Submitted:
07 September 2024
Posted:
09 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study 1 (S1)
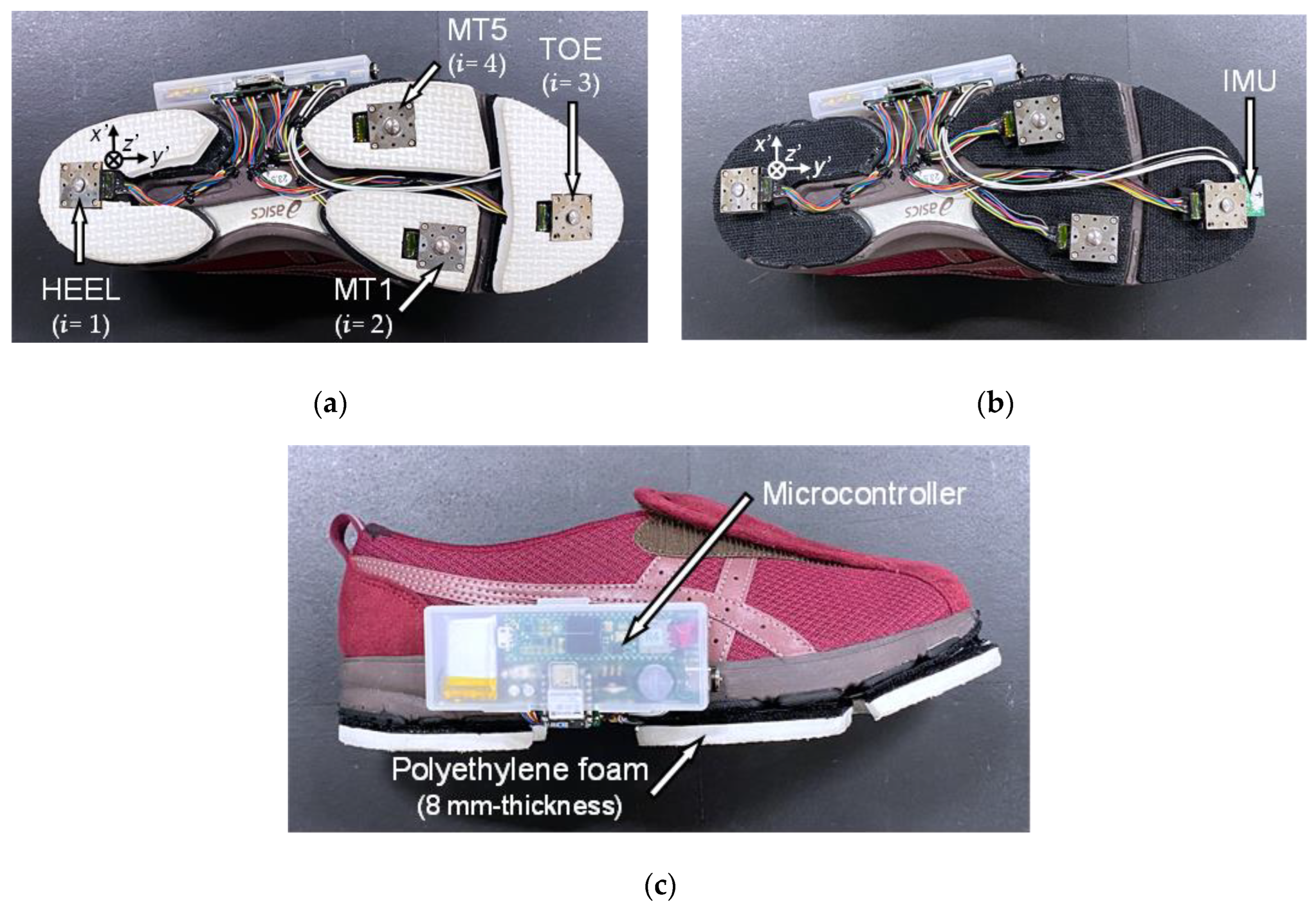
2.1.1. Developing the Shoe Sensor System
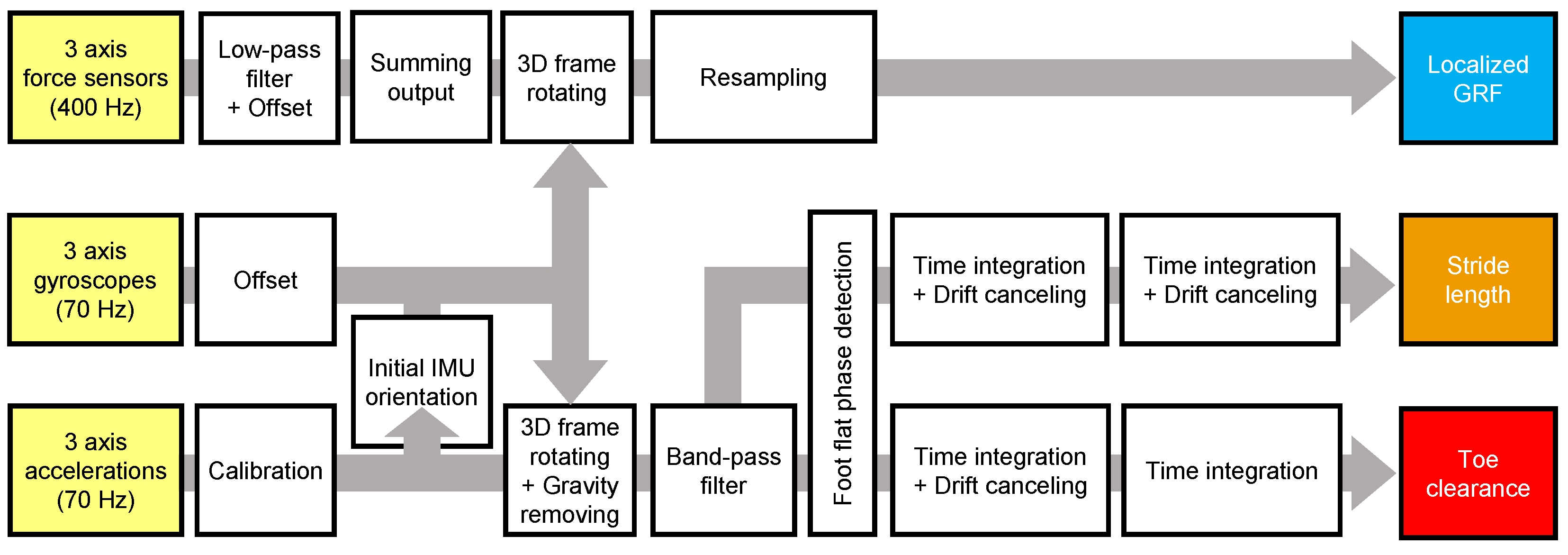
2.1.2. Data Processing Framework of the Gait Analysis System Using Shoe Sensor System
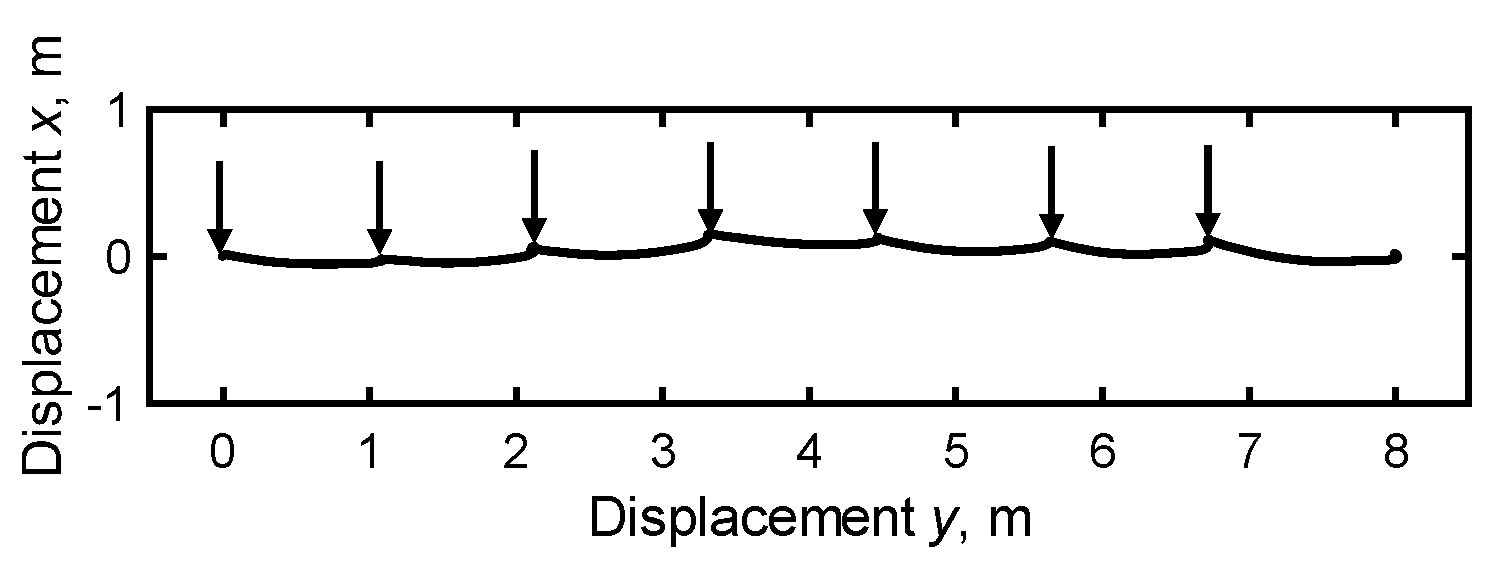
2.1.3. Verification Test for the Estimation Accuracy of Stride Length and Minimum Toe Clearance
2.2. Study 2 (S2)
3. Results
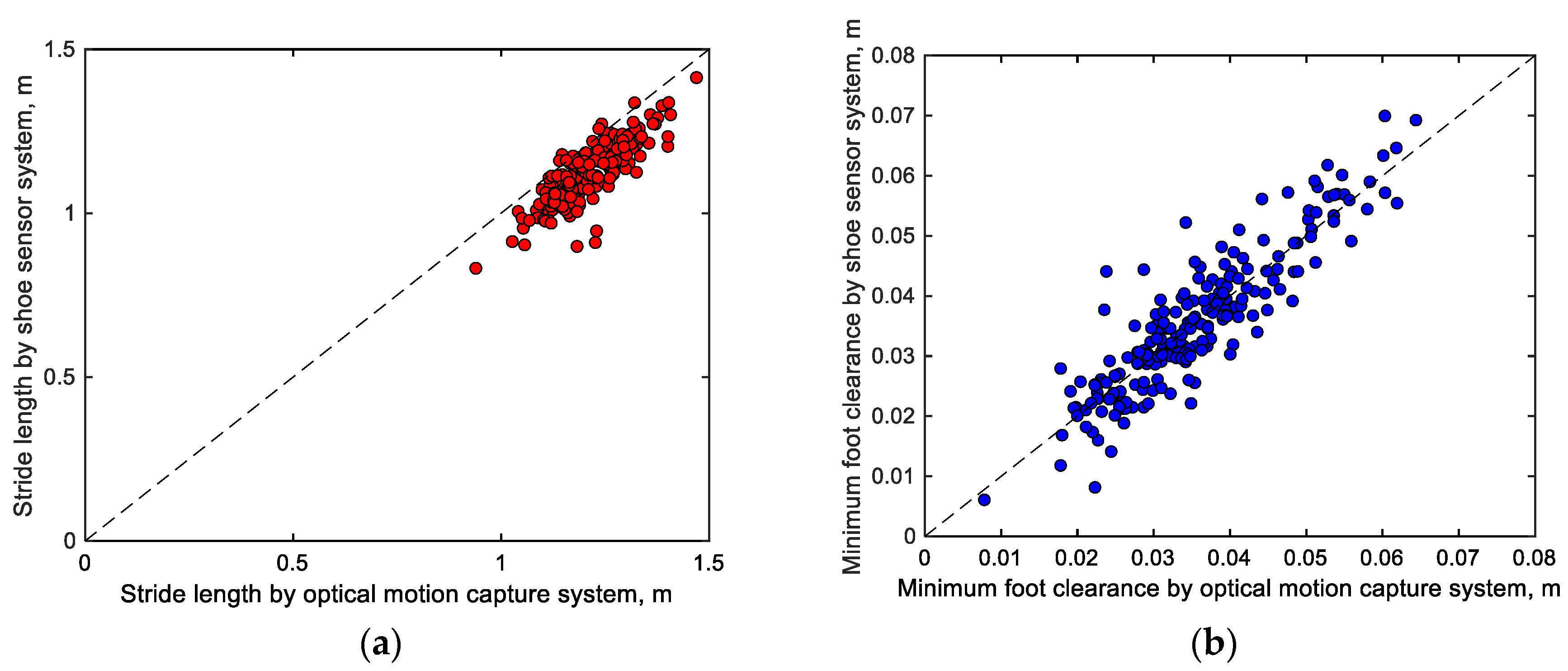
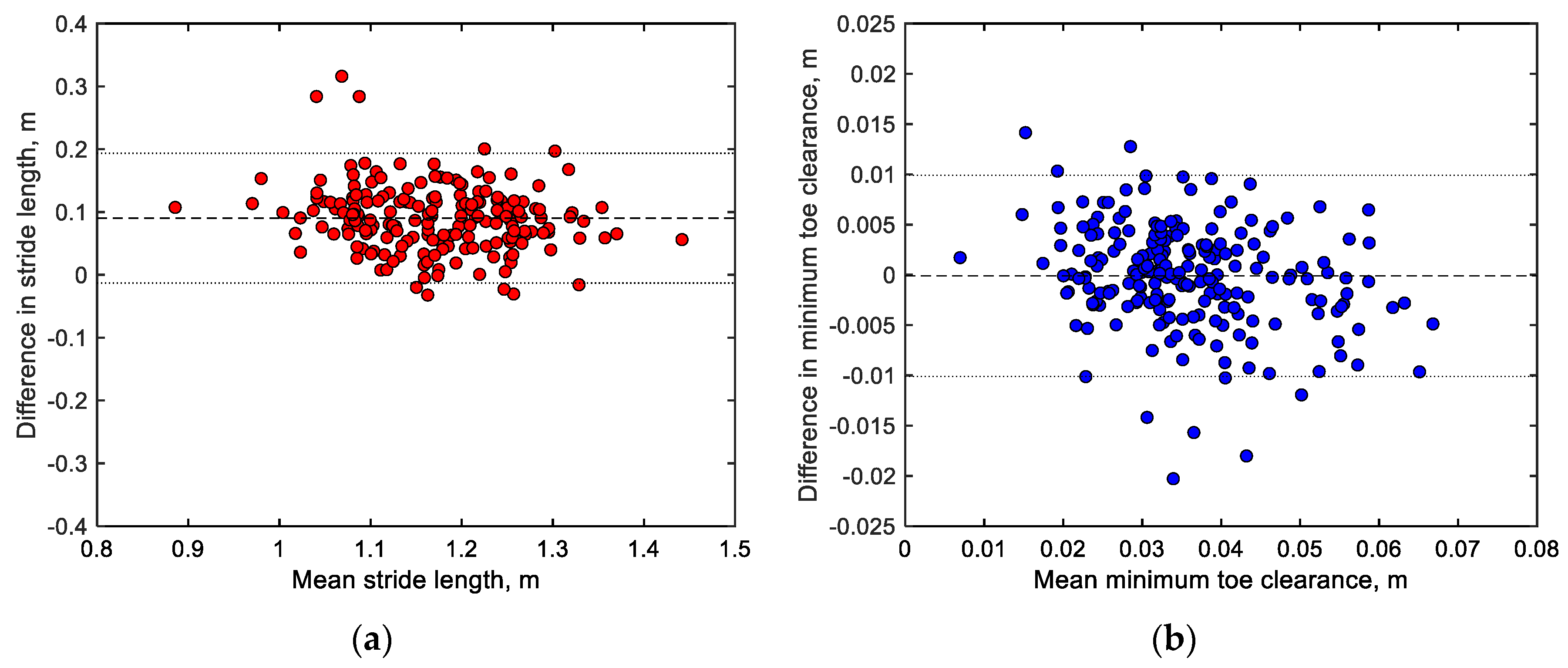
3.1. Accuracy Verification of Stride Length and Minimum Toe Clearance (S1)
3.2. Comparison of Gait Parameters between Young and Older Adults (S2)
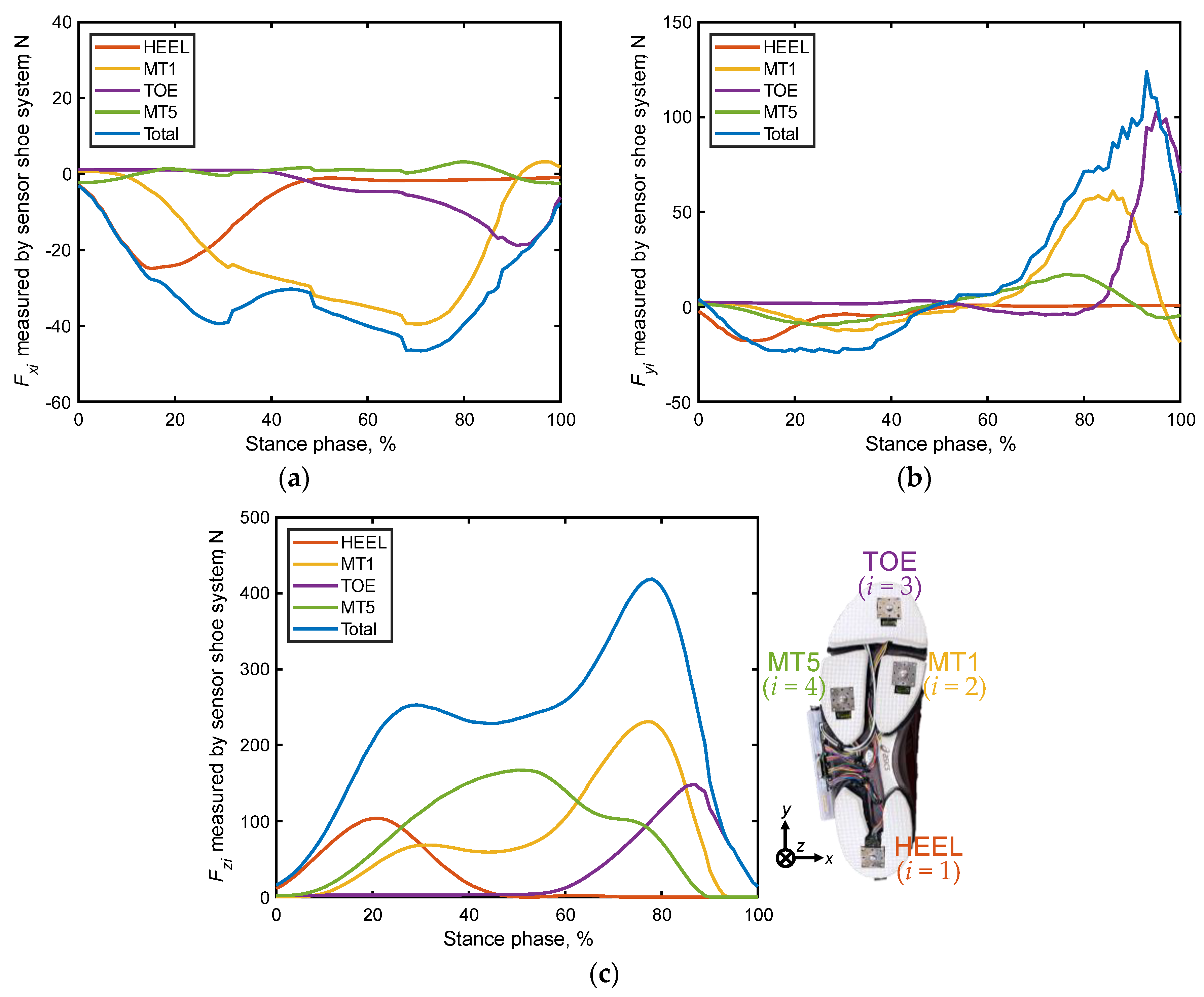
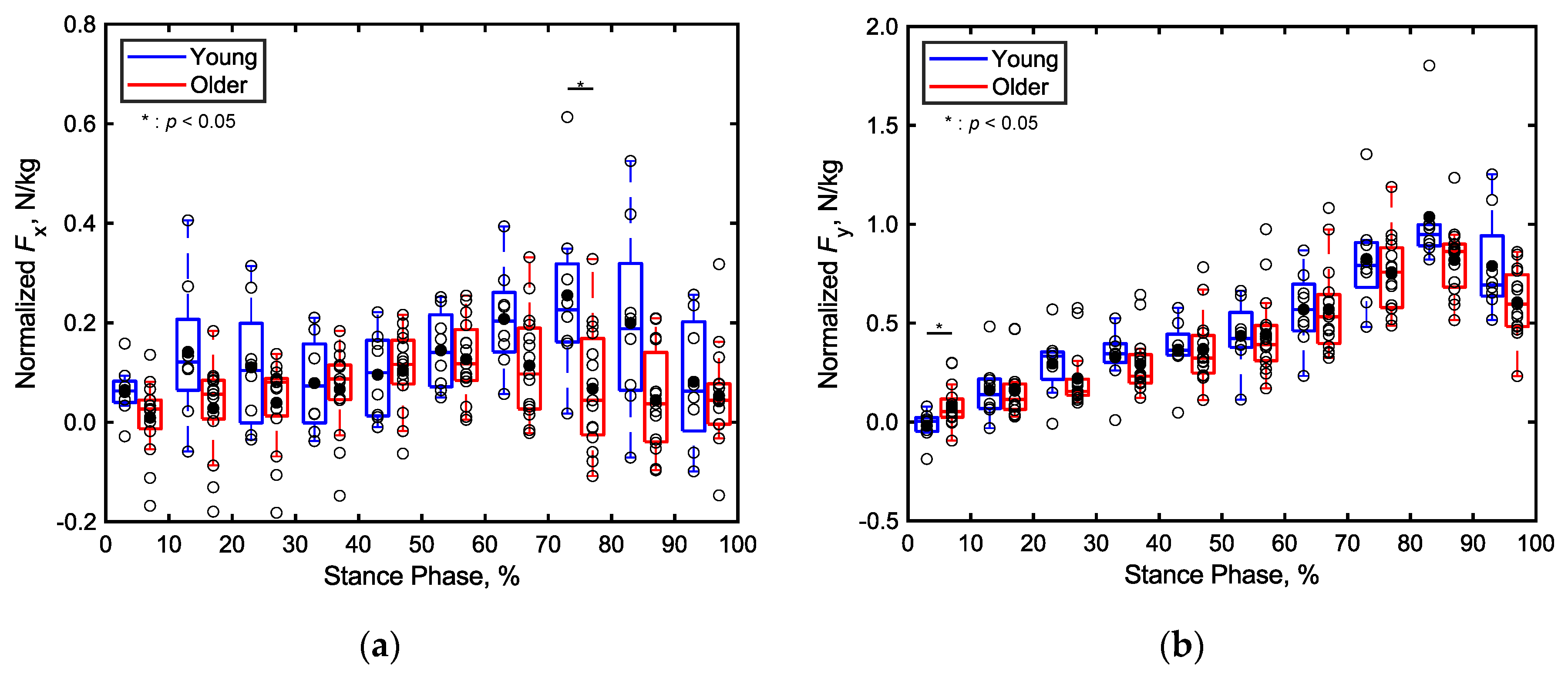
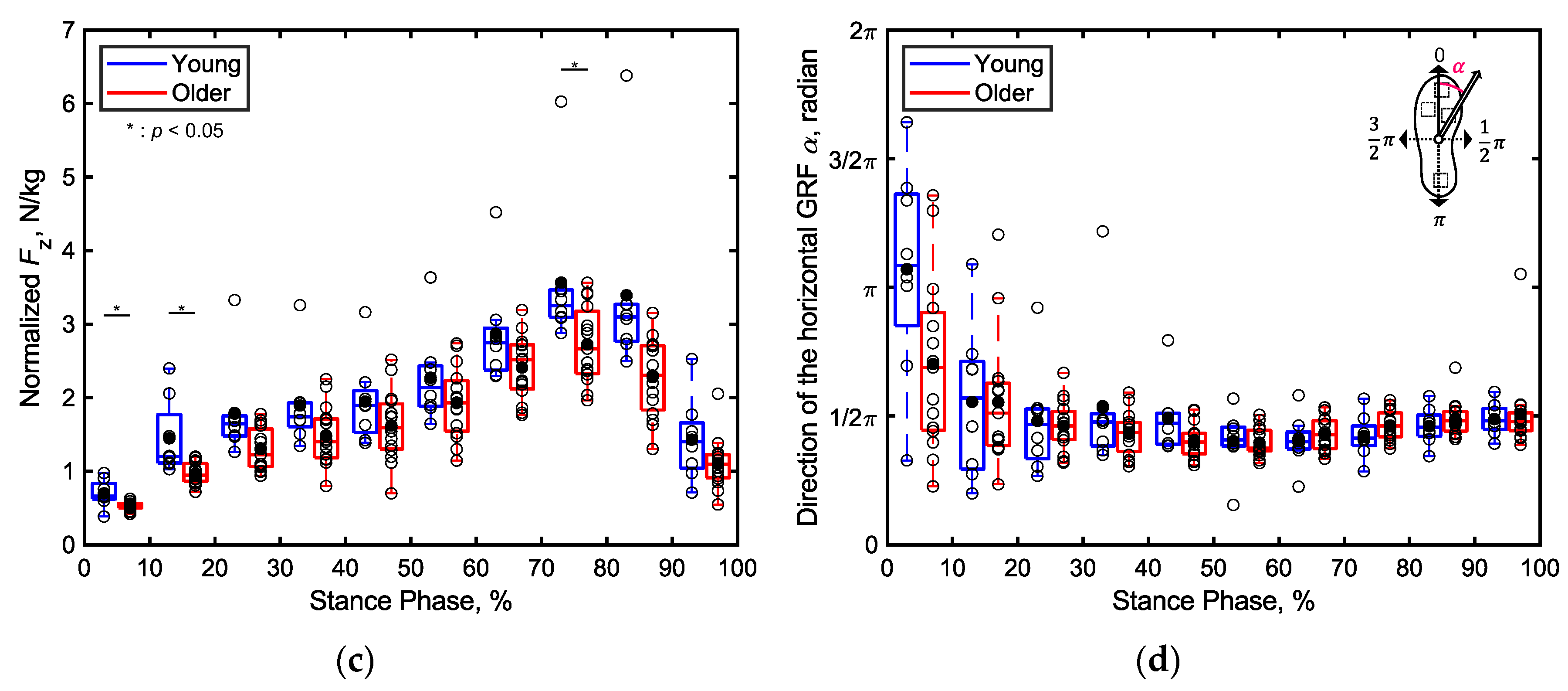
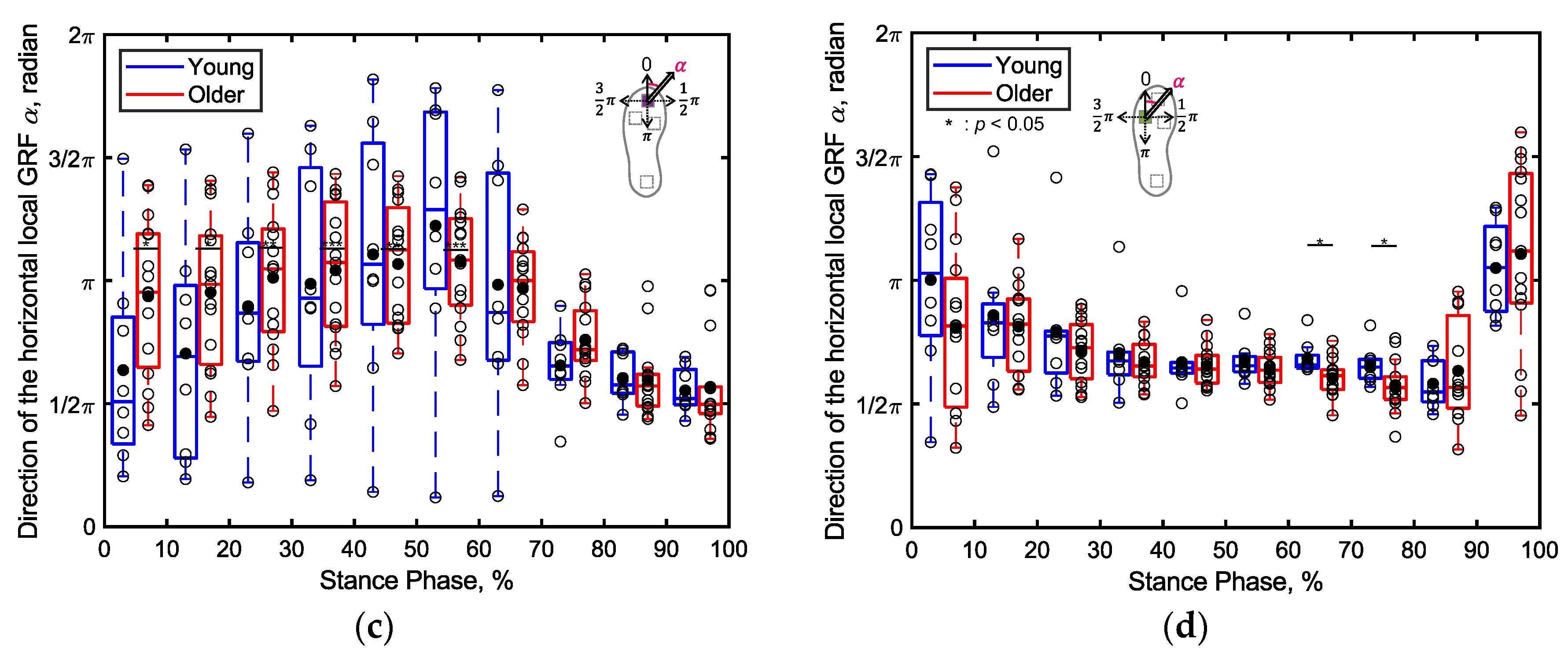
3.2.1. Total Ground Reaction Forces (GRF)
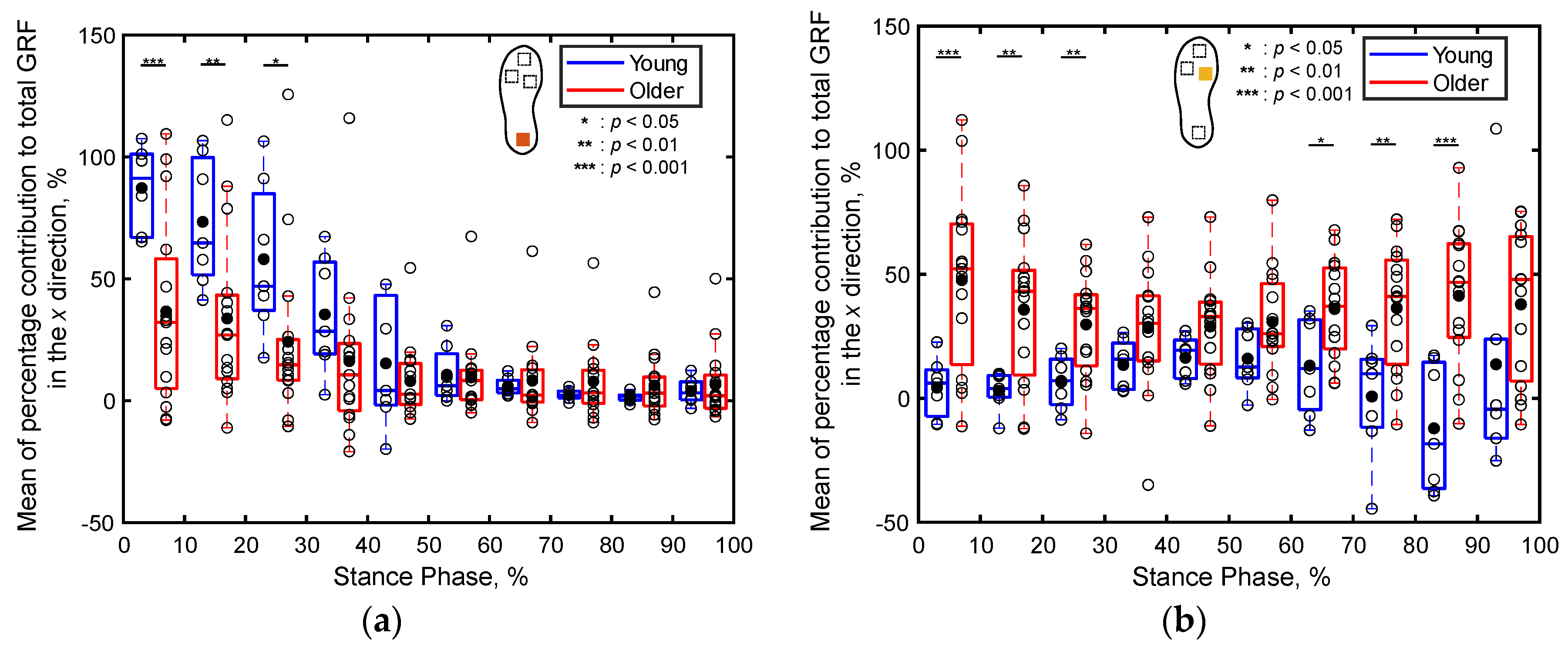
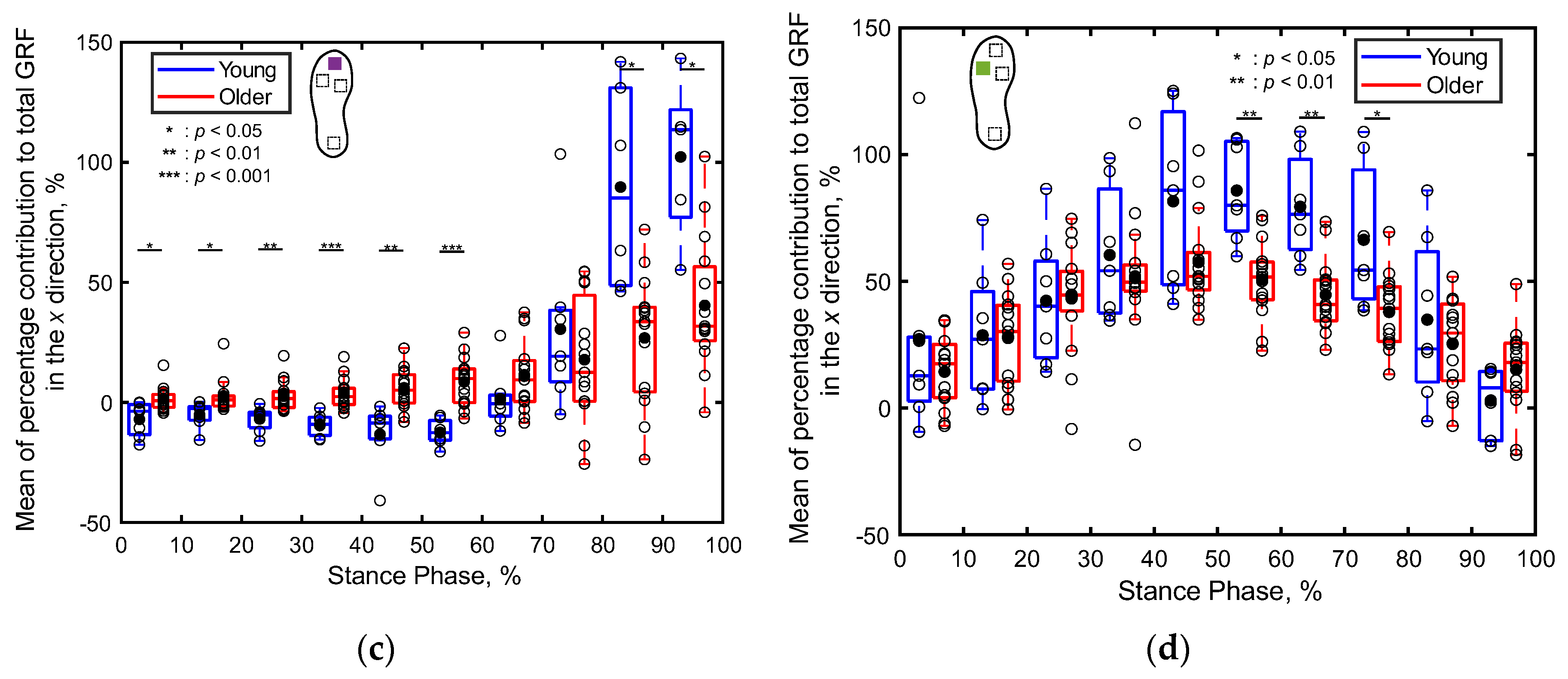
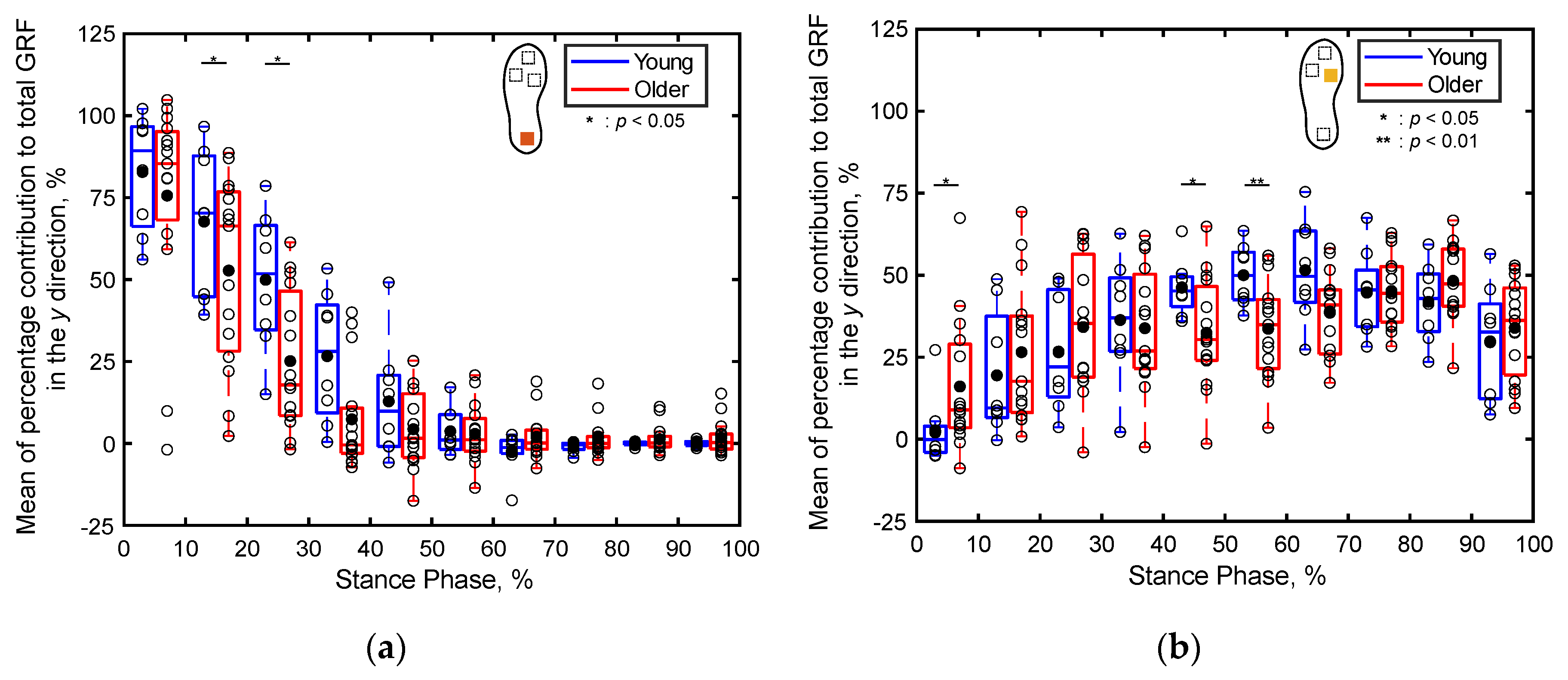
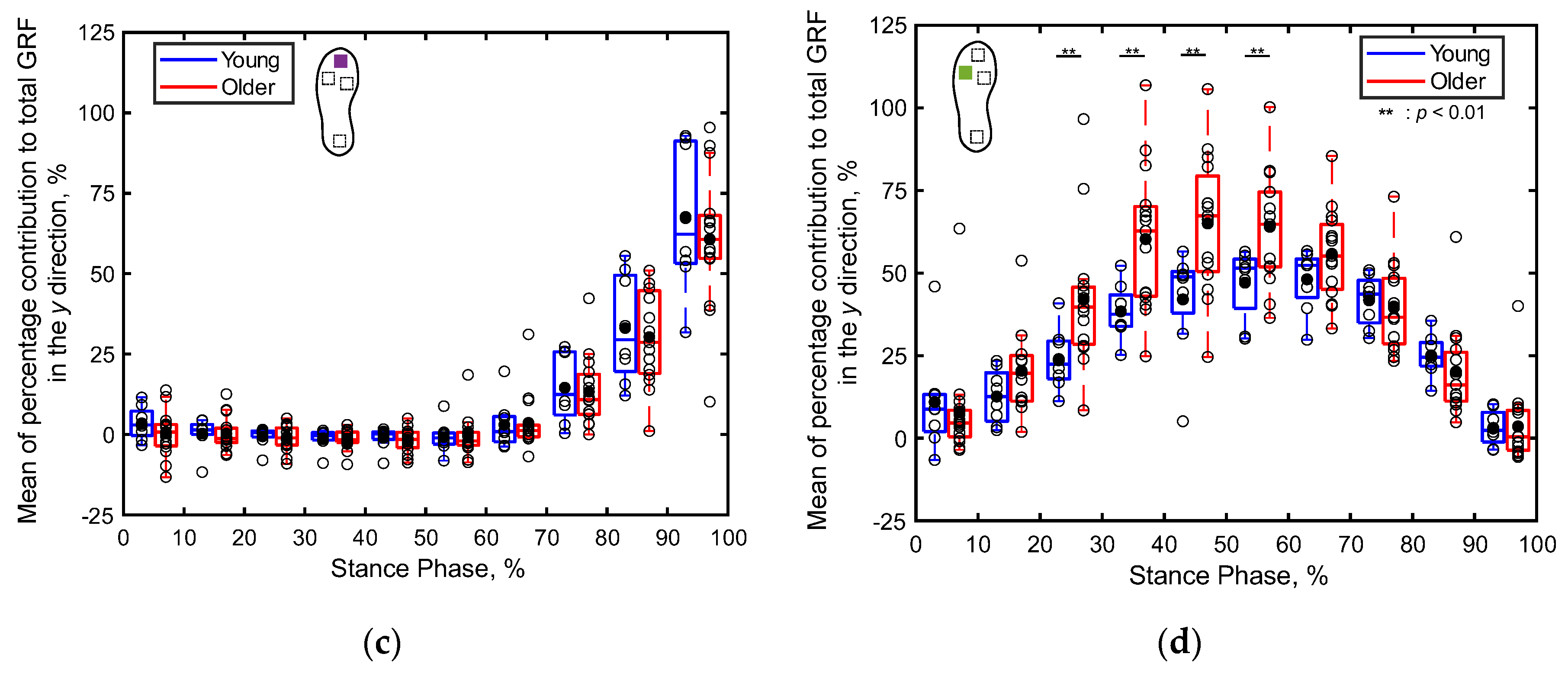
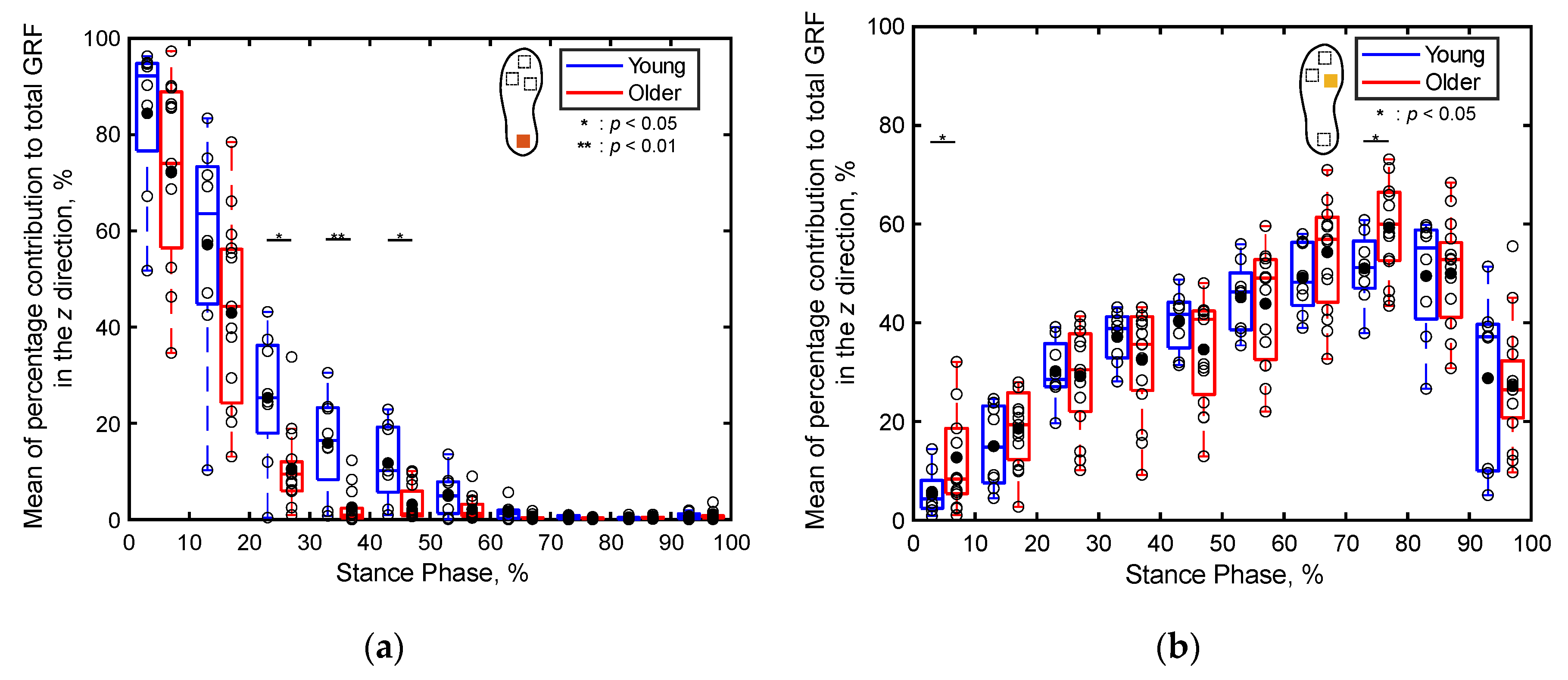
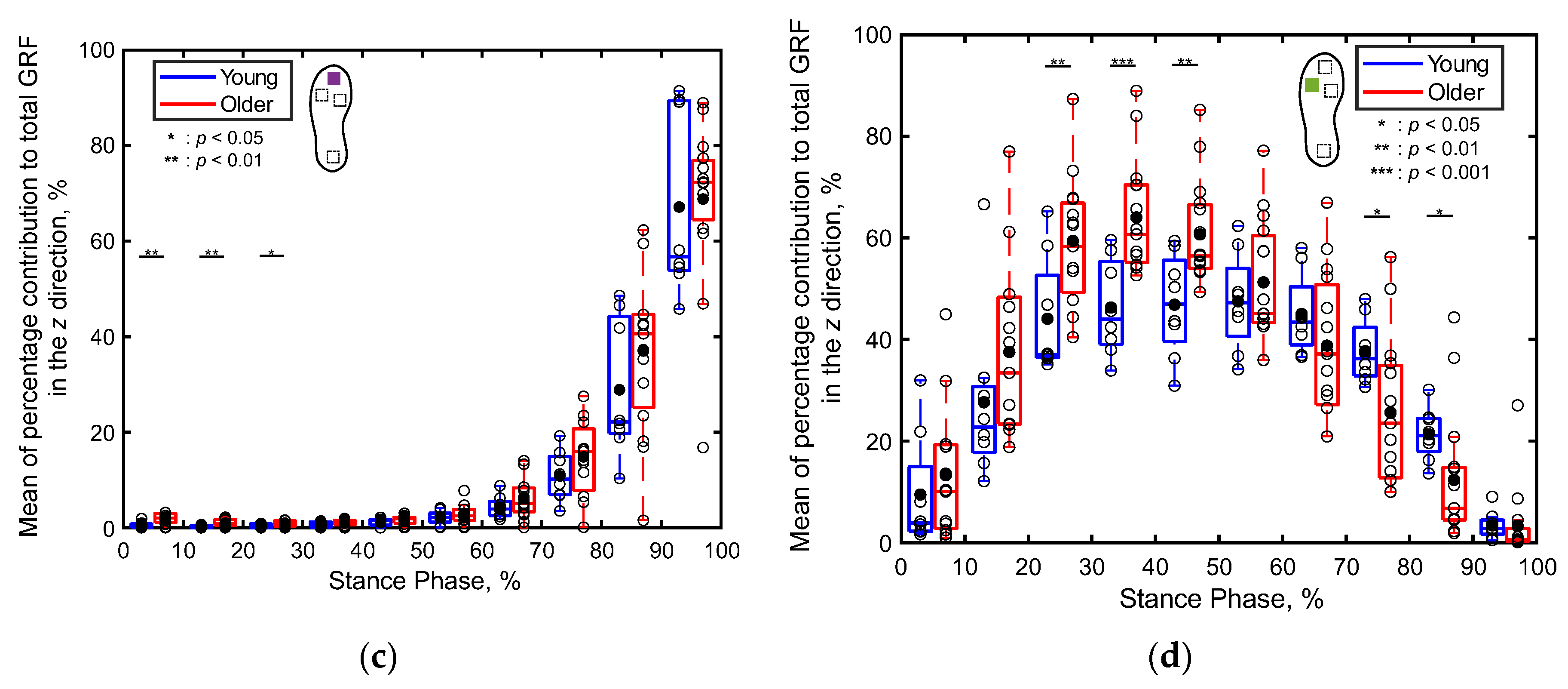
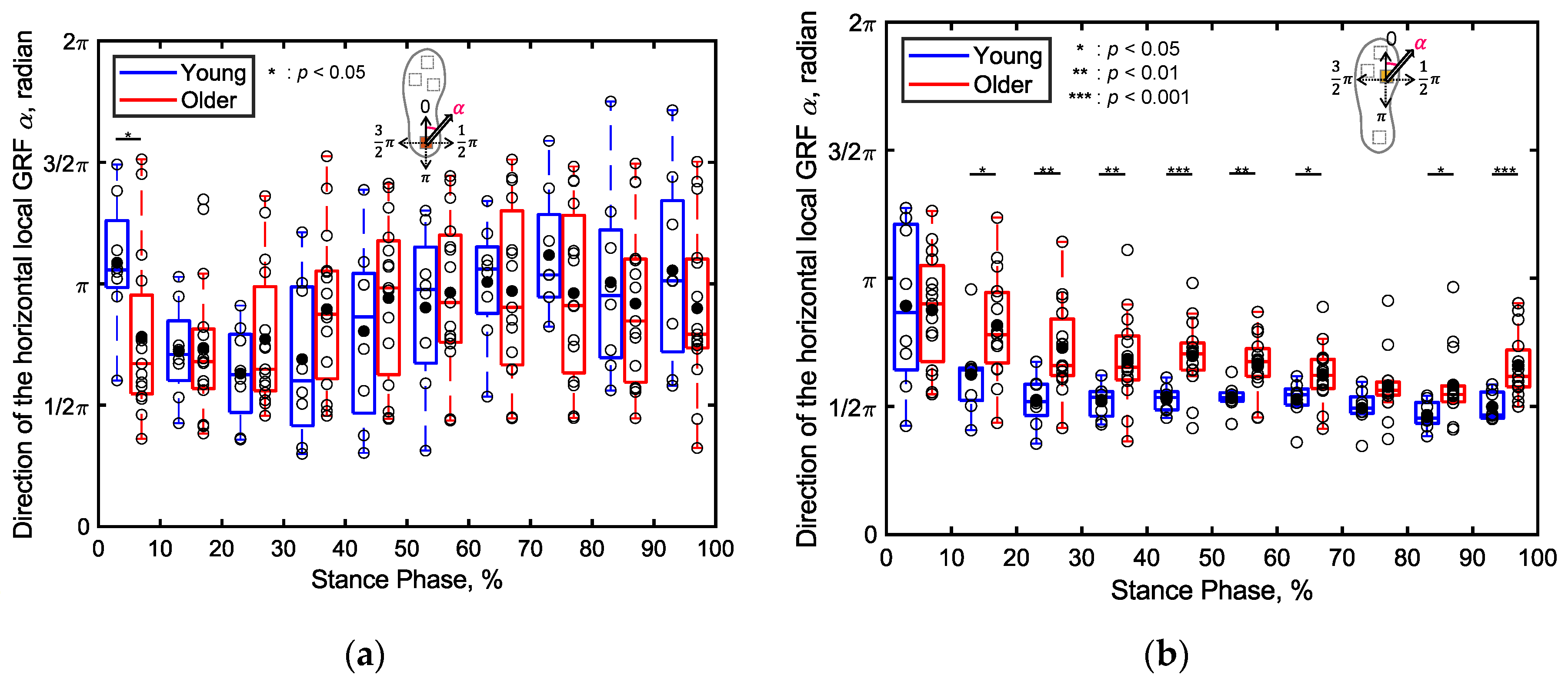
3.2.2. Percentage Contributions of Localized GRFs
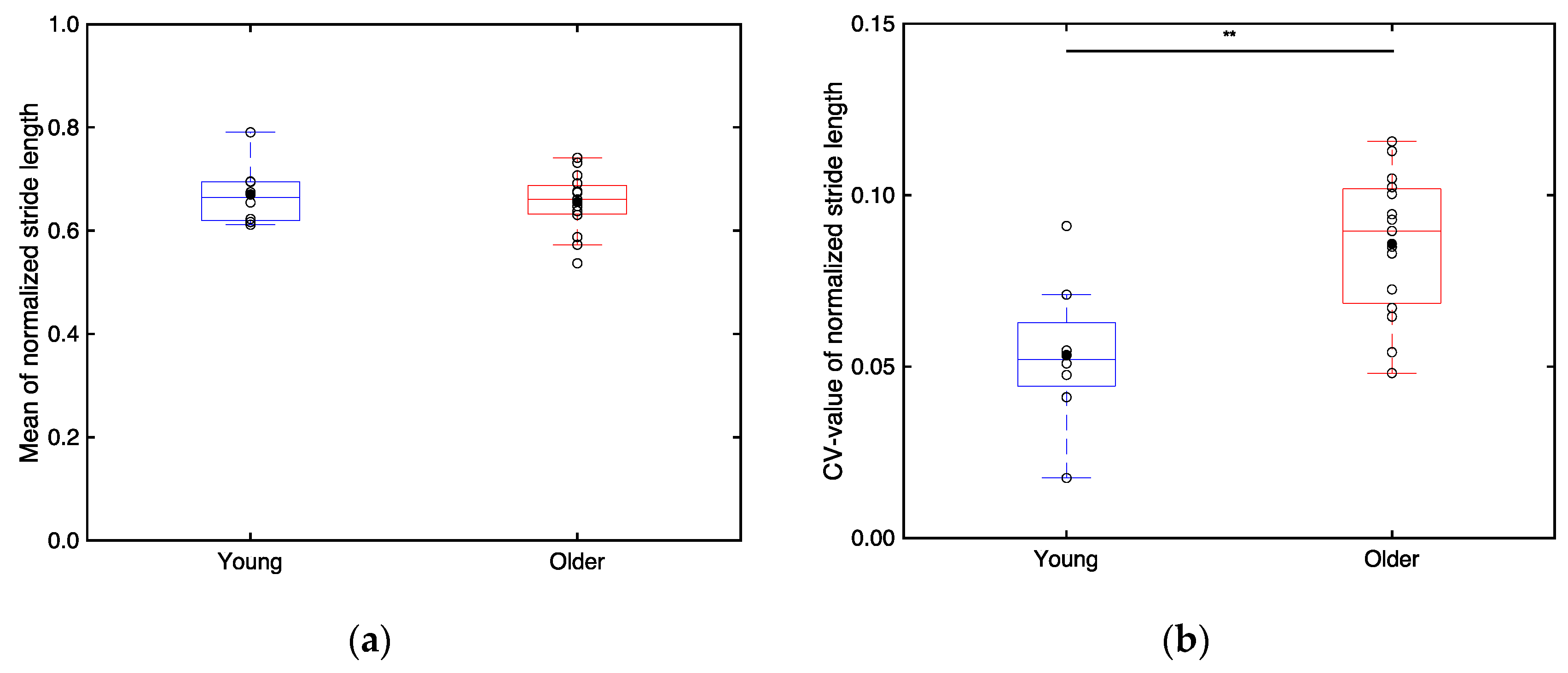
3.2.3. Stride Length
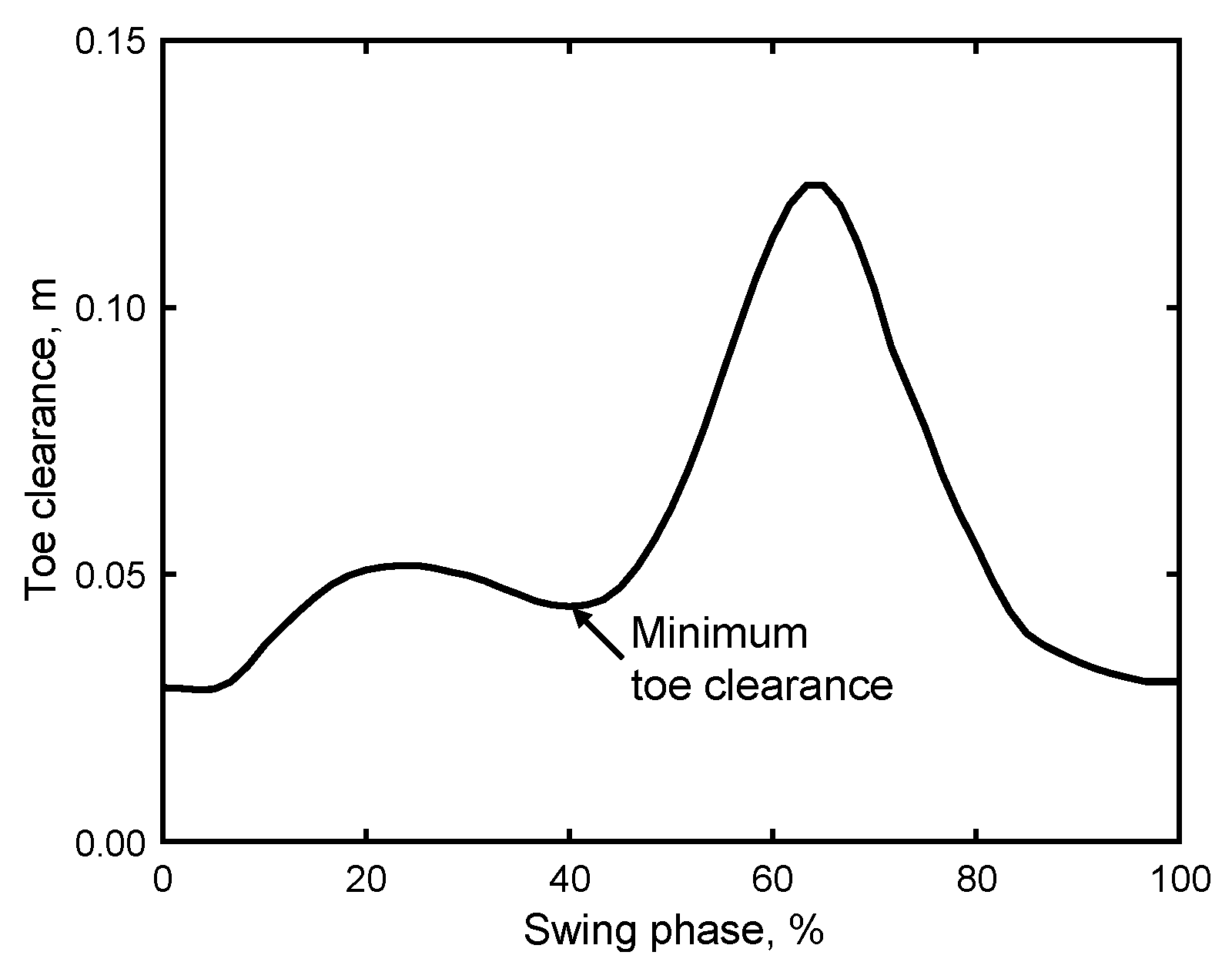
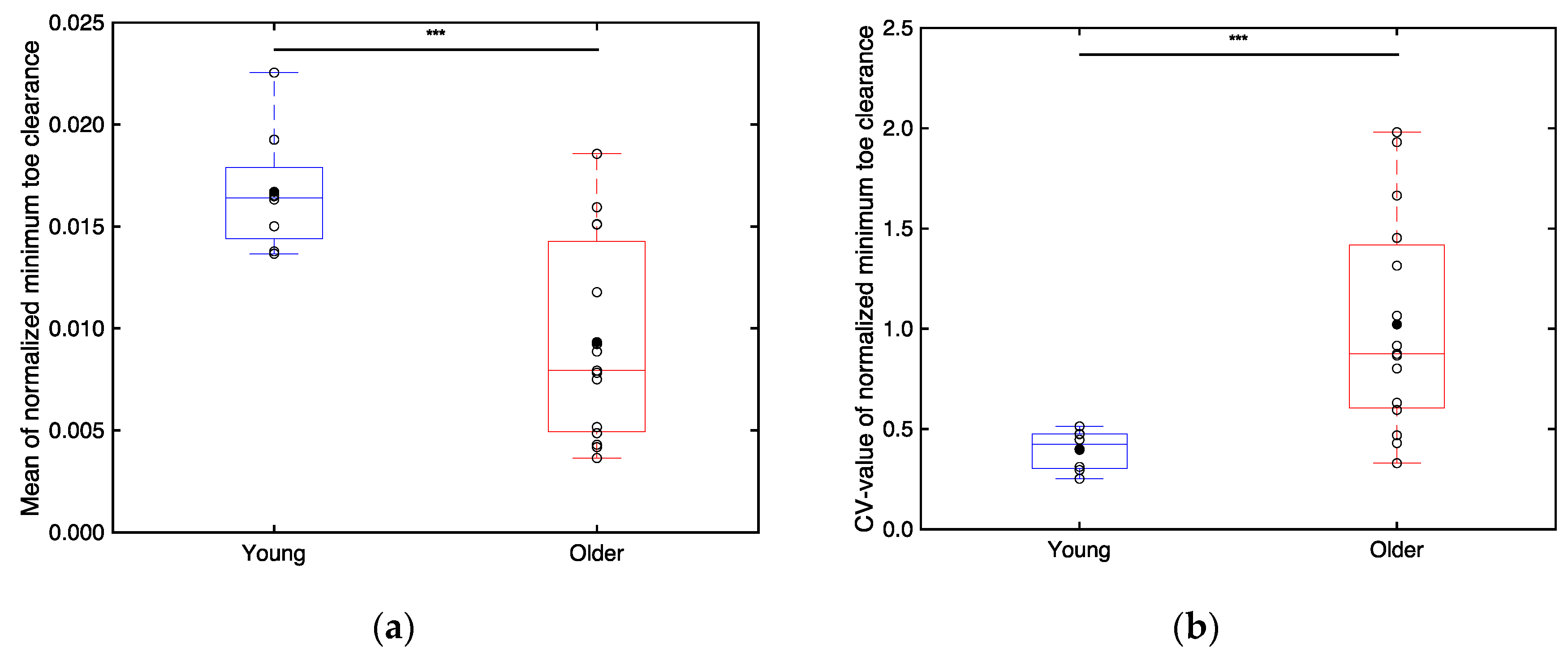
3.2.4. Minimum Toe Clearance
4. Discussion
4.1. Estimation Accuracy of the Stride Length and Minimum Toe Clearance (S1)
4.2. Differences in Localized GRFs between the Young and Older Adults (S2)
4.3. Difference in Stride Length and Minimum Toe Clearance between the Young and Older Adults (S2)
4.4. Study Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kakara, R.S.; Lee, R.; Eckstrom, E.N. Cause-Specific Mortality Among Adults Aged ≥65 Years in the United States, 1999 Through 2020. Public Health Reports® 2023, 139, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peel, N.M. Epidemiology of Falls in Older Age. Canadian Journal on Aging 2011, 30, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, P.M.; Barrett, R.S.; Morrison, S. Toe Clearance Variability during Walking in Young and Elderly Men. Gait Posture 2008, 28, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, R.S.; Mills, P.M.; Begg, R.K. A Systematic Review of the Effect of Ageing and Falls History on Minimum Foot Clearance Characteristics during Level Walking. Gait Posture 2010, 32, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menz, H.B.; Lord, S.R.; Fitzpatrick, R.C. Age-Related Differences in Walking Stability.
- Begg, R.; Best, R.; Dell’Oro, L.; Taylor, S. Minimum Foot Clearance during Walking: Strategies for the Minimisation of Trip-Related Falls. Gait Posture 2007, 25, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dapp, U.; Vinyard, D.; Golgert, S.; Krumpoch, S.; Freiberger, E. Reference Values of Gait Characteristics in Community-Dwelling Older Persons with Different Physical Functional Levels. BMC Geriatr 2022, 22, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingood, M.; Peterson, E.; Neville, C.; Vincenzo, J.L. Feet/Footwear-Related Fall Risk Screening Tool for Older Adults: Development and Content Validation. Front Public Health 2022, 9, 807019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, R.; Suzuki, H.; Ogawa, S.; Takahashi, M.; Fujiwara, Y. Hearing Loss and Increased Gait Variability among Older Adults. Gait Posture 2021, 87, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persch, L.N.; Ugrinowitsch, C.; Pereira, G.; Rodacki, A.L.F. Strength Training Improves Fall-Related Gait Kinematics in the Elderly: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clinical Biomechanics 2009, 24, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.U.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Ferrucci, L. Age-Associated Differences in the Gait Pattern Changes of Older Adults during Fast-Speed and Fatigue Conditions: Results from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroche, D.P.; Cook, S.B.; MacKala, K. Strength Asymmetry Increases Gait Asymmetry and Variability in Older Women. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2012, 44, 2172–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, H.Y.; Gray, V.L.; Creath, R.A.; Binder-Macleod, S.A.; Rogers, M.W. Control of Lateral Weight Transfer Is Associated with Walking Speed in Individuals Post-Stroke. J Biomech 2017, 60, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, J.R.; Maletis, M.; Kram, R. Real-Time Feedback Enhances Forward Propulsion during Walking in Old Adults. Clinical Biomechanics 2014, 29, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, P.E.; Marsh, A.P. STEP LENGTH AND FREQUENCY EFFECTS ON GROUND REACTION FORCES DURING WALKING. 1992; Volume 25. [Google Scholar]
- Cesari, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Penninx, B.W.H.J.; Nicklas, B.J.; Simonsick, E.M.; Newman, A.B.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Brach, J.S.; Satterfield, S.; Bauer, D.C.; et al. Prognostic Value of Usual Gait Speed in Well-Functioning Older People - Results from the Health, Aging and Body Composition Study. J Am Geriatr Soc 2005, 53, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verghese, J.; Holtzer, R.; Lipton, R.B.; Wang, C. Quantitative Gait Markers and Incident Fall Risk in Older Adults. Journals of Gerontology - Series A Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences 2009, 64, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuchi, C.A.; Fukuchi, R.K.; Duarte, M. Effects of Walking Speed on Gait Biomechanics in Healthy Participants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Syst Rev 2019, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Loo, M.A.; Moseley, A.M.; Bosman, J.M.; de Bie, R.A.; Hassett, L. Test–Re-Test Reliability of Walking Speed, Step Length and Step Width Measurement after Traumatic Brain Injury: A Pilot Study. Brain Inj 2004, 18, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, H.; Sparrow, W.A.; Mizukami, K.; Sarashina, E.; Begg, R. A Cross-Sectional Study of Foot-Ground Clearance in Healthy Community Dwelling Japanese Cohorts Aged 50, 60 and 70 Years. BMC Geriatr 2021, 21, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kruk, E.; Reijne, M.M. Accuracy of Human Motion Capture Systems for Sport Applications; State-of-the-Art Review. Eur J Sport Sci 2018, 18, 806–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.R. Quantification of Human Motion: Gait Analysis - Benefits and Limitations to Its Application to Clinical Problems. J Biomech 2004, 37, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepers, H.M.; Van Asseldonk, E.H.F.; Buurke, J.H.; Veltink, P.H. Ambulatory Estimation of Center of Mass Displacement during Walking. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2009, 56, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, W.; Tsujiuchi, N.; Koizumi, T.; Shiojima, K.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Inoue, Y. Development of Walking Analysis System Using by Motion Sensor with Mobile Force Plate. Journal of System Design and Dynamics 2012, 6, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyasu, K.; Nishiwaki, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hokkirigawa, K. New Technique of Three Directional Ground Reaction Force Distributions. Footwear Sci 2010, 2, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T. Distribution of the Local Required Coefficient of Friction in the Shoe–Floor Contact Area during Straight Walking: A Pilot Study. Biotribology 2019, 19, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, E.; Sasaki, Y. Cr-N Strain Sensitive Thin Films and Their Pressure Sensor Applications. IEEJ Transactions on Sensors and Micromachines 2014, 134, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, E.; Shirakawa, K.; Shingyochi, S.; Xiong, S.; Nakahara, K.; Ito, T.; Sasaki, Y. Load Vector Sensors Using Strain-Sensitive Cr-N Thin Films and Their Applications. Electronics and Communications in Japan 2016, 99, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Sasaki, Y. Prediction of Three-Directional Ground Reaction Forces during Walking Using a Shoe Sole Sensor System and Machine Learning. Sensors (Basel) 2023, 23, 8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashi, F.; Mariani, B.; Rochat, S.; Büla, C.J.; Santos-Eggimann, B.; Aminian, K. Gait and Foot Clearance Parameters Obtained Using Shoe-Worn Inertial Sensors in a Large-Population Sample of Older Adults. Sensors (Switzerland) 2014, 14, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobkin, B.H.; Xu, X.; Batalin, M.; Thomas, S.; Kaiser, W. Reliability and Validity of Bilateral Ankle Accelerometer Algorithms for Activity Recognition and Walking Speed after Stroke. Stroke 2011, 42, 2246–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salarian, A.; Horak, F.B.; Zampieri, C.; Carlson-Kuhta, P.; Nutt, J.G.; Aminian, K. ITUG, a Sensitive and Reliable Measure of Mobility. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 2010, 18, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojaniello, D.; Cereatti, A.; Della Croce, U. Accuracy, Sensitivity and Robustness of Five Different Methods for the Estimation of Gait Temporal Parameters Using a Single Inertial Sensor Mounted on the Lower Trunk. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfrey, A.; Bourke, A.K.; Ólaighin, G.M.; van de Ven, P.; Nelson, J. Activity Classification Using a Single Chest Mounted Tri-Axial Accelerometer. Med Eng Phys 2011, 33, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushi, K.; Huang, C.; Wang, Z.; Kajitani, H.; Nihey, F.; Nakahara, K. On-Line Algorithms of Stride-Parameter Estimation for in-Shoe Motion-Sensor System. IEEE Sens J 2022, 22, 9636–9648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.; Sukumar, P.T.; Hazas, M. Tutorial: Implementing a Pedestrian Tracker Using Inertial Sensors. IEEE Pervasive Comput 2013, 12, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frosio, I.; Pedersini, F.; Borghese, N.A. Autocalibration of MEMS Accelerometers. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 2009, 58, 2034–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoussaad, M.; Sijobert, B.; Mombaur, K.; Coste, C.A. Robust Foot Clearance Estimation Based on the Integration of Foot-Mounted IMU Acceleration Data. Sensors 2016, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luinge, H.J.; Veltink, P.H. Measuring Orientation of Human Body Segments Using Miniature Gyroscopes and Accelerometers. Med Biol Eng Comput 2005, 43, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryoga, N.; Motomichi, S.; Kiyoshi, H. Stride Estimation Based on Horizontal Acceleration Integration Using an Inertial Sensor. Transactions of the JSME (in Japanese) 2023, 89, 23–00194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Society of Information Fusion; Xi’an jiao tong da xue.; IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Society; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers; Chinese Society for Information Fusion 20th International Conference on Information Fusion: 2017 Proceedings. ISBN 9780996452700.
- Yamaguchi, T.; Yano, M.; Onodera, H.; Hokkirigawa, K. Kinematics of Center of Mass and Center of Pressure Predict Friction Requirement at Shoe-Floor Interface during Walking. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnfield, J.M.; Powers, C.M. The Role of Center of Mass Kinematics in Predicting Peak Utilized Coefficient of Friction during Walking. In Proceedings of the Journal of Forensic Sciences, November 2007; Volume 52, pp. 1328–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Lakens, D. Calculating and Reporting Effect Sizes to Facilitate Cumulative Science: A Practical Primer for t-Tests and ANOVAs. Front Psychol 2013, 4, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoussaad, M.; Mombaur, K.; Azevedo-Coste, C. Nonlinear Model Predictive Control of Joint Ankle by Electrical Stimulation for Drop Foot Correction. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems; 2013; pp. 983–989. [Google Scholar]
- Rampp, A.; Barth, J.; Schülein, S.; Gaßmann, K.G.; Klucken, J.; Eskofier, B.M. Inertial Sensor-Based Stride Parameter Calculation From Gait Sequences in Geriatric Patients. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2015, 62, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.; Ginis, P.; Hardegger, M.; Casamassima, F.; Rocchi, L.; Chiari, L. A Mobile Kalman-Filter Based Solution for the Real-Time Estimation of Spatio-Temporal Gait Parameters. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 2016, 24, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küderle, A.; Roth, N.; Zlatanovic, J.; Zrenner, M.; Eskofier, B.; Kluge, F. The Placement of Foot-Mounted IMU Sensors Does Affect the Accuracy of Spatial Parameters during Regular Walking. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0269567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, P.O.; Dellacroce, U.; Kerrigan, D.C. Effect of Age on Lower Extremity Joint Moment Contributions to Gait Speed; 2001; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Kerrigan, D.C.; Lee, L.W.; Collins, J.J.; Riley, P.O.; Lipsitz, L.A. Reduced Hip Extension during Walking: Healthy Elderly and Fallers versus Young Adults. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2001, 82, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.G.; Dingwell, J.B. Effects of Walking Speed, Strength and Range of Motion on Gait Stability in Healthy Older Adults. J Biomech 2008, 41, 2899–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrosky, K.M.; VanSwearingen, J.M.; Burdett, R.G.; Gee, Z. A Comparison of Gait Characteristics in Young and Old Subjects. Phys Ther 1994, 74, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, J.; Erhart-Hledik, J.C.; Andriacchi, T.P. Age-Related Differences in Sagittal-Plane Knee Function at Heel-Strike of Walking Are Increased in Osteoarthritic Patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2014, 22, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




