Submitted:
18 March 2024
Posted:
19 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Strains
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Molecular Identification through Sequencing
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Primer Design
2.6. In Silico PCR
2.7. PCR Optmization
2.8. Assessment of Nonspecific Amplification
2.9. Evaluation of the Minimum Amplification Threshold
3. Results
3.1. Isolates Used and Phylogenetic Analysis
3.2. Primers Designed and In Silico Specificity
3.3. Testing of the Primers through In Vitro PCR
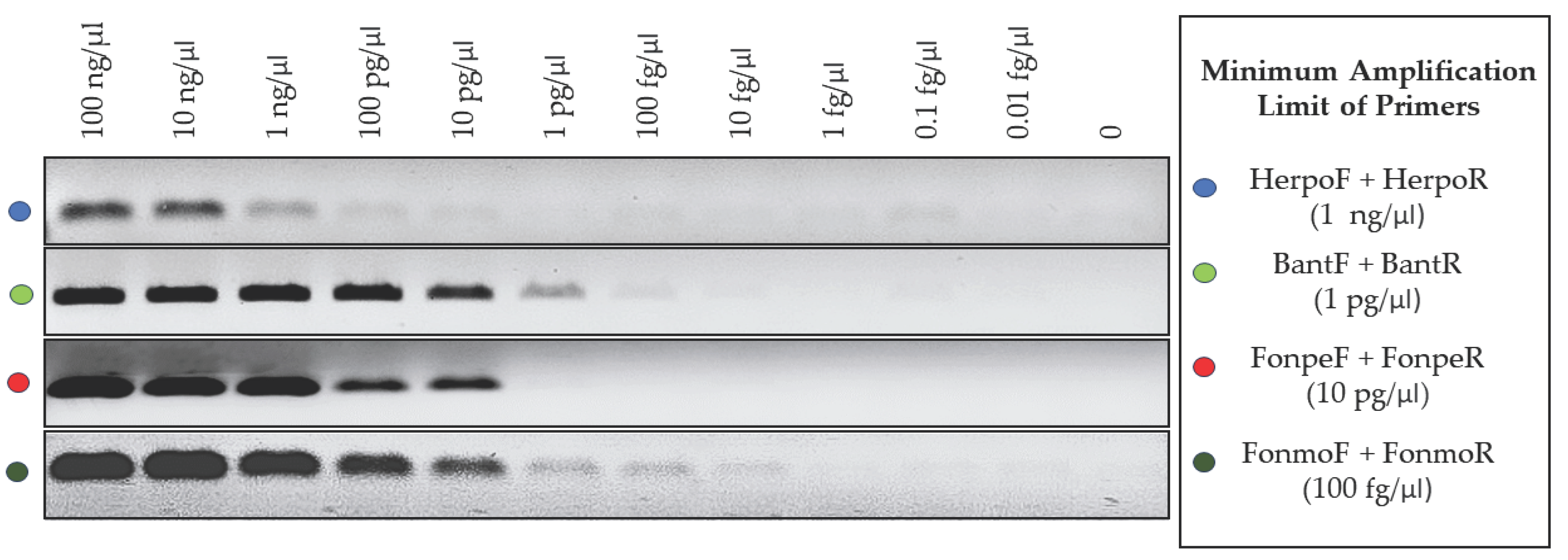
3.4. Detection Limit of the Primers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, Q.; Chomnunti, P.; Lumyong, S.; Liu, J. K.; Hyde, K. D. Phylogenetic Relationships and Morphological Reappraisal of Chaetothyriales. Mycosphere 2021, 12 (1), 1157–1261. [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Deng, S.; Prenafeta-Boldủ, F. X.; Mayer, V. E.; Muggia, L.; Cometto, A.; Vicente, V. A.; da Silva, N. M.; Grisolia, M. E.; Song, Y.; Ahmed, S. A.; Niu, X.; de Souza Lima, B. J. F.; Feng, P.; Vitale, R. G.; Teixeira, M.; Sudhadham, M.; de Azevedo, C. P. e. S.; Bocca, A.; Haase, G.; Selbmann, L.; Shi, D.; Kang, Y.; de Hoog, S. The Origin of Human Pathogenicity and Biological Interactions in Chaetothyriales. Fungal Divers 2023. [CrossRef]
- Seyedmousavi, S.; Netea, M. G.; Mouton, J. W.; Melchers, W. J. G.; Verweij, P. E.; de Hoog, G. S. Black Yeasts and Their Filamentous Relatives: Principles of Pathogenesis and Host Defense. Clin Microbiol Rev 2014, 27 (3), 527–542. [CrossRef]
- Abdolrasouli, A.; Gibani, M. M.; de Groot, T.; Borman, A. M.; Hoffman, P.; Azadian, B. S.; Mughal, N.; Moore, L. S. P.; Johnson, E. M.; Meis, J. F. A Pseudo-Outbreak of Rhinocladiella Similis in a Bronchoscopy Unit of a Tertiary Care Teaching Hospital in London, United Kingdom. Mycoses 2021, 64 (4), 394–404. [CrossRef]
- Arcobello, J. T.; Revankar, S. G. Phaeohyphomycosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2020, 41 (1), 131–140. [CrossRef]
- Santos, D. W. C. L.; de Azevedo, C. de M. P. e. S.; Vicente, V. A.; Queiroz-Telles, F.; Rodrigues, A. M.; de Hoog, G. S.; Denning, D. W.; Colombo, A. L. The Global Burden of Chromoblastomycosis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2021, 15 (8). [CrossRef]
- WHO. Ending the Neglect to Attain the Sustainable Development Goals: A Strategic Framework for Integrated Control and Management of Skin-Related Neglected Tropical Diseases; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Queiroz-Telles, F.; de Hoog, S.; Santos, D. W. C. L.; Salgado, C. G.; Vicente, V. A.; Bonifaz, A.; Roilides, E.; Xi, L.; Azevedo, C. de M. P. E. S.; Da Silva, M. B.; Pana, Z. D.; Colombo, A. L.; Walsh, T. J. Chromoblastomycosis. Clin Microbiol Rev 2017, 30 (1), 233–276. [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zheng, H. L.; Mei, H.; Lv, G. X.; Liu, W. Da; Li, X. F. Phaeohyphomycosis in China. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. Frontiers Media S.A. June 13, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, V.; Hallur, V.; Velvizhi, S.; Rajendran, T. Cerebral Phaeohyphomycosis Due to Cladophialophora Bantiana: Case Report and Systematic Review of Cases. Infection 2023. [CrossRef]
- Taneja, J.; Passi, S.; Ranjan, R.; Abbas, S. Z.; Ramesh, V. Sporotrichoid Lesions Caused by Rhinocladiella Similis. Journal of Medical Mycology. Elsevier Masson s.r.l. March 1, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Carolina Rojas, O.; León-Cachón, R. B. R.; Pérez-Maya, A. A.; Aguirre-Garza, M.; Moreno-Treviño, M. G.; González, G. M. Phenotypic and Molecular Identification of Fonsecaea Pedrosoi Strains Isolated from Chromoblastomycosis Patients in Mexico and Venezuela. Mycoses 2015, 58 (5), 267–272. [CrossRef]
- Coelho, R. A.; Brito-Santos, F.; Figueiredo-Carvalho, M. H. G.; Silva, J. V. dos S.; Gutierrez-Galhardo, M. C.; do Valle, A. C. F.; Zancopé-Oliveira, R. M.; Trilles, L.; Meyer, W.; Freitas, D. F. S.; Almeida-Paes, R. Molecular Identification and Antifungal Susceptibility Profiles of Clinical Strains of Fonsecaea Spp. Isolated from Patients with Chromoblastomycosis in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2018, 12 (7). [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhi, H.; Shen, H.; Lv, W.; Sang, B.; Li, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xia, X. Chromoblastomycosis: A Case Series from Eastern China. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2022, 16 (9). [CrossRef]
- Gomes, R. R.; Vicente, V. A.; Azevedo, C. M. P. S. de; Salgado, C. G.; da Silva, M. B.; Queiroz-Telles, F.; Marques, S. G.; Santos, D. W. C. L.; de Andrade, T. S.; Takagi, E. H.; Cruz, K. S.; Fornari, G.; Hahn, R. C.; Scroferneker, M. L.; Caligine, R. B.; Ramirez-Castrillon, M.; de Araújo, D. P.; Heidrich, D.; Colombo, A. L.; de Hoog, G. S. Molecular Epidemiology of Agents of Human Chromoblastomycosis in Brazil with the Description of Two Novel Species. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2016, 10 (11). [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Najafzadeh, M. J.; Gerrits van den Ende, A. H. G.; Vicente, V. A.; Feng, P.; Xi, L.; de Hoog, G. S. Molecular Characterization of Pathogenic Members of the Genus Fonsecaea Using Multilocus Analysis. PLoS One 2012, 7 (8). [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K. D. MAFFT Online Service: Multiple Sequence Alignment, Interactive Sequence Choice and Visualization. Brief Bioinform 2018, 20 (4), 1160–1166. [CrossRef]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L. T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B. Q. W-IQ-TREE: A Fast Online Phylogenetic Tool for Maximum Likelihood Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2016, 44 (W1), W232–W235. [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (ITOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49 (W1), W293–W296. [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol Biol Evol 2021, 38 (7), 3022–3027. [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Coulouris, G.; Zaretskaya, I.; Cutcutache, I.; Rozen, S.; Madden, T. L. Primer-BLAST: A Tool to Design Target-Specific Primers for Polymerase Chain Reaction; 2012. http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2105/13/134.
- Rodrigues, A. M.; de Hoog, G. S.; de Camargo, Z. P. Molecular Diagnosis of Pathogenic Sporothrix Species. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2015, 9 (12). [CrossRef]
- Castillo Bejarano, J. I.; de los Santos, A. M.; Saldaña, D. C.; Zambrano Lucio, M.; Pérez Cavazos, S.; Espinosa Villaseñor, F.; de la O Cavazos, M. E.; Vaquera Aparicio, D. N. Pediatric Phaeohyphomycosis: A 44-Year Systematic Review of Reported Cases. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc 2022. [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Singh, G.; Ghosh, A.; Verma, K. K.; Pandey, M.; Xess, I. Chromoblastomycosis in India: Review of 169 Cases. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. Public Library of Science August 1, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Revankar, S. G.; Sutton, D. A. Melanized Fungi in Human Disease. Clinical Microbiology Reviews. October 2010, pp 884–928. [CrossRef]
- Passero, L. F. D.; Cavallone, I. N.; Belda, W. Reviewing the Etiologic Agents, Microbe-Host Relationship, Immune Response, Diagnosis, and Treatment in Chromoblastomycosis. Journal of Immunology Research. Hindawi Limited 2021. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, E.; Bertolotti, A.; Barreau, A.; Klisnick, J.; Tournebize, P.; Borgherini, G.; Zemali, N.; Jaubert, J.; Jouvion, G.; Bretagne, S.; Picot, S. From Phaeohyphomycosis to Disseminated Chromoblastomycosis: A Retrospective Study of Infections Caused by Dematiaceous Fungi. Med Mal Infect 2018, 48 (4), 278–285. [CrossRef]
- de Brito, A. C.; Bittencourt, M. de J. S. Chromoblastomycosis: An Etiological, Epidemiological, Clinical, Diagnostic, and Treatment Update. An Bras Dermatol 2018, 93 (4), 495–506. [CrossRef]
- Sousa, G. S. M.; De Oliveira, R. S.; De Souza, A. B.; Monteiro, R. C.; Santo, E. P. T. E.; Franco Filho, L. C.; Da Silva, S. H. M. Identification of Chromoblastomycosis and Phaeohyphomycosis Agents through ITS-RFLP. Journal of Fungi 2024, 10 (2). [CrossRef]
- De Hoog, G.S.; Guarro, J.; Gené, J.; Figueras, M.J. Atlas of Clinical Fungi, 2nd ed.; Amer Society for Microbiology: Utrech, The Netherlands; Universitat Rovira i Virgili Reus: Reus, Spain, 2000; pp. 560–680.
- Wang, Y. C.; Wang, S. W.; Cia, C. T.; Chen, P. L.; Shih, H. I.; Choi, P. C.; Wu, C. J.; Chan, S. H. Pneumonia and Brain Abscess Likely Due to Cladophialophora Bantiana in a Patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Taiwan. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection. Elsevier Ltd February 1, 2024, pp 204–206. [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Xu, J.; Su, Q.; Chen, Y. Exophiala Dermatitis and Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. QJM 2019, 112 (11), 869–871. [CrossRef]
- Heidrich, D.; Pagani, D. M.; Koehler, A.; de Oliveira Alves, K.; Scrofernekera, M. L. Effect of Melanin Biosynthesis Inhibition on the Antifungal Susceptibility of Chromoblastomycosis Agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2021, 65 (8). [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, J.; Li, M.; Cai, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Xie, Z.; Zeng, W.; Xi, L. Molecular Characteristics of Regional Chromoblastomycosis in Guangdong, China: Epidemiological, Clinical, Antifungal Susceptibility, and Serum Cytokine Profiles of 45 Cases. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2022, 12. [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Jia, G.; Tan, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, L. Analysis of the Synergistic Antifungal Activity of Everolimus and Antifungal Drugs against Dematiaceous Fungi. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2023, 13. [CrossRef]
- Maubon, D.; Garnaud, C.; Ramarozatovo, L. S.; Fahafahantsoa, R. R.; Cornet, M.; Rasamoelina, T. Molecular Diagnosis of Two Major Implantation Mycoses: Chromoblastomycosis and Sporotrichosis. Journal of Fungi. MDPI April 1, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Xu, J. Fungal DNA Barcoding1. Genome. Canadian Science Publishing 2016, pp 913–932. [CrossRef]
- Fajarningsih, N. D. Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) as Dna Barcoding to Identify Fungal Species: A Review. Squalen Bulletin of Marine and Fisheries Postharvest and Biotechnology 2016, 11 (2), 37. [CrossRef]
- Assunção, C. B.; de Aguiar, E. L.; Al-Hatmi, A. M. S.; Silva Vieira, V. C.; Machado, A. S.; Junta, C.; de Hoog, S.; Caligiorne, R. B. New Molecular Marker for Phylogenetic Reconstruction of Black Yeast-like Fungi (Chaetothyriales) with Hypothetical EIF2AK2 Kinase Gene. Fungal Biol 2020, 124 (12), 1032–1038. [CrossRef]
- Firacative, C.; Meyer, W.; Castañeda, E. Cryptococcus Neoformans and Cryptococcus Gattii Species Complexes in Latin America: A Map of Molecular Types, Genotypic Diversity, and Antifungal Susceptibility as Reported by the Latin American Cryptococcal Study Group. Journal of Fungi 2021, 7 (4). [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M. M.; Moreno, L. F.; Stielow, B. J.; Muszewska, A.; Hainaut, M.; Gonzaga, L.; Abouelleil, A.; Patané, J. S. L.; Priest, M.; Souza, R.; Young, S.; Ferreira, K. S.; Zeng, Q.; da Cunha, M. M. L.; Gladki, A.; Barker, B.; Vicente, V. A.; de Souza, E. M.; Almeida, S.; Henrissat, B.; Vasconcelos, A. T. R.; Deng, S.; Voglmayr, H.; Moussa, T. A. A.; Gorbushina, A.; Felipe, M. S. S.; Cuomo, C. A.; de Hoog, G. S. Exploring the Genomic Diversity of Black Yeasts and Relatives (Chaetothyriales, Ascomycota). Stud Mycol 2017, 86, 1–28. [CrossRef]
- Kilbourn, K. J.; Green, J.; Zacharewski, N.; Aferzon, J.; Lawlor, M.; Jaffa, M. Intracranial Fungal Cladophialophora Bantiana Infection in a Nonimmunocompromised Patient: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Surgical Neurology International. Scientific Scholar 2022. [CrossRef]
- Santos, D. W. C. L.; Vicente, V. A.; Weiss, V. A.; Sybren de Hoog, G.; Gomes, R. R.; Batista, E. M. M.; Marques, S. G.; de Queiroz-Telles, F.; Colombo, A. L.; de Azevedo, C. de M. P. e. S. Chromoblastomycosis in an Endemic Area of Brazil: A Clinical-Epidemiological Analysis and a Worldwide Haplotype Network. Journal of Fungi 2020, 6 (4), 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Guevara, A.; Siqueira, N. P.; Nery, A. F.; Cavalcante, L. R. D. S.; Hagen, F.; Hahn, R. C. Chromoblastomycosis in Latin America and the Caribbean: Epidemiology over the Past 50 Years. Medical Mycology. Oxford University Press December 1, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Borman, A. M.; Fraser, M.; Patterson, Z.; Linton, C. J.; Palmer, M.; Johnson, E. M. Fungal Infections of Implantation: More Than Five Years of Cases of Subcutaneous Fungal Infections Seen at the UK Mycology Reference Laboratory. Journal of Fungi 2022, 8 (4). [CrossRef]
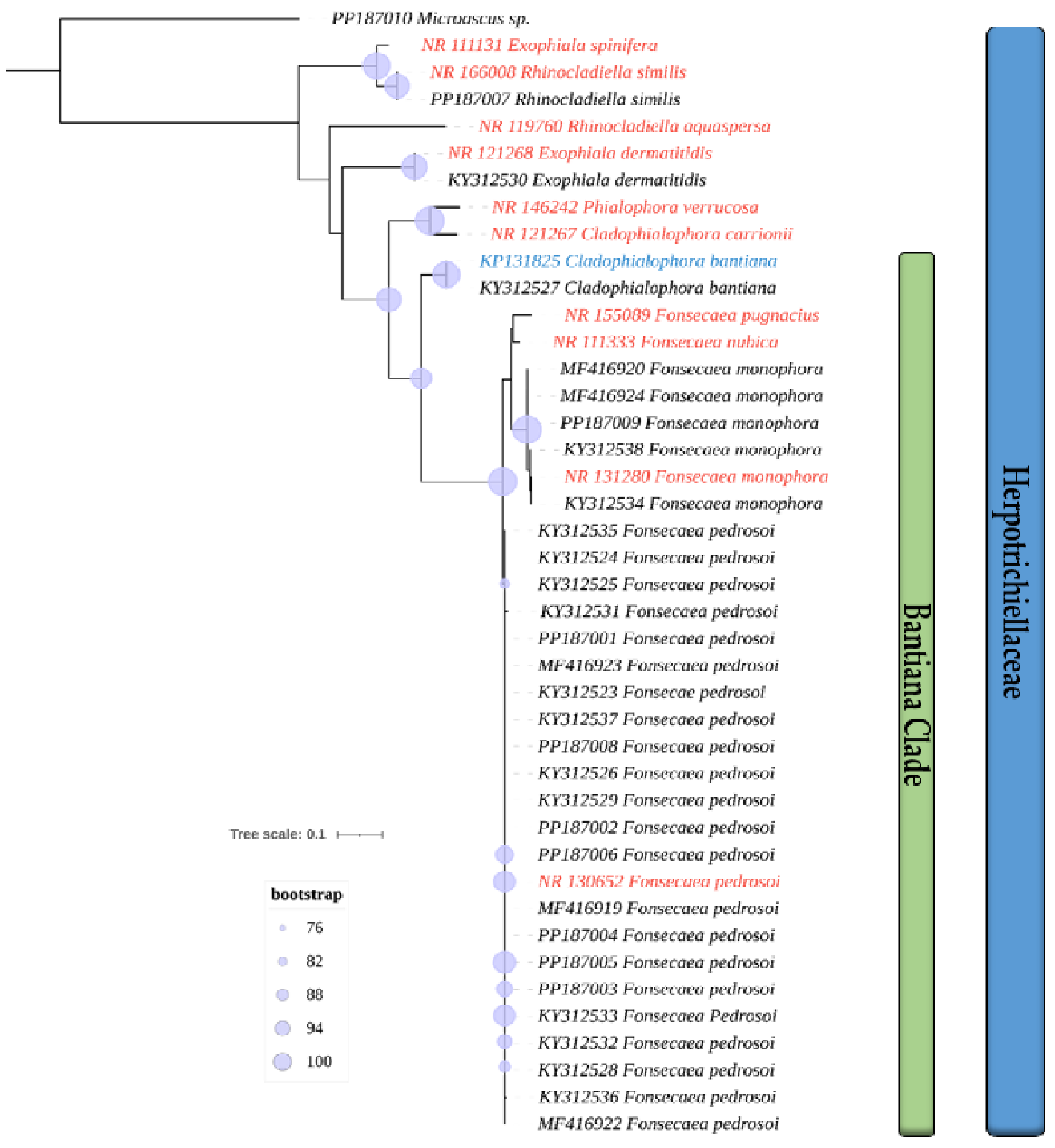
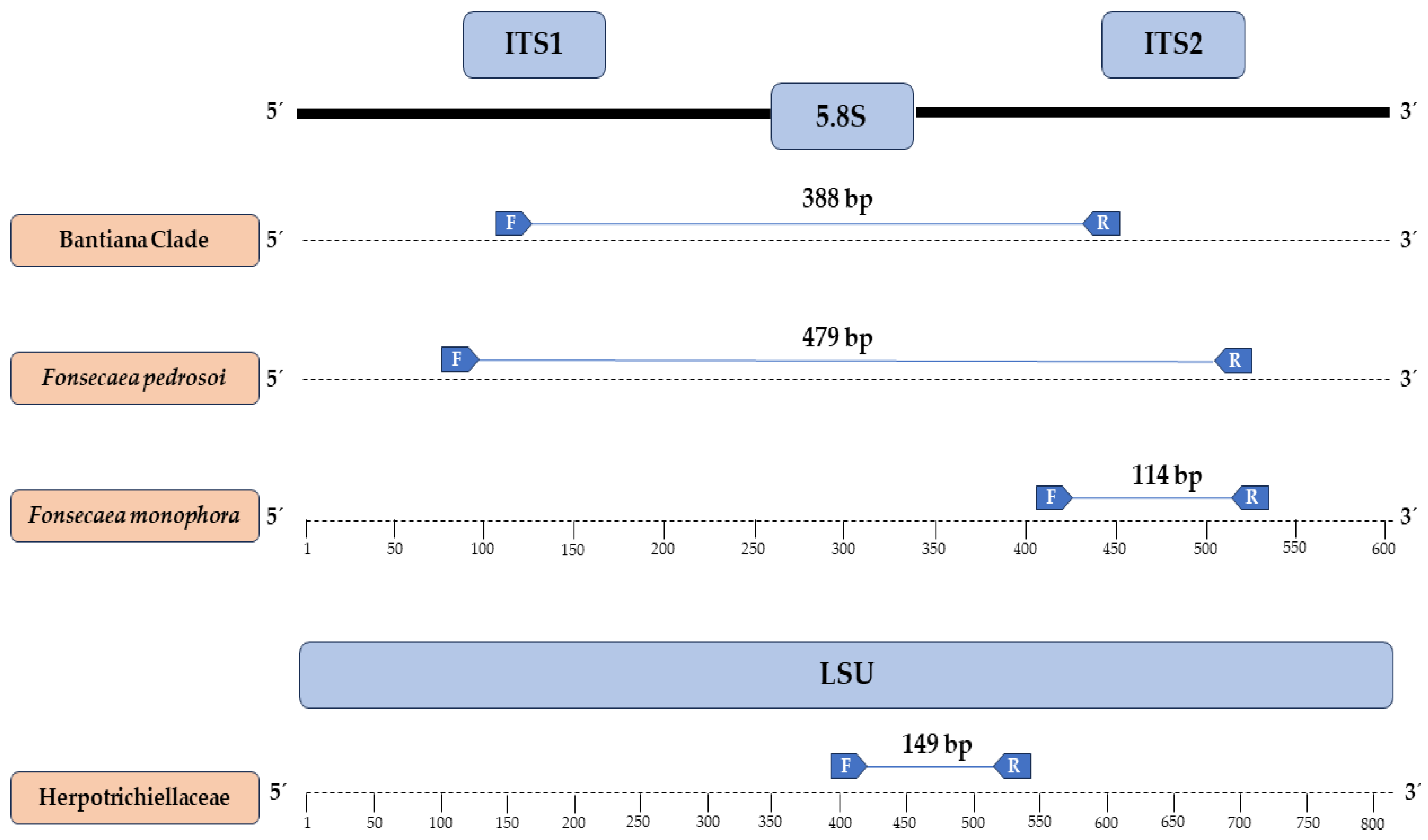
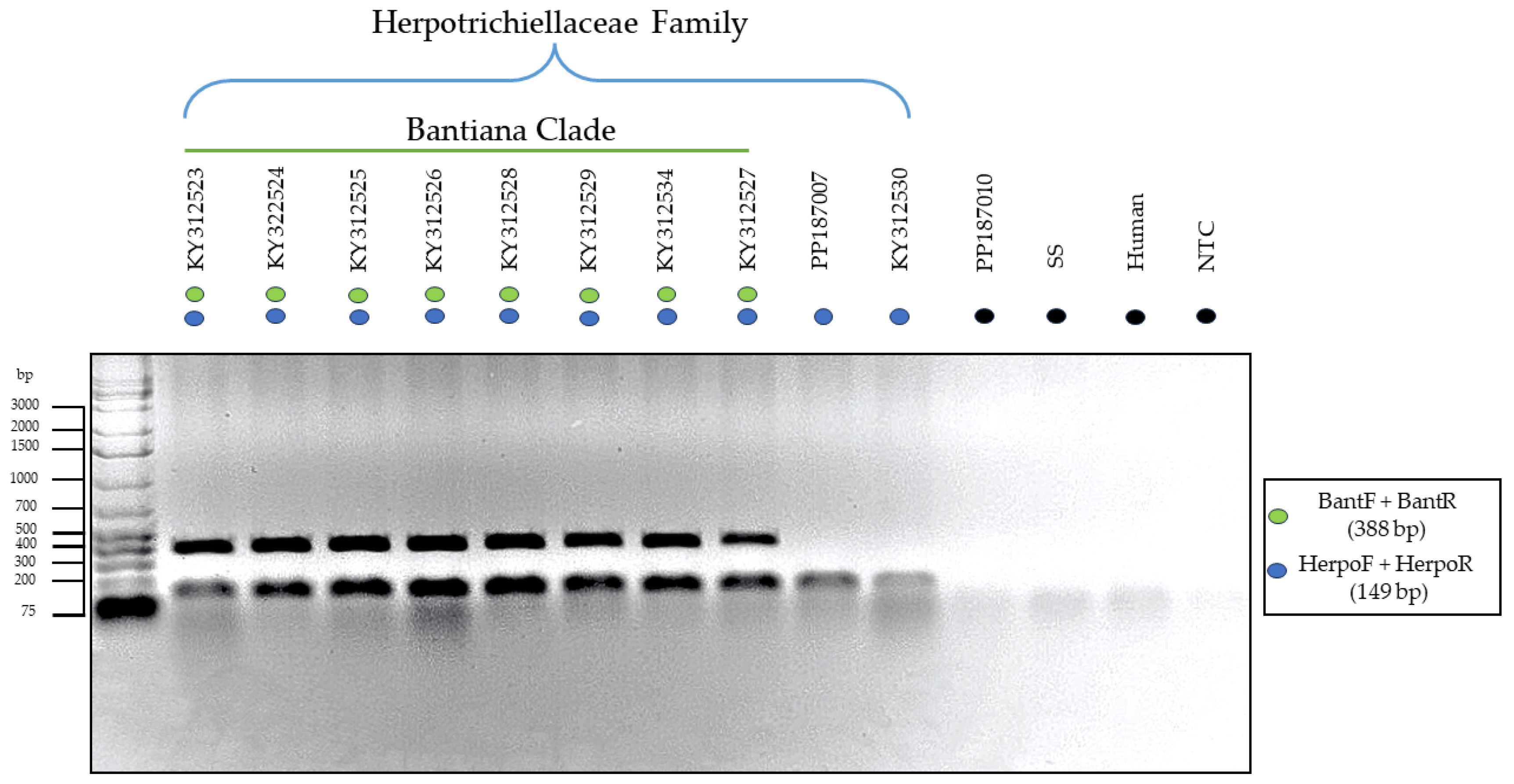
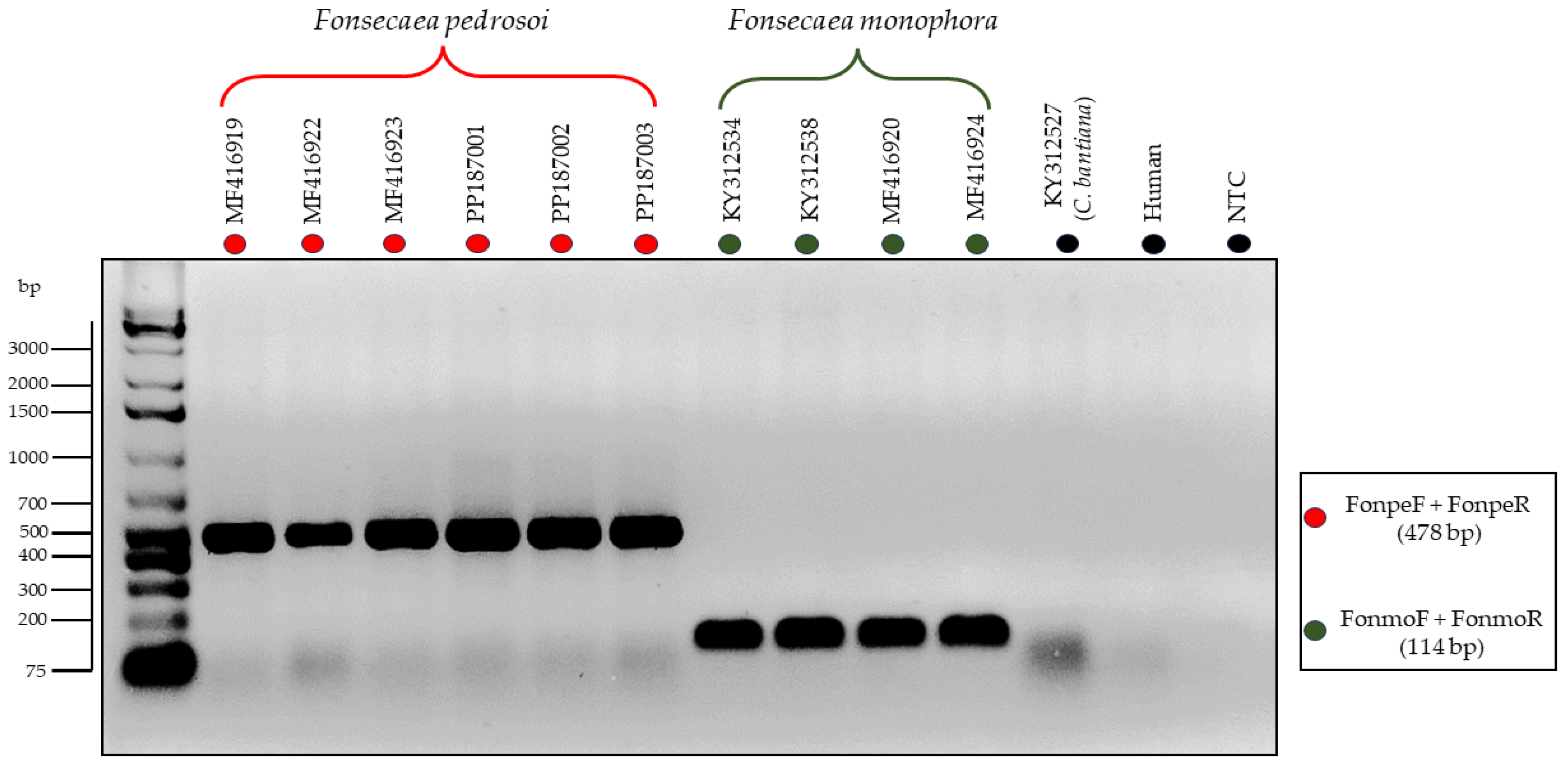
| Isolate | Genbank | Species | Anatomical Site | Host | Geographic Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IEC-CBM02 | KY312523 | F. pedrosoi | Thigh | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM03 | KY312524 | F. pedrosoi | Foot | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM04 | KY312525 | F. pedrosoi | Leg | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM05 | KY312526 | F. pedrosoi | Leg | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM06 | KY312527 | C. bantiana | CNS † | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM07 | KY312528 | F. pedrosoi | Hand | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM08 | KY312529 | F. pedrosoi | Leg | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM09 | KY312530 | E. dermatitidis | * | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM10 | KY312531 | F. pedrosoi | Arm | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM11 | KY312532 | F. pedrosoi | Leg | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM12 | KY312533 | F. pedrosoi | Foot | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM13 | KY312534 | F. monophora | Leg | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM14 | KY312535 | F. pedrosoi | * | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM15 | KY312536 | F. pedrosoi | * | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM16 | KY312537 | F. pedrosoi | Thigh | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM17 | KY312538 | F. monophora | Leg | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM18 | MF416919 | F. pedrosoi | Thigh | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM19 | MF416920 | F. monophora | Forearm | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM21 | MF416922 | F. pedrosoi | Fist | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM22 | MF416923 | F. pedrosoi | Ankle | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM23 | MF416924 | F. monophora | * | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM5804 | PP187001 | F. pedrosoi | Forearm | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM5805 | PP187002 | F. pedrosoi | Hand | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM6064 | PP187003 | F. pedrosoi | Leg | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM6504 | PP187004 | F.pedrosoi | Arm | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM6512 | PP187005 | F. pedrosoi | Foot | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM6568 | PP187006 | F. pedrosoi | Arm | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM6577 | PP187007 | R. similis | Foot | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM6610 | PP187008 | F. pedrosoi | Leg | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM6938 | PP187009 | F. monophora | * | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| IEC-CBM6563 | PP187010 | Microascus sp. | Foot | Human | Pará/Brazil |
| Target Species | Primer | Primer Sequence (5´-3´) |
|---|---|---|
| Herpotrichiellaceae Family | HerpoF HerpoR |
CTT GCA ACC AGA CTT GAG CGC G CGC ATG ACA CCC TGG TCT ATA AGT C |
| Bantiana clade | BantF BantR |
GGC AGG CCC GTC TTA ATC TGA CC GCC GTC ATT GTC TTT AGG AGG GGT G |
| Fonsecaea pedrosoi | FonpeF FonpeR |
CCA ACC CTT TGC TTA CTA GAC CTC CCC TTC ATC CGA TAC GTG CTC AA |
| Fonsecaea monophora | FonmoF FonmoR |
GGA CGG CTT GGT GGA GTA AG GCC CTT CAT CCG ATA CGT GCT CAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





