1. Introduction
The dynamics of even the simplest lasers are intimately connected to the fundamental models of nonlinear systems, linking them to a wide range of phenomena observed in various fields such as physics, engineering, and other scientific disciplines. From weather patterns to economic, chemical, and biological systems, chaotic dynamics appear to dominate [
1]. Unlike these more complex systems, lasers are relatively simple, and uniquely, controlling their degrees of freedom is possible. Historically, the first experimental evidence of chaotic behavior was observed in laser physics [
2], particularly in single-mode CO
2 lasers [
3,
4]. Studies of laser dynamics not only offer practical insights but also contribute to a broader understanding of complex yet unresolved phenomena. From the perspective of nonlinear dynamics, laser research presents clear advantages over the investigation of various physical phenomena, such as neuron dynamics [
5,
6,
7], electronics, optoelectronics, potentially population dynamics [
8,
9,
10], as well as epidemiological models [
11]. Another advantage of studying lasers is that the number of degrees of freedom, such as the number of modes, can be easily controlled. In laser research, the key parameters are typically well-known and controllable, and the experimental conditions are well-defined.
From a theoretical perspective, studying a specific laser system involves solving differential equations analytically or, more commonly, numerically for a wide range of initial and experimental conditions. This process often generates an overwhelming amount of data, making it challenging to understand the system’s behavior fully. As a result, techniques or methods to reduce the information or the number of degrees of freedom are essential, ensuring that the core properties of dynamic evolution are retained. Experimentally, measuring or analyzing the complete temporal evolution of all the dynamic variables in a laser is typically impossible. Only partial information is recorded, which must still capture the essential dynamic characteristics of the system. In recent years, dynamic exploration of lasers has primarily focused on reduced state variables, especially optical intensity [
1]. However, there has been limited attention to studying laser dynamics using the experimental state observer of the laser’s population inversion, which accounts for all state variables. Investigating the population inversion in laser models provides a way to explore chaos experimentally and draw comparisons with other well-known nonlinear systems, as discussed by Sprott [
12], Rössler [
13], Chen [
14,
15,
16], Chua [
17,
18], and Lorenz [
19]. In 1975, Haken [
20] demonstrated that the Lorenz model is analogous to a laser, thereby linking their dynamics.
On the other hand, state observers are commonly employed in control systems to estimate unmeasured states based on available measurements. Various methodologies have been developed for both linear and nonlinear systems. In linear systems, least squares methods can be utilized to design observers. More recent studies have concentrated on observers for uncertain nonlinear systems, employing Lyapunov stability criteria and linear matrix inequalities [
21]. Critical factors in observer design include stability, convergence, and robustness against measurement noise and model uncertainties. Observers can enhance the performance of control systems by providing more precise state estimates for feedback control.
Observers have been applied across a wide range of applications, such as in walking robots [
22], machine vision [
23,
24], power systems [
25], and electric motors [
26,
27]. Nonlinear observer designs include Luenberger-type observers [
28] and methods inspired by sliding mode control [
23,
24].
On the other hand, the Luenberger observer, originally designed for linear systems, has been extended to nonlinear systems in various ways. Researchers have proposed distributed Luenberger observers for networked systems [
29] and developed observers for specific applications like robot manipulators [
30]. Some approaches combine state and parameter estimation [
31], while others focus on existence conditions and dimensionality of Kazantzis-Kravaris/Luenberger observers [
32,
33]. Nonlinear extensions include the Luenberger-like observer for continuous-time systems [
28] and the extended Luenberger observer for multivariable systems [
34]. Numerical investigations have been conducted for infinite-dimensional vibrating systems [
35]. These extensions have broadened the applicability of Luenberger-type observers to a wide range of nonlinear systems, offering improved state estimation capabilities and addressing challenges such as observability and convergence in various contexts.
This work presents the design of a Luenberger state observer for the unmeasurable variable of a Multistable Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser (Population inversion). The aim is to design neural identifiers and controllers that can be applied in real-time in future works.
The sections of this paper are organized as follows: in
Section 2, the theoretical model of the Multistable Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser and normalized equations are presented;
Section 3 presents the State Observer Design;
Section 4 shows the simulation results; the experimental setup and the experimental results are given in
Section 5; discussion, conclusion and some remarks about the application of state observer are drawn in
Section 6.
2. Laser Model
The operation of a laser in a single emission mode is governed by three coupled equations. The key state variables are the optical field, population inversion, and polarization, each of which decays at different time scales. When one of these variables dominates, it relaxes quickly and adiabatically adjusts to the other variables, reducing the number of equations required to describe the laser.
Lasers where both population inversion and polarization decay rapidly compared to the optical field are categorized as class A lasers. In contrast, lasers where only the polarization relaxes quickly are known as class B lasers, while those where all three variables have similar relaxation rates are referred to as class C lasers. Class A lasers typically have a single constant output solution. Class B lasers exhibit energy oscillations between the optical field and population inversion, leading to relaxation oscillations. Class C lasers can display undamped periodic or non-periodic (chaotic) pulsations in their laser emissions. Furthermore, class B lasers can also exhibit periodic or chaotic dynamics if influenced externally, such as through parameter modulation. Solid-state and semiconductor lasers are examples of class B lasers. The semiconductor laser is modeled by the Lang and Kobayashi (LK) model [
36]. The LK equation describes the complex dynamics of these lasers through the electric field
E and population inversion (electron-hole pairs)
N within the laser. Due to their rapid chaotic dynamics, these lasers have been considered for cryptographic applications in secure communication systems [
37,
38,
39,
40,
41].
From a nonlinear dynamics perspective, rare-earth-doped fiber lasers with external modulation, such as solid-state, semiconductor, and gas lasers with electric discharge (e.g., CO2 and CO lasers), fall under the category of class B lasers [
42]. In these systems, polarization is adiabatically eliminated, and the dynamics are described by two rate equations for the optical field and population inversion. Despite extensive research on complex laser dynamics, the nonlinear behavior of erbium-doped fiber lasers (EDFLs) has only recently been explored. The dynamic characteristics of these lasers closely resemble those of other class B lasers, with various chaotic motion scenarios being identified in EDFLs [
43].
2.1. Complete EDFL Model
The dynamics of the EDFL studied here are modeled using two differential equations, known as power-balance equations, which incorporate excited state absorption (ESA). For erbium ions, this occurs at a wavelength of 1.5
m. The model averages the population inversion of the EDFL and includes key factors characteristic of fiber lasers, such as ESA at the laser emission wavelength and the depletion of the pump wave as it propagates through the doped fiber. These factors lead to undamped natural oscillations in the laser, which have been experimentally observed in setups without external modulation [
44,
45].
The power-balance equations describe the intracavity laser emission
P (defined as the sum of the intensities of the counter-propagating waves inside the cavity, measured in
) and the averaged population
N of the upper laser level 2 (a dimensionless variable, but considering
), as follows:
The system of equations (
1) has been widely applied in previous studies [
44,
46,
47]. In these equations,
L denotes the length of the erbium-doped fiber (EDF), and
represents the photon lifetime within the cavity, where
is the length of the intra-cavity tails of the fiber Bragg grating (FBG) couplers. The variable
P corresponds to the intracavity laser emission, with its value initially set as an initial condition.
The other parameters in equation (
1) include
, a factor that accounts for the match between the laser’s fundamental mode and the erbium-doped core volumes within the active fiber. Here,
is the fiber core radius, and
is the radius of the fundamental fiber mode. The parameter
represents the small-signal absorption of the erbium fiber at the laser emission wavelength.
denotes the total number of erbium ions in the active fiber, while
N is defined as:
where
is the population of the upper laser level 2, and
is the refractive index of a "cold" erbium-doped fiber core. The coefficient for the ratio between the excited-state absorption (ESA)
and the ground-state absorption cross-sections at the laser wavelength, expressed as
and
, considering that the cross-section of the return stimulated transition
has nearly the same intensity. The parameter
represents the intra-cavity losses at the threshold, where
corresponds to the non-resonant fiber loss, and
R defines the reflection coefficient of the FBG couplers. Additionally,
represents the spontaneous emission into the fundamental laser mode, where
is the lifetime of erbium ions in the excited state 2, and
is the laser wavelength. Finally, the pump power
is defined as
where
denotes the pump power at the fiber input, and
is the ratio of the absorption coefficients of the erbium fiber at the pump wavelength
and the laser wavelength
. This study set the laser spectrum width to
of the erbium luminescence spectral bandwidth.
Additionally, it is important to mention that the system of equations (
1) describes the dynamics of the EDFL without considering modulation. However, a harmonic modulation of
is introduced as
where
and
are the modulation depth and frequency, respectively, and
is the pump power without modulation at
.
The following parameter values were used for the numerical implementation of the results presented in this study, consistent with those in previous works [
44].
Table 1.
Parameters used in numerical simulations.
Table 1.
Parameters used in numerical simulations.
| Parameter |
Value |
|
Parameter |
Value |
|
Parameter |
Value |
| L |
70 cm |
|
|
1.45 |
|
|
cm |
|
8.7 nm |
|
|
20 cm |
|
|
cm |
The experimentally measured value of was slightly higher than cm, as predicted by the formula for a step-index single-mode fiber: . In this expression, the parameter V is linked to the numerical aperture and by , while the values of and yield .
The coefficients that describe the resonant absorption characteristics of the erbium-doped fiber at the emission and laser wavelengths, directly measured from a heavily doped fiber with an erbium concentration of 2300 ppm, are listed in
Table 2.
By applying the specified values to the system of equations (
1), the generated wavelength
cm (
J) is experimentally observed, with the peak reflection coefficients of both FBGs aligned at this wavelength. The pump parameters are expressed in terms of the excess above the laser threshold
, where
, and the threshold pump power is defined as follows
the threshold population of level 2 is defined as
with the pump beam radius, for simplicity, assumed to be the same as that of the generated beam (
).
2.2. Normalized Equations of EDFL
To synthesize and generalize the laser model, we modified the complete system (
1) into the next compact expression
the changes have been made in the variables:
and in the parameters:
The variable
represents the normalized laser intensity, while
corresponds to the population inversion. The parameter
denotes the pump power, and the pump modulation,
, is given by Equation (
2).
The values of the parameters used in the simulations are listed in
Table 3 [
48].
3. State Observer Design
Normalized equations of EDFL are given by
where
=
,
=
and
. These equations are represented in the general form
For system (
16), the following state observer is proposed
where
is the estimated state of
and
is the output from state observer,
L is a constant parameter. Defining
, the following dynamic error system results
For system (
15), Eq. (
17) becomes
For the purpose of this work, the state observer is designed for the state variable population investment (), given that in real time the variable cannot be measured because the electronic equipment does not exist to carry out this measurement.
4. Simulation Results
This section shows the simulation results of the estimation of the variable of the EDFL, equations (
15) through the state observer, equations (
19), the simulation in Matlab/Simulink has been implemented.
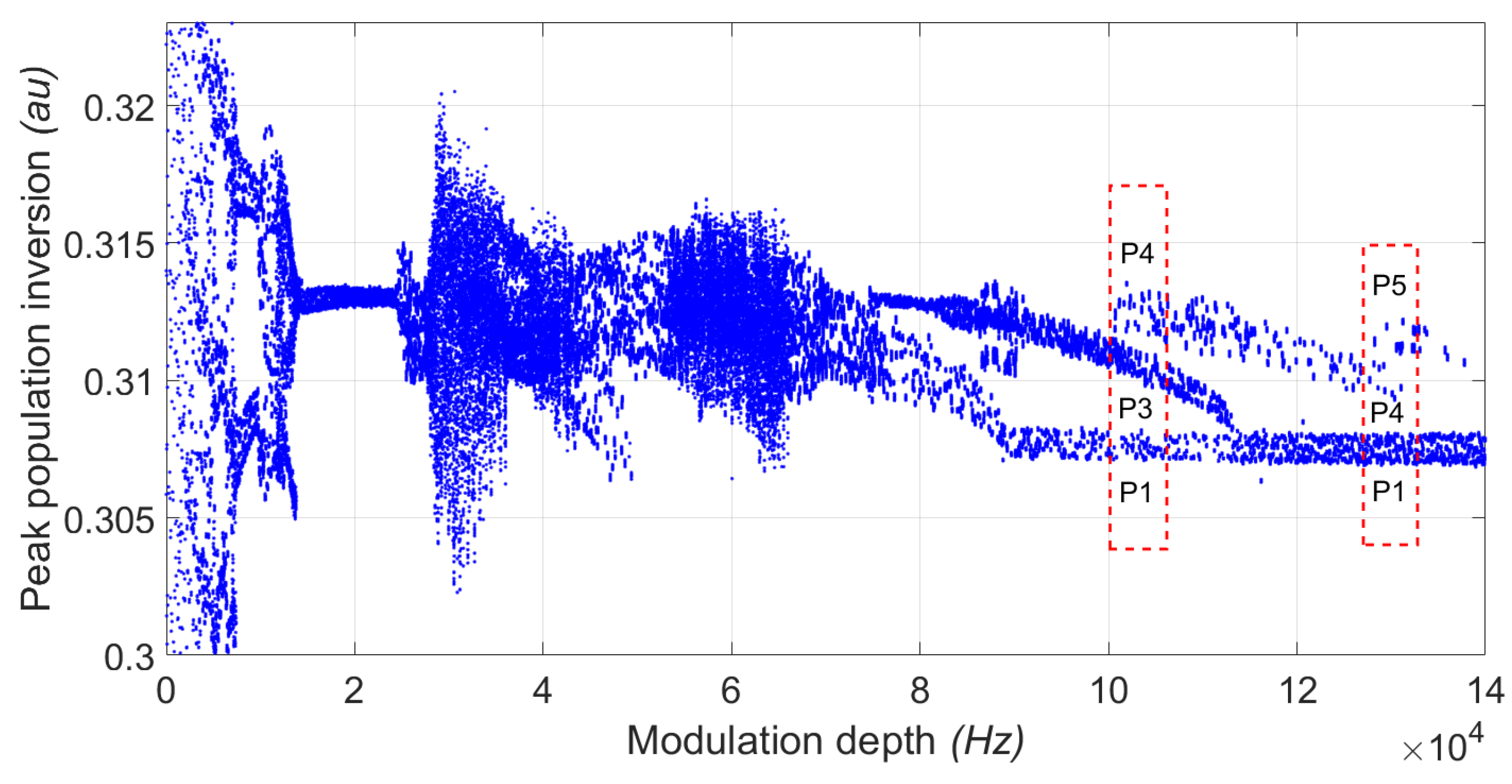
Figure 1 shows an extract of the numerical laser intensity bifurcation diagram, which was obtained through the time series of the multistable region corresponding to the coexistence of attractors, shown by (
,
,
,
), for a modulation frequency of 80 Hz. The complete bifurcation diagram can be consulted in the work [
49].
The parameters used in the mathematical model of the EDFL and numerical state observer are shown in
Table 2, in addition, the gains used for the state observer are
and
.
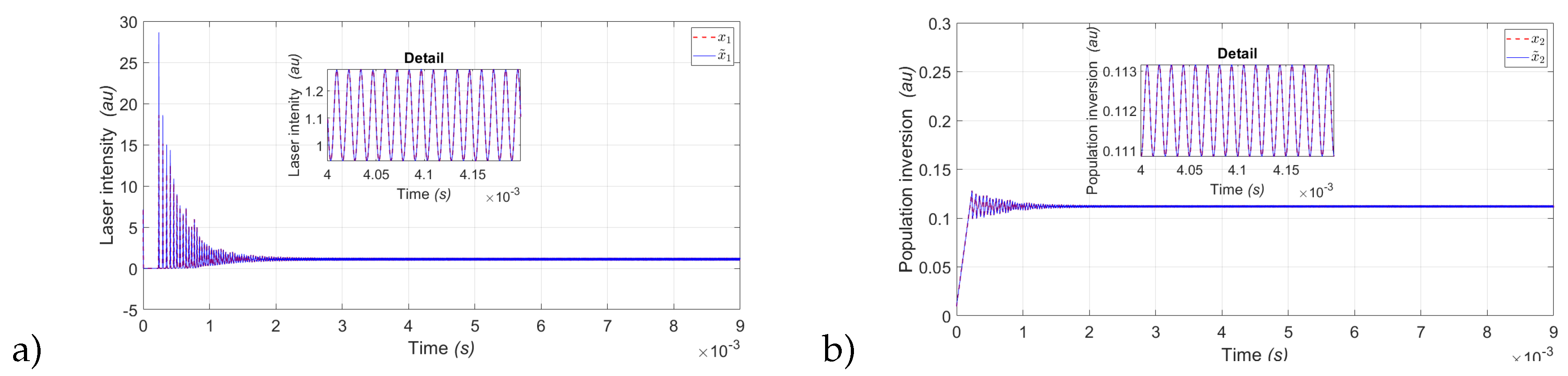
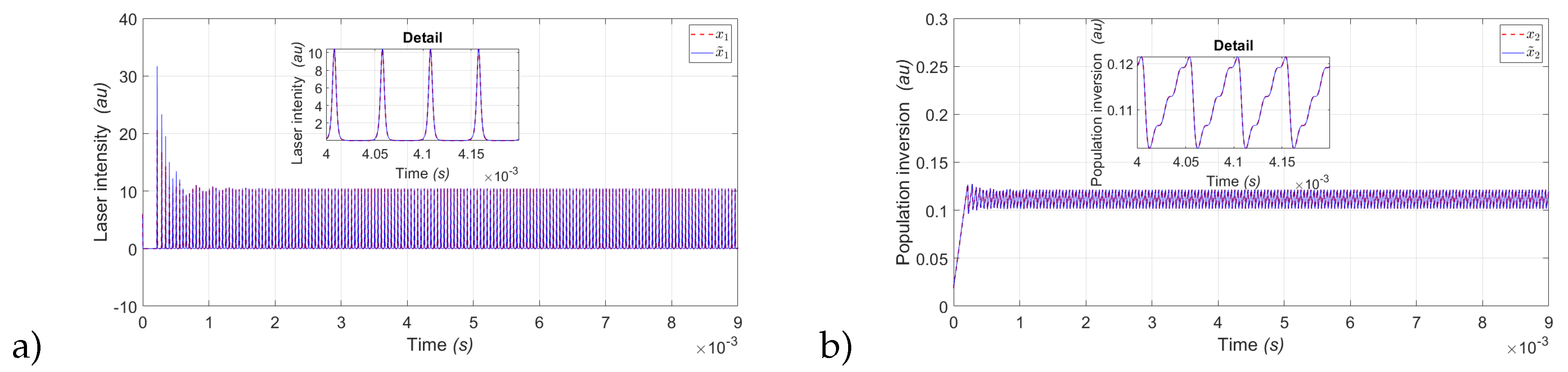
Figure 2 shows the simulation results of the state observer for the EDFL state variables. Since the laser states in simulation can be measured, the observation of both variables for different periods is presented (
,
,
, and
).
Figure 2a) shows the estimation of the Laser intensity (
) represented by the variable (
), where can see the convergence of the observer and
Figure 2b) shows the estimation of the Population inversion (
) represented by the variable (
), both variables are for period
.
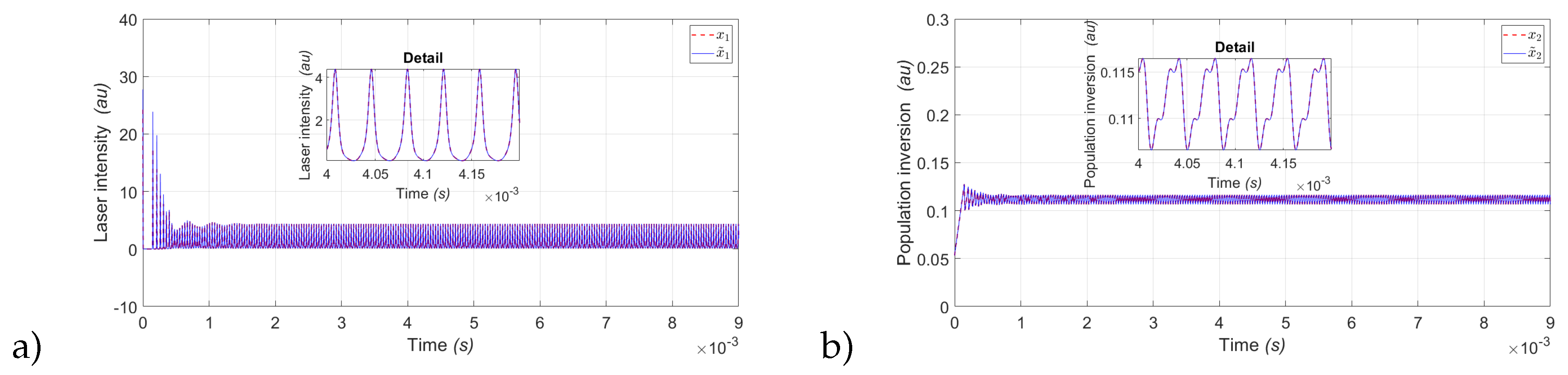
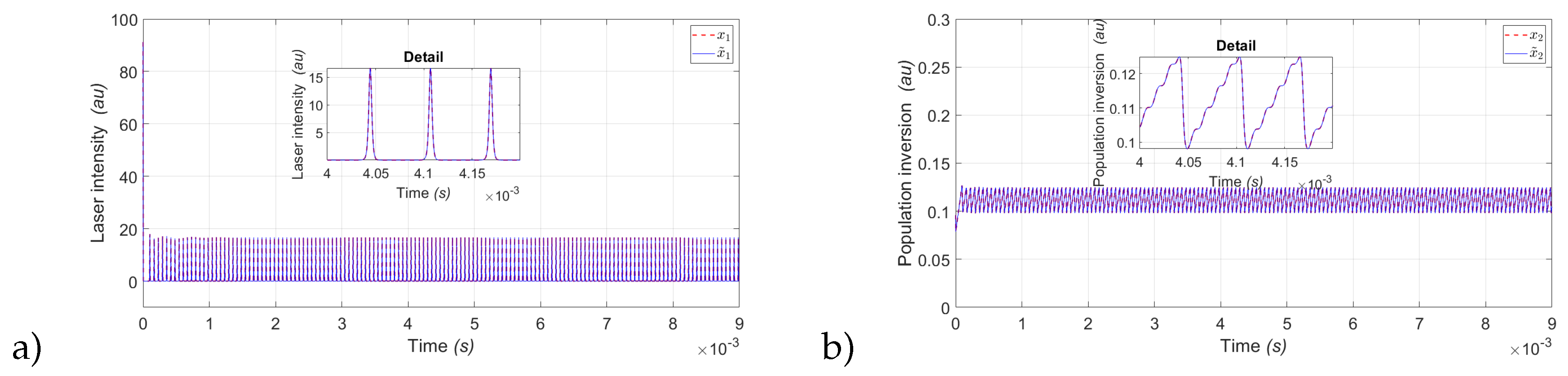
In the same way as
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5 show the estimation of the laser intensity (
) represented by the variable (
) and the estimate of the Population inversion (
) represented by the variable (
) of the periods
,
and
.
The effectiveness of the state observer depended on the correct selection of parameters and the design of the observer to ensure that the observer could provide accurate and reliable estimates. In addition, the experimental implementation of the state observer must consider aspects such as accuracy and effectiveness, as shown in the next section.
5. Experimental Setup
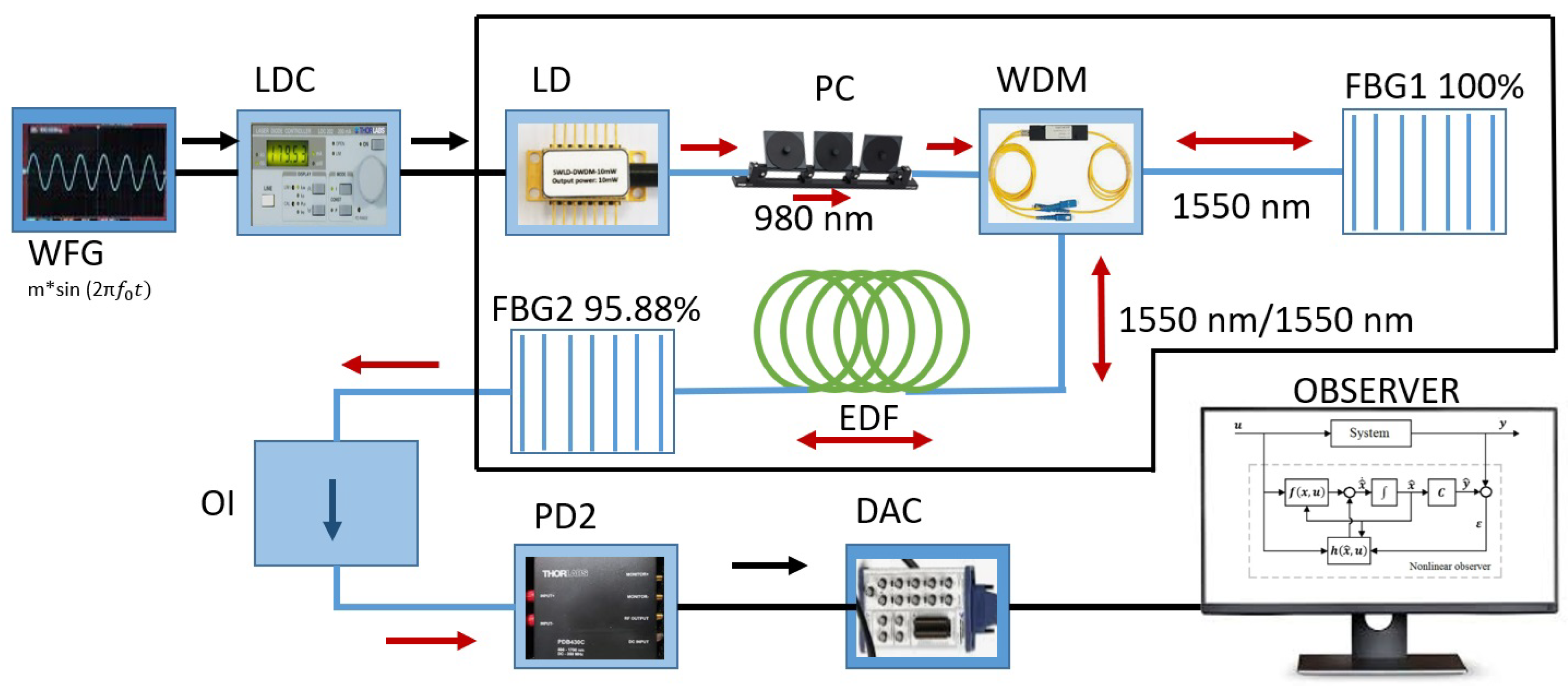
The implementation of the EDFL in the laboratory is shown in
Figure 6. This laser has a 6.5 m resonator with a 70-centimeter erbium fiber active region, made of fiber with a core diameter of 2.7 micrometers, including a wavelength division multiplexing coupler (WDM-WD9850FD) and two fiber Bragg gratings (FBG1 and FBG2). The FBGs have reflectivities of 100% and 95% for use at a
nm. The optical components are made with single-mode fiber (SMF-28) with a cladding diameter of 200 micrometers. The EDFL is pumped using a 977-nm laser diode (LD-BL976PAG500) through a polarization controller (PC), by using a laser diode controller (LDC-ITC510). During the experiments, the diode current was set to 145.5 mA, having an EDFL threshold at 110 mA. The system was modulated with a sinusoidal signal
from a periodic function generator (WFG-AFG3102) applied to the pump current. An optical isolator (OI) prevents back-reflections into the laser cavities. The optical output signal
from the FBG2 fiber Bragg grating is directed to the PD2 photodiode, which is connected to a data acquisition card (DAC) NI-BNC-2110 for subsequent analysis. Data is collected using the DAC.
5.1. Experimental Bifurcation Diagrams and Time Series
Using periodic modulation
, where
m is the modulation amplitude and
represents the frequency applied to the diode pump current via a periodic function generator (WFG). This EDFL has multistable behavior, having up to four periodic states, defined as Period 1 (P1), Period 3 (P3), Period 4 (P4), and Period 5 (P5) [
44]. The output signal of the laser was detected by a photodiode (PD2) and recorded through a data acquisition card (DAC) (
Figure 6).
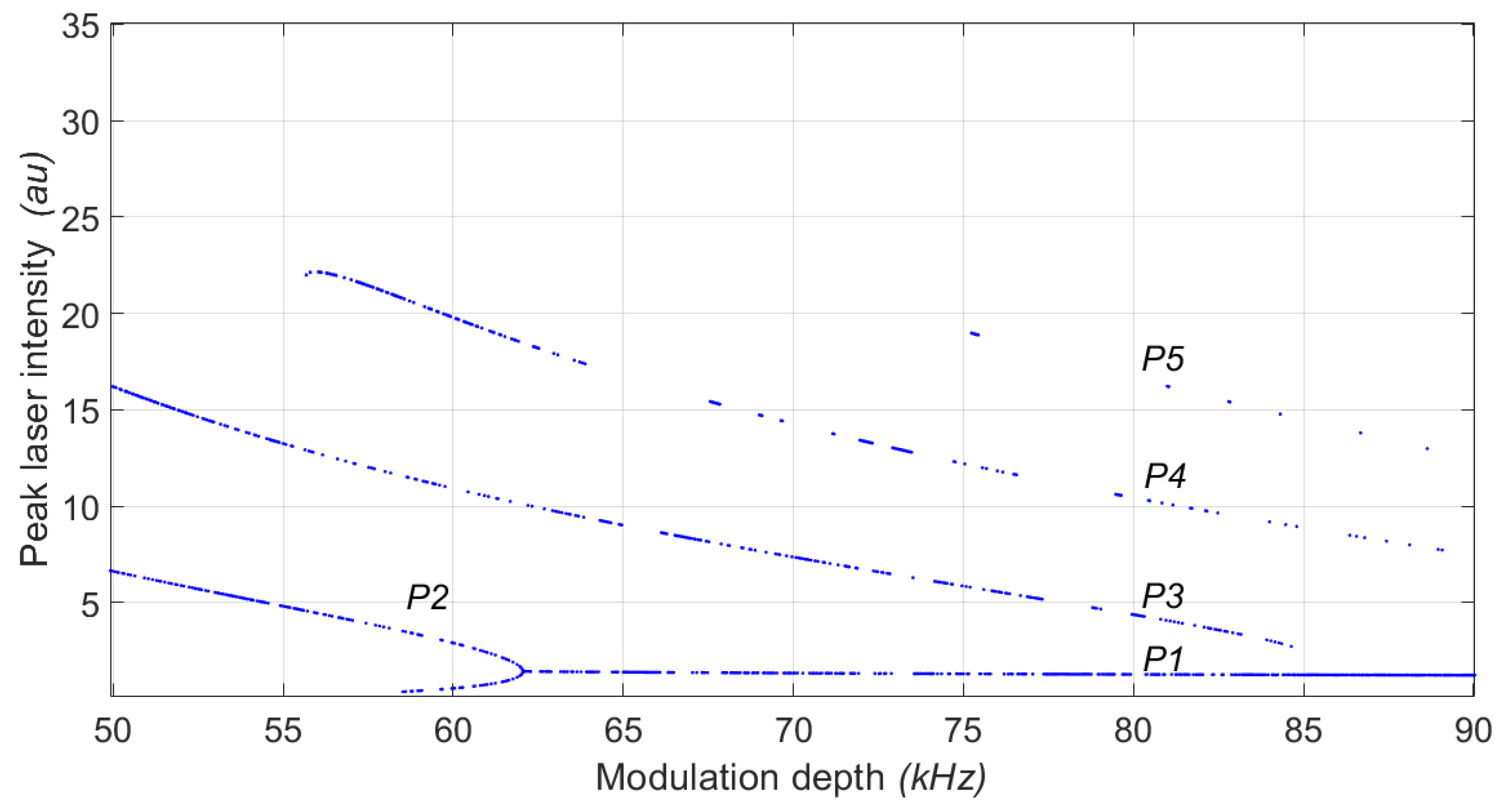
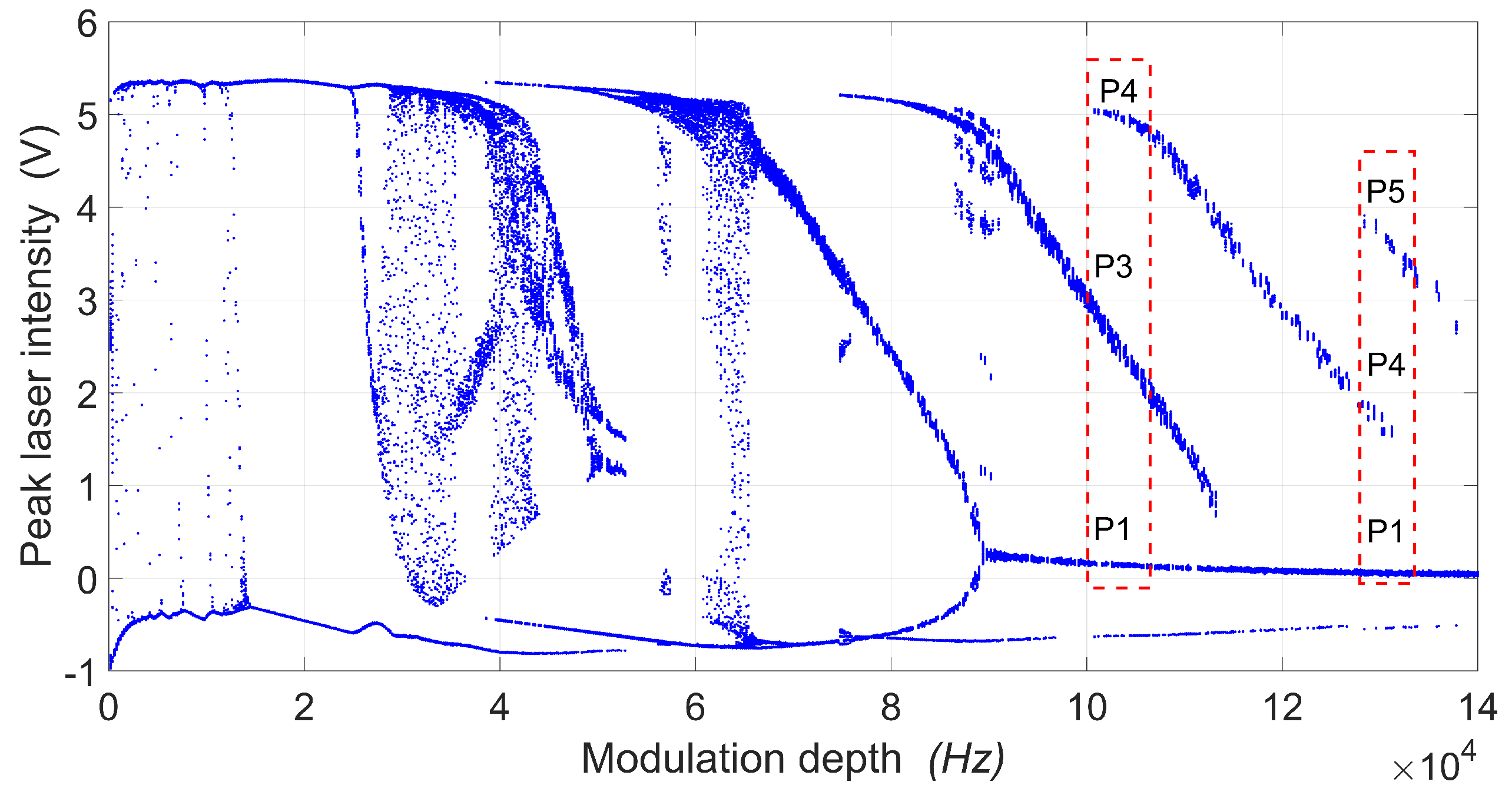
Figure 7 shows a bifurcation diagram (BD) constructed by randomly changing the system’s initial conditions by turning off and on the WFG ten times for
. The bifurcation diagram can show the system evolution corresponding to different dynamic regimes through saddle-node bifurcations when increasing the control parameter
. The attractor’s coexistence is present in different BD regions. We can see that in the range 100 kHz
kHz, P1, P3 and P4 coexist, and in the range 125 kHz
kHz, P1, P4 and P5 also coexist. The local maximum intensity in the different regimes with longer periods is significantly higher than in P1.
This section presents the experimental results for estimating the unmeasurable variables of the EDFL using the state observer equations (
19). The parameters used in the state observer equations (
19) are listed in
Table 2. In addition, the gains of the experimental state observer are
and
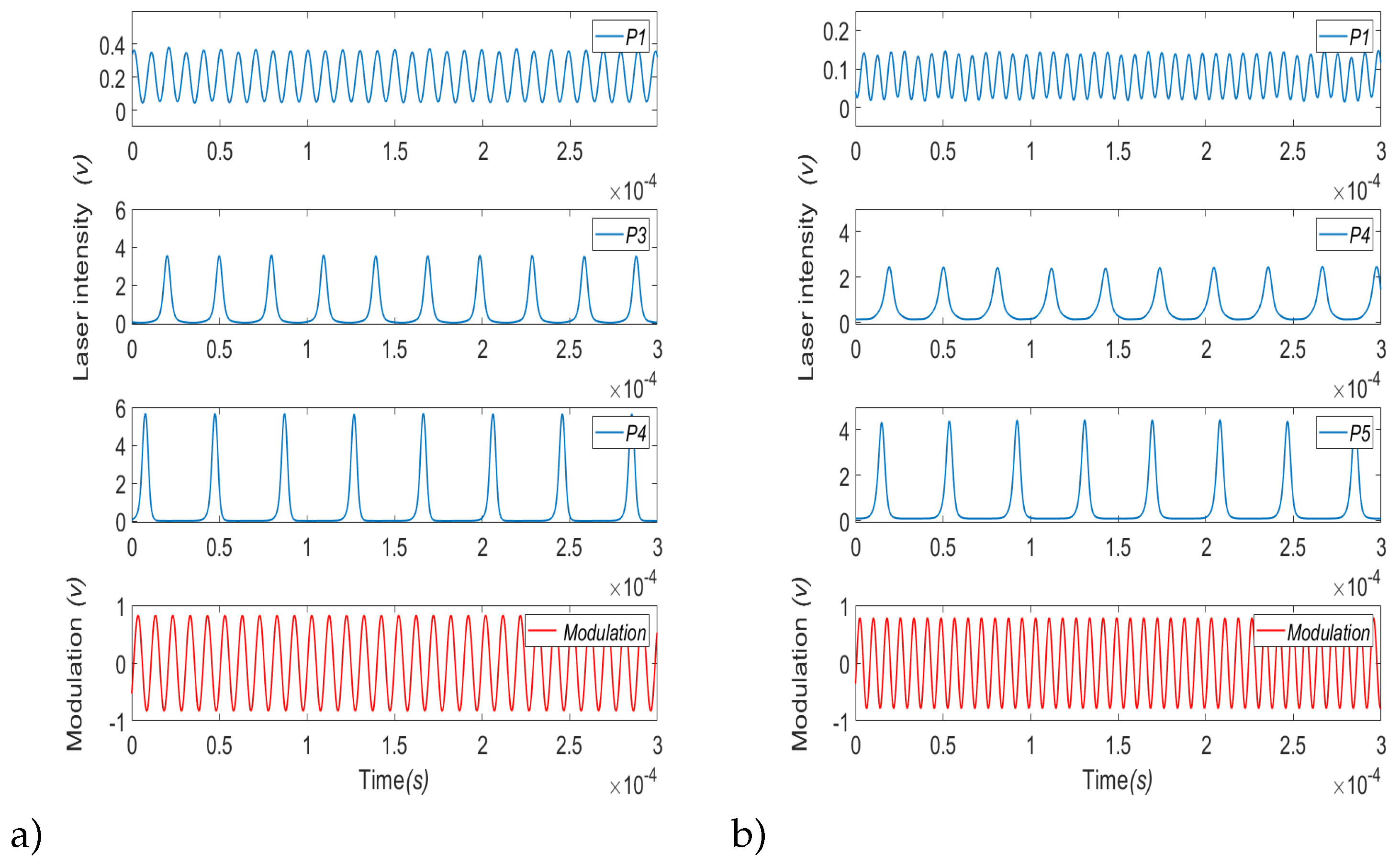
. The time series of the laser intensity corresponding to different coexisting periodic regimes are shown for a modulation frequency of
Hz and amplitude
in
Figure 8 a) and for a modulation frequency of
Hz and amplitude
in
Figure 8 b) is shown. A modulation signal
is shown in the bottom panel of both Figures.
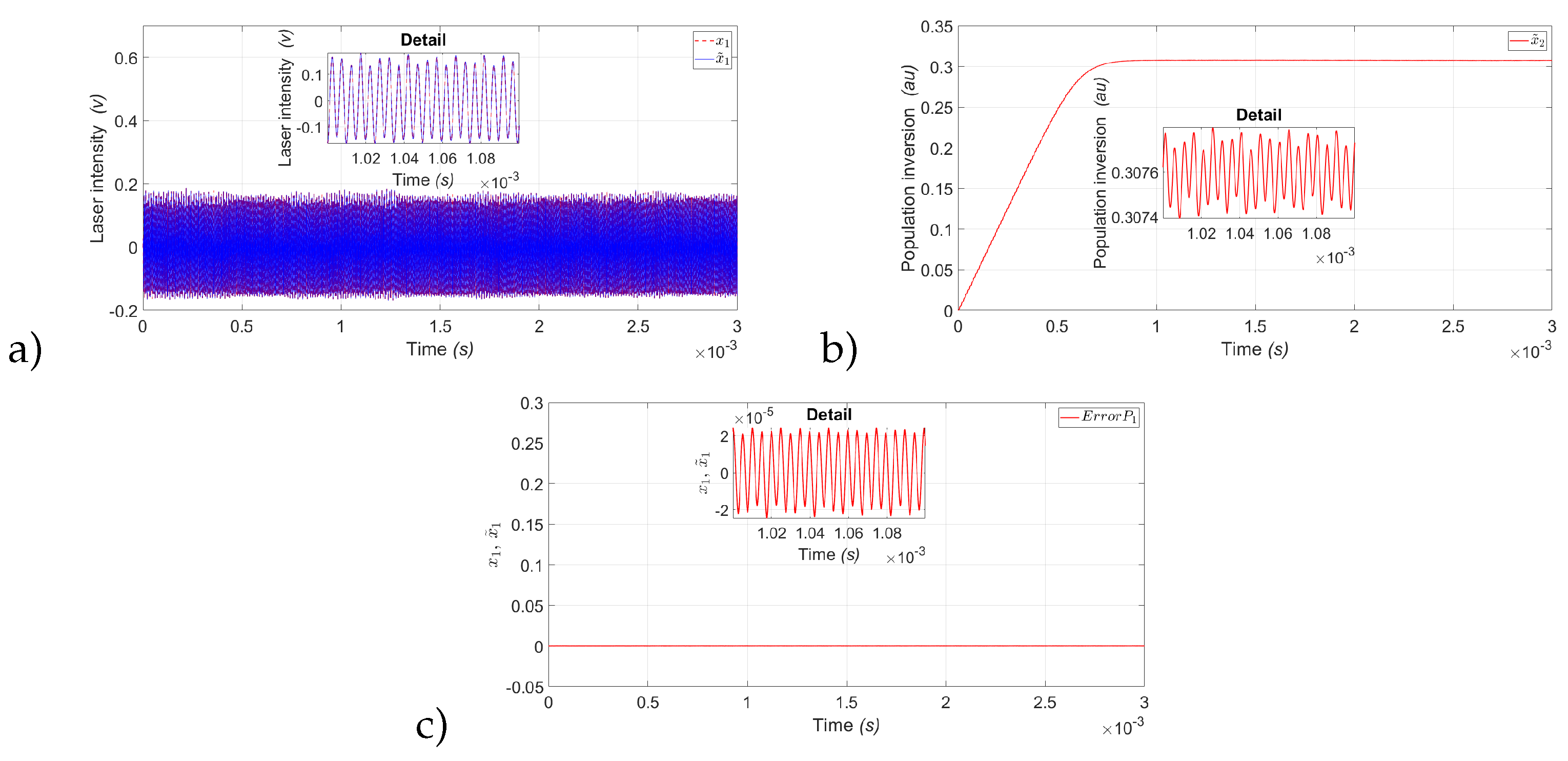
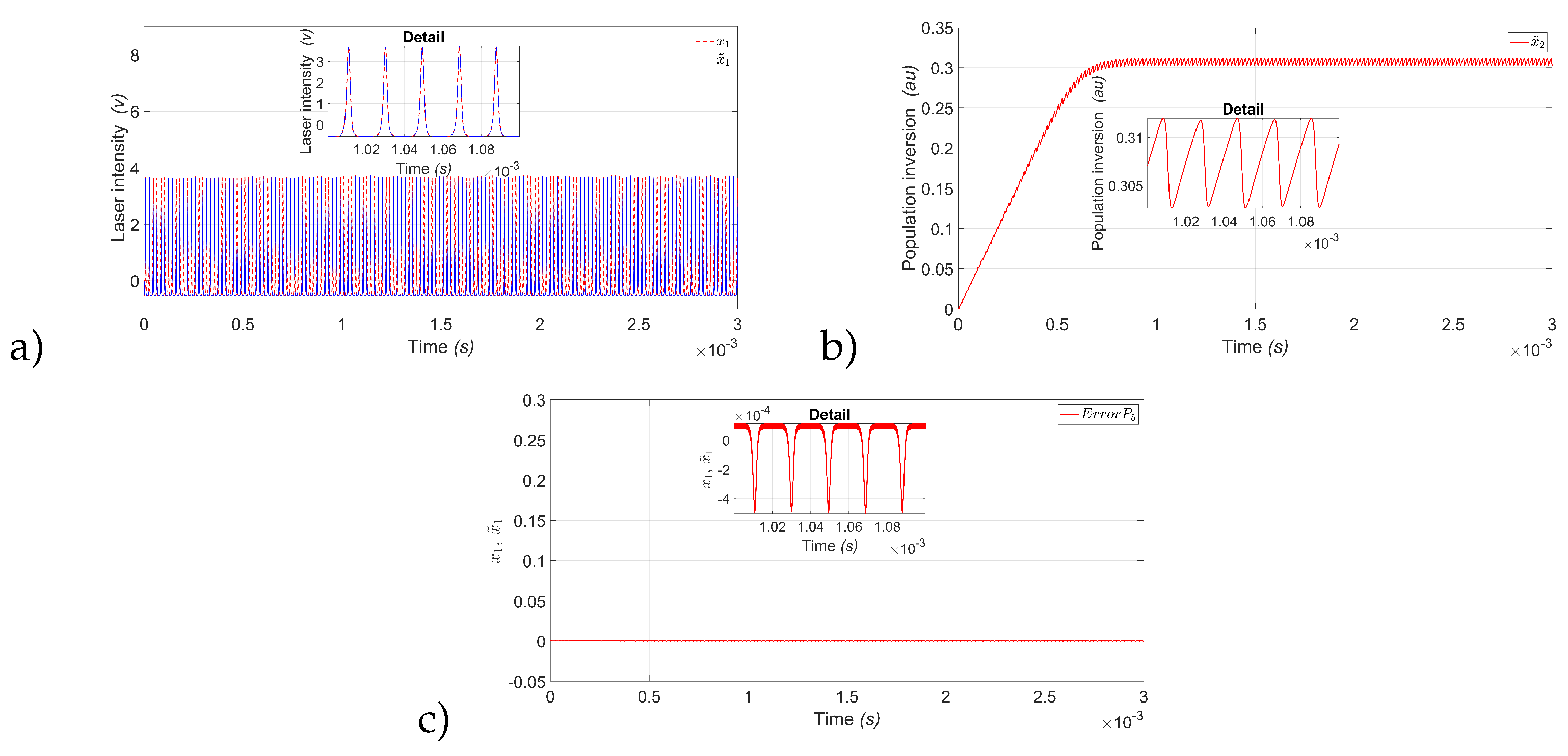
Figure 10 shows the experimental results of the state observer for the EDFL state variables for
.
Figure 10a) shows the estimation of the Laser intensity (
) represented by the variable (
), although the variable can be measured physically, the procedure is carried out to guarantee good estimation of the second non-measurable variable of EDFL. Figure.
Figure 10b) shows the estimation of the Population inversion (
), and
Figure 10c) shows the estimation error between
and
where can see that the error is very close to zero, which guarantees the good estimate of the population inversion variable.
Figure 9.
Experimental bifurcation diagram for Population inversion ().
Figure 9.
Experimental bifurcation diagram for Population inversion ().
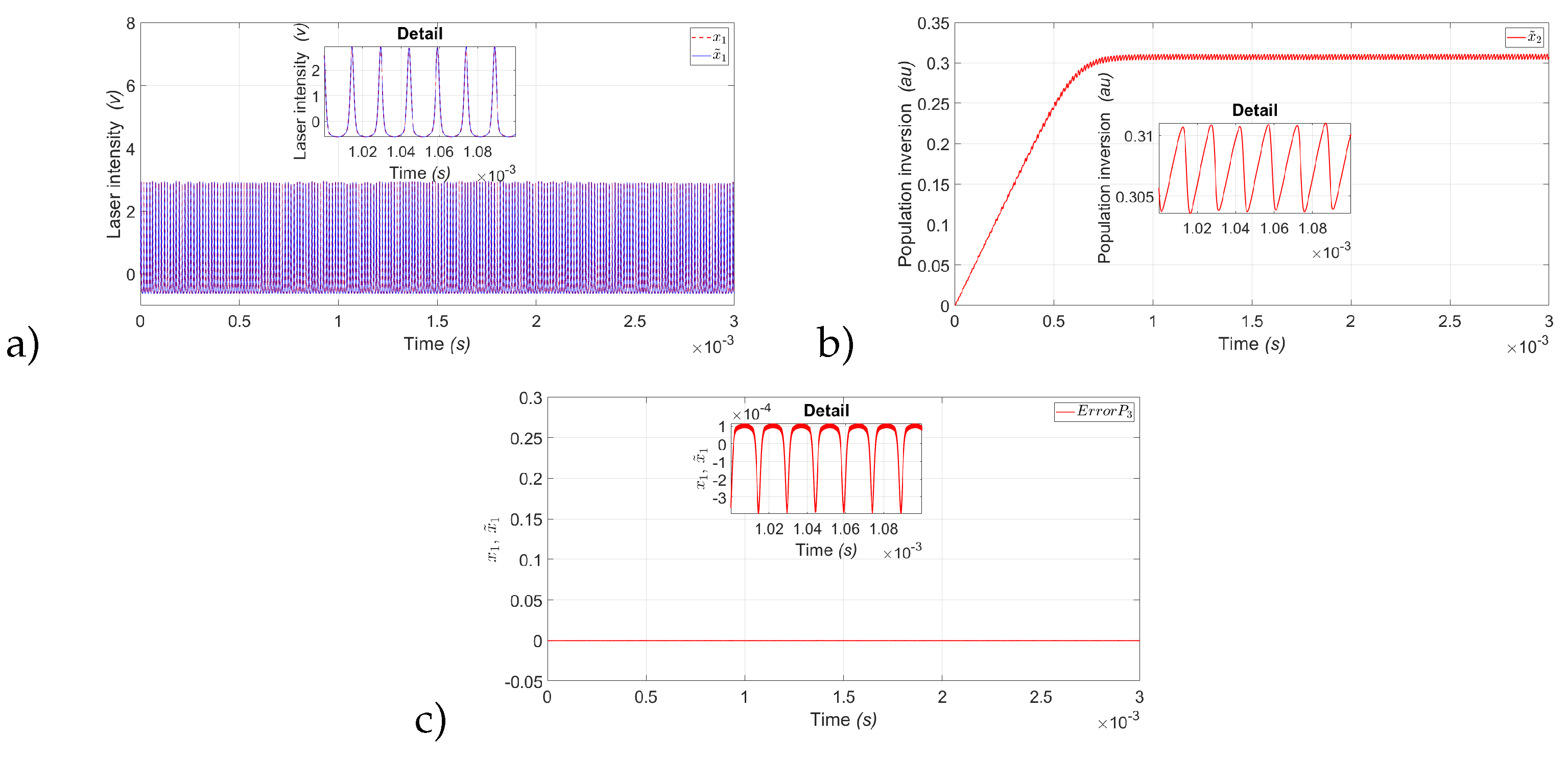
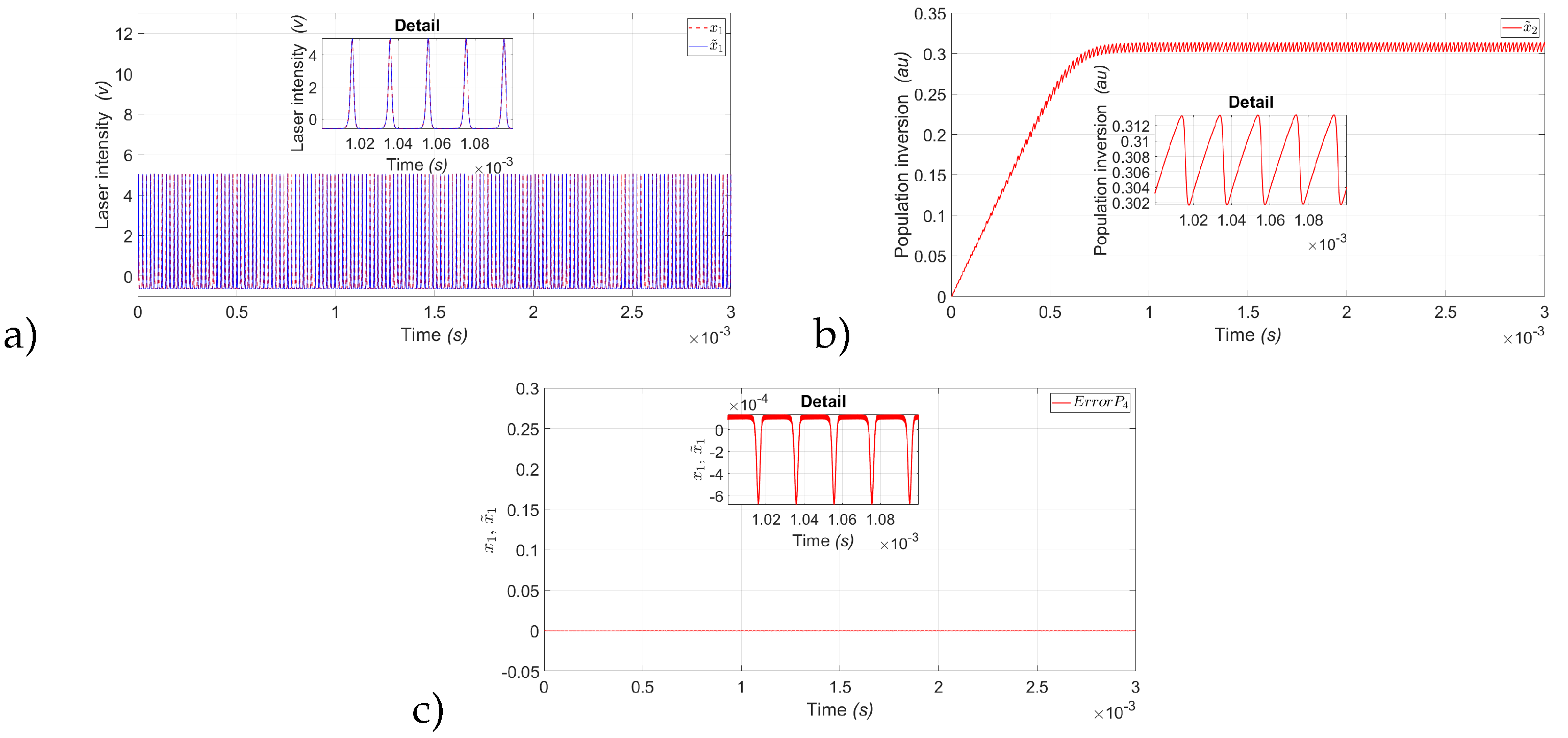
In the same way as
Figure 10,
Figure 11 and
Figure 12 show the estimation of the laser intensity (
) represented by the variable (
) and the estimate of the Population inversion, represented by the variable (
) of the periods
,
and
.
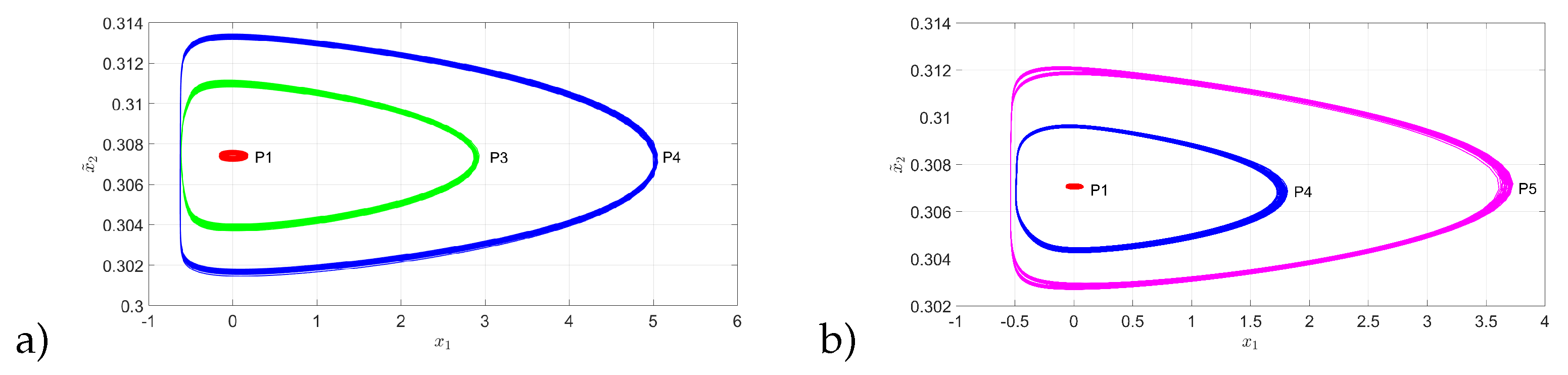
5.2. Experimental Phase space
Figure 14a) shows the phase space for periods P1, P3, and P4 of a multistable region, shown in
Figure 7a) with a red box at a modulation frequency of
kHz. Similarly, for
Figure 14, the phase space of the periods P1, P4, and P5 of a multistable region is observed in
Figure 7 with a red box at a modulation frequency of
kHz. It is worth mentioning that although the periods are at different frequencies, the state observer was able to estimate each period of the multistable regions.
5.3. Mean Square Error
The results of
Table 4 show that the MSE is very small for any of the periods (P1, P3, P4 and P5), which guarantees a good estimate of the measurable laser intensity variable (
), which leads to a good estimate of the (EDFL) population inversion (
).
6. Conclusions
This paper presents the design and implementation of a nonlinear state observer to identify the non-measurable variables of an erbium-doped fiber laser (EDFL). The experimental identification of the population inversion enabled the reconstruction of the laser dynamics and the construction of a state-space model using the measurable variable (laser intensity) and the observed variable (population inversion). The mean square error (MSE) analysis confirms the accurate observation of the non-measurable variable. Furthermore, the population inversion bifurcation diagram was constructed, revealing that the multistable regions of the population inversion align with those of the laser intensity bifurcation diagram. To our knowledge, this is the first report of experimental results using a state observer for the population inversion variable in an erbium-doped fiber laser or any other type of laser. The proposed state observer technique advances the understanding of multistable dynamics in EDFLs and offers potential applications in power enhancement and intra-cavity loss control. This approach contributes significantly to the field of optics and lasers. Finally, the estimation of EDFL state variables by state observer is crucial for effectively implementing advanced controls and improving the overall performance of dynamic systems.
Author Contributions
D.A.M.G.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review, and Editing. D.L.M.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review, and Editing. R.J.R.: Project administration, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—review, and Editing. J.H.G.L.: Project administration, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review, and Editing. G.H.C.: Project administration, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review, and Editing. L.J.O.G.: Validation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review, and Editing. F.S.C.: Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review, and Editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is funded by the "Consejo Nacional de Humanidades, Ciencia y Tecnología (CONAHCYT)" through project PCC-2022/320597.
Acknowledgments
D.A.M.G. acknowledges the support of the CONAHCyT, being benefited with an academic postdoctoral fellowship with application number: 2290436. R.J.R. and F.S.C. thank CONAHCYT for financial support, project PCC-2022/320597.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Stability Analysis
To analyze the stability of the complete system represented by Eq. (
15) and his state observer represented by Eq. (
19), the representation in terms of the observation error is defined as follows
Reducing the terms of the equation (
A1), can be written as
Reducing and factoring in terms of the error, the equation (
A2) can be rewritten as follows
A positive definite Lyapunov candidate function is proposed, as a function of the error
where the derivative of the candidate function can be written as follows
by substituting equation (
A3) in (
A5)
Using the parameters of the
Table 2 for
,
and
; moreover, the maximum amplitudes of the time series for
and
, the corresponding substitutions are made in equation (
A6)
The amplitude values of the time series are absorbed automatically because the parameters of the laser model are big enough. Therefore, the equation (
A7) can be written as follows
On the other hand, equation (
A8) can be written in matrix form, to find the values of L1 and L2 to find the optimal gains that guarantee the stability of the complete system
For the
matrix of equation (
A9) to be positive definite and ensure the stability of the complete system, the following conditions must be met
where the parameters
and
. In this way, the stability of the complete system is guaranteed.
References
- Weiss, C.; Vilaseca, R. Dynamics of lasers(Book). Research supported by Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt, DFG, and DGICYT. Weinheim, Federal Republic of Germany and New York, VCH(Nonlinear Systems. 1991, 1.
- Ricci, L.; Perinelli, A.; Castelluzzo, M.; Euzzor, S.; Meucci, R. Experimental Evidence of Chaos Generated by a Minimal Universal Oscillator Model. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos 2021, 31, 2150205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arecchi, F.; Gadomski, W.; Meucci, R. Generation of chaotic dynamics by feedback on a laser. Physical Review A 1986, 34, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arecchi, F.; Meucci, R.; Gadomski, W. Laser dynamics with competing instabilities. Physical review letters 1987, 58, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, M.R.; Glass, L.; Mackey, M.C.; Shrier, A. Chaos in neurobiology. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics 1983, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastri, B.J.; Nahmias, M.A.; Tait, A.N.; Wu, B.; Prucnal, P.R. SIMPEL: Circuit model for photonic spike processing laser neurons. Optics express 2015, 23, 8029–8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiana-Alsina, J.; Quintero-Quiroz, C.; Masoller, C. Comparing the dynamics of periodically forced lasers and neurons. New Journal of Physics 2019, 21, 103039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volterra, V. Variazioni e fluttuazioni del numero d’individui in specie animali conviventi; Società anonima tipografica" Leonardo da Vinci", 1926.
- Lotka, A.J. Contribution to the theory of periodic reactions. The Journal of Physical Chemistry 2002, 14, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotka, A.J. Analytical note on certain rhythmic relations in organic systems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1920, 6, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, I.B.; Smith, H. Infinite subharmonic bifurcation in an SEIR epidemic model. Journal of mathematical biology 1983, 18, 233–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprott, J.C.; Sprott, J.C. Chaos and time-series analysis; Vol. 69, Oxford university press Oxford, 2003.
- Rössler, O.E. An equation for continuous chaos. Physics Letters A 1976, 57, 397–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Kang, N.; Kong, X.; Chen, G.; Yan, G. On the non-equivalence of Lorenz system and Chen system. arXiv 2009, arXiv:0904.3594. [Google Scholar]
- Čelikovskỳ, S.; Chen, G. On a generalized Lorenz canonical form of chaotic systems. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos 2002, 12, 1789–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, J.; Chen, G. A new chaotic attractor coined. International Journal of Bifurcation and chaos 2002, 12, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T. A chaotic attractor from Chua’s circuit. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems 1984, 31, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, L.; Komuro, M. Matsumoto: The double scroll family. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst 1986, 33, 1072–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Deterministic nonperiodic flow. Journal of atmospheric sciences 1963, 20, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haken, H. Analogy between higher instabilities in fluids and lasers. Physics Letters A 1975, 53, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A. Farhangfar.; R. Shor. State Observer Design for a Class of Lipschitz Nonlinear System with Uncertainties 2020.
- S. Savin.; S. Jatsun.; L. Vorochaeva. State observer design for a walking in-pipe robot 2018.
- Chen, X.; Kano, H. State observer for a class of nonlinear systems and its application to machine vision. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhai, G. State observer for a class of nonlinear systems and its application. Proceedings of the International Conference on Control Applications 2002. [Google Scholar]
- E. Rosolowski.; M. Michalík. Fast identification of symmetrical components by use of a state observer 1994.
- L. Jones.; J. Lang. A state observer for the permanent-magnet 1989.
- Magallón, D.A.; Castañeda, C.E.; Jurado, F.; Morfin, O.A. Design of a Morlet wavelet control algorithm using super–twisting sliding modes applied to an induction machine. 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1–8.
- Ciccarella, G.; Dalla Mora, M.; Germani, A. A Luenberger-like observer for nonlinear systems. International Journal of Control 1993, 57, 537–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K., T.; S., H.; C., D.D. Distributed Luenberger observer design. 2016 IEEE 55th Conference on Decision and Control (CDC). IEEE, 2016, pp. 6928–6933.
- Celani, F. A Luenberger-style observer for robot manipulators with position measurements. 2006 14th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation. IEEE, 2006, pp. 1–6.
- Afri, C.; Andrieu, V.; Bako, L.; Dufour, P. State and parameter estimation: A nonlinear Luenberger observer approach. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 2016, 62, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrieu, V.; Praly, L. On the existence of a Kazantzis–Kravaris/Luenberger observer. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization 2006, 45, 432–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrieu, V.; Praly, L. Remarks on the existence of a Kazantzis-Kravaris/Luenberger observer. 2004 43rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC)(IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37601). IEEE, 2004, Vol. 4, pp. 3874–3879.
- Birk, J.; Zeitz, M. Extended Luenberger observer for non-linear multivariable systems. International Journal of Control 1988, 47, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.D.; Xu, C.Z.; Peng, Y.; Tucsnak, M. On the numerical investigation of a Luenberger type observer for infinite-dimensional vibrating systems. IFAC Proceedings Volumes 2008, 41, 7624–7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.; Kobayashi, K. External optical feedback effects on semiconductor injection laser properties. IEEE journal of Quantum Electronics 1980, 16, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, I.; Liu, Y.; Davis, P. Synchronization of chaotic semiconductor laser dynamics on subnanosecond time scales and its potential for chaos communication. Physical Review A 2000, 62, 011801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanwiggeren, G.D.; Roy, R. Communication with chaotic lasers. Science 1998, 279, 1198–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, S.; Mirasso, C.R. Introduction to the feature section on optical chaos and applications to cryptography. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics 2002, 38, 1138–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsubo, J.; Davis, P. Chaotic optical communication. Unlocking Dynamical Diversity: Optical Feedback Effects on Semiconductor Lasers 2005, pp. 307–334.
- Soriano, M.C.; Ruiz-Oliveras, F.; Colet, P.; Mirasso, C.R. Synchronization properties of coupled semiconductor lasers subject to filtered optical feedback. Physical Review E 2008, 78, 046218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arecchi, F.T.; Harrison, R.G. Instabilities and chaos in quantum optics; Vol. 34, Springer Science & Business Media, 2012.
- Lacot, E.; Stoeckel, F.; Chenevier, M. Dynamics of an erbium-doped fiber laser. Physical Review A 1994, 49, 3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reategui, R.; Kir’yanov, A.; Pisarchik, A.; Barmenkov, Y.O.; Il’ichev, N. Experimental study and modeling of coexisting attractors and bifurcations in an erbium-doped fiber laser with diode-pump modulation. Laser Phys 2004, 14, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar]
- Pisarchik, A.N.; Jaimes-Reátegui, R.; Sevilla-Escoboza, R.; Huerta-Cuellar, G.; Taki, M. Rogue waves in a multistable system. Physical Review Letters 2011, 107, 274101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Cuellar, G.; Pisarchik, A.; Kir’yanov, A.; Barmenkov, Y.O.; del Valle Hernández, J. Prebifurcation noise amplification in a fiber laser. Physical Review E 2009, 79, 036204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esqueda de la Torre, J.O.; García-López, J.H.; Jaimes-Reátegui, R.; Huerta-Cuellar, G.; Aboites, V.; Pisarchik, A.N. Route to chaos in a unidirectional ring of three diffusively coupled erbium-doped fiber lasers. Photonics 2023, 10, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarchik, A.N.; Kir’yanov, A.V.; Barmenkov, Y.O.; Jaimes-Reátegui, R. Dynamics of an erbium-doped fiber laser with pump modulation: theory and experiment. Journal of the Optical Society of America B 2005, 22, 2107–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magallón, D.A.; Jaimes-Reátegui, R.; García-López, J.H.; Huerta-Cuellar, G.; López-Mancilla, D.; Pisarchik, A.N. Control of multistability in an erbium-doped fiber laser by an artificial neural network: A numerical approach. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Bifurcation diagram for numerical laser intensity .
Figure 1.
Bifurcation diagram for numerical laser intensity .
Figure 2.
Simulation results of a state observer for P1: a) Laser intensity red dashed line () and b) Estimated laser intensity blue continuous line ().
Figure 2.
Simulation results of a state observer for P1: a) Laser intensity red dashed line () and b) Estimated laser intensity blue continuous line ().
Figure 3.
Simulation results of a state observer for P3: a) Laser intensity red dashed line () and estimated laser intensity blue continuous line ().
Figure 3.
Simulation results of a state observer for P3: a) Laser intensity red dashed line () and estimated laser intensity blue continuous line ().
Figure 4.
Simulation results of a state observer for P4: a) Laser intensity red dashed line () and b) Estimated laser intensity blue continuous line ().
Figure 4.
Simulation results of a state observer for P4: a) Laser intensity red dashed line () and b) Estimated laser intensity blue continuous line ().
Figure 5.
Simulation results of a state observer for P5: a) Laser intensity red dashed line () and b) Estimated laser intensity blue continuous line ().
Figure 5.
Simulation results of a state observer for P5: a) Laser intensity red dashed line () and b) Estimated laser intensity blue continuous line ().
Figure 6.
Experimental setup of the EDFL. PD2 represents the photodiode, EDF is the erbium-doped fiber, FBG1, and FBG2 are fiber Bragg gratings, LDC is the laser diode controller, LD is the diode pump laser, PC is the polarization controller, WFG is the wave function generator, WDM is the wavelength-division multiplexer, OI denotes the optical isolator, and DAC refers to the data acquisition cards.
Figure 6.
Experimental setup of the EDFL. PD2 represents the photodiode, EDF is the erbium-doped fiber, FBG1, and FBG2 are fiber Bragg gratings, LDC is the laser diode controller, LD is the diode pump laser, PC is the polarization controller, WFG is the wave function generator, WDM is the wavelength-division multiplexer, OI denotes the optical isolator, and DAC refers to the data acquisition cards.
Figure 7.
An experimental bifurcation diagram of the peak intensity of the EDFL as a function of the driving frequency for a fixed modulation amplitude of V is presented. The EDFL demonstrates the coexistence of three periodic attractors: period 1 (P1), period 3 (P3), and period 4 (P4) at a modulation frequency of kHz, as indicated by the red dashed line on the left side; and period 1 (P1), period 4 (P4), and period 5 (P5) at a modulation frequency of kHz, as shown by the red dashed line on the right side.
Figure 7.
An experimental bifurcation diagram of the peak intensity of the EDFL as a function of the driving frequency for a fixed modulation amplitude of V is presented. The EDFL demonstrates the coexistence of three periodic attractors: period 1 (P1), period 3 (P3), and period 4 (P4) at a modulation frequency of kHz, as indicated by the red dashed line on the left side; and period 1 (P1), period 4 (P4), and period 5 (P5) at a modulation frequency of kHz, as shown by the red dashed line on the right side.
Figure 8.
Time series of the laser intensity of the EDFL showing the coexistence of period 1 (P1), period 3 (P3) and period 4 (P4) for a) the modulation frequency
kHz, as indicated by the red dashed line on the left side of
Figure 7, and the coexistence of period 1 (P1), period 4 (P4) and period 5 (P5) for b) modulation frequency
kHz, characterized by the red dashed line on the right side of
Figure 7. In both cases, the lower trace shows the modulation signal
with
V.
Figure 8.
Time series of the laser intensity of the EDFL showing the coexistence of period 1 (P1), period 3 (P3) and period 4 (P4) for a) the modulation frequency
kHz, as indicated by the red dashed line on the left side of
Figure 7, and the coexistence of period 1 (P1), period 4 (P4) and period 5 (P5) for b) modulation frequency
kHz, characterized by the red dashed line on the right side of
Figure 7. In both cases, the lower trace shows the modulation signal
with
V.
Figure 10.
State observer results for P1: a) Experimental laser intensity red dashed line () and estimated laser intensity blue continuous line (). b) Estimated population inversion red continuous line (). c) Estimation error between (), and (); with a modulation frequency kHz.
Figure 10.
State observer results for P1: a) Experimental laser intensity red dashed line () and estimated laser intensity blue continuous line (). b) Estimated population inversion red continuous line (). c) Estimation error between (), and (); with a modulation frequency kHz.
Figure 11.
State observer results for P3: a) Experimental laser intensity red dashed line () and estimated laser intensity blue continuous line (). b) Estimated population inversion red continuous line (). c) Estimation error between () and (); with a modulation frequency kHz.
Figure 11.
State observer results for P3: a) Experimental laser intensity red dashed line () and estimated laser intensity blue continuous line (). b) Estimated population inversion red continuous line (). c) Estimation error between () and (); with a modulation frequency kHz.
Figure 12.
State observer results for P4: a) Experimental laser intensity red dashed line () and estimated laser intensity blue continuous line (). b) Estimated population inversion red continuous line (). c) Estimation error between () and (); with a modulation frequency kHz.
Figure 12.
State observer results for P4: a) Experimental laser intensity red dashed line () and estimated laser intensity blue continuous line (). b) Estimated population inversion red continuous line (). c) Estimation error between () and (); with a modulation frequency kHz.
Figure 13.
State observer results for P5: a) Experimental laser intensity red dashed line () and estimated laser intensity blue continuous line (). b) Estimated population inversion red continuous line (). c) Estimation error between () and (); with a modulation frequency kHz.
Figure 13.
State observer results for P5: a) Experimental laser intensity red dashed line () and estimated laser intensity blue continuous line (). b) Estimated population inversion red continuous line (). c) Estimation error between () and (); with a modulation frequency kHz.
Figure 14.
Phase space of EDFL obtained from experimental laser intensity () and estimated population inversion (): a) P1, P3 and P4 with modulation Hz and b) P1, P4 and P5 with modulation kHz.
Figure 14.
Phase space of EDFL obtained from experimental laser intensity () and estimated population inversion (): a) P1, P3 and P4 with modulation Hz and b) P1, P4 and P5 with modulation kHz.
Table 2.
Coefficients used in numerical simulations.
Table 2.
Coefficients used in numerical simulations.
| Coefficient |
Value |
|
Coefficient |
Value |
|
Coefficient |
Value |
|
|
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
2.0 |
|
|
0.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.038 |
|
|
|
| R |
0.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 3.
Parameters for numerical simulations.
Table 3.
Parameters for numerical simulations.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 4.
MSE of the state observer for Laser intensity and estimated laser intensity .
Table 4.
MSE of the state observer for Laser intensity and estimated laser intensity .
| Period |
Value |
| P1 |
0.0019 |
| P3 |
0.2488 |
| P4 |
0.0163 |
| P5 |
0.1303 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).