Submitted:
03 September 2024
Posted:
04 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- (1)
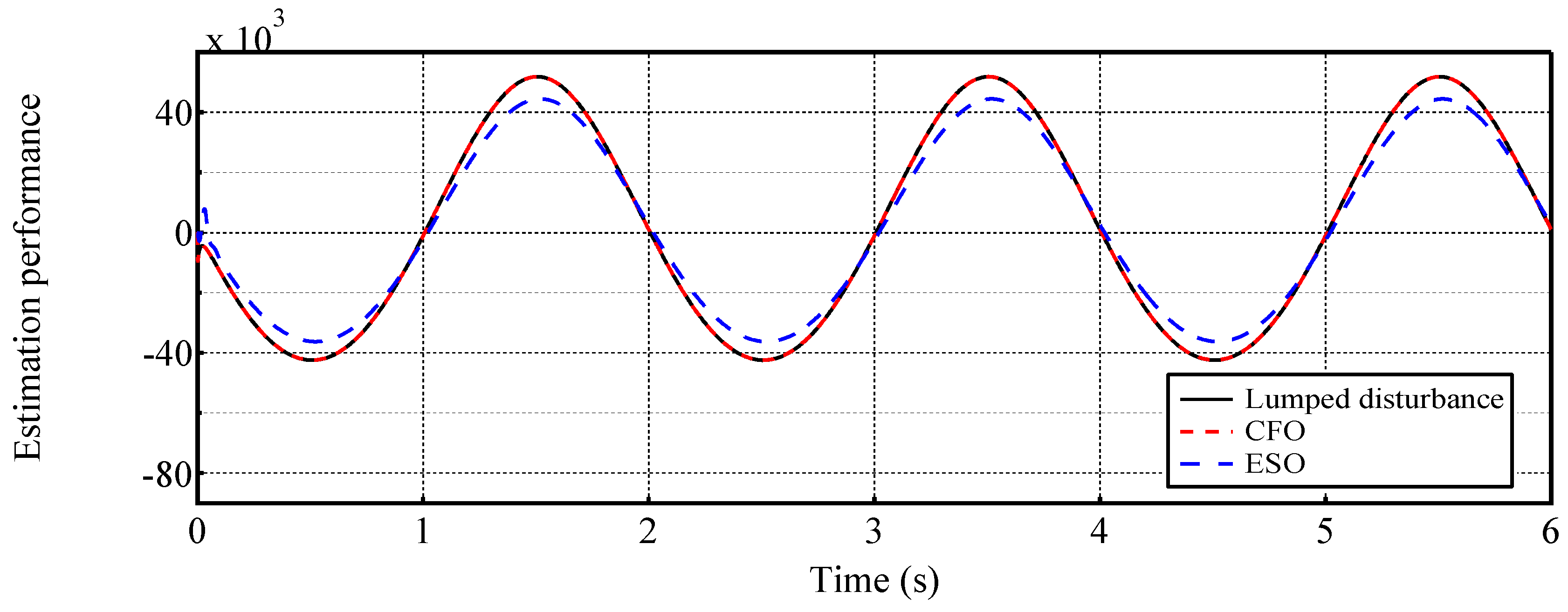
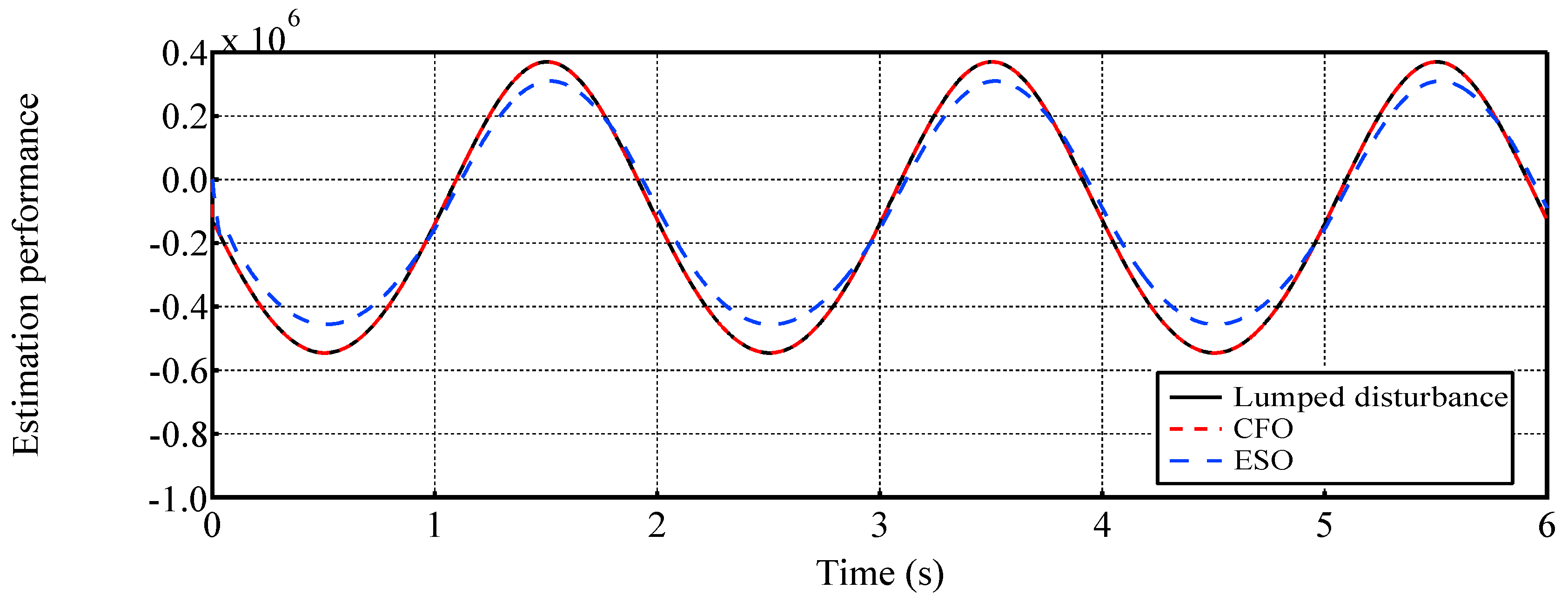
- Different from previous ESO-based methods (e.g., [37,40,41,43]), the CFO adopts a Type-III structure and fully utilizes system state information, which make it capable of estimating the disturbance with higher estimation accuracy. Detailed comparisons between the performance of ESO and CFO in estimation of different disturbances are examined by extensive comparison simulations.
- (2)
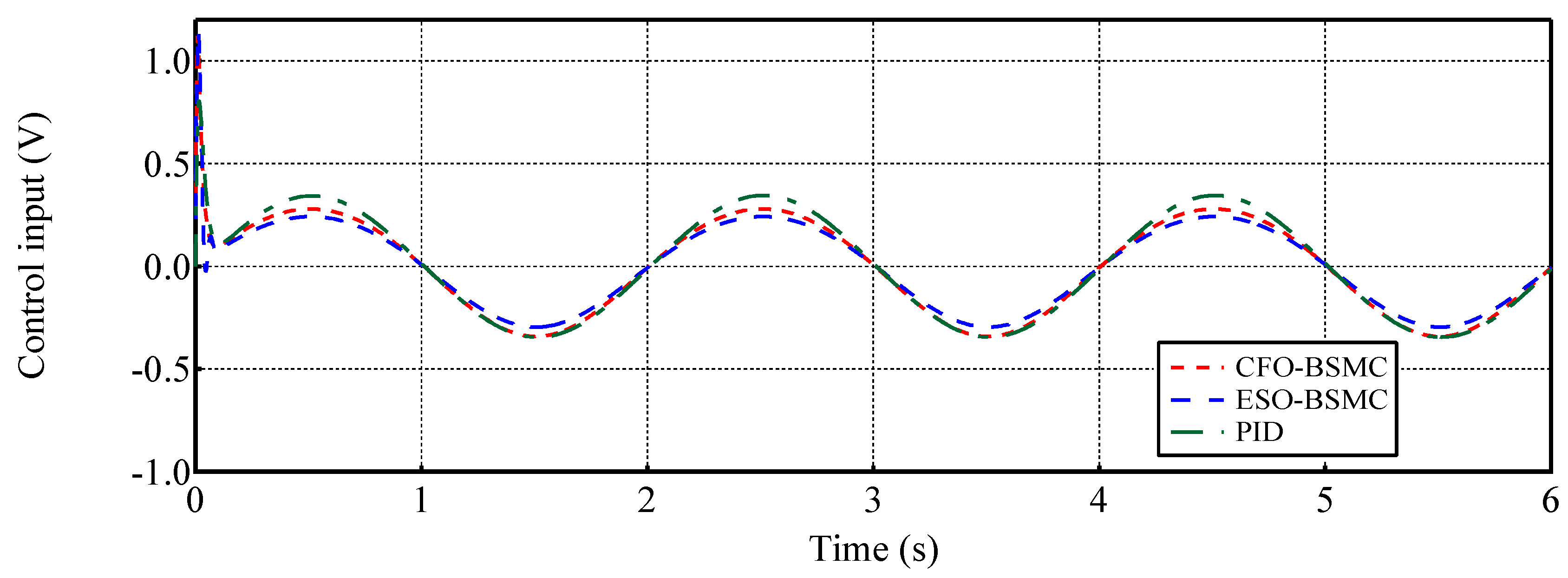
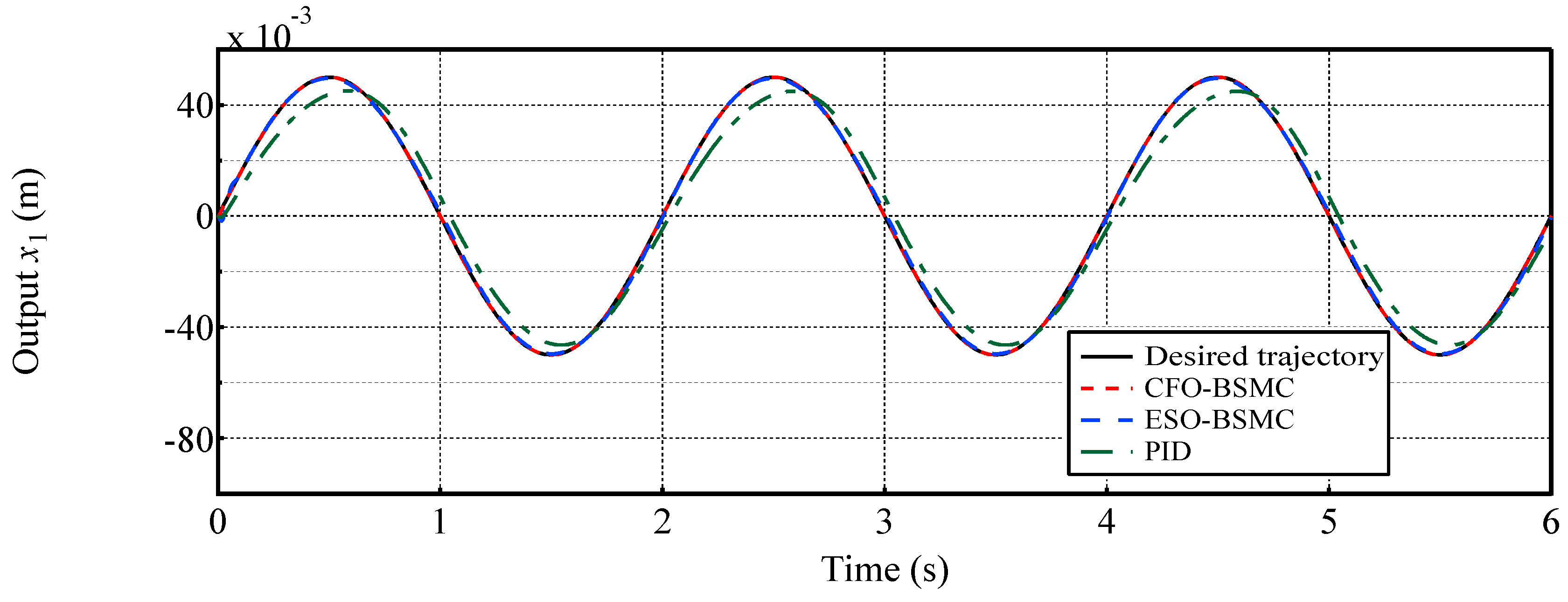
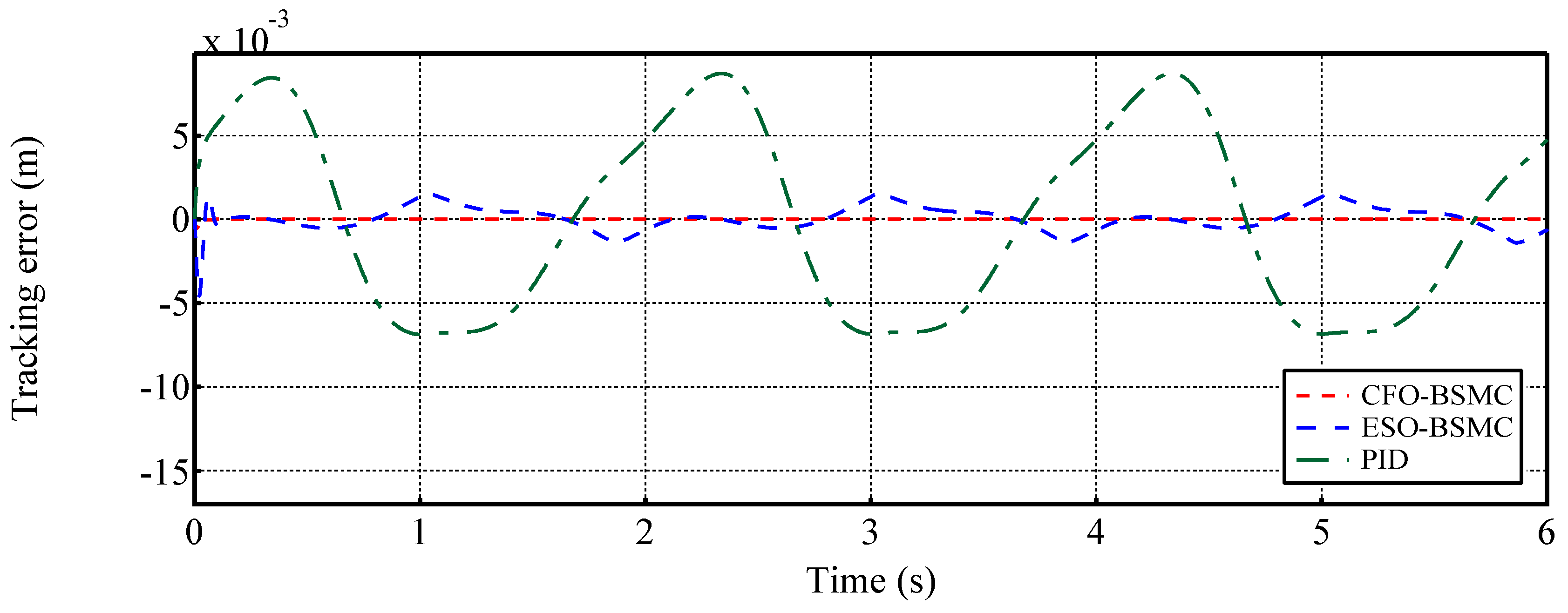
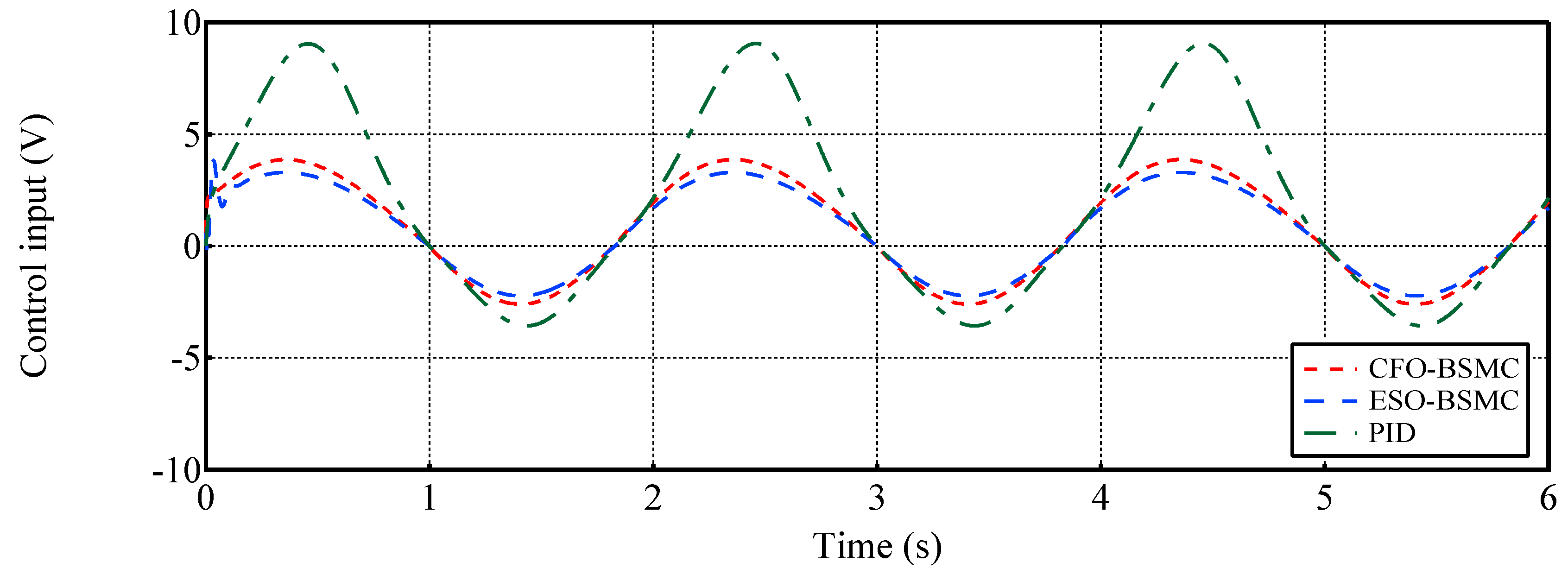
- In comparison with conventional PID and ESO-based BSMC [12,47], the proposed CFO-BMSC tracks the reference trajectory with no phase lag under the influence of large external load forces and disturbances, and the tracking accuracy is increased by and respectively, obtaining better transient and steady-state tracking performances. To our best knowledge, this is the first attempt to incorporate CFO into the backstepping sliding mode control of EHSS.
- (3)
- The stability of the overall system including the CFO and BSMC is rigorously analyzed by Lyapunov stability theory, which guarantees that the closed-loop control system is exponentially stable, and the tracking errors converge to the origin.
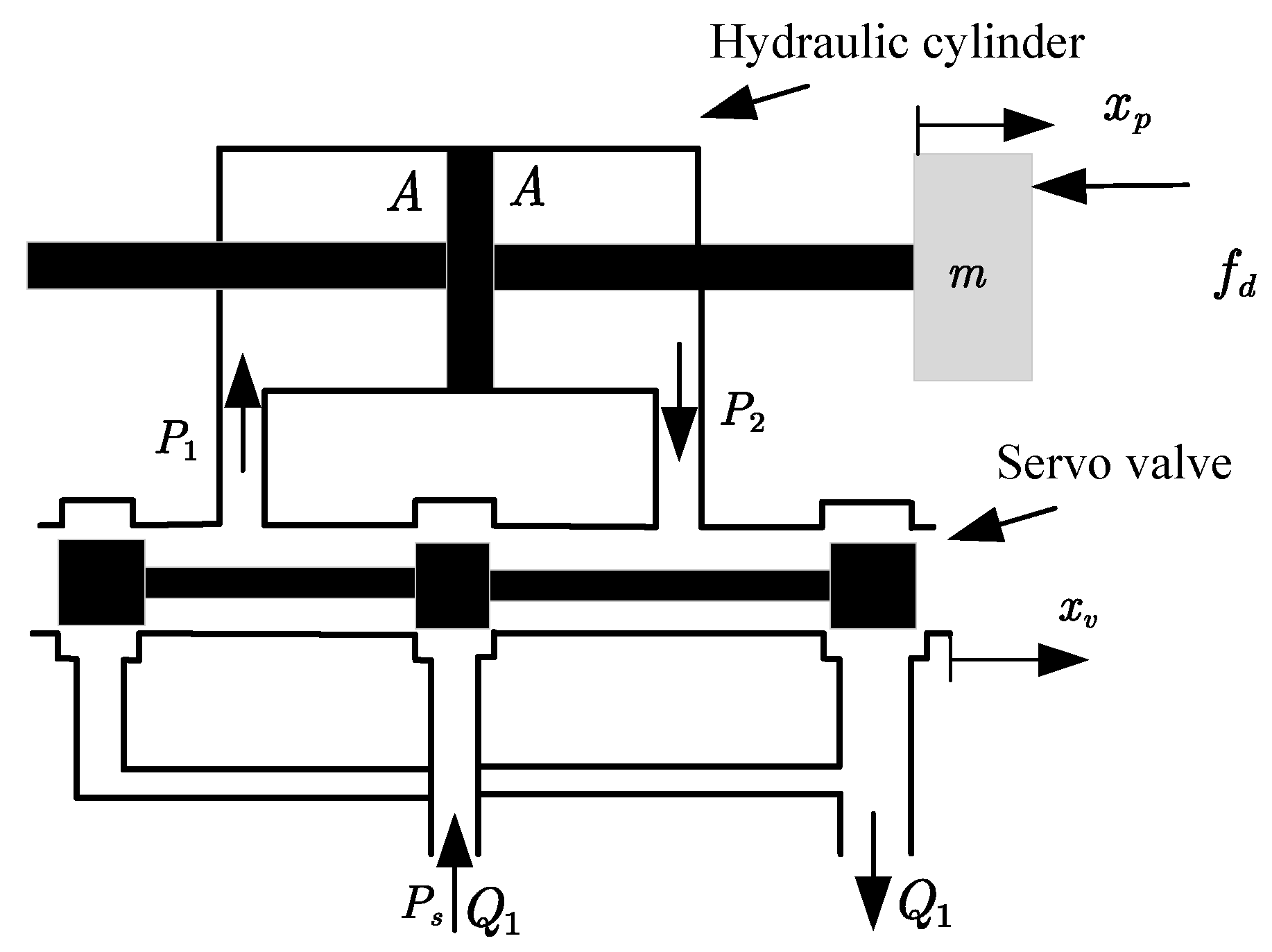
2. System Modeling and Problem Description
3. Control Design
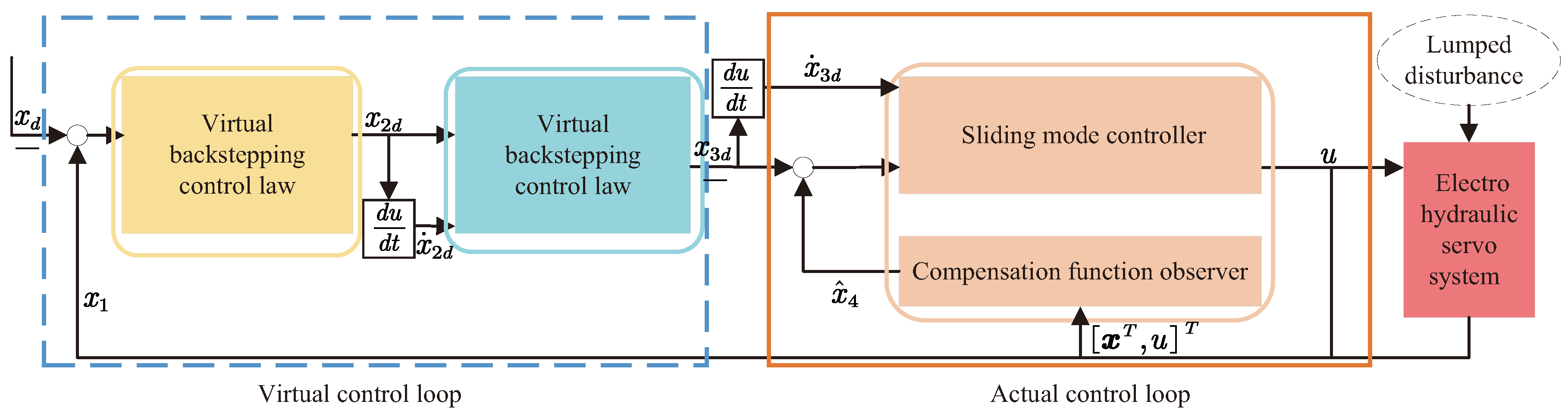
3.1. Structure of the Proposed Hierarchical Control Scheme
3.2. Design of Compensation Function Observer
| 1 | |||
| 0 | |||
3.3. Design of Backstepping Sliding Mode Controller
4. Simulation Results and Analysis
- (1)
- CFO-BSMC: This is the proposed backstepping silding mode controller based on CFO presented in Section 3. By trial and error, the parameters of the controller in (26), (30) and (37) are selected as , =2000. The bandwidth of the proposed CFO in Remark 1 is chosen as . Therefore, the gain parameters of the CFO are .
- (2)
- ESO-BSMC: This is the backstepping silding mode controller based on the ESO proposed in [47]. To ensure a fair comparison, the parameters of the controller are chosen as the same as those in CFO-BSMC. In addition, the poles of the ESO are assigned as the same as CFO, having the characteristic equation , where are gain parameters of the ESO. The bandwidth is also chosen as , which results in . Note that the maximum gainof the ESO is 240 times that of the CFO.
- (3)
- PID: This is the well-known proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller which has a wide range of application in industry [12]. By trial and error, the gain parameters of the PID controller are tuned as . It is notable that larger gains would achieve better tracking performance. However, it also may cause instability under the influence of lumped disturbances. Therefore, the gain parameters are ultimately obtained by the trial and error method.
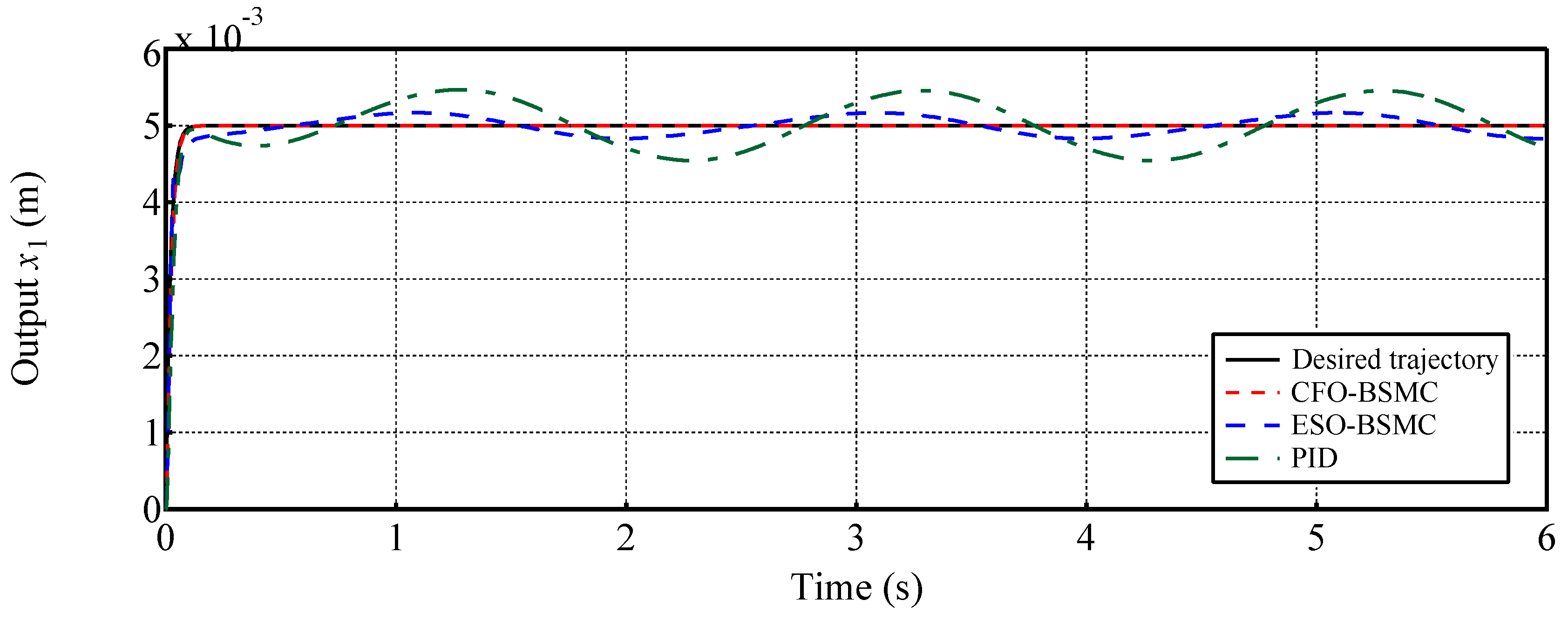
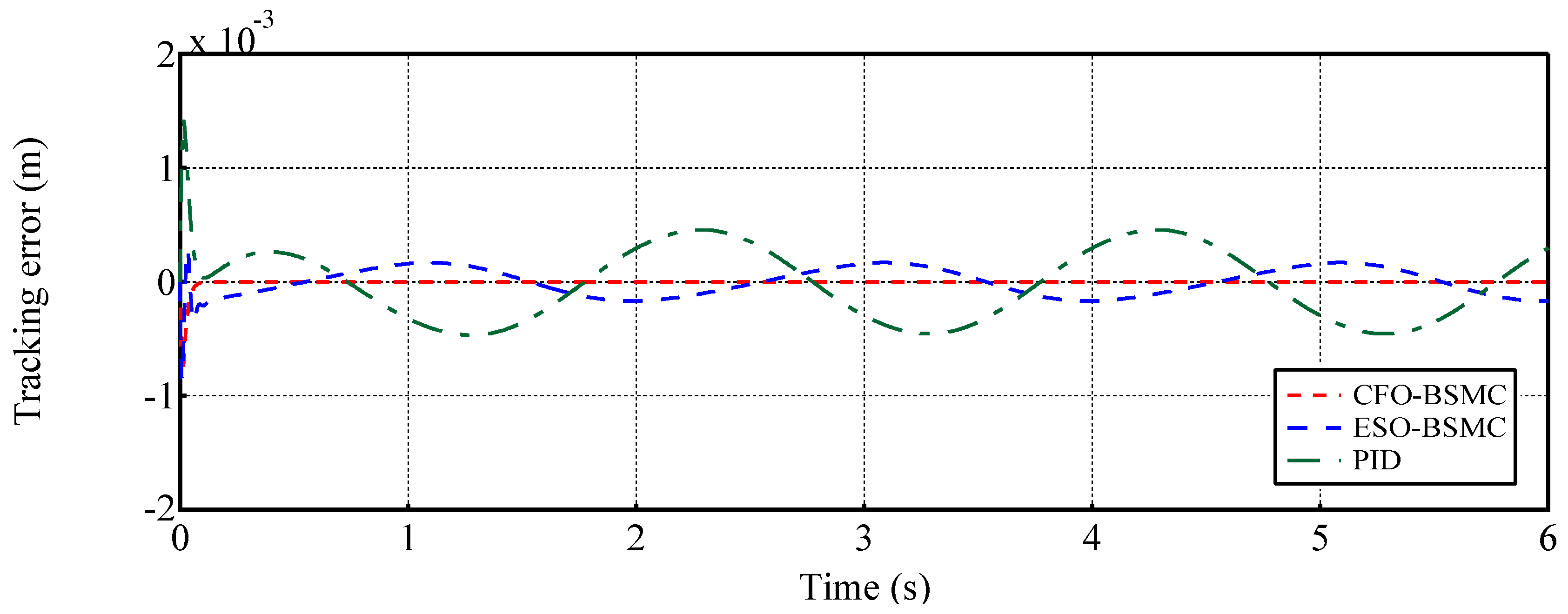
4.1. Case 1: Tracking an exponential-position trajectory
4.2. Case 2: Tracking a sinusoidal position trajectory
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonchis, A.; Corke, P, I.; Rye, D, C.; Ha, Q, P. Variable structure methods in hydraulic servo systems control. Automatica. 2001, 37,589-595. [CrossRef]
- Vladimir, M.; Željko, Š.; Mario, E. Robust H∞ position control synthesis of an electro-hydraulic servo system. ISA Transactions. 2010, 49,535-542. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, B, N.; Wang, S, P. Optimization based on convergence velocity and reliability for hydraulic servo system. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics. 2009, 22,407-412. [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Ma, W.; Yin, C, B.; Cao, D, H. Trajectory control of electro-hydraulic position servo system using improved PSO-PID controller. Automation in Construction. 2021, 127,103722. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhu, Z, H.; Hammadc, A. Automated excavators activity recognition and productivity analysis from construction site surveillance videos. Automation in Construction. 2020, 110,103045. [CrossRef]
- Keles, A.; Yildirim, M. Improvement of mechanical properties by means of titanium alloying to steel teeth used in the excavator. Engineering Science and Technology, an International Journal2020, 23,1208-1213. [CrossRef]
- Dindorf, R.; Wos, P. Energy-Saving Hot Open Die Forging Process of Heavy Steel Forgings on an Industrial Hydraulic Forging Press. Energies. 2020, 13,1620. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Chen, M. Energy efficiency improvement of heavy-load hydraulic fine blanking press for sustainable manufacturing assisted by multi-stages pressure source system. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhu, S. Dynamic response prediction of hydraulic soft robotic arms based on LSTM neural network. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part I, Journal of Systems and Control Engineering. Electronics. 2023. 237,1251-1265. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X, F.; Shi, G, L. Dual extended state observer-based adaptive dynamic surface control for a hydraulic manipulator with actuator dynamics. Mechanism and Machine Theory. 2022, 169,104647. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J, P.; Lu, B, C.; Fan, F.; Zhu, S, C.; Wu, J, X. A Nonlinear PID controller for electro-hydraulic servo system based on PSO algorithm. Applied Mechanics and Materials. 2012, 141, 157-161. [CrossRef]
- Karam, M, E.; Jiao, Z, X.; Zhang, H, Q. PID controller optimization by GA and its performances on the electro-hydraulic servo control system. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics. 2008, 21,378-384. [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyczak, L.; Macha, E. Selection of settings of the PID controller by automatic tuning at the control system of the hydraulic fatigue stand. Mech Syst Signal Process. 2008, 22, 1274–88. [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.; Ramli, R.; Ibrahim, M. Hybrid design of PID controller for four DoF lower limb exoskeleton. Appl Math Model. 2019, 72, 17–27. [CrossRef]
- Honorine, A, M.; Ravinder, V.; Jean, P, K.; Christian, B. Feedback linearization-based position control of an electrohydraulic servo system with supply pressure uncertainty. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology. 2012, 20, 1092-1099. [CrossRef]
- Aleksey, A, K. Feedback linearization of nonlinear singularly perturbed systems with state-dependent coefficients. International Journal of Control. 2020, 18, 1743-1750. [CrossRef]
- Angue, M, H.; Venugopal, R.; Kenne, J, P.; Belleau, C. Feedback linearization-based position control of an electrohydraulic servo system with supply pressure uncertainty. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology. 2012, 20, 1092-1099. [CrossRef]
- Yao, J, Y.; Deng, W, X.; Sun, W, C. Precision motion control for electro-hydraulic servo systems with noise alleviation, a desired compensation adaptive approach. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics. 2017, 22, 1859-1868. [CrossRef]
- Yang, G, C.; Y, J, Yao. High-precision motion servo control of double-rod electro-hydraulic actuators with exact tracking performance. ISA Transactions. 2020, 103, 266-279. [CrossRef]
- Feng, L, J.; Yan, H. Nonlinear adaptive robust control of the electro-hydraulic servo system. Applied Sciences (Switzerland). 2020, 10, 4494. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, Z, C.; Rui, G, C.; Cheng, D.; Shen, G.; Tang, Y. Force loading tracking control of an electro-hydraulic actuator based on a nonlinear adaptive fuzzy backstepping control scheme. Symmetry. 2018, 10, 155. [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Xia J.; Liu X.; Yue H.; Li C. Adaptive backstepping control of high-order fully actuated nonlinear systems with event-triggered strategy. Intelligence & Robotics 2023, 3(2), 176-89. [CrossRef]
- Zaare, S.; Soltanpour, M, R. Optimal robust adaptive fuzzy backstepping control of electro-hydraulic servo position system. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control. 2022, 44, 1247-1262. [CrossRef]
- Li, J, F.; Ji, R, H.; Liang, X, L.; Ge, S, S.; Yan, H. Command filter-based adaptive fuzzy finite-time output feedback control of nonlinear electrohydraulic servo system. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement. 2022, 71, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Niu, S, S.; Wang, J, Z.; Zhao, J, B.; Shen, W. Neural network-based finite-time command-filtered adaptive backstepping control of electro-hydraulic servo system with a three-stage valve. ISA Transactions. 2024, 144, 419-435. [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z, S.; Yue, L, W.; Fu, Y. Neural network based adaptive backstepping control for electro-hydraulic servo system position tracking. International Journal of Aerospace Engineering. 2022, 2022, 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Truong, H, V, A.; S, N.; Kim, S.; Kim, Y, W.; Chung, W, K. Backstepping-sliding-mode-based neural network control for electro-hydraulic actuator subject to completely unknown system dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Dang, X.; Zhao, X.; Dang, C. Incomplete differentiation-based improved adaptive backstepping integral sliding mode control for position control of hydraulic system. ISA transactions. 2021, 109, 199-217. [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q, Y.; Su, X, Y. Generalized super-twisting backstepping sliding mode control for electro-hydraulic servo systems considering the coexistence of matched and mismatched uncertainties. Applied Sciences. 2023, 13, 4931. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, W.; Du, X. Adaptive backstepping sliding mode compensation control for electro-hydraulic load simulator with backlash links. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control. 2024, 34, 8724-8743. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, G.; Liu, H.; Yan, G.; Zhang, T.; Liu, K.; Liu, Y.; Ai, C. Research on position control of an electro–hydraulic servo closed pump control system. Processes. 2022, 10, 1674. [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Song, Q, Y.; Ma, S, L.; Ma, W.; Yin, C, B.; Cao, D, H.; Yu, H, F. A new adaptive sliding mode controller based on the RBF neural network for an electro-hydraulic servo system. ISA Transactions. 2022. 29, 472-484. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X, C.; Li, D.; Yang, X, B.; Yu, Y, C. Identification Recurrent Type 2 Fuzzy Wavelet Neural Network and L2-Gain Adaptive Variable Sliding Mode Robust Control of Electro-Hydraulic Servo System (EHSS). Asian Journal of Control. 2018. 20, 1480-1490. [CrossRef]
- Guo, X, P.; Wang, H, S.; Liu, H. Parameter adaptive based neural network sliding mode control for electro-hydraulic system with application to rock drilling jumbo. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing. 2024. 38, 2554-2569. [CrossRef]
- Han, J, Q. From PID to Active Disturbance Rejection Control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics. 2009. 56(3), 900-906. [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Sun H.; Wu Q.; Su Y.; Sun N. GPI observer-based active disturbance rejection control for a morphing quadrotor. Intelligence & Robotics. 2023, 3(3): 274-87. [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H, X.; Sun, Q, L.; Chen, Z, Q. Sliding mode control for electro-hydraulic proportional directional valve-controlled position tracking system based on an extended state observer. Asian Journal of Control. 2021. 23, 1855-1869. [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q. Extended state observer-based finite time control of electro-hydraulic system via sliding mode technique. Asian Journal of Control. 2022. 24, 2311-2327. [CrossRef]
- LAO, L, M.; Chen, P, Z. Adaptive sliding mode control of an electro-hydraulic actuator with a kalman extended state observer. IEEE Access. 2024. 12, 8970-8982. [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Shen, C. An extended state observer-based control design for electro-hydraulic position servomechanism. Control Engineering Practice. 2021. 109, 104730. [CrossRef]
- Meng, F, L.; Yan, H.; Li, J, F.; Liu, X. Finite-time backstepping control for electro-hydraulic servo system via extended state observer with perturbation estimation performance improvement. Machines. 2022. 10, 1163. [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q, K.; Cai, Y.; Song, J, C.; Wang, B, L. A novel ESO-based adaptive RISE control for asymptotic position tracking of electro-hydraulic actuator systems. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control. 2024. 46, 1134-1145. [CrossRef]
- Yang, G, C. Dual extended state observer-based backstepping control of electro-hydraulic servo systems with time-varying output constraints. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control. 2020. 42, 1070-1080. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M, H.; Ahn, K, K. Output feedback robust tracking control for a variable-speed pump-controlled hydraulic system subject to mismatched uncertainties. Mathematics. 2023. 11, 1783. [CrossRef]
- Qi, G, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Z, Q. Problems of extended state observer and proposal of compensation function observer for unknown model and application in UAV. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems. 2022. 52, 2899-2910. [CrossRef]
- Shao, X, L.; Wang, H, L. Back-stepping active disturbance rejection control design for integrated missile guidance and control system via reduced-order ESO. ISA Transactions. 2015. 57, 10-22. [CrossRef]
- Guo, B, Z.; Zhao, Z, L. On the convergence of an extended state observer for nonlinear systems with uncertainty. Systems & Control Letters. 2011. 60(6), 420-430. [CrossRef]
- Qi, G, Y.; Deng, J, H.; Li, X.; Yu, X, C. Compensation function observer-based model-compensation backstepping control and application in anti-inference of quadrotor UAV. Control Engineering Practice. 2023. 140, 105633. [CrossRef]
- Qi, G, Y.; Hu, J, B.; Li, L, Y.;Li, K. Integral compensation cunction observer and its application to disturbance-rejection control of QUAV attitude. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics. 2024. 54, 4088-4099. [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | |||
| 10 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





