Submitted:
22 September 2024
Posted:
23 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Birds
2.2. Necropsy and Histological Evaluation
2.3. Microbiology
2.3.1. Bird Samples
2.3.2. Microbiological Environmental Samples
2.4. MALDI-TOF
2.5. Serotyping
3. Results
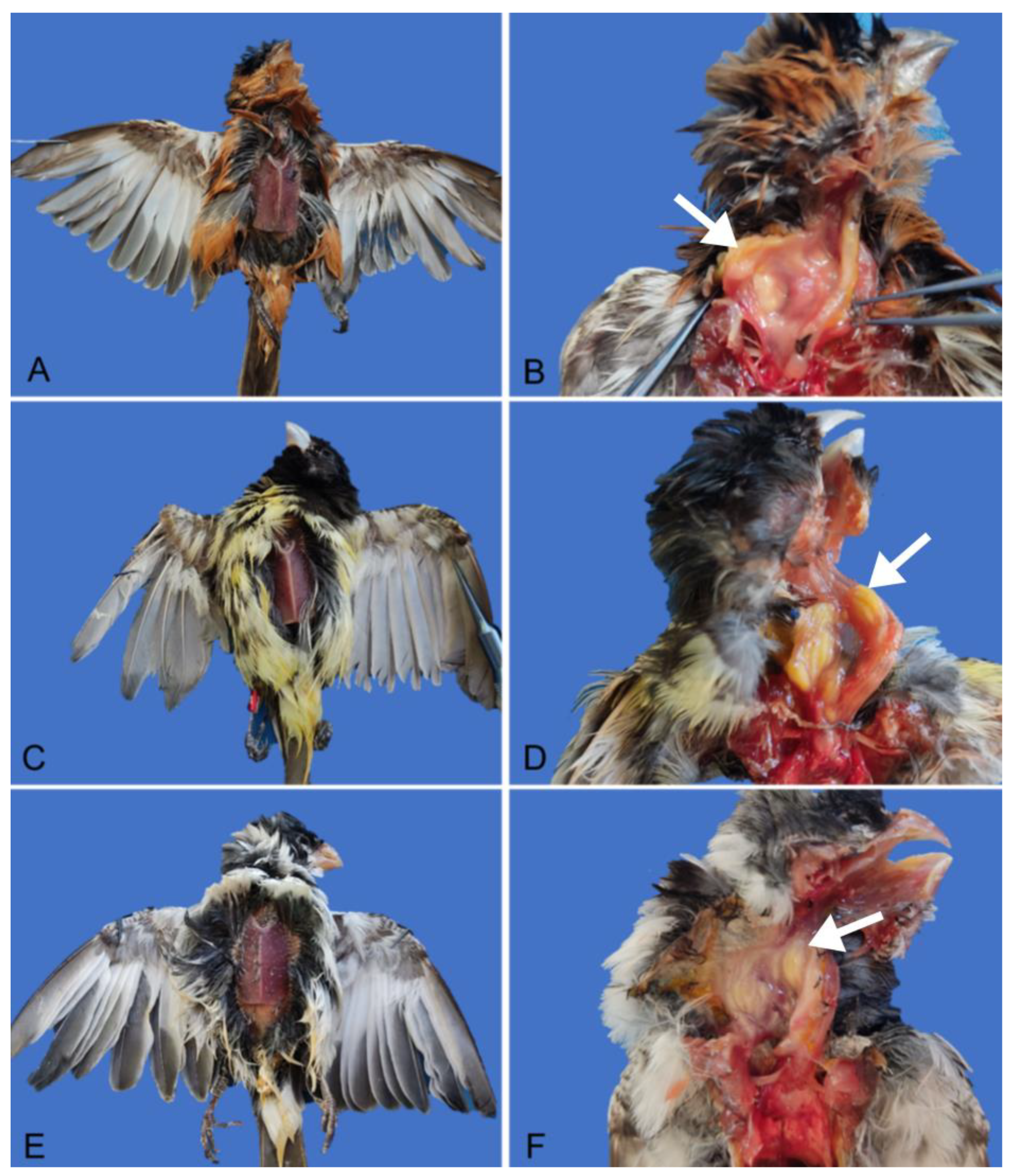
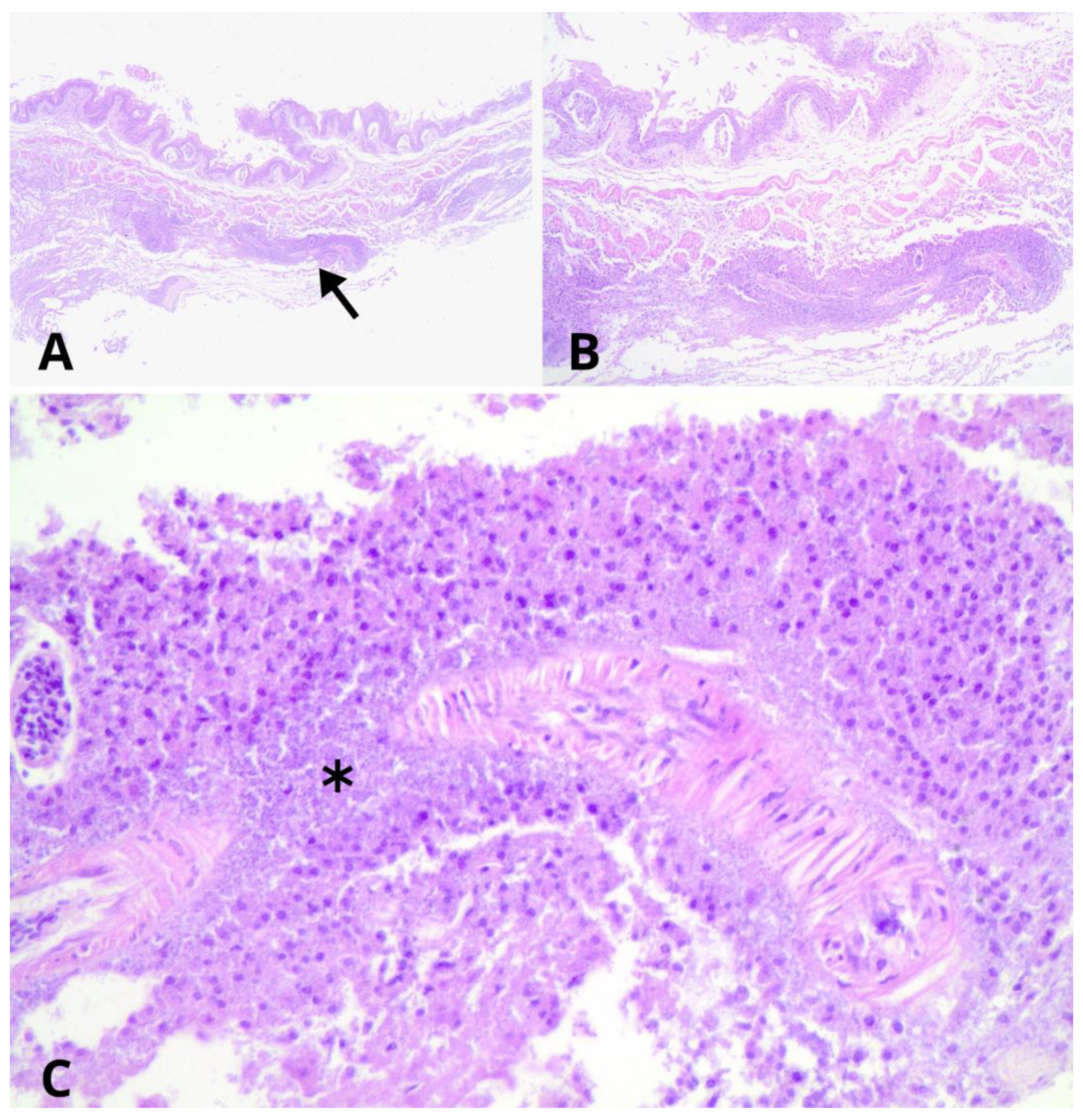
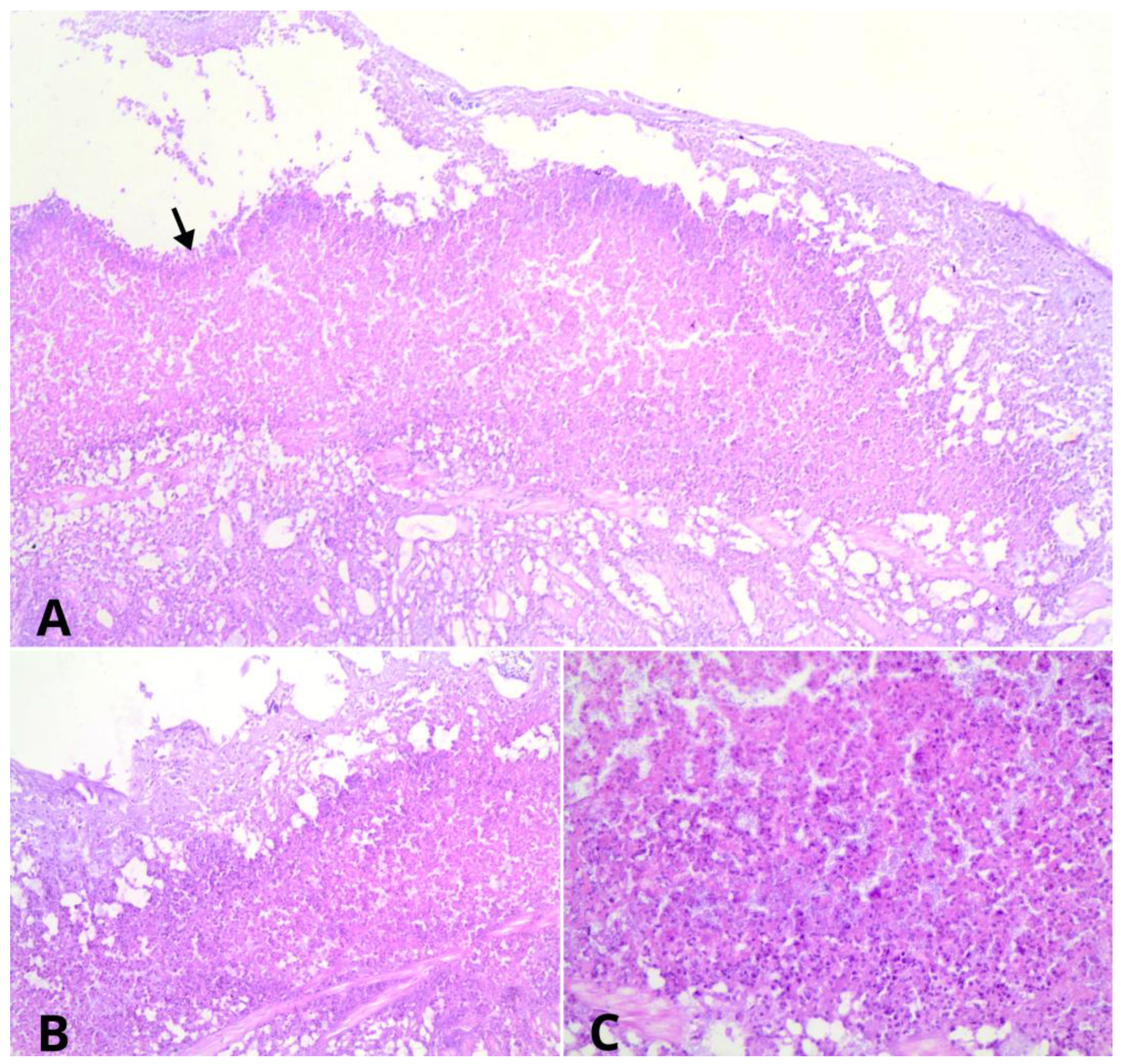
3.1. Necropsy and Histological Evaluation
3.2. Microbiology
3.3. MALDI-TOF
3.4. Serotyping
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Regueira, R.F.S.; Bernard, E. Wildlife sinks: Quantifying the impact of illegal bird trade in street markets in Brazil. Biological Conservation. 2012, 149, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, C.J.; Oliveira, A.M.; Santos, W.M.; Araújo, J.L.; Rola, L.D.; Guerra, R.R. Body condition, external morphology, parasitology, and histological and biometrical study of the gastro-intestinal tract of Sporophila nigricollis and Sporophila caerulescens seized from trafficking in Northeastern Brazil. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2024, 44, e07358–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, R.A.S.; de Lucena, R.B.; Cavalcanti, T.A.; de Lima Luna, A.C.; de Oliveira Firmino, M.; Guerra, R.R. Aspectos clínico-patológicos em papagaios-verdadeiros (Amazona aestiva, L. 1758) oriundos de apreensões do tráfico no estado da Paraíba, Brasil. Brazil. J. Vet. Med. 2016, 38, 439–444.
- Campos, J.A.; Guizelini, C.C.; Pavarini, S.P.; Azuaga, L.; Souza, M.L.; Leal, C.R.B.; Ramos, C.A.N.; Gomes, D.C. Pathological Aspects of a Septicemic Salmonellosis Outbreak Caused by Salmonella Serotype Typhimurium in Captive Blue-Fronted Amazon Parrots (Amazona aestiva). Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2024, 44, e07428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindall, B.J.; Grimont, P.A.D.; Garrity, G.M.; Euzeby, J.P. Nomenclature and Taxonomy of the Genus Salmonella. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trabulsi, L.R.; Alterthum, F. Microbiologia, 6ª ed.; Editora Atheneu: São Paulo, Brazil, 2015; Salmonella, pp. 351-360. [Google Scholar]
- Issenhuth-Jeanjean, S.; Roggentin, P. , Mikoleit, M.; Guibourdenche, M.; De Pinna, E.; Nair, S; Fields, P. I.; Weill, F. Supplement 2008–2010 (no. 48) to the White-Kauffmann-Le Minor Scheme. Res. Microbiol. 2014, 165, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibourdenche, M.; Roggentin, P. , Mikoleit, M.; Fields, P.I.; Bockemuhl, J.; Grimont, P.A.D.; Weill, F.X. Issenhuth-Jeanjean, S. Supplement 2003–2007 (No. 47) to the White-Kauffmann-Le Minor Scheme. Res. Microbiol. 2010, 161, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.H.A.; Salam, H.S.H.; Abdel-Latef, G.K. Serological Identification and Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella Isolates from Broiler Carcasses and Human Stools in Beni-Suef, Egypt. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 202–207. [CrossRef]
- Braga, P.R.C.; Basso, R.M.; Martins, L.S.A. Occurrence of Salmonella spp. in Fecal Samples from Foals with and without Diarrhea in the State of São Paulo: Microbiological Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile, and Molecular Detection. Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2023, 43, e07194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, P.N.; Torres, A.C.D.; Rodrigues, M.P.; Oliveira, L.B.; Costa, C.S.; Ecco, R.; Freitas Neto, O.C.; Martins, N.R.S. An Outbreak of Fatal Pullorum Disease (Salmonella Pullorum) in Guinea Fowl Keets (Numida meleagris). Pesq. Vet. Bras. 2023, 43, e07088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsythe, S.J. Microbiologia Segurança Alimentos, 2nd ed.; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, N.J.; Hunter, D.B.; Atkinson, C.T. Infectious Diseases of Wild Birds; Blackwell Publishing: Iowa, USA, 2007; Salmonellosis pp. 270–288. [Google Scholar]
- Giovannini, S.; Pewsner, M.; Hüssy, D.; Hächler, H.; Degiorgis, M-P. R.; Hirschheydt, J.; Origgi, F.C. Epidemic of Salmonellosis in Passerine Birds in Switzerland with Spillover to Domestic Cats. Vet. Pathol. 2013, 50, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.; Calva, E.; Maloy, S. One Health and Food-Borne Disease: Salmonella Transmission between Humans, Animals, and Plants. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söderlund, R.; Jernberg, C. ; Trönnberg, L; Pääjärvi, A; Agren, E.; Lahti, E.. Linked Seasonal Outbreaks of Salmonella Typhimurium among Passerine Birds, Domestic Cats, and Humans, Sweden, 2009 to 2016. Eurosurveillance, 2019; 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizard, I.R. Salmonellosis in Wild Birds. Semin. Avian Exot. Pet Med. 2004, 13, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapperud, G.; Stenwig, H.; Lassen, J. Epidemiology of Salmonella Typhimurium 0:4-12 Infection in Norway. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1998, 147, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refsump, T.; Vikoren, T.; Handeland, K.; Kapperud, G.; Holstad, G. Epidemiologic and Pathologic Aspects of Salmonella Typhimurium Infection in Passerine Birds in Norway. J. Wildl. Dis. 2003, 39, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauni, M.A.; Österlund, A. Outbreak of Salmonella Typhimurium in Cats and Humans Associated with Infection in Wild Birds. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2000, 41, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, L.A.; Shopland, S.; Wigley, P.; Bradon, H.; Leatherbarrow, A.H.; Williams, N.J.; Bennett, M.; Pinna, E.; Lawson, B.; Cunningham, A.A.; Chantrey, J. Characterisation of Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhimurium Isolates from Wild Birds in Northern England from 2005–2006. BMC Vet. Res. 2008, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, B.; Howard, T.; Kirkwood, J.K.; Macgregor, S.K.; Perkins, M.; Robinson, R.A.; Ward, L.R.; Cunningham, A.A. Epidemiology of Salmonellosis in Garden Birds in England and Wales, 1993 to 2003. EcoHealth 2010, 7, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, A.E.; Lawson, B.; Pinna, E.; Wigley, P.; Parkhill, J.; Thomson, N.R.; Page, A.J.; Holmes, M.A.; Paterson, G.K. Genomic Analysis of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium from Wild Passerines in England and Wales. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 6728–6735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, L.N.; Shillinger, R.B.; Jareed, T. Salmonellosis in Passerine Birds in Maryland and West Virginia. J. Wildl. Dis. 1973, 9, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.J.; Saito, E.K. Avian Wildlife Mortality Events Due to Salmonellosis in the United States, 1985–2004. J. Wildl. Dis. 2008, 44, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, S.M.; Keel, K.; Sanchez, S.; Trees, E.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Adams, J.K.; Cheng, Y.; Ray, A.; Martin, G.; Presotto, A.; et al. Epidemiology of a Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica Serovar Typhimurium Strain Associated with a Songbird Outbreak. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 7290–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, C.A.R.; Pereira, I.A.; Araújo, M.S.; Santos, A.F.M.; Lopes, R.P.; Christakis, S.; Rodrigues, D.P.; Siciliano, S. Characteristics of Salmonella spp. Isolated from Wild Birds Confiscated in Illegal Trade Markets, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. BioMed Res. Int. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunthaler, R.; Spergser, J.; Weissenböck, H. Multiple Epidemics in Austrian Fringillidae Caused by a Single Variant of Salmonella Typhimurium. J. Wildl. Dis. 2021, 57, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoust, P.Y.; Busby, D.G.; Ferns, L.; Goltz, J.; McBurney, S.; Poppe, C.; Whitney, H. Salmonellosis in Songbirds in the Canadian Atlantic Provinces During Winter-Summer 1997–98. Can. Vet. J. 2000, 41, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alley, M.R.; Connolly, J.H.; Fenwick, S.G.; Mackereth, G.F.; Leyland, M.J.; Rogers, L.E.; Haycock, M.; Nicol, C.; Reed, C.E. M. An Epidemic of Salmonellosis Caused by Salmonella Typhimurium DT160 in Wild Birds and Humans in New Zealand. N. Z. Vet. J. 2002, 50, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Une, Y.; Sanbe, A.; Suzuki, S.; Niwa, T.; Kawakami, K.; Kurosawa, R.; Izumiya, H.; Watanabe, H.; Kato, Y. Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhimurium Infection Causing Mortality in Eurasian Tree Sparrows (Passer montanus) in Hokkaido. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 61, 166–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, D.; Takahashi, K.; Kubo, M.; Une, Y.; Kato, Y.; Izumiya, H.; Teraoka, H.; Asakawa, M.; Yanagida, K.; Bando, G. Mass Mortality of Eurasian Tree Sparrows (Passer montanus) from Salmonella typhimurium DT40 in Japan, Winter 2008–09. J. Wildl. Dis. 2014, 50, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawiec, M.; Pietkiewicz, M.; Wieliczko, A. Salmonella spp. as a Cause of Mortality and Clinical Symptoms in Free-Living Garden Bird Species in Poland. Polish J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 17, 729–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelos, M.M.; Martins, L.; Grenfell, R.C.; Juliano, L.; Anderson, K.L.; Santos, M.V.; Gonçalves, J.L. Comparison of Standard and On-Plate Extraction Protocols for Identification of Mastitis-Causing Bacteria by MALDI-TOF MS. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2019, 50, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salfinger, Y.; Tortorello, M.L. Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination of Foods, 15th ed.; APHA Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; Salmonella, pp. 445–475. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, F.J.V.; Ribeiro, R. E.; Souza, C. A.; Navarro, R. D. Birds Species Trafficked in Brazil: A Meta-Analysis with Emphasis on Threatened Species. Fronteiras. 2018, 7, 324–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Biswas, S.; Paudyal, N.; Pan, H.; Li, X.; Fang, W.; Yue, M. Antibiotic Resistance in Salmonella Typhimurium Isolates Recovered from the Food Chain through National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System Between 1996 and 2016. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seribelli, A.A.; Cruz, M.F.; Vilela, F.P.; Frazão, M.R.; Paziani, M.H.; Almeida, F.; Medeiros, M.I.C.; Rodrigues, D.P.; Kress, M.R.Z.; Allard, M.W.; Falcão, J.P. Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Salmonella Typhimurium Isolates from Humans and Foods in Brazil. PLoS ONE. 2020, 15, e0236868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.F.; Müller, R.; Todte, M.; Taubert, A.; Hermosilla, C. Role of Free-Ranging Synanthropic Egyptian Geese (Alopochen aegyptiaca) as Natural Host Reservoirs for Salmonella spp. in Germany. Animals. 2023, 13, 3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradini, C.; De Bene, A.F.; Russini, V.; Carfora, V.; Alba, P.; Cordaro, G.; Senese, M.; Terracciano, G.; Fabbri, I.; Di Sirio, A.; et al. Detection of Salmonella Reservoirs in Birds of Prey Hosted in an Italian Wildlife Centre: Molecular and Antimicrobial Resistance Characterisation. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobuszewska, A.; Wysok, B. Pathogenic Bacteria in Free-Living Birds, and Its Public Health Significance. Animals. 2024, 14, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beleza, A.J.F.; Maciel, W.C.; Lopes, E.S.; Albuquerque, A.H.; Carreira, A.S; Nogueira, C.H.G.; Bandeira, J.M.; Vasconcelos, R.H.; Teixeira, R.S.C. Evidence of the Role of Free-Living Birds as Disseminators of Salmonella spp. Arq. Inst. Biol. 2020, 87, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.M.C. Seasonal Movements and Conservation of Seedeaters of the Genus Sporophila in South America. Studies in Avian Biology 1999, 19, 272–280. [Google Scholar]
- Trouwborst, A.; McCormack, P.C.; Camacho, E.M. Domestic Cats and Their Impacts on Biodiversity: A Blind Spot in the Application of Nature Conservation Law. People and Nature. 2020, 2, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenackers, H.; Hermans, K.; Vanderleyden, J.; Keersmaecker, S.C.J. Salmonella Biofilms: An Overview on Occurrence, Structure, Regulation and Eradication. Food Research International. 2012, 45, 502–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, D.J.; Rodríguez, F.I.; Machado, L.C.; Soria, M.A.; Procura, F.; Gómez, S.C.; Hoffmann, T.M.; Alcain, A.; Caffer, M.I.; Latorre, J.D.; et al. Study of Salmonella spp. from Cage Papers Belonging to Pet Birds in an Argentinean Canary Breeder Championship. Animals. 2024, 14, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, R. .; Costa, C.; Bravo, E.; Santana, A.; Félix, S.; Sant´Ana, G.; Baptista, L.; Sant´Ana, C. Avaliação Sanitária do Setor de Quarentena do Centro de Triagem de Animais Silvestres de Goiânia (Goiás). Rev. Processos Químicos. 2013, 7, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.; Junqueira, V.C.A.; Silveira, N.F. A.; Taniwaki, M.H.; Santos, R.F.S.; Gomes, R.A.R. Manual de Métodos de Análise Microbiológica de Alimentos e Água, 4th ed.; Livraria Varela: São Paulo, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- McDermott, P.F.; Tyson, G.H.; Kabera, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Folster, J.P.; Ayers, S.L.; Lam, C.; Tate, H.P.; Zhao, S. Whole-Genome Sequencing for Detecting Antimicrobial Resistance in Nontyphoidal Salmonella. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queenan, A.M.; Bush, K. Carbapenemases: The Versatile β-Lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 440–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, P.; Machado, J.; Sousa, J.C.; Peixe, L. Dissemination of Sulfonamide Resistance Genes (sul1, sul2, and sul3) in Portuguese Salmonella enterica Strains and Relation with Integrons. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berchieri Júnior, A.; Silva, A.V.; Gomes, A.P.; et al. Doenças das Aves, 2nd ed.; Fundação APINCO de Ciência e Tecnologia Avícola: Campinas, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
| Bacterial Culture Media | |||
| Sample | HE | SS | MacConkey Agar |
| Bird 1 | + | + | Lac- |
| Bird 2 | + | + | Lac- |
| Bird 3 | + | + | Lac- |
| Enclosure 1 | + | + | Lac- |
| Enclosure 2 | + | + | Lac- |
| Enclosure 3 | - | - | Lac+ |
| Cage 1 | - | - | Lac+ |
| Cage 2 | + | + | Lac- |
| Cage 3 | - | - | Lac+ |
| + : Production of hydrogen sulfide; - : No production of hydrogen sulfide; Lac + : Lactose-fermenting bacteria; Lac - : Non-lactose fermenting bacteria. | |||
| Class Antibiotic | Bird | Bird | Bird | Encl. | Encl. | Cag. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
| Ampicilin* | - | - | - | + | + | + |
| Amoxcicilin + | - | - | - | + | + | + |
| Clavulonate* Amoxicilin* |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| Sulfazotrim* | - | - | + | - | - | - |
|
Sulfonamides Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole** |
- | - | - | x | - | - |
| Phenicoles Chloranfenicol** | - | - | - | x | - | - |
| Gentamicin*/** | - | - | - | x | - | - |
| Streptomycin** | + | + | + | x | + | + |
| Carbapenems Meropenem** | - | - | - | x | - | - |
| Nalidixic Acid** | - | - | - | x | - | - |
| Ciprofloxacin** | - | - | - | x | - | - |
| Monobactams Aztreonam* | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Tetracycline Tetracyclin** | + | + | + | x | + | + |
| Cephazolin*/** Cephalosporins 1st Cephalexin* |
- */** +* |
- */** +* |
- */** - |
+*/x** - |
+*/-** - |
+*/-** - |
| Cephalosporins 2st Cefoxitin** | - | - | - | x | - | - |
| Ceftriaxone* | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Cefotaxime* | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Encl. 1 (Enclosure 1) and Encl. 2 (Enclosure 2): quarantine environment for passerines; Cag. 2 (Cage 2): quarantine cage for passerines within Enclosure 2; - : no antibiotic resistance; + : antibiotic resistance present; x : no growth in the sample. | ||||||
| Bird 1 | Bird 2 | Bird 3 | |
| Identified Bacterium |
Salmonella sp. Enterococcus faecalis |
Salmonella sp. | Salmonella sp. |
| Bird 1: Sporophila bouvreuil; Bird 2: Sporophila nigricollis; Bird 3: Sporophila albogularis. | |||
| Sample | Serotyping |
| Bird 1 | Salmonella enterica subesp. enterica (O:4,5) * |
| Bird 2 | Salmonella ser. Typhimurium |
| Bird 3 | Salmonella ser. Typhimurium |
| Cage 2 | Salmonella enterica subesp. enterica * |
| Enclosure 1 | Sample showed no bacterial growth in 24/48 hours. |
| Enclosure 2 | Salmonella enterica subesp. enterica (O:4,5) * |
| *: Flagellar structure not identifiable. | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





