Submitted:
22 August 2024
Posted:
22 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Fluid Model, Plasma Chemistry and Reactor Configuration
2.1. Fluid Model Formula
2.1.1. Electrons Equation
2.1.2. Heavy Species Equation
2.1.3. Electromagnetic Equation
2.1.4. Electrostatic Equation
2.2. Chemistry of Ar/SF6 Plasma
| No. | Reaction | Rate coefficienta | Threshold (eV) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elastic collisions | ||||
| 1 | Cross Section | 0 | [25] | |
| 2 | Cross Section | 0 | [25] | |
| 3 | Cross Section | 0 | [25] | |
| 4 | Cross Section | 0 | [25] | |
| Excitation and deexcitation reactions | ||||
| 5 | Cross Section | 11.6 | [25] | |
| 6 | Cross Section | -11.6 | [25] | |
| Ionization reactions | ||||
| 7 | Cross Section | 15.76 | [25] | |
| 8 | Cross Section | 4.43 | [25] | |
| 9 | 16 | [26,27] | ||
| 10 | 20 | [26,27] | ||
| 11 | 20.5 | [26,27] | ||
| 12 | 28 | [26,27] | ||
| 13 | 37.5 | [26,27] | ||
| 14 | 29 | [26,27] | ||
| 15 | 18 | [26,27] | ||
| 16 | 11 | [26,27] | ||
| 17 | 15 | [26,27] | ||
| 18 | 13 | [26,27] | ||
| 19 | 14.5 | [26,27] | ||
| 20 | 11 | [26,27] | ||
| 21 | 15 | [26,27] | ||
| 22 | 10 | [26,27] | ||
| 23 | 15.69 | [26,27] | ||
| Attachment and dissociative attachment reactions | ||||
| 24 | Cross Section | 0 | [25] | |
| 25 | Cross Section | 0.1 | [25] | |
| 26 | Cross Section | 5.4 | [25] | |
| 27 | Cross Section | 11.2 | [25] | |
| 28 | Cross Section | 12 | [25] | |
| 29 | Cross Section | 2.9 | [25] | |
| 30 | Cross Section | 5.4 | [25] | |
| 31 | Cross Section | 0 | [25] | |
| Dissociation reactions | ||||
| 32 | 9.6 | [26,27] | ||
| 33 | 12.4 | [26,27] | ||
| 34 | 16 | [26,27] | ||
| 35 | 18.6 | [26,27] | ||
| 36 | 22.7 | [26,27] | ||
| 37 | 5 | [26,27] | ||
| 38 | 8.5 | [26,27] | ||
| 39 | 5 | [26,27] | ||
| 40 | 8 | [26,27] | ||
| 41 | 7.9 | [26,27] | ||
| 42 | 1.6 | [26,27] | ||
| Neutral / neutral recombination reactions | ||||
| 43 | 0 | [26,27] | ||
| 44 | 0 | [26,27] | ||
| 45 | 0 | [26,27] | ||
| 46 | 0 | [26,27] | ||
| 47 | 0 | [26,27] | ||
| 48 | 0 | [26,27] | ||
| 49 | 0 | [26,27] | ||
| 50 | 0 | [26,27] | ||
| 51 | 0 | [26,27] | ||
| 52 | b | 0 | [26,27] | |
| Ion / ion recombination reactions | ||||
| 53 | c | 0 | [26,27] | |
| Detachment reactions | ||||
| 54 | d | 0 | [26,27] | |
| Other reactions | ||||
| 55 | 0 | [26,27] | ||
| 56 | 0 | [26,27] | ||
| 57 | 0 | [26,27] | ||
| 58 | 0 | [26,27] | ||
2.3. Chemistry of Ar/O2 Plasma and O- Chemical Kinetics
2.4. ICP Reactor Configuration
3. Results
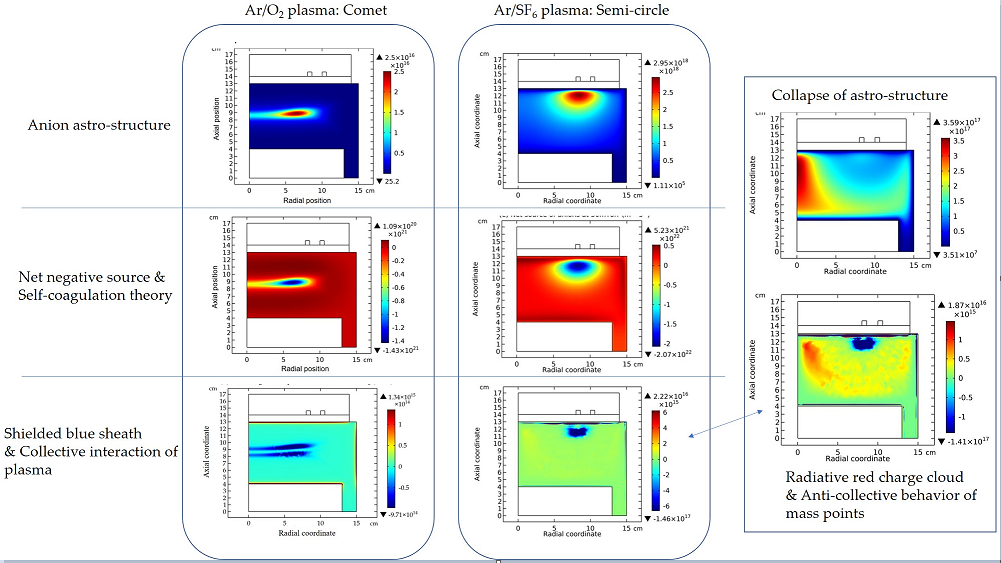
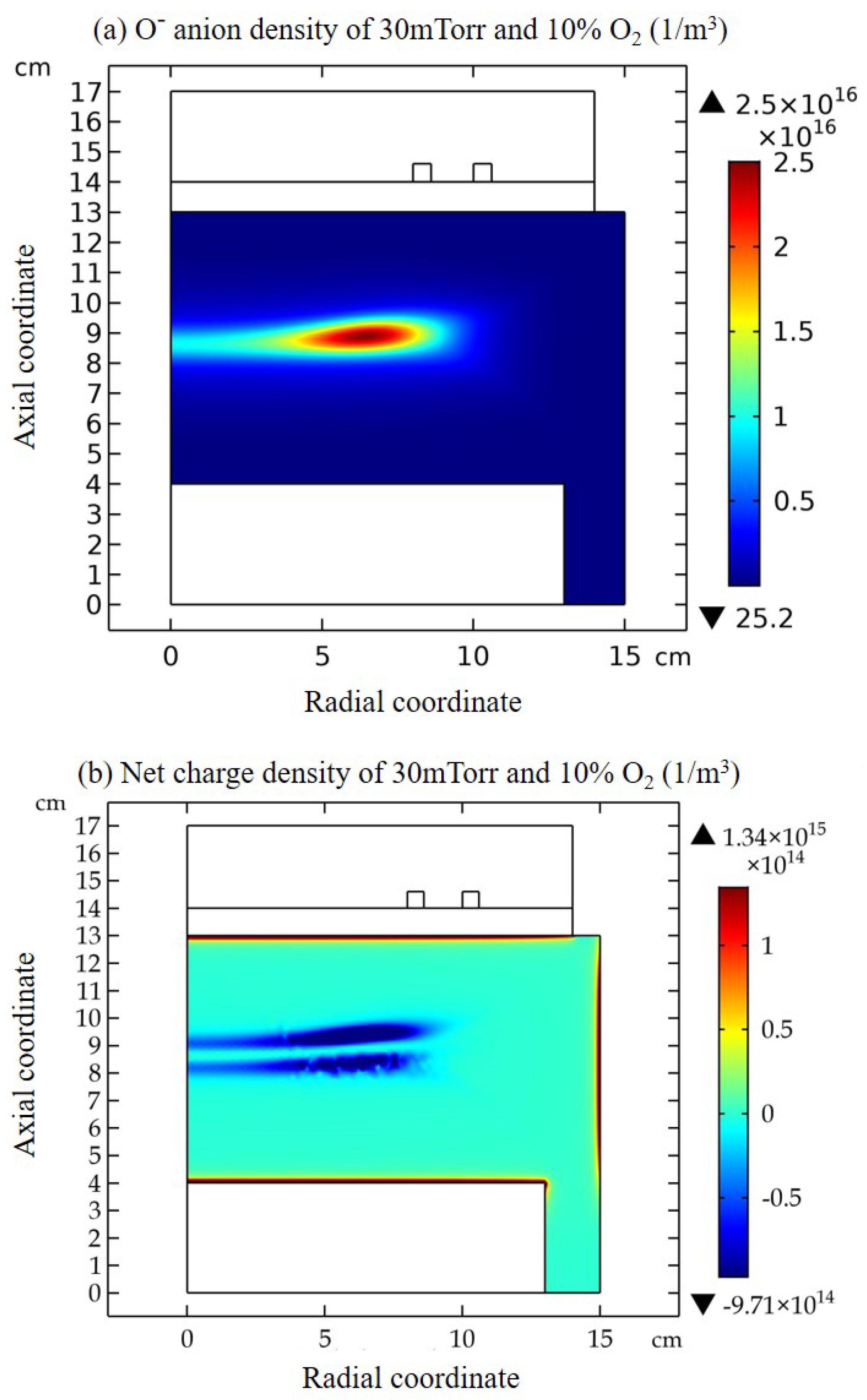
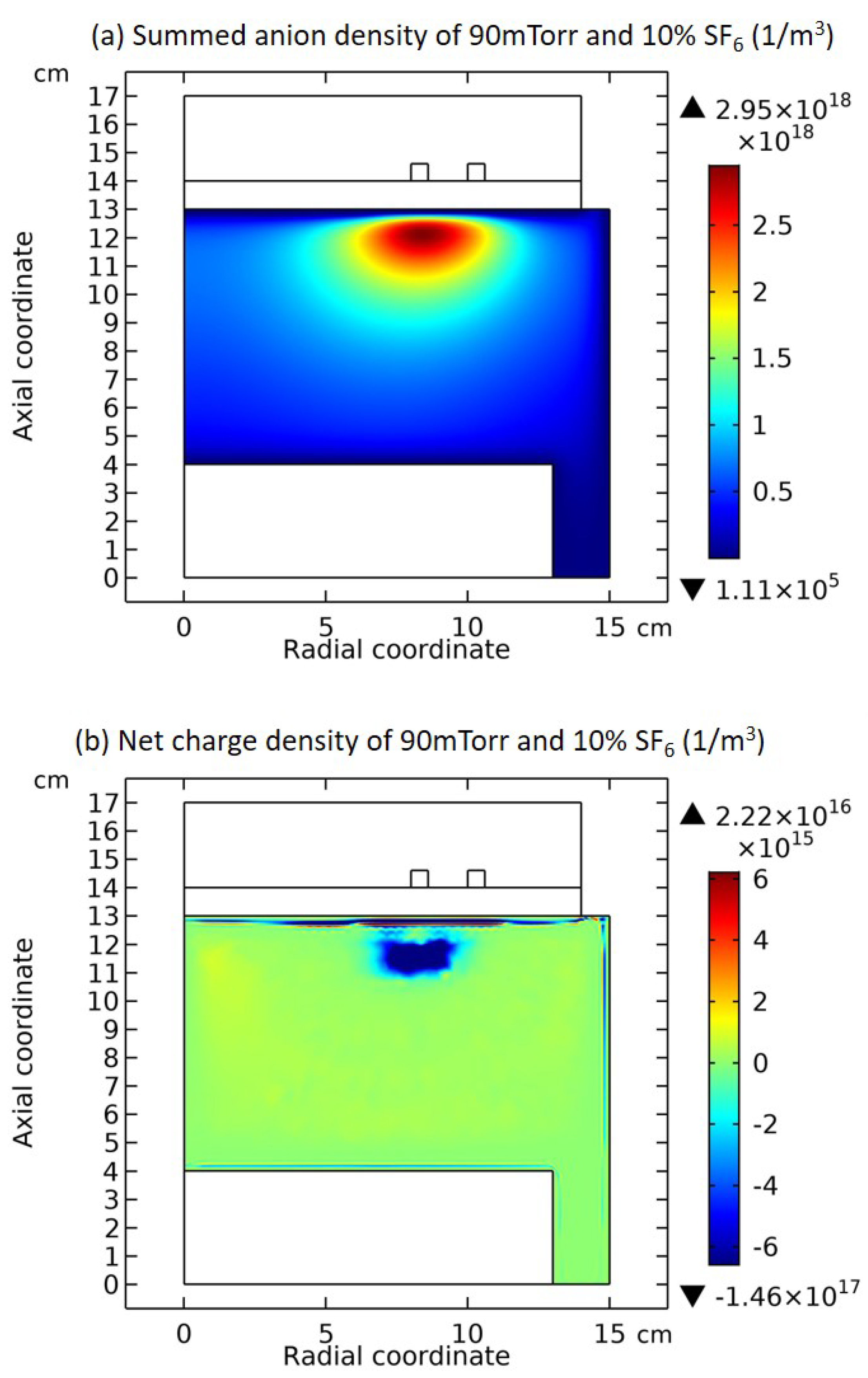
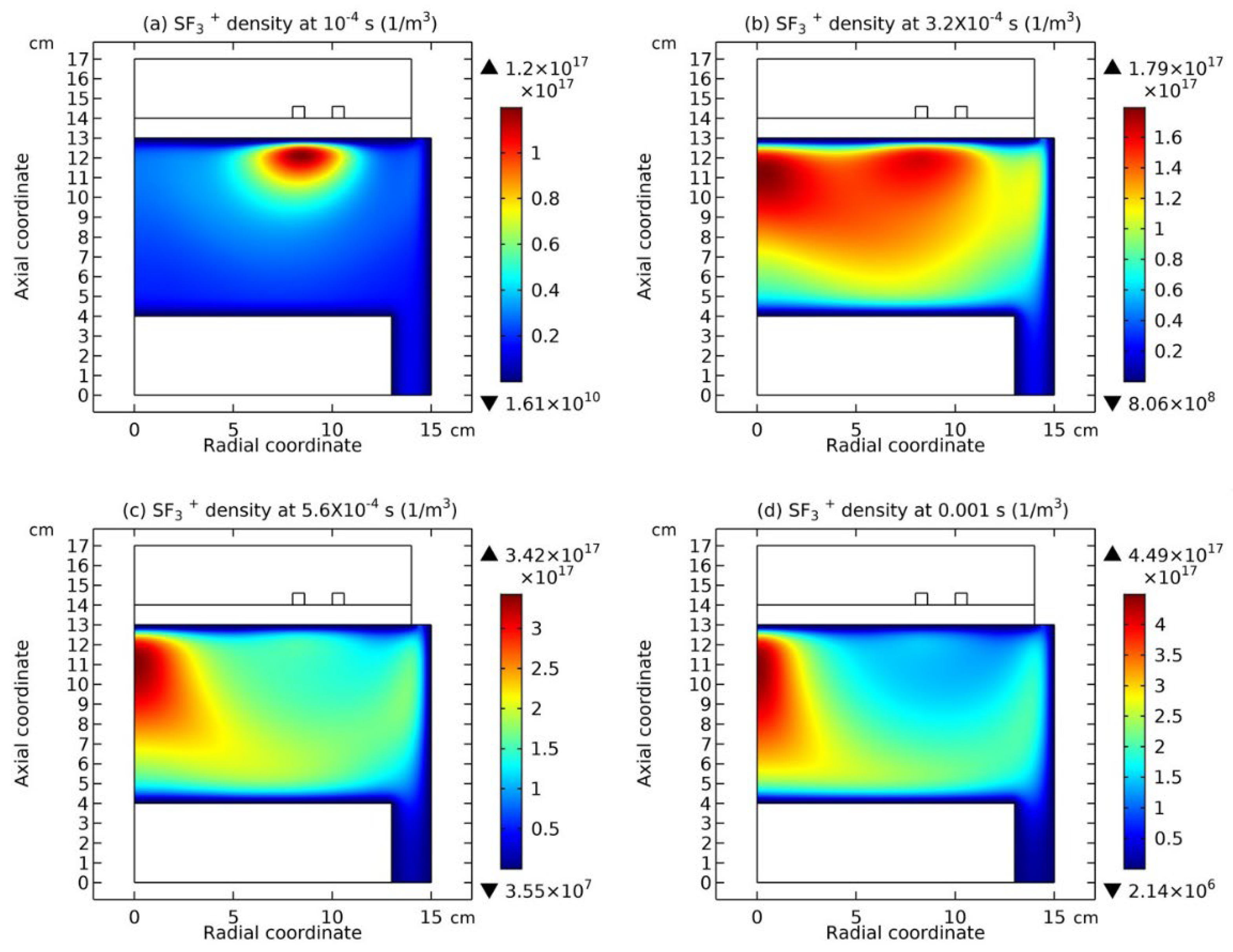
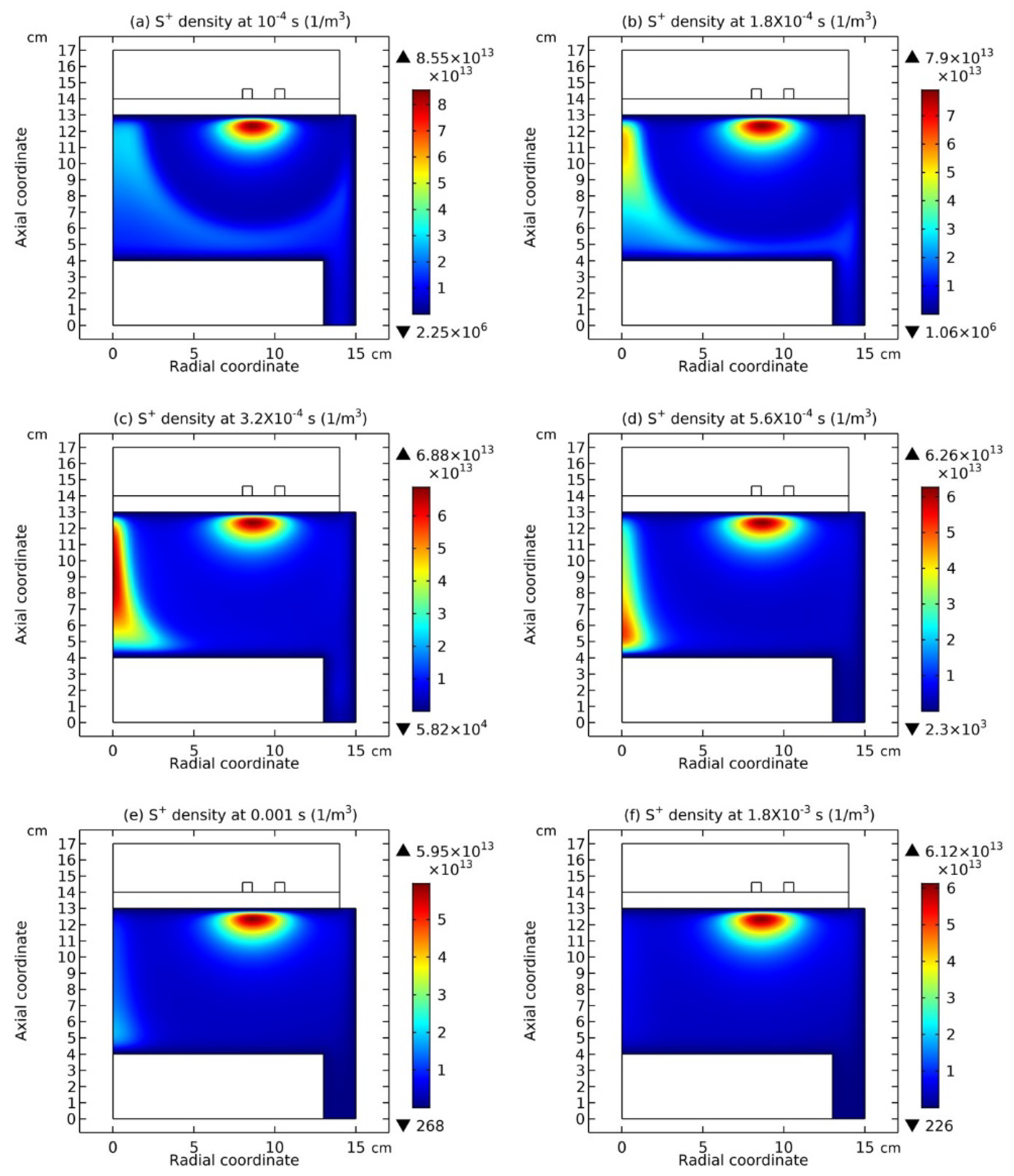
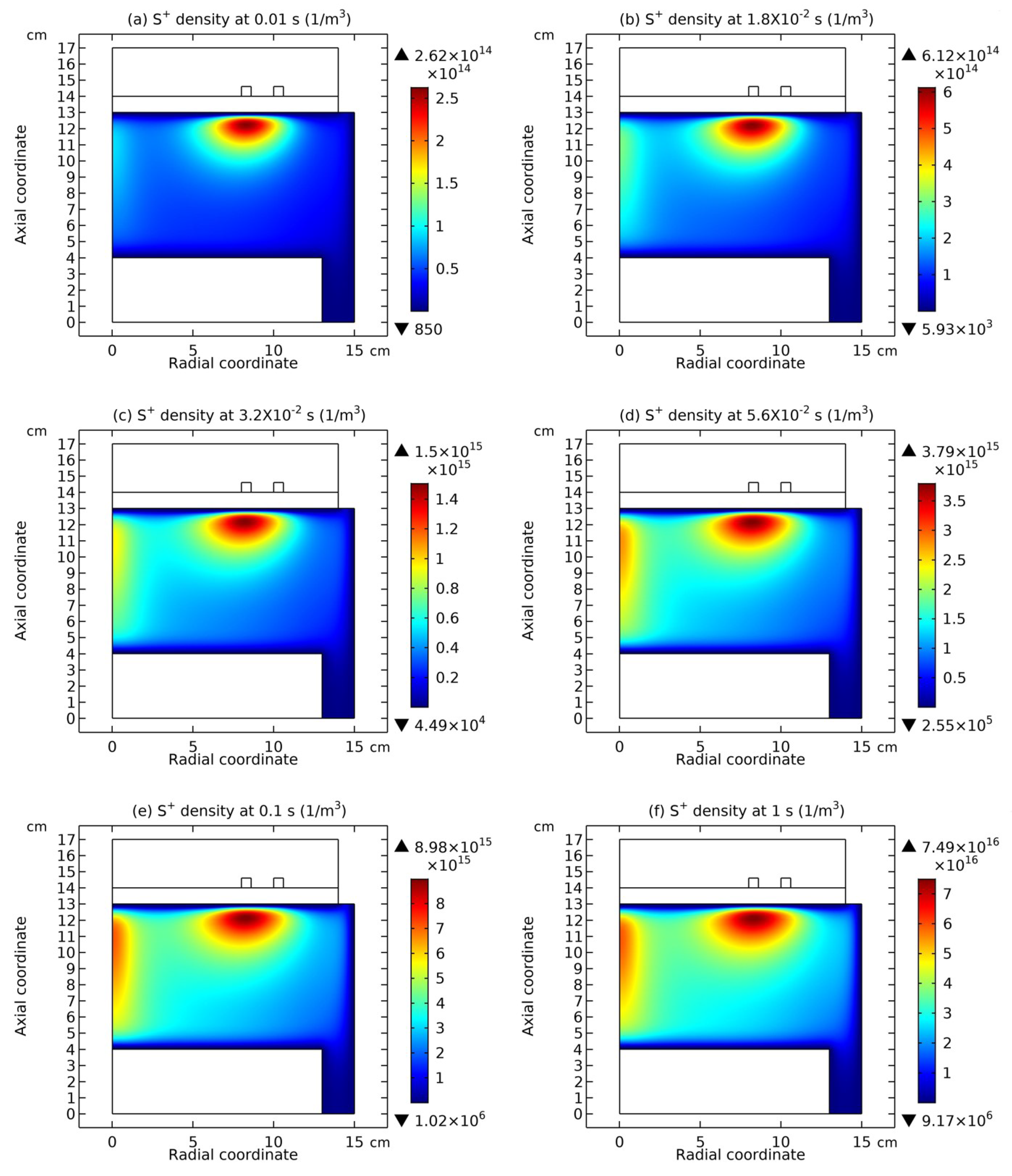
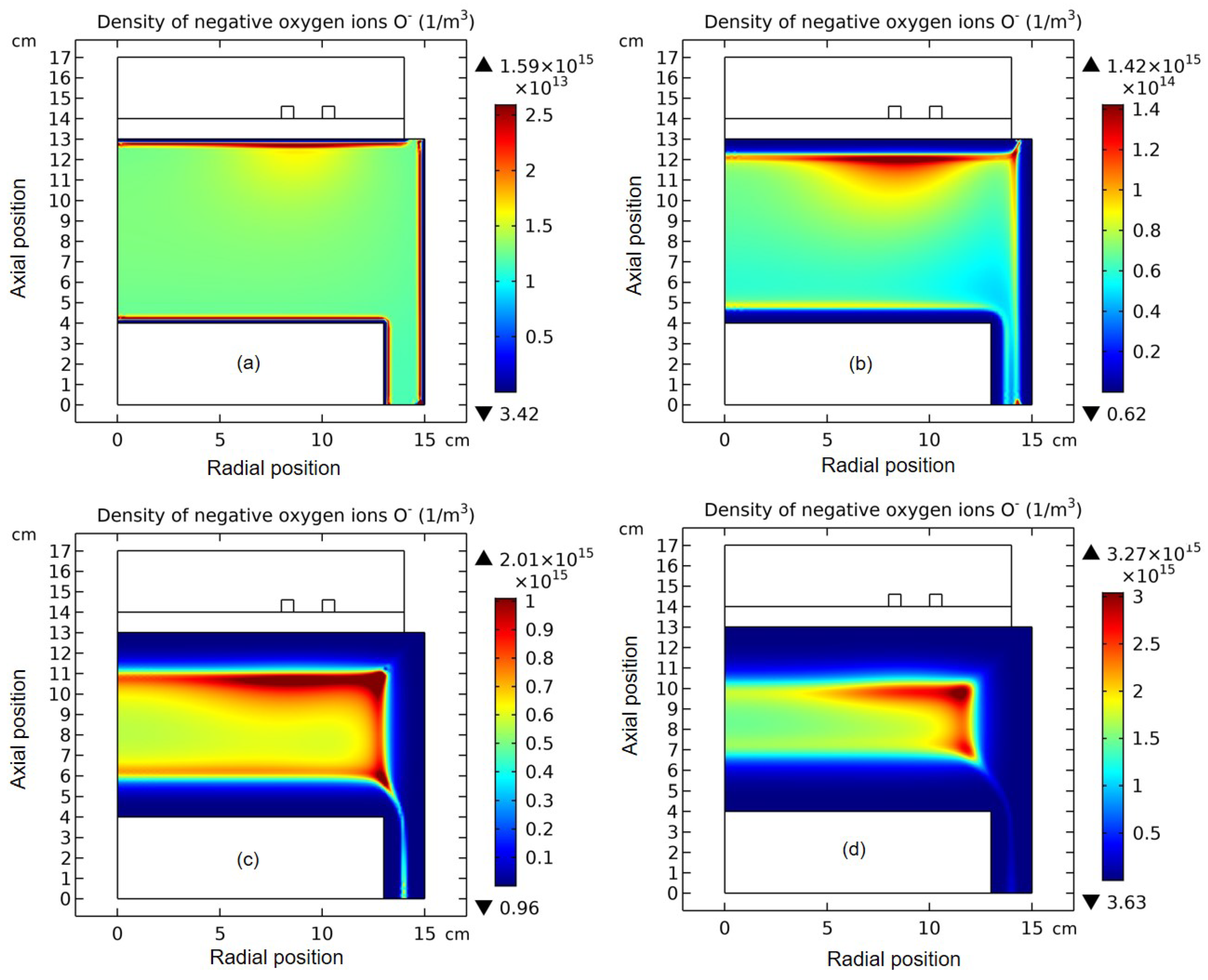
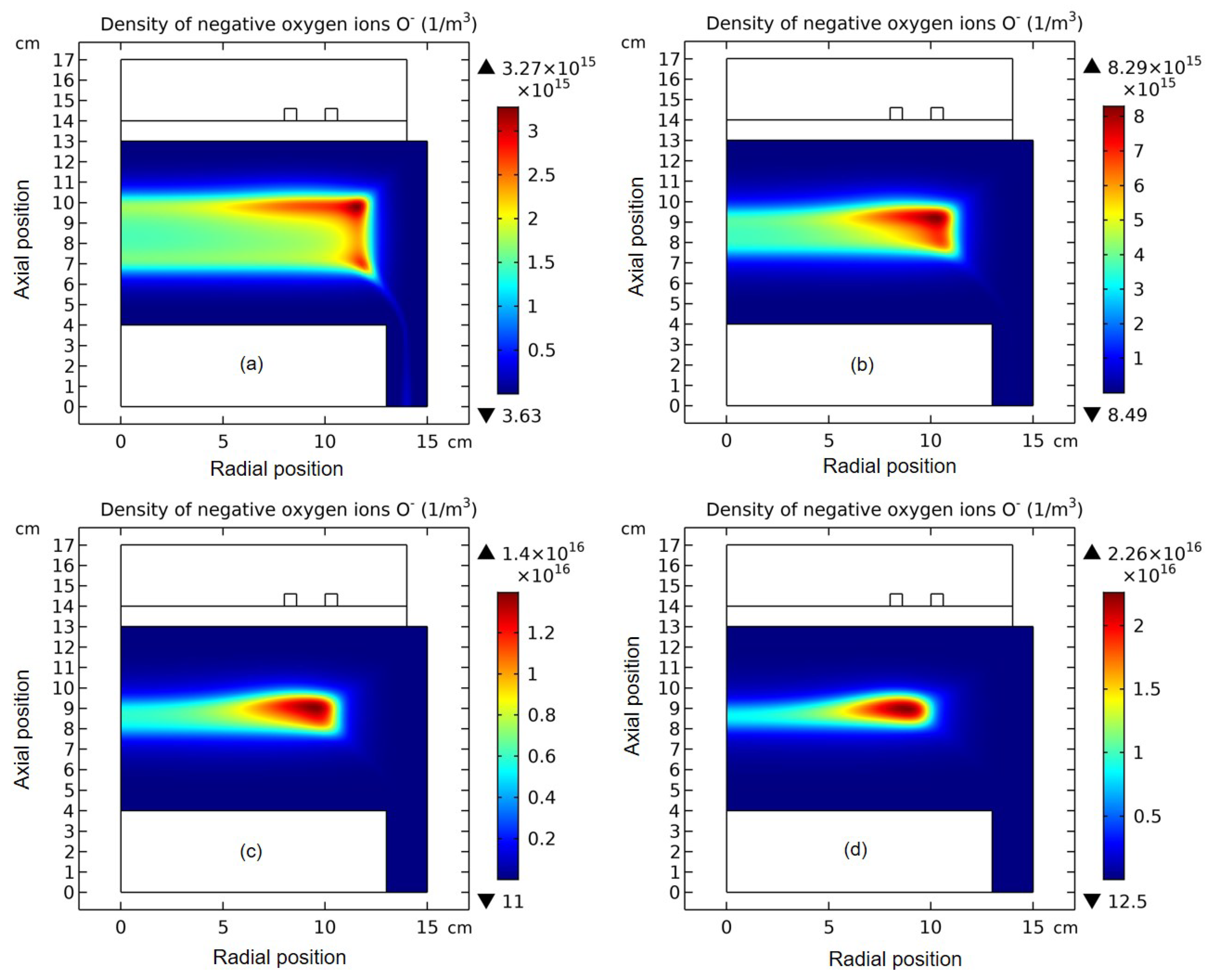
3.1. Comet Structure
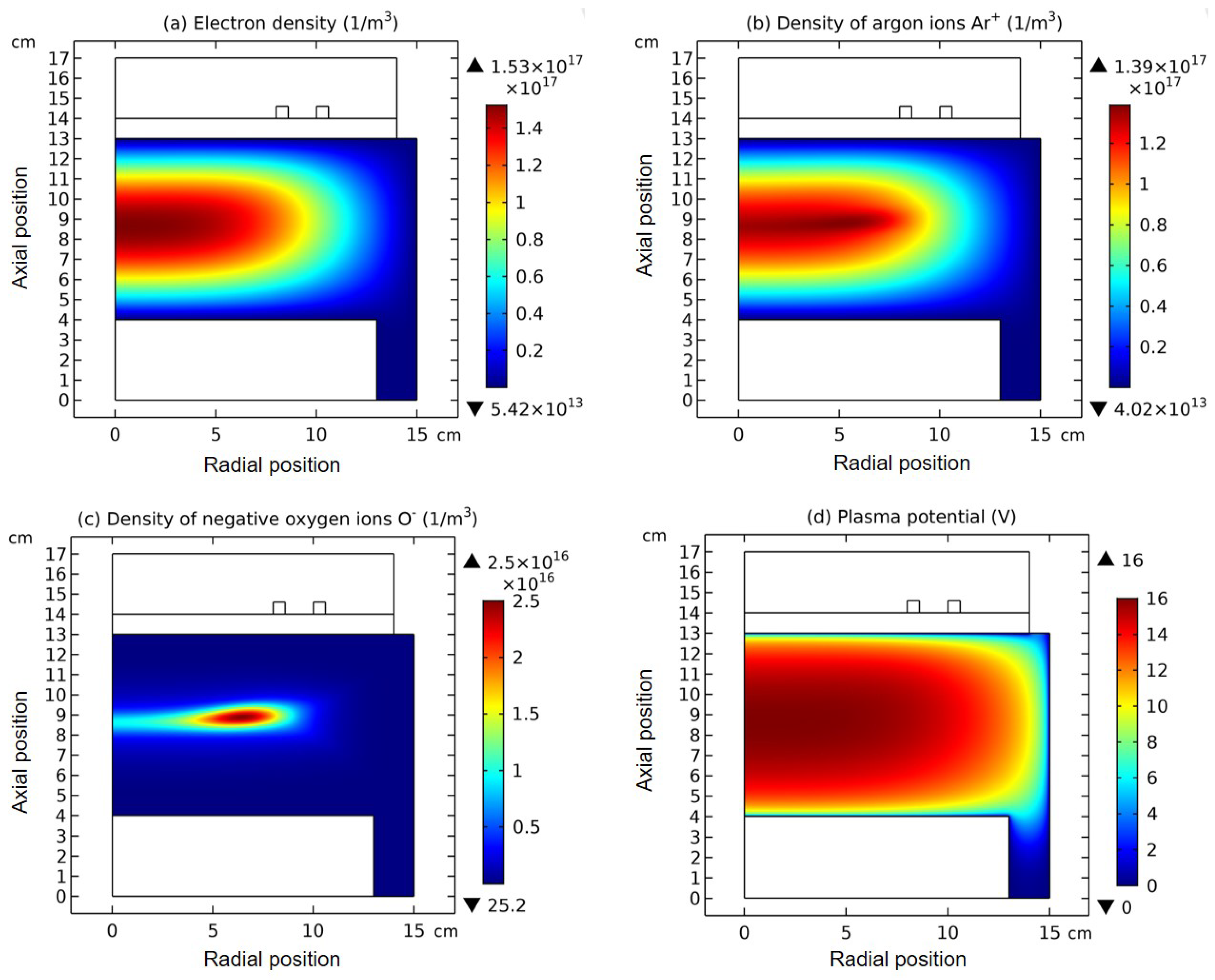
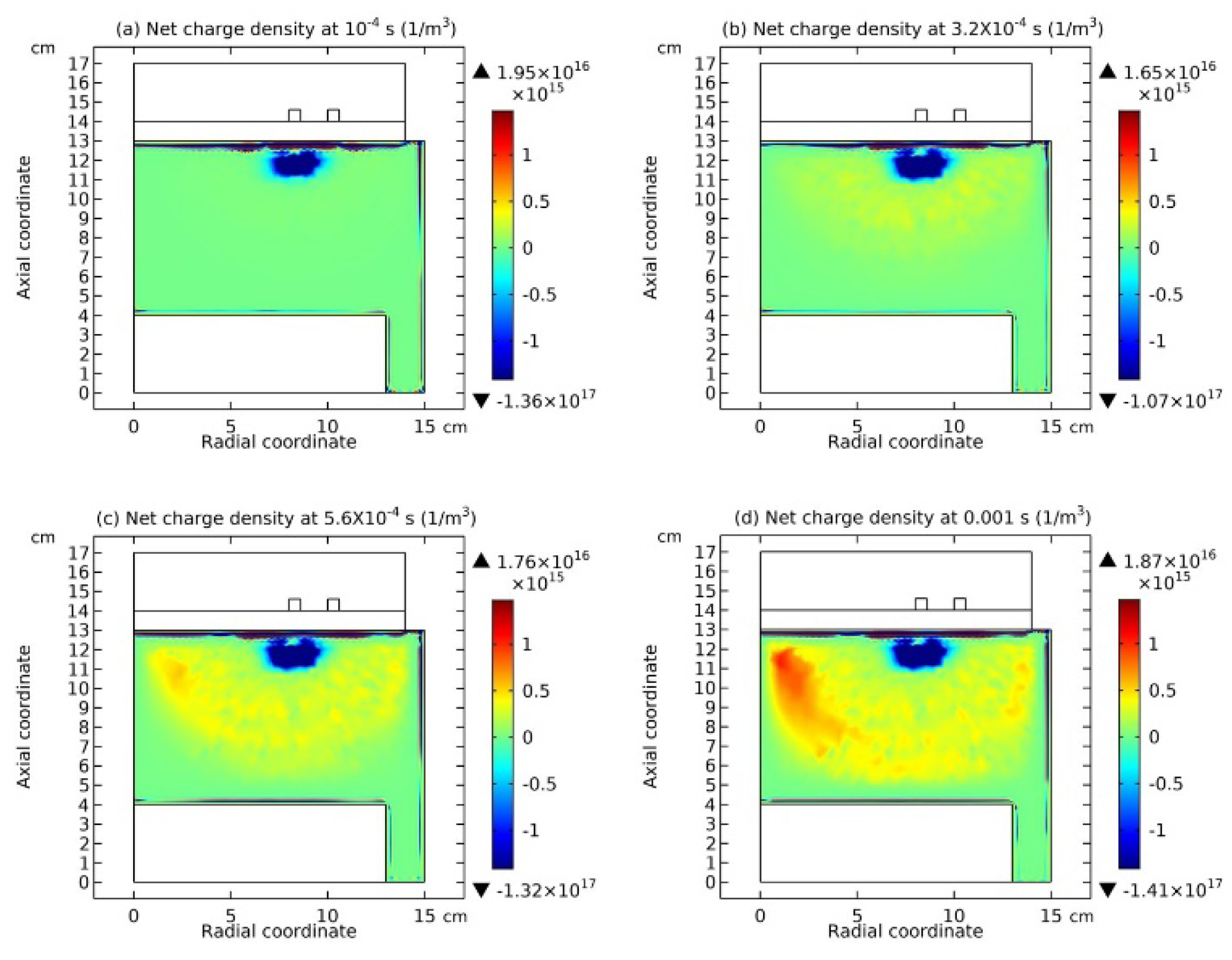
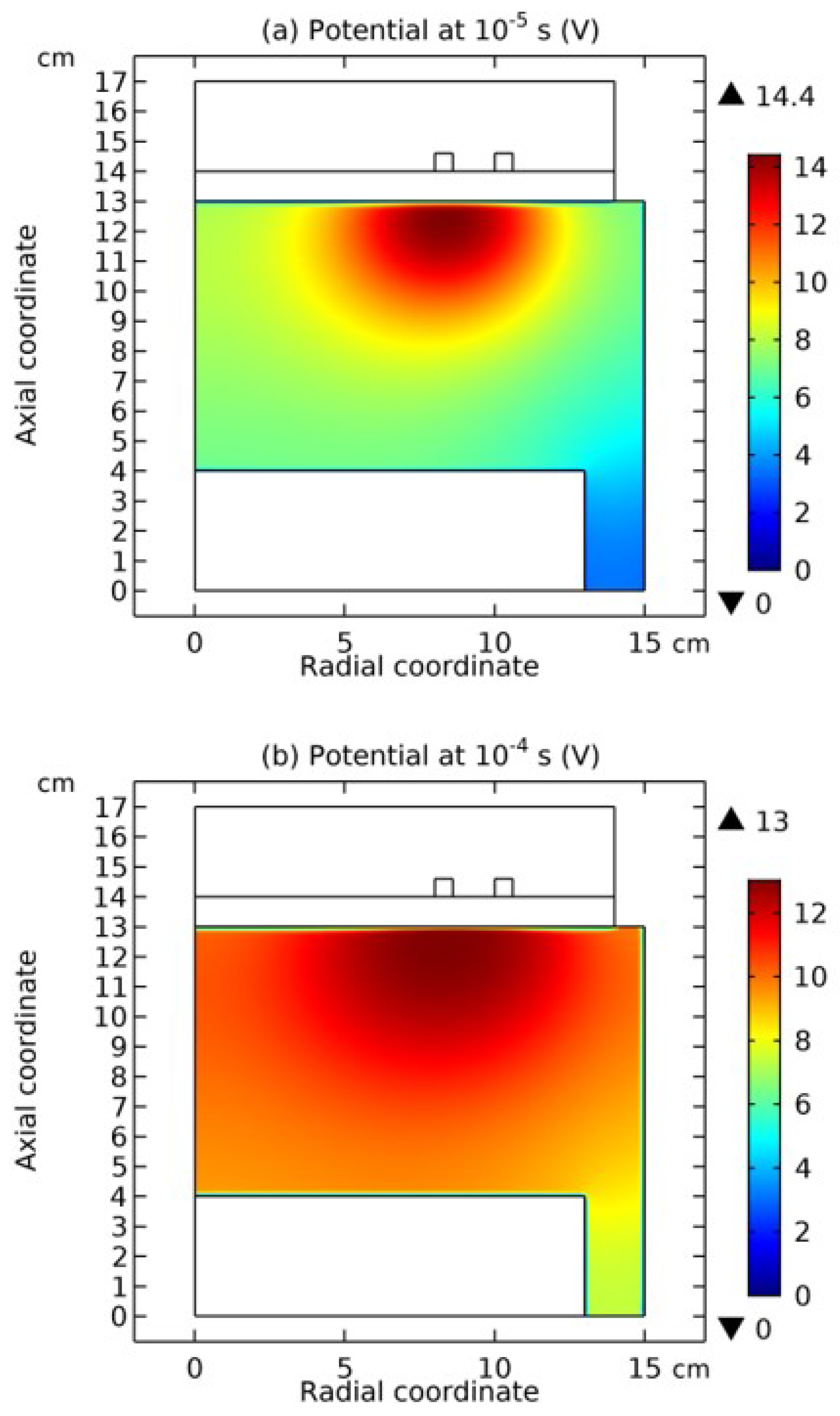
3.2. Blue Sheath Phenomenon
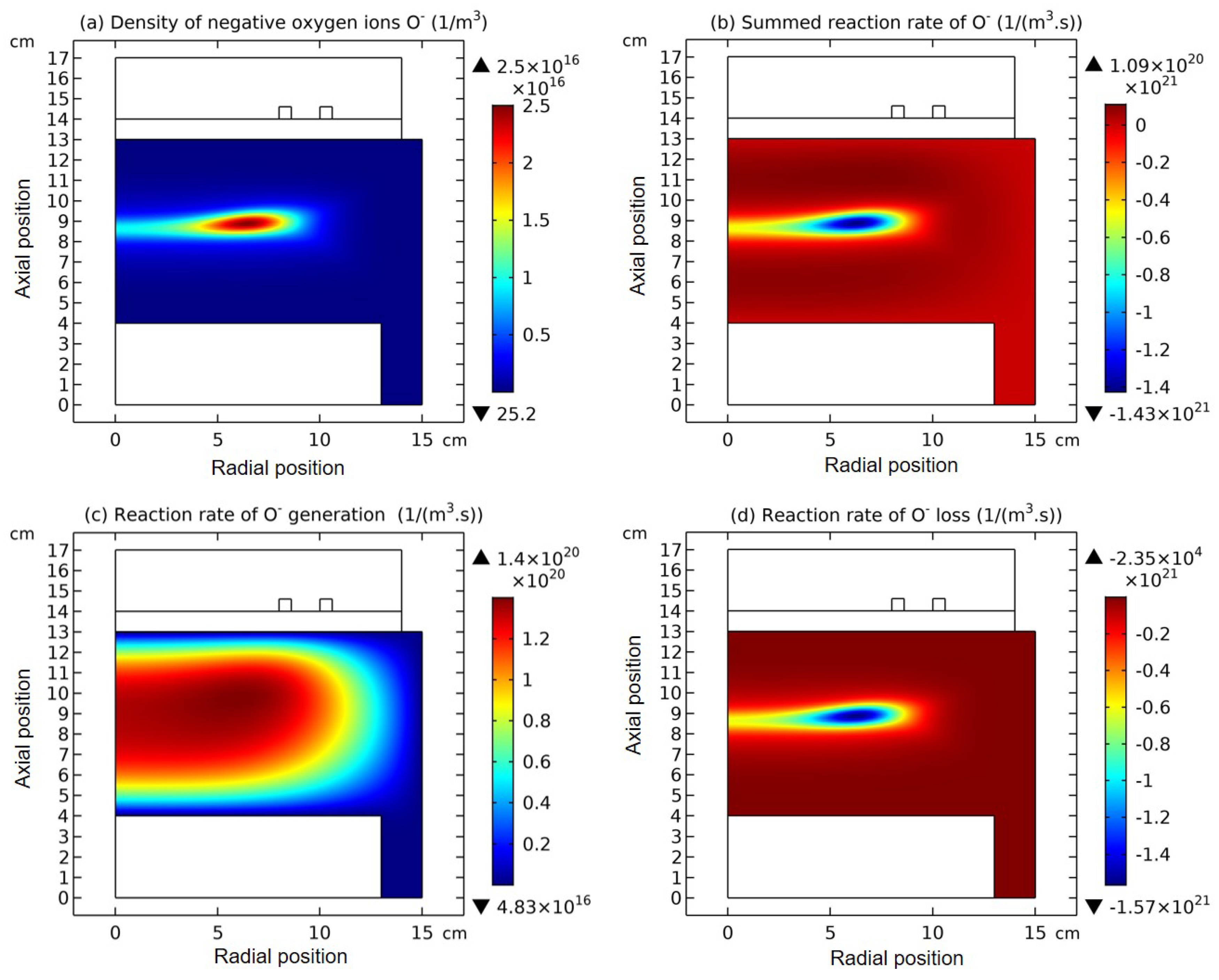
3.3. Collapse of Individual Semi-Circle Structure
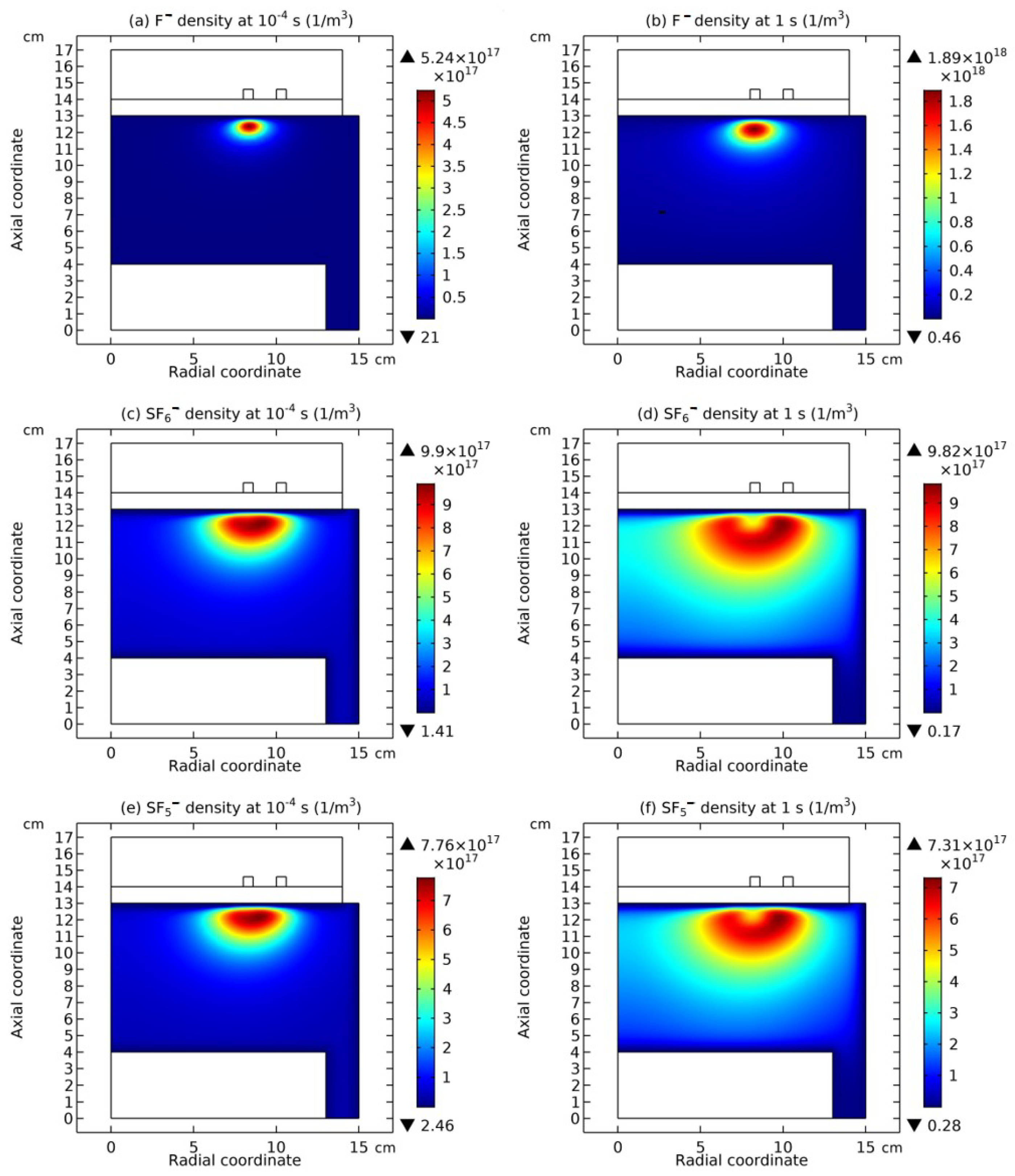
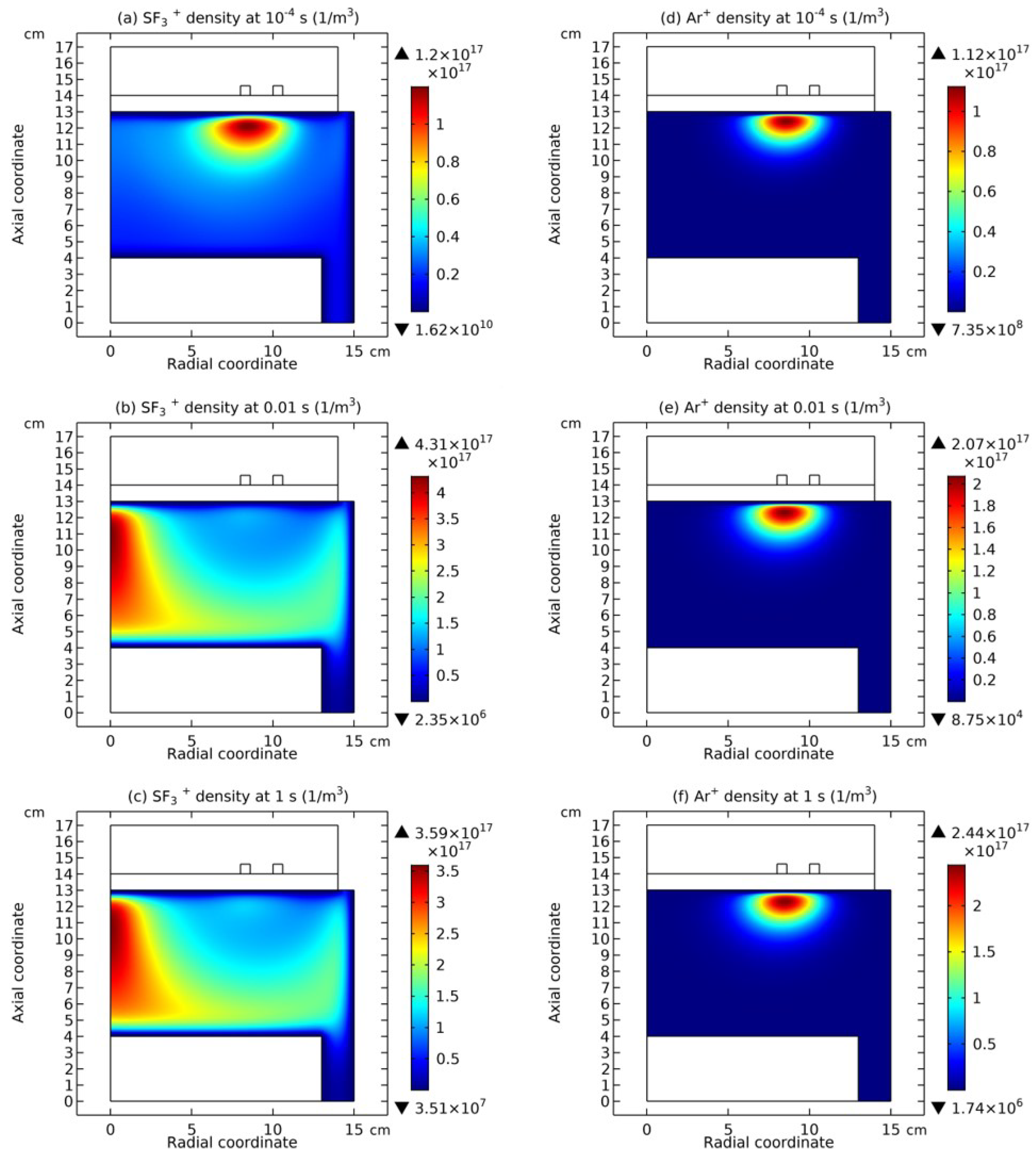
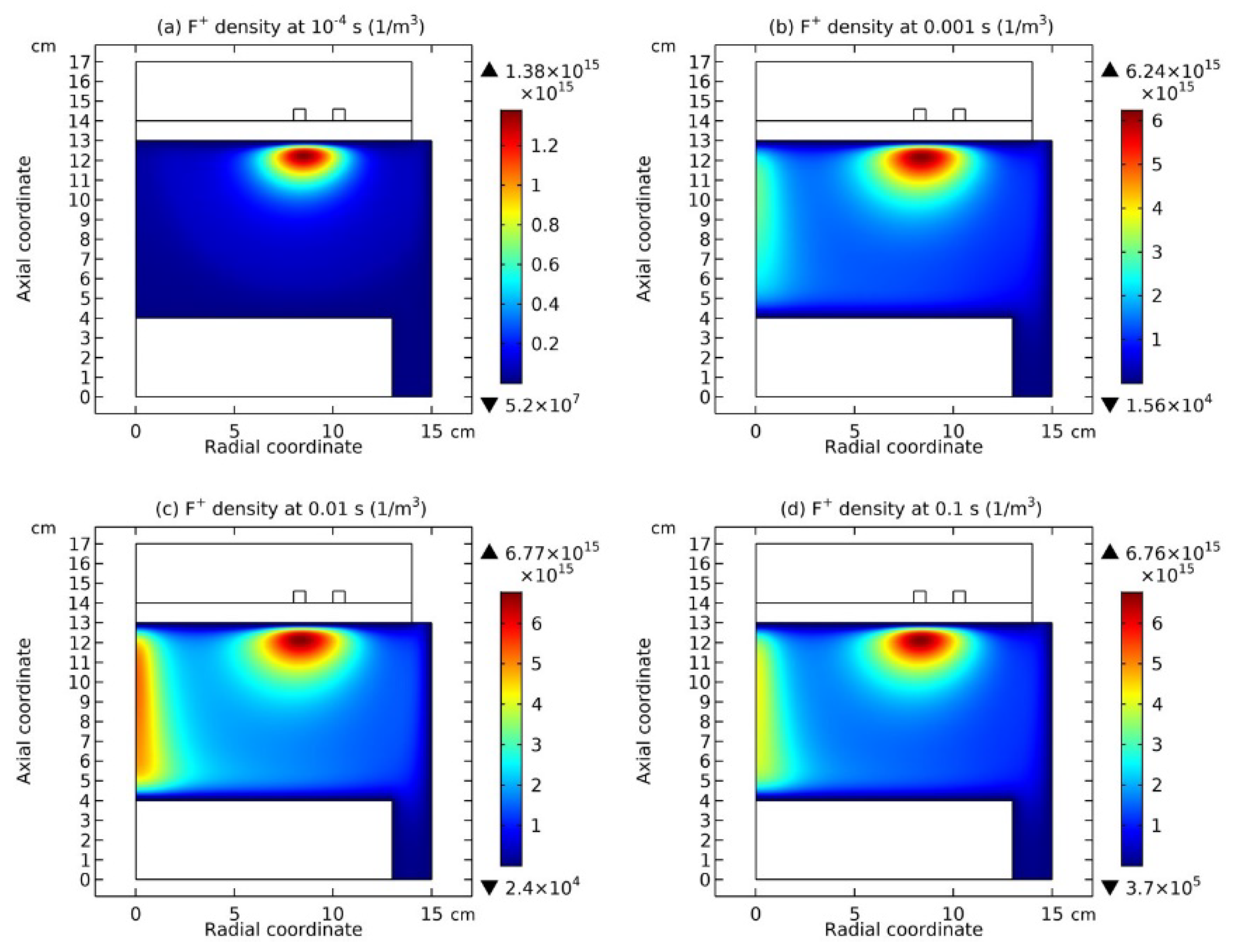
3.4. Rebuilding of Astro-Structure by Minor Species
4. Discussion
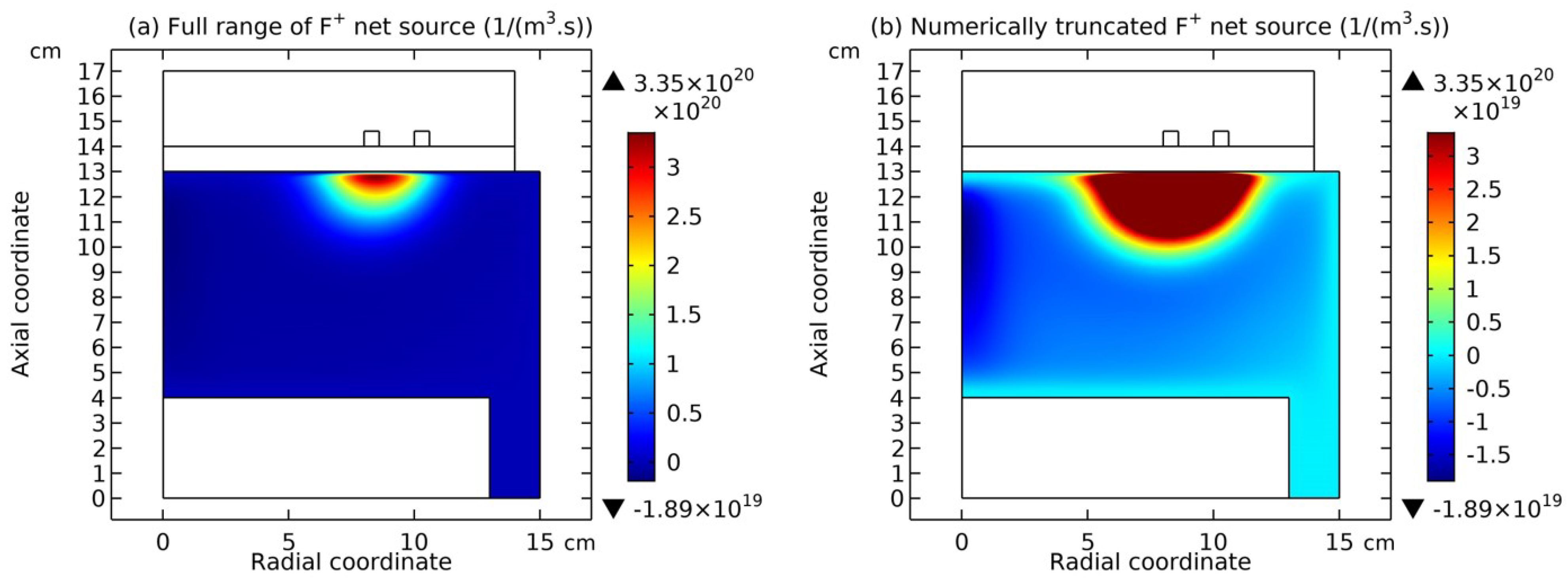
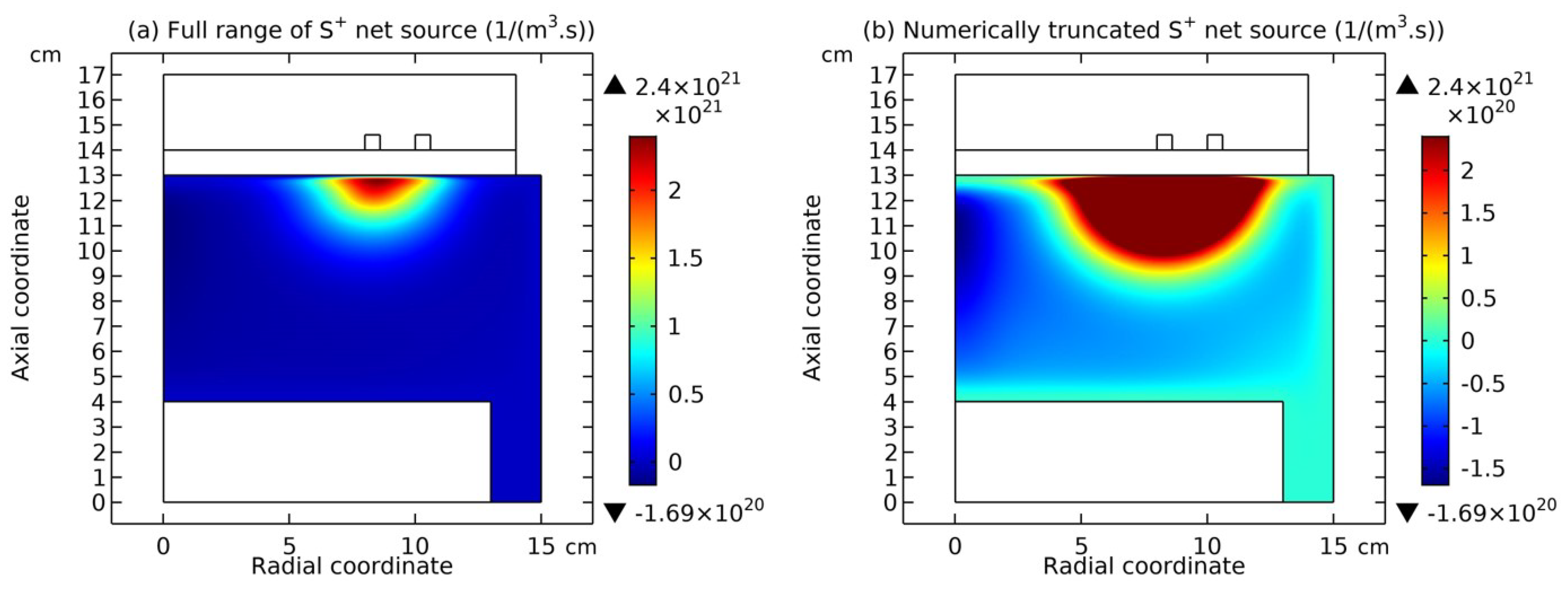
4.1. Self-Coagulation Theory
4.2. Advective Ambi-Polar Self-Coagulation
4.2.1. Comet Structrure for Advective Type
4.2.2. Semi-Circle Structrure for Ambi-Polar Type
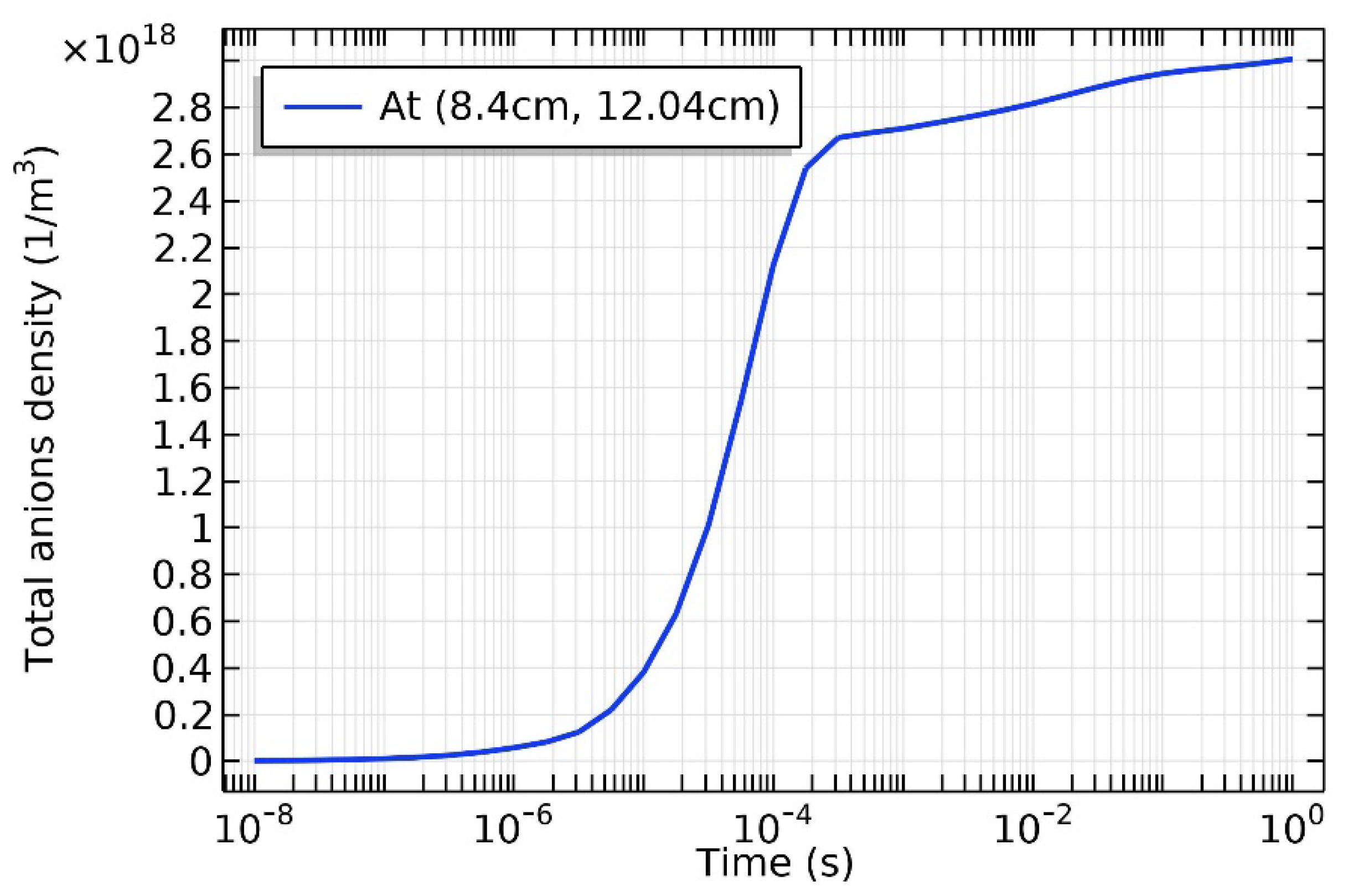
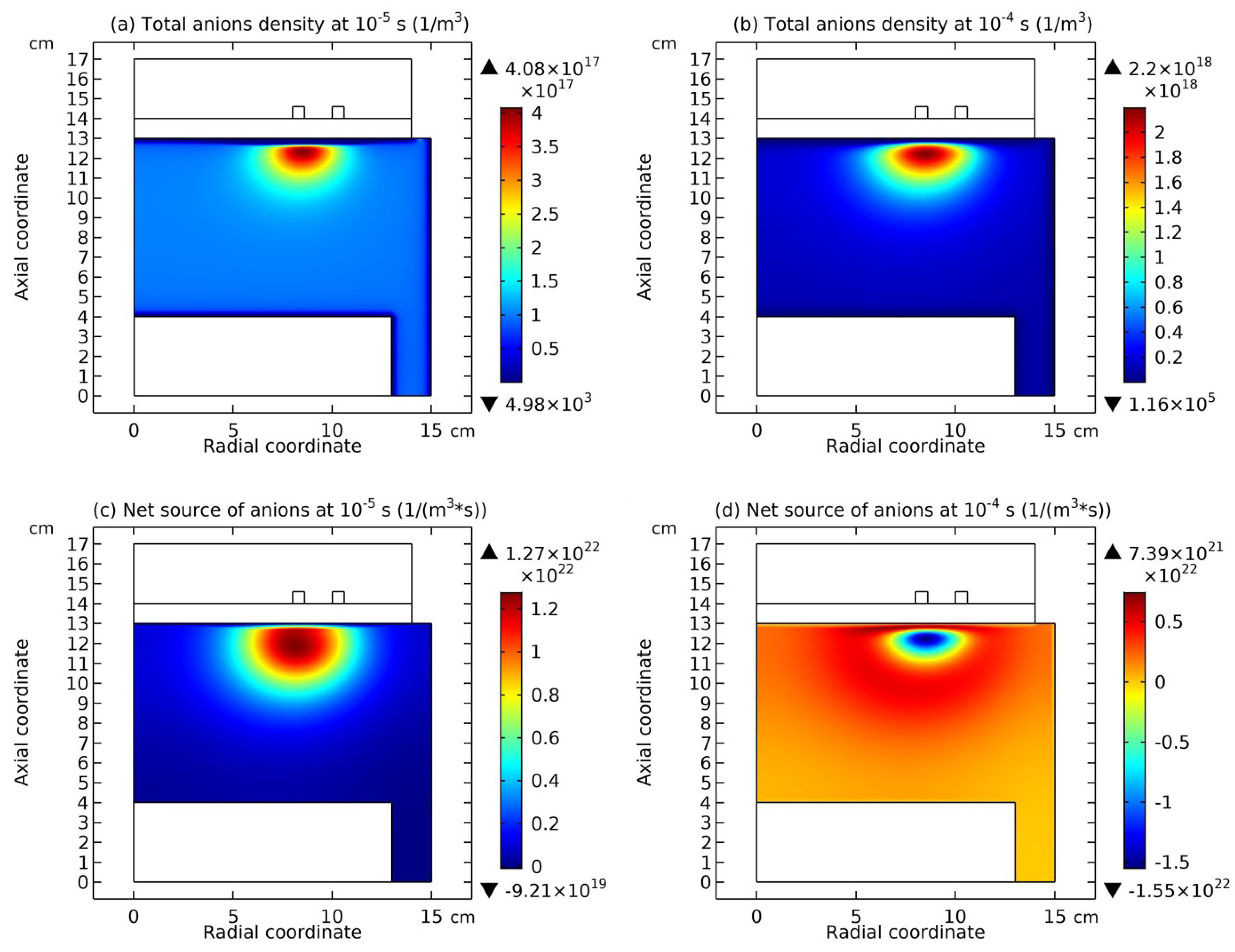
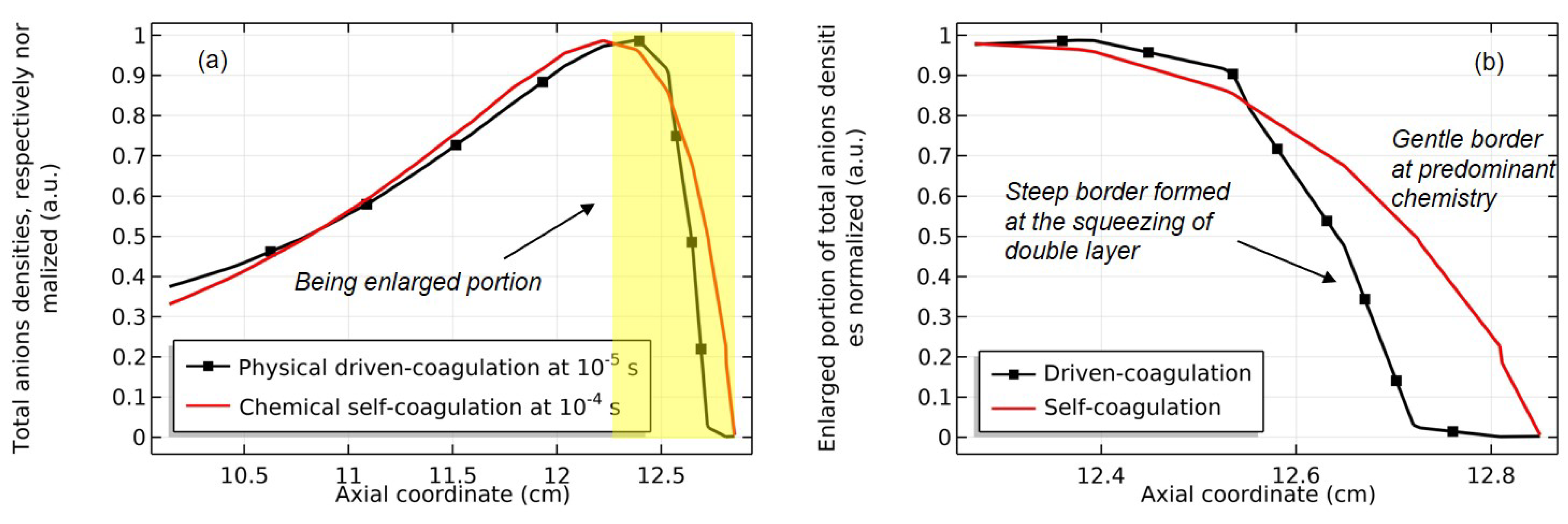
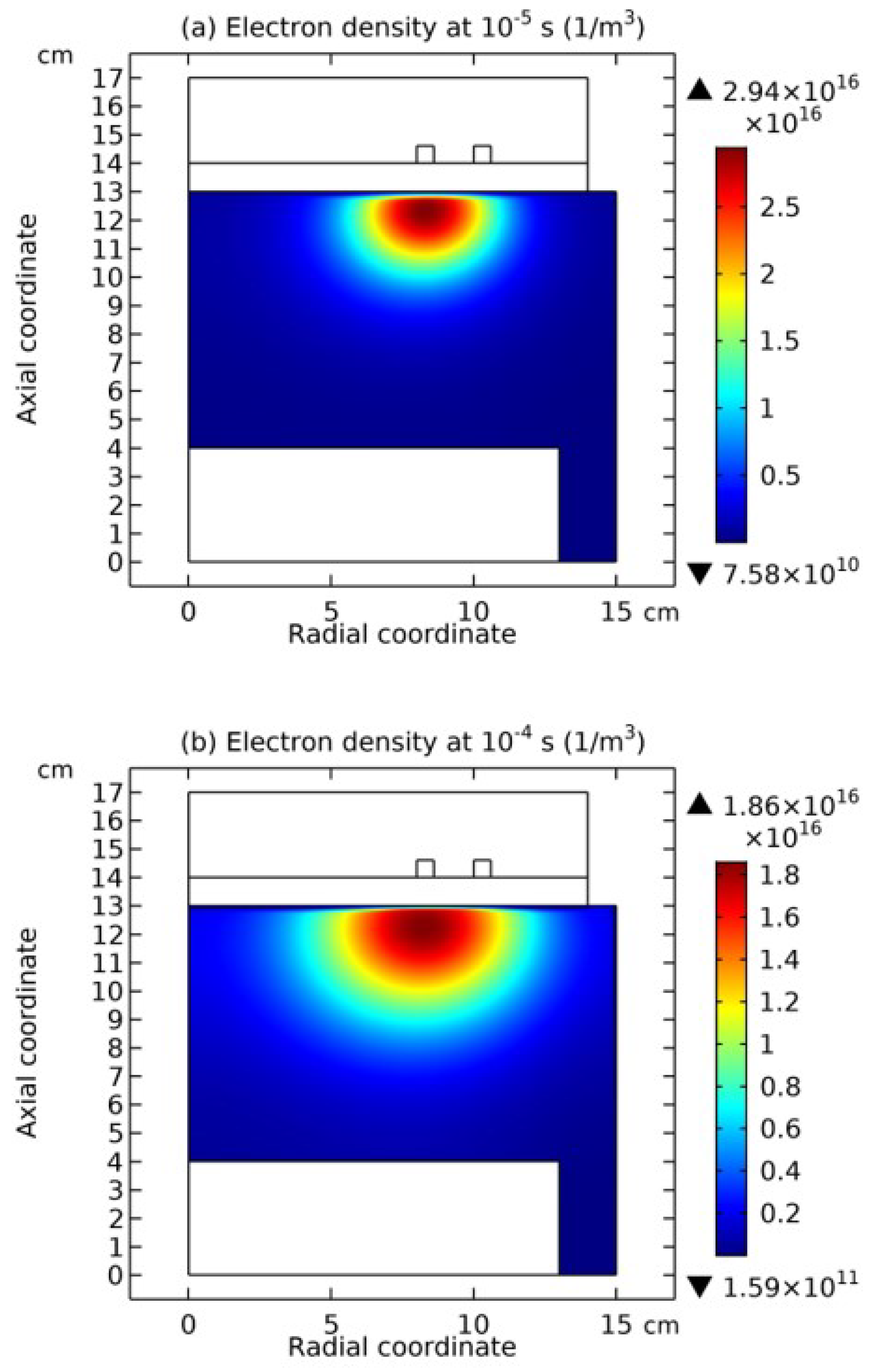
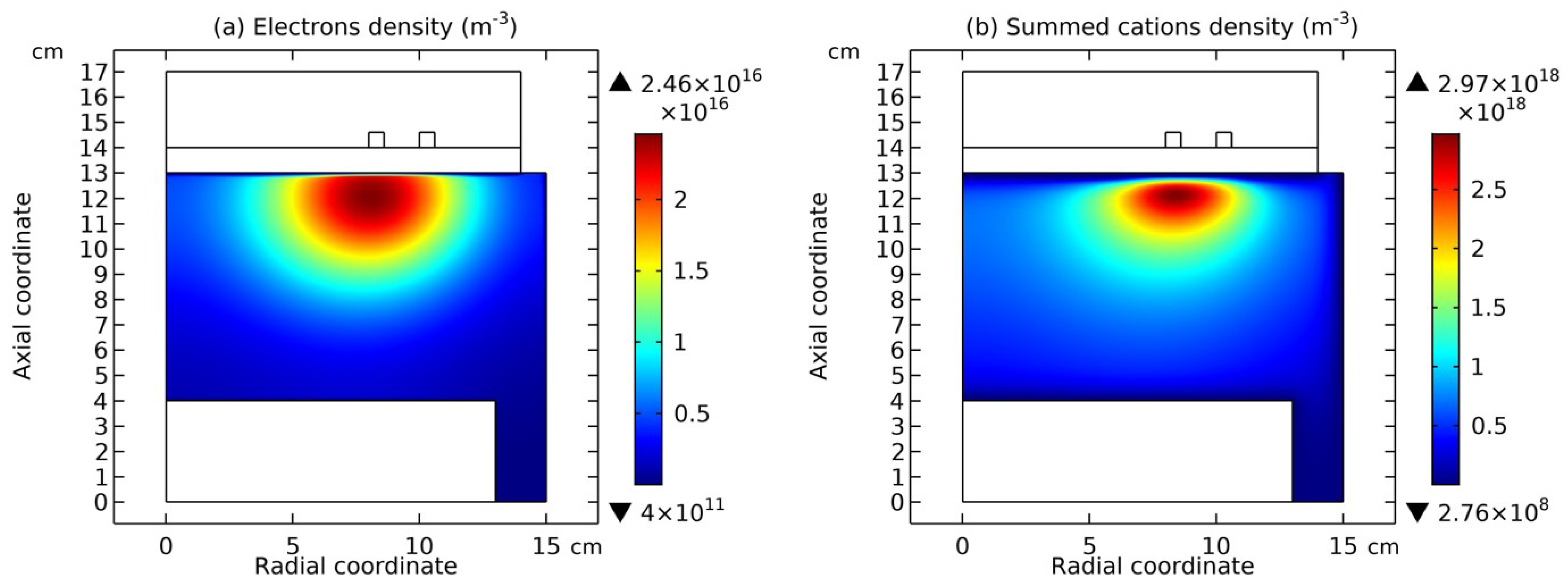
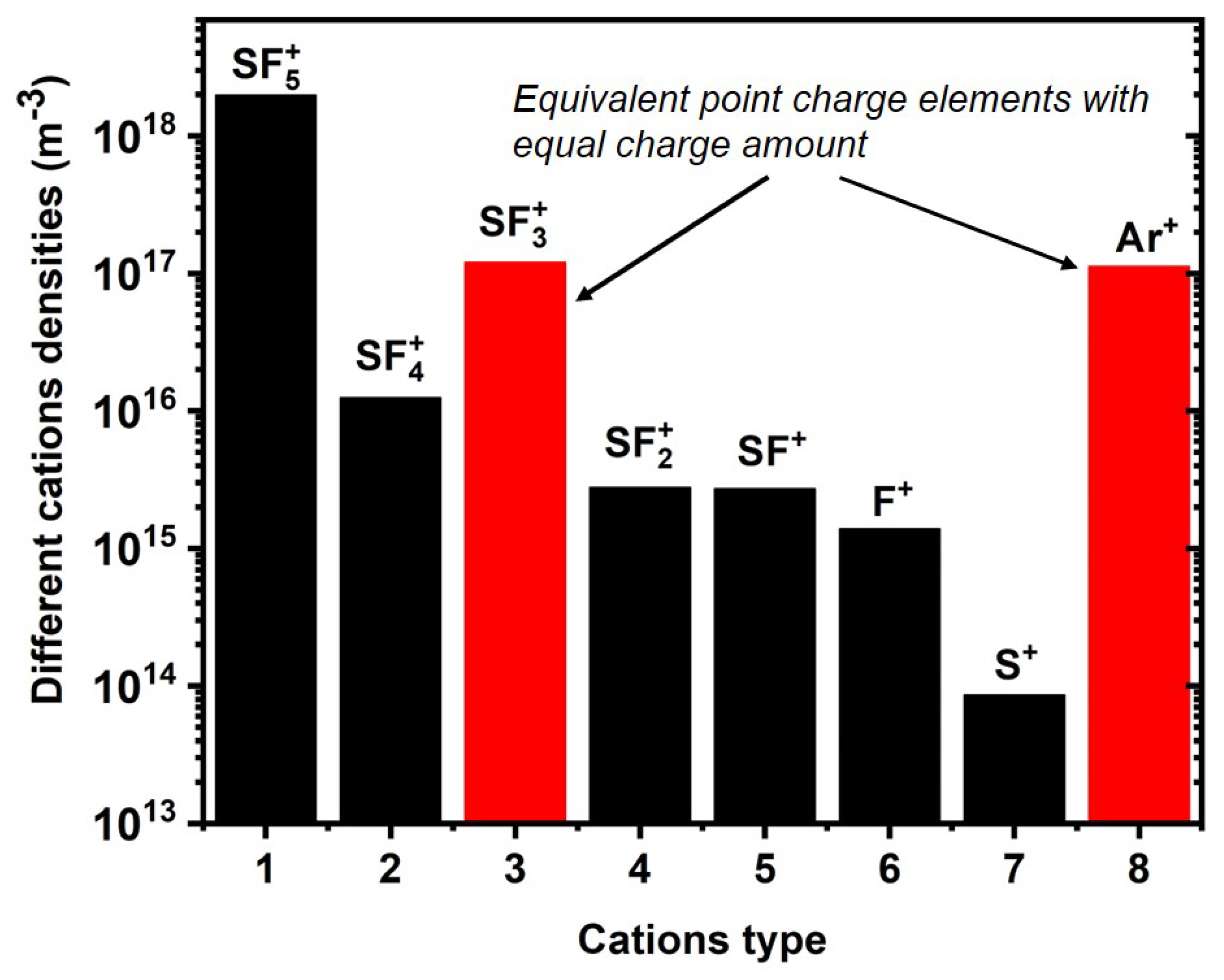
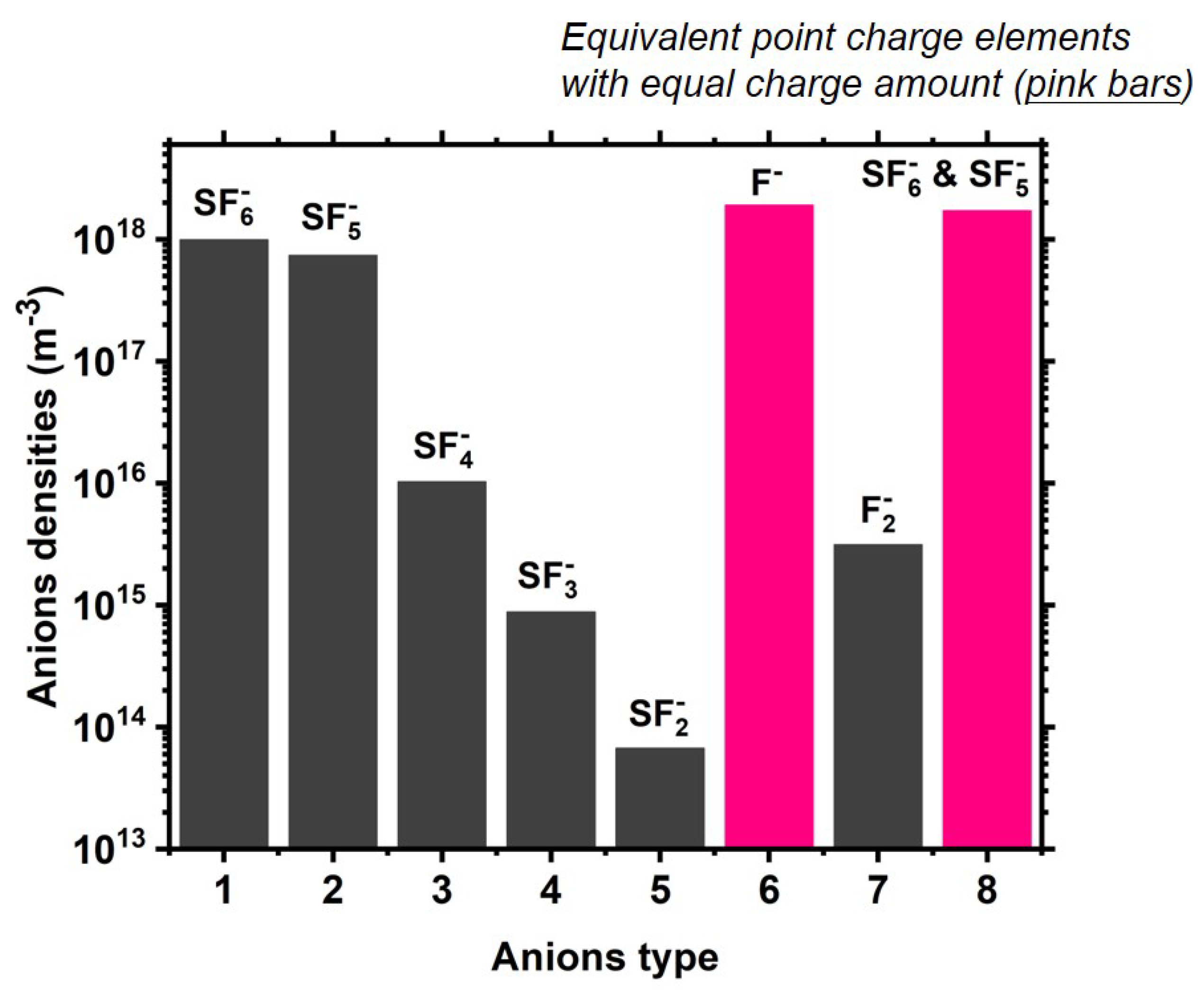
4.3. Expelling Effectt between Astro-Structures with the Same Charge Type
4.4. Spontaneous Monopolar Self-Coagulation
5. Conclusions and Further Remarks
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liberman, M.A.; Lichtenberg, A.J. Principles of Plasma Discharges and Materials processing, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, America, 2005; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chabert, P.; Braithwaite, N. Physics of Radio-Frequency Plasmas; Cambridge University Press: New York, America, 2011; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.N. Numerical investigation of ion energy distribution and ion angle distribution in a dual-frequency capacitively coupled plasma with a hybrid model. Phys. Plasmas 2007, 14, 113501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.X. , Xu, X., Li, X.C., Wang, Y.N. Fluid simulation of the E-H model transition in inductively coupled plasma. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 083306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.X. , Gao, F., Wang, Y.N. Dynamic investigation of mode transition in inductively coupled plasma with a hybrid model. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 225203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenberg, A.J.; Vahedi, V.; Lieberman, M.A. Modeling electronegative plasma discharges. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 75, 2339–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenberg, A.J. , Kouznetsov, I.G., Lee, Y.T., Lieberman, M.A., Kaganovich, I.D., Tsendin, L.D. Modelling plasma discharges at high electronegativity. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 1997, 6, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsov, I.G. , Lichtenberg, A.J., Lieberman, M.A. Internal sheaths in electronegative discharges. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 4142–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampe, M. , Manheimer, W.M., Fernsler, R.F., Slinker S.P., Joyce G. The physical and mathematical basis of stratification in electronegative plasmas. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2004, 13, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, T.E. Double layers in a modestly collisional electronegative discharge. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabert, P.; Sheridan, T.E. Kinetic model for a low-pressure discharge with negative ions. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2000, 33, 1854–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, R.N.; Snell, J. Are the oscillations found in electronegative plasmas at low pressure an artefact? J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2000, 33, 1990–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaganovich, I. Negative ion density fronts. Phys. Plasmas 2001, 8, 2540–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, J.; Derzsi, A.; Dittmann, K.; Hemke, T.; Meichsner, J.; Donko, Z. Ionization by Drift and Ambipolar Electric Field in Electronegative Capacitive Radio Frequency Plasmas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 275011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Schungel, E.; Korolov, I.; Donko, Z.; Wang, Y.N.; Schulze, J. Experimental Observation and Computational Analysis of Striations in Electronegative Capacitively Coupled Radio-Frequency Plasmas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 255002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.X. Quasi-delta negative ions density of Ar/O2 inductively coupled plasma at very low electronegativity. Chin. Phys. B 2021, 30, 055201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.X.; Li, J.Z. Delta distribution of electronegative plasma predicted by reformed spring oscillator dynamic equation with dispersing force. Chin. Phys. B 2021, 30, 055202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlqvist, P. On the acceleration of energetic cosmic particles by electrostatic double layers. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 1986, 14, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plihon, N.; Corr, C.S.; Chabert, P.; Raimbault, J.L. Periodic formation and propagation of double layers in the expanding chamber of an inductive discharge operating in Ar/SF6 mixtures. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 023306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.W. Fundamental of Plasma Theory; Peking University Press: Beijing, China, 1997; pp. 238–243. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.H. Study on the closed fluid mechanics model based on the kinetic theory and self-consistent solution for the transport coefficients of heavy species. PhD. Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, June 7th, 2023. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.H.; Zhao, S.X.; Dai, Z.L. A self-consistent method for solving ion diffusion and mobility coefficients. Phys. Plasmas 2021, 28, 103503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Zhao, S.X.; Dai, Z.L. The impact of ion mobility coefficients on plasma discharge characteristics. Phys. Plasmas 2022, 29, 073501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.L. Gaseous electronics; Huazhong Science and Technology University Press: Wuhan, China, 1999; pp. 36–39. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Plasma Data Exchange Project. Available online: https://fr.lxcat.net/instructions/ (accessed on 8 March 2020).
- Yang, W.; Zhao, S.X.; Wen, D.Q.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, X.C.; Wang, Y.N. F atom kinetics in SF6/Ar inductively coupled plasmas. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2016, 34, 031305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Wang, Y.N.; Bogaerts, A. Numerical study of the plasma chemistry in inductively coupled SF6 and SF6/Ar plasmas used for deep silicon etching application. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 435202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lallement, L.; Rhallabi, A.; Cardinaud, C.; Peignon-Fernandez, M.C.; Alves, L.L. Global model and diagnostic of a low-pressure SF6/Ar inductively coupled plasma. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2009, 18, 025001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.W.; Dai, Z.L.; Wang, Y.N. Simulations of capacitively coupled dual-frequency N2, O2, N2/O2 discharge: effects of external parameters on plasma characteristics. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2014, 16, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, J.T.; Kouznetsov, I.G.; Patel, K.K.; Lieberman, M.A. Electronegativity of low-pressure high-density oxygen discharges. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2001, 34, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.R.; Wang, Y.N. Fluid simulation of inductively coupled Ar/O2 plasma: Comparisons with experiment. Chin. Phys. B 2015, 24, 095203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezmes, A.O.; Breitkopf, C. Fast and reliable simulations of argon inductively coupled plasma using COMSOL. Vacuum 2015, 116, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levko, D. Decay of a low-pressure oxygen magnetized and unmagnetized plasma. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 116, 103304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C.; Neirode, M.A.; Coburn, J.W.; Graves, D.B. Comparison of model and experiment for Ar, Ar/O2, and Ar/O2/Cl2 inductively coupled plasmas. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2006, 39, 3272–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takechi, K.; Lieberman, M.A. Effect of Ar addition to an O2 plasma in an inductively coupled traveling wave driven, large area plasma source: O2/Ar mixture plasma modeling and photoresist etching. J. App. Phys. 2001, 90, 3205–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, D.B.; Kiehlbauch, M.K. Inductively coupled plasmas in oxygen: Modeling and experiment. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2003, 21, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.X. Non-monotonic behavior of electron temperature in argon inductively coupled plasma and its analysis via novel electron mean energy equation. Phys. Plasmas 2018, 25, 033516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.X.; Sun, Y.H. Discharge structure theory of highly electronegative plasma. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. submitted. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.F. Introduction to Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 3rd ed.; Springer: Switzerland, 2018; pp. 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Du, P. C.; Gao, F.; Wang, X.K.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, Y.N. Measurement of electronegativity during the E to H mode transition in a radio frequency inductively coupled Ar/O2 plasma. Chin. Phys. B 2021, 30, 035202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Liu, W.; Zhao, S.X. , Zhang, Y.R.; Sun, C.S.; Wang, Y.N. Changes of the electron dynamics in hydrogen inductively coupled plasma. Chin. Phys. B 2013, 22, 115205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
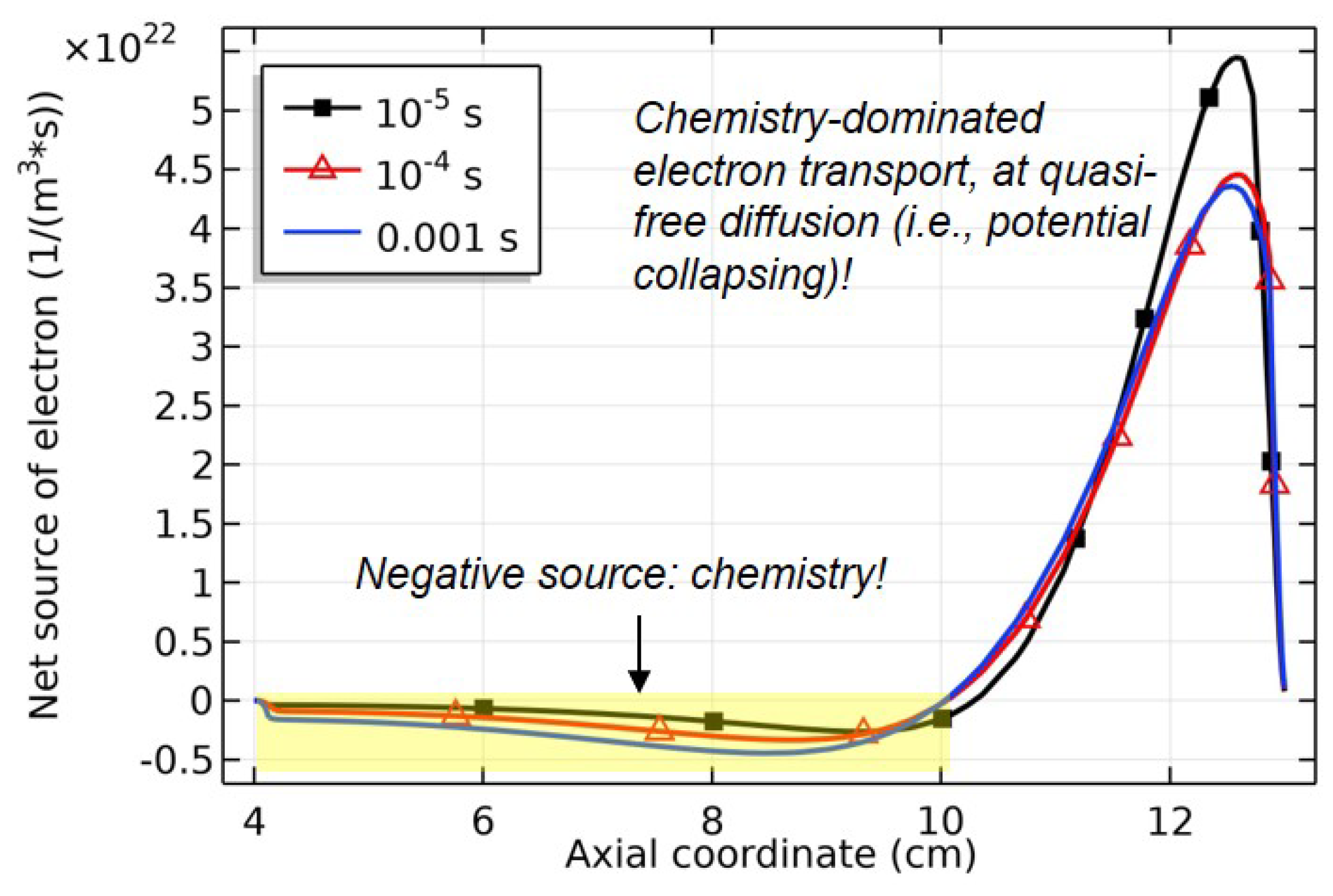
| No. | Surface reaction | Sticking coefficient | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ; | 1 | [26,27] |
| 2 | 1 | [26,27] | |
| 3 | 1 | [26,27] | |
| 4 | 1 | [26,27] | |
| 5 | 0.02 | [28] | |
| 6 | 1 | [26,27] | |
| 7 | 1 | [26,27] |
| No. | Reaction | Rate coefficient(cm3/s) | Threshold (eV) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [29] | |||
| 2 | 12.06 | [29] | ||
| 3 | 3.637 | [30] | ||
| 4 | 17 | [29] | ||
| 5 | 20 | [30] | ||
| 6 | 0.98 | [29] | ||
| 7 | 8.57 | [30] | ||
| 8 | 6.4 | [30] | ||
| 9 | 13 | [30] | ||
| 10 | 1.97 | [30] | ||
| 11 | -1.97 | [30] | ||
| 12 | 11.6 | [30] | ||
| 13 | 5.5 | [30] | ||
| 14 | -6.96 | [30] | ||
| 15 | -0.98 | [29] | ||
| 16 | 5.19 | [31] | ||
| 17 | 11.08 | [30] | ||
| 18 | 5.42 | [30] | ||
| 19 | 7.59 | [31] | ||
| 20 | 17.7 | [29] | ||
| 21 | Cross sectiona | 15.6 | [32] | |
| 22 | Cross section | 11.50 | [32] | |
| 23 | Cross section | -11.50 | [32] | |
| 24 | Cross section | 15.80 | [32] | |
| 25 | Cross section | 4.427 | [32] | |
| 26 | [31] | |||
| 27 | [33] | |||
| 28 | [31] | |||
| 29 | [31] | |||
| 30 | [33] | |||
| 31 | [31] | |||
| 32 | [31] | |||
| 33 | [33] | |||
| 34 | [33] | |||
| 35 | [33] | |||
| 36 | [31] | |||
| 37 | [31] | |||
| 38 | [34] | |||
| 39 | [34] | |||
| 40 | [34] | |||
| 41 | [34] | |||
| 42 | [31] | |||
| 43 | [31] | |||
| 44 | [35] |
| No. | Surface reactions | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [36] | |
| 2 | [36] | |
| 3 | [36] | |
| 4 | [36] | |
| 5 | [36] | |
| 6 | [36] | |
| 7 | [36] | |
| 8 | [32] | |
| 9 | [32] |
| No. | Reaction |
|---|---|
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 16 |
| No. | Reaction |
|---|---|
| 13 | |
| 26 | |
| 27 | |
| 28 | |
| 29 | |
| 37 | |
| 42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





