Submitted:
23 August 2024
Posted:
26 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction: A Needle in a Hastack
2. A (Semantic) Space Odyssey
- a)
- Red blood cells transport oxygen.
- b)
- Inflamed tissues are red.
- a)
- Red blood cells transport oxygen
- a’)
- Oxygen transports red blood cells
- a)
- Neurology is a difficult but interesting topic
- b)
- Neurology difficult interesting topic
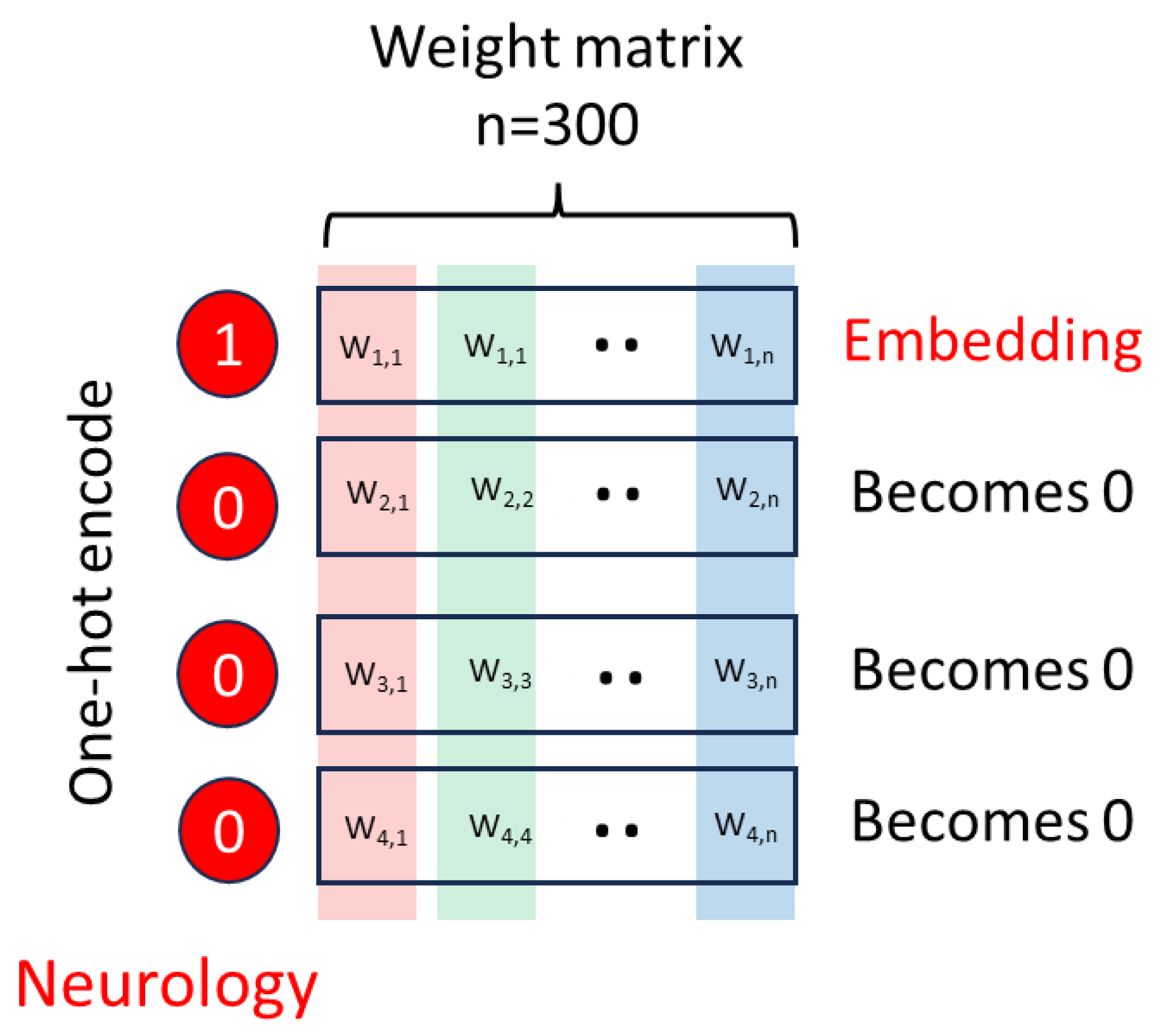
3. The Good, the Bad, the Ugly
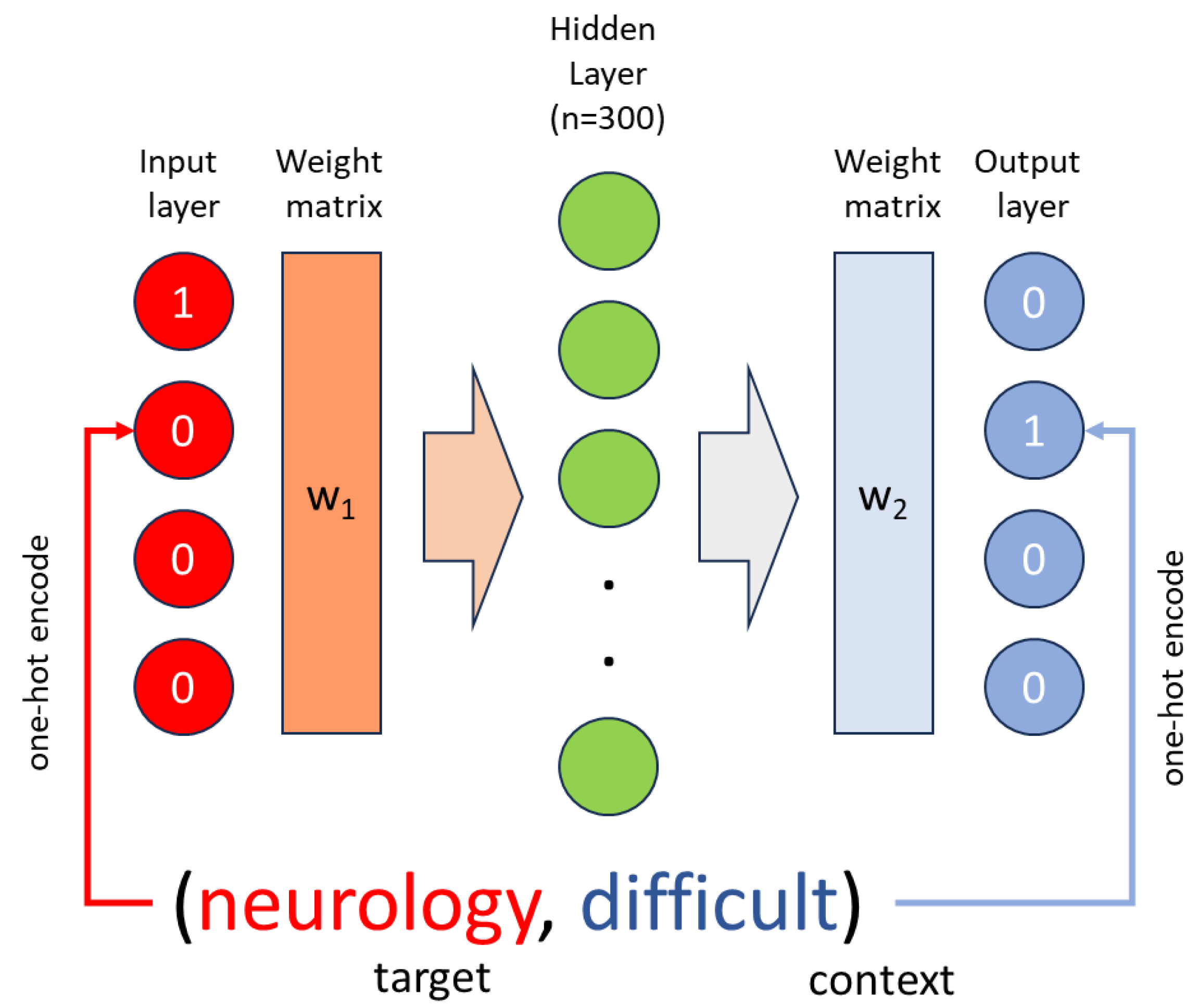
4. Transformers, More than Meets the Eye
5. Far Away, so Close
- Porous titanium granules in the treatment of peri-implant osseous defects-a 7-year follow-up study, reconstruction of peri-implant osseous defects: a multicenter randomized trial [56],
- Porous titanium granules in the surgical treatment of peri-implant osseous defects: a randomized clinical trial [57],
- D-plex500: a local biodegradable prolonged release doxycycline-formulated bone graft for the treatment for peri-implantitis. a randomized controlled clinical study [58],
- Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis with or without a deproteinized bovine bone mineral and a native bilayer collagen membrane: a randomized clinical trial [59],
- Effectiveness of enamel matrix derivative on the clinical and microbiological outcomes following surgical regenerative treatment of peri-implantitis. a randomized controlled trial [60],
- Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis using enamel matrix derivative, an rct: 3- and 5-year follow-up [61],
- Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis lesions with or without the use of a bone substitute-a randomized clinical trial [62],
- Peri-implantitis - reconstructive surgical therapy [63].
6. Everything Everywhere All at Once
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Landhuis, E. Scientific Literature: Information Overload. Nature 2016, 535, 457–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickersin, K.; Scherer, R.; Lefebvre, C. Systematic Reviews: Identifying Relevant Studies for Systematic Reviews. Bmj 1994, 309, 1286–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramer, W.M.; Rethlefsen, M.L.; Kleijnen, J.; Franco, O.H. Optimal Database Combinations for Literature Searches in Systematic Reviews: A Prospective Exploratory Study. Syst Rev 2017, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z. PubMed and beyond: A Survey of Web Tools for Searching Biomedical Literature. Database 2011, 2011, baq036–baq036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivell, L. Mining the Bibliome: Searching for a Needle in a Haystack? EMBO Rep 2002, 3, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, H.; Ameen, D.; Zarnegar, A. Tools to Support the Automation of Systematic Reviews: A Scoping Review. J Clin Epidemiol 2022, 144, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurafsky, D.; Martin, J.H. Vector Semantics and Embeddings. Speech and Language Processing 2019, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Turney, P.D.; Pantel, P. From Frequency to Meaning: Vector Space Models of Semantics. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 2010, 37, 141–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, Z.S. Distributional Structure. Word 1954, 10, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erk, K. Vector Space Models of Word Meaning and Phrase Meaning: A Survey. Lang Linguist Compass 2012, 6, 635–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, H.; Fernandez, M.; He, Y.; Alani, H. On Stopwords, Filtering and Data Sparsity for Sentiment Analysis of Twitter. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, R.; Zhou, Z.-H. Understanding Bag-of-Words Model: A Statistical Framework. International journal of machine learning and cybernetics 2010, 1, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.-P.; Huang, H.-K.; Shi, H.-B. Improved Feature Selection Approach TFIDF in Text Mining. In Proceedings of the Proceedings. International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics; IEEE, 2002; Vol. 2, pp. 944–946.
- Wang, S.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, C. A Survey of Word Embeddings Based on Deep Learning. Computing 2020, 102, 717–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolov, T.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space. arXiv preprint arXiv:1301.3781 2013. arXiv:1301.3781 2013.
- Di Gennaro, G.; Buonanno, A.; Palmieri, F.A.N. Considerations about Learning Word2Vec. J Supercomput 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saqqa, S.; Awajan, A. The Use of Word2vec Model in Sentiment Analysis: A Survey. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2019 international conference on artificial intelligence, robotics and control; 2019; pp. 39–43. 201939–43.
- Haider, M.M.; Hossin, M.A.; Mahi, H.R.; Arif, H. Automatic Text Summarization Using Gensim Word2vec and K-Means Clustering Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Region 10 Symposium (TENSYMP); IEEE, 2020; pp. 283–286.
- Ibrohim, M.O.; Setiadi, M.A.; Budi, I. Identification of Hate Speech and Abusive Language on Indonesian Twitter Using the Word2vec, Part of Speech and Emoji Features. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Advanced Information Science and System; 2019; pp. 1–5.
- Jatnika, D.; Bijaksana, M.A.; Suryani, A.A. Word2vec Model Analysis for Semantic Similarities in English Words. Procedia Comput Sci 2019, 157, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Kusner, M.J.; Blunsom, P. A Survey on Contextual Embeddings. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.07278 2020.
- Kruse, R.; Mostaghim, S.; Borgelt, C.; Braune, C.; Steinbrecher, M. Multi-Layer Perceptrons. In Computational intelligence: a methodological introduction; Springer, 2022; pp. 53–124.
- Salehinejad, H.; Sankar, S.; Barfett, J.; Colak, E.; Valaee, S. Recent Advances in Recurrent Neural Networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.01078 2017.
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Gulcehre, C.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning Phrase Representations Using RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1406.1078 2014.
- Yin, W.; Kann, K.; Yu, M.; Schütze, H. Comparative Study of CNN and RNN for Natural Language Processing. arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.01923 2017.
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, T.; Debut, L.; Sanh, V.; Chaumond, J.; Delangue, C.; Moi, A.; Cistac, P.; Rault, T.; Louf, R.; Funtowicz, M.; et al. Transformers: State-of-the-Art Natural Language Processing. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 38–45.
- Bramer, W.M.; Rethlefsen, M.L.; Kleijnen, J.; Franco, O.H. Optimal Database Combinations for Literature Searches in Systematic Reviews: A Prospective Exploratory Study. Syst Rev 2017, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, L.J.; Munro, S. The Literature Review: Demystifying the Literature Search. Diabetes Educ 2004, 30, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farouk, M. Measuring Text Similarity Based on Structure and Word Embedding. Cogn Syst Res 2020, 63, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Han, L. Distance Weighted Cosine Similarity Measure for Text Classification. In; 2013; pp. 611–618.
- Ivchenko, G.I.; Honov, S.A. On the Jaccard Similarity Test. Journal of Mathematical Sciences 1998, 88, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K. LIII. On Lines and Planes of Closest Fit to Systems of Points in Space. The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin philosophical magazine and journal of science 1901, 2, 559–572.
- Labrín, C.; Urdinez, F. In R for political data science; Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2020; pp. 375–393.
- Van der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G. Visualizing Data Using T-SNE. Journal of machine learning research 2008, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Xanthopoulos, P.; Pardalos, P.M.; Trafalis, T.B.; Xanthopoulos, P.; Pardalos, P.M.; Trafalis, T.B. Linear Discriminant Analysis. Robust data mining 2013, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, T. Nonlinear Dimensionality Reduction with Locally Linear Embedding and Isomap. University of Sheffield 2002.
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Melville, J. Umap: Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection for Dimension Reduction. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.03426 2018.
- Andersen, H.; Aass, A.M.; Wohlfahrt, J.C. Porous Titanium Granules in the Treatment of Peri-Implant Osseous Defects—a 7-Year Follow-up Study. Int J Implant Dent 2017, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlfahrt, J.C.; Lyngstadaas, S.P.; Rønold, H.J.; Saxegaard, E.; Ellingsen, J.E.; Karlsson, S.; Aass, A.M. Porous Titanium Granules in the Surgical Treatment of Peri-Implant Osseous Defects: A Randomized Clinical Trial. International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 2012, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel, N.; Machtei, E.E.; Reichart, M.; Shapira, L. D-PLEX. Quintessence Int (Berl) 2020, 51, 546–553. [Google Scholar]
- Renvert, S.; Giovannoli, J.; Roos-Jansåker, A.; Rinke, S. Surgical Treatment of Peri-implantitis with or without a Deproteinized Bovine Bone Mineral and a Native Bilayer Collagen Membrane: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J Clin Periodontol 2021, 48, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isehed, C.; Holmlund, A.; Renvert, S.; Svenson, B.; Johansson, I.; Lundberg, P. Effectiveness of Enamel Matrix Derivative on the Clinical and Microbiological Outcomes Following Surgical Regenerative Treatment of Peri-implantitis. A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Clin Periodontol 2016, 43, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isehed, C.; Svenson, B.; Lundberg, P.; Holmlund, A. Surgical Treatment of Peri-implantitis Using Enamel Matrix Derivative, an RCT: 3-and 5-year Follow-up. J Clin Periodontol 2018, 45, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Roos-Jansåker, A.; Persson, G.R. Surgical Treatment of Peri-implantitis Lesions with or without the Use of a Bone Substitute—a Randomized Clinical Trial. J Clin Periodontol 2018, 45, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nct Peri-Implantitis - Reconstructive Surgical Therapy. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03077061 2017 (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- Ahmad, N.; Nassif, A.B. Dimensionality Reduction: Challenges and Solutions. In Proceedings of the ITM Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences, 2022; Vol. 43, p. 01017.
- Sumithra, V.; Surendran, S. A Review of Various Linear and Non Linear Dimensionality Reduction Techniques. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol 2015, 6, 2354–2360. [Google Scholar]
- Zebari, R.; Abdulazeez, A.; Zeebaree, D.; Zebari, D.; Saeed, J. A Comprehensive Review of Dimensionality Reduction Techniques for Feature Selection and Feature Extraction. Journal of Applied Science and Technology Trends 2020, 1, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Du, Z.; Ding, M.; Qian, Y.; Yang, Z.; Tang, J. GPT Understands, Too. AI Open 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirunavukarasu, A.J.; Ting, D.S.J.; Elangovan, K.; Gutierrez, L.; Tan, T.F.; Ting, D.S.W. Large Language Models in Medicine. Nat Med 2023, 29, 1930–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaddour, J.; Harris, J.; Mozes, M.; Bradley, H.; Raileanu, R.; McHardy, R. Challenges and Applications of Large Language Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.10169 2023.
- Wei, J.; Tay, Y.; Bommasani, R.; Raffel, C.; Zoph, B.; Borgeaud, S.; Yogatama, D.; Bosma, M.; Zhou, D.; Metzler, D. Emergent Abilities of Large Language Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.07682 2022.
- Hersh, W.R. Search Still Matters: Information Retrieval in the Era of Generative AI. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.18550 2023.
- Zhu, Y.; Yuan, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Deng, C.; Dou, Z.; Wen, J.-R. Large Language Models for Information Retrieval: A Survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.07107 2023.
- Hadi, M.U.; Qureshi, R.; Shah, A.; Irfan, M.; Zafar, A.; Shaikh, M.B.; Akhtar, N.; Wu, J.; Mirjalili, S. A Survey on Large Language Models: Applications, Challenges, Limitations, and Practical Usage. Authorea Preprints 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, A.; Fleming, S.L.; Chiang, C.-C.; Shah, N. Clinfo. Ai: An Open-Source Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Model System for Answering Medical Questions Using Scientific Literature. In Proceedings of the PACIFIC SYMPOSIUM ON BIOCOMPUTING 2024; World Scientific, 2023; pp. 8–23.
- Agarwal, S.; Laradji, I.H.; Charlin, L.; Pal, C. LitLLM: A Toolkit for Scientific Literature Review. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.01788 2024.
| W | Red | Blood | Cell | To transport | Oxygen | Inflamed | Tissue | To be |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sent. A) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sent. B) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





