Submitted:
29 August 2024
Posted:
02 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
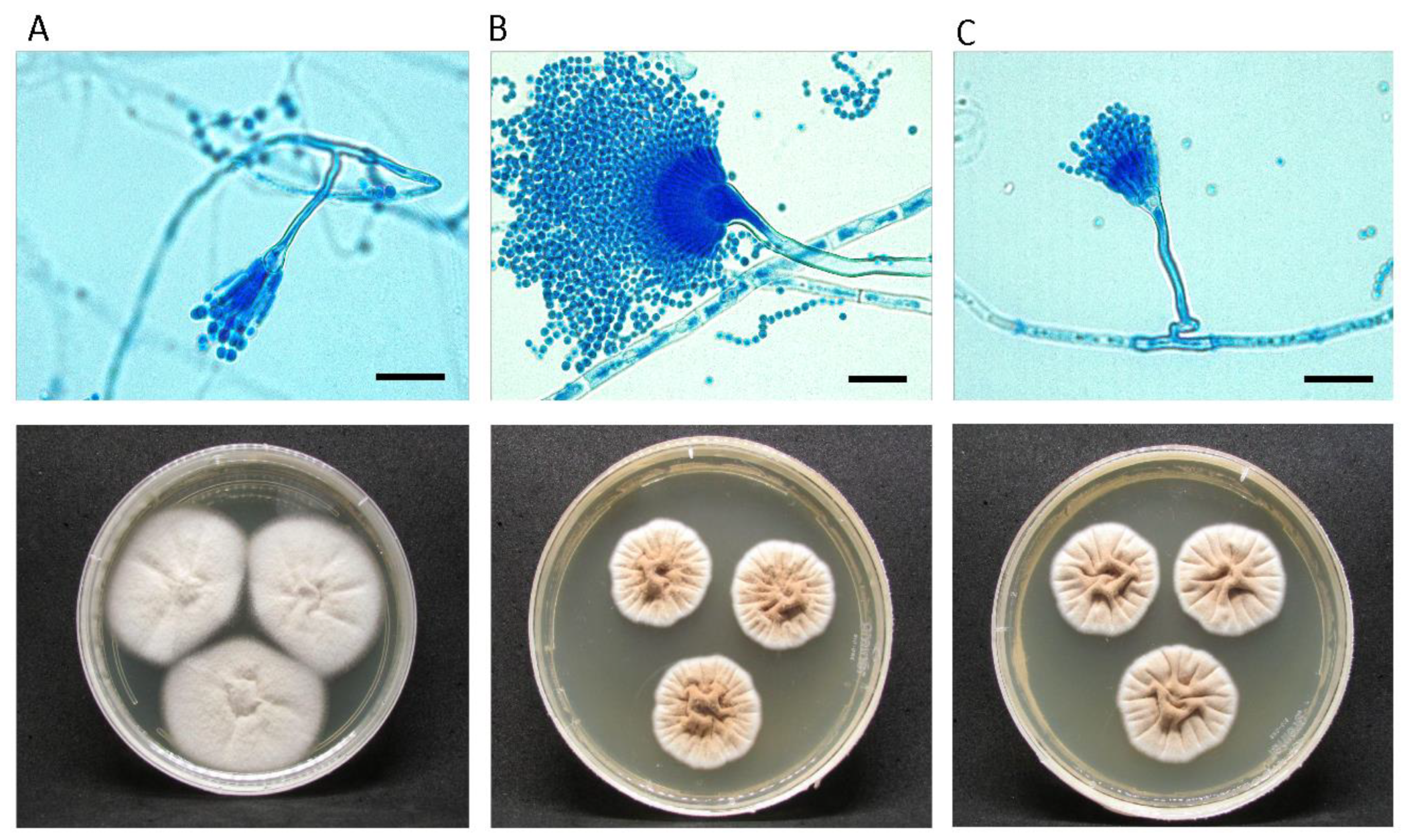
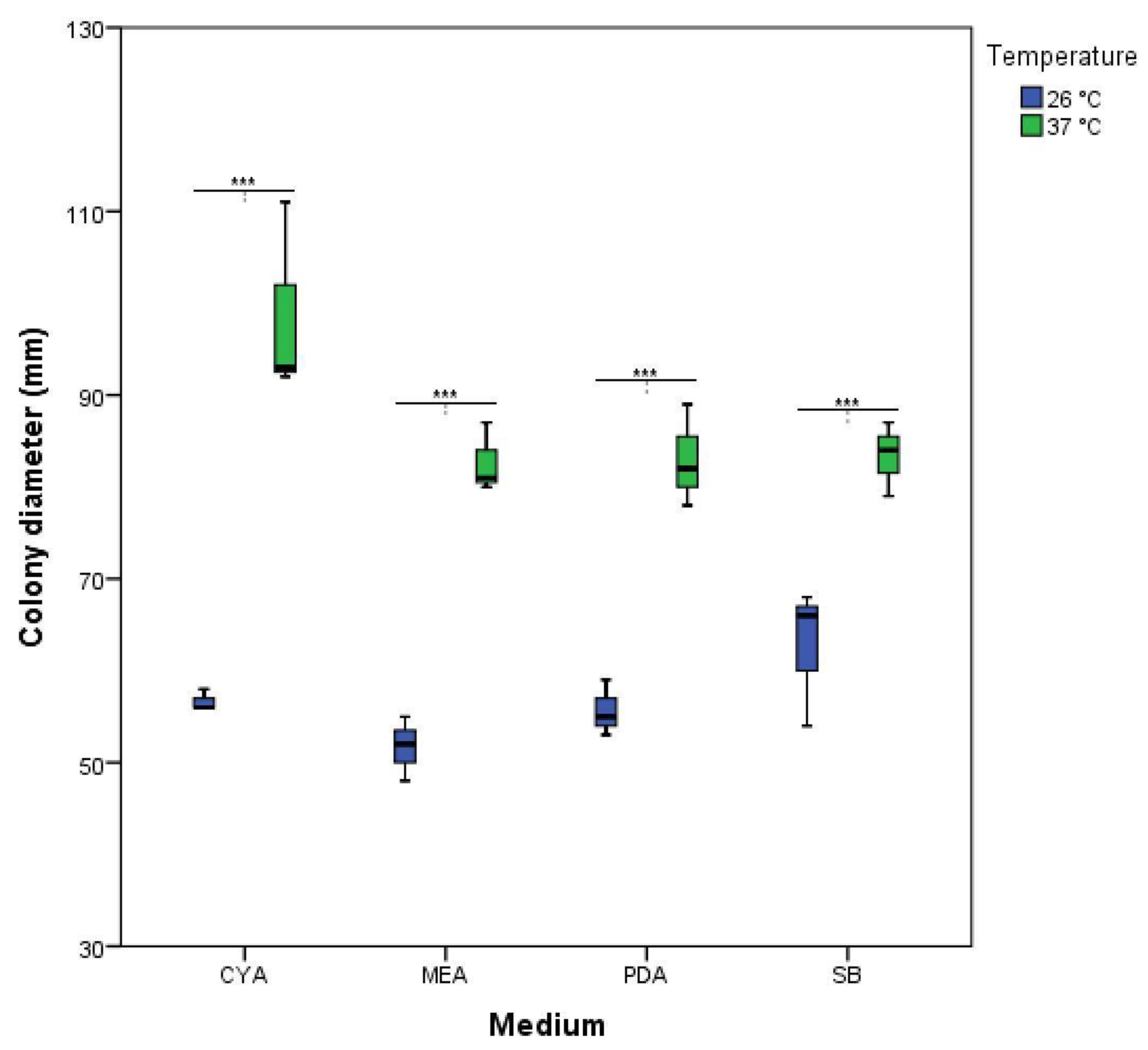
3.1. Morphological Analysis
3.2. Antifungal Susceptibility Testing
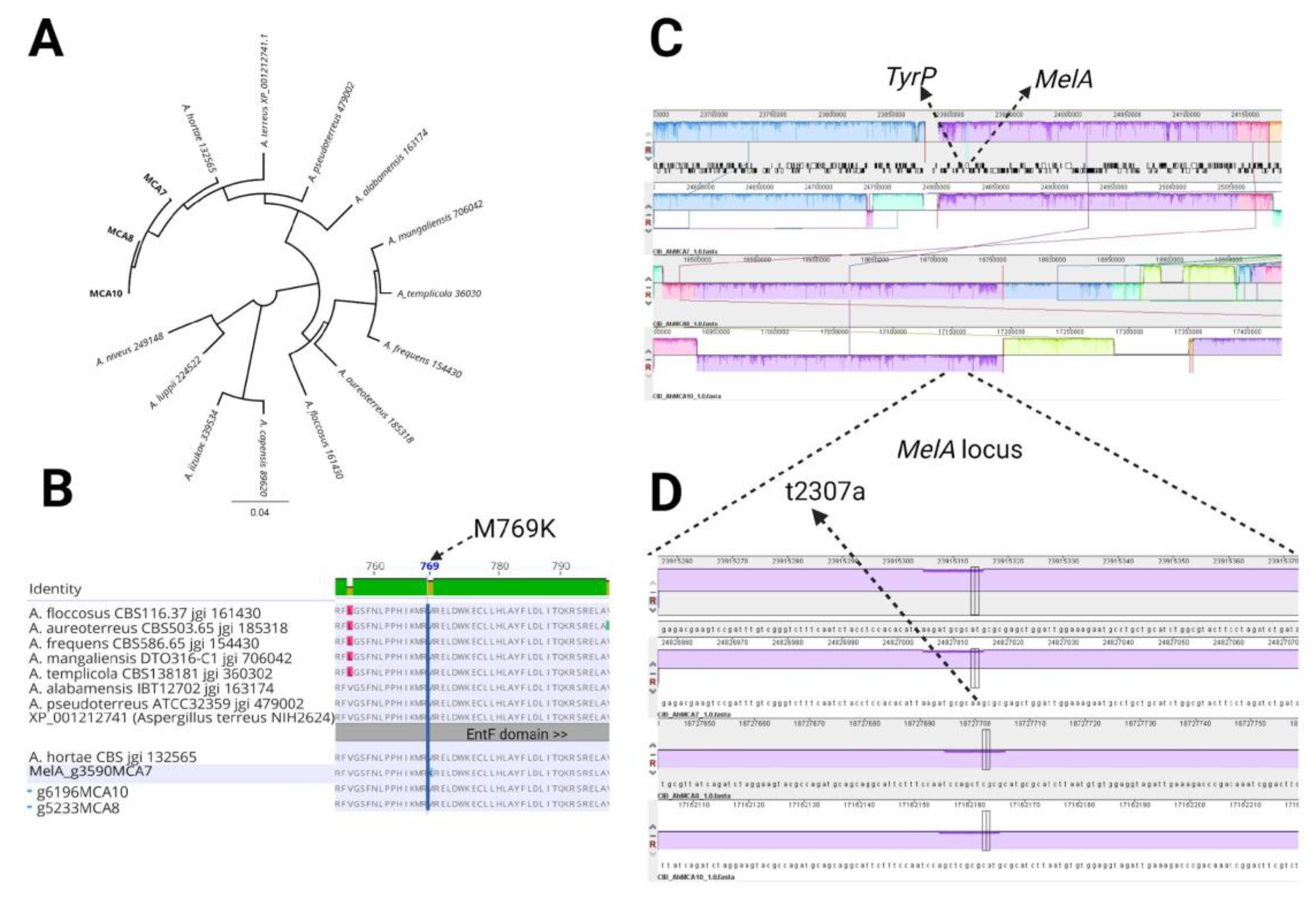
3.3. Genome Assembly and Analysis
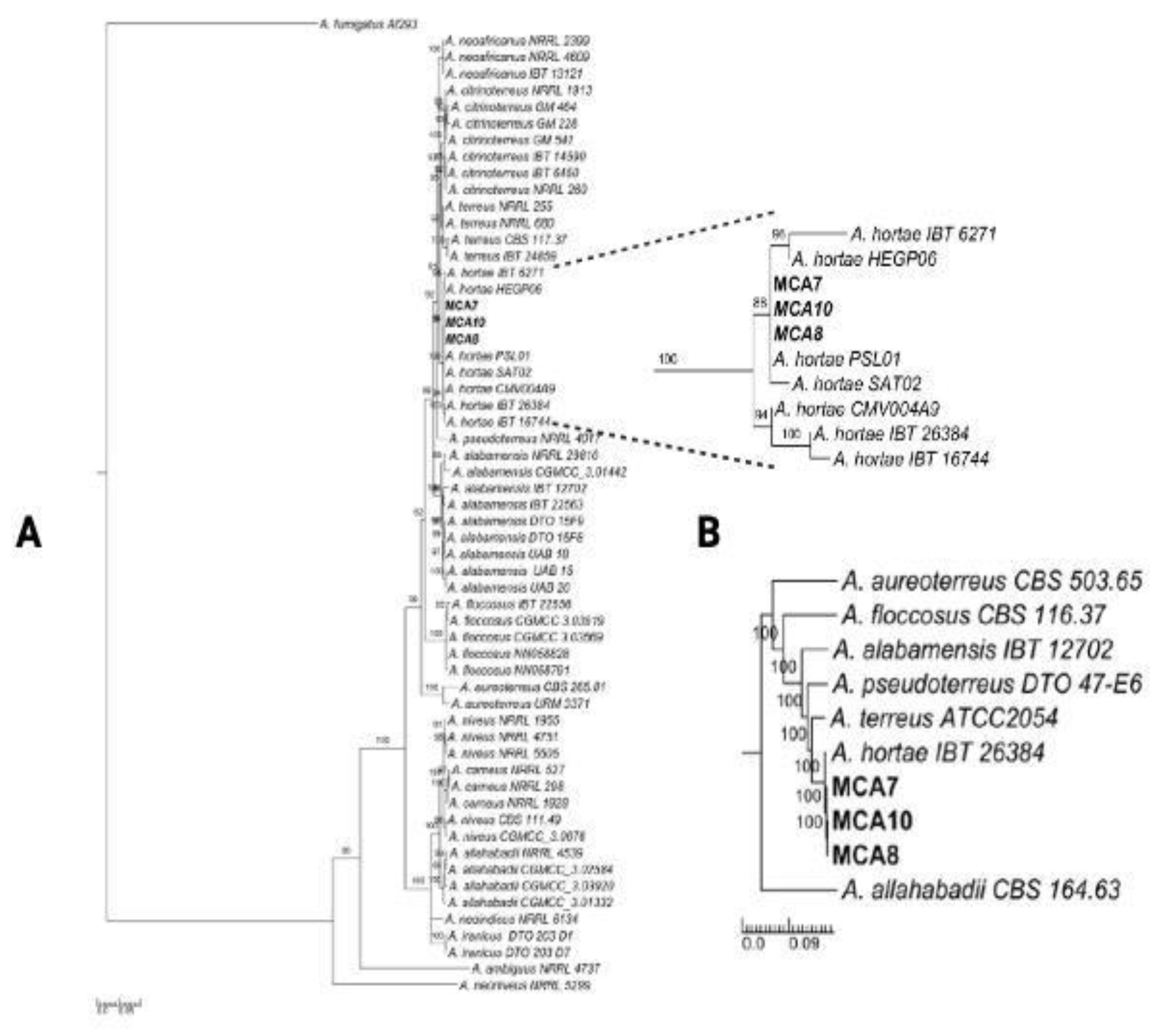
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samson, R.A.; Visagie, C.M.; Houbraken, J.; Hong, S.-B.; Hubka, V.; Klaassen, C.H.W.; Perrone, G.; Seifert, K.A.; Susca, A.; Tanney, J.B.; et al. Phylogeny, Identification and Nomenclature of the Genus Aspergillus. Stud. Mycol. 2014, 78, 141–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, L.A.R.; El-Refai, A.-M.H.; Hamdy, A.-H.A.; El-Minofi, H.A.; Abdel-Salam, I.S. Role of Some Fermentation Parameters on Cyclosporin A Production by a New Isolate of Aspergillus Terreus. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 49, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, A.W.; Chen, J.; Kuron, G.; Hunt, V.; Huff, J.; Hoffman, C.; Rothrock, J.; Lopez, M.; Joshua, H.; Harris, E.; et al. Mevinolin: A Highly Potent Competitive Inhibitor of Hydroxymethylglutaryl-Coenzyme A Reductase and a Cholesterol-Lowering Agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1980, 77, 3957–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risslegger, B.; Zoran, T.; Lackner, M.; Aigner, M.; Sánchez-Reus, F.; Rezusta, A.; Chowdhary, A.; Taj-Aldeen, S.J.; Arendrup, M.C.; Oliveri, S.; et al. A Prospective International Aspergillus Terreus Survey: An EFISG, ISHAM and ECMM Joint Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 776.e1–e776.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, R.A.; Peterson, S.W.; Frisvad, J.C.; Varga, J. New Species in Aspergillus Section Terrei. Stud. Mycol. 2011, 69, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbert, S.; Normand, A.C.; Ranque, S.; Costa, J.M.; Guitard, J.; Accoceberry, I.; Bonnal, C.; Fekkar, A.; Bourgeois, N.; Houzé, S.; et al. Species Identification and In Vitro Antifungal Susceptibility of Aspergillus Terreus Species Complex Clinical Isolates from a French Multicenter Study. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, M.; Normand, A.-C.; Ranque, S. Previously Unknown Species of Aspergillus. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoran, T.; Sartori, B.; Sappl, L.; Aigner, M.; Sánchez-Reus, F.; Rezusta, A.; Chowdhary, A.; Taj-Aldeen, S.J.; Arendrup, M.C.; Oliveri, S.; et al. Azole-Resistance in Aspergillus Terreus and Related Species: An Emerging Problem or a Rare Phenomenon? Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, D.Z.P.; Schwartz, I.S. Emerging Fungal Infections: New Patients, New Patterns, and New Pathogens. J Fungi (Basel) 2019, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, R.P.; Riley, R.; Wiebenga, A.; Aguilar-Osorio, G.; Amillis, S.; Uchima, C.A.; Anderluh, G.; Asadollahi, M.; Askin, M.; Barry, K.; et al. Comparative Genomics Reveals High Biological Diversity and Specific Adaptations in the Industrially and Medically Important Fungal Genus Aspergillus. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nargesi, S.; Valadan, R.; Abastabar, M.; Kaboli, S.; Thekkiniath, J.; Hedayati, M.T. A Whole Genome Sequencing-Based Approach to Track down Genomic Variants in Itraconazole-Resistant Species of Aspergillus from Iran. J Fungi (Basel) 2022, 8, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem-Bango, Z.; Price, T.K.; Chan, J.L.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Garner, O.B.; Yang, S. Fungal Whole-Genome Sequencing for Species Identification: From Test Development to Clinical Utilization. J Fungi (Basel) 2023, 9, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subcommittee on Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of the ESCMID European Committee for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing EUCAST Technical Note on the Method for the Determination of Broth Dilution Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations of Antifungal Agents for Conidia-Forming Moulds. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 982–984.
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 2001, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, S.; Lindenbaum, P.; Howard, B.; Ewels, P. FastQC A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/.
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolenko, S.I.; Korobeynikov, A.I.; Alekseyev, M.A. BayesHammer: Bayesian Clustering for Error Correction in Single-Cell Sequencing. BMC Genomics 2013, 14 Suppl 1, S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality Assessment Tool for Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanke, M.; Schöffmann, O.; Morgenstern, B.; Waack, S. Gene Prediction in Eukaryotes with a Generalized Hidden Markov Model That Uses Hints from External Sources. BMC Bioinformatics 2006, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emms, D.M.; Kelly, S. OrthoFinder: Phylogenetic Orthology Inference for Comparative Genomics. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenwyk, J.L.; Balamurugan, C.; Raja, H.A.; Gonçalves, C.; Li, N.; Martin, F.; Berman, J.; Oberlies, N.H.; Gibbons, J.G.; Goldman, G.H.; et al. Phylogenomics Reveals Extensive Misidentification of Fungal Strains from the Genus Aspergillus. bioRxiv, 2022; 2022.11.22.517304. [Google Scholar]
- Kathuria, S.; Sharma, C.; Singh, P.K.; Agarwal, P.; Agarwal, K.; Hagen, F.; Meis, J.F.; Chowdhary, A. Molecular Epidemiology and in-Vitro Antifungal Susceptibility of Aspergillus Terreus Species Complex Isolates in Delhi, India: Evidence of Genetic Diversity by Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism and Microsatellite Typing. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0118997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, G.; Hörtnagl, C.; Jukic, E.; Erbeznik, T.; Pümpel, T.; Dietrich, H.; Nagl, M.; Speth, C.; Rambach, G.; Lass-Flörl, C. New Insight into Amphotericin B Resistance in Aspergillus Terreus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1583–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashu, E.E.; Korfanty, G.A.; Samarasinghe, H.; Pum, N.; You, M.; Yamamura, D.; Xu, J. Widespread Amphotericin B-Resistant Strains of Aspergillus fumigatus in Hamilton, Canada. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1549–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Linden, J.W.M.; Warris, A.; Verweij, P.E. Aspergillus Species Intrinsically Resistant to Antifungal Agents. Med. Mycol. 2011, 49 Suppl 1, S82–S89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, R.; Sugita, T.; Jacobson, E.S.; Shinoda, T. Effects of Melanin upon Susceptibility of Cryptococcus to Antifungals. Microbiol. Immunol. 2003, 47, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolo, W.F., Jr.; Dadachova, E.; Mandal, P.; Casadevall, A.; Szaniszlo, P.J.; Nosanchuk, J.D. Effects of Disrupting the Polyketide Synthase Gene WdPKS1 in Wangiella [Exophiala] Dermatitidis on Melanin Production and Resistance to Killing by Antifungal Compounds, Enzymatic Degradation, and Extremes in Temperature. BMC Microbiol. 2006, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geib, E.; Gressler, M.; Viediernikova, I.; Hillmann, F.; Jacobsen, I.D.; Nietzsche, S.; Hertweck, C.; Brock, M. A Non-Canonical Melanin Biosynthesis Pathway Protects Aspergillus terreus Conidia from Environmental Stress. Cell Chem Biol 2016, 23, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, J.F.; Welsh, R.M.; Shea, T.; Batra, D.; Gade, L.; Howard, D.; Rowe, L.A.; Meis, J.F.; Litvintseva, A.P.; Cuomo, C.A. Clade-Specific Chromosomal Rearrangements and Loss of Subtelomeric Adhesins in Candida auris. Genetics 2021, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Liu, S.; Cao, S.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H. Long-Read Sequencing Settings for Efficient Structural Variation Detection Based on Comprehensive Evaluation. BMC Bioinformatics 2021, 22, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Cadavid, C.; Rudd, S.; Zaki, S.R.; Patel, M.; Moser, S.A.; Brandt, M.E.; Gómez, B.L. Improving Molecular Detection of Fungal DNA in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissues: Comparison of Five Tissue DNA Extraction Methods Using Panfungal PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2147–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valero, C.; de la Cruz-Villar, L.; Zaragoza, Ó.; Buitrago, M.J. New Panfungal Real-Time PCR Assay for Diagnosis of Invasive Fungal Infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 2910–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balajee, S.A.; Houbraken, J.; Verweij, P.E.; Hong, S.-B.; Yaghuchi, T.; Varga, J.; Samson, R.A. Aspergillus Species Identification in the Clinical Setting. Stud. Mycol. 2007, 59, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCusker, J.H.; Clemons, K.V.; Stevens, D.A.; Davis, R.W. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Virulence Phenotype as Determined with CD-1 Mice Is Associated with the Ability to Grow at 42 Degrees C and Form Pseudohyphae. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 5447–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemons, K.V.; McCusker, J.H.; Davis, R.W.; Stevens, D.A. Comparative Pathogenesis of Clinical and Nonclinical Isolates of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Infect. Dis. 1994, 169, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhabhra, R.; Askew, D.S. Thermotolerance and Virulence of Aspergillus fumigatus: Role of the Fungal Nucleolus. Med. Mycol. 2005, 43 (Suppl. 1), S87–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansey, M.R.; Brock, T.D. The Upper Temperature Limit for Eukaryotic Organisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1972, 69, 2426–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, M.; Obermair, J.; Naschberger, V.; Raschbichler, L.-M.; Kandelbauer, C.; Pallua, J.; Metzlaff, J.; Furxer, S.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Binder, U. Cryptic Species of Aspergillus Section Terrei Display Essential Physiological Features to Cause Infection and Are Similar in Their Virulence Potential in Galleria Mellonella. Virulence 2019, 10, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| VRC | ITC | POS | AmB | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Isolate | MIC | INT | MIC | INT | MIC | INT | MIC | INT |
| A. hortae | MCA-7 | 0.5 | S | 1 | S | 0.25 | S | 2 | R |
| A. hortae | MCA-8 | 0.5 | S | 1 | S | 0.25 | S | 4 | R |
| A. hortae | MCA-10 | 1 | S | 1 | S | 0.25 | S | 4 | R |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





