Submitted:
14 September 2024
Posted:
17 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
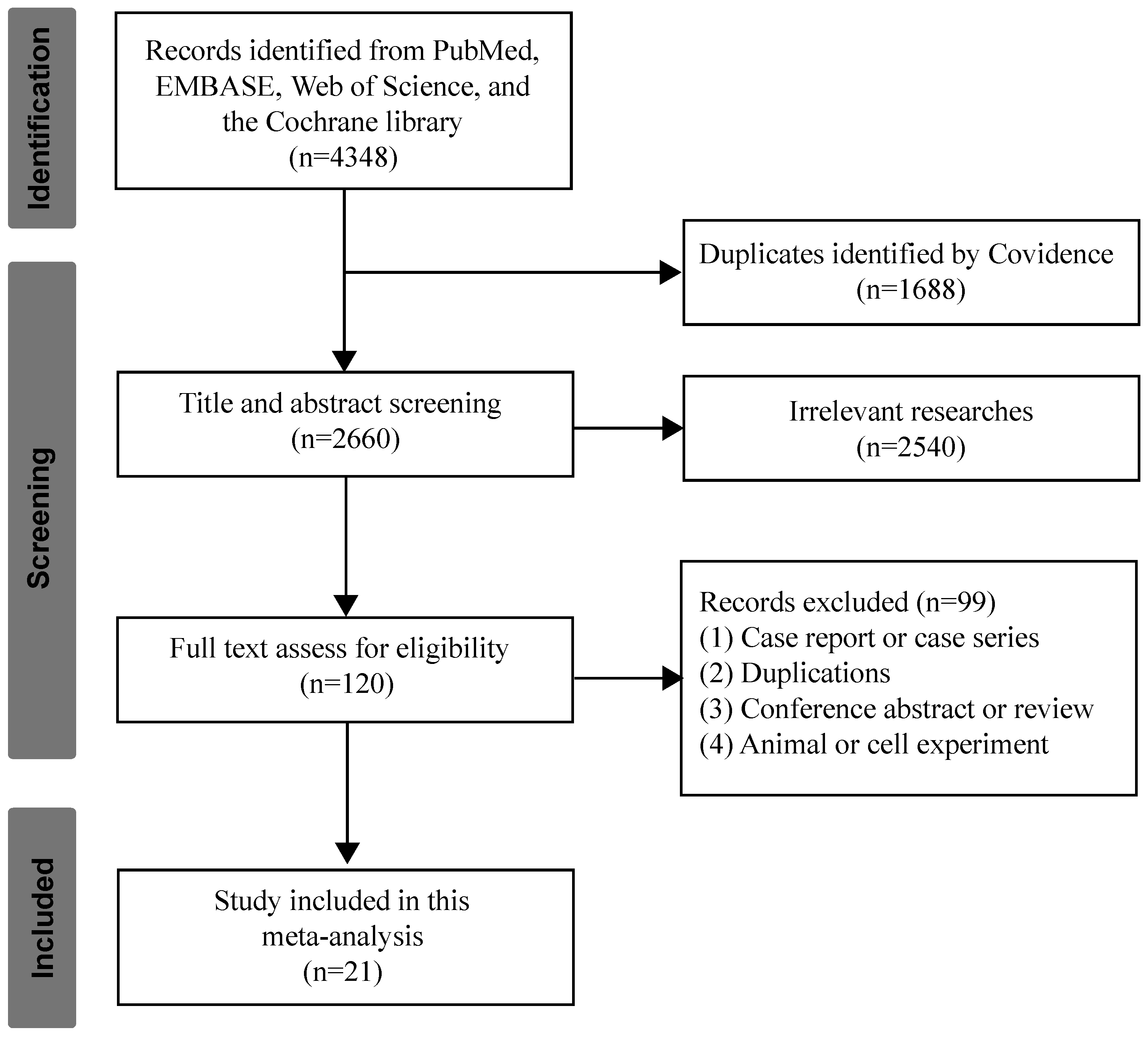
3.1. Studies Selection and Characteristics
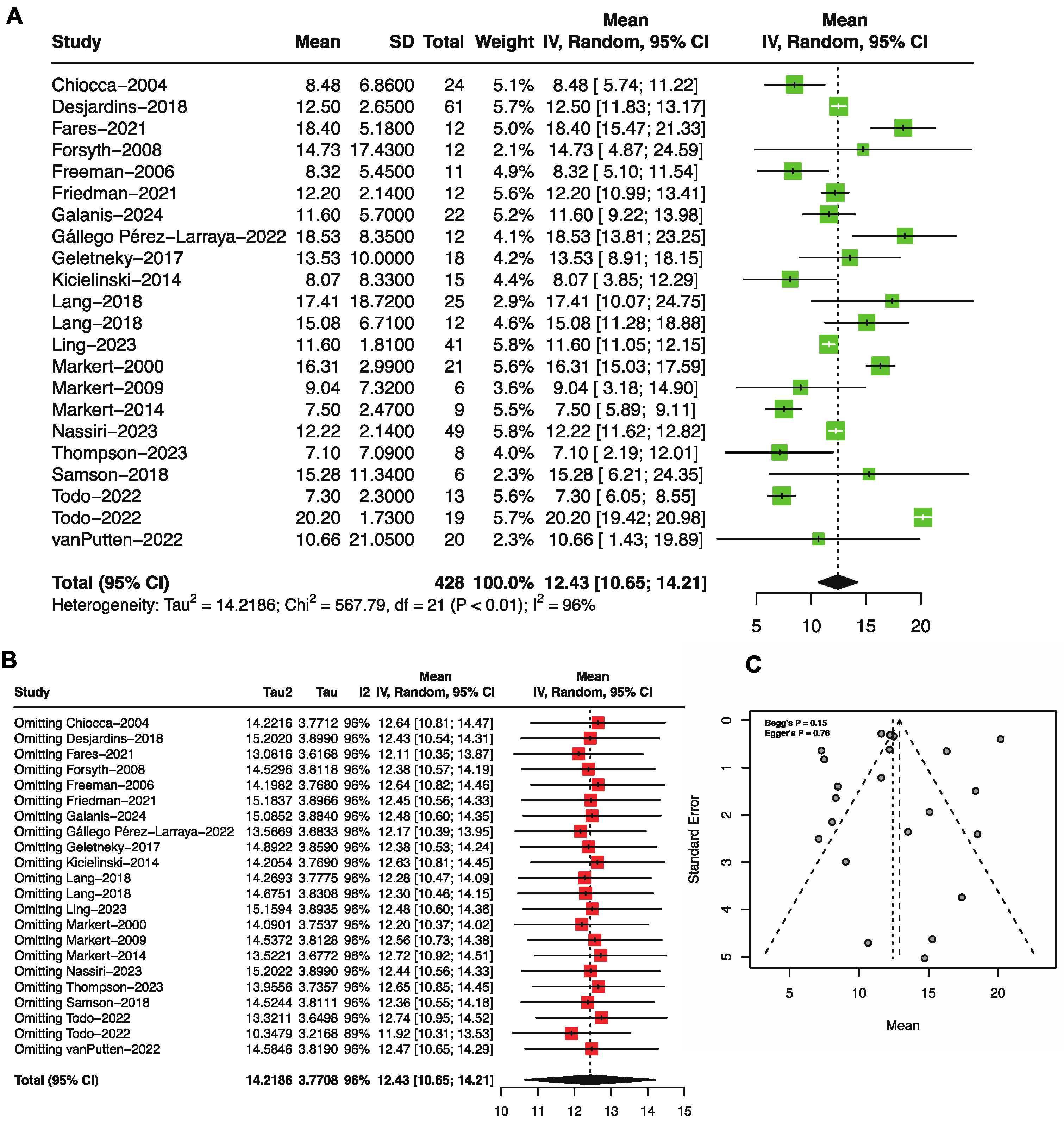
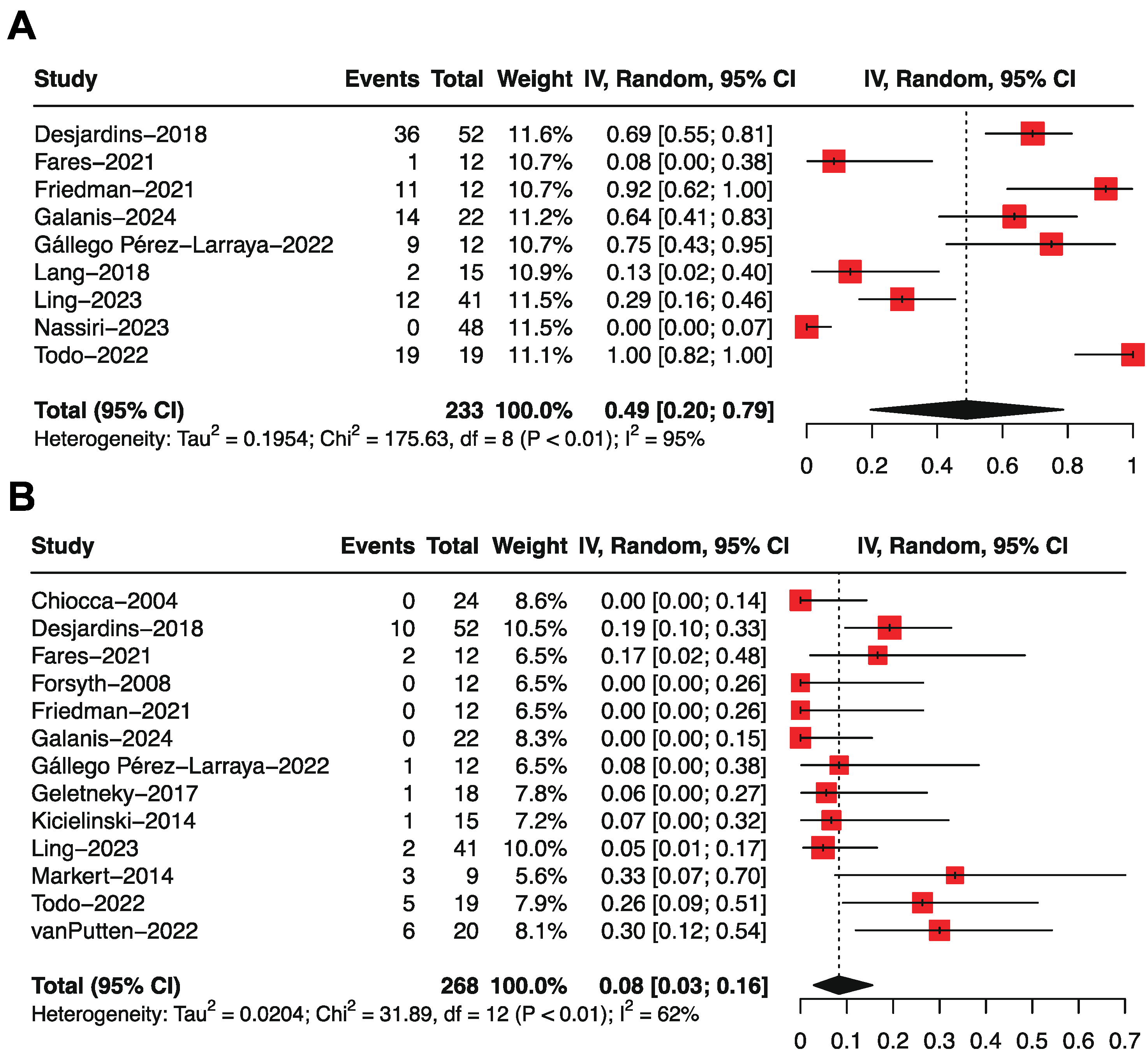
3.2. Overall Survival by Single-Arm Meta-Analysis
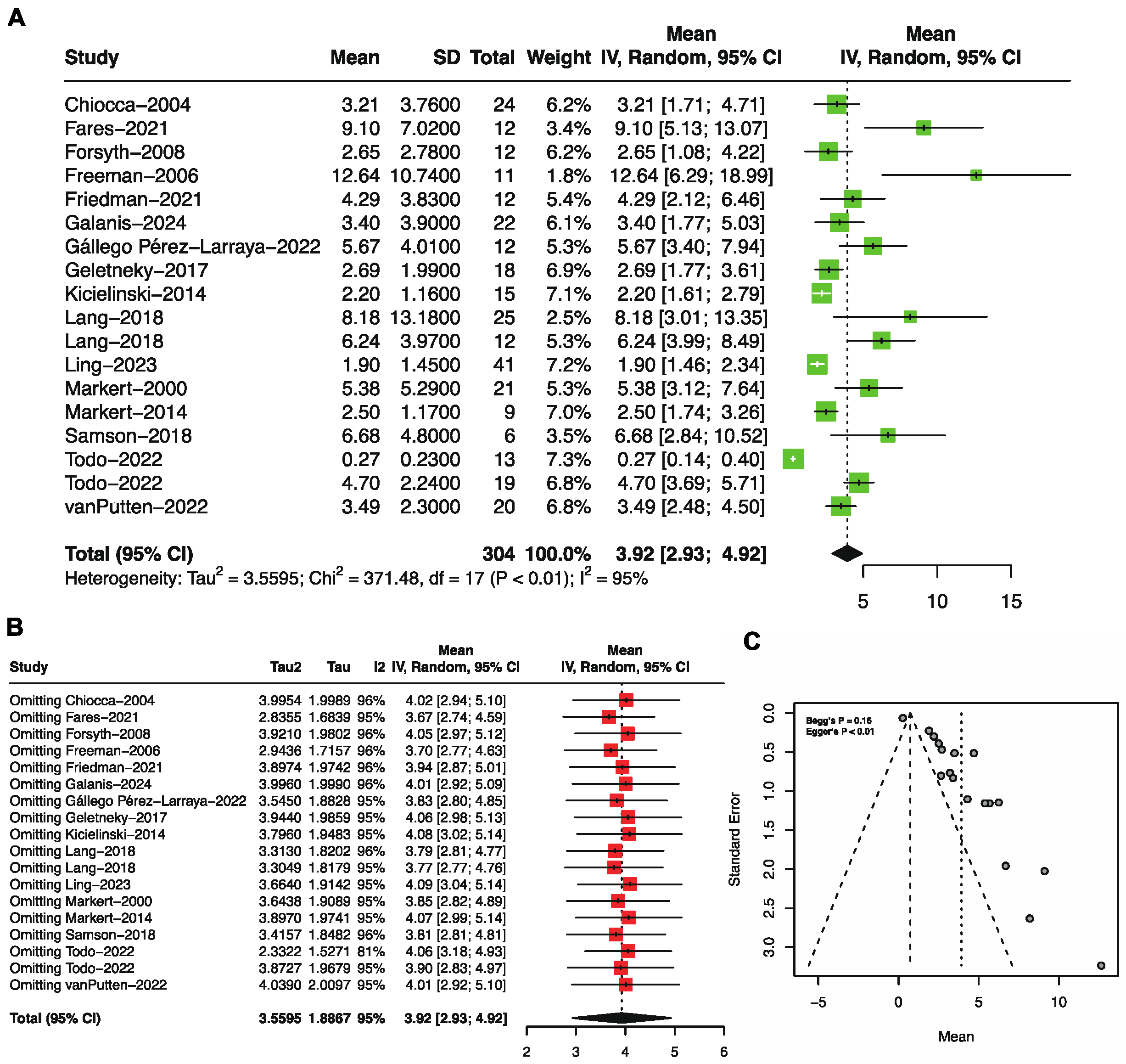
3.3. Progression-Free Survival by Single-Arm Meta-Analysis
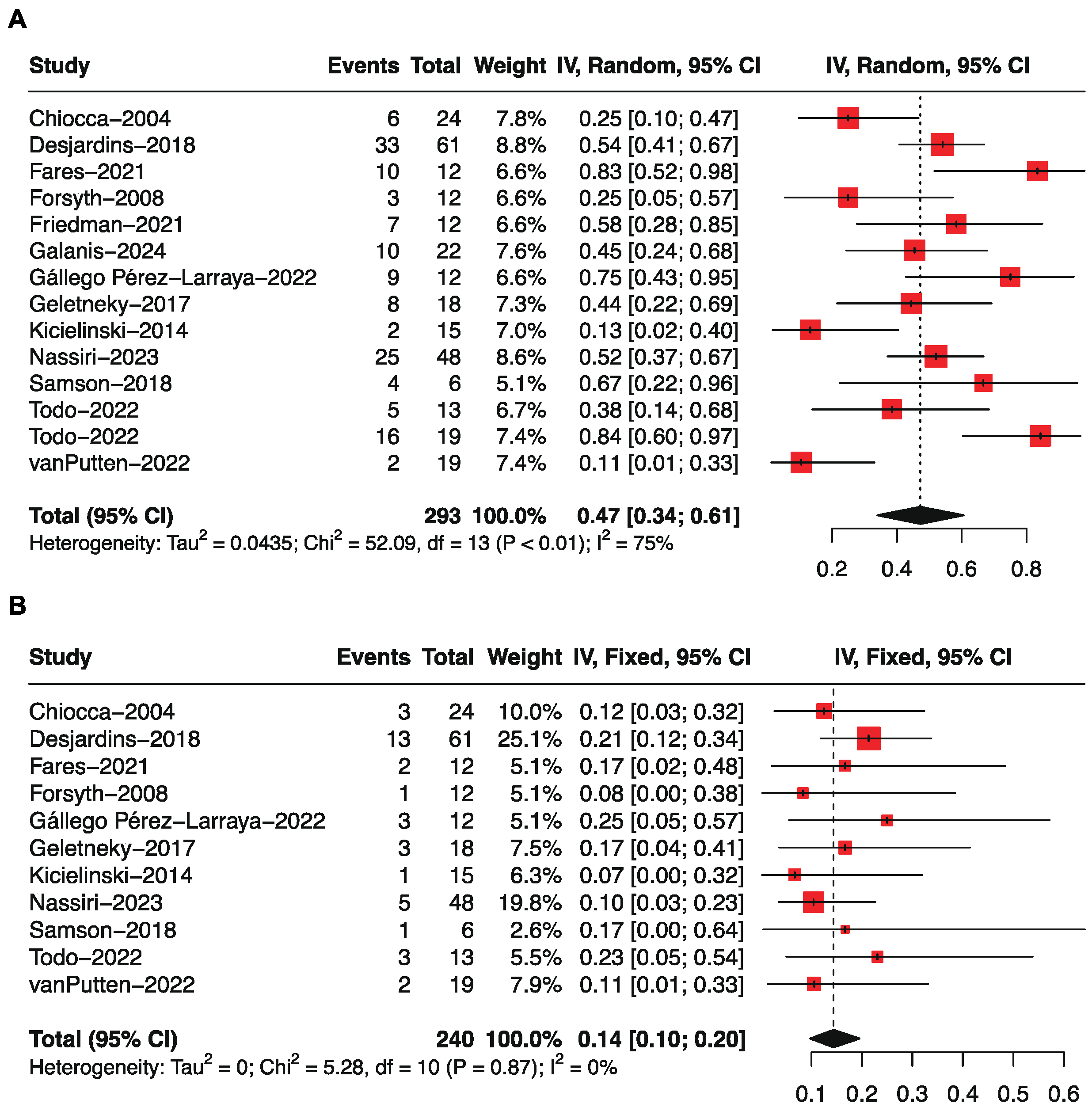
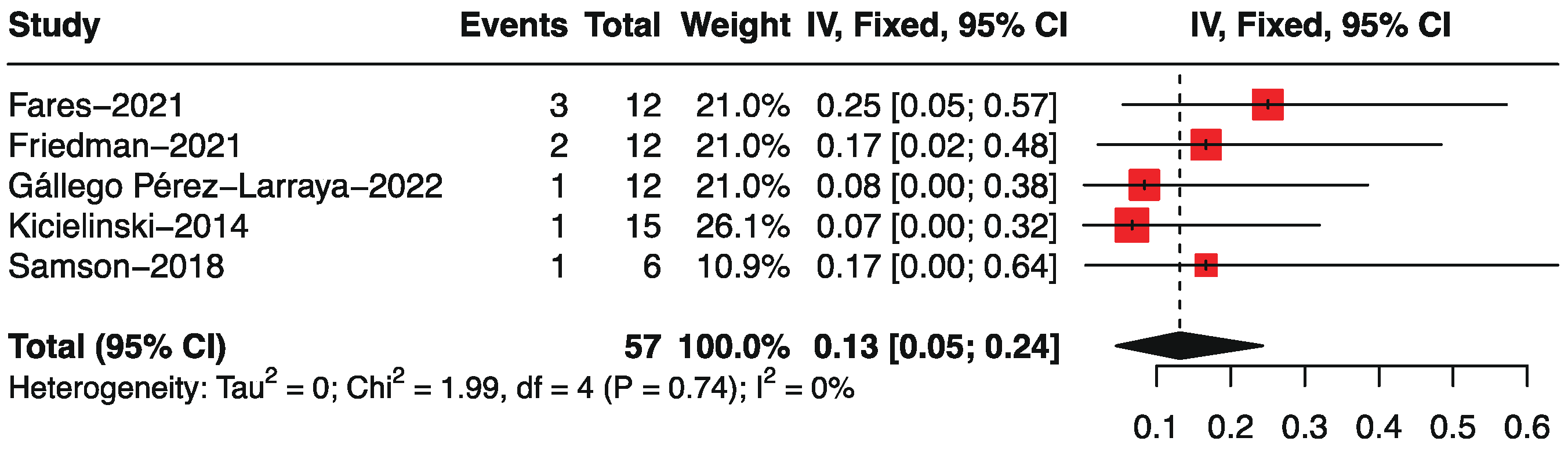
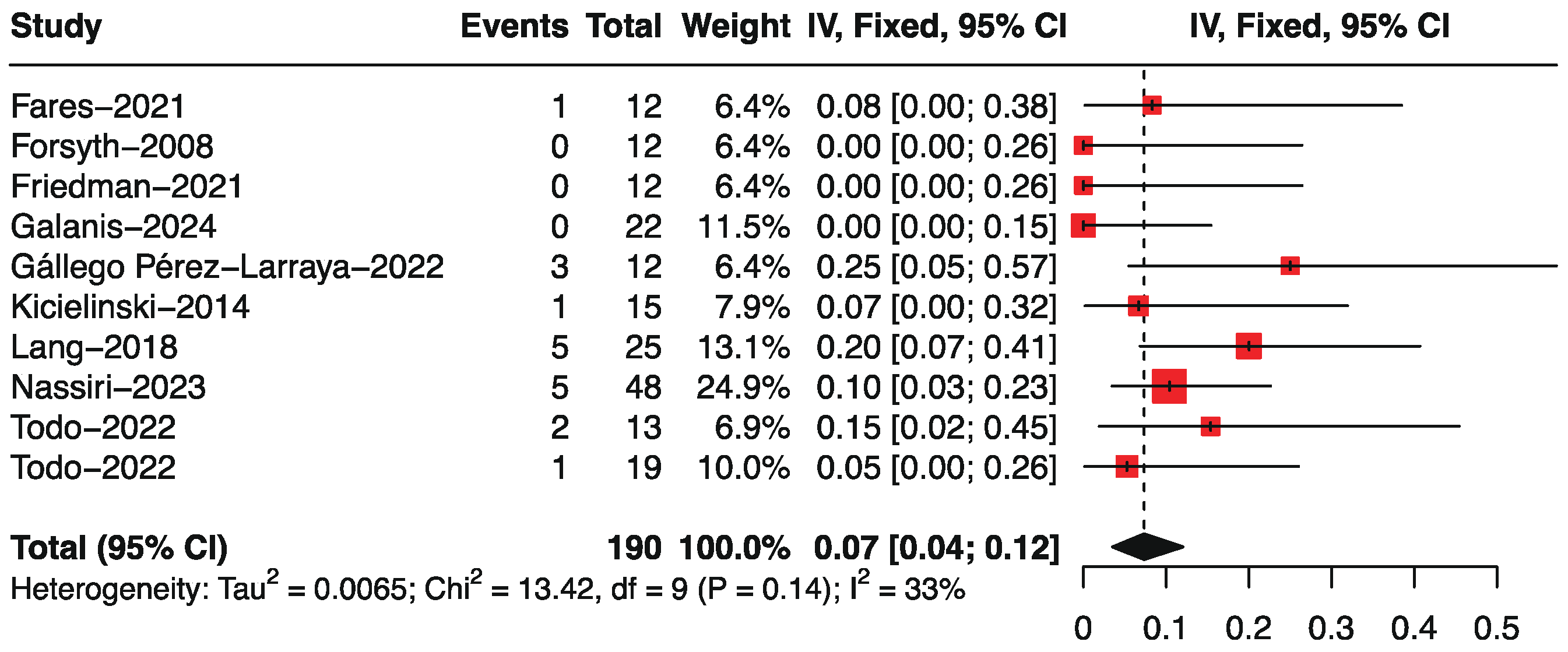
3.4. Objective Response Rate by Single-Arm Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schaff LR, Mellinghoff IK. Glioblastoma and Other Primary Brain Malignancies in Adults: A Review. JAMA. 2023; 329: 574-87.
- Ostrom QT, Cioffi G, Waite K, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2014-2018. Neuro Oncol. 2021; 23: iii1-iii105. [CrossRef]
- Louis DN, Perry A, Wesseling P, Brat DJ, Cree IA, Figarella-Branger D, Hawkins C, Ng HK, Pfister SM, Reifenberger G, Soffietti R, von Deimling A, Ellison DW. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021; 23: 1231-51. [CrossRef]
- Weller M, van den Bent M, Preusser M, Le Rhun E, Tonn JC, Minniti G, Bendszus M, Balana C, Chinot O, Dirven L, French P, Hegi ME, Jakola AS, et al. EANO guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of diffuse gliomas of adulthood. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021; 18: 170-86. [CrossRef]
- Tan AC, Ashley DM, Lopez GY, Malinzak M, Friedman HS, Khasraw M. Management of glioblastoma: State of the art and future directions. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020; 70: 299-312. [CrossRef]
- Ma R, Li Z, Chiocca EA, Caligiuri MA, Yu J. The emerging field of oncolytic virus-based cancer immunotherapy. Trends Cancer. 2023; 9: 122-39. [CrossRef]
- Yan Z, Zhang Z, Chen Y, Xu J, Wang J, Wang Z. Enhancing cancer therapy: the integration of oncolytic virus therapy with diverse treatments. Cancer Cell Int. 2024; 24: 242. [CrossRef]
- Wu YY, Sun TK, Chen MS, Munir M, Liu HJ. Oncolytic viruses-modulated immunogenic cell death, apoptosis and autophagy linking to virotherapy and cancer immune response. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023; 13: 1142172. [CrossRef]
- Yang C, Hua N, Xie S, Wu Y, Zhu L, Wang S, Tong X. Oncolytic viruses as a promising therapeutic strategy for hematological malignancies. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021; 139: 111573. [CrossRef]
- Larocca CA, LeBoeuf NR, Silk AW, Kaufman HL. An Update on the Role of Talimogene Laherparepvec (T-VEC) in the Treatment of Melanoma: Best Practices and Future Directions. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020; 21: 821-32. [CrossRef]
- Zhu X, Fan C, Xiong Z, Chen M, Li Z, Tao T, Liu X. Development and application of oncolytic viruses as the nemesis of tumor cells. Front Microbiol. 2023; 14: 1188526. [CrossRef]
- Bommareddy PK, Wakimoto H, Martuza RL, Kaufman HL, Rabkin SD, Saha D. Oncolytic herpes simplex virus expressing IL-2 controls glioblastoma growth and improves survival. J Immunother Cancer. 2024; 12.
- Li S, Guo Y, Ning W, Chen Y, Xu J, Zhao C, Wang J, Qu Y, Zhang M, Wang P, Wang Y, Wang S, Zhang H. Oncolytic virus Ad-TD-nsIL-12 inhibits glioma growth and reprograms the tumor immune microenvironment. Life Sci. 2024; 336: 122254. [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Velez N, Garcia-Moure M, Marigil M, Gonzalez-Huarriz M, Puigdelloses M, Gallego Perez-Larraya J, Zalacain M, Marrodan L, Varela-Guruceaga M, Laspidea V, Aristu JJ, Ramos LI, Tejada-Solis S, et al. The oncolytic virus Delta-24-RGD elicits an antitumor effect in pediatric glioma and DIPG mouse models. Nat Commun. 2019; 10: 2235. [CrossRef]
- Soldozy S, Skaff A, Soldozy K, Sokolowski JD, Norat P, Yagmurlu K, Sharifi KA, Tvrdik P, Park MS, Kalani MYS, Jane JA, Syed HR. From Bench to Bedside, the Current State of Oncolytic Virotherapy in Pediatric Glioma. Neurosurgery. 2020; 87: 1091-7. [CrossRef]
- Chiocca EA, Abbed KM, Tatter S, Louis DN, Hochberg FH, Barker F, Kracher J, Grossman SA, Fisher JD, Carson K, Rosenblum M, Mikkelsen T, Olson J, et al. A phase I open-label, dose-escalation, multi-institutional trial of injection with an E1B-Attenuated adenovirus, ONYX-015, into the peritumoral region of recurrent malignant gliomas, in the adjuvant setting. Mol Ther. 2004; 10: 958-66. [CrossRef]
- Desjardins A, Gromeier M, Herndon JE, Beaubier N, Bolognesi DP, Friedman AH, Friedman HS, McSherry F, Muscat AM, Nair S, Peters KB, Randazzo D, Sampson JH, et al. Recurrent Glioblastoma Treated with Recombinant Poliovirus. New England Journal of Medicine. 2018; 379: 150-61. [CrossRef]
- Fares J, Ahmed AU, Ulasov IV, Sonabend AM, Miska J, Lee-Chang C, Balyasnikova IV, Chandler JP, Portnow J, Tate MC, Kumthekar P, Lukas RV, Grimm SA, et al. Neural stem cell delivery of an oncolytic adenovirus in newly diagnosed malignant glioma: a first-in-human, phase 1, dose-escalation trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021; 22: 1103-14. [CrossRef]
- Forsyth P, Roldán G, George D, Wallace C, Palmer CA, Morris D, Cairncross G, Matthews MV, Markert J, Gillespie Y, Coffey M, Thompson B, Hamilton M. A phase I trial of intratumoral administration of reovirus in patients with histologically confirmed recurrent malignant gliomas. Mol Ther. 2008; 16: 627-32. [CrossRef]
- Freeman AI, Zakay-Rones Z, Gomori JM, Linetsky E, Rasooly L, Greenbaum E, Rozenman-Yair S, Panet A, Libson E, Irving CS, Galun E, Siegal T. Phase I/II trial of intravenous NDV-HUJ oncolytic virus in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Mol Ther. 2006; 13: 221-8. [CrossRef]
- Friedman GK, Johnston JM, Bag AK, Bernstock JD, Li R, Aban I, Kachurak K, Nan L, Kang KD, Totsch S, Schlappi C, Martin AM, Pastakia D, et al. Oncolytic HSV-1 G207 immunovirotherapy for pediatric high-grade gliomas. New England Journal of Medicine. 2021; 384: 1613-22. [CrossRef]
- Galanis E, Dooley KE, Keith Anderson S, Kurokawa CB, Carrero XW, Uhm JH, Federspiel MJ, Leontovich AA, Aderca I, Viker KB, Hammack JE, Marks RS, Robinson SI, et al. Carcinoembryonic antigen-expressing oncolytic measles virus derivative in recurrent glioblastoma: a phase 1 trial. Nature Communications. 2024; 15: 493. [CrossRef]
- Gállego Pérez-Larraya J, Garcia-Moure M, Labiano S, Patiño-García A, Dobbs J, Gonzalez-Huarriz M, Zalacain M, Marrodan L, Martinez-Velez N, Puigdelloses M, Laspidea V, Astigarraga I, Lopez-Ibor B, et al. Oncolytic DNX-2401 Virus for Pediatric Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma. N Engl J Med. 2022; 386: 2471-81. [CrossRef]
- Geletneky K, Hajda J, Angelova AL, Leuchs B, Capper D, Bartsch AJ, Neumann JO, Schöning T, Hüsing J, Beelte B, Kiprianova I, Roscher M, Bhat R, et al. Oncolytic H-1 Parvovirus Shows Safety and Signs of Immunogenic Activity in a First Phase I/IIa Glioblastoma Trial. Mol Ther. 2017; 25: 2620-34. [CrossRef]
- Kicielinski KP, Chiocca EA, Yu JS, Gill GM, Coffey M, Markert JM. Phase 1 clinical trial of intratumoral reovirus infusion for the treatment of recurrent malignant gliomas in adults. Mol Ther. 2014; 22: 1056-62. [CrossRef]
- Lang FF, Conrad C, Gomez-Manzano C, Yung WKA, Sawaya R, Weinberg JS, Prabhu SS, Rao G, Fuller GN, Aldape KD, Gumin J, Vence LM, Wistuba I, et al. Phase I Study of DNX-2401 (Delta-24-RGD) Oncolytic Adenovirus: Replication and Immunotherapeutic Effects in Recurrent Malignant Glioma. J Clin Oncol. 2018; 36: 1419-27. [CrossRef]
- Ling AL, Solomon IH, Landivar AM, Nakashima H, Woods JK, Santos A, Masud N, Fell G, Mo X, Yilmaz AS, Grant J, Zhang A, Bernstock JD, et al. Clinical trial links oncolytic immunoactivation to survival in glioblastoma. Nature. 2023; 623: 157-66. [CrossRef]
- Markert JM, Liechty PG, Wang W, Gaston S, Braz E, Karrasch M, Nabors LB, Markiewicz M, Lakeman AD, Palmer CA, Parker JN, Whitley RJ, Gillespie GY. Phase Ib trial of mutant herpes simplex virus G207 inoculated pre-and post-tumor resection for recurrent GBM. Molecular Therapy. 2009; 17: 199-207. [CrossRef]
- Markert JM, Medlock MD, Rabkin SD, Gillespie GY, Todo T, Hunter WD, Palmer CA, Feigenbaum F, Tornatore C, Tufaro F, Martuza RL. Conditionally replicating herpes simplex virus mutant, G207 for the treatment of malignant glioma: results of a phase I trial. Gene Therapy. 2000; 7: 867-74. [CrossRef]
- Markert JM, Razdan SN, Kuo HC, Cantor A, Knoll A, Karrasch M, Nabors LB, Markiewicz M, Agee BS, Coleman JM, Lakeman AD, Palmer CA, Parker JN, et al. A phase 1 trial of oncolytic HSV-1, G207, given in combination with radiation for recurrent GBM demonstrates safety and radiographic responses. Mol Ther. 2014; 22: 1048-55. [CrossRef]
- Samson A, Scott KJ, Taggart D, West EJ, Wilson E, Nuovo GJ, Thomson S, Corns R, Mathew RK, Fuller MJ, Kottke TJ, Thompson JM, Ilett EJ, et al. Intravenous delivery of oncolytic reovirus to brain tumor patients immunologically primes for subsequent checkpoint blockade. Science Translational Medicine. 2018; 10: eaam7577. [CrossRef]
- Thompson EM, Landi D, Brown MC, Friedman HS, McLendon R, Herndon JE, Buckley E, Bolognesi DP, Lipp E, Schroeder K, Becher OJ, Friedman AH, McKay Z, et al. Recombinant polio–rhinovirus immunotherapy for recurrent paediatric high-grade glioma: a phase 1b trial. The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health. 2023; 7: 471-8. [CrossRef]
- Todo T, Ino Y, Ohtsu H, Shibahara J, Tanaka M. A phase I/II study of triple-mutated oncolytic herpes virus G47∆ in patients with progressive glioblastoma. Nat Commun. 2022; 13: 4119. [CrossRef]
- van Putten EHP, Kleijn A, van Beusechem VW, Noske D, Lamers CHJ, de Goede AL, Idema S, Hoefnagel D, Kloezeman JJ, Fueyo J, Lang FF, Teunissen CE, Vernhout RM, et al. Convection Enhanced Delivery of the Oncolytic Adenovirus Delta24-RGD in Patients with Recurrent GBM: A Phase I Clinical Trial Including Correlative Studies. Clin Cancer Res. 2022; 28: 1572-85. [CrossRef]
- Todo T, Ito H, Ino Y, Ohtsu H, Ota Y, Shibahara J, Tanaka M. Intratumoral oncolytic herpes virus G47∆ for residual or recurrent glioblastoma: a phase 2 trial. Nat Med. 2022; 28: 1630-9. [CrossRef]
- Nassiri F, Patil V, Yefet LS, Singh O, Liu J, Dang RMA, Yamaguchi TN, Daras M, Cloughesy TF, Colman H, Kumthekar PU, Chen CC, Aiken R, et al. Oncolytic DNX-2401 virotherapy plus pembrolizumab in recurrent glioblastoma: a phase 1/2 trial. Nat Med. 2023; 29: 1370-8. [CrossRef]
- Marwah R, Xing D, Squire T, Soon YY, Gan HK, Ng SP. Reirradiation versus systemic therapy versus combination therapy for recurrent high-grade glioma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of survival and toxicity. J Neurooncol. 2023; 164: 505-24. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed R, Oborski MJ, Hwang M, Lieberman FS, Mountz JM. Malignant gliomas: current perspectives in diagnosis, treatment, and early response assessment using advanced quantitative imaging methods. Cancer Manag Res. 2014; 6: 149-70. [CrossRef]
- Zeng YF, Wei XY, Guo QH, Chen SY, Deng S, Liu ZZ, Gong ZC, Zeng WJ. The efficacy and safety of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 in treatment of glioma: a single-arm meta-analysis. Front Immunol. 2023; 14: 1168244. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Zhao L, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Ju H, Wang X, Ren H, Zhu X, Dong Y. The immunosuppressive microenvironment and immunotherapy in human glioblastoma. Front Immunol. 2022; 13: 1003651. [CrossRef]
- Liu J, Piranlioglu R, Ye F, Shu K, Lei T, Nakashima H. Immunosuppressive cells in oncolytic virotherapy for glioma: challenges and solutions. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023; 13: 1141034. [CrossRef]
- Blitz SE, Kappel AD, Gessler FA, Klinger NV, Arnaout O, Lu Y, Peruzzi PP, Smith TR, Chiocca EA, Friedman GK, Bernstock JD. Tumor-Associated Macrophages/Microglia in Glioblastoma Oncolytic Virotherapy: A Double-Edged Sword. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23. [CrossRef]
- Liu X, Liu Y, Qi Y, Huang Y, Hu F, Dong F, Shu K, Lei T. Signal Pathways Involved in the Interaction Between Tumor-Associated Macrophages/TAMs and Glioblastoma Cells. Front Oncol. 2022; 12: 822085. [CrossRef]
- Mills CD, Kincaid K, Alt JM, Heilman MJ, Hill AM. M-1/M-2 macrophages and the Th1/Th2 paradigm. J Immunol. 2000; 164: 6166-73. [CrossRef]
- Bonapace L, Coissieux MM, Wyckoff J, Mertz KD, Varga Z, Junt T, Bentires-Alj M. Cessation of CCL2 inhibition accelerates breast cancer metastasis by promoting angiogenesis. Nature. 2014; 515: 130-3. [CrossRef]
- Denton NL, Chen CY, Scott TR, Cripe TP. Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Oncolytic Virotherapy: Friend or Foe? Biomedicines. 2016; 4. [CrossRef]
- Meisen WH, Wohleb ES, Jaime-Ramirez AC, Bolyard C, Yoo JY, Russell L, Hardcastle J, Dubin S, Muili K, Yu J, Caligiuri M, Godbout J, Kaur B. The Impact of Macrophage- and Microglia-Secreted TNFalpha on Oncolytic HSV-1 Therapy in the Glioblastoma Tumor Microenvironment. Clin Cancer Res. 2015; 21: 3274-85. [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Cardenas M, Gowan C, Dryja P, Bartee MY, Bartee E. TNF blockade enhances the efficacy of myxoma virus-based oncolytic virotherapy. J Immunother Cancer. 2022; 10. [CrossRef]
- Kyula JN, Khan AA, Mansfield D, Karapanagiotou EM, McLaughlin M, Roulstone V, Zaidi S, Pencavel T, Touchefeu Y, Seth R, Chen NG, Yu YA, Zhang Q, et al. Synergistic cytotoxicity of radiation and oncolytic Lister strain vaccinia in (V600D/E)BRAF mutant melanoma depends on JNK and TNF-alpha signaling. Oncogene. 2014; 33: 1700-12. [CrossRef]
- Weber L, Vieyres G. The Railmap of Type I Interferon Induction: Subcellular Network Plan and How Viruses Can Change Tracks. Cells. 2022; 11. [CrossRef]
- Bommareddy PK, Shettigar M, Kaufman HL. Integrating oncolytic viruses in combination cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018; 18: 498-513. [CrossRef]
- Ferguson MS, Lemoine NR, Wang Y. Systemic delivery of oncolytic viruses: hopes and hurdles. Adv Virol. 2012; 2012: 805629. [CrossRef]
- Li L, Liu S, Han D, Tang B, Ma J. Delivery and Biosafety of Oncolytic Virotherapy. Front Oncol. 2020; 10: 475. [CrossRef]
- Chen L, Ma Z, Xu C, Xie Y, Ouyang D, Song S, Zhao X, Liu F. Progress in oncolytic viruses modified with nanomaterials for intravenous application. Cancer Biol Med. 2023; 20: 830-55. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed AU, Tyler MA, Thaci B, Alexiades NG, Han Y, Ulasov IV, Lesniak MS. A comparative study of neural and mesenchymal stem cell-based carriers for oncolytic adenovirus in a model of malignant glioma. Mol Pharm. 2011; 8: 1559-72. [CrossRef]
- Kim J, Zhu Y, Chen S, Wang D, Zhang S, Xia J, Li S, Qiu Q, Lee H, Wang J. Anti-glioma effect of ginseng-derived exosomes-like nanoparticles by active blood-brain-barrier penetration and tumor microenvironment modulation. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023; 21: 253. [CrossRef]
- Tseng YY, Chen TY, Liu SJ. Role of Polymeric Local Drug Delivery in Multimodal Treatment of Malignant Glioma: A Review. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021; 16: 4597-614. [CrossRef]
| Author | Year | Country | Study design | N (M/F) | Age | Diagnose | Viral family | Delivery | Dose (duration) | Previous treatment | End Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chiocca [16] | 2004 | USA | Phase I | 24 (17/7) | 52 (35–70) |
AA, AO, or GBM (Recurrent) |
ONYX-015, E1B-attenuated adenovirus | I.T. | 10^7 pfu inoculated into theresected tumor cavity | S: 24 RT:24 CT:24 |
OS, PFS |
| Desjardins [17] | 2018 | USA | Phase II (NCT01491893) | 61 (25/36) | 55 (20–75) |
GBM (Recurrent) |
PVSRIPO, polio–rhinovirus chimera | I.T. | 10^7–10^10 (7 doses) |
S: 61 RT: 61 CT: 61 BEV: 61 |
OS |
| Fares [18] | 2021 | UK | Phase I (NCT03072134) | 12 (7/5) | 52 (48–65) |
AA or GBM (ND) |
NSC-CRAd-S-pk7, adenovirus | I.T. | Corhort 1: 6.25 × 10^10 VP, Corhort 2: 1.25 × 10^11 VP, Cohort 3: 1.875 × 10^11 VP (1 dose) |
S: 12 | OS, PFS, ORR |
| Forsyth [19] | 2008 | USA | Phase I | 12 (5/7) | 53.5 (40–61) |
AA, AO, or GBM (Recurrent) | Reovirus | I.T. | 72h infusion of 10^7, 10^8, or 10^9 TCID50 | S: 12 RT: 12 CT: 10 |
OS, PFS, ORR |
| Freeman [20] | 2006 | USA | Phase I/II | 11 (5/6) | 44.5 | GBM (Recurrent) |
NDV-HUJ, Newcastle disease virus | I.V. | Part 1: 0.1, 0.32, 0.93, 5.9, and 11 BIU; Part 2: 11 BIU |
S: 10 Biopsy: 4 RT: 14 CT: 12 |
OS, PFS |
| Friedman [21] | 2021 | USA | Phase I (NCT02457845) | 12 (6/6) | 13.4 (7-18) |
AA or GBM (Recurrent) |
G207, HSV-1 | I.T. | 10^7-10^8 PFU | S: 12 RT: 12 CT: 12 BEV: 3 |
OS, PFS, ORR |
| Galanis [22] | 2024 | USA | Phase I/II (NCT00390299) | 22 (11/11) | 53.5 (37.0-69.0) |
AA or GBM (Recurrent) | MV-CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen-expressing oncolytic measles virus | I.T. | 2×10^6-2×10^7 PFU | CT: 22 BEV: 5 | OS, PFS, ORR |
| Geletneky [24] | 2017 | USA | Phase I/IIa (NCT01301430) | 18 (4/14) | 57.8 ± 10.6 | GBM (Recurrent) |
ParvOryx, H-1 parvovirus (H-1PV) |
I.T. | Arm1: 5×10^9 pfu; Arm2: 1×10^9 pfu | S: 18 RT: 18 CT: 18 |
OS, PFS |
| Kicielinski [25] | 2014 | USA | Phase I | 15 (5/10) | 51.52 (26.2–76.3) |
GBM, GS, AA, anaplastic mixed glioma, or AO (Recurrent) |
REOLYSIN, Reovirus | I.T. | 1×10^8-1×10^10 pfu | S: 15 RT: 15 CT: 15 |
OS, PFS, ORR |
| Lang [26] | 2018 | USA | Phase I (NCT00805376) | group A: 25(10/15); group B: 12 (6/6) |
group A: 52 (21-62), group B: 49 (29-60) | GBM, GS, or AA (Recurrent) |
DNX-2401, adenovirus | I.T. | 1×10^7–3×10^10 VP (1 dose) | S: 25 RT: 37 CT: 36 |
OS, PFS, ORR |
| Ling [27] | 2023 | USA | Phase I (NCT03152318) | 41 | 56 (27-74) |
GBM or HGG (Recurrent) |
CAN-3110, HSV | I.T. | 10^6–10^10 PFU | S: 38 RT: 41 CT: 41 BEV: 30 |
OS, PFS |
| Markert [29] | 2000 | USA | Phase I | 21 (14/7) | 54.1 (38–72) |
AA or GBM (Recurrent or progressive) |
G207, HSV | I.T. | 10^6-3×10^9 pfu injected over 2 min in 5 operative locations | S: 17 Biopsy: 4 RT: 21 CT: 10 | OS, PFS |
| Markert [28] | 2009 | USA | Phase Ib (F05041106) | 6 (4/2) | 54.5 (39–65) |
GBM (Recurrent) |
G207, HSV | I.T. | 1.5 × 10^8 pfu (2 doses) | S: 6 RT: 6 CT: 5 |
OS |
| Markert [30] | 2014 | USA | Phase I (NCT00157703) | 9 (3/6) | 50.4 (37–60) |
AA or GBM (Recurrent) |
G207, HSV | I.T. | 1.0 × 10^9 pfu (1 dose) | S: 9 RT: 9 CT: 9 |
OS, PFS |
| Nassiri [36] | 2023 | Canada | Phase I/II (NCT02798406) | 49 (20/29) | 53 (26–73) | GBM or GS (Recurrent) |
DNX-2401, adenovirus | I.T. | 5 × 10^8, 5 × 10^9 and 5 × 10^10 VP | S: 4, RT: 49 CT: 49 BEV: 6 |
OS, ORR |
| Pérez-Larraya [23] | 2022 | USA | Phase Ia (NCT03178032) | 12 (7/5) | 9 (3-18) | DIPG (ND) |
DNX-2401, adenovirus | I.T. | 1×10^10 and 5×10^10 VP | / | OS, PFS, ORR |
| Samson [31] | 2018 | UK | Phase Ib (EudraCT: 2011-005635-10) |
6 | 62 (45-66) | HGG (Recurrent) |
REOLYSIN, Reovirus | I.V. | 1×10^10 single dose | S: 6 RT: 6 CT: 6 BEV: 1 |
OS, PFS |
| Thompson [32] | 2023 | USA | Phase Ib (NCT03043391) | 8 (3/5) | 16.5 (11–18) |
HGG (Recurrent) |
PVSRIPO | I.T. | 5 × 10^7 | CT: 8 BEV: 2 | OS |
| Todo [33] | 2022 | Japan | Phase I/II (UMIN000002661) | 13 (5/8) | 46 (35–76) |
GBM (Recurrent) |
G47Δ, HSV | I.T. | Cohort 1: 6 × 10^8 pfu, Corhort 2: 2 × 10^9 pfu | S: 13 RT: 13 CT: 13 |
OS, PFS, ORR |
| Todo [35] | 2022 | Japan | Phase II (UMIN000015995) | 19 (4/15) | 50.89 (25-73) |
GBM (Residual or recurrent) |
G47Δ, HSV | I.T. | 1 × 10^9 pfu per dose (up to six doses) | S: 19 RT: 19 CT: 19 BEV: 7 |
OS, PFS, ORR |
| van Putten [34] | 2022 | USA | Phase I | 20 (8/12) | 53.5 (29–69) |
GBM (Recurrent) |
Delta24-RGD, adenovirus | I.T. | 10^7–1×10^11 VP | S: 19 RT: 20 CT: 19 BEV: 6 |
OS, PFS |
| Subgroup | No. of studies | Mean, months | 95% CI | P value between subgroups | heterogeneity within subgroups | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2 (%) | P value | |||||
| Study Phase | 0.21 | |||||
| Phase I | 15 | 12.50 | 10.31, 14.70 | 88 | < 0.01 | |
| Phase I/II | 2 | 10.40 | 8.07, 12.74 | 100 | < 0.01 | |
| Phase II | 5 | 16.35 | 8.80, 23.89 | 100 | < 0.01 | |
| Diagnose | < 0.01 | |||||
| ND | 2 | 18.44 | 15.95, 20.93 | 0 | 0.96 | |
| Recurrent | 20 | 11.82 | 10.07, 13.57 | 97 | < 0.01 | |
| Administration | 0.53 | |||||
| I.T. | 20 | 12.57 | 10.71, 14.44 | 97 | < 0.01 | |
| I.V. | 2 | 10.45 | 4.16, 16.74 | 50 | 0.16 | |
| Viral family | 0.25 | |||||
| ADV | 7 | 14.31 | 11.17, 17.45 | 83 | < 0.01 | |
| HSV | 7 | 12.16 | 8.53, 15.79 | 99 | < 0.01 | |
| Reovirus | 3 | 11.27 | 5.91, 16.63 | 33 | 0.22 | |
| Poliovirus | 2 | 10.37 | 5.20, 15.54 | 78 | 0.03 | |
| NDV | 1 | 8.32 | 5.10, 11.54 | / | / | |
| Measles virus | 1 | 11.60 | 9.22, 13.98 | / | / | |
| Parvovirus | 1 | 13.5 | 8.91, 18.15 | / | / | |
| Subgroup | No. of studies | Mean, months | 95% CI | P value between subgroups | heterogeneity within subgroups | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I2 (%) | P value | |||||
| Study Phase | 0.68 | |||||
| Phase I | 13 | 4.06 | 3.01, 5.12 | 80 | < 0.01 | |
| Phase I/II | 4 | 3.91 | 0.30, 8.12 | 94 | < 0.01 | |
| Phase II | 1 | 4.70 | 3.69, 5.71 | 95 | < 0.01 | |
| Diagnose | 0.05 | |||||
| ND | 2 | 6.98 | 3.71, 10.25 | 54 | 0.14 | |
| Recurrent | 16 | 3.54 | 2.61, 4.47 | 96 | < 0.01 | |
| Administration | 0.06 | |||||
| I.T. | 16 | 3.59 | 2.66, 4.51 | 96 | < 0.01 | |
| I.V. | 2 | 9.10 | 3.36, 14.84 | 60 | 0.12 | |
| Viral family | 0.25 | |||||
| ADV | 6 | 5.30 | 3.56, 7.05 | 70 | < 0.01 | |
| HSV | 6 | 2.99 | 1.42, 4.56 | 97 | < 0.01 | |
| Reovirus | 3 | 2.98 | 1.33, 4.63 | 62 | 0.07 | |
| NDV | 1 | 12.64 | 6.29, 18.99 | / | / | |
| Measles virus | 1 | 3.40 | 1.77, 5.03 | / | / | |
| Parvovirus | 1 | 2.69 | 1.77, 3.61 | / | / | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





