, G. Spatially Resolved Optical Absorption Spectroscopy of Single- and Few-Layer MoS2 by Hyperspectral Imaging. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 115705. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yap, C.C.R.; Tay, B.K.; Edwin, T.H.T.; Olivier, A.; Baillargeat, D. From Bulk to Monolayer MoS2 : Evolution of Raman Scattering. Adv Funct Materials 2012, 22, 1385–1390. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Rehman, W.; Khan, M.M.; Qureshi, M.T.; Gul, A.; Haq, S.; Ullah, R.; Rab, A.; Menaa, F. Phytogenic Fabrication of ZnO and Gold Decorated ZnO Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2021, 9, 104725. [CrossRef]
- Ngoma, M.M.; Mathaba, M.; Moothi, K. Effect of Carbon Nanotubes Loading and Pressure on the Performance of a Polyethersulfone (PES)/Carbon Nanotubes (CNT) Membrane. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23805. [CrossRef]
- Al-Taay, H.F.; Mahdi, M.A.; Parlevliet, D.; Jennings, P. Fabrication and Characterization of Solar Cells Based on Silicon Nanowire Homojunctions. Silicon 2017, 9, 17–23. [CrossRef]
- Ghasemipour, P.; Fattahi, M.; Rasekh, B.; Yazdian, F. Developing the Ternary ZnO Doped MoS2 Nanostructures Grafted on CNT and Reduced Graphene Oxide (RGO) for Photocatalytic Degradation of Aniline. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4414. [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Shen, W.; Li, L.; Wu, S.; Wang, W. 3D CoFe2O4 Nanorod/Flower-like MoS2 Nanosheet Heterojunctions as Recyclable Visible Light-Driven Photocatalysts for the Degradation of Organic Dyes. Applied Surface Science 2018, 447, 711–723. [CrossRef]
- Briggs, D.; Seah, M. Practical Surface Analysis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1994.
- Lee, H.-J.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Park, K.H.; Bae, J.-S.; Mubarak, M.; Lee, H. Elucidation of an Intrinsic Parameter for Evaluating the Electrical Quality of Graphene Flakes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 557. [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-J.; Kim, J.-P.; Park, J.-S. Effects of Al Interlayer Coating and Thermal Treatment on Electron Emission Characteristics of Carbon Nanotubes Deposited by Electrophoretic Method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 236. [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.M.; Ambrosi, A.; Chua, C.K.; Pumera, M. Electron Transfer Properties of Chemically Reduced Graphene Materials with Different Oxygen Contents. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 10668–10675. [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, N.; Kubo, T.; Nishina, Y. Tailoring the Oxygen Content of Graphite and Reduced Graphene Oxide for Specific Applications. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21715. [CrossRef]
- Zagorac, D.; Zagorac, J.; Pejić, M.; Matović, B.; Schön, J.C. Band Gap Engineering of Newly Discovered ZnO/ZnS Polytypic Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1595. [CrossRef]
- Hanif, Md.A.; Kim, Y.-S.; Akter, J.; Kim, H.G.; Kwac, L.K. Fabrication of Robust and Stable N-Doped ZnO/Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Characterization, Photocatalytic Application, Kinetics, Degradation Products, and Toxicity Analysis. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 16174–16185. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, I.A.; Purqon, A. First Principles Study of Molybdenum Disulfide Electronic Structure. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2017, 877, 012026. [CrossRef]
- Hutagalung, S.D.; Fadhali, M.M.; Areshi, R.A.; Tan, F.D. Optical and Electrical Characteristics of Silicon Nanowires Prepared by Electroless Etching. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 425. [CrossRef]
- Prabavathi, S.L.; Saravanakumar, K.; Nkambule, T.T.I.; Muthuraj, V.; Mamba, G. Enhanced Photoactivity of Cerium Tungstate-Modified Graphitic Carbon Nitride Heterojunction Photocatalyst for the Photodegradation of Moxifloxacin. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 11434–11447. [CrossRef]
- Jourshabani, M.; Shariatinia, Z.; Badiei, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Sm2O3/S-Doped g-C3N4 Nanocomposites with Enhanced Photocatalytic Activities under Visible Light Irradiation. Applied Surface Science 2018, 427, 375–387. [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Li, X.; Lin, H.; Chen, S.; Fu, X. In Situ Preparation of Novel p–n Junction Photocatalyst BiOI/(BiO)2CO3 with Enhanced Visible Light Photocatalytic Activity. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2012, 239–240, 316–324. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Bi, W.; Xia, Z.; Yuan, W.; Li, L. Hydrothermal Synthesis of the CuWO4/ZnO Composites with Enhanced Photocatalytic Performance. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 13185–13195. [CrossRef]
- Barpuzary, D.; Banik, A.; Gogoi, G.; Qureshi, M. Noble Metal-Free Counter Electrodes Utilizing Cu2ZnSnS4 Loaded with MoS2 for Efficient Solar Cells Based on ZnO Nanowires Co-Sensitized with CuInS2 –CdSe Quantum Dots. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 14378–14388. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mandal, R.; Ratchford, D.C.; Anthony, R.; Yeom, J. Si Nanocrystals/ZnO Nanowires Hybrid Structures as Immobilized Photocatalysts for Photodegradation. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 491. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ling, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y. Photocatalytic H2 Evolution on MoS2–TiO2 Catalysts Synthesized via Mechanochemistry. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 933–940. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Tian, W.; Li, X.; Tade, M.O.; Sun, H.; Wang, S. Flower-like MoS2 on Graphitic Carbon Nitride for Enhanced Photocatalytic and Electrochemical Hydrogen Evolutions. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2018, 239, 334–344. [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Fang, W.; Yuan, H.; Xia, W.; Zeng, X.; Shangguan, W. Few-Layered MoS2/ZnCdS/ZnS Heterostructures with an Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2022, 5, 4893–4902. [CrossRef]
- Zeimpekis, I.; Rahman, T.; Leung, O.M.; Tyson, J.; Ebert, M.; Boden, S.A.; Ponce De Leon, C.; Morgan, K.A. Scalable Large-Area 2D-MoS2/Silicon-Nanowire Heterostructures for Enhancing Energy Storage Applications. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2024, 7, 2299–2308. [CrossRef]
- Stoica, I.; Abraham, A.R.; Haghi, A.K. Advances in Energy Materials: New Composites and Techniques for Future Energy Applications; 1st ed.; Apple Academic Press: New York, 2023; ISBN 978-1-00-334607-4. [CrossRef]
- Anushya, G.; Benjamin, M.; Sarika, R.; Pravin, J.C.; Sridevi, R.; Nirmal, D. A Review on Applications of Molybdenum Disulfide Material: Recent Developments. Micro and Nanostructures 2024, 186, 207742. [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Hua, C.; Guo, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, X.; Wu, F.; Wang, J.; Chen, L. Lithium Storage in Commercial MoS2 in Different Potential Ranges. Electrochimica Acta 2012, 81, 155–160. [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Ye, J.; Chen, W.; Chen, D.; Yang Lee, J. Gemini Surfactant Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanotile-like MoS2/Graphene Hybrid with Enhanced Lithium Storage Performance. Nano Energy 2014, 10, 144–152. [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Meng, Y.; He, F.; Liu, E.; Shi, C.; He, C.; Ma, L.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Zhao, N. Thermal Decomposition-Reduced Layer-by-Layer Nitrogen-Doped Graphene/MoS2/Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Heterostructure for Promising Lithium-Ion Batteries. Nano Energy 2017, 41, 154–163. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Lu, S.; Zhang, H.; Varanasi, C.V.; Liu, J. Synergistic Effects from Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes Enable Flexible and Robust Electrodes for High-Performance Supercapacitors. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4206–4211. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Lou, X.W. (David) Synthesis of Highly Uniform Molybdenum–Glycerate Spheres and Their Conversion into Hierarchical MoS 2 Hollow Nanospheres for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7423–7426. [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Xi, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Wan, Z. Recent Progress in Silicon−Based Materials for Performance−Enhanced Lithium−Ion Batteries. Molecules 2023, 28, 2079. [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Chen, W. L -Cysteine-Assisted Synthesis of Layered MoS2/Graphene Composites with Excellent Electrochemical Performances for Lithium Ion Batteries. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4720–4728. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wong, J.I.; Tan, A.Y.S.; Hsu, C.-L.; Li, L.-J.; Lu, Y.-C.; Yang, H.Y. Self-Assembly of Hierarchical MoSx/CNT Nanocomposites (2<x<3): Towards High Performance Anode Materials for Lithium Ion Batteries. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2169. [CrossRef]
- Magali Gauthier. Electrodes negatives a Base de Silicium Pour Accumulateurs Au Lithium : Mecanisme reactionnel a l’ echelle Nanometrique et Optimisation Des Performances, 2013, Doctoral These.
- Obrovac, M.N.; Chevrier, V.L. Alloy Negative Electrodes for Li-Ion Batteries. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11444–11502. [CrossRef]
- Chhowalla, M.; Shin, H.S.; Eda, G.; Li, L.-J.; Loh, K.P.; Zhang, H. The Chemistry of Two-Dimensional Layered Transition Metal Dichalcogenide Nanosheets. Nature Chem 2013, 5, 263–275. [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, L.Y.; Eberman, K.W.; Turner, R.L.; Krause, L.J.; Dahn, J.R. Colossal Reversible Volume Changes in Lithium Alloys. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2001, 4, A137. [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Z.; Kim, D.; Alfaruqi, M.H.; Song, J.; Kim, S.; Duong, P.T.; Mathew, V.; Baboo, J.P.; Kim, J. Ultrafine Molybdenum Oxycarbide Nanoparticles Embedded in N-Doped Carbon as a Superior Anode Material for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2017, 696, 143–149. [CrossRef]
- Obrovac, M.N.; Christensen, L. Structural Changes in Silicon Anodes during Lithium Insertion/Extraction. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2004, 7, A93. [CrossRef]
- Pinilla, S.; Park, S.-H.; Fontanez, K.; Márquez, F.; Nicolosi, V.; Morant, C. 0D-1D Hybrid Silicon Nanocomposite as Lithium-Ion Batteries Anodes. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 515. [CrossRef]
- Mathayan, V.; Moro, M.V.; Morita, K.; Tsuchiya, B.; Ye, R.; Baba, M.; Primetzhofer, D. In-Operando Observation of Li Depth Distribution and Li Transport in Thin Film Li Ion Batteries. Applied Physics Letters 2020, 117, 023902. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




