Submitted:
26 August 2024
Posted:
27 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
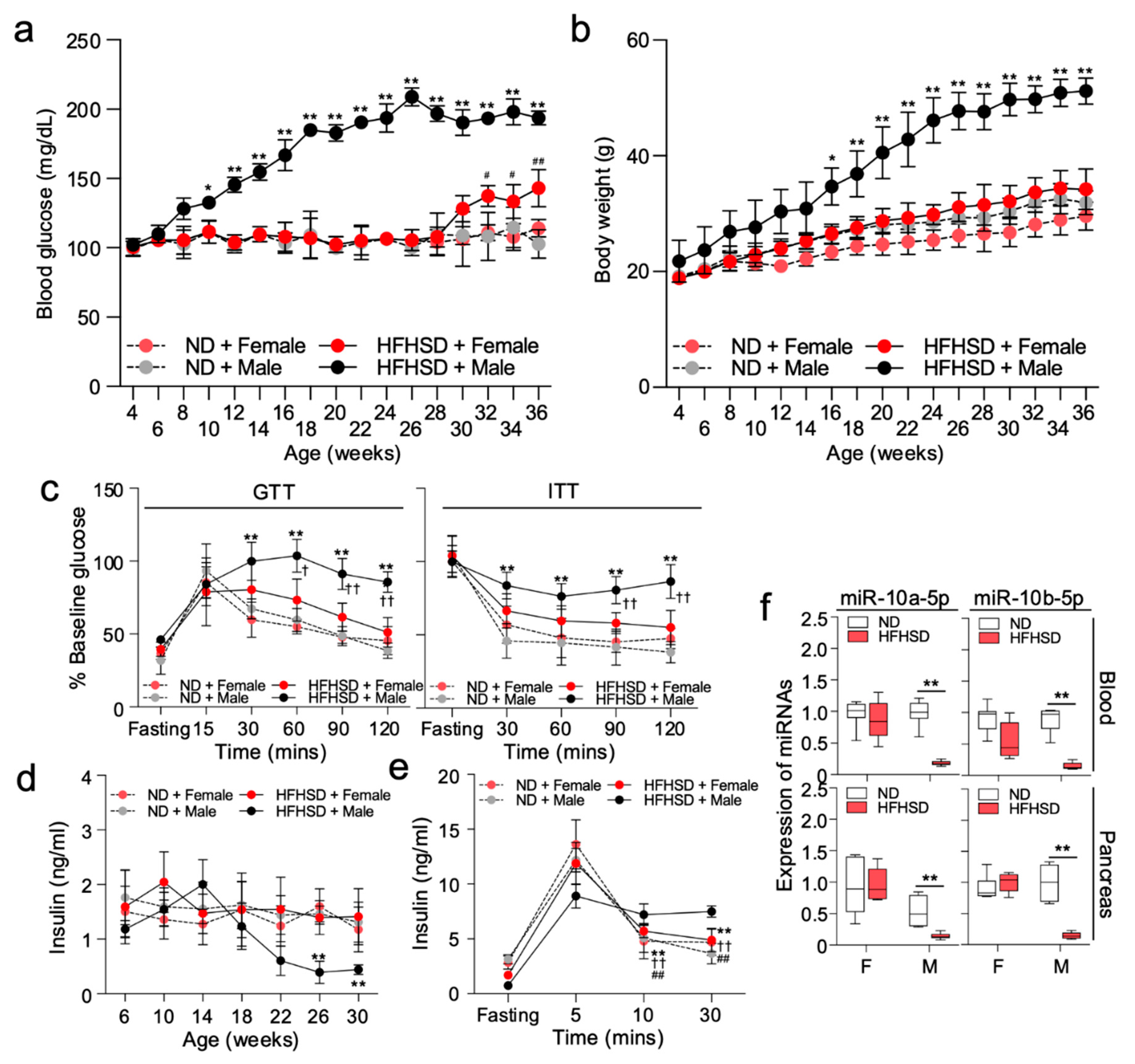
2.1. HFHSD-Fed Female Mice Delay the Development of Type 2 Diabetes
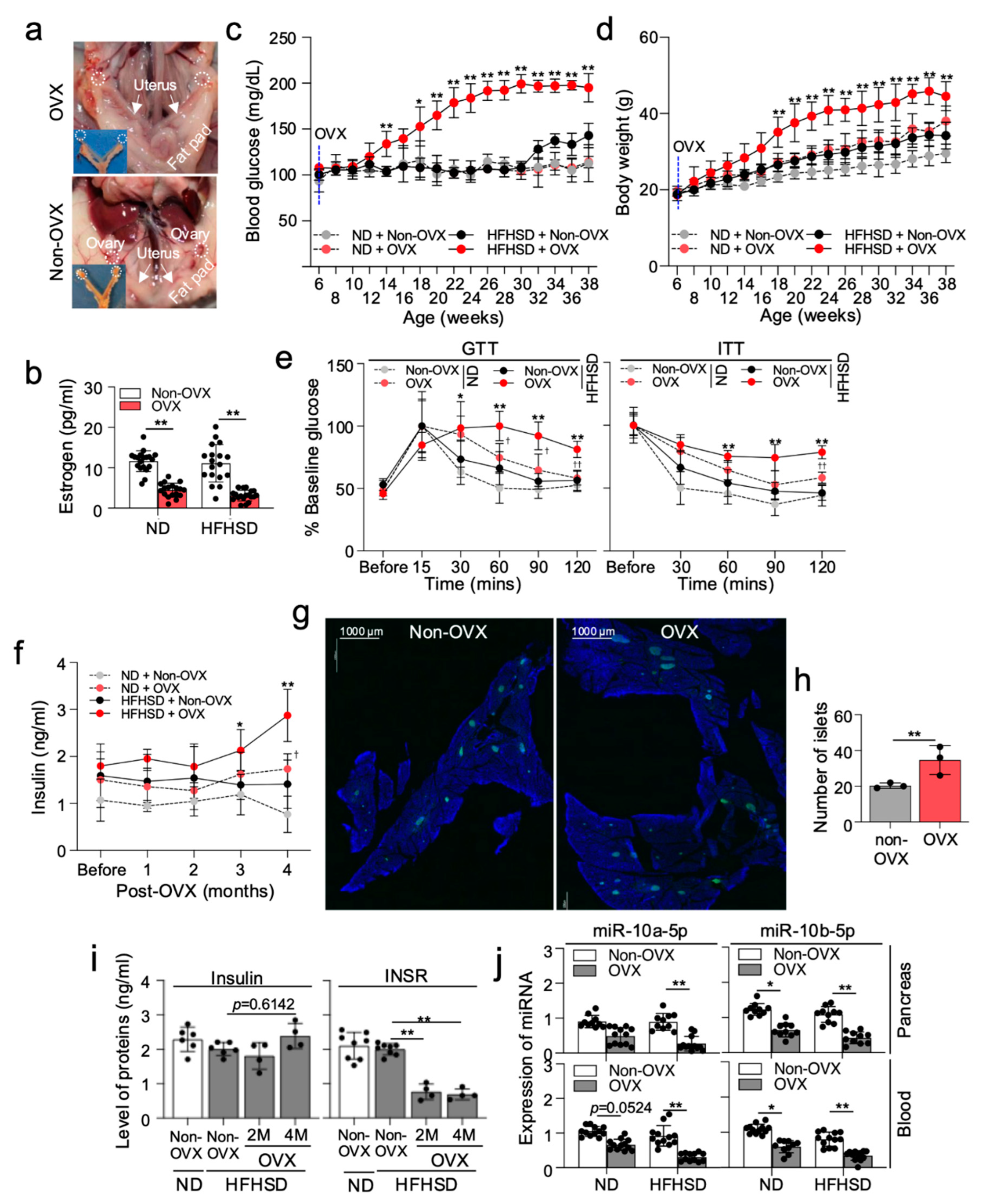
2.2. Ovariectomized HFHSD-Fed Female Mice Develop Type 2 Diabetes
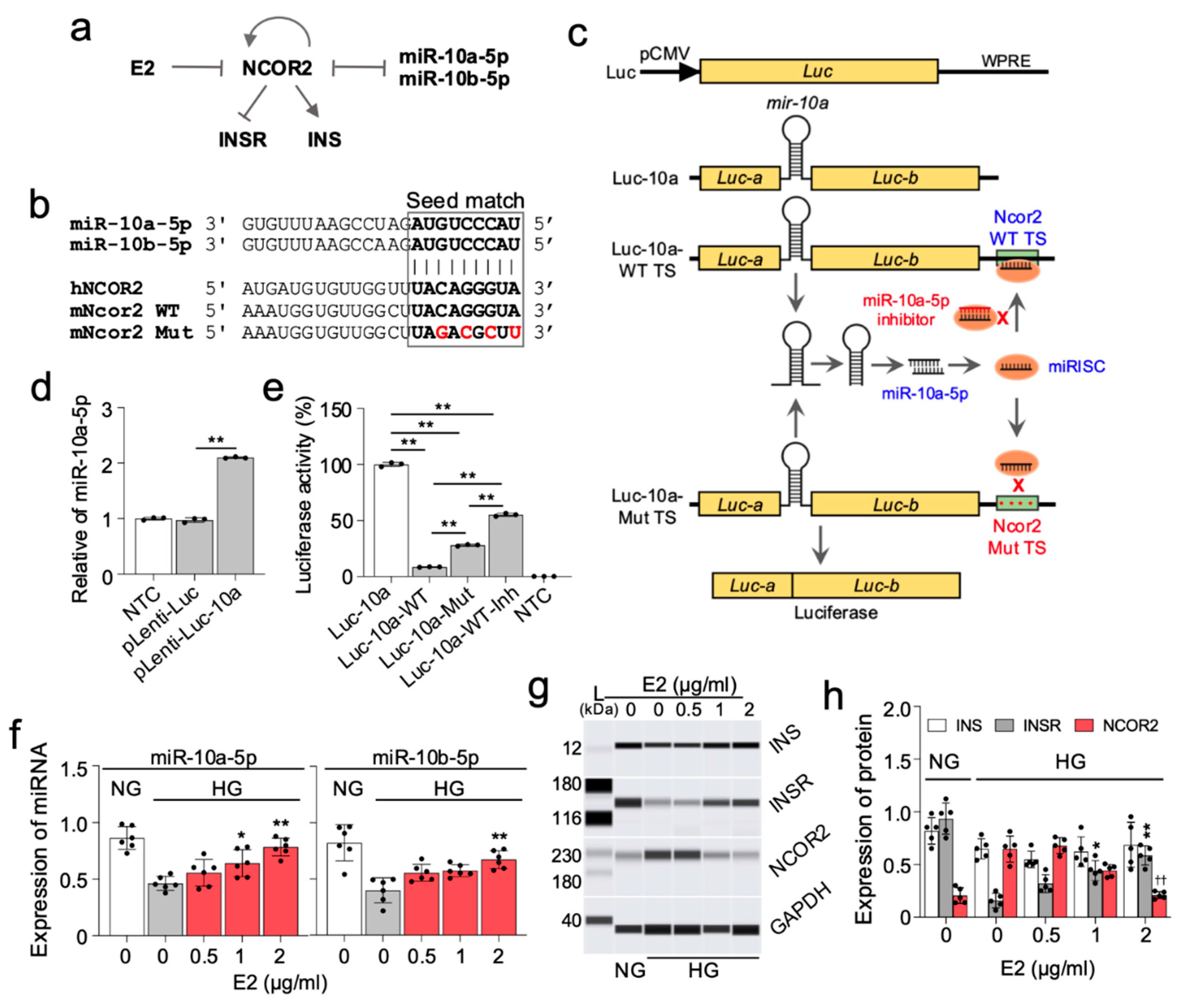
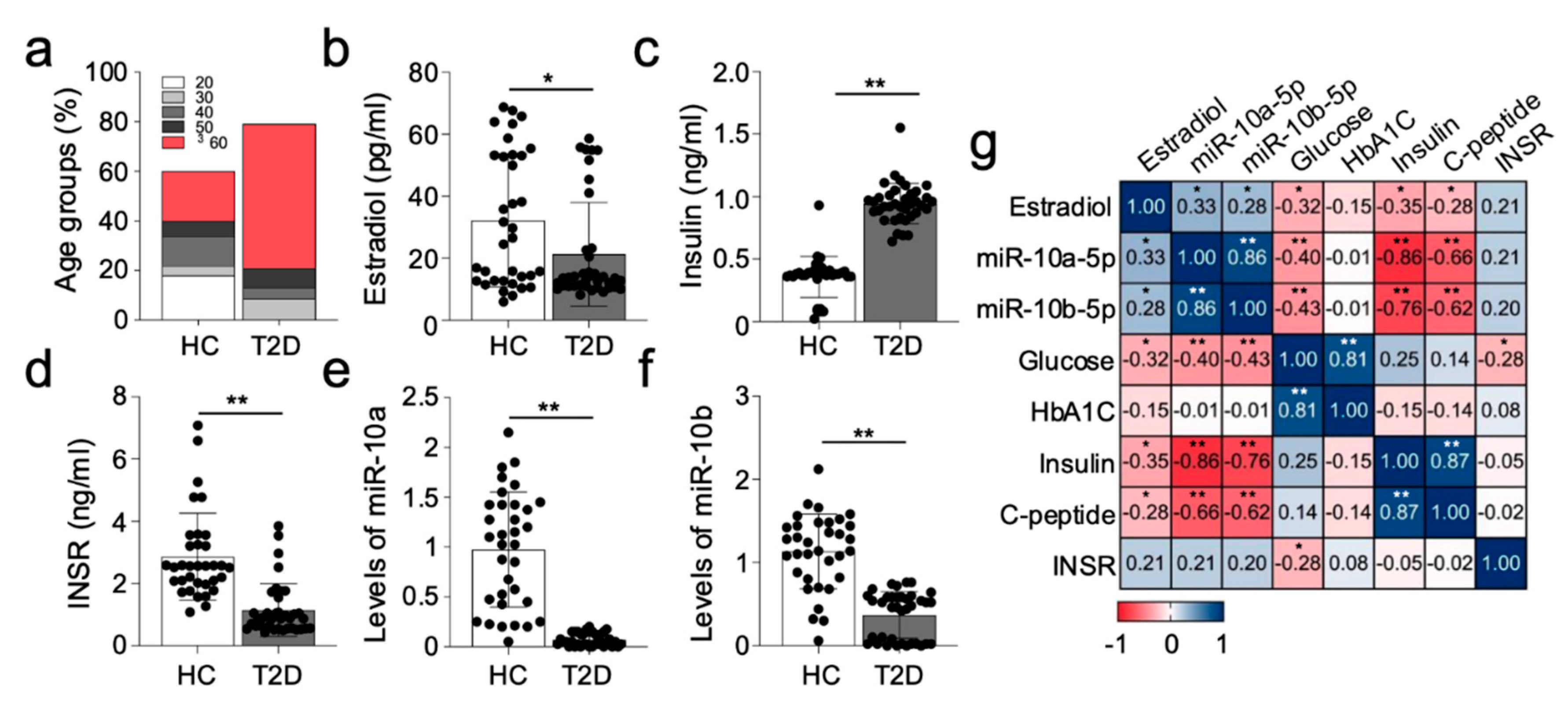
2.6. Female Diabetic Patients also Display Dysregulated Expression of miR-10a-5p Alongside Insulin and INSR
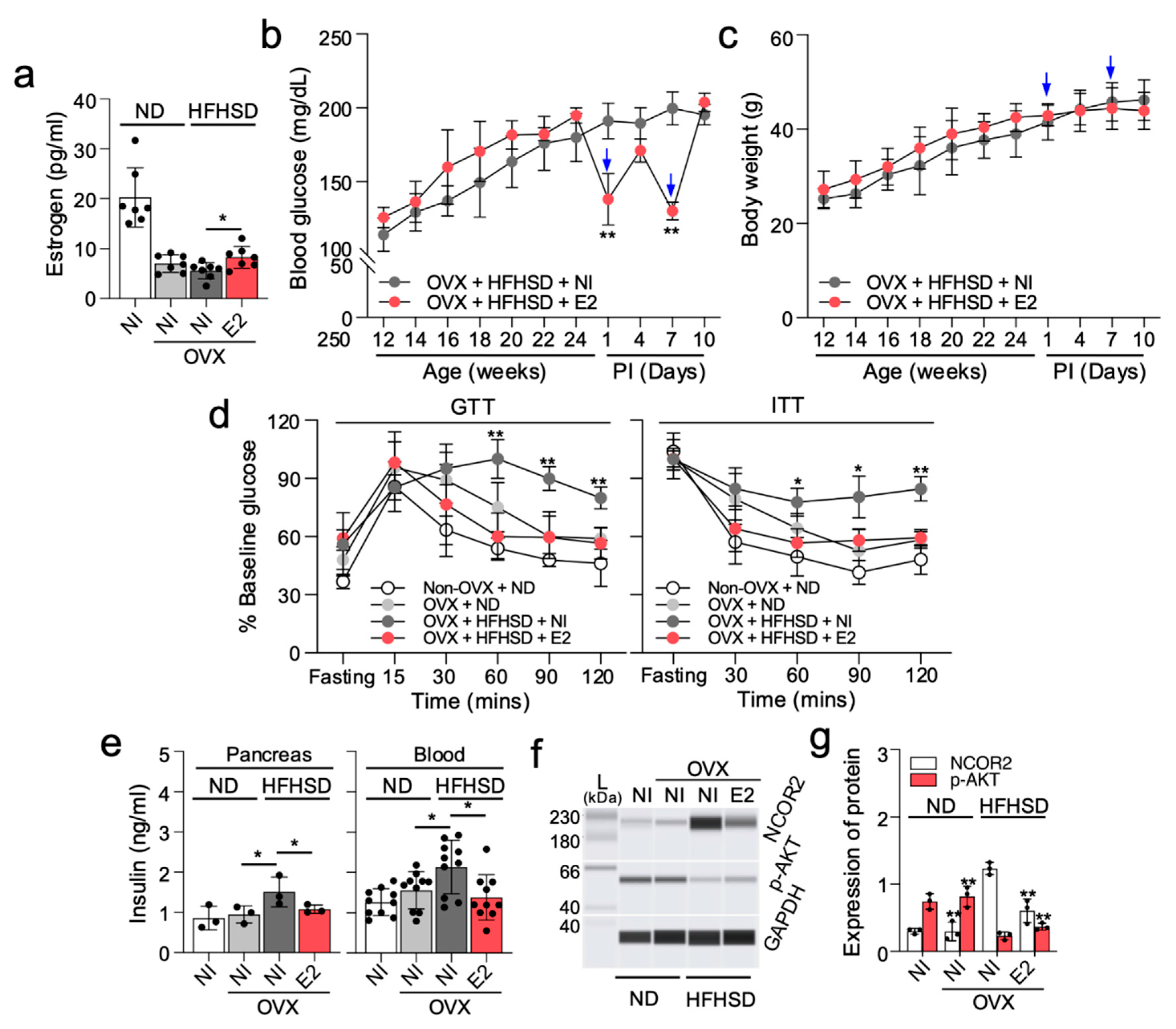
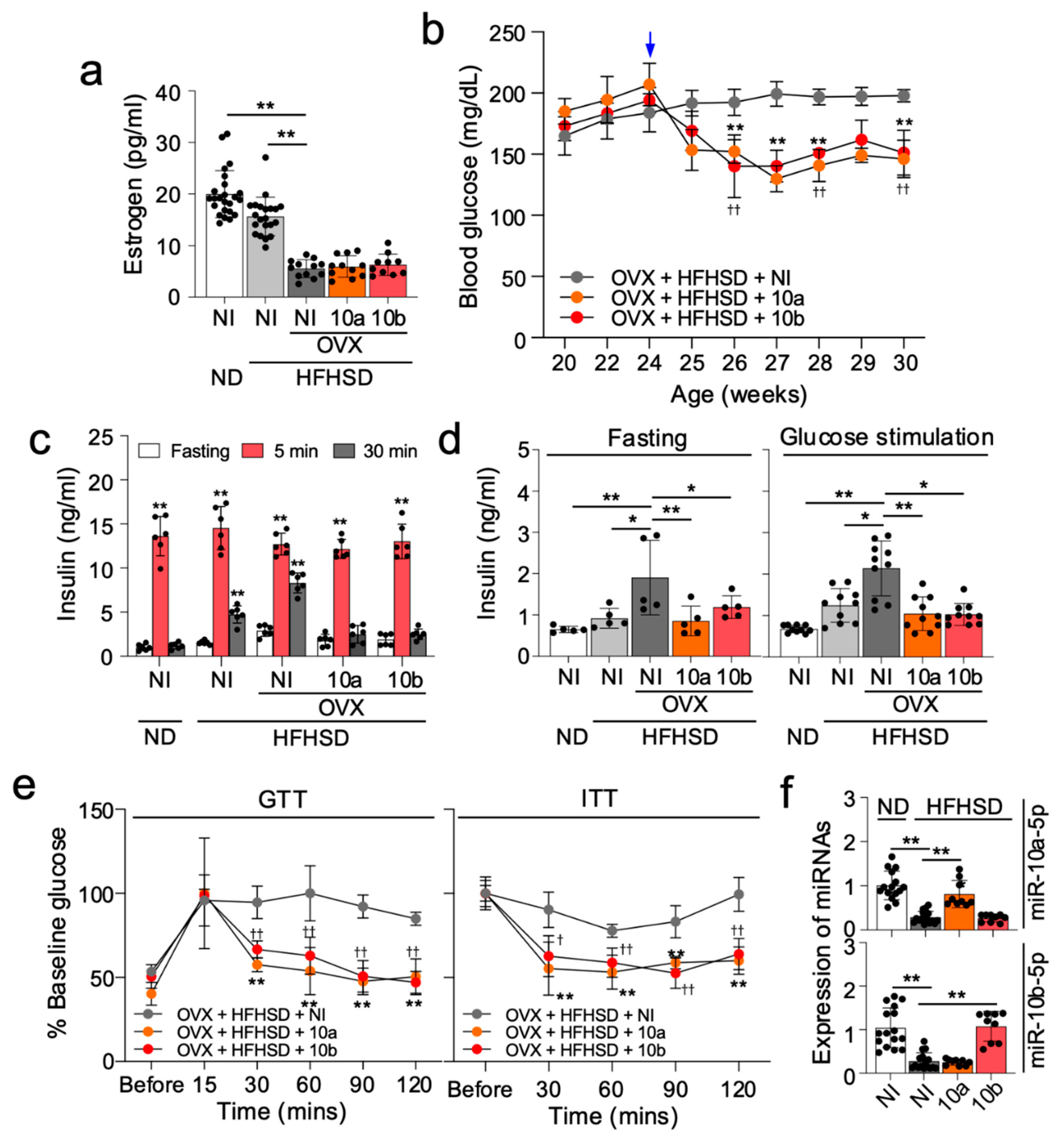
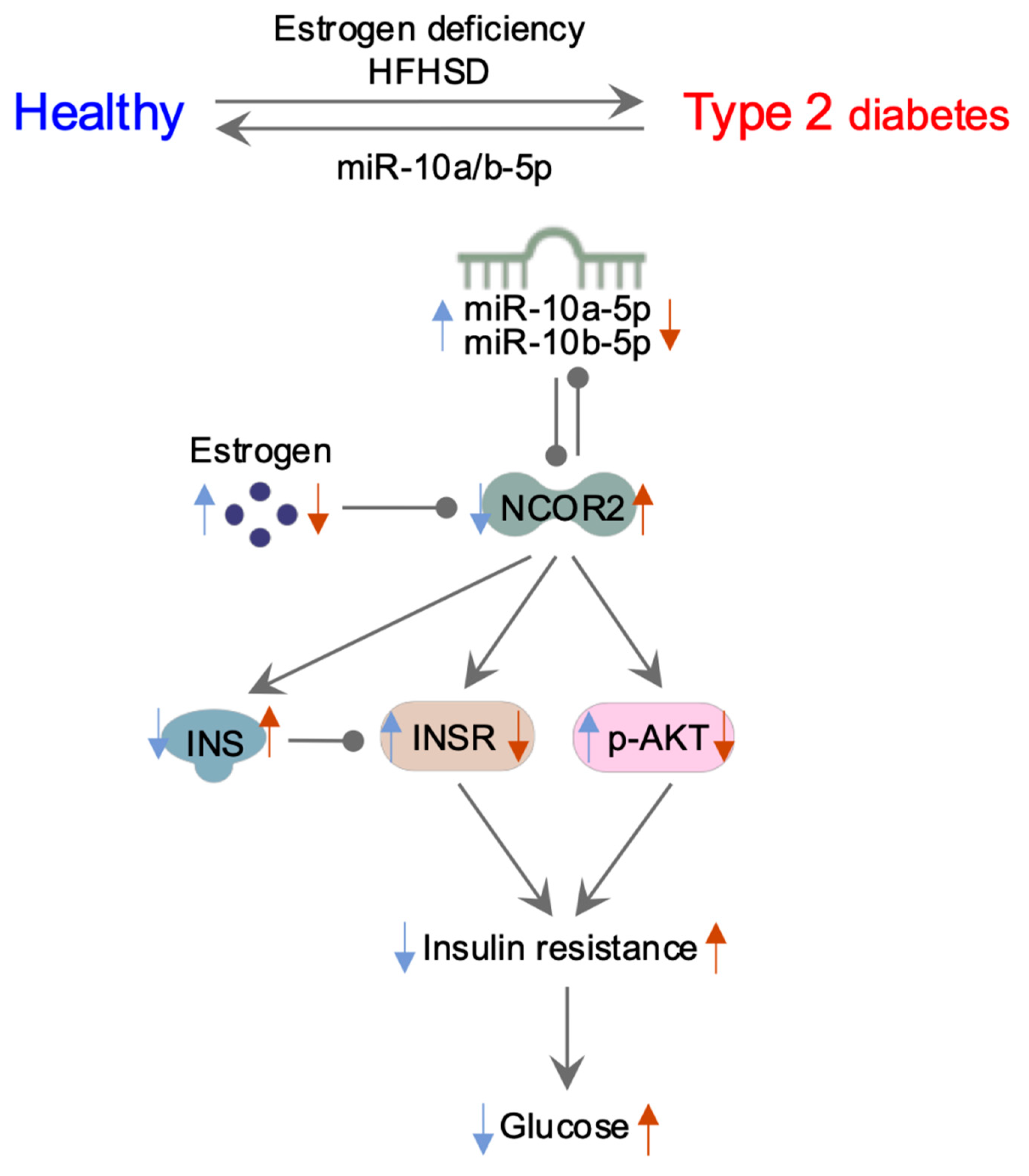
3. Discussion
4. Methods and Materials
4.1. Animal, Diet, and Ovariectomy (OVX) Surgery
4.2. Body Mass and Blood Glucose Measurements
4.3. Patient Samples
4.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.5. Reverse Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
4.6. Immunohistochemical Analysis
4.7. β-Estradiol (E2) Injection
4.8. In Vivo Delivery of miRNA Mimic
4.9. Construction of a Luciferase-miR-10a-Ncor2 Target Validation Vector and Transfection
4.10. Luciferase Activity
4.11. Automated Western Blot
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Nair, G.G.; Tzanakakis, E.S.; Hebrok, M. Emerging routes to the generation of functional beta-cells for diabetes mellitus cell therapy. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2020, 16, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordstrom, A.; Hadrevi, J.; Olsson, T.; Franks, P.W.; Nordstrom, P. Higher Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes in Men Than in Women Is Associated With Differences in Visceral Fat Mass. J Clin Endocr Metab 2016, 101, 3740–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louet, J.F.; LeMay, C.; Mauvais-Jarvis, F. Antidiabetic actions of estrogen: Insight from human and genetic mouse models. Curr Atheroscler Rep 2004, 6, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, B.; Garcia-Arevalo, M. , Sexual hormones and diabetes: The impact of estradiol in pancreatic beta cell. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 2021, 359, 81–138. [Google Scholar]
- Leiter, E.H.; Chapman, H.D. , Obesity-induced diabetes (diabesity) in C57BL/KsJ mice produces aberrant trans-regulation of sex steroid sulfotransferase genes. J Clin Invest 1994, 93, 2007–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, S.G.; Michelis, M.A.; Kim, Y.T.; Shin, S. , Induction of insulin-dependent diabetes by streptozotocin. Inhibition by estrogens and potentiation by androgens. Diabetes 1982, 31 Pt 1, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puah, J.A.; Bailey, C.J. , Insulinotropic effect of ovarian steroid hormones in streptozotocin diabetic female mice. Horm Metab Res 1985, 17, 216–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, J.L.; Smyth, C.A.; Bilbao, G.; Young, C.J.; Thompson, J.A.; Eckhoff, D.E. , 17beta-Estradiol protects isolated human pancreatic islets against proinflammatory cytokine-induced cell death: Molecular mechanisms and islet functionality. Transplantation 2002, 74, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faltas, C.L.; LeBron, K.A.; Holz, M.K. , Unconventional Estrogen Signaling in Health and Disease. Endocrinology 2020, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le May, C.; Chu, K.; Hu, M.; Ortega, C.S.; Simpson, E.R.; Korach, K.S.; Tsai, M.J.; Mauvais-Jarvis, F. , Estrogens protect pancreatic beta-cells from apoptosis and prevent insulin-deficient diabetes mellitus in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103, 9232–9237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Le May, C.; Wong, W.P.; Ward, R.D.; Clegg, D.J.; Marcelli, M.; Korach, K.S.; Mauvais-Jarvis, F. , Importance of extranuclear estrogen receptor-alpha and membrane G protein-coupled estrogen receptor in pancreatic islet survival. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2292–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Chen, X.; Cerne, R.; Syed, S.K.; Ficorilli, J.V.; Cabrera, O.; Obukhov, A.G.; Efanov, A.M. , Catechol estrogens stimulate insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells via activation of the transient receptor potential A1 (TRPA1) channel. J Biol Chem 2019, 294, 2935–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Allard, C.; Alvarez-Mercado, A.I.; Fuselier, T.; Kim, J.H.; Coons, L.A.; Hewitt, S.C.; Urano, F.; Korach, K.S.; Levin, E.R.; et al. Estrogens Promote Misfolded Proinsulin Degradation to Protect Insulin Production and Delay Diabetes. Cell Rep 2018, 24, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manson, J.E.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Stefanick, M.L.; Aragaki, A.K.; Rossouw, J.E.; Prentice, R.L.; Anderson, G.; Howard, B.V.; Thomson, C.A.; LaCroix, A.Z.; et al. Menopausal hormone therapy and health outcomes during the intervention and extended poststopping phases of the Women’s Health Initiative randomized trials. Jama 2013, 310, 1353–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, C.M.; Calin, G.A. , miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell 2005, 122, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Ha, S.E.; Wei, L.; Jin, B.; Zogg, H.; Poudrier, S.M.; Jorgensen, B.G.; Park, C.; Ronkon, C.F.; Bartlett, A.; et al. miR-10b-5p Rescues Diabetes and Gastrointestinal Dysmotility. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1662–1678.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanto, M.M.; Ferguson, K.K.; Sakuma, H.; Ye, H.; Brady, M.J.; Cohen, R.N. , The silencing mediator of retinoid and thyroid hormone receptors (SMRT) regulates adipose tissue accumulation and adipocyte insulin sensitivity in vivo. J Biol Chem 2010, 285, 18485–18495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofsinger, R.R.; Li, P.; Hong, S.H.; Jonker, J.W.; Barish, G.D.; Ying, H.; Cheng, S.Y.; Leblanc, M.; Xu, W.; Pei, L.; et al. SMRT repression of nuclear receptors controls the adipogenic set point and metabolic homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008, 105, 20021–20026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, J.; Kleinridders, A.; Kahn, C.R. , Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2014, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, N.H.; Bray, I.; Watters, K.M.; Das, S.; Bryan, K.; Bernas, T.; Prehn, J.H.M.; Stallings, R.L. , MicroRNAs 10a and 10b are potent inducers of neuroblastoma cell differentiation through targeting of nuclear receptor corepressor 2. Cell Death and Differentiation 2011, 18, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le May, C.; Chu, K.; Hu, M.; Ortega, C.S.; Simpson, E.R.; Korach, K.S.; Tsai, M.J.; Mauvais-Jarvis, F. , Estrogens protect pancreatic beta-cells from apoptosis and prevent insulin-deficient diabetes mellitus in mice. P Natl Acad Sci USA 2006, 103, 9232–9237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautzky-Willer, A.; Harreiter, J.; Pacini, G. , Sex and Gender Differences in Risk, Pathophysiology and Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Endocr Rev 2016, 37, 278–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickman, R.; Wainstein, J.; Glezerman, M.; Niv, Y.; Boaz, M. , Gender aspects suggestive of gastroparesis in patients with diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional survey. BMC gastroenterology 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderwald, C.; Gastaldelli, A.; Tura, A.; Krebs, M.; Promintzer-Schifferl, M.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Stadler, M.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Pacini, G.; Bischof, M.G. , Mechanism and Effects of Glucose Absorption during an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test Among Females and Males. J Clin Endocr Metab 2011, 96, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauvais-Jarvis, F.; Manson, J.E.; Stevenson, J.C.; Fonseca, V.A. , Menopausal Hormone Therapy and Type 2 Diabetes Prevention: Evidence, Mechanisms, and Clinical Implications. Endocr Rev 2017, 38, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.W.; Chi, X.W.; Wang, Y.; Setrerrahmane, S.; Xie, W.W.; Xu, H.M. , Trends in insulin resistance: Insights into mechanisms and therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct Tar 2022, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, J.F.; Sinha, M.K.; Raju, S.M.; Ittoop, O.; Pories, W.J.; Flickinger, E.G.; Meelheim, D.; Dohm, G.L. , Insulin-Receptor Kinase in Human Skeletal-Muscle from Obese Subjects with and without Noninsulin Dependent Diabetes. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1987, 79, 1330–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamula, P.W.; McDonald, A.R.; Brunetti, A.; Okabayashi, Y.; Wong, K.Y.; Maddux, B.A.; Logsdon, C.; Goldfine, I.D. , Regulating insulin-receptor-gene expression by differentiation and hormones. Diabetes care 1990, 13, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasuga, M.; Kahn, C.R.; Hedo, J.A.; Van Obberghen, E.; Yamada, K.M. , Insulin-induced receptor loss in cultured human lymphocytes is due to accelerated receptor degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1981, 78, 6917–6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanujan, S.A.; Cravens, E.N.; Krishfield, S.M.; Kyttaris, V.C.; Moulton, V.R. , Estrogen-Induced hsa-miR-10b-5p Is Elevated in T Cells From Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Down-Regulates Serine/Arginine-Rich Splicing Factor 1. Arthritis Rheumatol 2021, 73, 2052–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, B.J.; Barber, G.P.; Benet-Pages, A.; Casper, J.; Clawson, H.; Cline, M.S.; Diekhans, M.; Fischer, C.; Navarro Gonzalez, J.; Hickey, G.; et al. The UCSC Genome Browser database: 2024 update. Nucleic Acids Res 2024, 52, D1082–D1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, M.; Veres, A.; Wolock, S.L.; Faust, A.L.; Gaujoux, R.; Vetere, A.; Ryu, J.H.; Wagner, B.K.; Shen-Orr, S.S.; Klein, A.M.; et al. A Single-Cell Transcriptomic Map of the Human and Mouse Pancreas Reveals Inter- and Intra-cell Population Structure. Cell Syst 2016, 3, 346–360.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varlakhanova, N.; Snyder, C.; Jose, S.; Hahm, J.B.; Privalsky, M.L. , Estrogen receptors recruit SMRT and N-CoR corepressors through newly recognized contacts between the corepressor N terminus and the receptor DNA binding domain. Mol Cell Biol 2010, 30, 1434–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takimoto, G.S.; Graham, J.D.; Jackson, T.A.; Tung, L.; Powell, R.L.; Horwitz, L.D.; Horwitz, K.B. , Tamoxifen resistant breast cancer: Coregulators determine the direction of transcription by antagonist-occupied steroid receptors. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 1999, 69, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stossi, F.; Likhite, V.S.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. , Estrogen-occupied estrogen receptor represses cyclin G2 gene expression and recruits a repressor complex at the cyclin G2 promoter. J Biol Chem 2006, 281, 16272–16278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Brown, M. , Molecular determinants for the tissue specificity of SERMs. Science 2002, 295, 2465–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Hu, X.; DiRenzo, J.; Lazar, M.A.; Brown, M. , Cofactor dynamics and sufficiency in estrogen receptor-regulated transcription. Cell 2000, 103, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavinsky, R.M.; Jepsen, K.; Heinzel, T.; Torchia, J.; Mullen, T.M.; Schiff, R.; Del-Rio, A.L.; Ricote, M.; Ngo, S.; Gemsch, J.; et al. Diverse signaling pathways modulate nuclear receptor recruitment of N-CoR and SMRT complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998, 95, 2920–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, K.; Rosenfeld, M.G. , Biological roles and mechanistic actions of co-repressor complexes. J Cell Sci 2002, 115 Pt 4, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, K.; Hermanson, O.; Onami, T.M.; Gleiberman, A.S.; Lunyak, V.; McEvilly, R.J.; Kurokawa, R.; Kumar, V.; Liu, F.; Seto, E.; et al. Combinatorial roles of the nuclear receptor corepressor in transcription and development. Cell 2000, 102, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ro, S.; Park, C.; Young, D.; Sanders, K.M.; Yan, W. , Tissue-dependent paired expression of miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 2007, 35, 5944–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




