Submitted:
23 August 2024
Posted:
23 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
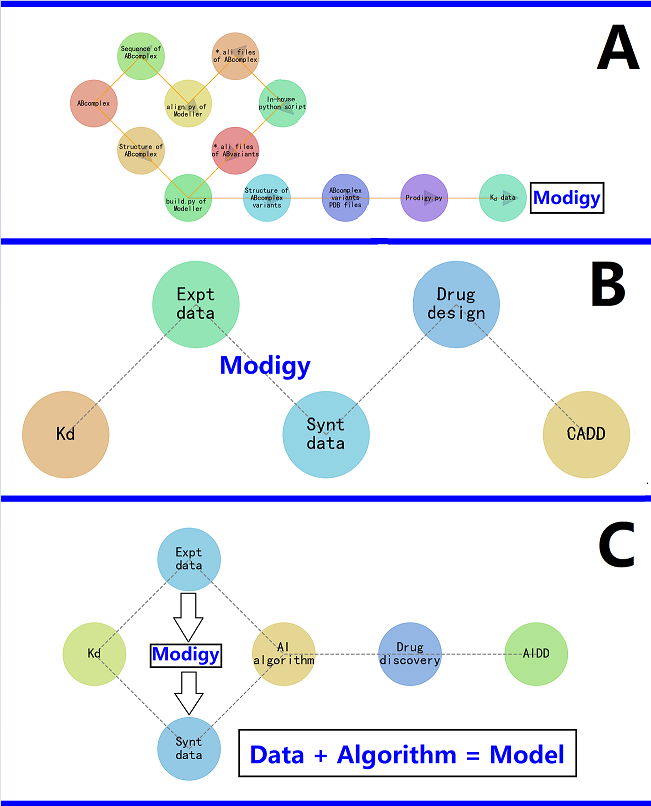
Keywords:
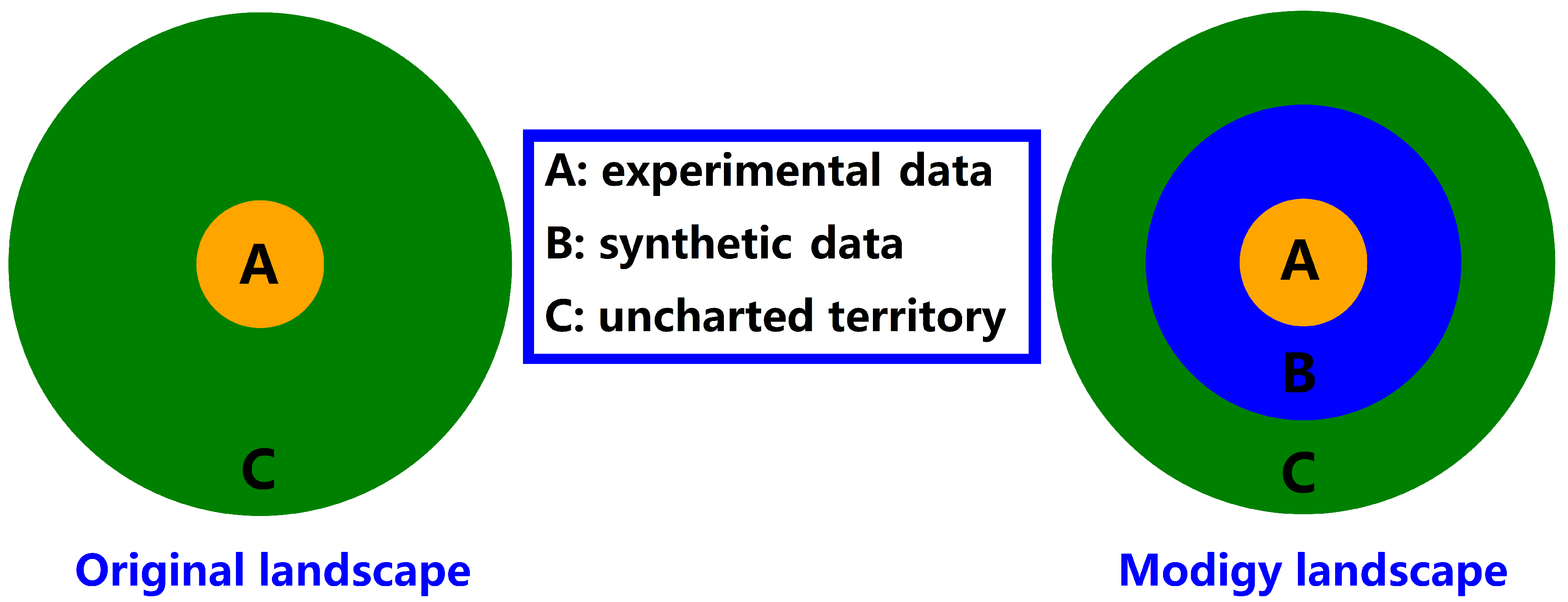
1. Background and Motivation
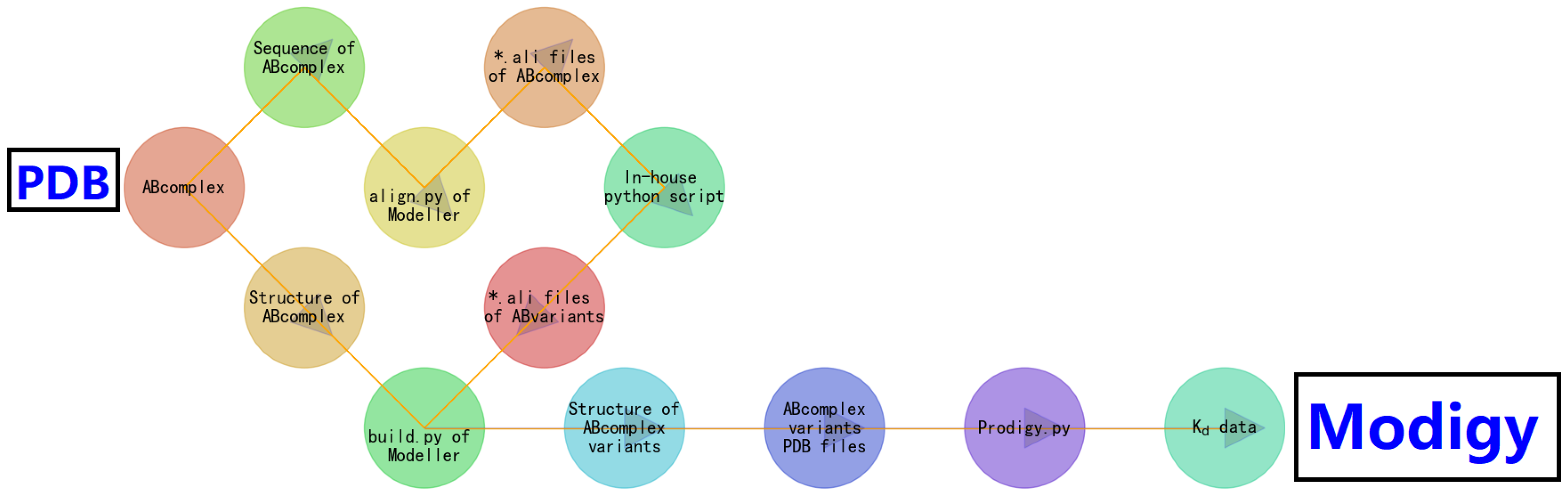
2. Modigy: a Computational Structural Biophysics-Based Workflow
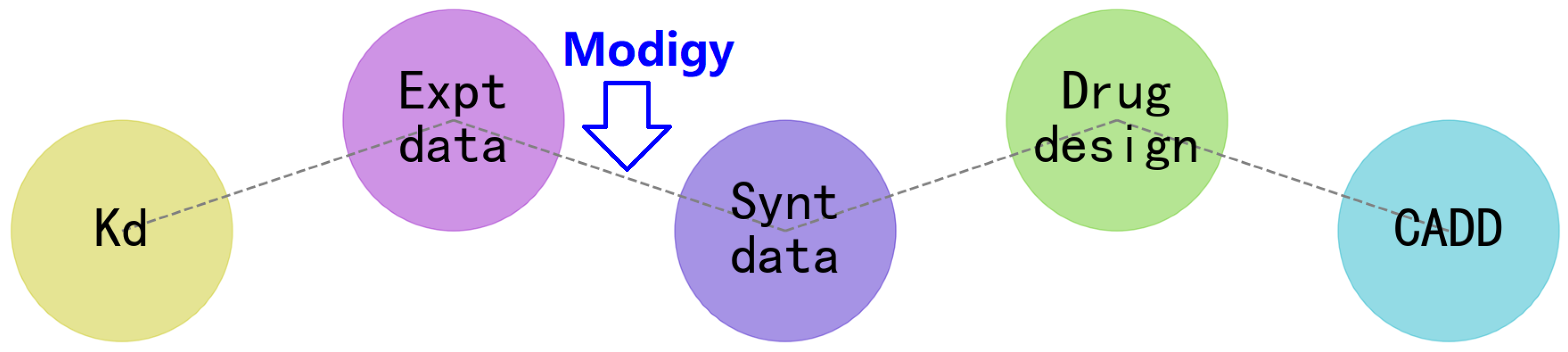
3. How Does the Modigy Workflow Contribute to Biomolecular CADD?
3.1. Design of Semaglutide Analogues with Enhanced Binding Affinity to GLP-1R
3.2. Scalable Antigen-Antibody Binding Affinity Landscape: A Case Study with ENHERTU
4. How Does the Modigy Workflow Contribute to Biomolecular AIDD?
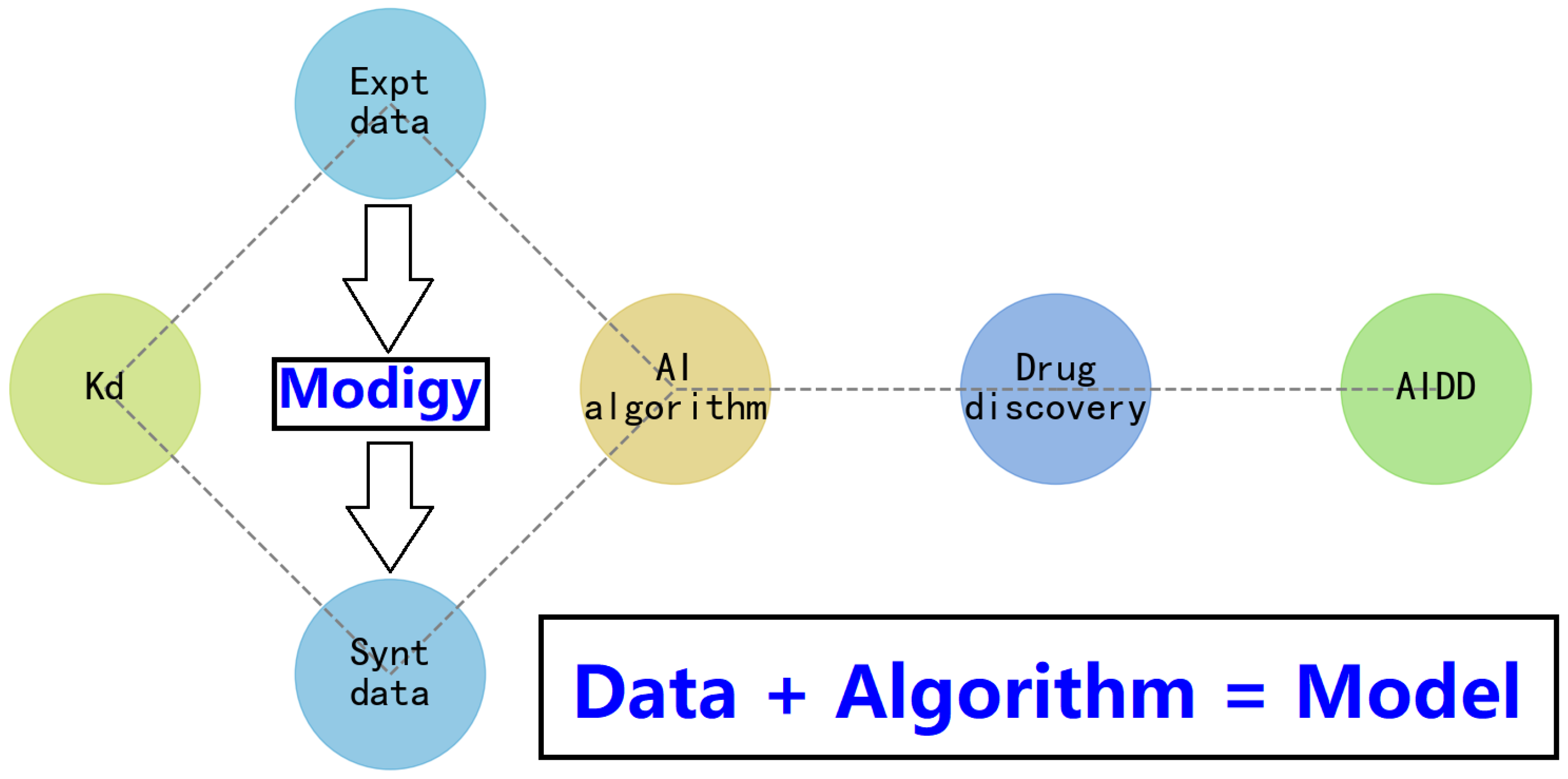
5. Limitations of the Modigy Workflow in Drug Design and Discovery
6. Conclusion
7. Ethical Statement
8. Declaration of Generative AI and AI-Assisted Technologies in the Writing Process
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schlander, M.; Hernandez-Villafuerte, K.; Cheng, C.Y.; Mestre-Ferrandiz, J.; Baumann, M. How Much Does It Cost to Research and Develop a New Drug? A Systematic Review and Assessment. PharmacoEconomics 2021, 39, 1243–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.H.; Siah, K.W.; Lo, A.W. Estimation of clinical trial success rates and related parameters. Biostatistics 2018, 20, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulic, M. Average R&D cost to develop a pharmaceutical compound from discovery to launch from 2010 to 2020, 2022. Accessed: (Aug 5, 2024).
- Niazi, S.K.; Mariam, Z. Computer-Aided Drug Design and Drug Discovery: A Prospective Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 17, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tropsha, A.; Bajorath, J. Computational Methods for Drug Discovery and Design. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2015, 59, 1–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogi, S. Computational Approaches for Drug Discovery. Molecules 2019, 24, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steven, A.C.; Baumeister, W. The future is hybrid. Journal of Structural Biology 2008, 163, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayarisseri, A. Experimental and Computational Approaches to Improve Binding Affinity in Chemical Biology and Drug Discovery. Current Topics in Medicinal Chemistry 2020, 20, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinberg, C.E.; Khare, S.D.; Dou, J.; Doyle, L.; Nelson, J.W.; Schena, A.; Jankowski, W.; Kalodimos, C.G.; Johnsson, K.; Stoddard, B.L.; Baker, D. Computational design of ligand-binding proteins with high affinity and selectivity. Nature 2013, 501, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.Q.; Nguyen, N.T.; Malagon-Lopez, J.; Topkar, V.V.; Aryee, M.J.; Joung, J.K. CIRCLE-seq: A highly sensitive in vitro screen for genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 nuclease off-targets. Nature Methods 2017, 14, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lin, Y.; Wen, X.; Jorissen, R.N.; Gilson, M.K. BindingDB: A web-accessible database of experimentally determined protein-ligand binding affinities. Nucleic Acids Research 2007, 35, D198–D201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, P.J.; Mitchell, J.B.O. A machine learning approach to predicting protein-ligand binding affinity with applications to molecular docking. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; He, X. Fragment-based quantum mechanical calculation of protein-protein binding affinities. Journal of Computational Chemistry 2018, 39, 1617–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, D.M.; Friedensohn, S.; Weber, C.R.; Jordi, C.; Wagner, B.; Meng, S.M.; Ehling, R.A.; Bonati, L.; Dahinden, J.; Gainza, P.; Correia, B.E.; Reddy, S.T. Optimization of therapeutic antibodies by predicting antigen specificity from antibody sequence via deep learning. Nature Biomedical Engineering 2021, 5, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Fang, X.; Lu, Y.; Yang, C.Y.; Wang, S. The PDBbind Database: Methodologies and Updates. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2005, 48, 4111–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, S.; Prema, K.; Balaji, S. Machine learning models for drug-target interactions: Current knowledge and future directions. Drug Discovery Today 2020, 25, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, N.; Ferdousi, R. AptaNet as a deep learning approach for aptamer-protein interaction prediction. Scientific Reports 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Shin, W.H.; Ko, J.; Lee, J. AK-Score: Accurate Protein-Ligand Binding Affinity Prediction Using an Ensemble of 3D-Convolutional Neural Networks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 8424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ávila, M.B.; Xavier, M.M.; Pintro, V.O.; de Azevedo, W.F. Supervised machine learning techniques to predict binding affinity. A study for cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2017, 494, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuji, H.; Qi, F.; Qu, L.; Takaesu, Y.; Hoshino, T. Prediction of Ligand Binding Affinity to Target Proteins by Molecular Mechanics Theoretical Calculation. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 2017, 65, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Protein Structure Modeling with MODELLER. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer US, 2020; pp. 239–255.
- Berman, H.; Henrick, K.; Nakamura, H. Announcing the worldwide Protein Data Bank. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 2003, 10, 980–980. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.C.; Rodrigues, J.P.; Kastritis, P.L.; Bonvin, A.M.; Vangone, A. PRODIGY: A web server for predicting the binding affinity of protein–protein complexes. Bioinformatics 2016, btw514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangone, A.; Bonvin, A.M. Contacts-based prediction of binding affinity in protein–protein complexes. eLife 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W. In Silico Generation of Structural and Intermolecular Binding Affinity Data with Reasonable Accuracy: Expanding Horizons in Drug Discovery and Design 2024. [CrossRef]
- Capecchi, A.; Probst, D.; Reymond, J.L. One molecular fingerprint to rule them all: Drugs, biomolecules, and the metabolome. Journal of Cheminformatics 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karplus, M.; McCammon, J.A. Molecular dynamics simulations of biomolecules. Nature structural biology 2002, 9, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, H.P.; Mortensen, K.K. Advanced genetic strategies for recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 115, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Strengthening Semaglutide-GLP-1R Binding Affinity via a Val27-Arg28 Exchange in the Peptide Backbone of Semaglutide: A Computational Structural Approach. Journal of Computational Biophysics and Chemistry 2021, 20, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M. Design of ultra-stable insulin analogues for the developing world. Journal of Health Specialties 2013, 1, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Scalable Antigen-Antibody Binding Affinity Landscape: A Case Study with ENHERTU 2024. [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Yu, X.; Bai, Y.; McBride, H.J.; Huang, X. Cryo-EM Structure of HER2-trastuzumab-pertuzumab complex. PLOS ONE 2019, 14, e0216095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reymond, J.L.; van Deursen, R.; Blum, L.C.; Ruddigkeit, L. Chemical space as a source for new drugs. MedChemComm 2010, 1, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. An Exhaustive Exploration of the Semaglutide-GLP-1R Sequence Space towards the Design of Semaglutide Analogues with Elevated Binding Affinity to GLP-1R 2024. [CrossRef]
- Granhall, C.; Donsmark, M.; Blicher, T.M.; Golor, G.; Sondergaard, F.L.; Thomsen, M.; Bakdal, T.A. Safety and Pharmacokinetics of Single and Multiple Ascending Doses of the Novel Oral Human GLP-1 Analogue, Oral Semaglutide, in Healthy Subjects and Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 2018, 58, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.K.; Kaur, G.; Haider, Z.; Rodriquez, E.; Beatson, C.; Snell-Bergeon, J. Efficacy of Semaglutide in Overweight and Obese Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics 2024, 26, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Europe, T.L.R.H. Semaglutide and beyond a turning point in obesity pharmacotherapy. The Lancet Regional Health Europe 2024, 37, 100860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrén, B.; Atkin, S.L.; Charpentier, G.; Warren, M.L.; Wilding, J.P.H.; Birch, S.; Holst, A.G.; Leiter, L.A. Semaglutide induces weight loss in subjects with type 2 diabetes regardless of baseline BMI or gastrointestinal adverse events in the SUSTAIN 1 to 5 trials. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism 2018, 20, 2210–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroda, V.R.; Rosenstock, J.; Terauchi, Y.; Altuntas, Y.; Lalic, N.M.; Villegas, E.C.M.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Christiansen, E.; Hertz, C.L.; Haluzík, M. PIONEER 1: Randomized Clinical Trial of the Efficacy and Safety of Oral Semaglutide Monotherapy in Comparison With Placebo in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1724–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W. Optimizing GLP-1R Agonist: A Computational Semaglutide Analogue with 112-fold Enhanced Binding Affinity to GLP-1R 2024. [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.; Bloch, P.; Schäffer, L.; Pettersson, I.; Spetzler, J.; Kofoed, J.; Madsen, K.; Knudsen, L.B.; McGuire, J.; Steensgaard, D.B.; Strauss, H.M.; Gram, D.X.; Knudsen, S.M.; Nielsen, F.S.; Thygesen, P.; Reedtz-Runge, S.; Kruse, T. Discovery of the Once-Weekly Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Analogue Semaglutide. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2015, 58, 7370–7380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marijic, J.; Neelankavil, J.P. Semaglutide: A New Medical Swiss Army Knife? Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia 2024, 38, 871–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowart, K. Oral Semaglutide: First-in-Class Oral GLP-1 Receptor Agonist for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2019, 54, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, L.B.; Lau, J. The Discovery and Development of Liraglutide and Semaglutide. Frontiers in Endocrinology 2019, 10, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Schladetsch, M.A.; Huang, X.; Balunas, M.J.; Wiemer, A.J. Stepping forward in antibody-drug conjugate development. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2022, 229, 107917. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.C.; Sun, W.; Khare, P.; Karimi, M.; Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Ober, R.J.; Ward, E.S. Engineering a HER2-specific antibody–drug conjugate to increase lysosomal delivery and therapeutic efficacy. Nature Biotechnology 2019, 37, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keam, S.J. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Park, Y.H. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan for HER2+ Advanced Breast Cancer. Future Oncology 2021, 18, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, H.; Oitate, M.; Hagihara, K.; Shiozawa, H.; Furuta, Y.; Ogitani, Y.; Kuga, H. Pharmacokinetics of trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd), a novel anti-HER2 antibody-drug conjugate, in HER2-positive tumour-bearing mice. Xenobiotica 2020, 50, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruedas, R.; Vuillemot, R.; Tubiana, T.; Winter, J.M.; Pieri, L.; Arteni, A.A.; Samson, C.; Jonic, S.; Mathieu, M.; Bressanelli, S. Structure and conformational variability of the HER2-trastuzumab-pertuzumab complex. Journal of Structural Biology 2024, 216, 108095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, A.S.; Sarker, A.; Gupta, R.D. Recent Developments Toward Antibody Engineering and Affinity Maturation. Protein & Peptide Letters 2018, 25, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comeau, S.R.; Thorsteinson, N.; Kumar, S. Structural Considerations in Affinity Maturation of Antibody-Based Biotherapeutic Candidates. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer US, 2022; p. 309–321. [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Al-Hashimi, H.M. AlphaFold3 takes a step toward decoding molecular behavior and biological computation. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 2024, 31, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; Bridgland, A.; Meyer, C.; Kohl, S.A.A.; Ballard, A.J.; Cowie, A.; Romera-Paredes, B.; Nikolov, S.; Jain, R.; Adler, J.; Back, T.; Petersen, S.; Reiman, D.; Clancy, E.; Zielinski, M.; Steinegger, M.; Pacholska, M.; Berghammer, T.; Bodenstein, S.; Silver, D.; Vinyals, O.; Senior, A.W.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Kohli, P.; Hassabis, D. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenidge, P.A.; Kramer, C.; Mozziconacci, J.C.; Wolf, R.M. MM/GBSA Binding Energy Prediction on the PDBbind Data Set: Successes, Failures, and Directions for Further Improvement. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling 2012, 53, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, D.W.M.; Kuleshova, L.N. A general force field by machine learning on experimental crystal structures. Calculations of intermolecular Gibbs energy with iFlexCryst. Acta Crystallographica Section A Foundations and Advances 2023, 79, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, P. AlphaFold2 and the future of structural biology. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 2021, 28, 704–705. [Google Scholar]
- Read, R.J.; Baker, E.N.; Bond, C.S.; Garman, E.F.; van Raaij, M.J. AlphaFold and the future of structural biology. Acta Crystallographica Section D Structural Biology 2023, 79, 556–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Shen, L.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. Surface-based multimodal protein–ligand binding affinity prediction. Bioinformatics 2024, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; He, X.; Li, M.; Shao, B.; Liu, T.Y. AIMD-Chig: Exploring the conformational space of a 166-atom protein Chignolin with ab initio molecular dynamics. Scientific Data 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, C.E.; Hansen, F.K.; Gütschow, M.; Lindsley, C.W.; Liotta, D. New Drug Modalities in Medicinal Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Translational Science. ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science 2021, 4, 1712–1713. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, B.; Stall, S.; Cutcher-Gershenfeld, J.; Vrouwenvelder, K.; Wirz, C.; Rao, Y.; Peng, G. Garbage in, garbage out: Mitigating risks and maximizing benefits of AI in research. Nature 2023, 623, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Vottevor, G. Towards a Truly General Intermolecular Binding Affinity Calculator for Drug Discovery & Design 2023. [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.S.; Honig, B. On the pH Dependence of Protein Stability. Journal of Molecular Biology 1993, 231, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, T.K.; Turner, G.J. Structural Basis of Perturbed pKa Values of Catalytic Groups in Enzyme Active Sites. IUBMB Life (International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology: Life) 2002, 53, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Gravity-driven pH adjustment for site-specific protein pKa measurement by solution-state NMR. Measurement Science and Technology 2017, 28, 127002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.L.; Kay, L.E. Measurement of histidine pKa values and tautomer populations in invisible protein states. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2014, 111, E1705–E1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herget, S.; Ranzinger, R.; Maass, K.; Lieth, C.W. GlycoCT—a unifying sequence format for carbohydrates. Carbohydrate Research 2008, 343, 2162–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.M.; Moreno, P.; Fabregat, A.; Hermjakob, H.; Steinbeck, C.; Apweiler, R.; Wakelam, M.J.O.; Vizcaíno, J.A. LipidHome: A Database of Theoretical Lipids Optimized for High Throughput Mass Spectrometry Lipidomics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, M.H.M.; Søndergaard, C.R.; Rostkowski, M.; Jensen, J.H. PROPKA3: Consistent Treatment of Internal and Surface Residues in Empirical pKa Predictions. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation 2011, 7, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Ju, T.; Niu, W.; Guo, J. Fine-tuning Interaction between Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase and tRNA for Efficient Synthesis of Proteins Containing Unnatural Amino Acids. ACS Synthetic Biology 2014, 4, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 6|cSize (s) of the synthetic structural and biophysical data set | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semaglutide backbone (28 Aa) | Molecule X (100 Aa) | ||||
| g(28,1) | 560 | g(100,1) | 2000 | ||
| g(28,2) | 151200 | g(100,2) | 1980000 | ||
| g(28,3) | 26208000 | g(100,3) | 1293600000 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





