Submitted:
26 September 2024
Posted:
30 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
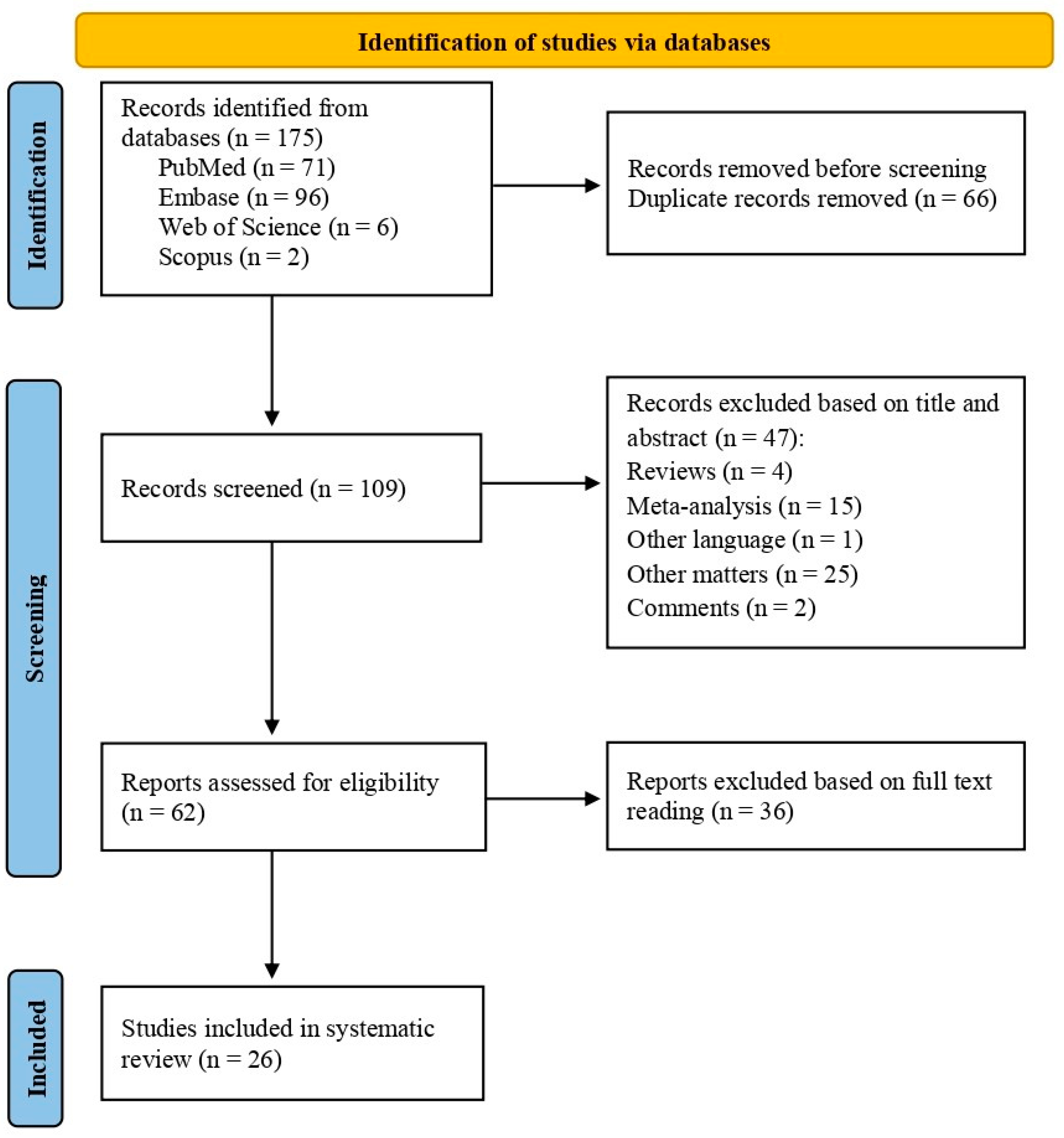
Methods
- Protocol and registration
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Literature search strategy
- Data
- collection
- Quality assessment and risk of bias
Results
- mirSNPs associated with the risk and prognosis of CRC
- mirSNPs associated with reduced risk and protection of CRC
- mirSNPs associated with CRC treatment
- mirSNPs not associated with CRC
- Quality assessment and risk of bias
Discussion
- rs4919510
- in miR-608
- rs2682818
- and rs1051690 in miR-618
- rs11614913
- in miR-196a2
- rs2292832
- in miR-149
- rs2910164
- in miR-146a
- rs895819
- in miR-27a
- rs187960998
- in miR-211
- rs2273626
- in miR-4707 and rs202195689 in miR-4274
- rs8176318
- in miR-525-5p
- rs12904
- in miR-200c
- KRAS-LCS6
- and rs868 in let-7
Conclusion
Declarations
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Authors’ contributions
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Availability of data and materials
Acknowledgements
Competing interests
Consent for publication
References
- Age standardized (World) incidence rates, colorectal cancer, males, all ages. Available from: https://gco.iarc.
- Simon, K. Clinical Interventions in Aging Dovepress Colorectal cancer development and advances in screening. Clin Interv Aging [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2024 Feb 6];11–967. [CrossRef]
- Rapado-González Ó, Álvarez-Castro A, López-López R, Iglesias-Canle J, Suárez-Cunqueiro MM, Muinelo-Romay L. Circulating microRNAs as Promising Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers (Basel) [Internet]. 2019 Jul 1 [cited 2024 Sep 16];11(7). [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee N, Shi J, García-Closas M. Developing and evaluating polygenic risk prediction models for stratified disease prevention. Nat Rev Genet [Internet]. 2016 Jul 1 [cited 2024 Feb 6];17(7):392. [CrossRef]
- Dunlop MG, Tenesa A, Farrington SM, Ballereau S, Brewster DH, Koessler T, et al. Cumulative impact of common genetic variants and other risk factors on colorectal cancer risk in 42,103 individuals. Gut [Internet]. 2013 Jun [cited 2024 Feb 6];62(6):871. [CrossRef]
- Zygulska AL, Pierzchalski P. Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer. Int J Mol Sci [Internet]. 2022 Jan 1 [cited 2024 Feb 6];23(2). [CrossRef]
- Andrei P, Battuello P, Grasso G, Rovera E, Tesio N, Bardelli A. Integrated approaches for precision oncology in colorectal cancer: The more you know, the better. Semin Cancer Biol [Internet]. 2022 Sep 1 [cited 2024 Feb 6];84:199–213. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33848627/.
- Gallo A, Tandon M, Alevizos I, Illei GG. The Majority of MicroRNAs Detectable in Serum and Saliva Is Concentrated in Exosomes. PLoS One [Internet]. 2012 Mar 9 [cited 2024 Feb 6];7(3):e30679. Available from: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0030679.
- Ortiz-Quintero, B. Cell-free microRNAs in blood and other body fluids, as cancer biomarkers. Cell Prolif [Internet]. 2016 Jun 1 [cited 2024 Feb 6];49(3):281. P: PMCID, 6496. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A [Internet]. 2008 Jul 7 [cited 2024 Feb 6];105(30):10513. [CrossRef]
- Shi Y, Liu Z, Lin Q, Luo Q, Cen Y, Li J, et al. MiRNAs and Cancer: Key Link in Diagnosis and Therapy. Genes (Basel) [Internet]. 2021 Aug 1 [cited 2024 Feb 6];12(8). [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam S, Jeet V, Gunter JH, Clements JA, Batra J. Allele-Specific MicroRNA-Mediated Regulation of a Glycolysis Gatekeeper PDK1 in Cancer Metabolism. Cancers (Basel) [Internet]. 2021 Jul 2 [cited 2024 Sep 16];13(14). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34298795/.
- Balacescu O, Sur D, Cainap C, Visan S, Cruceriu D, Manzat-Saplacan R, et al. The Impact of miRNA in Colorectal Cancer Progression and Its Liver Metastases. Int J Mol Sci [Internet]. 2018 Dec 1 [cited 2024 Sep 16];19(12). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30469518/.
- Radanova M, Levkova M, Mihaylova G, Manev R, Maneva M, Hadgiev R, et al. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in microRNA Genes and Colorectal Cancer Risk and Prognosis. Biomedicines [Internet]. 2022 Jan 1 [cited 2024 Sep 16];10(1). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35052835/.
- Wang Z, Sun X, Wang Y, Liu X, Xuan Y, Hu S. Association between miR-27a genetic variants and susceptibility to colorectal cancer. Diagn Pathol [Internet]. 2014 Jun 30 [cited 2024 Feb 7];9(1). [CrossRef]
- Kohler AF 1993-. The functional impact of a genetic variant in a microRNA binding site in MDM4, a breast cancer-associated gene. 2020 [cited 2024 Aug 11]; Available from: https://acervodigital.ufpr.br/handle/1884/76039.
- Dias F, Morais M, Teixeira AL, Medeiros R. Involving the microRNA Targetome in Esophageal-Cancer Development and Behavior. Cancers (Basel) [Internet]. 2018 Oct 12 [cited 2024 Feb 7];10(10). [CrossRef]
- Li YJ, Zhang ZY, Mao YY, Jin MJ, Jing FY, Ye ZH, et al. A genetic variant in MIR-146a modifies digestive system cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention. 2014;15(1):145–50. [CrossRef]
- Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ [Internet]. 2021 Mar 29 [cited 2024 Sep 12];372.
- Pace R, Pluye P, Bartlett G, Macaulay AC, Salsberg J, Jagosh J, et al. Testing the reliability and efficiency of the pilot Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) for systematic mixed studies review. Int J Nurs Stud [Internet]. 2012 Jan [cited 2024 Sep 12];49(1):47–53. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21835406/.
- Stang, A. Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol [Internet]. 2010 Sep [cited 2024 Sep 12];25(9):603–5. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20652370/.
- Landi D, Gemignani F, Naccarati A, Pardini B, Vodicka P, Vodickova L, et al. Polymorphisms within micro-RNA-binding sites and risk of sporadic colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis [Internet]. 2008 Mar [cited 2024 Sep 12];29(3):579–84. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18192692/.
- Ding L, Jiang Z, Chen Q, Qin R, Fang Y, Li H. A functional variant at miR-520a binding site in PIK3CA alters susceptibility to colorectal cancer in a Chinese Han population. Biomed Res Int [Internet]. 2015 [cited 2024 Sep 12];2015. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25834816/.
- Ni H, Su B, Pan L, Li X, Zhu X, Chen X. Functional variants inPXRare associated with colorectal cancer susceptibility in Chinese populations. Cancer Epidemiol [Internet]. 2015 Dec 1 [cited 2024 Sep 12];39(6):972–7. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26547791/.
- Xie L, Li S, Jin J, He L, Xu K, Zhu L, et al. Genetic variant in miR-21 binding sites is associated with colorectal cancer risk. J Cell Mol Med [Internet]. 2019 Mar 1 [cited 2024 Sep 12];23(3):2012–9. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30569605/.
- Ke J, Tian J, Li J, Gong Y, Yang Y, Zhu Y, et al. Identification of a functional polymorphism affecting microRNA binding in the susceptibility locus 1q25.3 for colorectal cancer. Mol Carcinog [Internet]. 2017 Sep 1 [cited 2024 Sep 12];56(9):2014–21. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28277607/.
- KANG BW, JEON H-S, CHAE YS, LEE SJ, PARK JS, CHOI GS, et al. Impact of Genetic Variation in MicroRNA-binding Site on Susceptibility to Colorectal Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2016;36(7). [CrossRef]
- Lee AR, Park J, Jung KJ, Jee SH, Kim-Yoon S. Genetic variation rs7930 in the miR-4273-5p target site is associated with a risk of colorectal cancer. Onco Targets Ther [Internet]. 2016 Nov 7 [cited 2024 Sep 14];9:6885. [CrossRef]
- Xicola RM, Bontu S, Doyle BJ, Rawson J, Garre P, Lee E, et al. Association of a let-7 miRNA binding region of TGFBR1 with hereditary mismatch repair proficient colorectal cancer (MSS HNPCC). Carcinogenesis [Internet]. 2016 Aug 1 [cited 2024 Aug 9];37(8):751. [CrossRef]
- Mullany LE, Wolff RK, Herrick JS, Buas MF, Slattery ML. SNP Regulation of microRNA Expression and Subsequent Colon Cancer Risk. PLoS One [Internet]. 2015 Dec 1 [cited 2024 Aug 9];10(12). [CrossRef]
- Chayeb V, Mahjoub S, Zitouni H, Jrah-Harzallah H, Zouari K, Letaief R, et al. Contribution of microRNA-149, microRNA-146a, and microRNA-196a2 SNPs in colorectal cancer risk and clinicopathological features in Tunisia. Gene [Internet]. 2018 Aug 5 [cited 2024 Sep 14];666:100–7. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29715515/.
- Cao Y, Hu J, Fang Y, Chen Q, Li H. Association between a functional variant in microRNA-27a and susceptibility to colorectal cancer in a Chinese Han population. Genet Mol Res [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2024 Sep 14];13(3):7420–7. [CrossRef]
- Hu X, Li L, Shang M, Zhou J, Song X, Lu X, et al. Association between microRNA genetic variants and susceptibility to colorectal cancer in Chinese population. Tumour Biol [Internet]. 2014 Mar 1 [cited 2024 Sep 14];35(3):2151–6. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24136745/.
- Kim JG, Chae YS, Lee SJ, Kang BW, Park JY, Lee EJ, et al. Genetic variation in microRNA-binding site and prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol [Internet]. 2015 Jan 1 [cited 2024 Aug 9];141(1):35–41. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25079514/.
- Salem E, Keshvari A, Mahdavinezhad A, Soltanian AR, Saidijam M, Afshar S. Role of EFNA1 SNP (rs12904) in Tumorigenesis and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer: A Bioinformatic Analysis and HRM SNP Genotyping Verification. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev [Internet]. 2022 [cited 2024 Aug 9];23(10):3523. [CrossRef]
- Smits KM, Paranjape T, Nallur S, Wouters KAD, Weijenberg MP, Schouten LJ, et al. A Let-7 MicroRNA SNP in the KRAS 3′UTR Is Prognostic in Early-Stage Colorectal Cancer. Clin Cancer Res [Internet]. 2011 Dec 12 [cited 2024 Aug 9];17(24):7723.
- Ryan BM, McClary AC, Valeri N, Robinson D, Paone A, Bowman ED, et al. rs4919510 in hsa-mir-608 Is Associated with Outcome but Not Risk of Colorectal Cancer. PLoS One [Internet]. 2012 May 11 [cited 2024 Sep 14];7(5). [CrossRef]
- Zhan J fang, Chen L hua, Chen Z xian, Yuan Y wei, Xie G zhu, Sun A min, et al. A functional variant in microRNA-196a2 is associated with susceptibility of colorectal cancer in a Chinese population. Arch Med Res [Internet]. 2011 Feb [cited 2024 Sep 14];42(2):144–8. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21565628/.
- Huang Y, Feng Y, Ren H, Zhang M, Li H, Qiao Y, et al. Associations of Genetic Variations in MicroRNA Seed Regions With Acute Adverse Events and Survival in Patients With Rectal Cancer Receiving Postoperative Chemoradiation Therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys [Internet]. 2018 Mar 15 [cited 2024 Sep 14];100(4):1026–33. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29485044/.
- Chen Y, Du M, Chen W, Zhu L, Wu C, Zhang Z, et al. Polymorphism rs2682818 in miR-618 is associated with colorectal cancer susceptibility in a Han Chinese population. Cancer Med [Internet]. 2018 Apr 1 [cited 2024 Sep 14];7(4):1194–200. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29533012/.
- Zhu L, Wang R, Zhang L, Zuo C, Zhang R, Zhao S. rs187960998 polymorphism in miR-211 prevents development of human colon cancer by deregulation of 3′UTR in CHD5. Onco Targets Ther [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2024 Sep 14];12:405–12. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30655677/.
- Radanova M, Mihaylova G, Mihaylova Z, Ivanova D, Tasinov O, Nazifova-Tasinova N, et al. Circulating miR-618 Has Prognostic Significance in Patients with Metastatic Colon Cancer. Curr Oncol [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2024 Sep 14];28(2):1204–15. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33804070/.
- Jiang H, Ge F, Hu B, Wu L, Yang H, Wang H. rs35301225 polymorphism in miR-34a promotes development of human colon cancer by deregulation of 3′UTR in E2F1 in Chinese population. Cancer Cell Int [Internet]. 2017 Mar 9 [cited 2024 Sep 14];17(1). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28293146/.
- Sclafani F, Chau I, Cunningham D, Lampis A, Hahne JC, Ghidini M, et al. Sequence variation in mature microRNA-608 and benefit from neo-adjuvant treatment in locally advanced rectal cancer patients. Carcinogenesis [Internet]. 2016 Sep 1 [cited 2024 Sep 14];37(9):852–7. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27381831/.
- Chen H, Sun LY, Chen LL, Zheng HQ, Zhang QF. A variant in microRNA-196a2 is not associated with susceptibility to and progression of colorectal cancer in Chinese. Intern Med J [Internet]. 2012 Jun [cited 2024 Sep 14];42(6). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21241442/.
- Ayadilord M, Tavakoli T, Fakharian T, Soltaninejad E, Naseri M. Relationship analysis of the miR-196a2 polymorphism (rs11614913) with colorectal cancer risk in southern Khorasan, eastern Iran. Meta Gene. 2020 Dec 1;26:100813. [CrossRef]
- Simonian M, Mosallaei M, Khosravi S, Salehi R. rs12904 polymorphism in the 3′-untranslated region of ephrin A1 ligand and the risk of sporadic colorectal cancer in the Iranian population. J Cancer Res Ther [Internet]. 2019 Jan 1 [cited 2024 Sep 14];15(1):15–9. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30880748/.
- Zhao Y, Du Y, Zhao S, Guo Z. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms of microRNA processing machinery genes and risk of colorectal cancer. Onco Targets Ther [Internet]. 2015 Feb 12 [cited 2024 Sep 16];8:421–5. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25709475/.
- Cipollini M, Landi S, Gemignani F. MicroRNA binding site polymorphisms as biomarkers in cancer management and research. Pharmgenomics Pers Med [Internet]. 2014 Jul 23 [cited 2024 Sep 16];7(1):173–91. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25114582/.
- Jiang Y, Cao Y, Wang Y, Li W, Liu X, Lv Y, et al. Cysteine transporter SLC3A1 promotes breast cancer tumorigenesis. Theranostics [Internet]. 2017 [cited 2024 Sep 16];7(4):1036–46. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28382174/.
- Shen MH, Huang CJ, Ho TF, Liu CY, Shih YY, Huang CS, et al. Colorectal cancer concurrent gene signature based on coherent patterns between genomic and transcriptional alterations. BMC Cancer [Internet]. 2022 Dec 1 [cited 2024 Sep 16];22(1). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35637462/.
- Schneiderova M, Naccarati A, Pardini B, Rosa F, Gaetano C Di, Jiraskova K, et al. MicroRNA-binding site polymorphisms in genes involved in colorectal cancer etiopathogenesis and their impact on disease prognosis. Mutagenesis [Internet]. 2017 Oct 17 [cited 2024 Mar 7];32(5):533–42. [CrossRef]
- Xing J, Wan S, Zhou F, Qu F, Li B, Myers RE, et al. Genetic polymorphisms in pre-microRNA genes as prognostic markers of colorectal cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev [Internet]. 2012 Jan [cited 2024 Sep 16];21(1):217–27. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22028396/.
- Ying HQ, Peng HX, He BS, Pan YQ, Wang F, Sun HL, et al. MiR-608, pre-miR-124-1 and pre-miR26a-1 polymorphisms modify susceptibility and recurrence-free survival in surgically resected CRC individuals. Oncotarget [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2024 Sep 16];7(46):75865–73. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27713147/.
- Pardini B, Rosa F, Naccarati A, Vymetalkova V, Ye Y, Wu X, et al. Polymorphisms in microRNA genes as predictors of clinical outcomes in colorectal cancer patients. Carcinogenesis [Internet]. 2015 Jan 1 [cited 2024 Feb 29];36(1):82–6. [CrossRef]
- Lv M, Dong W, Li L, Zhang L, Su X, Wang L, et al. Association between genetic variants in pre-miRNA and colorectal cancer risk in a Chinese population. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol [Internet]. 2013 Aug [cited 2024 Sep 16];139(8):1405–10. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23728616/.
- Xu Y, Gu L, Pan Y, Li R, Gao T, Song G, et al. Different effects of three polymorphisms in MicroRNAs on cancer risk in Asian population: evidence from published literatures. PLoS One [Internet]. 2013 Jun 4 [cited 2024 Sep 16];8(6). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23750236/.
- Choupani J, Nariman-Saleh-Fam Z, Saadatian Z, Ouladsahebmadarek E, Masotti A, Bastami M. Association of mir-196a-2 rs11614913 and mir-149 rs2292832 Polymorphisms With Risk of Cancer: An Updated Meta-Analysis. Front Genet [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2024 Sep 15];10(MAR). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30930933/.
- Fakhrezare F, Ebrahimi SO, Reiisi S. The association between genetic variation rs2292832 and the processing efficiency of pre-mir-149 affects the risk of breast cancer. Mol Biol Rep [Internet]. 2023 Jan 1 [cited 2024 Feb 29];50(1):679–85. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11033-022-08027-3.
- Iguchi T, Nambara S, Masuda T, Komatsu H, Ueda M, Kidogami S, et al. miR-146a Polymorphism (rs2910164) Predicts Colorectal Cancer Patients’ Susceptibility to Liver Metastasis. PLoS One [Internet]. 2016 Nov 1 [cited 2024 Sep 16];11(11):e0165912. Available from: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0165912.
- Nguyen TTN, Tran MTH, Nguyen VTL, Nguyen UDP, Nguyen GDT, Huynh LH, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in microRNAs action as biomarkers for breast cancer. Turkish J Biol [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2024 Sep 16];44(5):284. [CrossRef]
- Jiang Y, Lin DH, Xu JP, Chen WX, Zheng SJ, Song L. Genotype GG of rs895819 Functional Polymorphism Within miR-27a Might Increase Genetic Susceptibility to Colorectal Cancer in Han Chinese Population. J Clin Lab Anal [Internet]. 2016 Jul 1 [cited 2024 Sep 16];30(4):351–5. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26302683/.
- Wang Z, Sun X, Wang Y, Liu X, Xuan Y, Hu S. Association between miR-27a genetic variants and susceptibility to colorectal cancer. Diagn Pathol [Internet]. 2014 Jun 30 [cited 2024 Sep 16];9(1).
- Kupcinskas J, Bruzaite I, Juzenas S, Gyvyte U, Jonaitis L, Kiudelis G, et al. Lack of association between miR-27a, miR-146a, miR-196a-2, miR-492 and miR-608 gene polymorphisms and colorectal cancer. Sci Reports 2014 41 [Internet]. 2014 Aug 8 [cited 2024 Sep 16];4(1):1–6. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/srep05993.
- Sümbül AT, Göğebakan B, Bayram S, Batmacı CY, Öztuzcu S. MicroRNA 211 expression is upregulated and associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer: a case–control study. Tumor Biol [Internet]. 2015 Dec 1 [cited 2024 Mar 21];36(12):9703–9. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13277-015-3708-4.
- Lotfi E, Kholghi A, Golab F, Mohammadi A, Barati M. Circulating miRNAs and lncRNAs serve as biomarkers for early colorectal cancer diagnosis. Pathol Res Pract [Internet]. 2024 Mar 1 [cited 2024 Sep 17];255. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38377721/.
- Ghanbari M, Iglesias AI, Springelkamp H, van Duijn CM, Ikram MA, Dehghan A, et al. A Genome-Wide Scan for MicroRNA-Related Genetic Variants Associated With Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci [Internet]. 2017 Oct 1 [cited 2024 Mar 5];58(12):5368.
- Landeros N, Corvalan AH, Musleh M, Quiñones LA, Varela NM, Gonzalez-Hormazabal P. Novel Risk Associations between microRNA Polymorphisms and Gastric Cancer in a Chilean Population. Int J Mol Sci [Internet]. 2021 Jan 1 [cited 2024 Mar 5];23(1). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35008894/.
- Nguyen TTN, Tran MTH, Nguyen VTL, Nguyen UDP, Nguyen GDT, Huynh LH, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in microRNAs action as biomarkers for breast cancer. Turkish J Biol [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2024 Sep 16];44(5):284.
- Cao J, Luo C, Yan R, Peng R, Wang K, Wang P, et al. rs15869 at miRNA binding site in BRCA2 is associated with breast cancer susceptibility. Med Oncol [Internet]. 2016 Dec 1 [cited 2024 Sep 16];33(12). Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27807724/.
- Li Y, Nie Y, Cao J, Tu S, Lin Y, Du Y, et al. G-A variant in miR-200c binding site of EFNA1 alters susceptibility to gastric cancer. Mol Carcinog [Internet]. 2014 Mar 1 [cited 2024 Sep 16];53(3):219–29. Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/mc.21966.
- Saridaki Z, Weidhaas JB, Lenz HJ, Laurent-Puig P, Jacobs B, De Schutter J, et al. A let-7 microRNA-binding site polymorphism in KRAS predicts improved outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) patients treated with salvage cetuximab/panitumumab monotherapy. Clin Cancer Res [Internet]. 2014 Sep 9 [cited 2024 Sep 16];20(17):4499.
- Christensen BC, Moyer BJ, Avissar M, Ouellet LG, Plaza SL, Mcclean MD, et al. A let-7 microRNA-binding site polymorphism in the KRAS 3′ UTR is associated with reduced survival in oral cancers. Carcinogenesis [Internet]. 2009 [cited 2024 Sep 16];30(6):1003.
- Sajjad EA, Radkowski M, Perkowska-Ptasińska A, Pacholczyk M, Durlik M, Fedorowicz M, et al. Negative Correlation Between Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) and Let-7 MicroRNA Family in Transplanted Livers: The Role of rs868 Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism. Ann Transplant [Internet]. 2017 Oct 24 [cited 2024 Sep 16];22:638. [CrossRef]
| STUDY DESIGN | AUTHOR | POPULATION | SNP ID | ALLELE/ GENOTYPE |
GENE ID | miR ID | ASSOCIATION OF mirSNPS WITH CRC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case-control study | Landi et al. | Czech Republic | rs17281995 rs1051690 | G/A | CD86 INSR |
miR-337, miR-582, miR-200a, miR-184, and miR-212 miR-618 and miR-612 |
Increased risk |
| Case-control study | Ding et al. | Chinese | rs141178472 | CC | PIK3CA | miR-520a | Increased risk |
| Case-control study | Ni et al. | Chinese | rs3814058 | C>T | PXR | hsa-miR-129-5p | Increased risk |
| Case-control study | Xie et al. | Chinese | rs6504593 | T | IGF2BP1 | miR-21 | Increased risk; cell proliferation and apoptosis |
| Case-control study | Ke et al. | Chinese | rs1062044 | A | LAMC1 | miR-423-5p | Increased risk; colon adenocarcinomas |
| Case-control study | Kang et al. | Korea | rs2279398 | G>A | DOK3 | miR-370 | Increased risk |
| Case-control study | Lee et al. | Korea | rs7930 | AG | TOMM20 | miR-4273-5p | rs7930 AG: Increased risk; Suppression of TOMM20 gene expression |
| Case-control study | Xicola et al. | Spain | rs868 | TGFBR1 | let-7 | Increased risk | |
| Case-control study | Mullany et al. | United States | rs8176318 rs8905 | AA GG |
BRCA1 PRKAR1A | miR-525-5p miR-miR-214-3p | Increased risk |
| Case-control study | Chayeb et al. | Tunisian | rs2292832 rs2910164 | C/T G/C |
hsa-mir-149 hsa-mir-146a |
Increased risk | |
| Case-control study | Cao et al. | Chinese | rs895819 | GG | miR-27a | Increased risk | |
| STUDY DESIGN | AUTHOR | POPULATION | SNP ID |
ALLELE/ GENOTYPE |
GENE ID | miR ID | ASSOCIATION OF mirSNPS WITH CRC |
| Case-control study | Hu et al. | Chinese | rs2910164 | G>C | miR-146a | Susceptibility and differentiation | |
| Cohort Studies | Kim et al. | Korea | rs3757417 rs12373 | T>G A>C |
TPST1 PAUF | miR-571 | Prognostic markers |
| Case-control study | Salem et al. | Iran | rs12904 | AA/ A>G | EFNA1 | miR-200C and miR-429 | rs12904 AA: Pathogenesis and metástasis; rs12904 A>G: reduced disease progression; regulation of EFNA1 gene expression. |
| Cohort Studies | Smits et al. | Dutch | KRAS-LCS6 | T>G | KRAS | let-7 | Prognostic biomarker |
| Case-control study | Ryan et al. | Caucasian and African-American | rs4919510 | GG | hsa-miR-608 | Increased risk of death in Caucasians and a reduced risk in African Americans | |
| Case-control study | Zhan et al. | Chinese | rs11614913 | CC | miR-196a2 | Increased susceptibility in patients who have undergone chemotherapy treatment | |
| Cohort Studies | Huang et al. | Chinese | rs2273626 rs202195689 | A>C CCCCA>del |
hsa-miR-4707-3p hsa-miR-4274 | Predictive and prognostic biomarkers after chemoradiotherapy | |
| Case-control study | Chen et al. | Chinese | rs2682818 | AA and AC/AA | miR-618 | Reduction of risk | |
| Case-control study | Zhu et al. | Chinese | rs187960998 | C>T | CHD5 | miR-211 | Decreased risk and protective factor for CC by preventing binding of the tumor suppressor gene CHD5 |
| Case-control study | Radanova et al. | Bulgaria | rs2682818 | AC | miR-618 | Decreased risk of susceptibility to mCC | |
| Case-control study | Jiang eta al. | Chinese | rs35301225 | C/A | E2F1 | miR-34a | Tumor suppression and protection by downregulating the E2F1 gene; rs35301225 C/A: upregulation of E2F1 expression, resulting in worse survival. |
| STUDY DESIGN | AUTHOR | POPULATION | SNP ID |
ALLELE/ GENOTYPE |
GENE ID | miR ID | ASSOCIATION OF mirSNPS WITH CRC |
| Randomized study | Sclafani et al. | Multicenter study | rs4919510 | CC | miR-608 | Prognostic biomarker | |
| Case-control study | Chen et al. | Chinese | rs11614913 | T>C | miR-196a2 | No significant association with increased risk or disease progression was identified | |
| Case-control study | Ayadilord et al. | Iran | rs11614913 | C/T | miR-196a2 | No significant association was identified between the SNP rs11614913 in miR-196a2 and CRC | |
| Case-control study | Simonian et al. | Iran | rs12904 | EFNA1 | miR-200c | No significant association was demonstrated between rs12904 and CRC risk |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





