Submitted:
01 October 2024
Posted:
01 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Interferons as Active Ingredients
2.1.2. Encapsulation Materials
2.1.3. Cell Lines
2.1.4. Animal Models
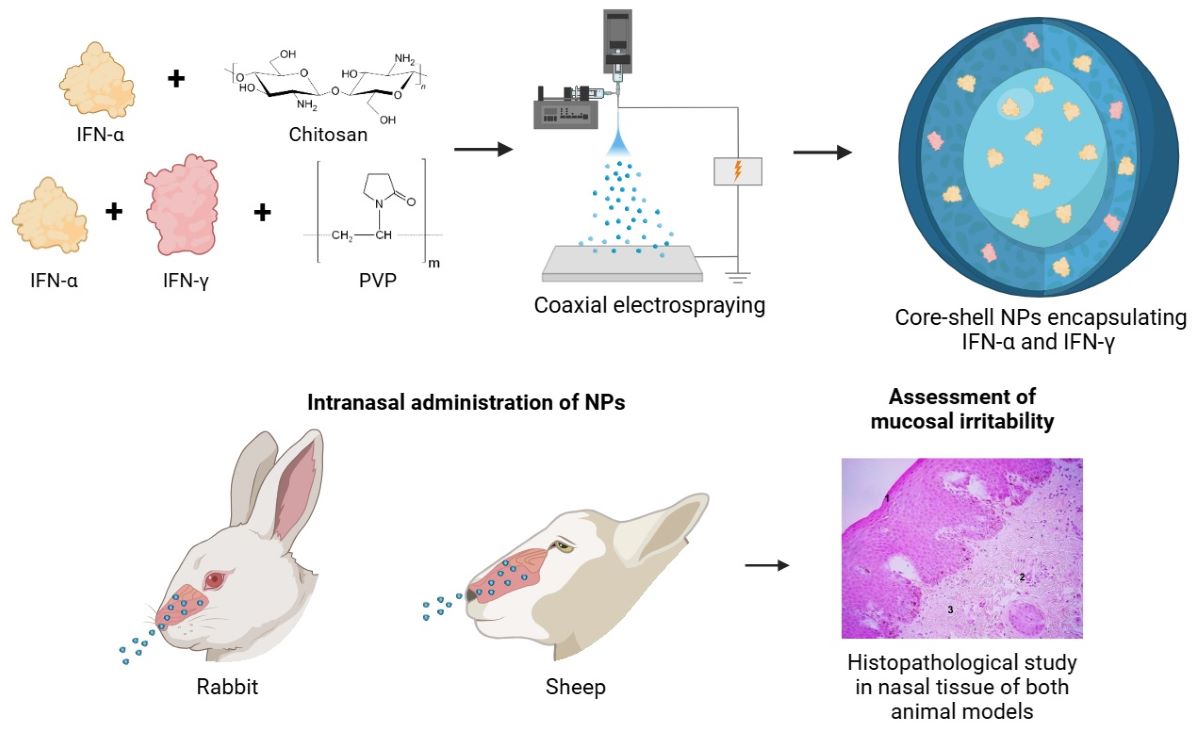
2.2. Synthesis of Core-Shell NPs with Interferons Alpha and Gamma
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization of Nanoparticles
2.3.1. Morphology and Size
2.3.2. Encapsulation Efficiency
2.3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.3.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry Analysis
2.3.5. In Vitro Kinetic Release Study
2.4. Biological Characterization of Nanoparticles
2.4.1. Effect of Encapsulated Active Ingredients on Cell Viability
2.4.2. In Vitro Antiviral Biological Activity
2.4.3. Monolayer Study of the Interaction of NPs by Confocal Microscopy
2.4.4. Formulation Stability under Accelerated Conditions
2.4.5. In Vitro Statistical Analysis
2.5. Evaluation of Initial Toxicity In Vivo
2.5.1. Study of the Mucosal Irritant Potential of the CS Core-Coated Formulation in Rabbits
2.5.2. Study of Release Kinetics and Biological Activity in Sheep
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of Nanoformulations
3.1.1. Morphology and Size
3.1.2. Mean Diameters and Zeta Potential
3.1.3. Encapsulation Efficiency
3.1.4. Characterization by Attenuated Total Reflectance Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR)
3.1.5. Thermal Analysis by Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.1.6. Evaluation of the In Vitro Nanoformulations Release Kinetics
3.2. Biological Characterization of the Nanoformulations
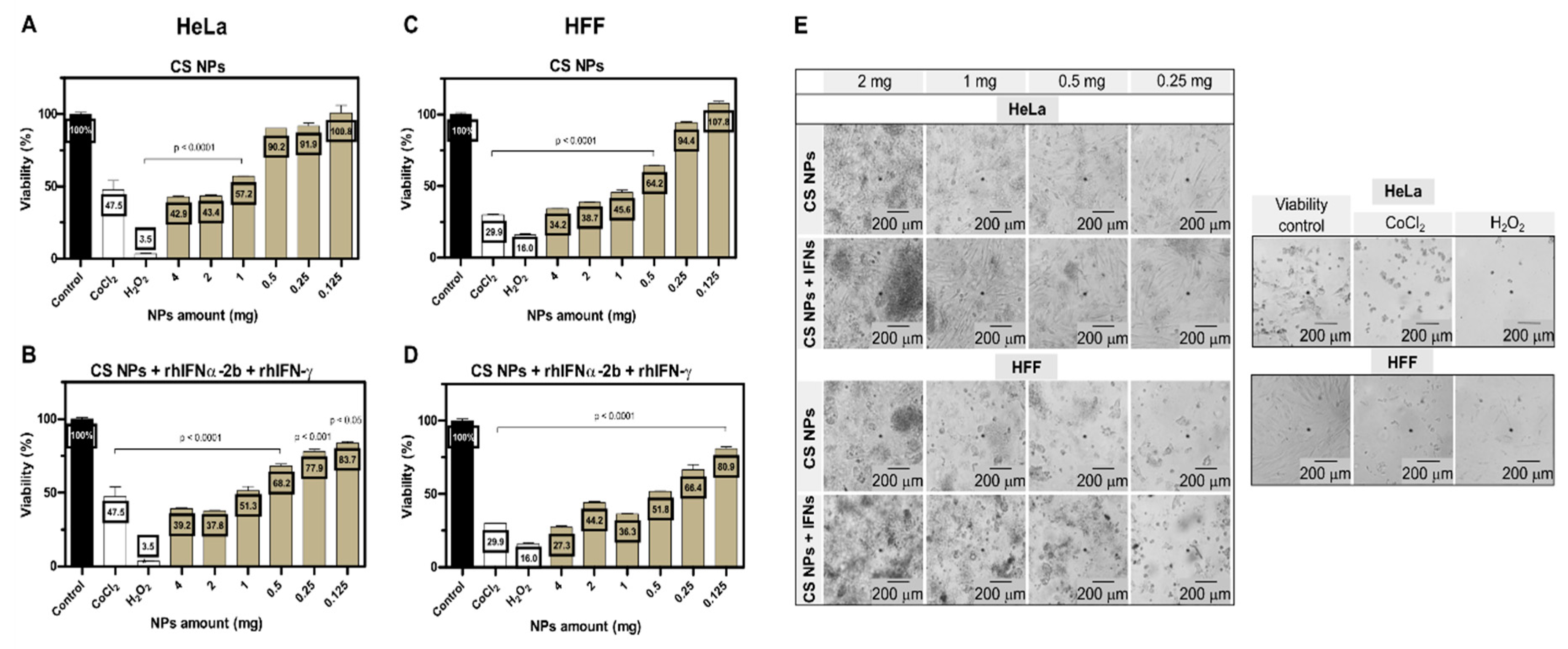
3.2.1. Effect of Encapsulated Active Ingredients on Cell Viability
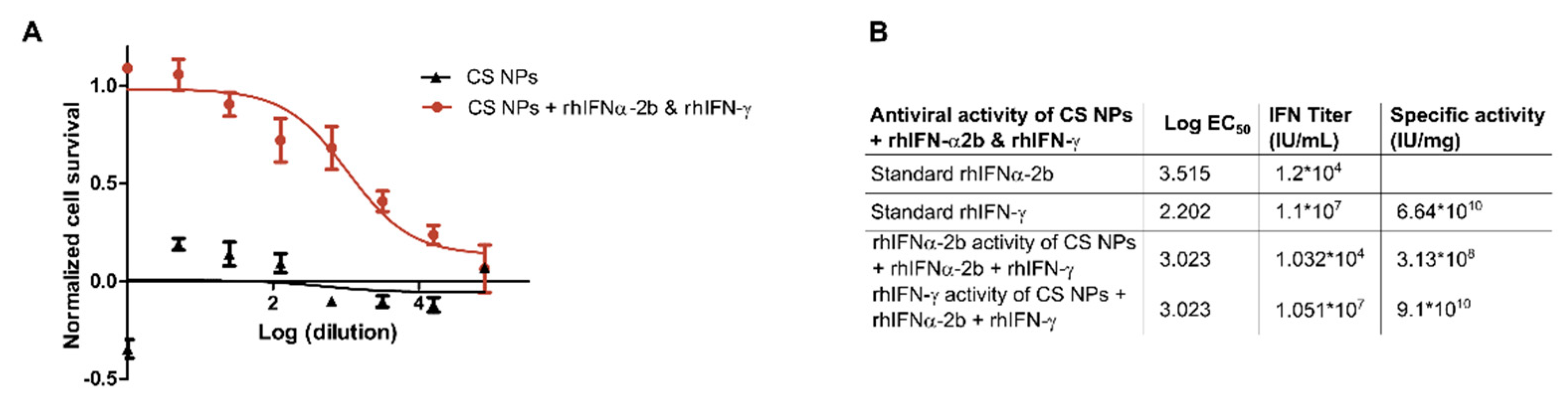
3.2.2. In Vitro Antiviral Biological Activity of Nanoformulations
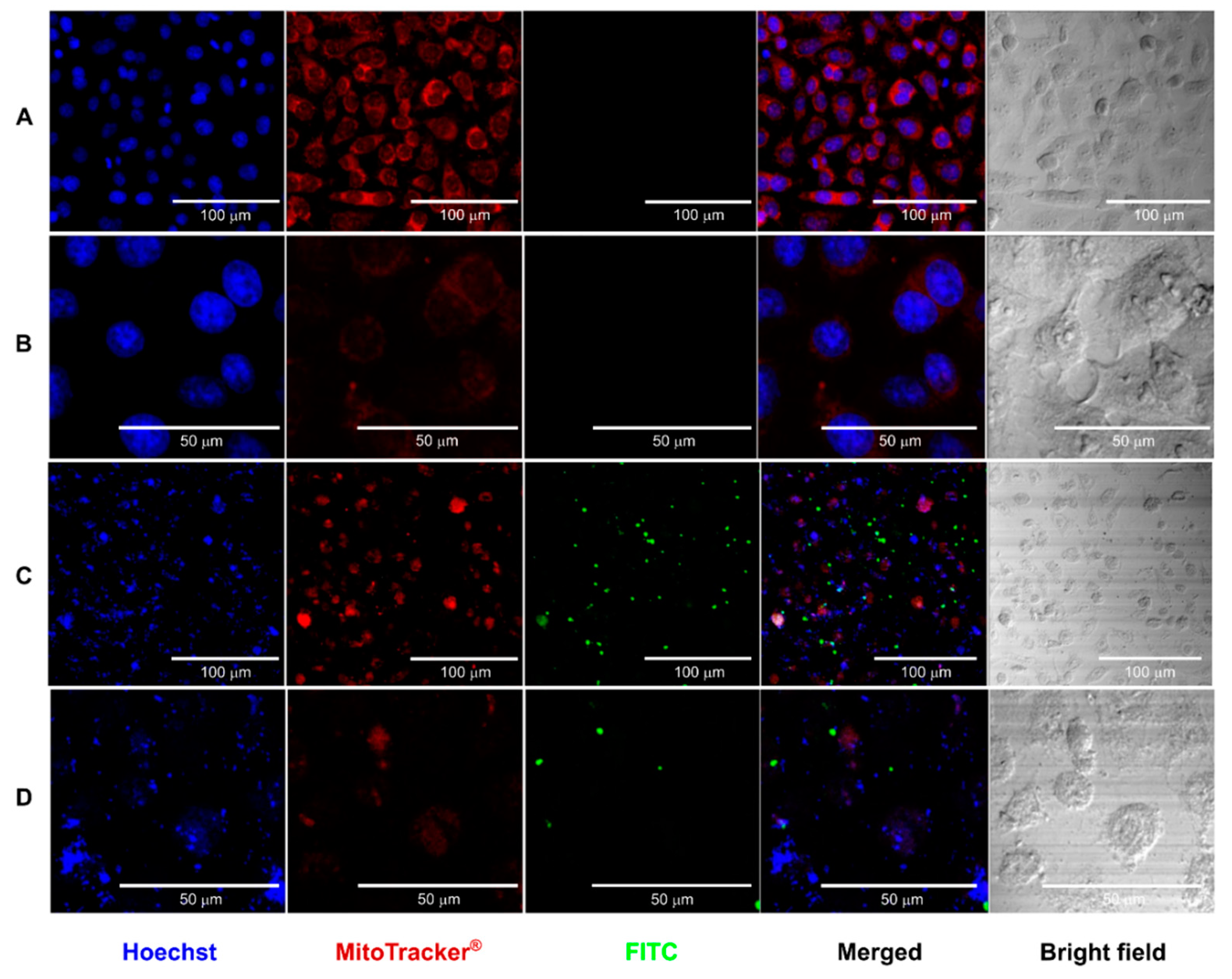
3.2.3. Confocal Microscopy Study of the Interaction of CS Core-Shell NPs
3.2.4. Stability of Nanoformulations under Accelerated Conditions
3.3. Initial Safety Evaluation of NPs in Animal Models Such as Oryctolagus Cuniculus and Ovis Aries
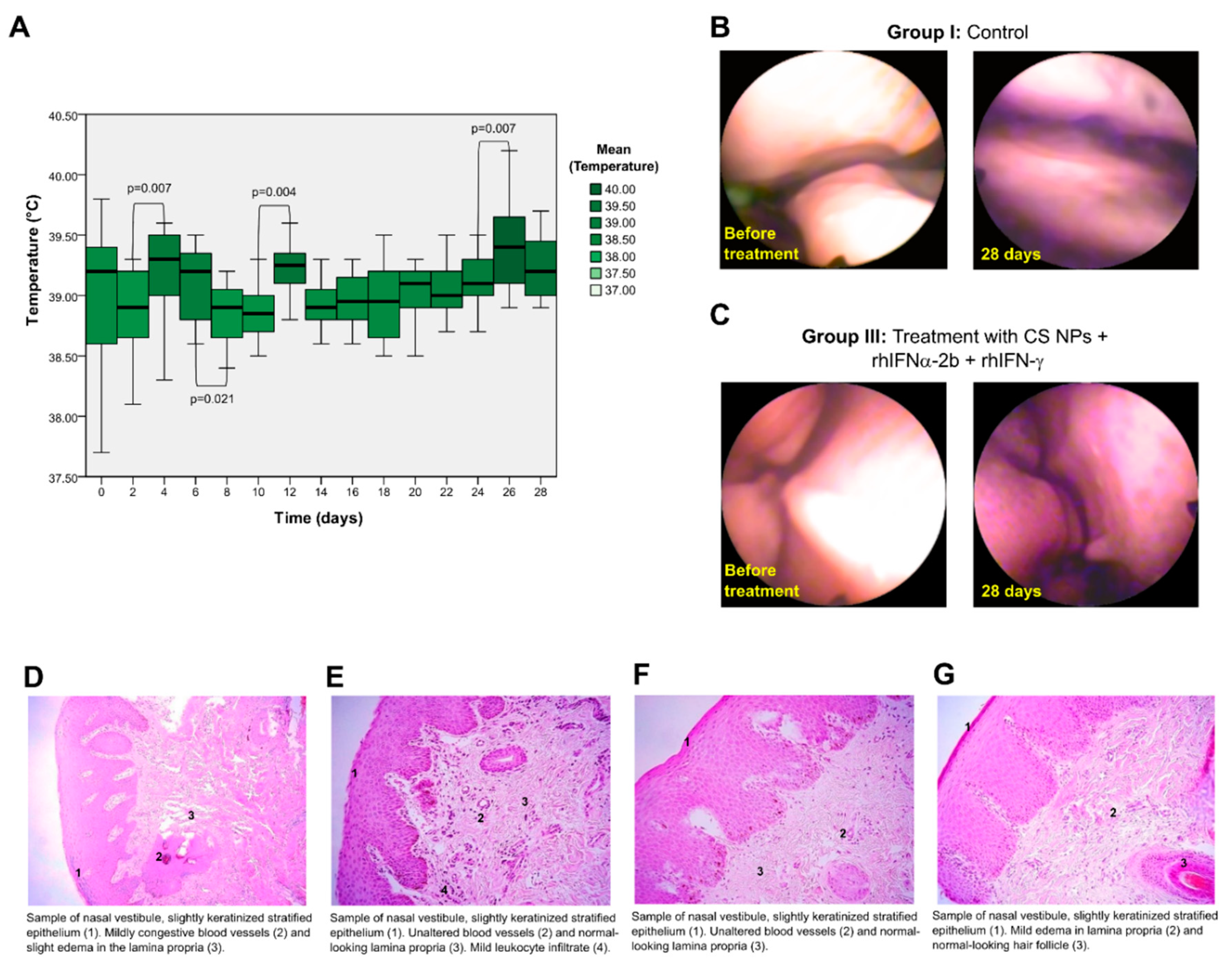
3.3.1. Study of the Mucosal Irritant Potential of CS NPs in Rabbits
3.3.2. Histopathological Study
3.3.3. Safety Study of CS NPs in Sheep
3.3.4. Histopathological Study
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chidiac, C.; Ferry, T. Agents infectieux émergents. Transfusion Clinique et Biologique 2016, 23, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, E.; Petrosillo, N.; Koopmans, M.; Beeching, N.; Di Caro, A.; Gkrania-Klotsas, E.; Kantele, A.; Kohlmann, R.; Koopmans, M.; Lim, P.L.; et al. Emerging infections—an increasingly important topic: review by the Emerging Infections Task Force. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2018, 24, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanne, J.H. US faces triple epidemic of flu, RSV, and covid. BMJ 2022, o2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, C.S.; Chibale, K.; Goss, R.J.M.; Jaspars, M.; Newman, D.J.; Dorrington, R.A. Antiviral drug discovery: preparing for the next pandemic. Chemical Society Reviews 2021, 50, 3647–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch, S.; Jasny, E.; Schmidt, K.E.; Petsch, B. New Vaccine Technologies to Combat Outbreak Situations. Frontiers in Immunology 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, M.; Cihlar, T.; Bostwick, J.R.; Whitley, R.J. Accelerating drug development: antiviral therapies for emerging viruses as a model. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology 2017, 57, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikkert, M. Innate Immune Evasion by Human Respiratory RNA Viruses. J Innate Immun 2020, 12, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Innate immunity to virus infection. Immunol Rev 2009, 227, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, H.; Taniguchi, T.; Yanai, H. The Interferon (IFN) Class of Cytokines and the IFN Regulatory Factor (IRF) Transcription Factor Family. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 2018, 10, a028423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhao, P.; Ma, B.; Guo, G.; Sun, Y.; Xing, M. Cloning, expression and antiviral bioactivity of Red-crowned Crane interferon-α. Gene 2014, 544, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, A.; D’Angelo, J.A.; Romney-Vanterpool, A.; Chu, T.; Bertoletti, A.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Gehring, A.J. IFN-α Suppresses Myeloid Cytokine Production, Impairing IL-12 Production and the Ability to Support T-Cell Proliferation. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 2020, 222, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.X.; Fish, E.N. Global virus outbreaks: Interferons as 1st responders. Semin Immunol 2019, 43, 101300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lembo, D.; Cavalli, R. Nanoparticulate delivery systems for antiviral drugs. Antiviral Chemistry and Chemotherapy 2010, 21, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Wei, G.; Huang, Y.; Yu, H.; Gan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mei, L.; et al. Recent progress in drug delivery. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 2019, 9, 1145–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Thareja, S. In vitro and in vivo characterization of pharmaceutical nanocarriers used for drug delivery. Artificial cells, nanomedicine, and biotechnology 2019, 47, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, L.S.; Lobo, G.S.; Pereira, P.; Freire, M.G.; Neves, M.C.; Pedro, A.Q. Interferon-Based Biopharmaceuticals: Overview on the Production, Purification, and Formulation. Vaccines 2021, 9, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickow, J.; Francois, S.; Kaiserling, R.-L.; Malyshkina, A.; Drexler, I.; Westendorf, A.M.; Lang, K.S.; Santiago, M.L.; Dittmer, U.; Sutter, K. Diverse Immunomodulatory Effects of Individual IFNα Subtypes on Virus-Specific CD8(+) T Cell Responses. Frontiers in immunology 2019, 10, 2255–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri; Tomar, P.; Karwasara, V.S.; Pandey, R.S.; Dixit, V.K. Targeted novel surface-modified nanoparticles for interferon delivery for the treatment of hepatitis B. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica 2011, 43, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherzad, A.; Hagen, R.; Hackenberg, S. Current understanding of nasal epithelial cell mis-differentiation. Journal of Inflammation Research 2019, 12, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantachit, N.; Sunintaboon, P.; Ubol, S. Responses of primary human nasal epithelial cells to EDIII-DENV stimulation: the first step to intranasal dengue vaccination. Virol J 2016, 13, 142–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.; Yoo, H.S. The Application of Mucoadhesive Chitosan Nanoparticles in Nasal Drug Delivery. Mar Drugs 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-González, G.L.; Villarreal-Gómez, L.J.; Serrano-Medina, A.; Torres-Martínez, E.J.; Cornejo-Bravo, J.M. Mucoadhesive electrospun nanofibers for drug delivery systems: applications of polymers and the parameters' roles. Int J Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 5271–5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Far, J.; Abdel-Haq, M.; Gruber, M.; Abu Ammar, A. Developing Biodegradable Nanoparticles Loaded with Mometasone Furoate for Potential Nasal Drug Delivery. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 7432–7439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenthamara, D.; Subramaniam, S.; Ramakrishnan, S.G.; Krishnaswamy, S.; Essa, M.M.; Lin, F.-H.; Qoronfleh, M.W. Therapeutic efficacy of nanoparticles and routes of administration. Biomater Res 2019, 23, 20–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.U.; Shehzad, A.; Ahmed, M.B.; Lee, Y.S. Intranasal Delivery of Nanoformulations: A Potential Way of Treatment for Neurological Disorders. Molecules 2020, 25, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.D.P.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects. Journal of Nanobiotechnology 2018, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard, I.a. European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/EC/es/product/sial/i0320301 (accessed on.
- Standard, I.g. Invitrogen. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/antibody/product/Human-IFN-gamma-Recombinant-Protein/RP-8607 (accessed on.
- Vanharova, L.; Julinova, M.; Slavik, R. PVP Based Materials: Biodegradation in Different Environments. Ecological Chemistry and Engineering S 2017, 24, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abyadeh, M.; Aghajani, M.; Mahmoudabad, A.; Amani, A. Preparation and Optimization of Chitosan/pDNA Nanoparticles Using Electrospray. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India Section B: Biological Sciences 2018, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y.; Yu, T.; Lou, D.; Guo, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, Z.; Ran, H. Drug release from core-shell PVA/silk fibroin nanoparticles fabricated by one-step electrospraying. Scientific Reports 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, A.W.; Azzalini, A. Applied Smoothing Techniques for Data Analysis. 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Pedroso-Santana, S.; Sarabia-Saínz, A.; Fleitas-Salazar, N.; Santacruz-Gómez, K.; Acosta-Elías, M.; Pedroza-Montero, M.; Riera, R. Deagglomeration and characterization of detonation nanodiamonds for biomedical applications. Journal of Applied Biomedicine 2017, 15, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso-Santana, S.; Lamazares Arcia, E.; Fleitas-Salazar, N.; Gancino Guevara, M.; Mansilla, R.; Gómez-Gaete, C.; Altamirano, C.; Fernandez, K.; Ruiz, A.; Toledo Alonso, J.R. Polymeric nanoencapsulation of alpha interferon increases drug bioavailability and induces a sustained antiviral response in vivo. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2020, 116, 111260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiernan, H.; Byrne, B.; Kazarian, S.G. ATR-FTIR spectroscopy and spectroscopic imaging for the analysis of biopharmaceuticals. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2020, 241, 118636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, L.Y.; Lim, Y.Y.; Tan, C.P.; Siow, L.F. Effects of spray-, oven-, and freeze drying on the physicochemical properties of poorly aqueous-soluble xanthone encapsulated by coacervation: A comparative study. Drying Technology 2022, 40, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Duan, X.; Cao, W.; Ren, X.; Ren, G.; Liu, P.; Chen, J. Effects of Different Drying Methods on the Characterization, Dissolution Rate and Antioxidant Activity of Ursolic Acid-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles. Foods 2021, 10, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, F.; Fang, Y.; Yang, W.; An, X.; Zhao, L.; Xin, Z.; Cao, L.; Hu, Q. Synthesis, characterization and cytotoxicity studies of chitosan-coated tea polyphenols nanoparticles. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2011, 82, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. Micro BCA Protein Assay Kit. Available online: https://assets.thermofisher.com/TFS-Assets/LSG/manuals/MAN0011237_Micro_BCA_Protein_Asy_UG.pdf (accessed on.
- van de Loosdrecht, A.A.; Beelen, R.H.J.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Broekhoven, M.G.; Langenhuijsen, M.M.A.C. A tetrazolium-based colorimetric MTT assay to quantitate human monocyte mediated cytotoxicity against leukemic cells from cell lines and patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Journal of Immunological Methods 1994, 174, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.-Y.; Cao, C.; Liu, L. Interferon α Induces the Apoptosis of Cervical Cancer HeLa Cells by Activating both the Intrinsic Mitochondrial Pathway and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2016, 17, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P. Chapter Eight - Structural basis of viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase nucleotide addition cycle in picornaviruses. In The Enzymes; Cameron, C.E., Arnold, J.J., Kaguni, L.S., Eds.; Academic Press, 2021; Volume 49, pp. 215–233. [Google Scholar]
- Pestka, S.; Baron, S. Definition and classification of the interferons. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press, 1981; Volume 78, pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Di Veroli, G.Y.; Fornari, C.; Goldlust, I.; Mills, G.; Koh, S.B.; Bramhall, J.L.; Richards, F.M.; Jodrell, D.I. An automated fitting procedure and software for dose-response curves with multiphasic features. Scientific Reports 2015, 5, 14701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, N.; Barolo, C.; Viscardi, G. Bovine serum albumin bioconjugation with FITC. World Journal of Chemical Education 2016, 4, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso-Santana, S.; Fleitas-Salazar, N. Ionotropic gelation method in the synthesis of nanoparticles/microparticles for biomedical purposes. Polymer International 2020, 69, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Stability testing of active pharmaceutical ingredients and finished pharmaceutical products. WHO Technical Report Series, No. 953, Annex 2. 2015.
- Nornadiah, M.R.; Wah, Y.B. Power Comparisons of Shapiro-Wilk, Kolmogorov-Smirnov, Lilliefors and Anderson-Darling tests. Teknologi MARA University. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yamagiwa, Y.; Kurata, M.; Satoh, H. Histological Features of the Nasal Passage in Juvenile Japanese White Rabbits. Toxicologic Pathology 2022, 50, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murkunde, Y.V. Necropsy Procedures for Laboratory Animals. In Essentials of Laboratory Animal Science: Principles and Practices; Nagarajan, P., Gudde, R., Srinivasan, R., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2021; pp. 743–781. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, C.P.; Moreira, J.N.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Silva, A.C. Intranasal delivery of nanostructured lipid carriers, solid lipid nanoparticles and nanoemulsions: A current overview of in vivo studies. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B 2021, 11, 925–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipiäinen, T.; Peltoniemi, M.; Sarkhel, S.; Yrjönen, T.; Vuorela, H.; Urtti, A.; Juppo, A. Formulation and stability of cytokine therapeutics. J Pharm Sci 2015, 104, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N.; Mauser, A.; Ko, Y.; Lahann, J. Protein Nanoparticles: Uniting the Power of Proteins with Engineering Design Approaches. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2022, 9, e2104012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipiäinen, T.; Peltoniemi, M.; Sarkhel, S.; Yrjönen, T.; Vuorela, H.; Urtti, A.; Juppo, A. Formulation and Stability of Cytokine Therapeutics. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2015, 104, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abyadeh, M.; Aghajani, M.; Gohari Mahmoudabad, A.; Amani, A. Preparation and Optimization of Chitosan/pDNA Nanoparticles Using Electrospray. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India Section B: Biological Sciences 2019, 89, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okay, S. Single-Molecule Characterization of Drug Delivery Systems. Assay Drug Dev Technol 2020, 18, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teulon, J.M.; Godon, C.; Chantalat, L.; Moriscot, C.; Cambedouzou, J.; Odorico, M.; Ravaux, J.; Podor, R.; Gerdil, A.; Habert, A.; et al. On the Operational Aspects of Measuring Nanoparticle Sizes. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D. Advanced electron microscopy characterization of nanomaterials for catalysis. Green Energy & Environment 2017, 2, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikes, J.C.; Wonner, K.; Nicholson, A.; Cignoni, P.; Fritsch, I.; Tschulik, K. Characterization of Nanoparticles in Diverse Mixtures Using Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance and Nanoparticle Tracking by Dark-Field Microscopy with Redox Magnetohydrodynamics Microfluidics. ACS Phys Chem Au 2022, 2, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandi, S.P.; Kumbhar, Y.S.; Venuganti, V.V.K. Effect of particle size and surface charge of nanoparticles in penetration through intestinal mucus barrier. Journal of Nanoparticle Research 2020, 22, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, F.; Clogston, J.; Calzolai, L.; Rösslein, M.; Prina-Mello, A. Measuring particle size distribution of nanoparticle enabled medicinal products, the joint view of EUNCL and NCI-NCL. A step by step approach combining orthogonal measurements with increasing complexity. Journal of Controlled Release 2019, 299, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Mello, S.R.; Cruz, C.N.; Chen, M.L.; Kapoor, M.; Lee, S.L.; Tyner, K.M. The evolving landscape of drug products containing nanomaterials in the United States. Nat Nanotechnol 2017, 12, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clogston, J.D.; Hackley, V.A.; Prina-Mello, A.; Puri, S.; Sonzini, S.; Soo, P.L. Sizing up the Next Generation of Nanomedicines. Pharm Res 2019, 37, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, P.M.; Rasulev, B.; Roy, K. QSPR Modeling of the Refractive Index for Diverse Polymers Using 2D Descriptors. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 13374–13386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, M.; Sarode, A.; Hoore, M.; Fedosov, D.A.; Mitragotri, S.; Sen Gupta, A. Influence of particle size and shape on their margination and wall-adhesion: implications in drug delivery vehicle design across nano-to-micro scale. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 15350–15364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Drug Products, Including Biological Products, that Contain Nanomaterials Guidance for Industry. 2017.
- Bajpai, P. Chapter 10 - Papermaking Chemistry. In Biermann's Handbook of Pulp and Paper (Third Edition); Bajpai, P., Ed.; Elsevier, 2018; pp. 207–236. [Google Scholar]
- Lowry, G.V.; Hill, R.J.; Harper, S.; Rawle, A.F.; Hendren, C.O.; Klaessig, F.; Nobbmann, U.; Sayre, P.; Rumble, J. Guidance to improve the scientific value of zeta-potential measurements in nanoEHS. Environmental Science: Nano 2016, 3, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aibani, N.; Rai, R.; Patel, P.; Cuddihy, G.; Wasan, E.K. Chitosan Nanoparticles at the Biological Interface: Implications for Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Németh, Z.; Csóka, I.; Semnani Jazani, R.; Sipos, B.; Haspel, H.; Kozma, G.; Kónya, Z.; Dobó, D.G. Quality by Design-Driven Zeta Potential Optimisation Study of Liposomes with Charge Imparting Membrane Additives. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadiri, M.; Young, P.M.; Traini, D. Strategies to Enhance Drug Absorption via Nasal and Pulmonary Routes. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.Z.; Sabri, A.H.B.; Anjani, Q.K.; Domínguez-Robles, J.; Abdul Latip, N.; Hamid, K.A. Design and Development of Levodopa Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles for Intranasal Delivery. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Say, K.M. Maximizing the encapsulation efficiency and the bioavailability of controlled-release cetirizine microspheres using Draper-Lin small composite design. Drug design, development and therapy 2016, 10, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaikwad, V.; Choudhari, P.; Bhatia, N.; Bhatia, M. Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery and Therapy; William Andrew: New York, 2019; Epub 2019 Oct 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cánepa, C.; Imperiale, J.C.; Berini, C.A.; Lewicki, M.; Sosnik, A.; Biglione, M.M. Development of a drug delivery system based on chitosan nanoparticles for oral administration of interferon-α. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3302–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Kikugawa, M.; Sudo, E. Attenuated Total Reflection Surface-Enhanced Infrared Absorption (ATR SEIRA) Spectroscopy for the Analysis of Fatty Acids on Silver Nanoparticles. Appl Spectrosc 2017, 71, 2083–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyva-Porras, C.; Cruz-Alcantar, P.; Espinosa-Solís, V.; Martínez-Guerra, E.; Piñón-Balderrama, C.I.; Compean Martínez, I.; Saavedra-Leos, M.Z. Application of Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Modulated Differential Scanning Calorimetry (MDSC) in Food and Drug Industries. Polymers 2019, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempel, N.-J.; Merkl, P.; Knopp, M.M.; Berthelsen, R.; Teleki, A.; Hansen, A.K.; Sotiriou, G.A.; Löbmann, K. The Effect of the Molecular Weight of Polyvinylpyrrolidone and the Model Drug on Laser-Induced In Situ Amorphization. Molecules 2021, 26, 4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkawi, R.; Malkawi, W.I.; Al-Mahmoud, Y.; Tawalbeh, J. Current Trends on Solid Dispersions: Past, Present, and Future. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci 2022, 2022, 5916013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Jain, C.P. Preparation and characterization of solid dispersions of carvedilol with PVP K30. Res Pharm Sci 2010, 5, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.B.; Liu, D.X.; Liu, D.K.; Wu, G. Application of Solid Dispersion Technique to Improve Solubility and Sustain Release of Emamectin Benzoate. Molecules 2019, 24, 4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, P.; Geczy, A.; Polanský, R.; Bušek, D. Glass transition temperature of nanoparticle-enhanced and environmentally stressed conductive adhesive materials for electronics assembly. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics 2019, 30, 4895–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik-Pastuszka, D.; Krzak, J.; Macikowski, B.; Berkowski, R.; Osiński, B.; Musiał, W. Evaluation of the Release Kinetics of a Pharmacologically Active Substance from Model Intra-Articular Implants Replacing the Cruciate Ligaments of the Knee. Materials (Basel) 2019, 12, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, J.; Tong, H.H.Y.; Chow, S.F. In Vitro Release Study of the Polymeric Drug Nanoparticles: Development and Validation of a Novel Method. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owonubi, S.J.; Aderibigbe, B.A.; Mukwevho, E.; Sadiku, E.R.; Ray, S.S. Characterization and in vitro release kinetics of antimalarials from whey protein-based hydrogel biocomposites. International Journal of Industrial Chemistry 2018, 9, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamani, F.; Hamoudi, M.C.; Danede, F.; Willart, J.F.; Siepmann, F.; Siepmann, J. Towards a better understanding of the release mechanisms of caffeine from PLGA microparticles. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 2020, 137, 48710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurakula, M.; Rao, G. Pharmaceutical assessment of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP): As excipient from conventional to controlled delivery systems with a spotlight on COVID-19 inhibition. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 2020, 60, 102046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frigaard, J.; Jensen, J.L.; Galtung, H.K.; Hiorth, M. The Potential of Chitosan in Nanomedicine: An Overview of the Cytotoxicity of Chitosan Based Nanoparticles. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 880377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, N.; Maitra, S.S. In vitro and in vivo toxicity assessment of nanoparticles. International Nano Letters 2017, 7, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.A.; Uppada, S.; Achkar, I.W.; Hashem, S.; Yadav, S.K.; Shanmugakonar, M.; Al-Naemi, H.A.; Haris, M.; Uddin, S. Tight Junction Proteins and Signaling Pathways in Cancer and Inflammation: A Functional Crosstalk. Front Physiol 2018, 9, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, F.; Gardner, Q.A.; Rashid, N.; Towers, G.J.; Akhtar, M. Preventing the N-terminal processing of human interferon α-2b and its chimeric derivatives expressed in Escherichia coli. Bioorganic Chemistry 2018, 76, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prego, C.; Paolicelli, P.; Díaz, B.; Vicente, S.; Sánchez, A.; González-Fernández, Á.; Alonso, M.J. Chitosan-based nanoparticles for improving immunization against hepatitis B infection. Vaccine 2010, 28, 2607–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katas, H.; Raja, M.A.G.; Lam, K.L. Development of Chitosan Nanoparticles as a Stable Drug Delivery System for Protein/siRNA. International Journal of Biomaterials 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ahmed, S. A review on chitosan and its nanocomposites in drug delivery. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2018, 109, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Deng, X.; He, S.; Li, X.; Jia, W.; Wei, D.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, J. Study on biodegradable microspheres containing recombinant interferon-α-2a. Journal of pharmacy and pharmacology 2002, 54, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwan, M.; Park, T.G. Stabilization of recombinant interferon-α by pegylation for encapsulation in PLGA microspheres. International journal of pharmaceutics 2003, 252, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Song, F.-L.; Pan, Y.-F.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Yang, Y.-q.; Zhao, Y.-M.; Liang, S.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-M. Preparation and characteristics of interferon-alpha poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres. Journal of microencapsulation 2010, 27, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Luo, F.; Mei, X. Development of interferon alpha-2b microspheres with constant release. International journal of pharmaceutics 2011, 410, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, M.; Sun, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Gao, W. Polymerization induced self-assembly of a site-specific interferon α-block copolymer conjugate into micelles with remarkably enhanced pharmacology. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2018, 140, 10435–10438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, P.; Ong, C.; Bay, B.; Baeg, G. Nanotoxicity: An Interplay of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Cell Death. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 1163–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadar, H.; Maqbool, F.; Niaz, K.; Abdollahi, M. Toxicity of Nanoparticles and an Overview of Current Experimental Models. Iran Biomed J 2016, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan Park, S.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, K.; Kim, J.; Choi, S.-O. Influence of shell compositions of solution blown PVP/PCL core–shell fibers on drug release and cell growth. RSC Advances 2018, 8, 32470–32480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.J.; Jung, S.M.; Kang, M.; Shin, H.S.; Youk, J.H. Preparation of hydrophilic PCL nanofiber scaffolds via electrospinning of PCL/PVP-b-PCL block copolymers for enhanced cell biocompatibility. Polymer 2015, 69, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, E.R.A.; Lima, B.M.M.P.; de Moura, W.C.; de, A. Nogueira, A.C.M. Reduction of cell viability induced by IFN-alpha generates impaired data on antiviral assay using Hep-2C cells. Journal of Immunological Methods 2013, 400-401, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamshiri, M.K.; Jaafari, M.R.; Badiee, A. Preparation of liposomes containing IFN-gamma and their potentials in cancer immunotherapy: In vitro and in vivo studies in a colon cancer mouse model. Life Sciences 2021, 264, 118605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrahari, V.; Burnouf, P.-A.; Burnouf, T.; Agrahari, V. Nanoformulation properties, characterization, and behavior in complex biological matrices: Challenges and opportunities for brain-targeted drug delivery applications and enhanced translational potential. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2019, 148, 146–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imperiale, J.C.; Schlachet, I.; Lewicki, M.; Sosnik, A.; Biglione, M.M. Oral Pharmacokinetics of a Chitosan-Based Nano- Drug Delivery System of Interferon Alpha. Polymers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feczko, T.; Fodor-Kardos, A.; Sivakumaran, M.; Haque Shubhra, Q.T. In vitro IFN-alpha release from IFN-alpha- and pegylated IFN-alpha-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) and pegylated poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2016, 11, 2029–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joraholmen, M.W.; Basnet, P.; Acharya, G.; Skalko-Basnet, N. PEGylated liposomes for topical vaginal therapy improve delivery of interferon alpha. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2017, 113, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristó, K.; Szekeres, M.; Makai, Z.; Márki, Á.; Kelemen, A.; Bali, L.; Pallai, Z.; Dékány, I.; Csóka, I. Preparation and investigation of core-shell nanoparticles containing human interferon-α. International journal of pharmaceutics 2020, 573, 118825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Hu, Q.; Xu, C.; Qiao, Q.; Qin, X.; Song, Q.; Peng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Co-delivery of doxorubicin and interferon-γ by thermosensitive nanoparticles for cancer immunochemotherapy. Molecular pharmaceutics 2018, 15, 4161–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, A.D. Confocal Microscopy: Principles and Modern Practices. Current Protocols in Cytometry 2020, 92, e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, S.; Serpooshan, V.; Tao, W.; Hamaly, M.A.; Alkawareek, M.Y.; Dreaden, E.C.; Brown, D.; Alkilany, A.M.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Mahmoudi, M. Cellular uptake of nanoparticles: journey inside the cell. Chemical Society Reviews 2017, 46, 4218–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosse, K.M.; Monson, E.A.; Beard, M.R.; Helbig, K.J. Interferon-Stimulated Genes as Enhancers of Antiviral Innate Immune Signaling. J Innate Immun 2018, 10, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekisz, J.; Baron, S.; Balinsky, C.; Morrow, A.; Zoon, K.C. Antiproliferative Properties of Type I and Type II Interferon. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2010, 3, 994–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybchenko, V.S.; Aliev, T.K.; Panina, A.A.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Dolgikh, D.A. Targeted Cytokine Delivery for Cancer Treatment: Engineering and Biological Effects. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgovanovic, D.; Song, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Roles of IFN-γ in tumor progression and regression: a review. Biomarker Research 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marth, C.; Daxenbichler, G.; Dapunt, O. Synergistic antiproliferative effect of human recombinant interferons and retinoic acid in cultured breast cancer cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 1986, 77, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.Q.; Feng, H.W.; Jia, T.; Chen, X.M.; Zhang, H.; Xu, A.T.; Zhang, H.L.; Fan, X.L. Antiproliferative effects of celecoxib in Hep-2 cells through telomerase inhibition and induction of apoptosis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2014, 15, 4919–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.I.; Villacis-Aguirre, C.A.; Santiago Vispo, N.; Santiago Padilla, L.; Pedroso Santana, S.; Parra, N.C.; Alonso, J.R.T. Forms and Methods for Interferon’s Encapsulation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holder, P.G.; Lim, S.A.; Huang, C.S.; Sharma, P.; Dagdas, Y.S.; Bulutoglu, B.; Sockolosky, J.T. Engineering interferons and interleukins for cancer immunotherapy. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2022, 182, 114112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, K.; Masram, D.T. Biological Activities of Nanoparticles and Mechanism of Action; Springer Singapore, 2020; pp. 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cicha, I.; Chauvierre, C.; Texier, I.; Cabella, C.; Metselaar, J.M.; Szebeni, J.; Dézsi, L.; Alexiou, C.; Rouzet, F.; Storm, G.; et al. From design to the clinic: practical guidelines for translating cardiovascular nanomedicine. Cardiovasc Res 2018, 114, 1714–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albalawi, F.; Hussein, M.Z.; Fakurazi, S.; Masarudin, M.J. Engineered Nanomaterials: The Challenges and Opportunities for Nanomedicines. Int J Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 161–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, P.P.; Patravale, V.B. In Vitro–In Vivo Correlation for Pharmaceutical Nano-and Microsystems. Biology 2021, 137–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolskaia, M.A. Pre-clinical immunotoxicity studies of nanotechnology-formulated drugs: Challenges, considerations and strategy. J Control Release 2015, 220, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, N.; Bhardwaj, P.; Bhatia, E.; Banerjee, R. Clinical Toxicity of Nanomedicines. In Nano Medicine and Nano Safety: Recent Trends and Clinical Evidences; Das, M.K., Pathak, Y.V., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2020; pp. 533–560. [Google Scholar]
- Inc., M.C. INTRON A® interferon alfa-2b. 2019.
- Gao, H.; Zhang, L.L.; Wei, Q.; Duan, Z.J.; Tu, X.M.; Yu, Z.A.; Deng, W.; Zhang, L.P.; Bao, L.L.; Zhang, B.; et al. [Preventive and therapeutic effects of recombinant IFN-alpha2b nasal spray on SARS-CoV infection in Macaca mulata]. Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi 2005, 19, 207–210. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, M.E.; Macri, N.P.; Creasy, D.M. Evaluation of the Rabbit Nasal Cavity in Inhalation Studies and a Comparison with Other Common Laboratory Species and Man. Toxicologic Pathology 2011, 39, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalak, I.; Dziergowska, K.; Alagawany, M.; Farag, M.R.; El-Shall, N.A.; Tuli, H.S.; Emran, T.B.; Dhama, K. The effect of metal-containing nanoparticles on the health, performance and production of livestock animals and poultry. Vet Q 2022, 42, 68–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducournau, C.; Moiré, N.; Carpentier, R.; Cantin, P.; Herkt, C.; Lantier, I.; Betbeder, D.; Dimier-Poisson, I. Effective Nanoparticle-Based Nasal Vaccine Against Latent and Congenital Toxoplasmosis in Sheep. Front Immunol 2020, 11, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias-Valle, L.; Finkelstein-Kulka, A.; Manji, J.; Okpaleke, C.; Al-Salihi, S.; Javer, A.R. Evaluation of sheep sinonasal endoscopic anatomy as a model for rhinologic research. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2018, 4, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klas, S.D.; Petrie, C.R.; Warwood, S.J.; Williams, M.S.; Olds, C.L.; Stenz, J.P.; Cheff, A.M.; Hinchcliffe, M.; Richardson, C.; Wimer, S. A single immunization with a dry powder anthrax vaccine protects rabbits against lethal aerosol challenge. Vaccine 2008, 26, 5494–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimer-Mackin, S.; Hinchcliffe, M.; Petrie, C.R.; Warwood, S.J.; Tino, W.T.; Williams, M.S.; Stenz, J.P.; Cheff, A.; Richardson, C. An intranasal vaccine targeting both the Bacillus anthracis toxin and bacterium provides protection against aerosol spore challenge in rabbits. Vaccine 2006, 24, 3953–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebar, A.; Koller, C.; Seifert, J.-M.; Chabicovsky, M.; Bodenteich, A.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Grassauer, A.; Prieschl-Grassauer, E. Non-Clinical Safety Evaluation of Intranasal Iota-Carrageenan. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0122911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Sara, U.V.S.; Chauhan, I.; Gaur, P.K.; Singh, A.P.; Puri, D.; Ameeduzzafar. Solid lipid nanoparticles for nose to brain delivery of donepezil: formulation, optimization by Box–Behnken design, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology 2017, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonasch, E.; Haluska, F.G. Interferon in oncological practice: review of interferon biology, clinical applications, and toxicities. Oncologist 2001, 6, 34–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrescu, L.; Constantinescu, C.S.; Tanasescu, R. Recent developments in interferon-based therapies for multiple sclerosis. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2018, 18, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vial, T.; Descotes, J. Clinical toxicity of the interferons. Drug Saf 1994, 10, 115–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddrey, W.C. Safety of combination interferon alfa-2b/ribavirin therapy in chronic hepatitis C-relapsed and treatment-naive patients. Semin Liver Dis 1999, 19 Suppl 1, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama, M.; Hugentobler, W.J.; Iwasaki, A. Seasonality of Respiratory Viral Infections. Annual Review of Virology 2020, 7, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, L.; McCloskey, A.P.; Higgins, G.; Ramsey, J.M.; Cryan, S.-A.; Macloughlin, R. Effective nebulization of interferon-γ using a novel vibrating mesh. Respiratory Research 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, V.; Gadeval, A.; Asati, S.; Jain, P.; Jain, N.; Roy, R.K.; Tekade, M.; Soni, V.; Tekade, R.K. Formulation strategies for nose-to-brain delivery of therapeutic molecules; Elsevier, 2019; pp. 291–332. [Google Scholar]
- Tanwar, H.; Sachdeva, R. Transdermal Drug Delivery System: a Review. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research 2015, 7, 2274–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferis, R. Recombinant Proteins and Monoclonal Antibodies. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 2021, 175, 281–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, G. Biopharmaceutical benchmarks 2018. Nature Biotechnology 2018, 36, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.C.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Cytokines and growth factors. In Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology; Silva, A.C., Moreira, J.N., Lobo, J.M., Almeida, H., Eds.; Springer: Cham, 2019; Volume 171. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, T.I.; Villacis-Aguirre, C.A.; López-Aguilar, K.V.; Santiago Padilla, L.; Altamirano, C.; Toledo, J.R.; Santiago Vispo, N. The Hitchhiker’s Guide to Human Therapeutic Nanoparticle Development. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazear, H.M.; Schoggins, J.W.; Diamond, M.S. Shared and distinct functions of type I and type III interferons. Immunity 2019, 50, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fodor-Kardos, A.; Kiss, Á.F.; Monostory, K.; Feczkó, T. Sustained in vitro interferon-beta release and in vivo toxicity of PLGA and PEG-PLGA nanoparticles. RSC Advances 2020, 10, 15893–15900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-Y.; Yang, J.-A.; Jung, H.S.; Beack, S.; Choi, J.E.; Hur, W.; Koo, H.; Kim, K.; Yoon, S.K.; Hahn, S.K. Hyaluronic Acid–Gold Nanoparticle/Interferon α Complex for Targeted Treatment of Hepatitis C Virus Infection. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 9522–9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwestka, J.; Stoger, E. Microparticles and Nanoparticles from Plants-The Benefits of Bioencapsulation. Vaccines (Basel) 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cleland, J.L. Factors affecting the in vitro release of recombinant human interferon- γ (rhIFN-γ) from PLGA microspheres. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 1997, 86, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleland, J.L.; Jones, A.J. Stable formulations of recombinant human growth hormone and interferon-gamma for microencapsulation in biodegradable microspheres. Pharm Res 1996, 13, 1464–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, B.R.; Alpar, H. Single and Coencapsulation of lnterferon-γ in Biodegradable PLA Microspheres for Optimization of Multicomponent Vaccine Delivery Vehicles. Drug Delivery 1997, 4, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Sun, J.; Sun, L.; Dai, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Weng, J.; Jia, W.; Zhang, Z. Preparation and characterization of interferon-loaded magnetic biodegradable microspheres. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials: An Official Journal of The Society for Biomaterials, The Japanese Society for Biomaterials, and The Australian Society for Biomaterials and the Korean Society for Biomaterials 2008, 87, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondiah, P.P.; Tomar, L.K.; Tyagi, C.; Choonara, Y.E.; Modi, G.; du Toit, L.C.; Kumar, P.; Pillay, V. A novel pH-sensitive interferon-β (INF-β) oral delivery system for application in multiple sclerosis. International journal of pharmaceutics 2013, 456, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez, V.; Ramón, J.A.; Caballero, L.; Aldana, R.; Cruz, E.; Peniche, C.; Paez, R. Extraction of PLGA-microencapsulated proteins using a two-immiscible liquid phases system containing surfactants. Pharmaceutical research 2013, 30, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-m.; Yang, F.; Yang, Y.-q.; Song, F.-l.; Xu, A.-l. Recombinant interferon-alpha2b poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres: pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics study in rhesus monkeys following intramuscular administration. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2008, 29, 1370–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.H.; Yu, H.Y.; Gao, J.Q.; Sun, X.Y.; Liang, W.Q. Hydrophilic biodegradable microspheres of interferon-alpha and its pharmacokinetics in mice. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials: An Official Journal of The Society for Biomaterials, The Japanese Society for Biomaterials, and The Australian Society for Biomaterials and the Korean Society for Biomaterials 2008, 85, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulia, M.; Rai, S.; Jain, U.K.; Katare, O.P.; Katyal, A.; Madan, J. Sustained-release protamine sulphate-impregnated microspheres may reduce the frequent administration of recombinant interferon alpha-2b in ovarian cancer: in-vitro characterization. Anticancer Drugs 2014, 25, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, V.; Anuradha, V. Microencapsulation and Nanoencapsulation: A Review. Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H. New era of drug innovation in China. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica. B 2019, 9, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizeq, B.R.; Younes, N.N.; Rasool, K.; Nasrallah, G.K. Synthesis, Bioapplications, and Toxicity Evaluation of Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles. Int J Mol Sci 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monfared, M.; Taghizadeh, S.; Zare-Hoseinabadi, A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Ranjbar, S.; Amani, A.M. Emerging frontiers in drug release control by core-shell nanofibers: a review. Drug Metab Rev 2019, 51, 589–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
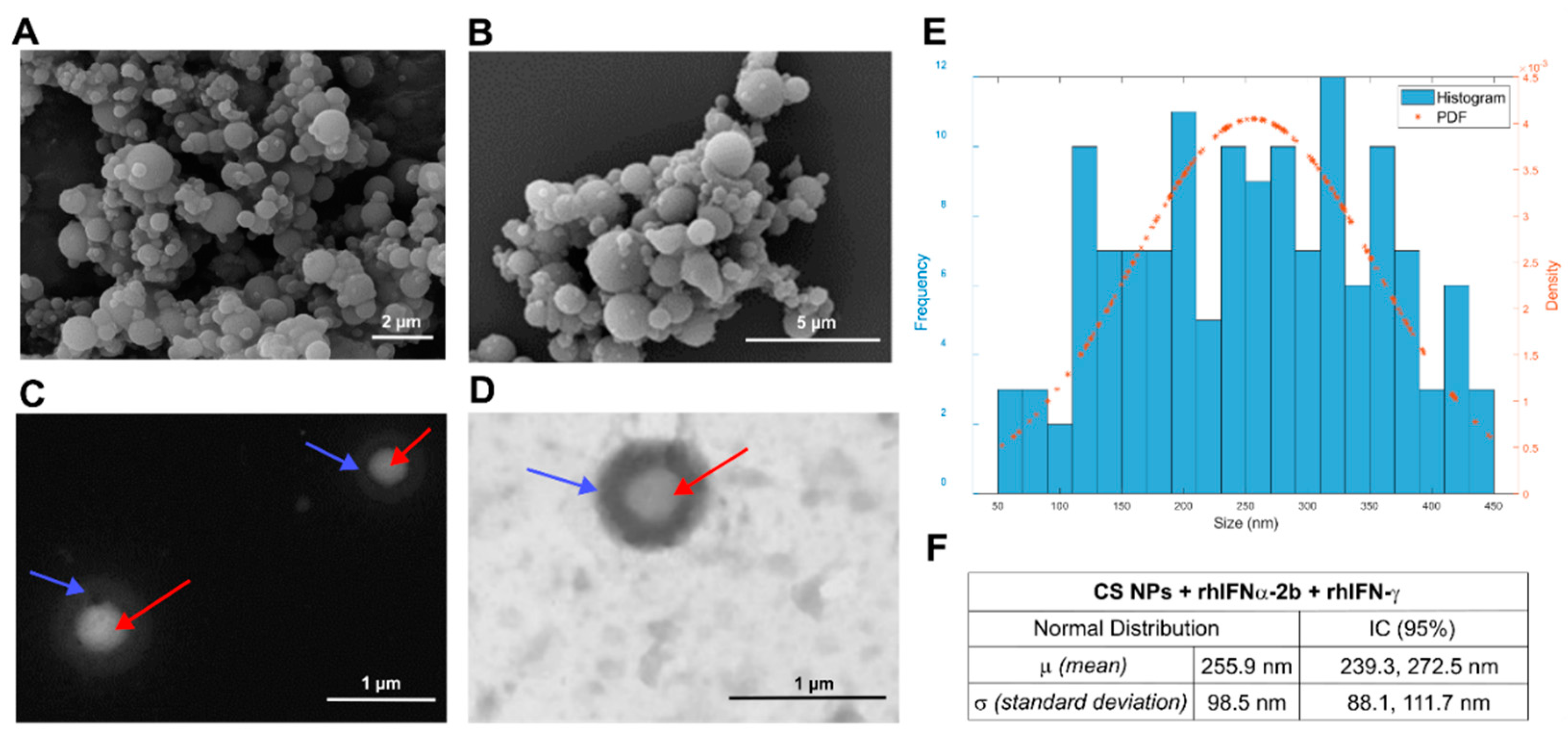
| Nanoformulations | No. of measured parts | Average particle size | Histogram filter 450 nm Fiji© Software | Shapiro Wilk statistical test | DLS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zeta potential |
Average diameter |
||||||
| Empty CS NPs | 298 | 345.4 ± 352.2 nm | 209.3 ± 84.6 nm | W=0.953 p=0.000 | + 25.9 ± 4.89 mV | 205.7 nm 12.36 nm |
92% (peak 1) 8% (peak 2) |
| CS NPs + rhIFNα-2b & rhIFN-γ | 223 | 472.4 ± 337.6 nm | 255.9 ± 98.5 nm | W=0.977 p=0.021 | + 24.5 ± 3.15 mV | 174.5 nm 12.72 nm |
75.4% (peak 1) 24.6% (peak 2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





