Submitted:
08 September 2024
Posted:
09 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
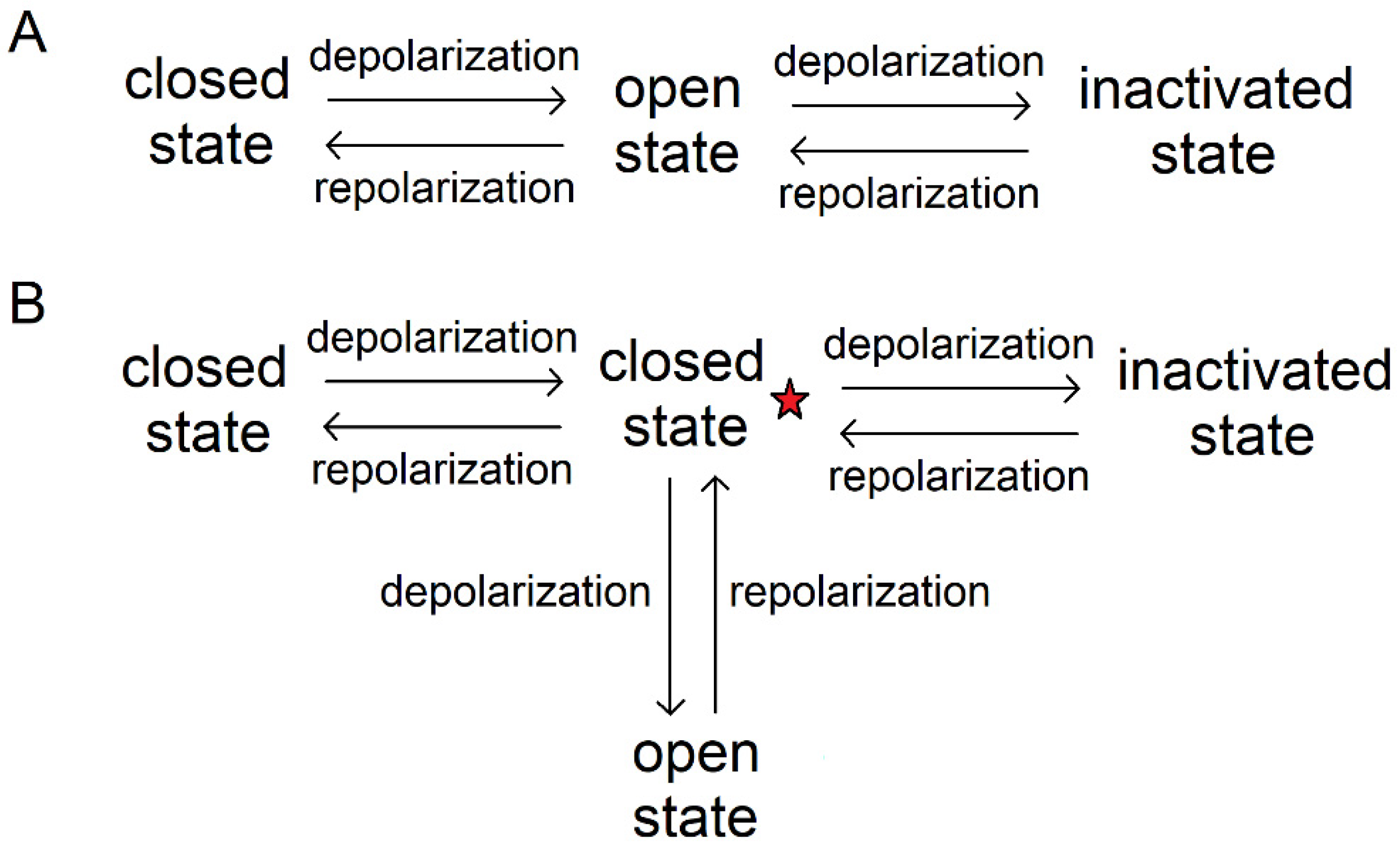
2. Topology and Classification of Cation Channels
- (i)
- A pore domain (PD) with a narrow selective filter that conducts ions of a certain type;
- (ii)
- A gate that regulates the opening and closing of a channel;
- (iii)
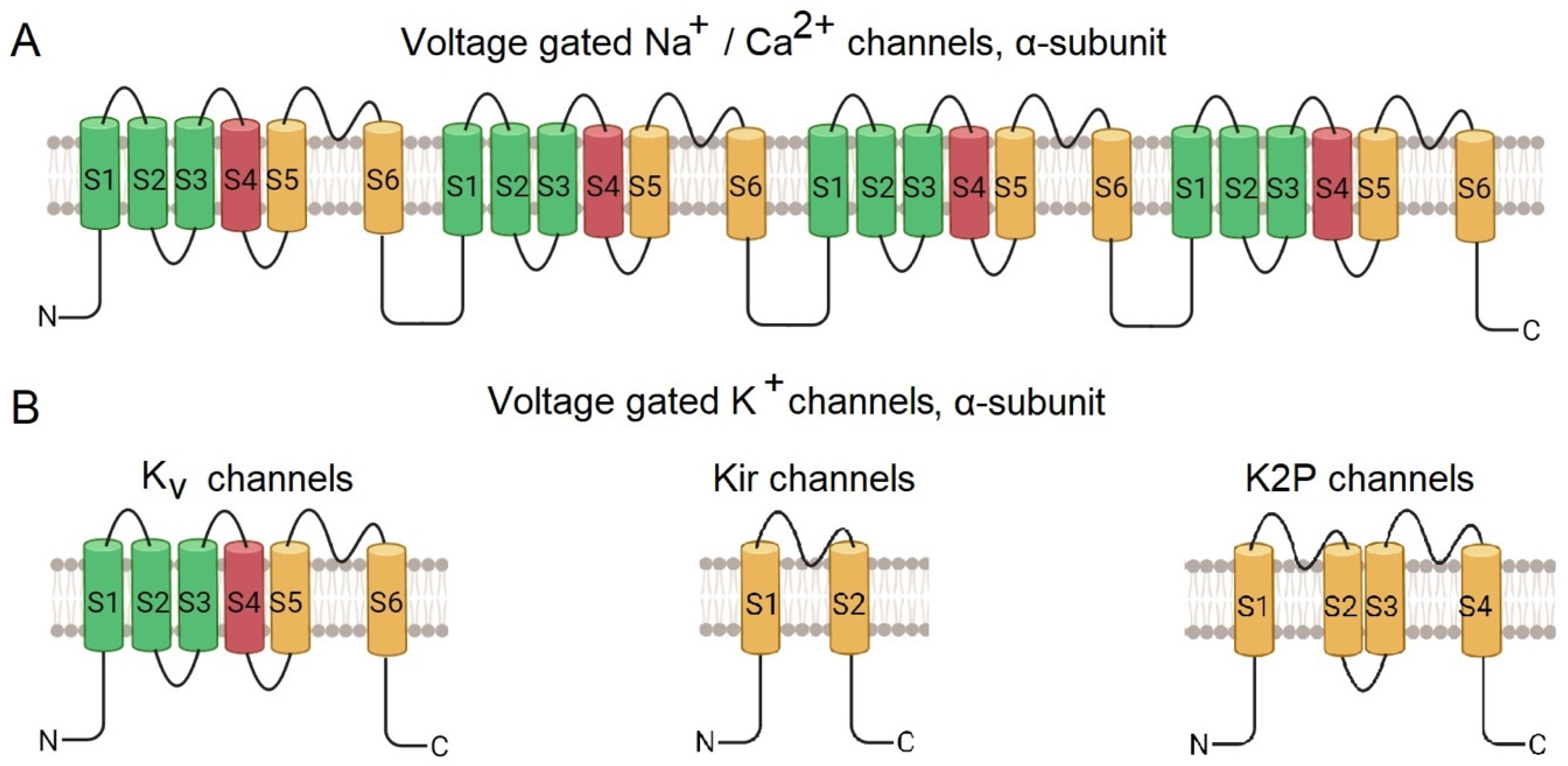
- Sensors that respond to external signals. In cationic voltage-gated channels, four repetitive subunits are radially arranged around the pore [20]. The transmembrane α-subunit of Nav and Cav channels consists of four transmembrane domains comprising of S1-S6 helices, encoded by a single polypeptide chain (Figure 1A). Helixes S1-S4 form the voltage-gated domain, while S4, the voltage sensor, being rich in positively charged amino acid residues, changes its position upon changing the membrane potential. The S5 and S6 helixes form a pore domain [2,21,22].
- (i)
- Kv (voltage-gated) possess six transmembrane helices (S1-S6), with S1-S4 forming a potential-sensing domain and S5-S6 – a pore domain;
- (ii)
- Kir (internally rectifying) through which ions pass easily into the cell, but not out; they have two transmembrane helices,
- (iii)
- K2P (bipore delayed rectification), with four transmembrane helices,
- (iiii)
- KCa (calcium-activated), have six transmembrane helices, similar to those of Kv.
3. Experimental Prerequisites for Studying the Structure of Ion Channels
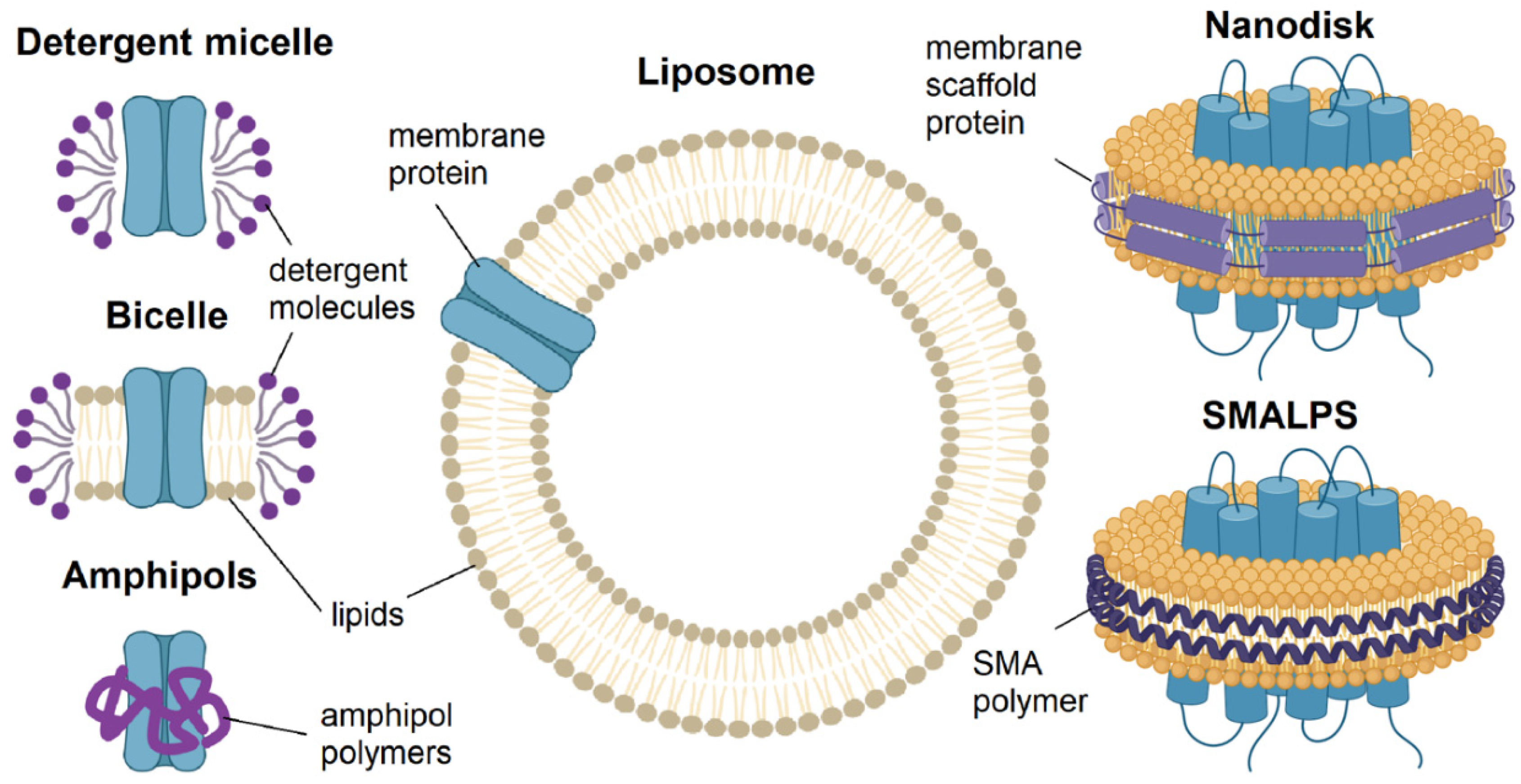
3.1. Purification Strategies
3.1.1. Detergents: Micelles and Bicelles
3.1.2. Polymers: Amphipols, Nanodiscs, Lipodiscs
3.1.3. Lipids: Liposomes and Membrane Vesicles
3.2. Methods for Obtaining Ion Channels in Specific Functional States
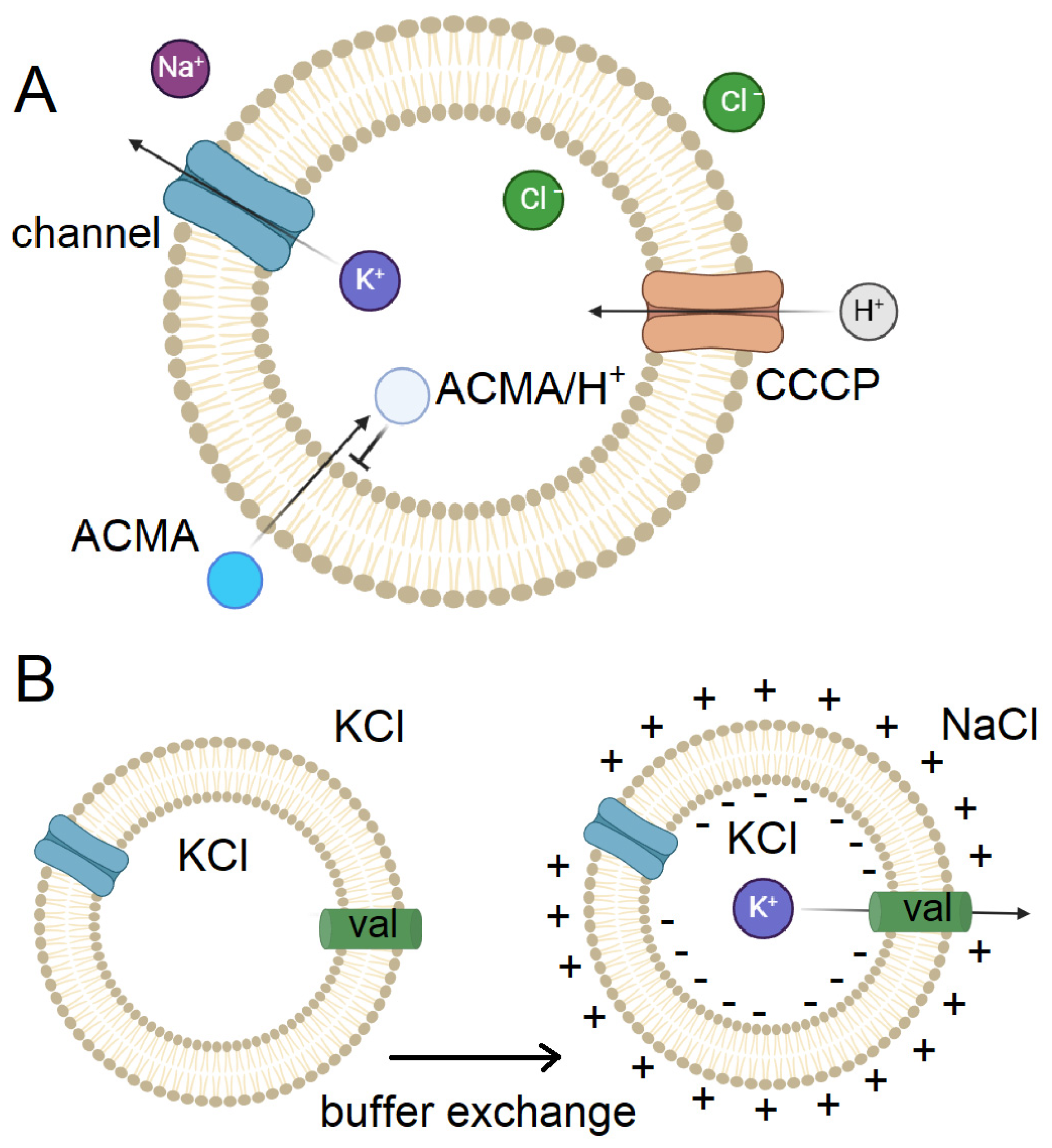
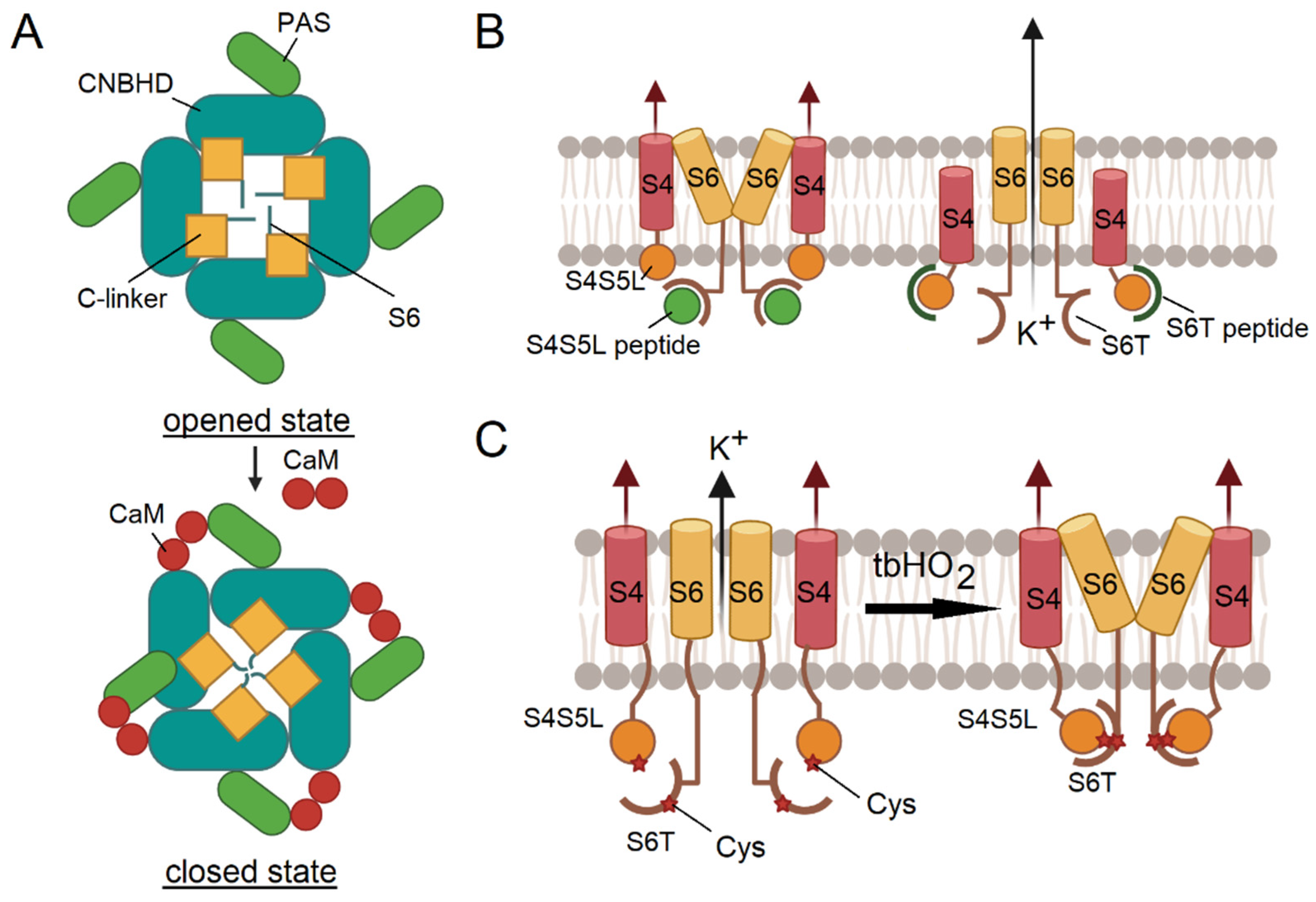
3.2.1. Application of Ion Channel Modulators
3.2.2. Peptide Binding Mimics the Functional States of Ion Channels
3.2.3. Chemical Cross-Linking and Coordination of Metal Ions
3.3. Application of Toxins with Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
3.4. New Approach – Polarized Membrane Vesicles
4. Advanced Structural Methods for the Study of Voltage-Gated Ion Channel Conformational Changes
4.1. Cryo-Electron Microscopy
4.2. Development of New Algorithms for the Identifшсation of Distinct Conformational States of Ion Channels
4.3. Cryo-Electron Tomography
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.M.; Nimigean, C.M. Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels: A Structural Examination of Selectivity and Gating. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2016, 8, a029231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catterall, W.A.; Lenaeus, M.J.; Gamal El-Din, T.M. Structure and Pharmacology of Voltage-Gated Sodium and Calcium Channels. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 60, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Hassani Nia, F.; Stauber, T. Ion Channels and Transporters in Muscle Cell Differentiation. IJMS 2021, 22, 13615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevarskaya, N.; Skryma, R.; Bidaux, G.; Flourakis, M.; Shuba, Y. Ion Channels in Death and Differentiation of Prostate Cancer Cells. Cell Death Differ 2007, 14, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, T.M.; Isseroff, R.R.; Lasarow, R.; Pappone, P.A. Ion Channels Are Linked to Differentiation in Keratinocytes. J. Membarin Biol. 1993, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becchetti, A. Ion Channels and Transporters in Cancer. 1. Ion Channels and Cell Proliferation in Cancer. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology 2011, 301, C255–C265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.; Föller, M.; Lang, K.S.; Lang, P.A.; Ritter, M.; Gulbins, E.; Vereninov, A.; Huber, S.M. Ion Channels in Cell Proliferation and Apoptotic Cell Death. J Membrane Biol 2005, 205, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Vincent, J.-D.; Clarke, I.J. Ion Channels and the Signal Transduction Pathways in the Regulation of Growth Hormone Secretion. Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism 1994, 5, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, E.; Calorio, C.; Vandael, D.H.F. T-Type Channel-Mediated Neurotransmitter Release. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 2014, 466, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, L.; Wible, B.; Arcangeli, A.; Taglialatela, M.; Morra, F.; Castaldo, P.; Crociani, O.; Rosati, B.; Faravelli, L.; Olivotto, M.; et al. Herg Encodes a K+ Current Highly Conserved in Tumors of Different Histogenesis: A Selective Advantage for Cancer Cells? Cancer Res 1998, 58, 815–822. [Google Scholar]
- Imbrici, P.; Liantonio, A.; Camerino, G.M.; De Bellis, M.; Camerino, C.; Mele, A.; Giustino, A.; Pierno, S.; De Luca, A.; Tricarico, D.; et al. Therapeutic Approaches to Genetic Ion Channelopathies and Perspectives in Drug Discovery. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Karlova, M.; Zhang, H.; Pustovit, O.B.; Mai, L.; Novoseletsky, V.; Podolyak, D.; Zaklyazminskaya, E.V.; Abramochkin, D.V.; Sokolova, O.S. A Mutation in the Cardiac KV7.1 Channel Possibly Disrupts Interaction with Yotiao Protein. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2024, 714, 149947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramochkin, D.; Li, B.; Zhang, H.; Kravchuk, E.; Nesterova, T.; Glukhov, G.; Shestak, A.; Zaklyazminskaya, E.; Sokolova, O.S. Novel Gain-of-Function Mutation in the Kv11.1 Channel Found in the Patient with Brugada Syndrome and Mild QTc Shortening. Biochemistry Moscow 2024, 89, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlova, M.; Abramochkin, D.V.; Pustovit, K.B.; Nesterova, T.; Novoseletsky, V.; Loussouarn, G.; Zaklyazminskaya, E.; Sokolova, O.S. Disruption of a Conservative Motif in the C-Terminal Loop of the KCNQ1 Channel Causes LQT Syndrome. IJMS 2022, 23, 7953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaklyazminskaya, E.; Polyak, M.; Shestak, A.; Sadekova, M.; Komoliatova, V.; Kiseleva, I.; Makarov, L.; Podolyak, D.; Glukhov, G.; Zhang, H.; et al. Variable Clinical Appearance of the Kir2.1 Rare Variants in Russian Patients with Long QT Syndrome. Genes 2022, 13, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlova, M.; Rusinova, V.; Abramochkin, D.; Zaklyazminskaya, E.; Sokolova, O. Novel Kv7.1 Missense Mutation Lys422Glu Leads to the Development of LQT Syndrome. Microsc Microanal 2021, 27, 1742–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Glukhov, G.S.; Pustovit, K.B.; Kacher, Yu.G.; Rusinova, V.S.; Kiseleva, I.I.; Komolyatova, V.N.; Makarov, L.M.; Zaklyazminskaya, E.V.; Sokolova, O.S. Phenotypic Manifestations of Val93Ile Missense Mutation and Its Influence on Kir2.1 Channel Functioning. Moscow Univ. Biol.Sci. Bull. 2021, 76, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minor, D.L., Jr. Searching for Interesting Channels: Pairing Selection and Molecular Evolution Methods to Study Ion Channel Structure and Function. Mol. BioSyst. 2009, 5, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.H.; Yarov-Yarovoy, V.; Gutman, G.A.; Catterall, W.A. Overview of Molecular Relationships in the Voltage-Gated Ion Channel Superfamily. Pharmacol Rev 2005, 57, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouaux, E.; MacKinnon, R. Principles of Selective Ion Transport in Channels and Pumps. Science 2005, 310, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findeisen, F.; Minor, D.L., Jr. Progress in the Structural Understanding of Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel (Ca V ) Function and Modulation. Channels 2010, 4, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lera Ruiz, M.; Kraus, R.L. Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels: Structure, Function, Pharmacology, and Clinical Indications. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7093–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, R. Potassium Channels. FEBS Letters 2003, 555, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islas, L.D. Functional Diversity of Potassium Channel Voltage-Sensing Domains. Channels 2016, 10, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhu, W.; Gao, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xing, B. Nanoparticles-Mediated Ion Channels Manipulation: From Their Membrane Interactions to Bioapplications. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2023, 195, 114763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evolution of Ionic Channels of Biological Membranes. Molecular Biology and Evolution 1989. [CrossRef]
- Grizel, A.V.; Glukhov, G.S.; Sokolova, O.S. Mechanisms of Activation of Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels. Acta Naturae 2014, 6, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Zhao, H.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lo, Y.; Jan, L.Y.; Lee, C.-H. Activation and Closed-State Inactivation Mechanisms of the Human Voltage-Gated KV4 Channel Complexes. Molecular Cell 2022, 82, 2427–2442.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Lee, A.; Limapichat, W.; Dougherty, D.A.; MacKinnon, R. A Gating Charge Transfer Center in Voltage Sensors. Science 2010, 328, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delemotte, L.; Tarek, M.; Klein, M.L.; Amaral, C.; Treptow, W. Intermediate States of the Kv1.2 Voltage Sensor from Atomistic Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2011, 108, 6109–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, E.; Bezanilla, F.; Roux, B. In Search of a Consensus Model of the Resting State of a Voltage-Sensing Domain. Neuron 2011, 72, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; MacKinnon, R. Cryo-EM Structure of a KCNQ1/CaM Complex Reveals Insights into Congenital Long QT Syndrome. Cell 2017, 169, 1042–1050.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Zhong, L.; Yan, Z.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, F.; Huang, Y.; Lai, D.; Yang, W.; Hou, P.; et al. Structural Mechanisms for the Activation of Human Cardiac KCNQ1 Channel by Electro-Mechanical Coupling Enhancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2022, 119, e2207067119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandala, V.S.; MacKinnon, R. The Membrane Electric Field Regulates the PIP 2 -Binding Site to Gate the KCNQ1 Channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2023, 120, e2301985120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Shan, Y.; Pei, D. Mechanism Underlying Delayed Rectifying in Human Voltage-Mediated Activation Eag2 Channel. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, F.; De La Peña, P.; Domínguez, P.; Sierra, L.M.; Pardo, L.A. The EAG Voltage-Dependent K+ Channel Subfamily: Similarities and Differences in Structural Organization and Gating. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malak, O.A.; Es-Salah-Lamoureux, Z.; Loussouarn, G. hERG S4-S5 Linker Acts as a Voltage-Dependent Ligand That Binds to the Activation Gate and Locks It in a Closed State. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malak, O.A.; Gluhov, G.S.; Grizel, A.V.; Kudryashova, K.S.; Sokolova, O.S.; Loussouarn, G. Voltage-Dependent Activation in EAG Channels Follows a Ligand-Receptor Rather than a Mechanical-Lever Mechanism. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2019, 294, 6506–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choveau, F.S.; Abderemane-Ali, F.; Coyan, F.C.; Es-Salah-Lamoureux, Z.; Baró, I.; Loussouarn, G. Opposite Effects of the S4–S5 Linker and PIP2 on Voltage-Gated Channel Function: KCNQ1/KCNE1 and Other Channels. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaydman, M.A.; Cui, J. PIP2 Regulation of KCNQ Channels: Biophysical and Molecular Mechanisms for Lipid Modulation of Voltage-Dependent Gating. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; MacKinnon, R. Structural Basis of Human KCNQ1 Modulation and Gating. Cell 2020, 180, 340–347.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, P.; Chen, Z.; Li, M.; Jiang, H.; Gao, Z.; Yang, H. Dynamic PIP 2 Interactions with Voltage Sensor Elements Contribute to KCNQ2 Channel Gating. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2013, 110, 20093–20098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popot, J.-L. Folding Membrane Proteins in Vitro: A Table and Some Comments. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 2014, 564, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, V.; Goode, A.; Bonev, B.B. Membrane Protein Structure Determination and Characterisation by Solution and Solid-State NMR. Biology 2020, 9, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonenko, Y.N.; Gluhov, G.S.; Firsov, A.M.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Kovalchuk, S.I.; Pechnikova, E.V.; Kotova, E.A.; Sokolova, O.S. Gramicidin A Disassembles Large Conductive Clusters of Its Lysine-Substituted Derivatives in Lipid Membranes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 17461–17470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-Y.S.; Dijkman, P.M.; Wiessing, S.A.; Kudryashev, M. Determining the Structure of the Bacterial Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel NaChBac Embedded in Liposomes by Cryo Electron Tomography and Subtomogram Averaging. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 11523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Maire, M.; Champeil, P.; Møller, J.V. Interaction of Membrane Proteins and Lipids with Solubilizing Detergents. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2000, 1508, 86–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garavito, R.M.; Ferguson-Miller, S. Detergents as Tools in Membrane Biochemistry. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2001, 276, 32403–32406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, O. Structure of Cation Channels, Revealed by Single Particle Electron Microscopy. FEBS Letters 2004, 564, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whicher, J.R.; MacKinnon, R. Structure of the Voltage-Gated K + Channel Eag1 Reveals an Alternative Voltage Sensing Mechanism. Science 2016, 353, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; MacKinnon, R. Cryo-EM Structure of the Open Human Ether-à-Go-Go -Related K + Channel hERG. Cell 2017, 169, 422–430.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.S.; Youn, T.; Byrne, B.; Chae, P.S. Impact of Novel Detergents on Membrane Protein Studies. Chem 2022, 8, 980–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, R.S.; Evanics, F.; Kitevski, J.L.; Al-Abdul-Wahid, M.S. Current Applications of Bicelles in NMR Studies of Membrane-Associated Amphiphiles and Proteins. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 8453–8465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, C.R.; Landis, G.C. Reconstitution of Membrane Proteins into Lipid-Rich Bilayered Mixed Micelles for NMR Studies. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 4030–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.M.; Dikiy, I.; Upadhyay, V.; Posson, D.J.; Eliezer, D.; Nimigean, C.M. Conformational Heterogeneity in Closed and Open States of the KcsA Potassium Channel in Lipid Bicelles. Journal of General Physiology 2016, 148, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biverståhl, H.; Lind, J.; Bodor, A.; Mäler, L. Biophysical Studies of the Membrane Location of the Voltage-Gated Sensors in the HsapBK and KvAP K+ Channels. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2009, 1788, 1976–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payandeh, J.; Scheuer, T.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. The Crystal Structure of a Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel. Nature 2011, 475, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, S.; Ahmad, A.B.; Sehar, U.; Georgieva, E.R. Lipid Membrane Mimetics in Functional and Structural Studies of Integral Membrane Proteins. Membranes 2021, 11, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribet, C.; Audebert, R.; Popot, J.-L. Amphipols: Polymers That Keep Membrane Proteins Soluble in Aqueous Solutions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1996, 93, 15047–15050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzkorn, M.; Raschle, T.; Hagn, F.; Gelev, V.; Rice, A.J.; Walz, T.; Wagner, G. Cell-Free Expressed Bacteriorhodopsin in Different Soluble Membrane Mimetics: Biophysical Properties and NMR Accessibility. Structure 2013, 21, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthies, D.; Bae, C.; Toombes, G.E.; Fox, T.; Bartesaghi, A.; Subramaniam, S.; Swartz, K.J. Single-Particle Cryo-EM Structure of a Voltage-Activated Potassium Channel in Lipid Nanodiscs. eLife 2018, 7, e37558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autzen, H.E.; Myasnikov, A.G.; Campbell, M.G.; Asarnow, D.; Julius, D.; Cheng, Y. Structure of the Human TRPM4 Ion Channel in a Lipid Nanodisc. Science 2018, 359, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winterstein, L.-M.; Kukovetz, K.; Rauh, O.; Turman, D.L.; Braun, C.; Moroni, A.; Schroeder, I.; Thiel, G. Reconstitution and Functional Characterization of Ion Channels from Nanodiscs in Lipid Bilayers. Journal of General Physiology 2018, 150, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Cao, E.; Julius, D.; Cheng, Y. TRPV1 Structures in Nanodiscs Reveal Mechanisms of Ligand and Lipid Action. Nature 2016, 534, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenkarev, Z.O.; Karlova, M.G.; Kulbatskii, D.S.; Kirpichnikov, M.P.; Lyukmanova, E.N.; Sokolova, O.S. Recombinant Production, Reconstruction in Lipid–Protein Nanodiscs, and Electron Microscopy of Full-Length α-Subunit of Human Potassium Channel Kv7.1. Biochemistry Moscow 2018, 83, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, T.J.; Finka, R.; Smith, C.; Lin, Y.-P.; Dafforn, T.; Overduin, M. Membrane Proteins Solubilized Intact in Lipid Containing Nanoparticles Bounded by Styrene Maleic Acid Copolymer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7484–7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orwick-Rydmark, M.; Lovett, J.E.; Graziadei, A.; Lindholm, L.; Hicks, M.R.; Watts, A. Detergent-Free Incorporation of a Seven-Transmembrane Receptor Protein into Nanosized Bilayer Lipodisq Particles for Functional and Biophysical Studies. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4687–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glukhov, G.; Karlova, M.; Kravchuk, E.; Glukhova, A.; Trifonova, E.; Sokolova, O.S. Purification of Potassium Ion Channels Using Styrene–Maleic Acid Copolymers. In Potassium Channels; Furini, S., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer US: New York, NY, 2024; Volume 2796, pp. 73–86. ISBN 978-1-07-163817-0. [Google Scholar]
- Orekhov, P.S.; Bozdaganyan, M.E.; Voskoboynikova, N.; Mulkidjanian, A.Y.; Karlova, M.G.; Yudenko, A.; Remeeva, A.; Ryzhykau, Y.L.; Gushchin, I.; Gordeliy, V.I.; et al. Mechanisms of Formation, Structure, and Dynamics of Lipoprotein Discs Stabilized by Amphiphilic Copolymers: A Comprehensive Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlova, M.G.; Voskoboynikova, N.; Gluhov, G.S.; Abramochkin, D.; Malak, O.A.; Mulkidzhanyan, A.; Loussouarn, G.; Steinhoff, H.-J.; Shaitan, K.V.; Sokolova, O.S. Detergent-Free Solubilization of Human Kv Channels Expressed in Mammalian Cells. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids 2019, 219, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Gennis, R.B. Single-Particle Cryo-EM Studies of Transmembrane Proteins in SMA Copolymer Nanodiscs. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids 2019, 221, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangham, A.D. Lipid Bilayers and Biomembranes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1972, 41, 753–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangham, A.D. Liposomes: The Babraham Connection. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids 1993, 64, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodle, M.C.; Papahadjopoulos, D. [9] Liposome Preparation and Size Characterization. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier, 1989; Volume 171, pp. 193–217. ISBN 978-0-12-182072-5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Tonggu, L. Membrane Protein Reconstitution for Functional and Structural Studies. Sci. China Life Sci. 2015, 58, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorev, D.S.; Baker, L.A.; Wu, D.; Beilsten-Edmands, V.; Rouse, S.L.; Zeev-Ben-Mordehai, T.; Jiko, C.; Samsudin, F.; Gerle, C.; Khalid, S.; et al. Protein Assemblies Ejected Directly from Native Membranes Yield Complexes for Mass Spectrometry. Science 2018, 362, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Zhao, C.; MacKinnon, R. Membrane Protein Isolation and Structure Determination in Cell-Derived Membrane Vesicles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2023, 120, e2302325120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hille, B.; Armstrong, C.M.; MacKinnon, R. Ion Channels: From Idea to Reality. Nat Med 1999, 5, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catterall, W.A. Structure and Function of Voltage-Gated Ion Channels. Trends in Neurosciences 1993, 16, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlin, A.; Akabas, M.H. [8] Substituted-Cysteine Accessibility Method. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier, 1998; Volume 293, pp. 123–145. ISBN 978-0-12-182194-4. [Google Scholar]
- Liapakis, G.; Simpson, M.M.; Javitch, J.A. The Substituted-Cysteine Accessibility Method ( SCAM ) to Elucidate Membrane Protein Structure. CP Neuroscience 1999, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glauner, K.S.; Mannuzzu, L.M.; Gandhi, C.S.; Isacoff, E.Y. Spectroscopic Mapping of Voltage Sensor Movement in the Shaker Potassium Channel. Nature 1999, 402, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinac, B. Single-Molecule FRET Studies of Ion Channels. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology 2017, 130, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capener, C.E. Ion Channels: Structural Bioinformatics and Modelling. Human Molecular Genetics 2002, 11, 2425–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, K.; Fowler, P.; Mokrab, Y.; Stansfeld, P.; Sansom, M.S.P. Chapter 12 Molecular Modeling and Simulation Studies of Ion Channel Structures, Dynamics and Mechanisms. In Methods in Cell Biology; Elsevier, 2008; Volume 90, pp. 233–265. ISBN 978-1-59749-270-6. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, D.A.; Cabral, J.M.; Pfuetzner, R.A.; Kuo, A.; Gulbis, J.M.; Cohen, S.L.; Chait, B.T.; MacKinnon, R. The Structure of the Potassium Channel: Molecular Basis of K + Conduction and Selectivity. Science 1998, 280, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherezov, V.; Clogston, J.; Misquitta, Y.; Abdel-Gawad, W.; Caffrey, M. Membrane Protein Crystallization In Meso: Lipid Type-Tailoring of the Cubic Phase. Biophysical Journal 2002, 83, 3393–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherezov, V.; Clogston, J.; Papiz, M.Z.; Caffrey, M. Room to Move: Crystallizing Membrane Proteins in Swollen Lipidic Mesophases. Journal of Molecular Biology 2006, 357, 1605–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; McMullan, G.; Scheres, S.H.W. How Cryo-EM Is Revolutionizing Structural Biology. Trends in Biochemical Sciences 2015, 40, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, P.; Fernández-Mariño, A.I.; Khanra, N.; He, C.; Paquette, A.J.; Wang, B.; Huang, R.; Smider, V.V.; Rice, W.J.; Swartz, K.J.; et al. Structures of the T Cell Potassium Channel Kv1.3 with Immunoglobulin Modulators. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Huang, J.; Jin, X.; Yan, N. Cryo-EM Structure of Human Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Na v 1.6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2023, 120, e2220578120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Research 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špačková, A.; Vávra, O.; Raček, T.; Bazgier, V.; Sehnal, D.; Damborský, J.; Svobodová, R.; Bednář, D.; Berka, K. ChannelsDB 2.0: A Comprehensive Database of Protein Tunnels and Pores in AlphaFold Era. Nucleic Acids Research 2024, 52, D413–D418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R.; Khazen, G.; Gambazzi, L.; Ramaswamy, S.; Hill, S.L.; Schürmann, F.; Markram, H. Channelpedia: An Integrative and Interactive Database for Ion Channels. Front. Neuroinform. 2011, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Pan, X.; Yan, N. Structural Biology and Molecular Pharmacology of Voltage-Gated Ion Channels. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonherr, R. Inhibition of Human Ether a Go-Go Potassium Channels by Ca2+/Calmodulin. The EMBO Journal 2000, 19, 3263–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziechner, U.; Schönherr, R.; Born, A.; Gavrilova-Ruch, O.; Glaser, R.W.; Malesevic, M.; Küllertz, G.; Heinemann, S.H. Inhibition of Human Ether à Go-go Potassium Channels by Ca 2+ /Calmodulin Binding to the Cytosolic N- and C-termini. The FEBS Journal 2006, 273, 1074–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malak, O.A.; Abderemane-Ali, F.; Wei, Y.; Coyan, F.C.; Pontus, G.; Shaya, D.; Marionneau, C.; Loussouarn, G. Up-Regulation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels by Peptides Mimicking S4-S5 Linkers Reveals a Variation of the Ligand-Receptor Mechanism. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haitin, Y.; Wiener, R.; Shaham, D.; Peretz, A.; Cohen, E.B.-T.; Shamgar, L.; Pongs, O.; Hirsch, J.A.; Attali, B. Intracellular Domains Interactions and Gated Motions of IKS Potassium Channel Subunits. EMBO J 2009, 28, 1994–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aivar, P.; Fernández-Orth, J.; Gomis-Perez, C.; Alberdi, A.; Alaimo, A.; Rodríguez, M.S.; Giraldez, T.; Miranda, P.; Areso, P.; Villarroel, A. Surface Expression and Subunit Specific Control of Steady Protein Levels by the Kv7.2 Helix A-B Linker. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Abderemane-Ali, F.; Hura, G.L.; Rossen, N.D.; Gate, R.E.; Minor, D.L. A Calmodulin C-Lobe Ca2+-Dependent Switch Governs Kv7 Channel Function. Neuron 2018, 97, 836–852.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachyani, D.; Dvir, M.; Strulovich, R.; Tria, G.; Tobelaim, W.; Peretz, A.; Pongs, O.; Svergun, D.; Attali, B.; Hirsch, J.A. Structural Basis of a Kv7.1 Potassium Channel Gating Module: Studies of the Intracellular C-Terminal Domain in Complex with Calmodulin. Structure 2014, 22, 1582–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisedchaisri, G.; Tonggu, L.; McCord, E.; Gamal El-Din, T.M.; Wang, L.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. Resting-State Structure and Gating Mechanism of a Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel. Cell 2019, 178, 993–1003.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clairfeuille, T.; Cloake, A.; Infield, D.T.; Llongueras, J.P.; Arthur, C.P.; Li, Z.R.; Jian, Y.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.-F.; Bougis, P.E.; Ciferri, C.; et al. Structural Basis of α-Scorpion Toxin Action on Na v Channels. Science 2019, 363, eaav8573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, T.; Rohou, A.; Arthur, C.P.; Tzakoniati, F.; Wong, E.; Estevez, A.; Kugel, C.; Franke, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Structural Basis of Nav1.7 Inhibition by a Gating-Modifier Spider Toxin. Cell 2019, 176, 702–715.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Brown, E.C.; Wang, W.; MacKinnon, R. Novel Cell-Free High-Throughput Screening Method for Pharmacological Tools Targeting K + Channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2016, 113, 5748–5753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandala, V.S.; MacKinnon, R. Voltage-Sensor Movements in the Eag Kv Channel under an Applied Electric Field. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2022, 119, e2214151119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühlbrandt, W. The Resolution Revolution. Science 2014, 343, 1443–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egelman, E.H. The Current Revolution in Cryo-EM. Biophysical Journal 2016, 110, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliushcheuskaya, P.; Künze, G. Recent Advances in Computer-Aided Structure-Based Drug Design on Ion Channels. IJMS 2023, 24, 9226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owji, A.P.; Wang, J.; Kittredge, A.; Clark, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hendrickson, W.A.; Yang, T. Structures and Gating Mechanisms of Human Bestrophin Anion Channels. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biou, V. Lipid-Membrane Protein Interaction Visualised by Cryo-EM: A Review. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2023, 1865, 184068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.B.; Tao, X.; Campbell, E.B.; MacKinnon, R. Atomic Structure of a Voltage-Dependent K+ Channel in a Lipid Membrane-like Environment. Nature 2007, 450, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergh, C.; Rovšnik, U.; Howard, R.; Lindahl, E. Discovery of Lipid Binding Sites in a Ligand-Gated Ion Channel by Integrating Simulations and Cryo-EM. eLife 2024, 12, RP86016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Nisler, C.R.; Fluck, E.C.; Walujkar, S.; Sotomayor, M.; Moiseenkova-Bell, V.Y. Structure of the Ancient TRPY1 Channel from Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Reveals Mechanisms of Modulation by Lipids and Calcium. Structure 2022, 30, 139–155.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, W.R.; Mancino, A.; Moss, F.R.; Frost, A.; Julius, D.; Cheng, Y. Structural Basis of TRPV1 Modulation by Endogenous Bioactive Lipids. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidpeter, P.A.M.; Petroff, J.T.; Khajoueinejad, L.; Wague, A.; Frankfater, C.; Cheng, W.W.L.; Nimigean, C.M.; Riegelhaupt, P.M. Membrane Phospholipids Control Gating of the Mechanosensitive Potassium Leak Channel TREK1. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Valinsky, W.C.; On, N.C.; Houlihan, P.R.; Qu, Q.; Liu, L.; Pan, X.; Clapham, D.E.; Yan, N. Employing NaChBac for Cryo-EM Analysis of Toxin Action on Voltage-Gated Na + Channels in Nanodisc. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2020, 117, 14187–14193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisedchaisri, G.; Tonggu, L.; Gamal El-Din, T.M.; McCord, E.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. Structural Basis for High-Affinity Trapping of the NaV1.7 Channel in Its Resting State by Tarantula Toxin. Molecular Cell 2021, 81, 38–48.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kschonsak, M.; Jao, C.C.; Arthur, C.P.; Rohou, A.L.; Bergeron, P.; Ortwine, D.F.; McKerrall, S.J.; Hackos, D.H.; Deng, L.; Chen, J.; et al. Cryo-EM Reveals an Unprecedented Binding Site for NaV1.7 Inhibitors Enabling Rational Design of Potent Hybrid Inhibitors. eLife 2023, 12, e84151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; MacKinnon, R. Voltage Sensor Movements during Hyperpolarization in the HCN Channel. Cell 2019, 179, 1582–1589.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yu, M.; Jia, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Yang, F.; Lei, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Structural Basis for the Activity Regulation of a Potassium Channel AKT1 from Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, H.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ong, S.T.; Chandy, K.G.; Zhang, L.; Tian, C. Structures of Wild-Type and H451N Mutant Human Lymphocyte Potassium Channel KV1.3. Cell Discov 2021, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, D.; Zhou, P.; Tian, C.; Liu, S. Cryo-EM Structure Reveals a Symmetry Reduction of the Plant Outward-Rectifier Potassium Channel SKOR. Cell Discov 2023, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whicher, J.R.; MacKinnon, R. Regulation of Eag1 Gating by Its Intracellular Domains. eLife 2019, 8, e49188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-N.; Cho, H.-J.; Jeong, H.; Ryu, B.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, M.; Yoo, J.; Woo, J.-S.; Lee, H.H. Cryo-EM Structures of Human Cx36/GJD2 Neuronal Gap Junction Channel. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayagam, D.; Quentin, D.; Yu-Strzelczyk, J.; Sitsel, O.; Merino, F.; Stabrin, M.; Hofnagel, O.; Yu, M.; Ledeboer, M.W.; Nagel, G.; et al. Structural Basis of TRPC4 Regulation by Calmodulin and Pharmacological Agents. eLife 2020, 9, e60603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluck, E.C.; Yazici, A.T.; Rohacs, T.; Moiseenkova-Bell, V.Y. Structural Basis of TRPV5 Regulation by Physiological and Pathophysiological Modulators. Cell Reports 2022, 39, 110737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Kumari, S.; Guldhe, A.; Misra, R.; Rawat, I.; Bux, F. Trends and Novel Strategies for Enhancing Lipid Accumulation and Quality in Microalgae. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2016, 55, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barret, D.C.A.; Schuster, D.; Rodrigues, M.J.; Leitner, A.; Picotti, P.; Schertler, G.F.X.; Kaupp, U.B.; Korkhov, V.M.; Marino, J. Structural Basis of Calmodulin Modulation of the Rod Cyclic Nucleotide-Gated Channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2023, 120, e2300309120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Fang, J.; Zhao, G.; et al. Ligand Activation Mechanisms of Human KCNQ2 Channel. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiharan, Y.K.; Glaaser, I.W.; Zhao, Y.; Robertson, M.J.; Skiniotis, G.; Slesinger, P.A. Structural Insights into GIRK2 Channel Modulation by Cholesterol and PIP2. Cell Reports 2021, 36, 109619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Dang, S.; Han, T.W.; Ye, W.; Jin, P.; Cheng, T.; Li, J.; Jan, Y.N.; Jan, L.Y.; Cheng, Y. Cryo-EM Studies of TMEM16F Calcium-Activated Ion Channel Suggest Features Important for Lipid Scrambling. Cell Reports 2019, 28, 567–579.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Roth, B.; Lü, W.; Du, J. Ligand Recognition and Gating Mechanism through Three Ligand-Binding Sites of Human TRPM2 Channel. eLife 2019, 8, e50175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willegems, K.; Eldstrom, J.; Kyriakis, E.; Ataei, F.; Sahakyan, H.; Dou, Y.; Russo, S.; Van Petegem, F.; Fedida, D. Structural and Electrophysiological Basis for the Modulation of KCNQ1 Channel Currents by ML277. Nat Commun 2022, 13, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, P.; Fu, J.; Mei, L.; Lv, D.; Wang, J.; Lai, D.; Ye, S.; Yang, H.; et al. Molecular Basis for Ligand Activation of the Human KCNQ2 Channel. Cell Res 2021, 31, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, S.; Li, G.-L.; Shu, Y.; Xu, F. Structural Insights into the Lipid and Ligand Regulation of a Human Neuronal KCNQ Channel. Neuron 2022, 110, 237–247.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbeke, E.J.; Zhou, Y.; Horton, A.P.; Mallam, A.L.; Taylor, D.W.; Marcotte, E.M. Separating Distinct Structures of Multiple Macromolecular Assemblies from Cryo-EM Projections. Journal of Structural Biology 2020, 209, 107416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Yu, H.; Gu, K.; Wang, Z.; Ruan, H.; Wang, K.; Ren, S.; Li, B.; Gan, L.; Xu, S.; et al. A Particle-Filter Framework for Robust Cryo-EM 3D Reconstruction. Nat Methods 2018, 15, 1083–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punjani, A.; Rubinstein, J.L.; Fleet, D.J.; Brubaker, M.A. cryoSPARC: Algorithms for Rapid Unsupervised Cryo-EM Structure Determination. Nat Methods 2017, 14, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorzano, C.O.S.; Jiménez, A.; Mota, J.; Vilas, J.L.; Maluenda, D.; Martínez, M.; Ramírez-Aportela, E.; Majtner, T.; Segura, J.; Sánchez-García, R.; et al. Survey of the Analysis of Continuous Conformational Variability of Biological Macromolecules by Electron Microscopy. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 2019, 75, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toader, B.; Sigworth, F.J.; Lederman, R.R. Methods for Cryo-EM Single Particle Reconstruction of Macromolecules Having Continuous Heterogeneity. Journal of Molecular Biology 2023, 435, 168020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnat, C.; Levy, A.; Poitevin, F.; Zhong, E.D.; Miolane, N. Deep Generative Modeling for Volume Reconstruction in Cryo-Electron Microscopy. Journal of Structural Biology 2022, 214, 107920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
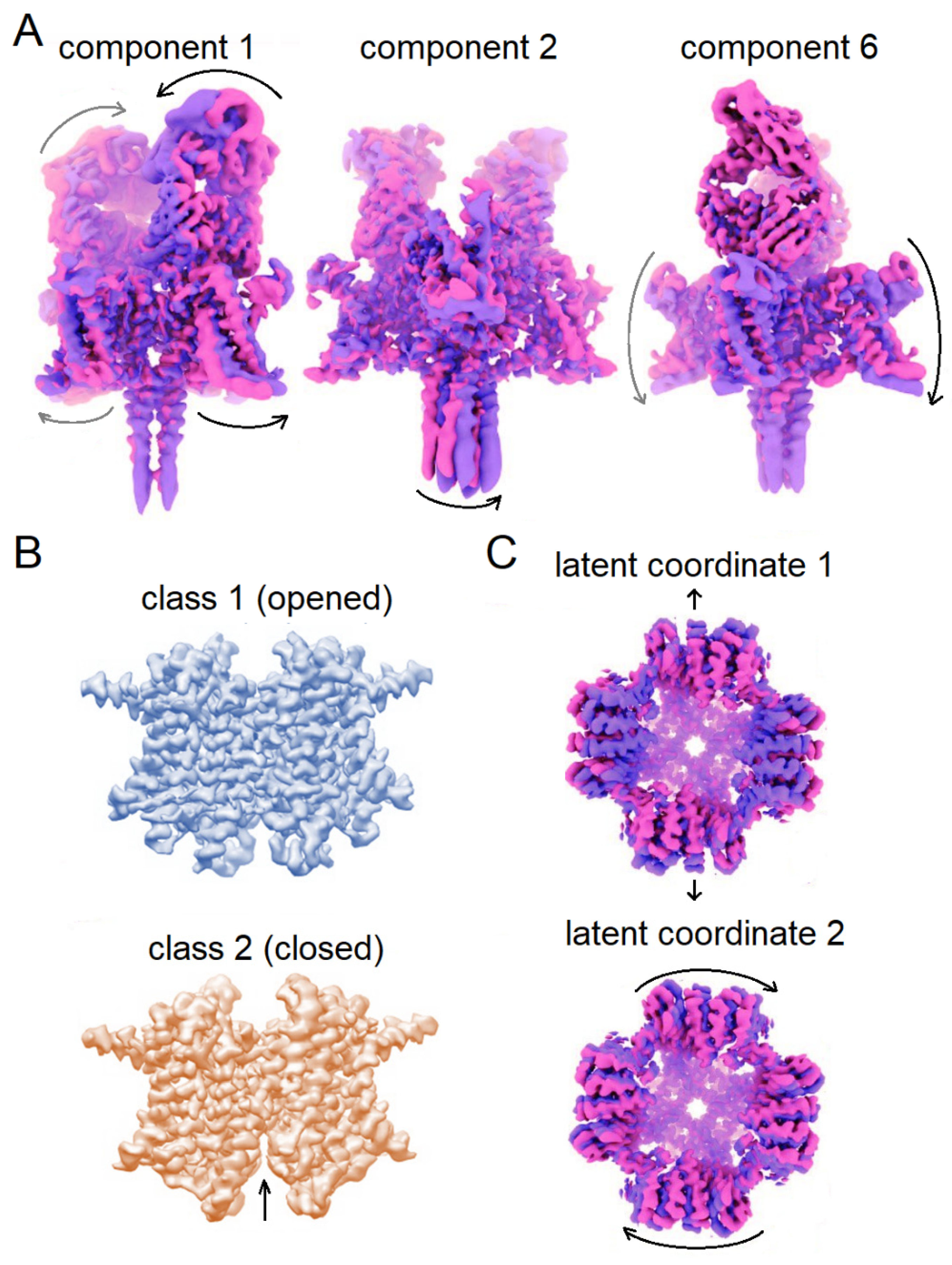
- Penczek, P.A.; Kimmel, M.; Spahn, C.M.T. Identifying Conformational States of Macromolecules by Eigen-Analysis of Resampled Cryo-EM Images. Structure 2011, 19, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagare, H.D.; Kucukelbir, A.; Sigworth, F.J.; Wang, H.; Rao, M. Directly Reconstructing Principal Components of Heterogeneous Particles from Cryo-EM Images. Journal of Structural Biology 2015, 191, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punjani, A.; Fleet, D.J. 3D Variability Analysis: Resolving Continuous Flexibility and Discrete Heterogeneity from Single Particle Cryo-EM. Journal of Structural Biology 2021, 213, 107702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsevich, E.; Katsevich, A.; Singer, A. Covariance Matrix Estimation for the Cryo-EM Heterogeneity Problem. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2015, 8, 126–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andén, J.; Singer, A. Structural Variability from Noisy Tomographic Projections. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2018, 11, 1441–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punjani, A.; Zhang, H.; Fleet, D.J. Non-Uniform Refinement: Adaptive Regularization Improves Single-Particle Cryo-EM Reconstruction. Nat Methods 2020, 17, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Paknejad, N.; Hite, R.K. Gating and Selectivity Mechanisms for the Lysosomal K+ Channel TMEM175. eLife 2020, 9, e53430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punjani, A.; Fleet, D.J. 3DFlex: Determining Structure and Motion of Flexible Proteins from Cryo-EM. Nat Methods 2023, 20, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilles, M.A.; Singer, A. Cryo-EM Heterogeneity Analysis Using Regularized Covariance Estimation and Kernel Regression 2023.
- Punjani, A.; Fleet, D. 3D Flexible Refinement: Structure and Motion of Flexible Proteins from Cryo-EM. Microscopy and Microanalysis 2022, 28, 1218–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andén, O.; Rovsnik, U.; Lycksell, M.; Howard, R.J.; Lindahl, E.R. Structural Characterization of Regulation by a Dynamic N-Terminal Module in the Pentameric Ligand-Gated Ion Channel DeCLIC. Biophysical Journal 2024, 123, 394a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Briggs, J.A.G. Cryo-Electron Tomography and Subtomogram Averaging. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier, 2016; Volume 579, pp. 329–367. ISBN 978-0-12-805382-9. [Google Scholar]
- Pyle, E.; Zanetti, G. Current Data Processing Strategies for Cryo-Electron Tomography and Subtomogram Averaging. Biochemical Journal 2021, 478, 1827–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeev-Ben-Mordehai, T.; Vasishtan, D.; Siebert, C.A.; Whittle, C.; Grünewald, K. Extracellular Vesicles: A Platform for the Structure Determination of Membrane Proteins by Cryo-EM. Structure 2014, 22, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamm, L.; Righetto, R.D.; Wietrzynski, W.; Pöge, M.; Martinez-Sanchez, A.; Peng, T.; Engel, B.D. MemBrain: A Deep Learning-Aided Pipeline for Detection of Membrane Proteins in Cryo-Electron Tomograms. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 2022, 224, 106990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yan, X.; Li, S.; Huang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhao, T.; Huang, M.; Zhou, N.; Shen, Y. MPicker: Visualizing and Picking Membrane Proteins for Cryo-Electron Tomography 2024.
- Martinez-Sanchez, A.; Kochovski, Z.; Laugks, U.; Meyer Zum Alten Borgloh, J.; Chakraborty, S.; Pfeffer, S.; Baumeister, W.; Lučić, V. Template-Free Detection and Classification of Membrane-Bound Complexes in Cryo-Electron Tomograms. Nat Methods 2020, 17, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himes, B.A.; Zhang, P. emClarity: Software for High-Resolution Cryo-Electron Tomography and Subtomogram Averaging. Nat Methods 2018, 15, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaño-Díez, D.; Kudryashev, M.; Arheit, M.; Stahlberg, H. Dynamo: A Flexible, User-Friendly Development Tool for Subtomogram Averaging of Cryo-EM Data in High-Performance Computing Environments. Journal of Structural Biology 2012, 178, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, P.; Scaramuzza, S.; Stahlberg, H.; Castaño-Díez, D. The Dynamo Software Package for Cryo-Electron Tomography and Subtomogram Averaging. Microsc Microanal 2020, 26, 3142–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balyschew, N.; Yushkevich, A.; Mikirtumov, V.; Sanchez, R.M.; Sprink, T.; Kudryashev, M. Streamlined Structure Determination by Cryo-Electron Tomography and Subtomogram Averaging Using TomoBEAR. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudryashev, M.; Castaño-Díez, D.; Deluz, C.; Hassaine, G.; Grasso, L.; Graf-Meyer, A.; Vogel, H.; Stahlberg, H. The Structure of the Mouse Serotonin 5-HT 3 Receptor in Lipid Vesicles. Structure 2016, 24, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Kudryashev, M. Structure of RyR1 in Native Membranes. EMBO Reports 2020, 21, e49891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, R.M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Dietrich, L.; Kudryashev, M. Subnanometer-Resolution Structure Determination in Situ by Hybrid Subtomogram Averaging - Single Particle Cryo-EM. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjin, X.; Ling, L. Developments, Applications, and Prospects of Cryo-electron Microscopy. Protein Science 2020, 29, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).