Submitted:
12 September 2024
Posted:
13 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Investigation Methodology
- A.
- Define research questions
- B.
- Search
- ACM Digital Library (http://dl.acm.org)
- IEEE Explore (https://explore.ieee.com)
- SpringerLink (https://link.springer.com)
- ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/)
- Scopus (https://www.scopus.com)
- C.
- Selection of relevant articles
- D.
- Classification of articles according to keywords
- E.
- Data extraction
3. Results
- A.
- Search and selection
| Library | Initial |
|---|---|
| IEEE Explore | 780 |
| ScienceDirect | 503 |
| ACM Digital Library | 520 |
| SpringerLink | 912 |
| Scopus | 637 |
- B.
- Classification
4. Discussion
5. Emerging trends
- (1)
- Green Consensus Algorithms: With a growing focus on sustainability, greener and more efficient consensus algorithms are expected to continue to be an important trend (Jiang et al., 2022).
- (2)
- Advanced Proof-of-Stake (PoS): Implementation of enhanced PoS, such as reputation-based PoS or liquid staking PoS, could gain traction to address security and scalability challenges (Xu et al., 2021).
- (3)
- Multi-Blockchain Interoperability: An increase in efforts to achieve greater interoperability between different blockchains is expected, which could lead to consensus algorithms that facilitate this communication (Bhargav-Spantzel et al., 2022).
- (4)
- Hybrid and Multichain Consensus: Combining multiple consensus algorithms in hybrid or multichain systems could gain popularity to address specific performance and security challenges (Conti et al., 2020).
- (5)
- Privacy and Secure Sandboxes: A greater emphasis is expected on consensus algorithms that improve transaction privacy, such as secure sandboxes and coin mixing techniques (Chaum, 1988; Ben-Sasson et al., 2018).
- (6)
- Consensus Algorithms for IoT and Vehicular Networks: As blockchain adoption expands in the Internet of Things (IoT) and vehicular networks, specific consensus algorithms can be developed for these applications (Tian et al., 2021).
- (7)
- Optimization of Communication Networks: Additional research into consensus algorithms that optimize the efficiency of communication between nodes that can be crucial for scalability (Sun et al., 2022).
- (8)
- Quantum Fault Tolerance: As quantum computing advances, consensus algorithms resistant to quantum attacks can be explored (Khan et al., 2021).
6. Current Challenges
- (1)
- Efficiency and Scalability: One of the most pressing challenges is to improve the efficiency and scalability of consensus algorithms. As blockchain networks grow in size and transaction volume, it is critical to design algorithms that can handle increasingly larger workloads (Gencer et al., 2018).
- (2)
- Sustainability and Energy Consumption: The sustainability and high energy consumption of some consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Work (PoW), are significant concerns. Greener and more energy-efficient solutions are being sought (Jiang et al., 2022).
- (3)
- Privacy and Security: Privacy and security of blockchain transactions remain key challenges. Advances in anonymity techniques and the implementation of privacy solutions are growing areas of research (Ben-Sasson et al., 2018).
- (4)
- Interoperability: The need for interoperability between different blockchain chains is an obstacle to widespread adoption. Researchers are working on protocols and standards that allow seamless communication between different blockchains (Bhargav-Spantzel et al., 2022).
- (5)
- Quantum Consensus: With the advent of quantum computing, there is a threat that current consensus algorithms may be vulnerable. Algorithms resistant to quantum attacks are investigated (Khan et al., 2021).
- (6)
- Governance and Decision-Making: The governance of blockchain networks and decision-making on protocol changes are areas of constant debate. More decentralized and efficient governance mechanisms are sought (Gupta et al., 2019).
- (7)
- Practical Implementation: Effective implementation of consensus algorithms in real-world environments remains challenging. Solutions are needed that are practical and can be adapted to various applications (Conti et al., 2020).
- (8)
- Attacks and Cyber Security: Attacks and vulnerabilities in consensus algorithms can compromise the security of a blockchain network. Defense strategies and early detection of threats are investigated (Kumar et al., 2020).
- (9)
- Performance in Mobile and Low-Power Networks: The application of Blockchain in mobile devices and low-power networks presents specific performance challenges that require tailored solutions (Tian et al., 2021).
7. Recommendations for future research
- Have green and energy-efficient approaches.
- Resist quantum attacks to protect the security of blockchain networks.
- Incorporate advanced anonymity and privacy preservation techniques.
- Combine multiple custom consensus algorithms tailored to specific applications and needs.
- Propose new decentralized and efficient decision-making mechanisms.
8. Conclusions
- (1)
- An exhaustive systematic mapping study has been carried out to identify and classify peer-reviewed research papers related to consensus algorithms applied in blockchain networks. The main objective of this study is to understand the current research areas in this field and, from this understanding, identify possible research gaps that can serve as a basis for future work.
- (2)
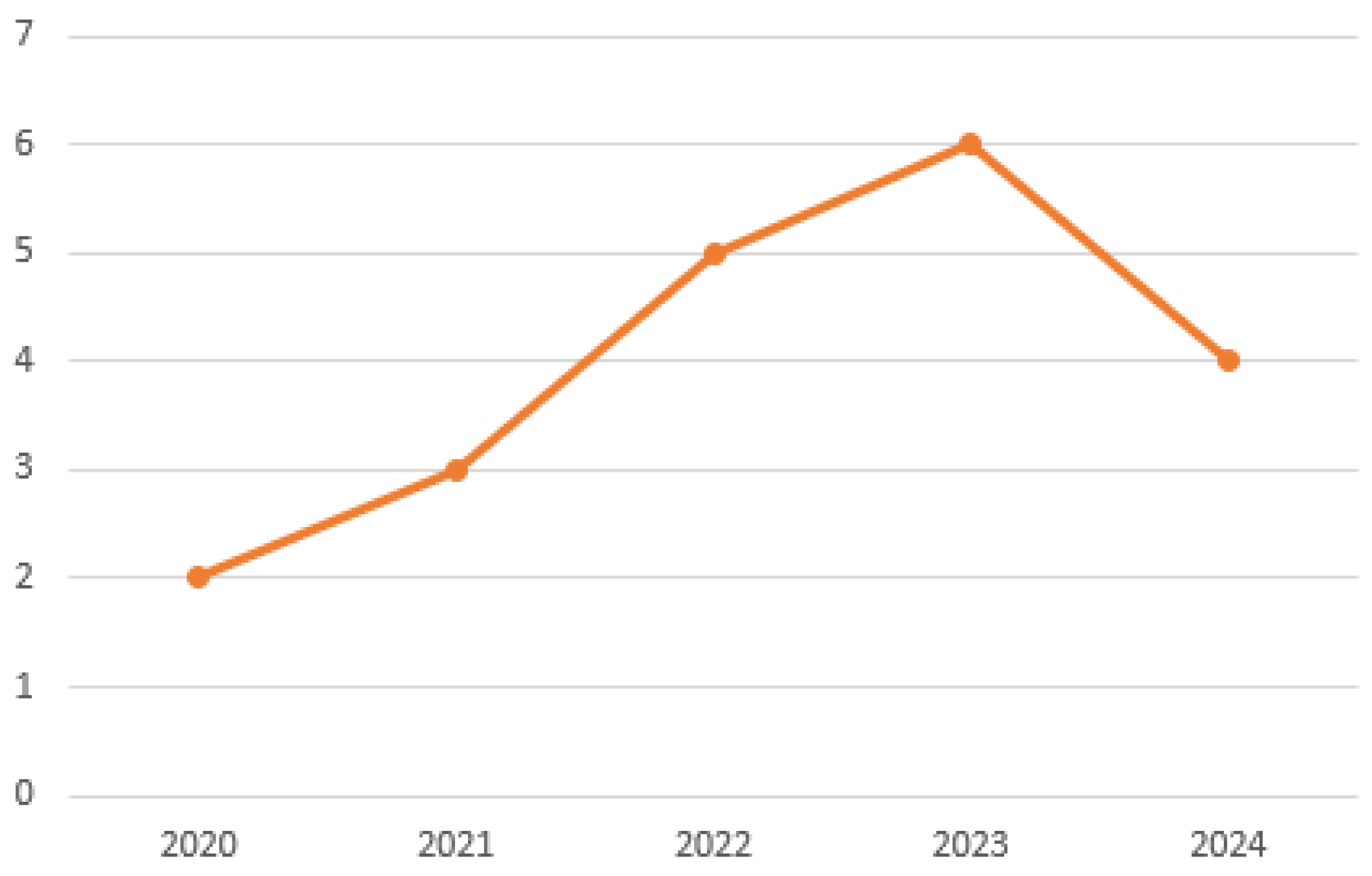
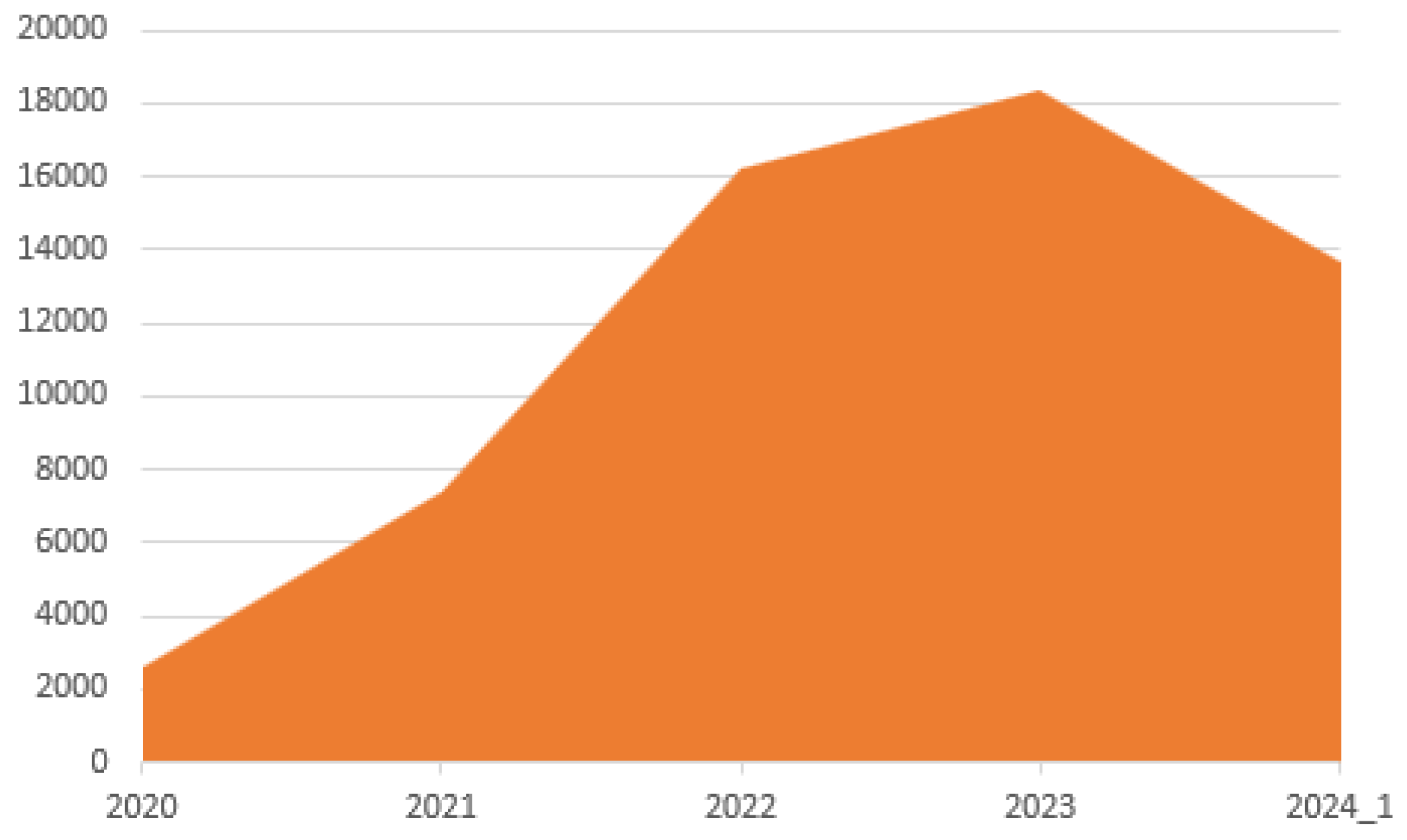
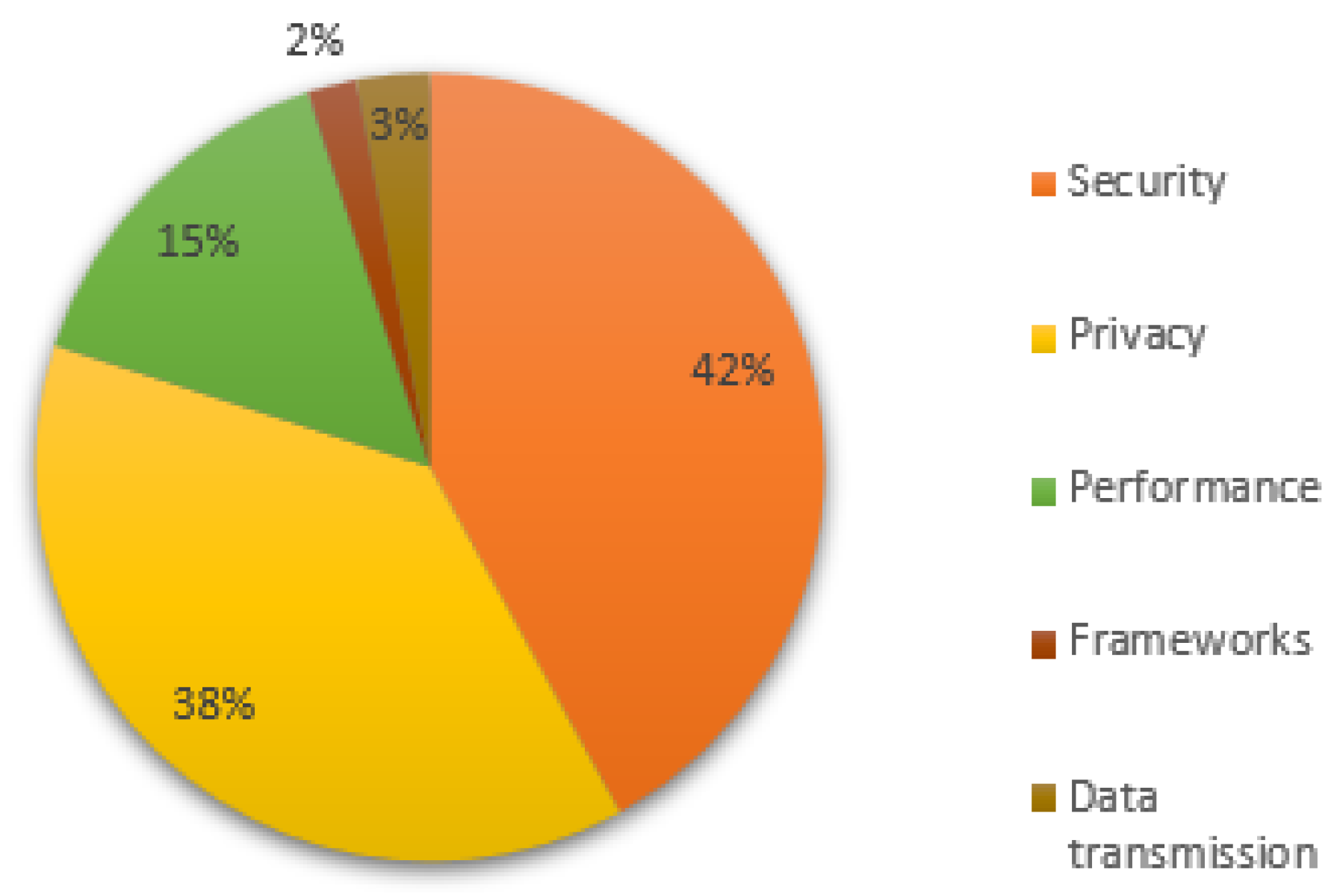
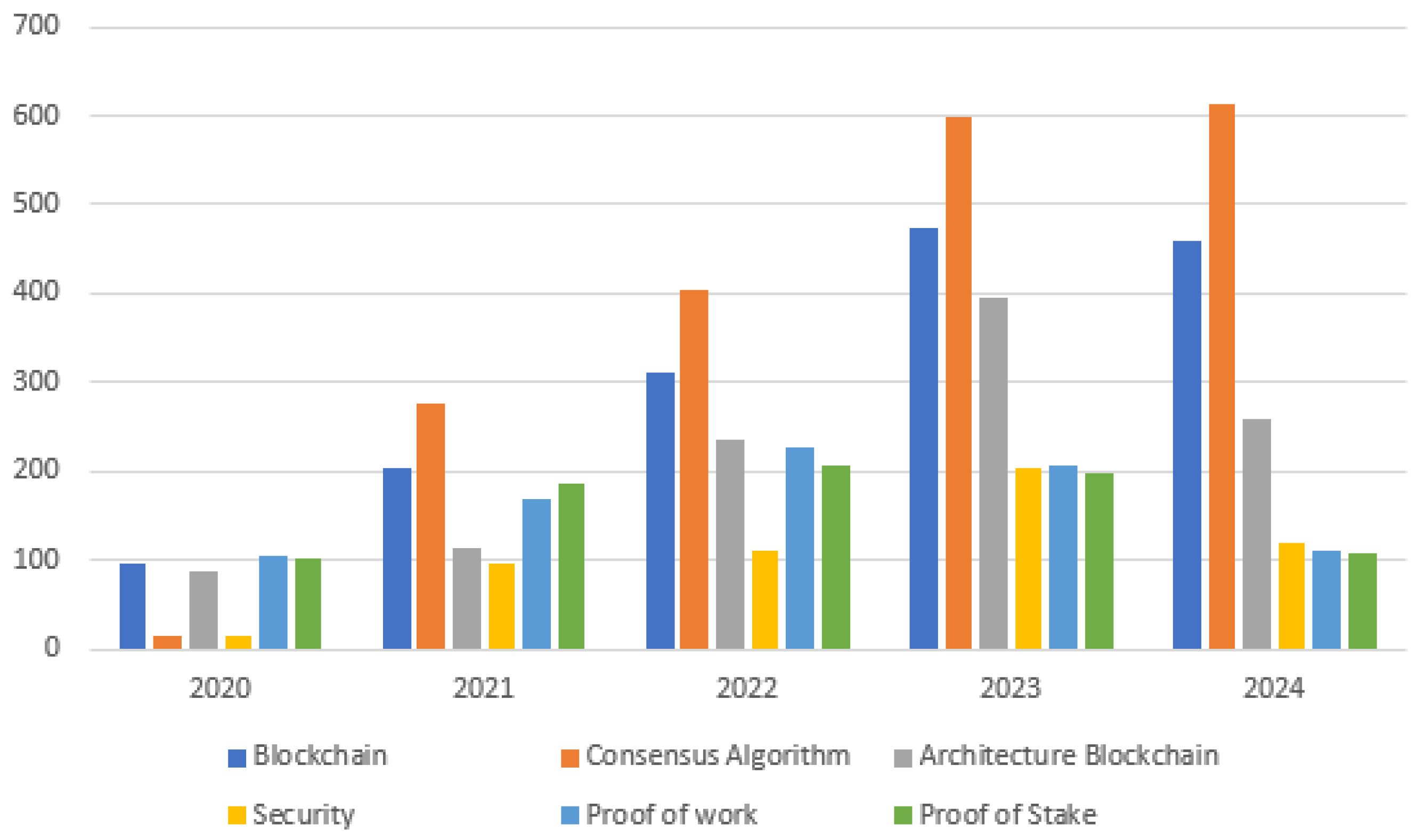
- The analysis was carried out on a set of 912 articles obtained from five renowned scientific databases. These articles have been classified into six different categories: Privacy, Performance, Frameworks, Security, Data Transmission, and other topics related to consensus algorithms applied in blockchain networks. One of the key findings is that the number of articles related to these topics has seen a notable increase since 2021.
- (3)
- This increase in interest and research in the field of consensus algorithms applied to blockchain networks reflects the growing importance of this technology in the academic community and industry. Furthermore, it demonstrates the need to address significant challenges in areas such as security, privacy, and performance, as well as the continuous evolution of Frameworks and applications related to data transmission on Blockchain.
- (4)
- The evaluation of consensus algorithms reveals that energy consumption is one of the most critical factors when measuring their environmental impact. Algorithms such as Proof of Work are energy intensive, resulting in low energy efficiency and a high carbon footprint. On the other hand, options such as Proof of Stake and Delegated Proof of Stake are much more efficient, as they consume significantly less energy and therefore generate a much smaller carbon footprint. In addition, these algorithms require less resource usage in terms of hardware, making them more sustainable alternatives for the future of blockchain networks.
- (5)
- Finding a consensus algorithm that efficiently balances security, scalability, and sustainability in blockchain networks is a challenge, as each algorithm tends to prioritize one of these aspects over the others.
- (6)
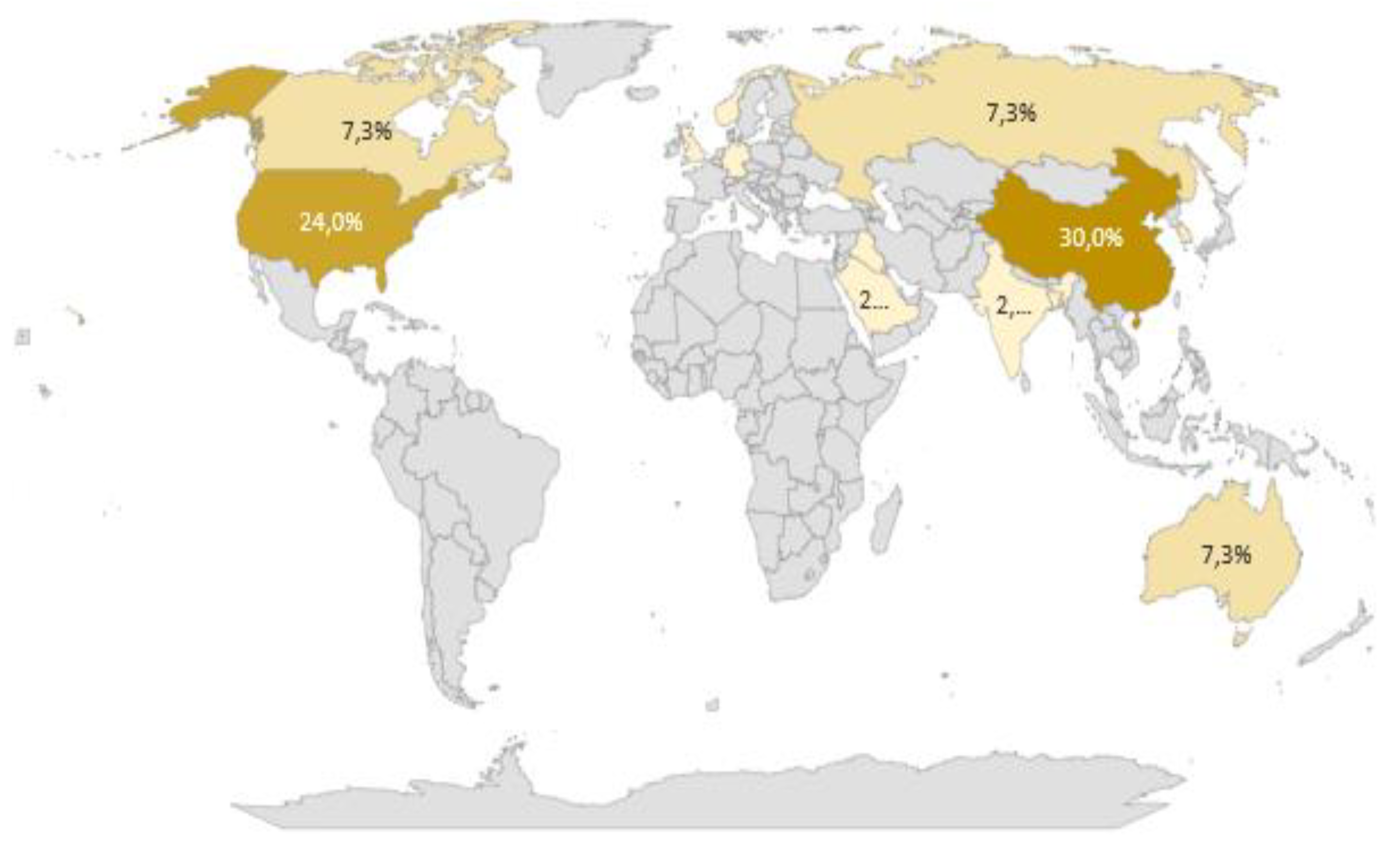
- On the other hand, the geographical location of the authors of the different articles allows us to sense that the research topic is essential to the academic community since it shows authors from different parts of the world. The geographical diversity in these authors indicates the breadth and global applicability of the consensus algorithms applied to blockchain technology
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reyna, A., Martín, C., Chen, J., Soler, E., & Díaz, M. (2018). On blockchain and its integration with IoT. Challenges and opportunities. Future Generation Computer Systems, 88, 173-190. [CrossRef]
- Viriyasitavat, W. y Hoonsopon, D. (2018). Blockchain characteristics and consensus in modern business processes. Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 13, 32-39. [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, A. M. (2017). Mastering Bitcoin: Programming the open blockchain. " O'Reilly Media, Inc.".
- Nespral, D., & Hergueta, R.F. (2021). Blockchain: el modelo descentralizado hacia la economía digital. Ra-Ma.
- K. Petersen, R. Feldt, S. Mujtaba, and M. Mattsson, “Systematic mapping studies in software engineering.,” in EASE, vol. 8, pp. 68–77, 2008.
- Yli-Huumo, D. Ko, S. Choi, S. Park, and K. Smolander, “Where is current research on blockchain technology?a systematic review,” PloS one, vol. 11, no. 10, p. e0163477, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, M. S., Chowdhury, M. J. M., & Hoque, M. A. (2021). A survey of consensus algorithms in public blockchain systems for crypto-currencies. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 103035. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A. A., & Ibrahim, A. O. (2020). Blockchain Consensuses Algorithms Based on Proof of Work: A Comparative Analysis. International Journal of Computing and Communication Networks, 2(1), 12-20.
- Zheng, Z., Xie, S., Dai, H. N., Chen, X., & Wang, H. (2018). Blockchain challenges and opportunities: A survey. International Journal of Web and Grid Services, 14(4), 352-375.
- Debus, J. (2017). Consensus methods in blockchain systems. Frankfurt School of Finance & Management, Blockchain Center, Tech. Rep.
- Salimitari, M., Chatterjee, M., & Fallah, Y. P. (2020). A survey on consensus methods in blockchain for resource-constrained IoT networks. Internet of Things, 11, 100212. [CrossRef]
- Bou Abdo, J., El Sibai, R., & Demerjian, J. (2021). Permissionless proof-of-reputation-X: A hybrid reputation-based consensus algorithm for permissionless blockchains. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 32(1), e4148.
- Wang, D., Jin, C., Li, H., & Perkowski, M. (2020, September). Proof of Activity Consensus Algorithm Based on Credit Reward Mechanism. In International Conference on Web Information Systems and Applications (pp. 618-628). Springer, Cham.
- Lindell, Y., Lysyanskaya, A., & Rabin, T. (2006). On the composition of authenticated byzantine agreement. Journal of the ACM (JACM), 53(6), 881-917. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y., Qiao, L., & Lv, Z. (2021). An optimized byzantine fault tolerance algorithm for consortium blockchain. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Mazieres, D. (2015). The stellar consensus protocol: A federated model for internet-level consensus. Stellar Development Foundation, 32.
- Schwartz, D., Youngs, N., & Britto, A. (2014). The ripple protocol consensus algorithm. Ripple Labs Inc White Paper, 5(8), 151.
- Dinh, T. T. A., Liu, R., Zhang, M., Chen, G., Ooi, B. C., & Wang, J. (2018). Untangling blockchain: A data processing view of blockchain systems. IEEE transactions on knowledge and data engineering, 30(7), 1366-1385. [CrossRef]
- Xie, J., Yu, F. R., Huang, T., Xie, R., Liu, J., & Liu, Y. (2019). A survey on the scalability of blockchain systems. IEEE Network, 33(5), 166-173. [CrossRef]
- Gilad, Y., Hemo, R., Micali, S., Vlachos, G., & Zeldovich, N. (2017, October). Algorand: Scaling byzantine agreements for cryptocurrencies. In Proceedings of the 26th symposium on operating systems principles (pp. 51-68).
- Zhou, Q., Huang, H., Zheng, Z., & Bian, J. (2020). Solutions to scalability of blockchain: A survey. IEEE Access, 8, 16440-16455. [CrossRef]
- Danezis, G., & Meiklejohn, S. (2015). Centrally banked cryptocurrencies. arXiv preprint arXiv:1505.06895.
- Halgamuge, M. N., Hettikankanamge, S. C., & Mohammad, A. (2020, December). Trust model to minimize the influence of malicious attacks in sharding based blockchain networks. In 2020 IEEE Third International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Knowledge Engineering (AIKE) (pp. 162-167). IEEE.
- Kokoris-Kogias, E., Jovanovic, P., Gasser, L., Gailly, N., Syta, E., & Ford, B. (2018, May). Omniledger: A secure, scale-out, decentralized ledger via sharding. In 2018 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP) (pp. 583-598). IEEE.
- Zamani, M., Movahedi, M., & Raykova, M. (2018, October). Rapidchain: Scaling blockchain via full sharding. In Proceedings of the 2018 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security (pp. 931-948).
- Li, C., Zhang, J., Yang, X., & Youlong, L. (2021). Lightweight blockchain consensus mechanism and storage optimization for resource-constrained IoT devices. Information Processing & Management, 58(4), 102602. [CrossRef]
- Song, H., Zhu, N., Xue, R., He, J., Zhang, K., & Wang, J. (2021). Proof-of-Contribution consensus mechanism for blockchain and its application in intellectual property protection. Information Processing & Management, 58(3), 102507. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D. H., Ullah, R., & Kim, B. S. (2019, September). RSP Consensus Algorithm for Blockchain. In 2019 20th Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS) (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
- D. Wood, “Ethereum: A secure decentralised generalised transaction ledger,” 2014.
- T. L. Foundation, “Hyperledger,” cited July 09. [Online]. Available: https://www.hyperledger.org/.
- V. Buterin, “A next generation smart contract & decentralized application platform,” 2015.
- Xu, X., Weber, I., & Staples, M. (2019). Architecture for blockchain applications. Springer.
- D. Meshkov, A. Chepurnoy, and M. Jansen, “Revisiting difficulty control for blockchain systems,” IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive, vol. 2017, p. 731, 2017.
- S. Nakamoto, “Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system, Available: http://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf.
- L. Guillaume, J. van de Sype, L. Schumacher, G. Di Stasi, and R. Canonico, “Adding reputation extensions to aodv-uu,” in 2010 17th IEEE SCVT2010, Nov 2010, pp. 1–6.
- X. Li, P. Jiang, T. Chen, X. Luo, and Q. Wen, “A survey on the security of blockchain systems,” Future Generation Computer Systems, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Q. Xing, B. Wang, and X. Wang, “Bgpcoin: Blockchain-based internet number resource authority and bgp security solution,” Symmetry, vol. 10, no. 9, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Saghiri, A. M. (2020). Blockchain architecture. In Advanced applications of blockchain technology (pp. 161-176). Springer, Singapore.
- Xu, X., Pautasso, C., Zhu, L., Lu, Q., & Weber, I. (2018, July). A pattern collection for blockchain-based applications. In Proceedings of the 23rd European Conference on Pattern Languages of Programs (pp. 1-20).
- Indhuja, E., & Venkatesulu, M. (2021). A Survey of Blockchain Technology Applications and Consensus Algorithm. In Sustainable Communication Networks and Application (pp. 173-187). Springer, Singapore.
- Harish, V., & Sridevi, R. (2020). A Brief Survey on Blockchain Technology. ICCII 2018, 249.
- Patidar, K., & Jain, S. (2021). Implementation of Blockchain Based Distributed Architecture for Enhancing Security and Privacy in Peer-To-Peer Networks. In Advanced Computing: 10th International Conference, IACC 2020, Panaji, Goa, India, December 5–6, 2020, Revised Selected Papers, Part II 10 (pp. 94-105). Springer Singapore.
- Bandara, E., Liang, X., Foytik, P., Shetty, S., Ranasinghe, N., & De Zoysa, K. (2021). Rahasak—Scalable blockchain architecture for enterprise applications. Journal of Systems Architecture, 116, 102061. [CrossRef]
- McConaghy, T., Marques, R., Müller, A., De Jonghe, D., McConaghy, T., McMullen, G., ... & Granzotto, A. (2016). Bigchaindb: a scalable blockchain database. white paper, BigChainDB.
- Sahoo, M. S., & Baruah, P. K. (2018, March). Hbasechaindb–a scalable blockchain framework on hadoop ecosystem. In Asian Conference on Supercomputing Frontiers (pp. 18-29). Springer, Cham.
- Jie, S. O. N. G., ZHANG, P., ALKUBATI, M., Yubin, B. A. O., & Ge, Y. U. (2021). Research advances on blockchain-as-a-service: architectures, applications and challenges. Digital Communications and Networks.
- Zheng, W., Zheng, Z., Chen, X., Dai, K., Li, P., & Chen, R. (2019). Nutbaas: A blockchain-as-a-service platform. Ieee Access, 7, 134422-134433. [CrossRef]
- Ammi, M., Alarabi, S., & Benkhelifa, E. (2021). Customized blockchain-based architecture for secure smart home for lightweight IoT. Information Processing & Management, 58(3), 102482. [CrossRef]
- Cha, J., Singh, S. K., Kim, T. W., & Park, J. H. (2021). Blockchain-empowered cloud architecture based on secret sharing for smart city. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 57, 102686. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q., Han, Y. Y., Su, Z. B., Fang, J. L., Liu, Z. Q., & Wang, K. Y. (2020). A storage architecture for high-throughput crop breeding data based on improved blockchain technology. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 173, 105395. [CrossRef]
- T. Xue, Y. Yuan, Z. Ahmed, K. Moniz, G. Cao and C. Wang, "Proof of Contribution: A Modification of Proof of Work to Increase Mining Efficiency," 2018 IEEE 42nd Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), 2018, pp. 636-644. [CrossRef]
- Mingxiao, D., Xiaofeng, M., Zhe, Z., Xiangwei, W., & Qijun, C. (2017, October). A review on consensus algorithm of blockchain. In 2017 IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics (SMC) (pp. 2567-2572). IEEE.
- Jiang, S., Ding, X., Zhang, W., Li, L., & Yang, D. (2022). Sustainable Consensus Mechanisms for Blockchain: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics.
- Li, D., Han, D., Weng, T. H., Zheng, Z., Li, H., Liu, H., ... & Li, K. C. (2022). Blockchain for federated learning toward secure distributed machine learning systems: a systemic survey. Soft Computing, 26(9), 4423-4440. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z., Zhang, X., & Li, L. (2021). Enhanced Proof of Stake (ePoS) Blockchain Consensus Mechanism: Design and Performance Analysis. IEEE Access, 9, 36536-36545.
- Yang, F., Zhou, W., Wu, Q., Long, R., Xiong, N. N., & Zhou, M. (2019). Delegated proof of stake with downgrade: A secure and efficient blockchain consensus algorithm with downgrade mechanism. IEEE Access, 7, 118541-118555.
- Ge, L., Wang, J., & Zhang, G. (2022). Survey of consensus algorithms for proof of stake in blockchain. Security and Communication Networks, 2022, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Tkachuk, R. V., Ilie, D., Tutschku, K., & Robert, R. (2021). A survey on blockchain-based telecommunication services marketplaces. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 19(1), 228-255. [CrossRef]
- Lin, I. C., & Liao, T. C. (2017). A survey of blockchain security issues and challenges. Int. J. Netw. Secur., 19(5), 653-659.
- Dorri, A., Kanhere, S. S., Jurdak, R., & Gauravaram, P. (2017, March). Blockchain for IoT security and privacy: The case study of a smart home. In 2017 IEEE international conference on pervasive computing and communications workshops (PerCom workshops) (pp. 618-623). IEEE.
- Xu, X., Sun, G., & Yu, H. (2021, November). An efficient blockchain pbft consensus protocol in energy constrained iot applications. In 2021 International Conference on UK-China Emerging Technologies (UCET) (pp. 152-157). IEEE.
- Li, C., Zhang, J., Yang, X., & Youlong, L. (2021). Lightweight blockchain consensus mechanism and storage optimization for resource-constrained IoT devices. Information Processing & Management, 58(4), 102602. [CrossRef]
- Mollah, M. B., Zhao, J., Niyato, D., Lam, K. Y., Zhang, X., Ghias, A. M., ... & Yang, L. (2020). Blockchain for future smart grid: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(1), 18-43. [CrossRef]
- Belchior, R., Vasconcelos, A., Guerreiro, S., & Correia, M. (2021). A survey on blockchain interoperability: Past, present, and future trends. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 54(8), 1-41. [CrossRef]
- Bao, J., He, D., Luo, M., & Choo, K. K. R. (2020). A survey of blockchain applications in the energy sector. IEEE Systems Journal, 15(3), 3370-3381. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y., Lu, Q., Zhu, L., Paik, H. Y., & Staples, M. (2023). A systematic literature review on blockchain governance. Journal of Systems and Software, 197, 111576. [CrossRef]
- Gao, W., Hatcher, W. G., & Yu, W. (2018, July). A survey of blockchain: Techniques, applications, and challenges. In 2018 27th international conference on computer communication and networks (ICCCN) (pp. 1-11). IEEE.
- Monrat, A. A., Schelén, O., & Andersson, K. (2019). A survey of blockchain from the perspectives of applications, challenges, and opportunities. IEEE Access, 7, 117134-117151. [CrossRef]
- Lin, I. C., & Liao, T. C. (2017). A survey of blockchain security issues and challenges. Int. J. Netw. Secur., 19(5), 653-659.
- De La Rosa, J. L., Torres-Padrosa, V., El-Fakdi, A., Gibovic, D., Hornyák, O., Maicher, L., & Miralles, F. (2017, December). A survey of blockchain technologies for open innovation. In Proceedings of the 4th Annual World Open Innovation Conference (pp. 14-15).
- Chaudhry, N., & Yousaf, M. M. (2018, December). Consensus algorithms in blockchain: Comparative analysis, challenges and opportunities. In 2018 12th International Conference on Open Source Systems and Technologies (ICOSST) (pp. 54-63). IEEE.
- Xiong, H., Chen, M., Wu, C., Zhao, Y., & Yi, W. (2022). Research on progress of blockchain consensus algorithm: A review on recent progress of blockchain consensus algorithms. Future Internet, 14(2), 47. [CrossRef]
- Bach, L. M., Mihaljevic, B., & Zagar, M. (2018, May). Comparative analysis of blockchain consensus algorithms. In 2018 41st international convention on information and communication technology, electronics and microelectronics (MIPRO) (pp. 1545-1550). Ieee.
- Alsunaidi, S. J., & Alhaidari, F. A. (2019, April). A survey of consensus algorithms for blockchain technology. In 2019 International Conference on Computer and Information Sciences (ICCIS) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Ferdous, M. S., Chowdhury, M. J. M., Hoque, M. A., & Colman, A. (2020). Blockchain consensus algorithms: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.07091.
- Sharma, K., & Jain, D. (2019, July). Consensus algorithms in blockchain technology: A survey. In 2019 10th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT) (pp. 1-7). IEEE.
- Pahlajani, S., Kshirsagar, A., & Pachghare, V. (2019, April). Survey on private blockchain consensus algorithms. In 2019 1st International Conference on Innovations in Information and Communication Technology (ICIICT) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Bamakan, S. M. H., Motavali, A., & Bondarti, A. B. (2020). A survey of blockchain consensus algorithms performance evaluation criteria. Expert Systems with Applications, 154, 113385. [CrossRef]
- Fu, X., Wang, H., & Shi, P. (2021). A survey of Blockchain consensus algorithms: mechanism, design and applications. Science China Information Sciences, 64, 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Yim, J. C., Yoo, H. K., Kwak, J. Y., & Kim, S. M. (2018). Blockchain and consensus algorithm. Electronics and telecommunications trends, 33(1), 45-56.
- Frikha, T., Chaabane, F., Aouinti, N., Cheikhrouhou, O., Ben Amor, N., & Kerrouche, A. (2021). Implementation of blockchain consensus algorithm on embedded architecture. Security and Communication Networks, 2021, 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M., Muzammal, M., Hameed, M. K., Javed, I. T., Alamri, B., & Crespi, N. (2021). CBCIoT: a consensus algorithm for blockchain-based IoT applications. Applied Sciences, 11(22), 11011. [CrossRef]
- Panda, S. S., Mohanta, B. K., Satapathy, U., Jena, D., Gountia, D., & Patra, T. K. (2019, October). Study of blockchain based decentralized consensus algorithms. In TENCON 2019-2019 IEEE Region 10 Conference (TENCON) (pp. 908-913). IEEE.
- Biswas, S., Sharif, K., Li, F., Maharjan, S., Mohanty, S. P., & Wang, Y. (2019). PoBT: A lightweight consensus algorithm for scalable IoT business blockchain. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(3), 2343-2355. [CrossRef]
- Andrey, A., & Petr, C. (2019, September). Review of existing consensus algorithms blockchain. In 2019 International Conference" Quality Management, Transport and Information Security, Information Technologies"(IT&QM&IS) (pp. 124-127). IEEE.
- Du, M., Chen, Q., & Ma, X. (2020). MBFT: A new consensus algorithm for consortium blockchain. IEEE Access, 8, 87665-87675. [CrossRef]
- Chen, R., Wang, L., Peng, C., & Zhu, R. (2022). An effective sharding consensus algorithm for blockchain systems. Electronics, 11(16), 2597. [CrossRef]
- Velliangiri, S., & Karthikeyan, P. (2020, January). Blockchain technology: challenges and security issues in consensus algorithm. In 2020 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI) (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
- Chaudhry, N., & Yousaf, M. M. (2018, December). Consensus algorithms in blockchain: Comparative analysis, challenges and opportunities. In 2018 12th International Conference on Open Source Systems and Technologies (ICOSST) (pp. 54-63). IEEE.
- Lunardi, R. C., Michelin, R. A., Nunes, H. C., Neu, C. V., Zorzo, A. F., & Kanhere, S. S. (2022). Consensus algorithms on appendable-block blockchains: impact and security analysis. Mobile Networks and Applications, 27(4), 1408-1420. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q., Huang, J., Wang, S., Chen, Y., Zhang, P., & He, L. (2020). A comparative study of blockchain consensus algorithms. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 1437, No. 1, p. 012007). IOP Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, B. K., Samal, K., Jena, D., Ramasubbareddy, S., & Karuppiah, M. (2022). Blockchain-based consensus algorithm for solving security issues in distributed internet of things. International Journal of Electronic Business, 17(3), 283-304. [CrossRef]
- Drăgoi, C., Henzinger, T. A., Veith, H., Widder, J., & Zufferey, D. (2014). A logic-based framework for verifying consensus algorithms. In Verification, Model Checking, and Abstract Interpretation: 15th International Conference, VMCAI 2014, San Diego, CA, USA, January 19-21, 2014, Proceedings 15 (pp. 161-181). Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
- He, X., Yu, J., Huang, T., Li, C., & Li, C. (2018). Average quasi-consensus algorithm for distributed constrained optimization: Impulsive communication framework. IEEE transactions on cybernetics, 50(1), 351-360. [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y., Wu, H., & Paik, H. Y. (2021). DR-BFT: A consensus algorithm for blockchain-based multi-layer data integrity framework in dynamic edge computing system. Future Generation Computer Systems, 124, 33-48. [CrossRef]
- Bamakan, S. M. H., Motavali, A., & Bondarti, A. B. (2020). A survey of blockchain consensus algorithms performance evaluation criteria. Expert Systems with Applications, 154, 113385. [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z., Xiang, H., Zhou, Z., Wang, N., & Jin, H. (2021, May). AlphaBlock: An Evaluation Framework for Blockchain Consensus Algorithms. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Workshop on Security in Blockchain and Cloud Computing (pp. 17-22).
- Prasad, J. C., Comeau, S. R., Vajda, S., & Camacho, C. J. (2003). Consensus alignment for reliable framework prediction in homology modeling. Bioinformatics, 19(13), 1682-1691. [CrossRef]
- Fu, X., Wang, H., & Shi, P. (2021). A survey of Blockchain consensus algorithms: mechanism, design and applications. Science China Information Sciences, 64, 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y., Li, Y., Dong, X., Fang, L., & Chen, P. (2018, June). Performance analysis of consensus algorithm in private blockchain. In 2018 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV) (pp. 280-285). IEEE.
- Cao, M., Spielman, D. A., & Morse, A. S. (2005, December). A lower bound on convergence of a distributed network consensus algorithm. In Proceedings of the 44th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (pp. 2356-2361). IEEE.
- Sun, Y., Wu, X., Wang, J., Hou, D., & Wang, S. (2020). Power compensation of network losses in a microgrid with BESS by distributed consensus algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 51(4), 2091-2100. [CrossRef]
- Velliangiri, S., & Karthikeyan, P. (2020, January). Blockchain technology: challenges and security issues in consensus algorithm. In 2020 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI) (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
- Maitra, S., Yanambaka, V. P., Abdelgawad, A., Puthal, D., & Yelamarthi, K. (2020, June). Proof-of-authentication consensus algorithm: Blockchain-based IoT implementation. In 2020 IEEE 6th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT) (pp. 1-2). IEEE.
- Gao, S., Yu, T., Zhu, J., & Cai, W. (2019). T-PBFT: An EigenTrust-based practical Byzantine fault tolerance consensus algorithm. China Communications, 16(12), 111-123.
- Ferrag, M. A., Shu, L., Yang, X., Derhab, A., & Maglaras, L. (2020). Security and privacy for green IoT-based agriculture: Review, blockchain solutions, and challenges. IEEE access, 8, 32031-32053.
- Zhang, R., Xue, R., & Liu, L. (2019). Security and privacy on blockchain. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 52(3), 1-34. [CrossRef]
- Xie, A., Wang, X., & Ren, X. (2021, December). Privacy-Preserving Average Consensus in Finite Time. In 2021 60th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC) (pp. 2743-2749). IEEE.
- Qu, X., Wang, S., Hu, Q., & Cheng, X. (2021). Proof of federated learning: A novel energy-recycling consensus algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 32(8), 2074-2085. [CrossRef]
- Bamakan, S. M. H., Motavali, A., & Bondarti, A. B. (2020). A survey of blockchain consensus algorithms performance evaluation criteria. Expert Systems with Applications, 154, 113385. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H., Chen, M., Wu, C., Zhao, Y., & Yi, W. (2022). Research on progress of blockchain consensus algorithm: A review on recent progress of blockchain consensus algorithms. Future Internet, 14(2), 47. [CrossRef]
- Alsunaidi, S. J., & Alhaidari, F. A. (2019, April). A survey of consensus algorithms for blockchain technology. In 2019 International Conference on Computer and Information Sciences (ICCIS) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Sharma, K., & Jain, D. (2019, July). Consensus algorithms in blockchain technology: A survey. In 2019 10th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT) (pp. 1-7). IEEE.
- Chen, R., Wang, L., Peng, C., & Zhu, R. (2022). An effective sharding consensus algorithm for blockchain systems. Electronics, 11(16), 2597.. [CrossRef]
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
|
|
| AUTHOR | QUALIFICATION | YEAR |
|---|---|---|
| Bamakan, S. y otros | A survey of blockchain consensus algorithms performance evaluation criteria. | 2020 |
| Ferdous, M. S. y otros | Blockchain consensus algorithms: A survey. | 2020 |
| Li, D. | Green technology innovation path based on blockchain algorithm | 2021 |
| Khan, S. A. R. y otros | Green data analytics, blockchain technology for sustainable development, and sustainable supply chain practices: evidence from small and medium enterprises. | 2021 |
| Sharma, A. y otros | Sustainable smart cities: convergence of artificial intelligence and blockchain. | 2021 |
| Jiang, S. y otros | A tertiary review on blockchain and sustainability with focus on Sustainable Development Goals. | 2022 |
| Sasikumar, A.y otros | Sustainable smart industry: a secure and energy efficient consensus mechanism for artificial intelligence enabled industrial internet of things | 2022 |
| Alofi, A. y otros | Optimizing the energy consumption of blockchain-based systems using evolutionary algorithms: A new problem formulation. | 2022 |
| Liu, Y. y otros | An incentive mechanism for sustainable blockchain storage. | 2022 |
| Wang, C. y otros | Sustainable blockchain-based digital twin management architecture for IoT devices. | 2022 |
| Alzoubi, Y. I., & Mishra, A. | Green blockchain–A move towards sustainability. | 2023 |
| Biswas, D. y otros | Traceability vs. sustainability in supply chains: The implications of blockchain. | 2023 |
| Li, H. y otros | Decentralized energy management of microgrid based on blockchain-empowered consensus algorithm with collusion prevention. | 2023 |
| Liu, Y. y otros | Mechanism design for blockchain storage sustainability. | 2023 |
| Wendl, M. y otros | The environmental impact of cryptocurrencies using proof of work and proof of stake consensus algorithms: A systematic review. | 2023 |
| Yang, Z. y otros. | Blockchain technology in building environmental sustainability: A systematic literature review and future perspectives. | 2023 |
| Alazab, M., y otros | Industry 4.0 Innovation: A Systematic Literature Review on the Role of Blockchain Technology in Creating Smart and Sustainable Manufacturing Facilities | 2024 |
| Giganti, P. y otros | The impact of blockchain technology on enhancing sustainability in the agri-food sector: A scoping review. | 2024 |
| Rani, P. y otros | Toward a greener future: A survey on sustainable blockchain applications and impact. | 2024 |
| Rukhiran, M., y otros | Sustainable Optimizing Performance and Energy Efficiency in Proof of Work Blockchain: A Multilinear Regression Approach. | 2024 |
| AUTHOR | COUNTRY |
|---|---|
| Ahmed Zahir | China |
| Amirhossein Motavali | Canada |
| Avinash Kshirsagar | India |
| Beng Chin OOI | Singapore |
| Brian Armstrong | USA |
| Changpeng Zhao | China |
| Craig Steven Wright | Australia |
| Elaine Shi | Canada |
| Emin Gün Sirer | USA |
| F.Richard Yu | Canada |
| Fred Ehrsam | USA |
| Gavin Andresen | USA |
| Gavin Wood | United Kingdom |
| hal finney | USA |
| Hong Ning Dai | China |
| Jae Kwon | South Korea |
| Jiang Peng | Germany |
| Kyungbaek Kim | South Korea |
| Md Sadek Ferdous | Bangladesh |
| Meihui ZHANG | China |
| Mingxiao du | China |
| Mohammad Jabed Morshed Chowdhury | Australia |
| Nick Sabo | USA |
| Renchao Xie | China |
| Rui Liu | USA |
| Sam Bankman-Fried | USA |
| Satoshi Nakamoto | USA |
| Sergey Nazarov | Russia |
| Sergey Nazarov | Russia |
| Seyed Mojtaba Hosseini Bamakan | Iran |
| Shaoan Xie | USA |
| Shikah J. Alsunaidi | Saudi Arabia |
| Tao Huang | China |
| Tien Tuan Anh Dinh | Australia |
| Ting Chen | China |
| Vitalik Buterin | Russia |
| Xiangping Chen | China |
| Xiangwei Wang | China |
| Xiaoqi Li | China |
| Yan Zhang | Norway |
| Zibin Zheng | China |
| KEYWORD | NUMBER OF ARTICLES IN WHICH IT APPEARS | RELEVANCE |
|---|---|---|
| Blockchain | 903 | high |
| Consensus Algorithms | 874 | high |
| Proof of work | 724 | Half |
| Proof of stake | 705 | Half |
| Delegated proof of stake | 672 | Low |
| Byzantine fault tolerance | 400 | Low |
| Smart contracts | 568 | Low |
| Architecture Blockchain | 908 | high |
| forks | 200 | Low |
| Security | 603 | high |
| Decentralization | 412 | Low |
| Tokenomics | 285 | Low |
| Network security | 681 | Low |
| Cryptography | 698 | Low |
| Consensus Algorithm |
Energy Consumption |
Energy Efficiency |
Carbon Footprint | Resource Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proof of Work (PoW) | Very High | Low | High | High (Mining) |
| Proof of Stake (PoS) | Low | High | Low | Low |
| Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) | Very Low | High | Very Low | Low |
| Proof of Authority (PoA) | Very Low | High | Very Low | Low |
| Hybrid Algorithms (PoW/PoS) | Moderate | Medium | Moderate | Moderate |
| Consensus Algorithm | Security | Scalability | Sustainability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proof of Work (PoW) | Very High | Low | Low |
| Proof of Stake (PoS) | High | Medium | High |
| Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) | Medium | High | Very High |
| Proof of Authority (PoA) | Medium | High | Very High |
| Hybrid Algorithms (PoW/PoS) | High | Medium | Medium |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





