Submitted:
03 September 2024
Posted:
04 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
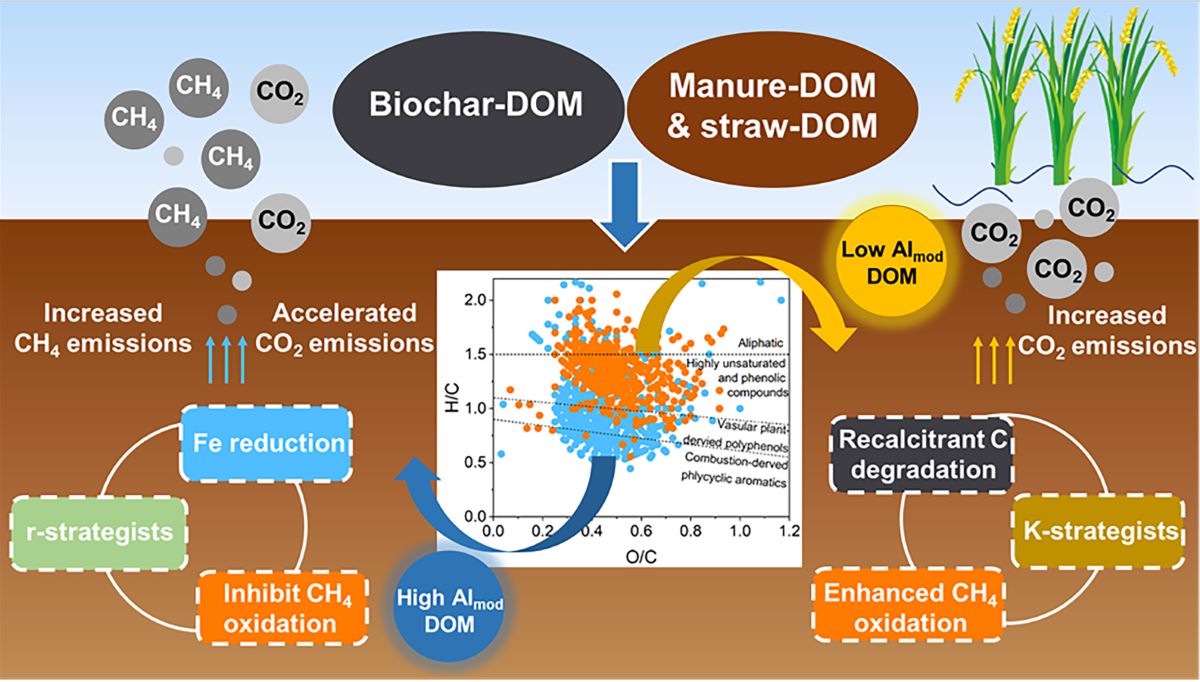
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sampling and Biochar Preparation
2.2. Soil Anaerobic Incubation and Measurements
2.3. DOM Extraction and Characterization
2.4. Bacterial 16S rRNA Gene Amplification, Illumina Sequencing, and Data Analysis
2.5. Quantification of Gene Abundances
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
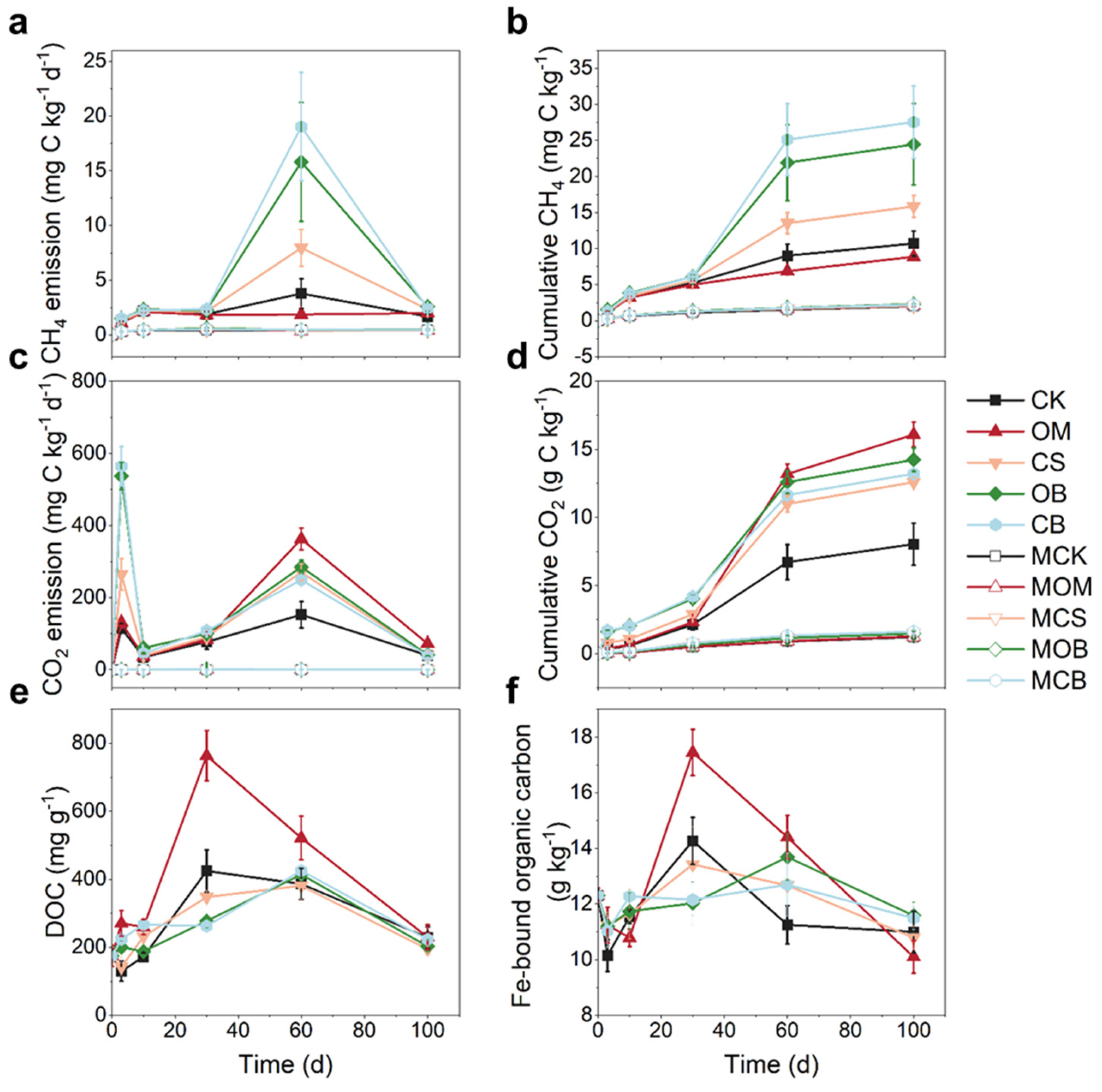
3.1. Soil Properties and C Emission
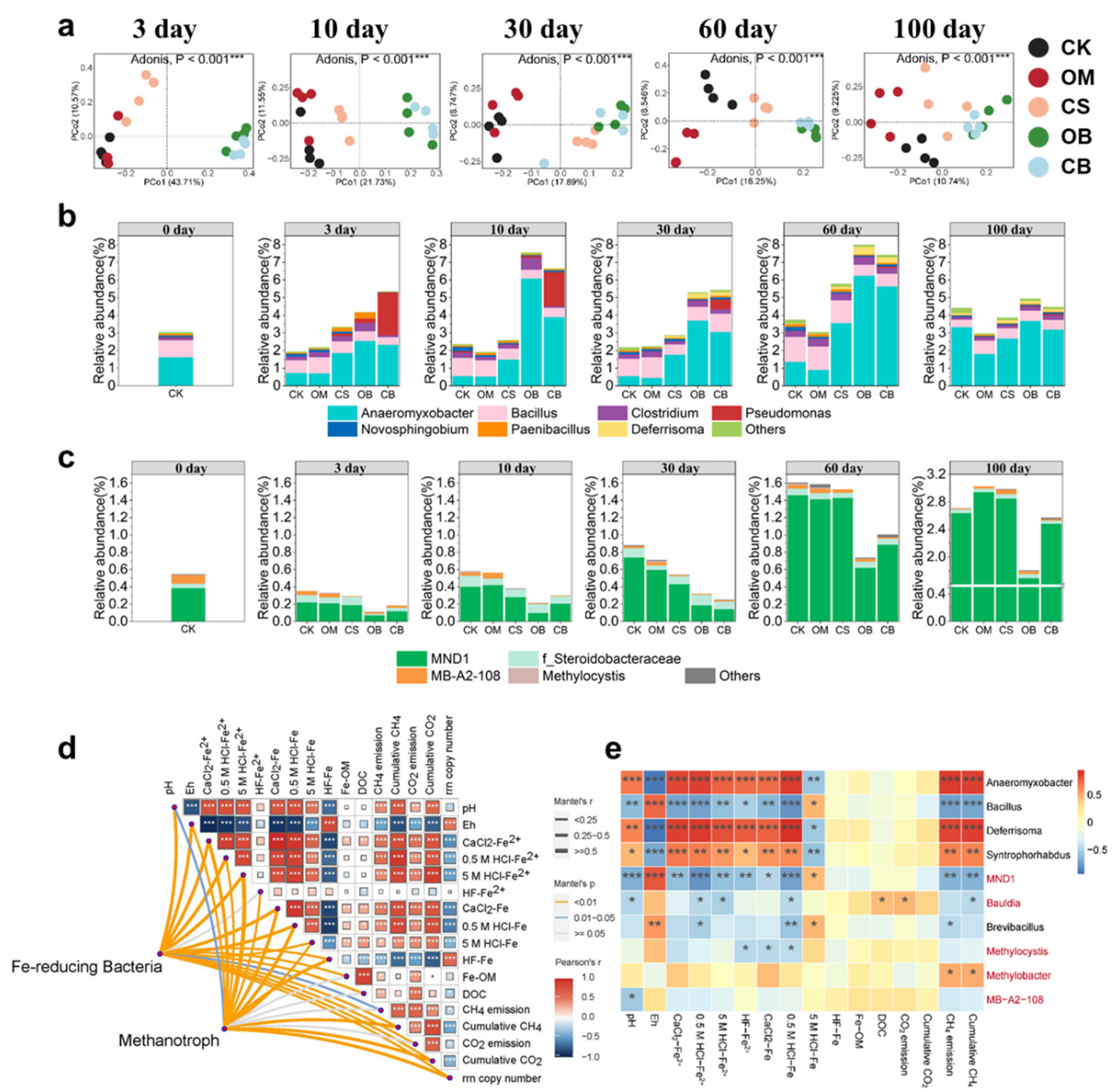
3.2. Dissimilatory Fe reduction and Fe Species Transformation
3.3. Soil Microbial Communities
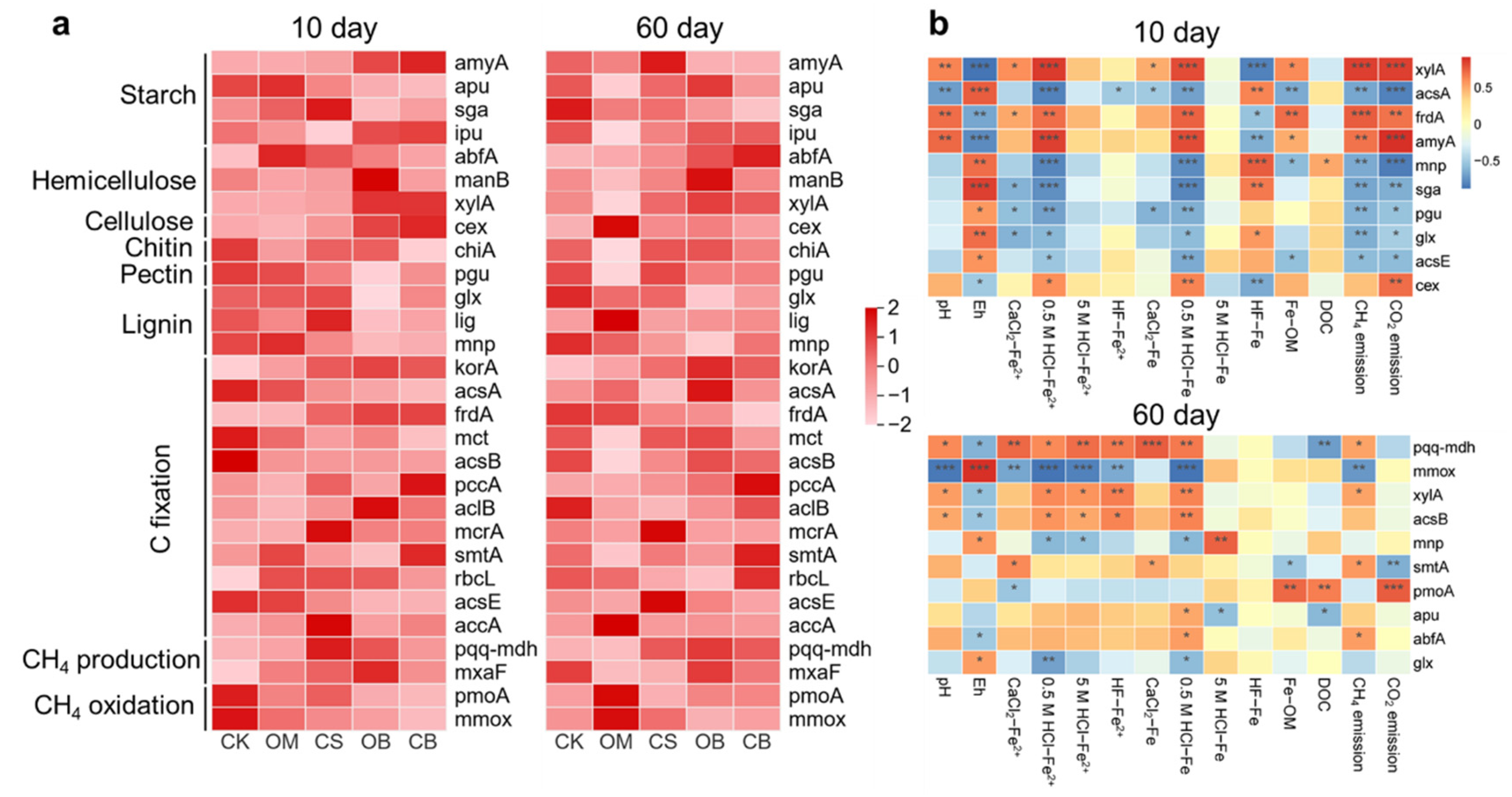
3.4. Abundance of Microbial C-Cycling Genes
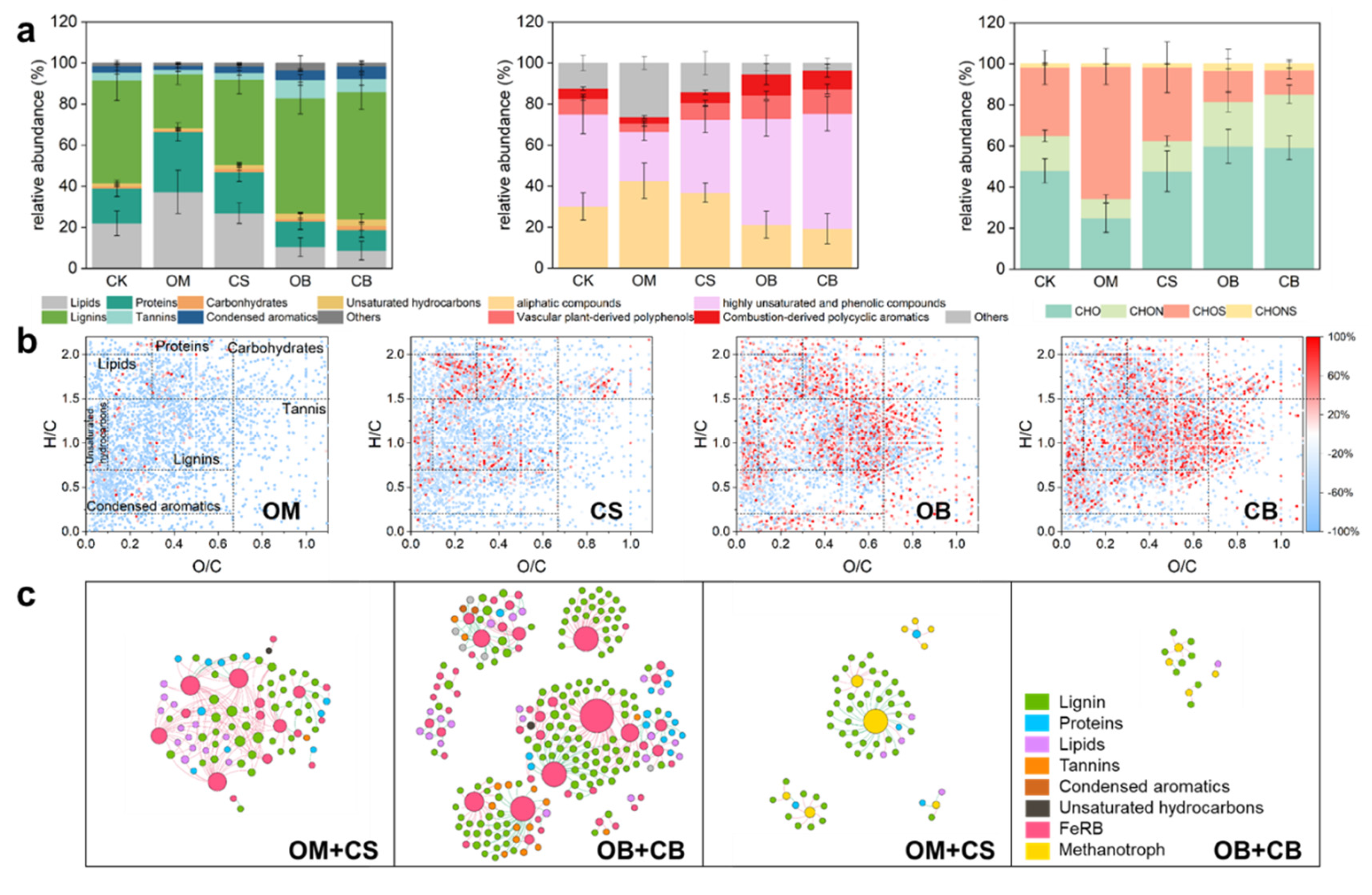
3.5. Characterization of Dissolved Organic Matter
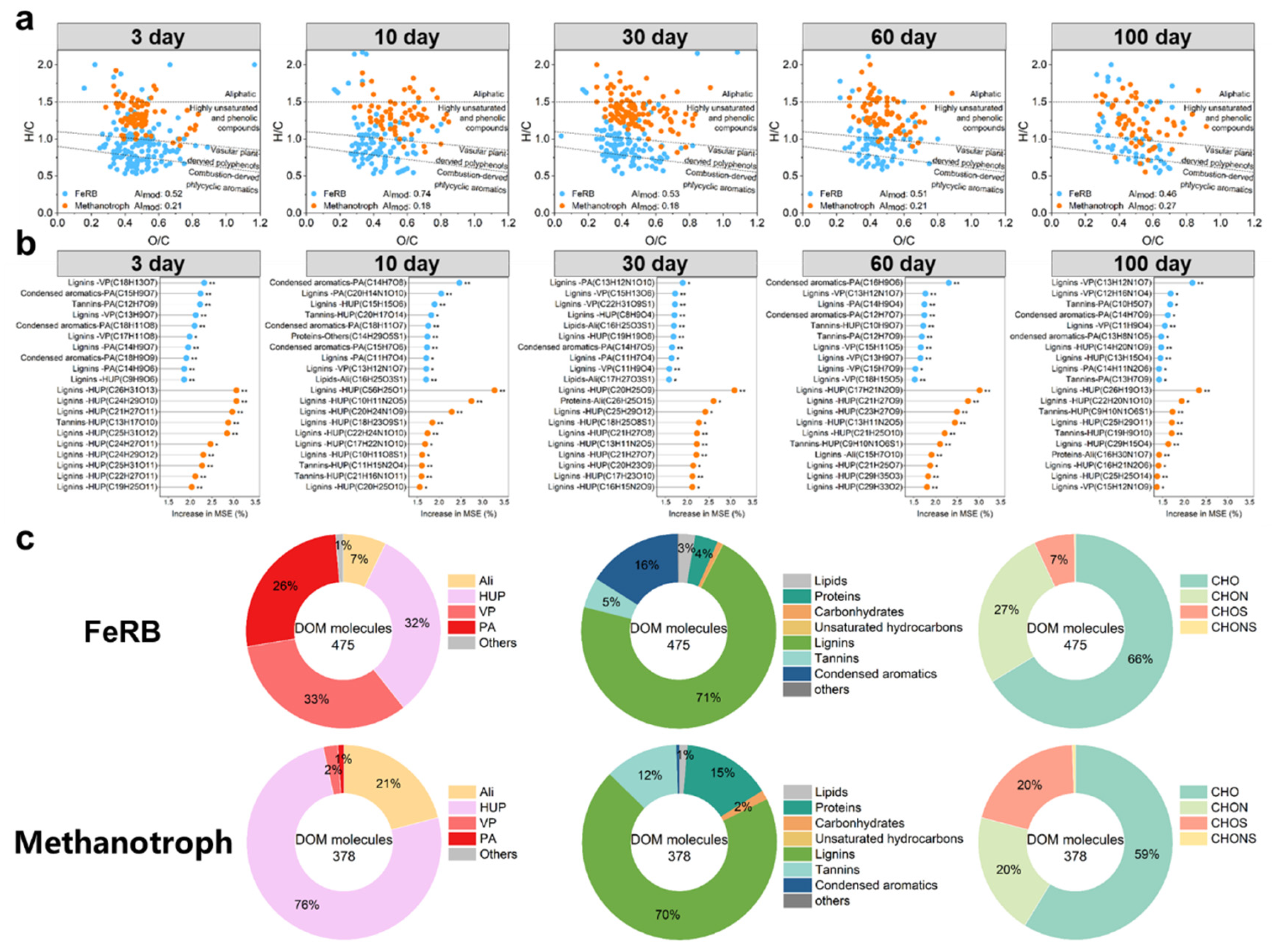
3.5. Specific DOM Molecules Associated with FeRB, Methanotrophs and Community r/K Strategy
4. Discussion
4.1. Exogenous DOM Promotes Microbial-Driven Fe Reduction in Paddy Soil
4.2. Exogenous DOM Affects Soil C Emissions
4.2.1. Exogenous DOM Regulates Soil CH4 Emission
4.2.2. Exogenous DOM Affects Soil CO2 Emission
4.3. Environmental Implications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, D.; Ren, C.; Ren, D.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, Q. New insights into carbon mineralization in tropical paddy soil under land use conversion: Coupled roles of soil microbial community, metabolism, and dissolved organic matter chemodiversity. Geoderma 2023, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zheng, S.; Ma, C.; Rui, Y.; He, H.; Huang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Ge, T.; et al. Contrasting pathways of carbon sequestration in paddy and upland soils. Global Change Biology 2021, 27, 2478–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, J.; Fan, Y.; Wang, L.; Putnis, C. V.; Zhang, W. Retention of soil organic matter by occlusion within soil minerals. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/Technology 2022, 21, 727–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, R. C.; Lynch, L.; Webster, T. M.; Schweizer, S.; Inagaki, T. M.; Tfaily, M. M.; Kukkadapu, R.; Hoeschen, C.; Buckley, D. H.; Lehmann, J. Susceptibility of new soil organic carbon to mineralization during dry-wet cycling in soils from contrasting ends of a precipitation gradient. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2022, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hall, S. J.; Coward, E.; Thompson, A. Iron-mediated organic matter decomposition in humid soils can counteract protection. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patzner, M. S.; Mueller, C. W.; Malusova, M.; Baur, M.; Nikeleit, V.; Scholten, T.; Hoeschen, C.; Byrne, J. M.; Borch, T.; Kappler, A.; et al. Iron mineral dissolution releases iron and associated organic carbon during permafrost thaw. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J. X.; Li, X. M.; Sun, G. X.; Cui, L.; Ding, L. J.; He, C.; Li, L. G.; Shi, Q.; Smets, B. F.; Zhu, Y. G. Fate of Labile Organic Carbon in Paddy Soil Is Regulated by Microbial Ferric Iron Reduction. Environ Sci Technol 2019, 53, 8533–8542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L. J.; Su, J. Q.; Xu, H. J.; Jia, Z. J.; Zhu, Y. G. Long-term nitrogen fertilization of paddy soil shifts iron-reducing microbial community revealed by RNA-(13)C-acetate probing coupled with pyrosequencing. ISME J 2015, 9, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kögel-Knabner, I.; Amelung, W.; Cao, Z.; Fiedler, S.; Frenzel, P.; Jahn, R.; Kalbitz, K.; Kölbl, A.; Schloter, M. Biogeochemistry of paddy soils. Geoderma 2010, 157, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeewani, P. H.; Ling, L.; Fu, Y.; Van Zwieten, L.; Zhu, Z.; Ge, T.; Guggenberger, G.; Luo, Y.; Xu, J. The stoichiometric C-Fe ratio regulates glucose mineralization and stabilization via microbial processes. Geoderma 2021, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, O. W.; Curti, L.; Woulds, C.; Bradley, J. A.; Babakhani, P.; Mills, B. J. W.; Homoky, W. B.; Xiao, K.-Q.; Bray, A. W.; Fisher, B. J.; et al. Long-term organic carbon preservation enhanced by iron and manganese. Nature 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Gong, X. Effects of Dissolved Organic Matter on the Bioavailability of Heavy Metals During Microbial Dissimilatory Iron Reduction: A Review. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology Volume 257; de Voogt, P., Ed.; Springer International Publishing, 2021; pp. 69–92. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Zeng, Q.; Sheng, Y.; Chen, C.; Yu, G.; Kappler, A. Coupled iron cycling and organic matter transformation across redox interfaces. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Meile, C.; Wilmoth, J.; Barcellos, D.; Thompson, A. Influence of pO(2) on Iron Redox Cycling and Anaerobic Organic Carbon Mineralization in a Humid Tropical Forest Soil. Environ Sci Technol 2018, 52, 7709–7719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.; Wang, Z.; Lv, J.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, G. H.; Li, G.; Zhu, Y. G. Multiple Effects of Humic Components on Microbially Mediated Iron Redox Processes and Production of Hydroxyl Radicals. Environ Sci Technol 2022, 56, 16419–16427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X. M.; Chen, Q. L.; He, C.; Shi, Q.; Chen, S. C.; Reid, B. J.; Zhu, Y. G.; Sun, G. X. Organic Carbon Amendments Affect the Chemodiversity of Soil Dissolved Organic Matter and Its Associations with Soil Microbial Communities. Environ Sci Technol 2019, 53, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Li, Y.; Yao, H.; Chapman, S. J. Effects of different carbon sources on methane production and the methanogenic communities in iron rich flooded paddy soil. Sci Total Environ 2022, 823, 153636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Fahad, S.; Wu, L.; Zhou, W.; Xu, P.; Sun, Z.; Salam, A.; Imran, M.; Jiang, M.; Kuzyakov, Y.; et al. Labile organic matter intensifies phosphorous mobilization in paddy soils by microbial iron (III) reduction. Geoderma 2019, 352, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, C.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Godoy, K.; Jofre, I.; Najera, F.; Matus, F. Iron-reducing bacteria decompose lignin by electron transfer from soil organic matter. Sci Total Environ 2021, 761, 143194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, T.; Kleindienst, S.; Straub, D.; Kretzschmar, R.; Angenent, L. T.; Kappler, A. A coupled function of biochar as geobattery and geoconductor leads to stimulation of microbial Fe(III) reduction and methanogenesis in a paddy soil enrichment culture. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2021, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, M.; Cai, C.; Rabiee, H.; Wang, Z.; Virdis, B.; Tyson, G. W.; McIlroy, S. J.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, S. Pyrogenic Carbon Promotes Anaerobic Oxidation of Methane Coupled with Iron Reduction via the Redox-Cycling Mechanism. Environmental Science & Technology 2023, 57, 19793–19804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Yu, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chapman, S. J.; Yao, H. A joint role of iron oxide and temperature for methane production and methanogenic community in paddy soils. Geoderma 2023, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M. A.; Kujawinski, E. B.; Stubbins, A.; Fatland, R.; Aluwihare, L. I.; Buchan, A.; Crump, B. C.; Dorrestein, P. C.; Dyhrman, S. T.; Hess, N. J.; et al. Deciphering ocean carbon in a changing world. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2016, 113, 3143–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klappenbach Joel, A.; Dunbar John, M.; Schmidt Thomas, M. rRNA Operon Copy Number Reflects Ecological Strategies of Bacteria. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2000, 66, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Jason Shi, Z.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, S.; Qu, Y.; Ma, Q.; He, Z.; et al. Microbial functional trait of rRNA operon copy numbers increases with organic levels in anaerobic digesters. The ISME Journal 2017, 11, 2874–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, P.; Anderson, I. C.; Singh, B. K. Microbial modulators of soil carbon storage: integrating genomic and metabolic knowledge for global prediction. Trends in Microbiology 2013, 21, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, J.; Lv, J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.-G. Carbon Sequestration Strategies in Soil Using Biochar: Advances, Challenges, and Opportunities. Environmental Science & Technology 2023, 57, 11357–11372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozjek, K.; Manoharan, L.; Urich, T.; Ahrén, D.; Hedlund, K. Microbial gene activity in straw residue amendments reveals carbon sequestration mechanisms in agricultural soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2023, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musadji, N. Y.; Lemée, L.; Caner, L.; Porel, G.; Poinot, P.; Geffroy-Rodier, C. Spectral characteristics of soil dissolved organic matter: Long-term effects of exogenous organic matter on soil organic matter and spatial-temporal changes. Chemosphere 2020, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, C.; Bravin, M. N.; Crouzet, O.; Pelosi, C.; Tillard, E.; Lecomte, P.; Lamy, I. Increased soil pH and dissolved organic matter after a decade of organic fertilizer application mitigates copper and zinc availability despite contamination. Science of The Total Environment 2020, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, R.; Ren, T.; Lei, M.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Cong, R.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J. Tillage and straw-returning practices effect on soil dissolved organic matter, aggregate fraction and bacteria community under rice-rice-rapeseed rotation system. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2020, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Liu, H.; Mao, J.; Chu, W.; Li, Q.; Alvarez, P. J. J.; Qu, X.; Zhu, D. Photochemistry of Dissolved Black Carbon Released from Biochar: Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and Phototransformation. Environmental Science & Technology 2016, 50, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xiong, X.; He, M.; Xu, Z.; Hou, D.; Zhang, W.; Ok, Y. S.; Rinklebe, J.; Wang, L.; Tsang, D. C. W. Roles of biochar-derived dissolved organic matter in soil amendment and environmental remediation: A critical review. Chemical Engineering Journal 2021, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Fu, Q.; Wu, T.; Cui, P.; Fang, G.; Liu, C.; Chen, C.; Liu, G.; Wang, W.; Wang, D.; et al. Active Iron Phases Regulate the Abiotic Transformation of Organic Carbon during Redox Fluctuation Cycles of Paddy Soil. Environ Sci Technol 2021, 55, 14281–14293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Bi, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, C.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, X. Unveiling the role of dissolved organic matter on phosphorus sorption and availability in a 5-year manure amended paddy soil. Sci Total Environ 2022, 838 Pt 1, 155892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lv, J.; He, A.; Cao, D.; He, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G. Investigation with ESI FT-ICR MS on sorbent selectivity and comprehensive molecular composition of landfill leachate dissolved organic matter. Water Research 2023, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, L.; Deng, Y.; Zhi, X.; Jiang, Y. H.; Tu, Q.; Xie, J.; Van Nostrand, J. D.; He, Z.; Yang, Y. Reproducibility and quantitation of amplicon sequencing-based detection. ISME J 2011, 5, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Zhu, Y.; Sardans, J.; Penuelas, J.; Su, J. QMEC: a tool for high-throughput quantitative assessment of microbial functional potential in C, N, P, and S biogeochemical cycling. Sci China Life Sci 2018, 61, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kugler, S.; Cooper, R. E.; Wegner, C. E.; Mohr, J. F.; Wichard, T.; Kusel, K. Iron-organic matter complexes accelerate microbial iron cycling in an iron-rich fen. Sci Total Environ 2019, 646, 972–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Adhikari, D.; Huang, R.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Roden, E.; Yang, Y. Biochar-Facilitated Microbial Reduction of Hematite. Environmental Science & Technology 2016, 50, 2389–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-B.; Liu, X.-P.; Jin, B.-J.; Shu, Y.-C.; Sun, C.-L.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Lin, X.-Y. High-molecular-weight dissolved organic matter enhanced phosphorus availability in paddy soils: Evidence from field and microcosm experiments. Soil and Tillage Research 2024, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iorio, E.; Circelli, L.; Angelico, R.; Torrent, J.; Tan, W.; Colombo, C. Environmental implications of interaction between humic substances and iron oxide nanoparticles: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 303 Pt 2, 135172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ThomasArrigo, L. K.; Vontobel, S.; Notini, L.; Nydegger, T. Coprecipitation with Ferrihydrite Inhibits Mineralization of Glucuronic Acid in an Anoxic Soil. Environmental Science & Technology 2023, 57, 9204–9213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappler, A.; Bryce, C.; Mansor, M.; Lueder, U.; Byrne, J. M.; Swanner, E. D. An evolving view on biogeochemical cycling of iron. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2021, 19, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Rotaru, A.-E.; Shrestha, P. M.; Malvankar, N. S.; Nevin, K. P.; Lovley, D. R. Promoting direct interspecies electron transfer with activated carbon. Energy & Environmental Science 2012, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, B.; Lv, J.; Meng, C.; Liao, Y.; Reid, B. J.; Ding, F.; Lu, Z.; Kuzyakov, Y.; et al. Biochar induces mineralization of soil recalcitrant components by activation of biochar responsive bacteria groups. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2022, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Jang, K.-S.; Dolfing, J.; Spencer, R. G. M.; Jeppesen, E. Terrestrial dissolved organic matter inputs drive the temporal dynamics of riverine bacterial ecological networks and assembly processes. Water Research 2024, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Dong, H.; Reguera, G.; Beyenal, H.; Lu, A.; Liu, J.; Yu, H. Q.; Fredrickson, J. K. Extracellular electron transfer mechanisms between microorganisms and minerals. Nat Rev Microbiol 2016, 14, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Dong, H.; Kukkadapu, R. K.; Ni, S.; Zeng, Q.; Hu, J.; Coffin, E.; Zhao, S.; Sommer, A. J.; McCarrick, R. M.; et al. Lignin-enhanced reduction of structural Fe(III) in nontronite: Dual roles of lignin as electron shuttle and donor. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 2021, 307, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, N.; Mejia, J.; He, S.; Yang, Y.; Ginder-Vogel, M.; Roden, E. E. Dual Role of Humic Substances As Electron Donor and Shuttle for Dissimilatory Iron Reduction. Environ Sci Technol 2018, 52, 5691–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovley, D. R. Syntrophy Goes Electric: Direct Interspecies Electron Transfer. Annu Rev Microbiol 2017, 71, 643–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kölbl, A.; Kaiser, K.; Thompson, A.; Mosley, L.; Fitzpatrick, R.; Marschner, P.; Sauheitl, L.; Mikutta, R. Rapid remediation of sandy sulfuric subsoils using straw-derived dissolved organic matter. Geoderma 2022, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Tang, S.; Pan, W.; Zhou, J.; Chadwick, D. R.; Hill, P. W.; Wu, L.; Jones, D. L. Effects of farmyard manure on soil S cycling: Substrate level exploration of high- and low-molecular weight organic S decomposition. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2021, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, C.; Liang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, K.; Zhang, P. Enhanced biomethane production from anthracite by application of an electric field. International Journal of Coal Geology 2020, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, J.; Ji, Q.; Chen, X.; Pan, X. Long-term effects of four environment-related iron minerals on microbial anaerobic oxidation of methane in paddy soil: A previously overlooked role of widespread goethite. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2021, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Bi, Q.; Ding, K.; Lin, X. Manure application effects on subsoils: Abundant taxa initiate the diversity reduction of rare bacteria and community functional alterations. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2022, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, A. The Family Comamonadaceae. In The Prokaryotes: Alphaproteobacteria and Betaproteobacteria; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E. F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin Heidelberg, 2014; pp. 777–851. [Google Scholar]
- McLeod, M. L.; Bullington, L.; Cleveland, C. C.; Rousk, J.; Lekberg, Y. Invasive plant-derived dissolved organic matter alters microbial communities and carbon cycling in soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2021, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Wang, O.; Jiao, J.-Y.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.-J.; Liu, F. Methylobacter couples methane oxidation and N2O production in hypoxic wetland soil. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2022, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Yuan, H.; Gao, W.; Chen, X.; Ge, T.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Z. Iron–organic carbon associations stimulate carbon accumulation in paddy soils by decreasing soil organic carbon priming. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2023, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Moorhead, D. L.; Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Zhu, Z.; Ge, T.; Peng, S.; Zhu, B.; et al. Decreasing microbial phosphorus limitation increases soil carbon release. Geoderma 2022, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nottingham, A. T.; Turner, B. L.; Stott, A. W.; Tanner, E. V. J. Nitrogen and phosphorus constrain labile and stable carbon turnover in lowland tropical forest soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2015, 80, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Chen, J.; Zhou, F.; Nie, M.; Hou, D.; Liu, H.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Ni, H.; Huang, W.; Zhou, J.; et al. Relative increases in CH4 and CO2 emissions from wetlands under global warming dependent on soil carbon substrates. Nature Geoscience 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Shang, Y.; Song, K.; Liu, G.; Hou, J.; Lyu, L.; Tao, H.; Li, S.; He, C.; Shi, Q.; et al. Composition of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in lakes responds to the trophic state and phytoplankton community succession. Water Res 2022, 224, 119073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Ma, Q.; Marsden, K. A.; Chadwick, D. R.; Luo, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Wu, L.; Jones, D. L. Microbial community succession in soil is mainly driven by carbon and nitrogen contents rather than phosphorus and sulphur contents. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2023, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




