Submitted:
06 September 2024
Posted:
06 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Electrical Characteristics of Locomotive Arrester Based on High-frequency Tests
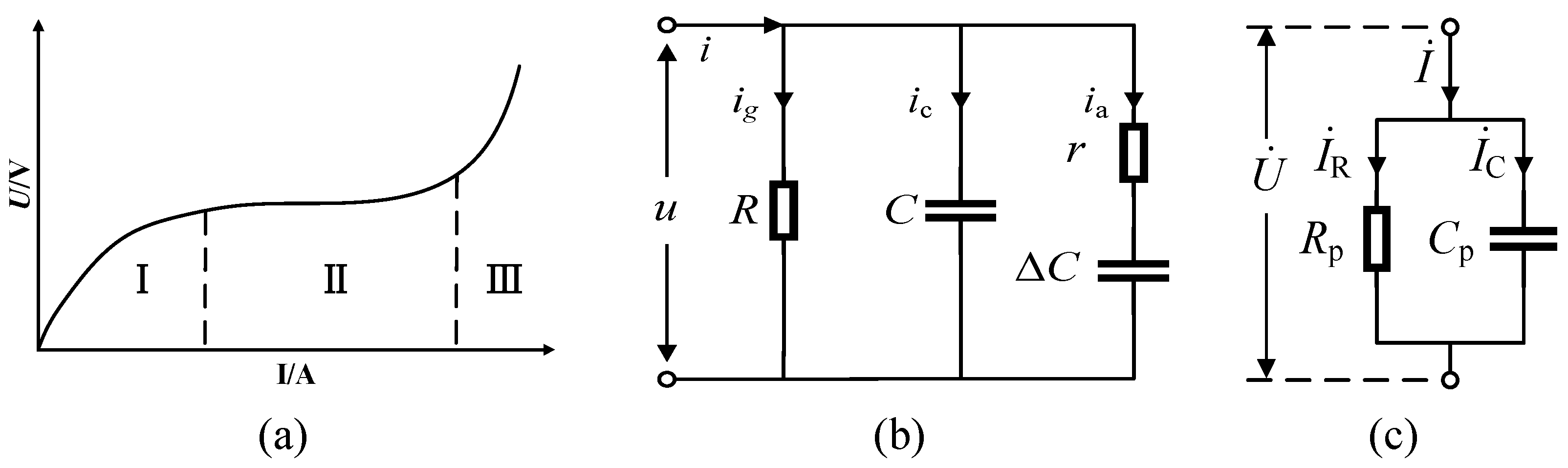
2.1. Equivalent Circuit Model of ZnO Arrester
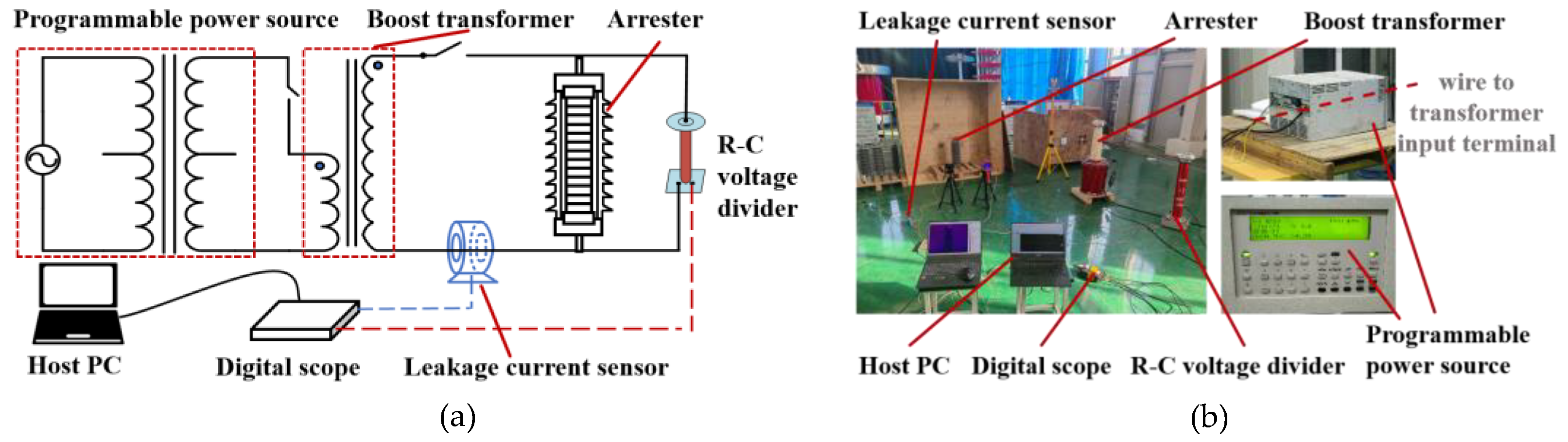
2.2. Test Scheme Design
2.3. Test 1: Electrical Characteristics of Arrester under Fundamental Voltage
2.4. Test 2: Valve Plate Electrical Characteristics under Harmonic Voltages
2.5. Test 3: Valve Plate Electrical Characteristics under Voltage Combination of Fundamental and Harmonics
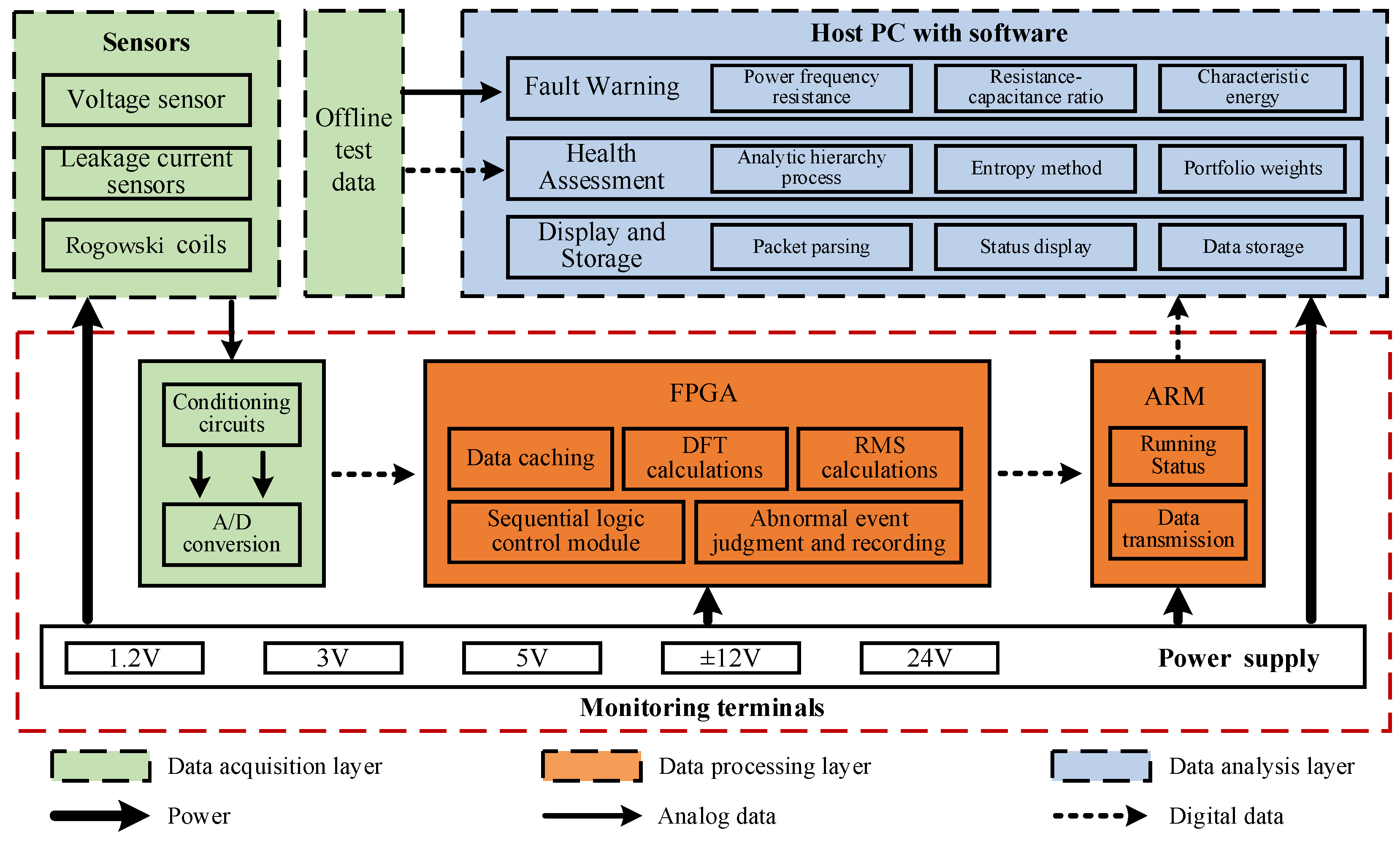
3. PHM Design for Locomotive Arrest
3.1. PHM Architecture Design and Parameter Indicators
- Considering the characteristics of harmonic overvoltage on the traction supply network, 100-order harmonic analyzing ability is required. Thus, the voltage sensor and the leakage current sensor need a bandwidth over 5000 Hz.
- According to the features of various transients, e.g., lightning impulse, the onboard vacuum circuit breaker open/close, the pantograph goes up/down, etc., the Rogowski coil requires a more than 1 MHz bandwidth.
- To address the spectrum analysis demand, the A/D conversion stage is designed with a sampling rate ≥ 20 kHz, a resolution of 16bits and an accuracy ≤ 1%.
- To ensure real-time performance, it is demanded to meet the computational ability that completing continuously ten power frequency cycles’ calculation of the RMS, peak value, and 100-order DFT within 1 second.
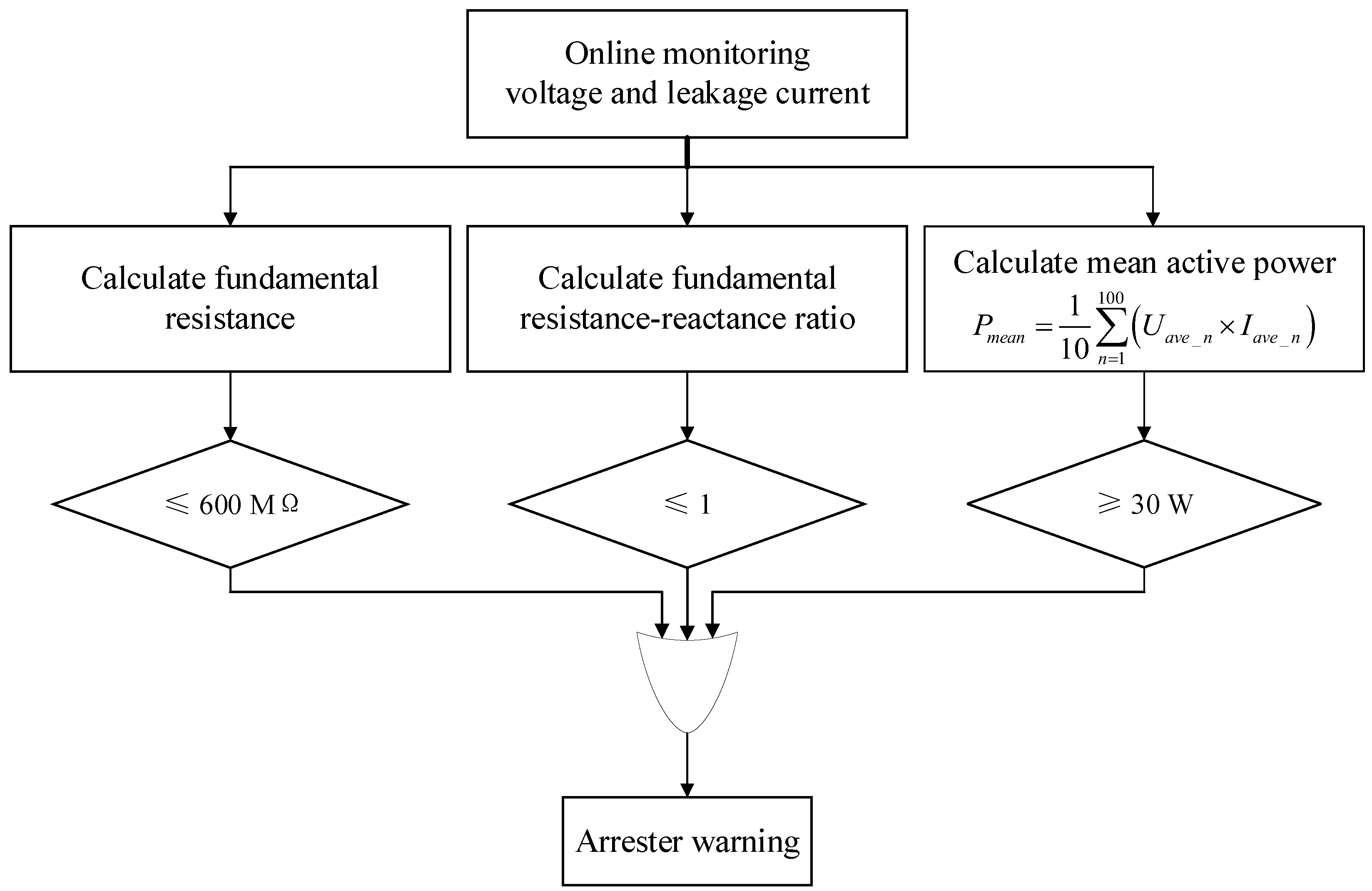
3.2. Fault Warning Method
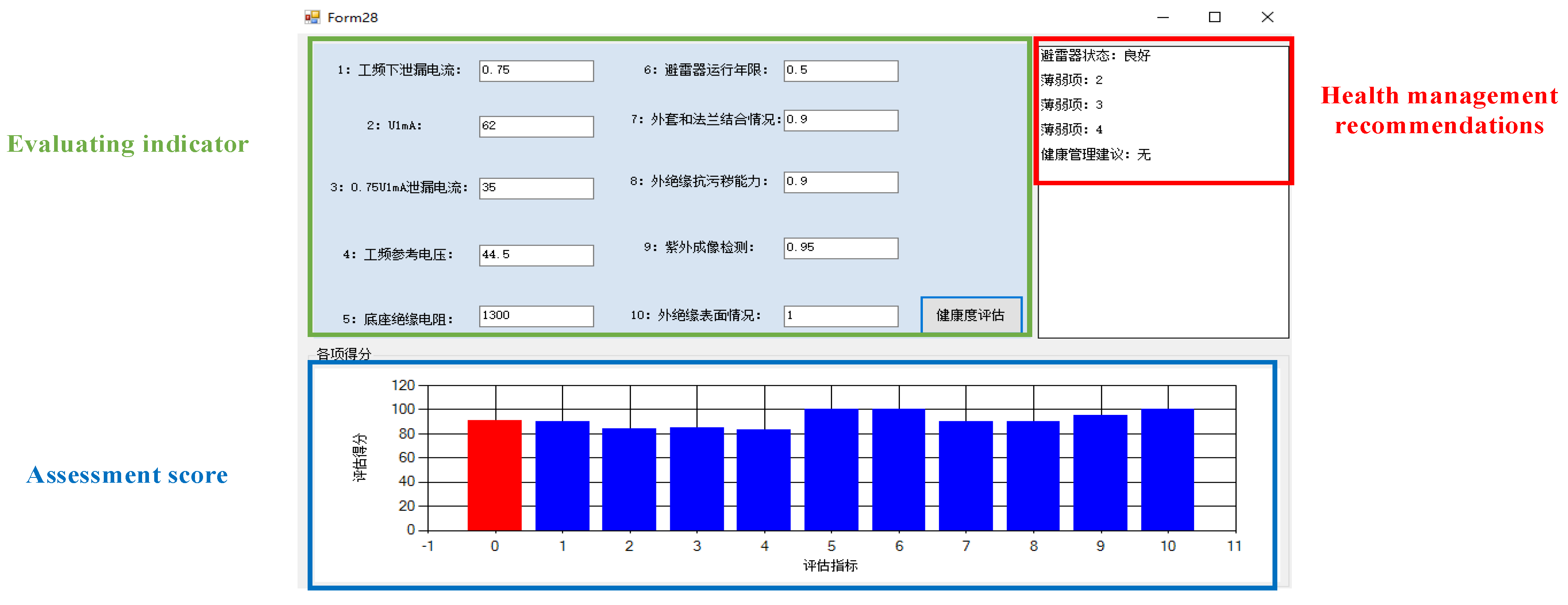
3.3. Health Assessment Method
3.3.1. Health Status Indicators
3.3.2. Evaluation Weight Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Arrester Defects | Defect Diagnosis Indicators | Diagnostic Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| Internal moisture | Leakage current under dc U1mA and 0.75 U1mA, and its resistive component under the voltage of traction supply network, temperature, insulation resistance | Resistive component of leakage current increases, dc U1mA reference voltage decreases, the leakage current under 0.75 U1mA increases, relative temperature difference larger than 1K |
| Insulation aging | Leakage current under dc U1mA and 0.75 U1mA, and its resistive component under the voltage of traction supply network, temperature, high frequency partial discharge | Resistive component of leakage current increases, dc U1mA reference voltage decreases, the leakage current under 0.75 U1mA increases, relative temperature difference larger than 1K |
| External insulation pollution/aging | Leakage current and its resistive component under the voltage of traction supply network, Temperature | Leakage current and its resistive component increase apparently |
| Abnormal discharge | UV imaging detection, external insulation anti pollution capability | Determine the source of discharge |
Appendix B
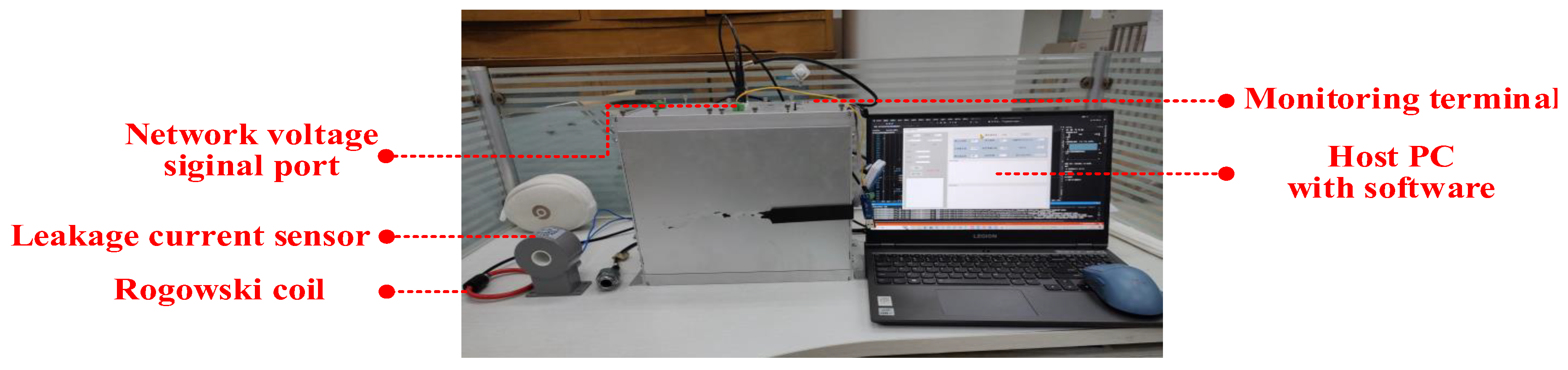
Appendix C
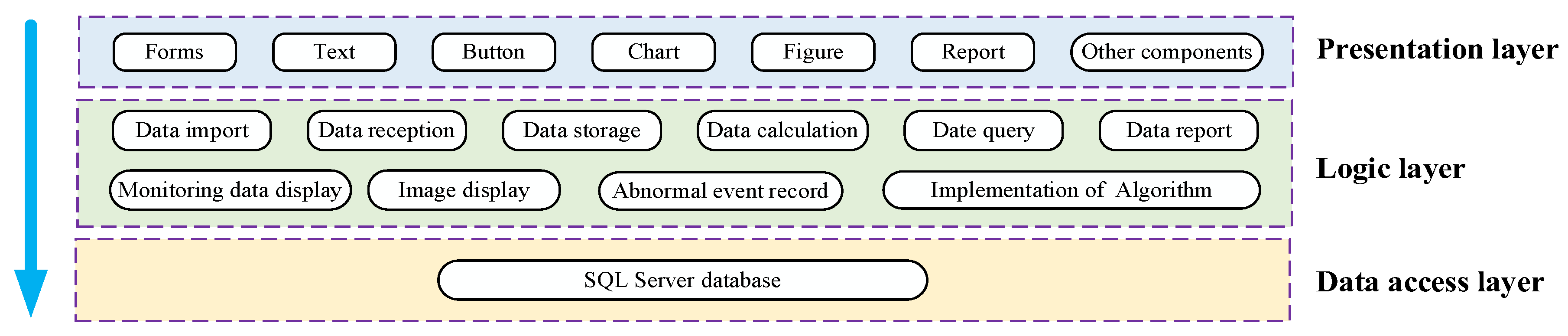
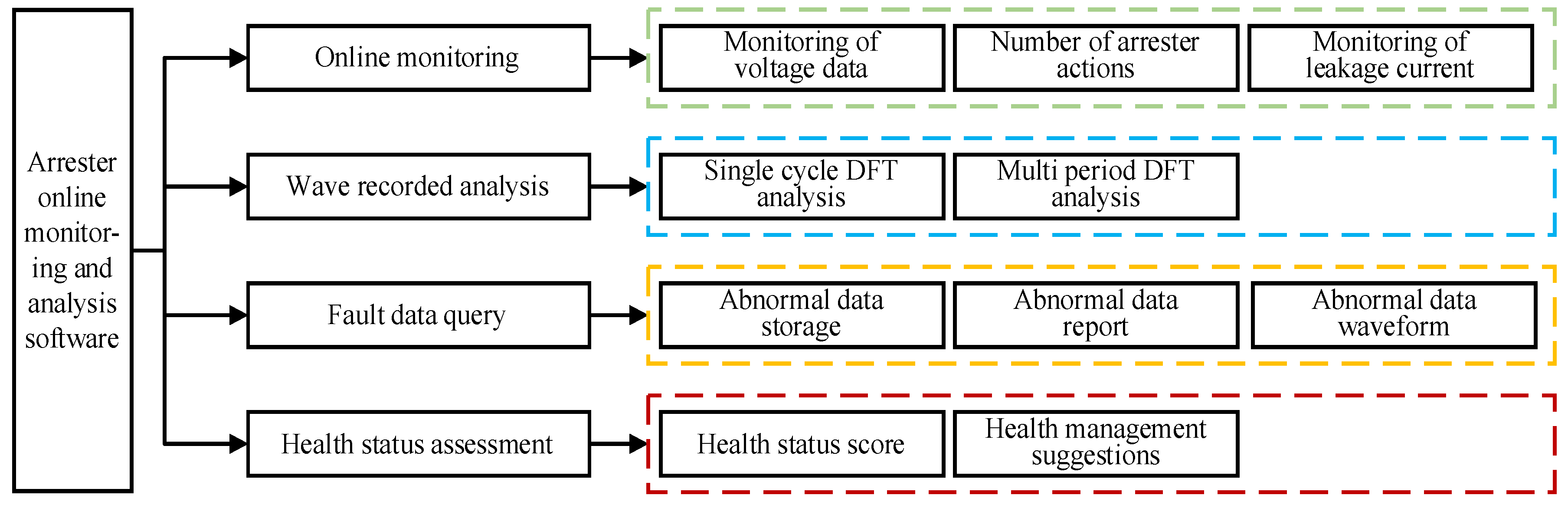
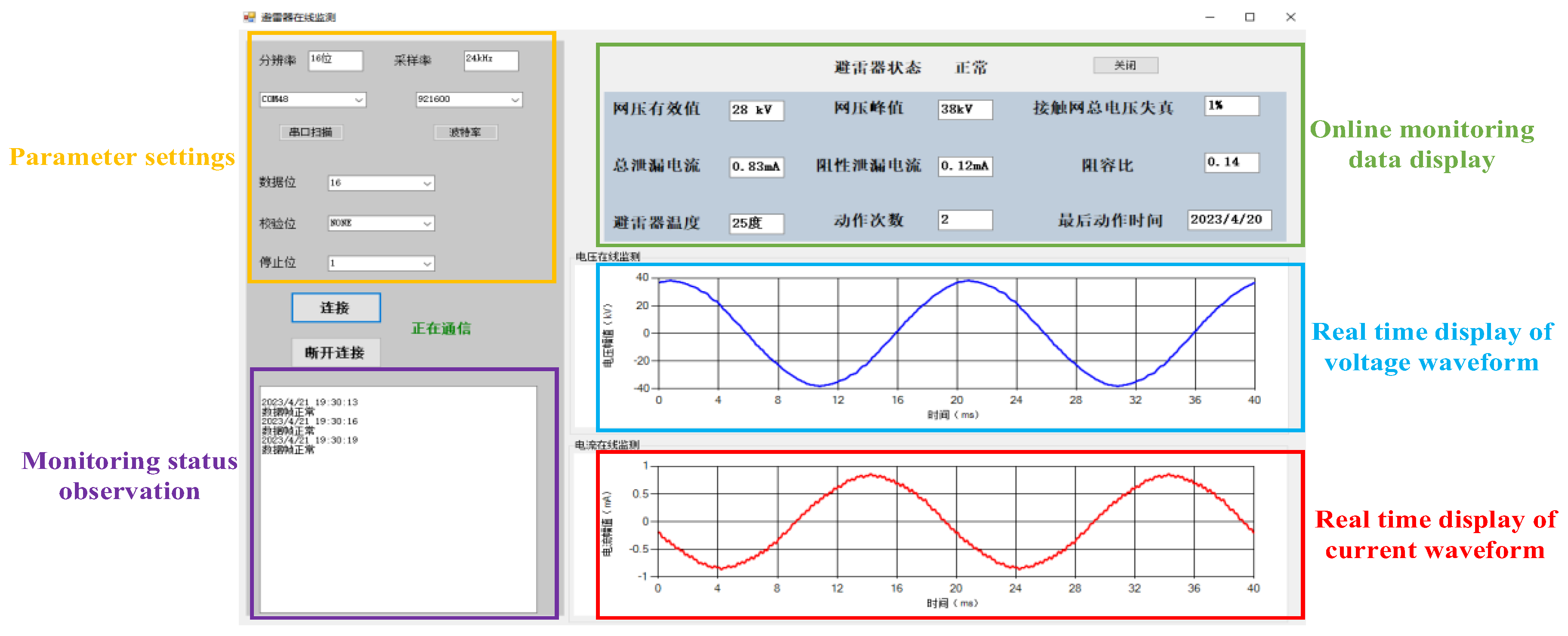
References
- Jia, Y.; Wang, L., Analysis and Countermeasures of Arrester Failure in HXD1 Electric Locomotive. Technology and Market 2018, 25, (5), 27-30.
- Latiff, N. A.; Illias, H. A.; Bakar, A. H.; Dabbak, S. Z., Measurement and modelling of leakage current behaviour in ZnO surge arresters under various applied voltage amplitudes and pollution conditions. Energies 2018, 11, (4), 875. [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y. Research on the Overvoltage Protection Scheme for High Voltage Electrical System of Electric Locomotives. Beijing Jiaotong University 2016.
- Qu, Z.; Liu, M.; Guo, L.; Liu, Y. Transient processes time series analysis of high-speed railway power traction and over-voltage protection, 2012 International Conference on Computer Distributed Control and Intelligent Environmental Monitoring, 2012; IEEE: 2012; pp 818-821. [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, K. S. A Review of zinc oxide varistors for surge arrester, 2018 4th International Conference on Electrical Energy Systems (ICEES) 2018; IEEE: 2018; pp 470-474. [CrossRef]
- Ru, X.; Peng, Y.; Guo, X.; Wu, J., Analysis and Failure of HXD1 Electric Locomotive Arrester Explosion Damage. Electric Drive for Locomotives 2018, (1), 122-125. [CrossRef]
- Du, J., Analysis and preventive measures for the explosion fault of arrester on HXD3C locomotive. Electric Locomotives & Mass Transit Vehicles 2016, 39, (5), 87-89. [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Funabashi, T.; Sasaki, H.; Hagiwara, T.; Kobayashi, M., Study of ZnO arrester model for steep front wave. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery 1996, 11, (2), 834-841. [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hu, J.; Chen, S.; He, J., Harmonic characteristics of leakage currents of ZnO varistors under impulse aging. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery 2016, 32, (4), 1758-1765. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ma, Y.; Ma, Y.; Pan, H.; Du, H. Analysis of the mechanism of thermal collapse of MOA valve plates caused by multiple lightning strikes, Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021; IOP Publishing: 2021; p 012152. [CrossRef]
- Ishida, K.; Dokai, K.; Tsozaki, T.; Irie, T.; Nakayama, T.; Fujita, H.; Arakawa, K.; Aihara, Y., Development of a 500 kV transmission line arrester and its characteristics. IEEE transactions on power delivery 1992, 7, (3), 1265-1274. [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Yan, S., The Leakage Current Characteristics of High-Gradient MOA Plate and Its Heating Analysis with Coatings under High-Frequency Overvoltage. Coatings 2023, 13, (3), 497. [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ding, F.; Lv, Y.; Ren, J.; Song, S.; Li, T.; Zhi, Q.; Guo, C., Leakage current characteristics and ageing assessment technology of roof arrester under ultra harmonics overvoltage. High Voltage 2022, 7, (2), 346-356. [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Tong, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang S.; Cao J. Study on the frequency and temperature dependence of electrical conductivity of zinc oxide valve plate. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation 2023, 30, (3), 1302-1311. [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Wu, M.; Yang, S.; Liu, Q.; Agelidis, V. G.; Konstantinou, G., High-order harmonic resonances in traction power supplies: A review based on railway operational data, measurements, and experience. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2019, 35, (3), 2501-2518. [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hu, H.; Zhou, Y.; He, Z., A rapid modal analysis method for harmonic resonance using modified power iteration. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery 2016, 33, (3), 1495-1497. [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Tao, H.; Blaabjerg, F.; Wang, X.; He, Z.; Gao, S., Train–network interactions and stability evaluation in high-speed railways–Part I: Phenomena and modeling. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics 2017, 33, (6), 4627-4642. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z. Research and Application of Prognostics and Health Management Technology Framework in Heavy Haul Locomotiv.Control and Information Technology 2022, (6), 115-122. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Miao, X.; Si, Y.; Pan, E.; Zio, E., Prognostics and health management: A review from the perspectives of design, development and decision. Reliability Engineering & System Safety 2022, 217, 108063. [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, B.; Darvishi, A.; Dashti, R.; Shaker, H. R., A survey of diagnostic and condition monitoring of metal oxide surge arrester in the power distribution network. Energies 2022, 15, (21), 8091. [CrossRef]
- Lijun, Q.; Minghui, W., Overview of PHM Technology Framework and Its Key Technologies. Foreign Electric Measurement Technology 2018, 37, (2), 10-15. [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Liu, D.; Peng, X., Overview of Fault Prediction and Health Management Technologies. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation 2010, 24, (1), 1-9.
- Yang,T. Railway passenger car bogie fault prediction system based on PHM technology. Intelligent City 2024,10(1):27-29. [CrossRef]
- Raju, K.; Prasad, V.; Elavarasan, R. M.; Subramaniam, U.; Almakhles, D. J., Development of high gradient ZnO arrester material for high voltage applications. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 115685-115693. [CrossRef]
- Brito, V. S.; Lira, G. R.; Costa, E. G.; Maia, M. J., A wide-range model for metal-oxide surge arrester. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery 2017, 33, (1), 102-109. [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Yang, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, Z., Review of Launch Vehicle Engine PHM Technology and Analysis Methods Research. Aerospace 2023, 10, (6), 517. [CrossRef]
- DL/T 1703-2017 Guide for condition evaluation of mental oxide arrester.
- GB/T 11034-2020 Metal-oxide surge arresters without gaps for a.c. systems.
- Darko, A.; Chan, A. P. C.; Ameyaw, E. E.; Owusu, E. K.; Pärn, E.; Edwards, D. J., Review of application of analytic hierarchy process (AHP) in construction. International journal of construction management 2019, 19, (5), 436-452. [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M. R.; Al Noman, A.; Tasnim, F.; Nafisa, N.; Hossain, S. In A Hybrid MCDM Approach based on AHP, and TOPSIS to select an ERP system in Bangladesh, 2021 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for Sustainable Development (ICICT4SD), 2021; IEEE: 2021; pp 161-165. [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Y.; Cao, Y.; Chen, L.; Nie, J.; Huang, Y.; Liang, Y. In Research on evaluation model based on analytic hierarchy process and entropy weight method for smart grid, 2022 5th International Conference on Energy, Electrical and Power Engineering (CEEPE), 2022; IEEE: 2022; pp 729-734. [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Han, L.; Ma, L.; Cai, H.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Sun, G. In Evaluation of terminal signal quality based on entropy weight method, 2022 4th International Conference on Intelligent Control, Measurement and Signal Processing (ICMSP), 2022; IEEE: 2022; pp 855-858. [CrossRef]
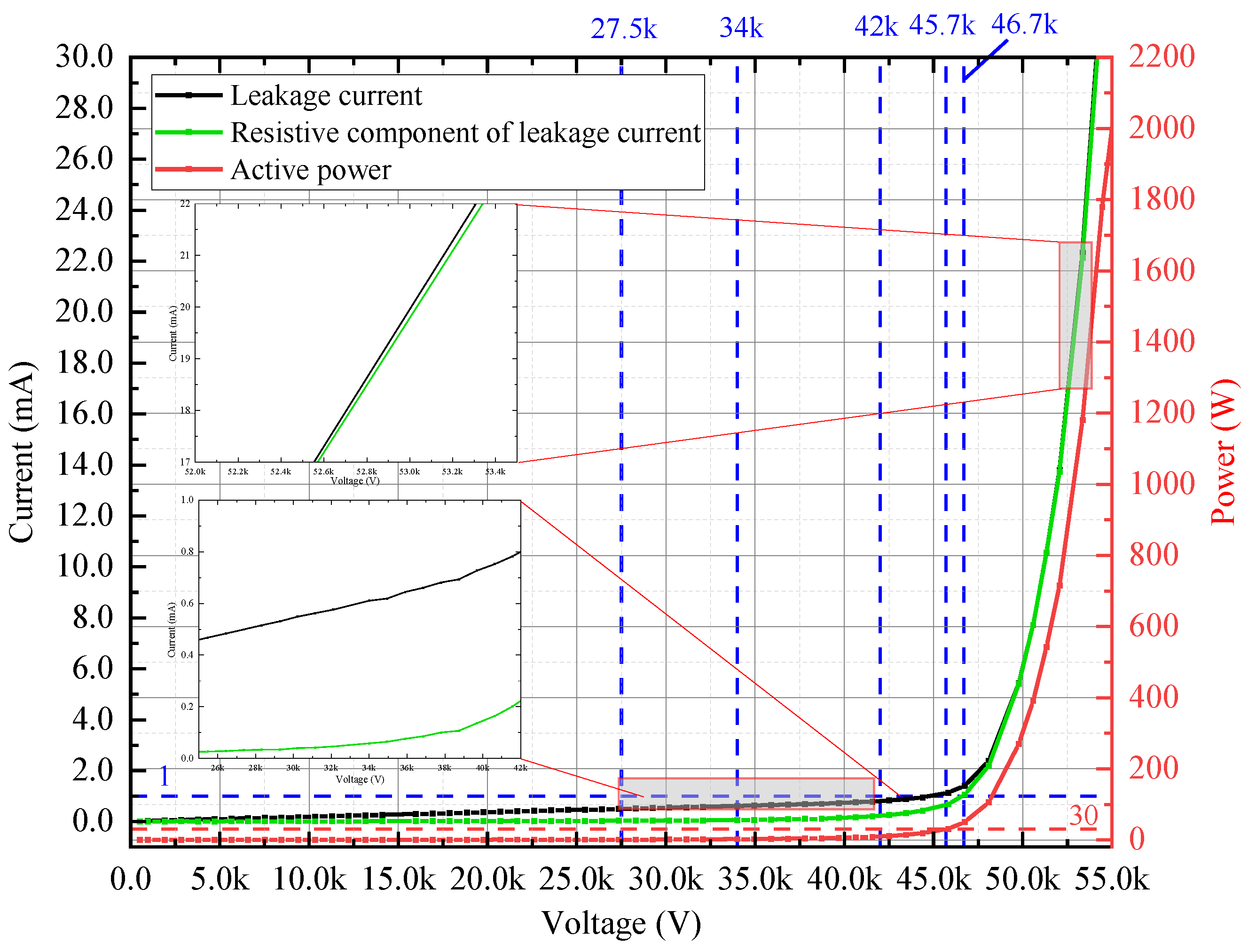
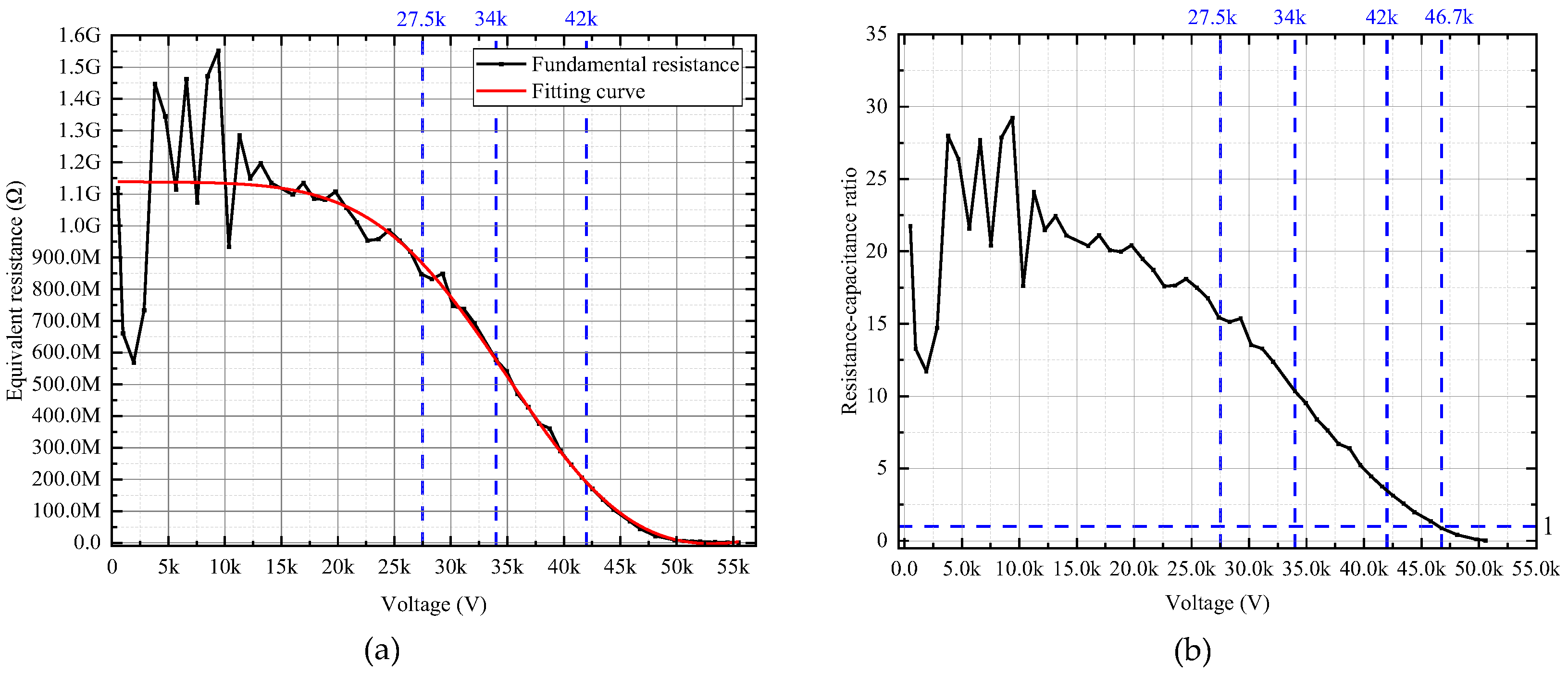
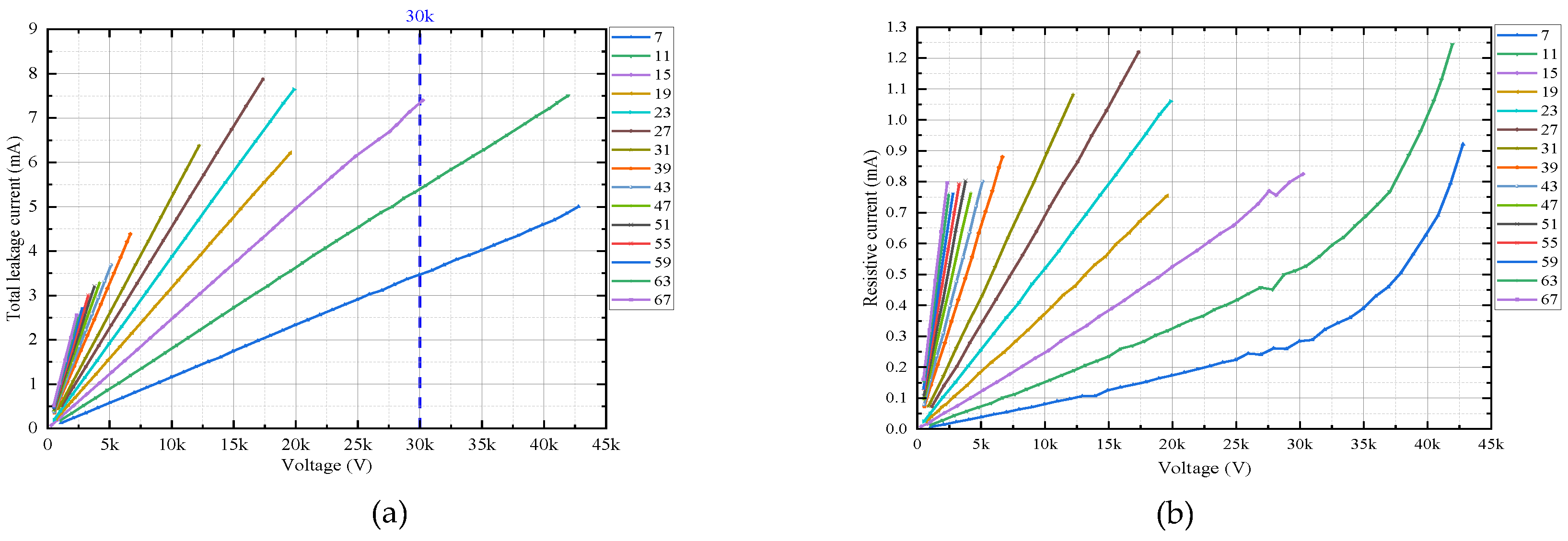
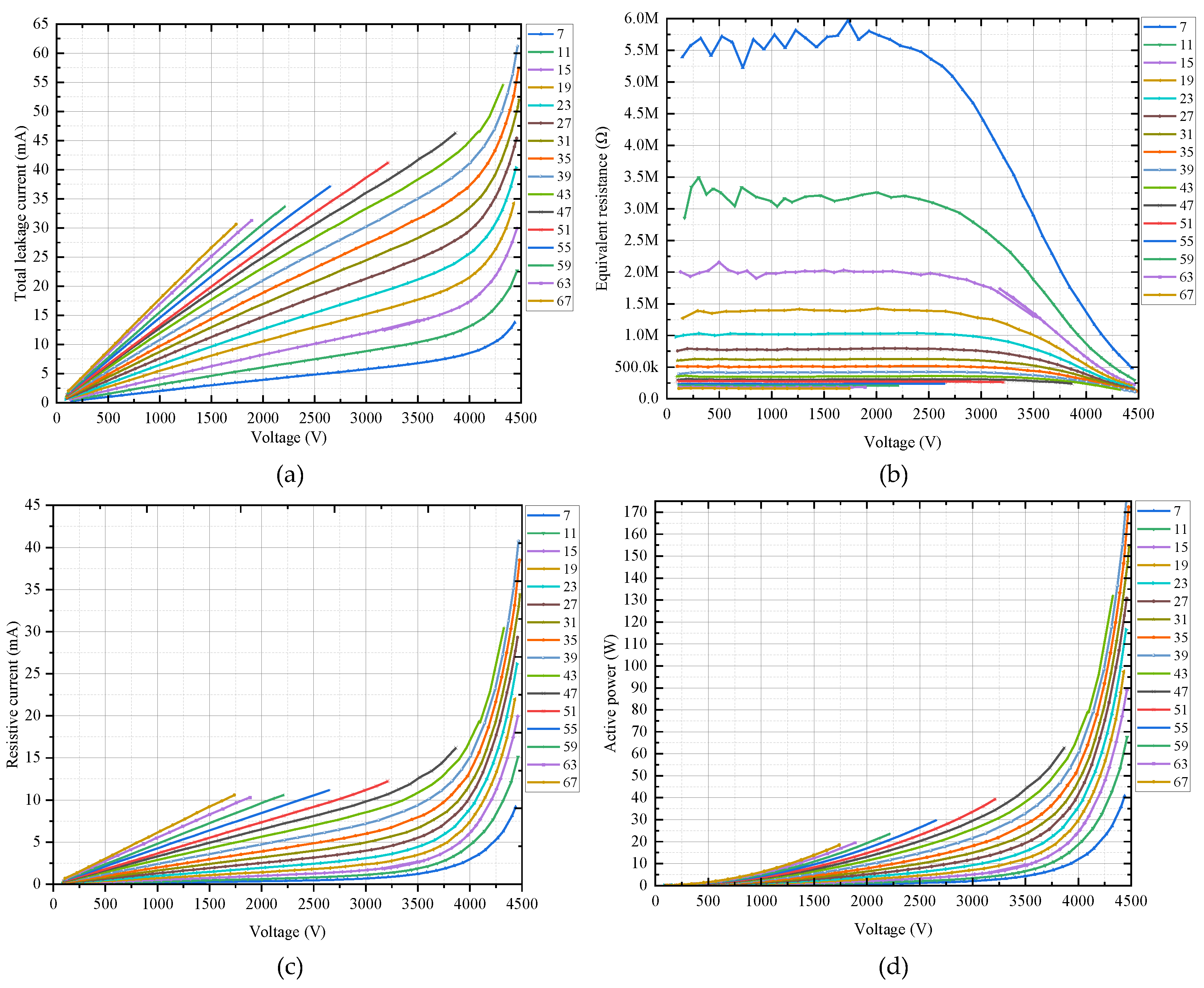
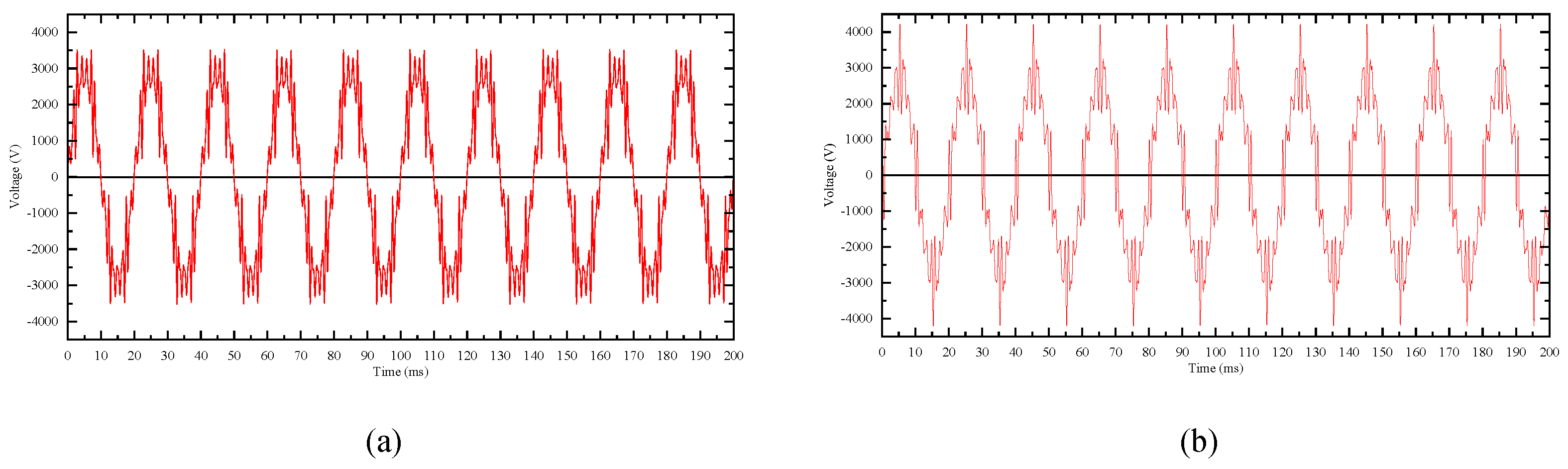
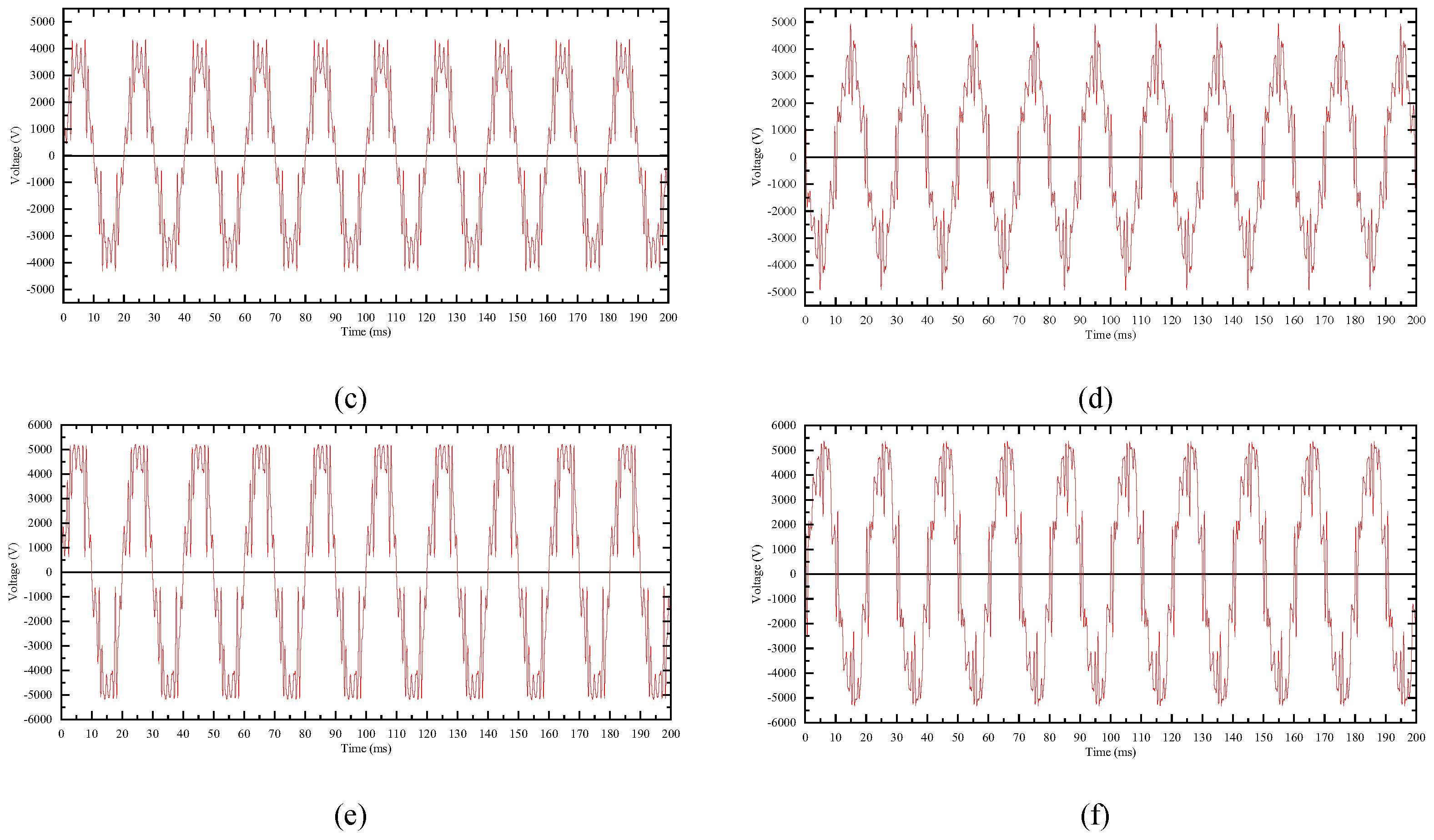
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated voltage (kV) | 42 |
| Continuous operating voltage (kV) | 34 |
| Nominal discharge current (A) | 10 |
| Residual voltage of lightning impulse current ≤ (kV) | 105 |
| Residual voltage of steep wave impulse voltage ≤ (kV) | 118 |
| Residual voltage of operating impulse current ≤ (kV) | 89 |
| DC reference voltage (1 mA) ≥ (kV) | 58 |
| AC reference voltage ≥ (kV) | 42 |
| 2 ms square wave current capacity (A) | 800 |
| High current withstand capability (kA) | 100 |
| Test group |
Fundamental Voltage | Harmonic voltage | Peak value of combin-ation voltage (V) | Fundamental equivalent resistance (MΩ) |
Fundamental active power (W) |
Total active power (W) |
||||||||
| 750Hz | 950Hz | 1150Hz | 1350Hz | |||||||||||
| RMS (V) |
Phase(°) | RMS (V) |
Phase(°) | RMS (V) |
Phase(°) | RMS(V) | Phase(°) | RMS(V) | Phase(°) | |||||
| 1-1 | 2000 | 0 | 389 | 0 | 235 | 180 | 215 | 0 | 190 | 180 | 3500 | 61.4 | 0.0669 | 0.141 |
| 1-2 | 2000 | 0 | 389 | 0 | 235 | 0 | 215 | 0 | 190 | 0 | 4200 | 27.0 | 0.151 | 0.249 |
| 2-1 | 2500 | 0 | 485 | 0 | 300 | 180 | 270 | 0 | 240 | 180 | 4351 | 22.5 | 0.282 | 0.429 |
| 2-2 | 2500 | 0 | 485 | 0 | 300 | 0 | 270 | 0 | 240 | 0 | 4931 | 12.4 | 0.506 | 0.735 |
| 3-1 | 3000 | 0 | 540 | 0 | 330 | 180 | 310 | 0 | 273 | 180 | 5000 | 6.30 | 1.47 | 2.00 |
| 3-2 | 3000 | 0 | 540 | 0 | 330 | 0 | 310 | 0 | 273 | 0 | 5394 | 3.90 | 3.32 | 2.95 |
| Identifier | Evaluation Parameters | Good | Normal | Attention | Abnormal | Fault |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | Fundamental leakage current / mA | < 0.5 | 0.5 - 1 | 1 - 1.5 | 1.5 - 5 | > 5 |
| I2 | DC U1mA /kV | > 63.8 | 58 - 63.8 | 52.3 - 58 | 46.4 - 52.3 | < 46.4 |
| I3 | Leakage current under 0.75 U1mA / uA | 10 - 30 | 30 - 50 | 50 - 70 | 70 - 100 | > 100 |
| I4 | Reference voltage / kV | > 46.2 | 42 - 46.2 | 37.8 - 42 | 33.6 - 37.8 | < 33.6 |
| I5 | Base insulation resistance / kMΩ | > 1.2 | 1 - 1.2 | 0.8 - 1 | 0.6 - 0.8 | < 0.6 |
| I6 | Arrester service life / year | 0 - 1 | 1 - 3 | 3 - 6 | 6 - 12 | > 12 |
| I7 | Combination of insulation jacket and flange | 0.8 - 1 | 0.6 - 0.8 | 0.5 - 0.6 | 0.3 - 0.5 | 0 - 0.3 |
| I8 | External insulation anti-pollution capability | 0.8 - 1 | 0.6 - 0.8 | 0.5 - 0.6 | 0.3 - 0.5 | 0 - 0.3 |
| I9 | UV imaging detection | 0.8 - 1 | 0.6 - 0.8 | 0.5 - 0.6 | 0.3 - 0.5 | 0 - 0.3 |
| I10 | External insulation surface condition | 0.8 - 1 | 0.6 - 0.8 | 0.5 - 0.6 | 0.3 - 0.5 | 0 - 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




