Submitted:
14 August 2024
Posted:
15 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. An Overview of the Fintech Ecosystem in Saudi Arabia
2.2. Saudi Arabia’s Strategy towards Sustainable Development Goals
3. Materials & Methods
| Sr. No | Sustainable Development Goals |
|---|---|
| 1 | No Poverty |
| 2 | Zero Hunger |
| 5 | Gender Equality |
| 8 | Decent work and economic growth |
| 17 | Strong Global partnership and cooperation for the goals |
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
References
- Akmal, S.; Talha, M.; Faisal, S.M.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, A.K. Perceptions about FinTech: New evidences from the Middle East. Cogent Economics & Finance 2023, 11, 2217583. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, F.; Demirguc-Kunt, A.; Klapper, L.; Peria, M.S.M. The foundations of financial inclusion: Understanding ownership and use of formal accounts. Journal of financial Intermediation 2016, 27, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arestis, P. 21 Financial liberalization and the relationship between finance and growth. In A handbook of alternative monetary economics; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham; UK; Northampton, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 346–364. [Google Scholar]
- Barata, A. Strengthening national economic growth and equitable income through sharia digital economy in Indonesia. Journal of Islamic Monetary Economics and Finance 2019, 5, 145–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, F.; Kanie, N.; Kim, R.E. Global governance by goal setting: The novel approach of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability 2017, 26, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collste, D.; Pedercini, M.; Cornell, S.E. Policy coherence to achieve the SDGs: Using integrated simulation models to assess effective policies. Sustainability science 2017, 12, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emara, N. Asymmetric and threshold effects of FinTech on poverty in SSA countries. Journal of Economic Studies 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emara, N.; Mohieldin, M. Beyond the Digital Dividends: Fintech and Extreme Poverty in the Middle East and Africa. Topics in Middle Eastern & North African Economies: Proceedings of the Middle East Economic Association 2021, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Farahani, M.S.; Esfahani, A.; Moghaddam, M.N.F.; Ramezani, A. The impact of Fintech and artificial intelligence on COVID 19 and sustainable development goals. International Journal of Innovation in Management, Economics and Social Sciences 2022, 2, 14–31. [Google Scholar]
- Fullwiler, S. Sustainable finance: Building a more general theory of finance. In Routledge handbook of social and sustainable finance; Routledge: 2016; pp. 17–34.
- Hinson, R.; Lensink, R.; Mueller, A. Transforming agribusiness in developing countries: SDGs and the role of FinTech. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability 2019, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.G.; Nguyen, G.N.T.; Le, D.A. Developments in financial technologies for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): FinTech and SDGs. In Disruptive technologies and eco-innovation for sustainable development; IGI Global: 2022; pp. 1–19.
- Hudaefi, F.A.; Zaenal, M.H.; Farchatunnisa, H.; Junari, U.L. How does zakat institution respond to fintech? Evidence from BAZNAS Indonesia. Journal website: Journal. zakatkedah. com. My 2020, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Khaki, A.R.; Messaadia, M.; Jreisat, A.; Al-Mohammad, S. Fintech Adoption for Poverty Alleviation in African Countries: Application of Supervised Machine Learning Approach. In Africa Case Studies in Operations Research: A Closer Look into Applications and Algorithms; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 197–210. [Google Scholar]
- Kroll, C. spotlight europe, August 2015: Sustainable Development Goals: Are the rich countries ready? 2015.
- Lukonga, I. Fintech and the real economy: Lessons from the Middle East, North Africa, Afghanistan, and Pakistan (MENAP) region. The Palgrave handbook of fintech and blockchain 2021, 187–214. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.C.; Lou, R.; Wang, F. Digital financial inclusion and poverty alleviation: Evidence from the sustainable development of China. Economic Analysis and Policy 2023, 77, 418–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhlanga, D. The role of financial inclusion and FinTech in addressing climate-related challenges in the industry 4.0: Lessons for sustainable development goals. Frontiers in Climate 2022, 4, 949178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, S.W. Does fintech matter for Indonesia’s economic growth? Buletin Ekonomi Moneter Dan Perbankan 2019, 22, 437–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasution, L.N.; Sadalia, I.; Ruslan, D. Investigation of Financial Inclusion, Financial Technology, Economic Fundamentals, and Poverty Alleviation in ASEAN-5: Using SUR Model. ABAC Journal 2022, 42, 132–147. [Google Scholar]
- Panjwani, K.; Shili, N. The impact of fintech on development of islamic banking sector in the contemporary world. Saudi Journal of Economics and Finance 2020, 4, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puschmann, T. Fintech. Business & Information Systems Engineering 2017, 59, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Saba, I.; Kouser, R.; Chaudhry, I.S. FinTech and Islamic finance-challenges and opportunities. Review of Economics and Development Studies 2019, 5, 581–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q. Investment Analysis on Precision Medicine Project in Saudi Arabia. Highlights in Business, Economics and Management 2023, 8, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.J.; Choi, Y. Feasibility of the FinTech industry as an innovation platform for sustainable economic growth in Korea. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Appiah-Otoo, I. The impact of fintech on economic growth: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, C. Financial technology as a driver of poverty alleviation in China: Evidence from an innovative regression approach. Journal of Innovation & Knowledge 2022, 7, 100164. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Han, Y.; Qian, M.; Guo, X.; Chen, R.; Chen, Y. The contribution of Fintech to sustainable development in the digital age: Ant forest and land restoration in China. Land use policy 2021, 103, 105306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhu, J.; Luo, S. The impact of fintech innovation on green growth in China: Mediating effect of green finance. Ecological Economics 2022, 193, 107308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuliansyah, A.; Pratomo, D.; Supriyaningsih, O. The Role of Financial Technology (Fintech) in ZIS Management to Overcome Poverty. Indonesian Interdisciplinary Journal of Sharia Economics (IIJSE) 2022, 5, 203–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
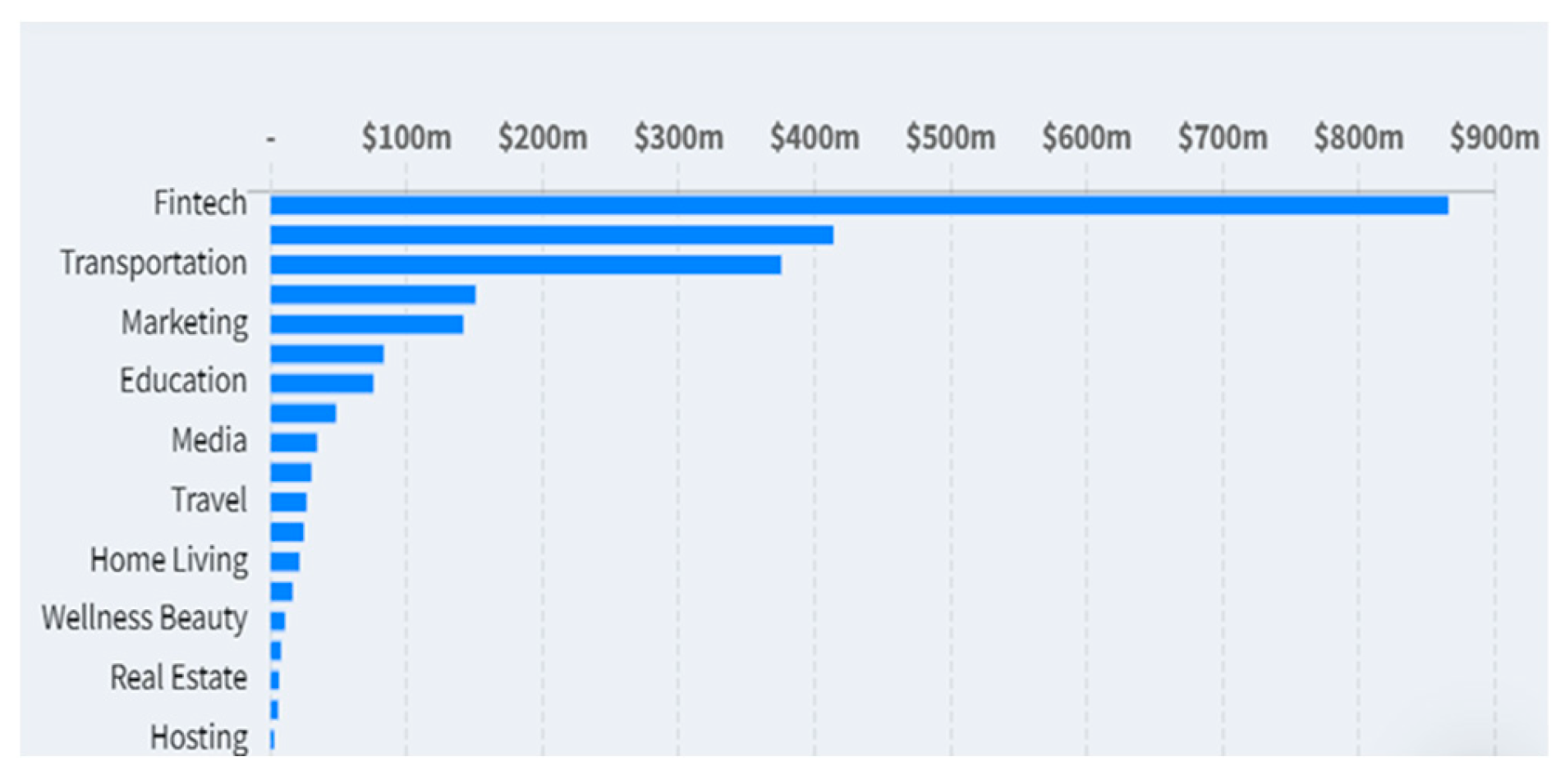
| SDG Goals & Indicators | Fintech Program Helping to Achieve SDG | Fintech Program Product & Services | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Goal 1. End Poverty in All its Forms Everywhere | |||
| Indicator 1.1.1. The proportion of the Population Below the International Poverty Line Indicator 1.4.1 The proportion of the population living in households with access to basic services |
Lendo: Digital Lending for Information Technology (Debt – CrowdFunding Platform) SURE (Digital Payments) |
Invoice financing, A relatively new method for SMEs to borrow money directly from investors is through invoice financing, also known as receivables financing. This method allows SMEs to borrow money against the payments they are expected to receive from their clients or customers. Peer-to-peer (P2P) Lending, commonly referred to as social lending or crowd lending, is a form of alternative financing that enables people to borrow money from other people. When compared to conventional finance (like banks), this approach is becoming more and more popular because it: the inconvenience of a middleman (financial institution) is reduced requires neither party to physically inconvenience themselves makes the waiting period shorter, from weeks to only a few days allows for more flexible terms than banks offers a wide range of interest rates based on the applicant’s creditworthiness. Fandaqah a comprehensive hotel management program for hotels, resorts, and furnished flats. It’s simple, and you may use it right away and without any difficulties. gives management complete control over all lease requirements, stages, and alternatives. The system may be accessed from anywhere using a mobile phone, allowing the owner to track the facility and receive complete reports at any time. Sure Pay No matter the type of transaction—unattended, in-store, outdoor, or mobile—our smart payment systems can handle it. They support all forms of cashless payment and adhere to the strictest security standards. Many industries, such as hotels, retail, banks, and transportation, benefit from their multimedia possibilities, which can provide a rich user experience. |
https://lendo.sa/about-lendo/?lang=en https://www.sure.com.sa/en/ https://surepay.sa/ |
| Haseel App Fruits, vegetables, and other catering services are all provided by Haseel. |
https://haseelapp.com/ |
||
| Majles tech The Majles Tech platform is a system that can control general assemblies and administrative councils to provide best practices in line with established governance systems. Majles Tech’s jobs encompass all needs and procedures and shift them away from paper and files to the digital world rather than being restricted to a single sort of operation. |
https://site.majles.tech/ |
||
|
Goal 2. End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture. | |||
| 2.1.1 Prevalence of undernourishment 2.3.2 Average income of small-scale food producers ) |
Foodies |
Point of Sale Solution Foodics is a complete point-of-sale system and restaurant management program that can be customized to meet all of your requirements. Use a single platform to control all restaurant operations, including orders and inventory. Foodics Pay is a payment method that is incorporated into your Foodics Cashier App. Accept all card payments safely and sync your bank accounts every day. |
https://www.foodics.com/rms-pos/ https://www.foodics.com/pay/ |
| Foodics Online store You may quit paying third-party commission costs by offering straightforward self-ordering directly from your website, mobile application, and QR menu. |
https://www.foodics.com/online/ |
||
| Self-Ordering Increase the average order size per customer to increase average sales while reducing costs in the restaurant by enhancing operational effectiveness. |
https://www.foodics.com/self-ordering/ |
||
| All You Get Is One Device Easily manage your business with just one device that includes a built-in cashier, quick printer, and secure payment gateway. businesses including flower shops, vehicle washes, and hair salons |
https://www.foodics.com/one/ |
||
|
Goal 8. Promote sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment, and decent work for all | |||
| 8.2 Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading, and innovation, including through a focus on high-value-added and labor-intensive sectors |
Saudi Fintech Company (Alinma Pay) (Digital Payments) |
AlinmaPay Fund When you enrolled for AlinmaPay, an IBAN was generated for you and may be used to transfer money from any domestic or international bank account. Digital Card from AlinmaPay AlinmaPay provides you with a digital card that can be used for online shopping and is compatible with various payment methods like ApplePay and Mandalay. Buying You can use a digital card to pay for all of your purchases from stores, eateries, and online. Money Transfer on a Local and Global Scale Your preferred choice for quick local or international money transfers is AlinmaPay. You can also use a few of the well-known services for sending money abroad, such Western Union and AlinmaPay Direct. SADAD: Paying Services Bills Utilize AlinmaPay, which includes all SADAD and government payments, to pay your expenses quickly. |
https://www.alinmapay.com.sa/ |
| Zain Payments (Limited) (Consumable Micro-lending) |
Tamam offers instant financing without complicated documentation or visiting bank branches. Loans comply with the Shariah Tawaruq model. The product has been approved and certified by a well know Shariah Committee. |
https://tamam.life/ |
|
| Money Loop (Digital Savings Association) |
Investing Money Funded Forex Account Money Invest |
http://ww7.moneyloop.org/ |
|
|
Goal 5. Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls | |||
| 5.1.1 Whether or not legal frameworks are in place to promote, enforce and monitor equality and non-discrimination based on sex |
Noon Hakbah Co for Information Technology (Digital Savings Association) |
By providing a full one-stop-shop solution for Savings Groups to begin, administer, join, and pay directly within the mobile app, Hakbah is modernizing financial saving through its intelligent platform. Customers are given a practical and straightforward technique for Savings Groups’ habits by the solution. It intends to help close the gender savings gap and expand financial inclusion for all people. |
https://hakbah.sa/?lang=en |
| Savings Circles company for Information Technology (Digital Savings Association) |
At Circles, we organize the circles by opening new circles monthly and supervising each circle as we make sure to obtain guarantees to avoid stumbling, and this process lasts until the circle expires. Additionally, we work to verify the eligibility of each member who enters the circle through several entities. | https://circlys.com/#who-we-are | |
| Business research storming company (Digital Savings Solutions) |
Without the need for manual entry, you can automatically and intelligently track your spending and get complete summaries of your purchases and payments. Wafer makes it simple to manage your finances, grow your savings, and improve your expenditures. | https://wafeer.net/ | |
|
Goal 17. Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the Global Partnership for Sustainable Development | |||
| 17.1 Strengthen domestic resource mobilization, including through international support to developing countries, to improve domestic capacity for tax and other revenue collection 17.3 Mobilize additional financial resources for developing countries from multiple sources |
Nayifat Finance Company (Debt – CrowdFunding Platform) |
SME Finance enables SMEs to finance their business needs through different structured financing programs including working capital financing, Trade Financing, and lease financing to expand and grow their business in the kingdom. Financing several industries such as Healthcare, Accommodation & Food services, Real estate, Education, Electricity, Gas, Steam & Air Conditioning supply, and Manufacturing. Consumer Finance: Enables consumers to instantly finance their personal needs and repay the amount through flexible repayment solutions. Personal finance programs are available for individuals in public and private sectors up to SR 300,000 and an instant smart loans program enables the customer to avail of financing facilities up to SR 100,000 without salary transfer or personal guarantor in line with Shari’a principles such as (Tawaruq, Murabaha, Ijarah) Credit Card Nayifat VISA Card brings you a growing range of benefits. Say goodbye to your worries, with immediate acceptance at all VISA Card merchants & ATMs All over the world. Live comfortably with stress-free and safe transactions 24/7, and provide SMS alerts for every transaction, giving you total control. |
https://www.nayifat.com https://www.nayifat.com/sme-finance/overview-4/ https://www.nayifat.com/consumer-finance-3/overview-consumer-finance/ https://www.nayifat.com/home/credit-cards/overview-2/ |
| Platform Company Ltd. Tameed Financing (Debt – CrowdFunding Platform) |
Performance Bond and PO Financing Comprehensive financing solutions to all of your PO needs from performance bond to PO needs, all in one financing package! Debt-Based Crowd Lending For Government Purchase Orders As the first Debt Based Crowd Lending Platform specializing in financing Purchase Order licensed by Saudi Central Bank, Tameed offers fast financing for your PO E-Invoicing Free E-invoice service for B2B which is compliant with Zatca and will ease the organization’s relationship with their customers |
https://www.ta3meed.com/en https://www.ta3meed.com/en/get-funding |
|
| Manafa capital (Debt – CrowdFunding Platform) |
Proprietary Platform Equity crowdfunding is your ideal and fastest destination to enable your project. Religious PlatformIt helps you, as a financing student, to obtain immediate cash liquidity and achieve attractive returns for investors in short-term investment Financing solutions compatible with Islamic Shariah |
https://manafa.co/ https://manafa.sa/shariah |
|
| Funding Souq Company (Debt – CrowdFunding Platform) |
Funding Souq company helps in investing and borrowing Earn regular income. Up to 13%per year. Grow your wealth by financing small and medium-sized businesses. |
https://www.fundingsouq.com/en/ | |
| Raqamyah Platform (Debt- Crowdfunding Platform) |
Finance enables established companies of all sizes to achieve their next business objective or stage. To choose the best SMEs, Get Financed combines the best in technology and financial research. Applications are chosen and presented to financiers only if they are creditworthy. Finance POS Raqamyah’s point of sale (POS) finance is a quick funding option that satisfies your funding requirements. Your POS sales will determine how much financing you receive. By taking a certain proportion from each swipe made on the POS Machines, automatic payback is made possible with POS finance. The funding options for SMEs include term financing, POS financing, invoice financing, and inventory financing. |
https://www.raqamyah.com/en/Finance https://www.raqamyah.com/en/Get_financed https://www.raqamyah.com/en/Pos_Finance https://www.raqamyah.com/en/Smes |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





