Submitted:
08 August 2024
Posted:
09 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
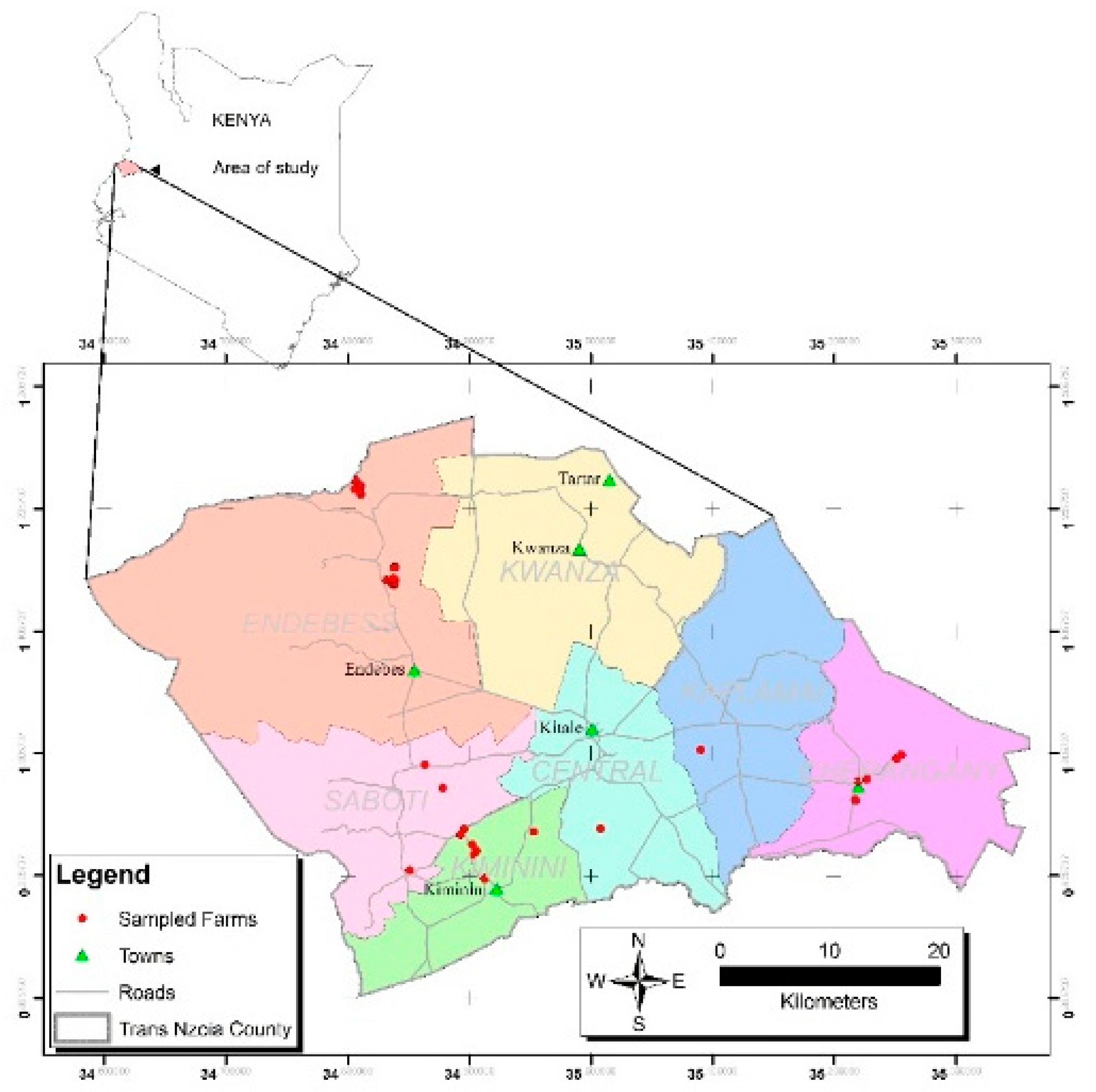
2.1. Area of Study
2.2. Sampling Design
2.3. Laboratory Analysis of Soil Samples
2.3.1. Measurement of Soil PH and Electrical Conductivity
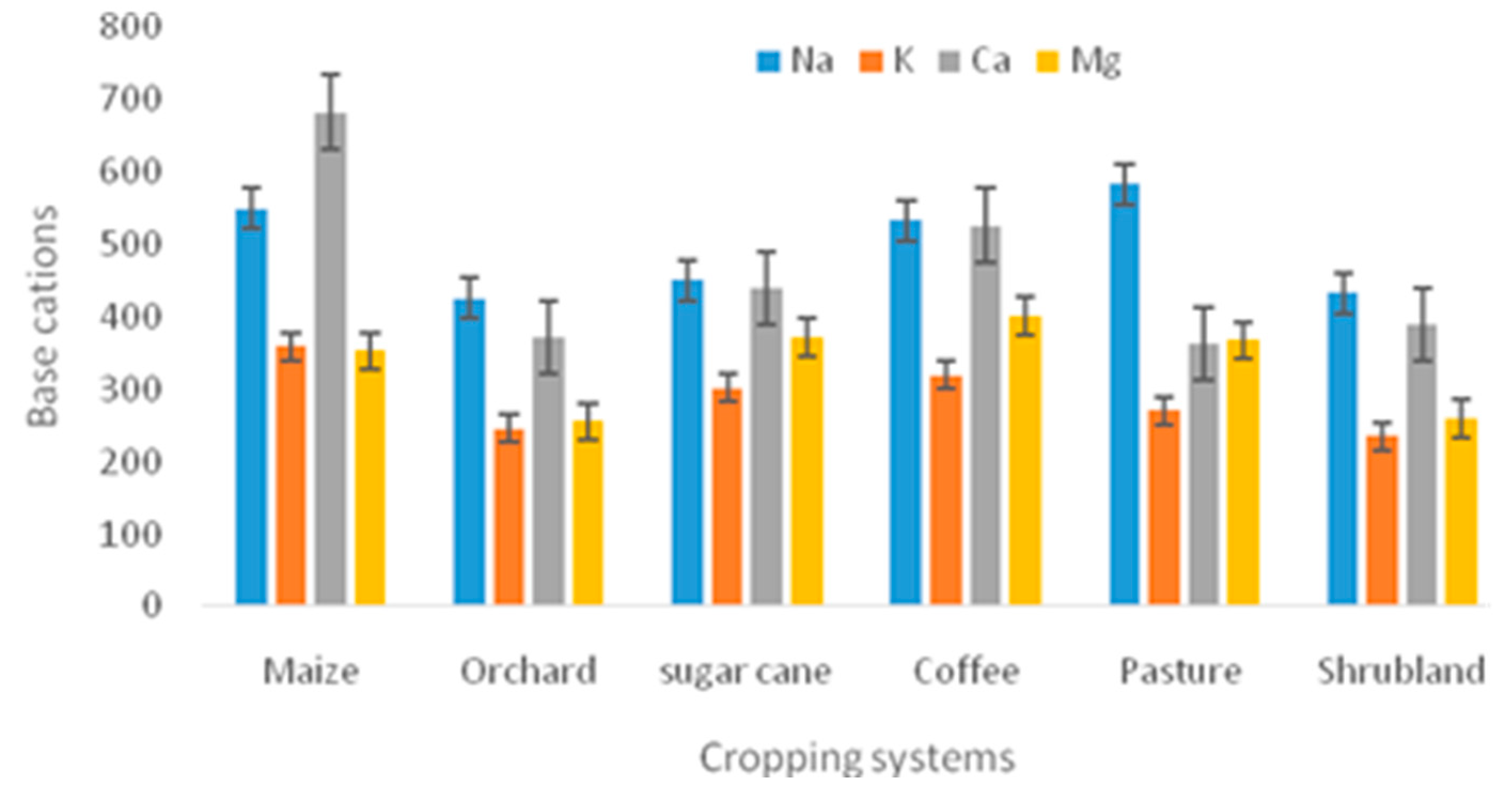
2.3.2. Determination of Base Cations
2.3.3. Determination of Heavy Metals
Quality Control
Sample Preparation and Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Pollution Index Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Heavy Metal Concentrations under Various Cropping Systems
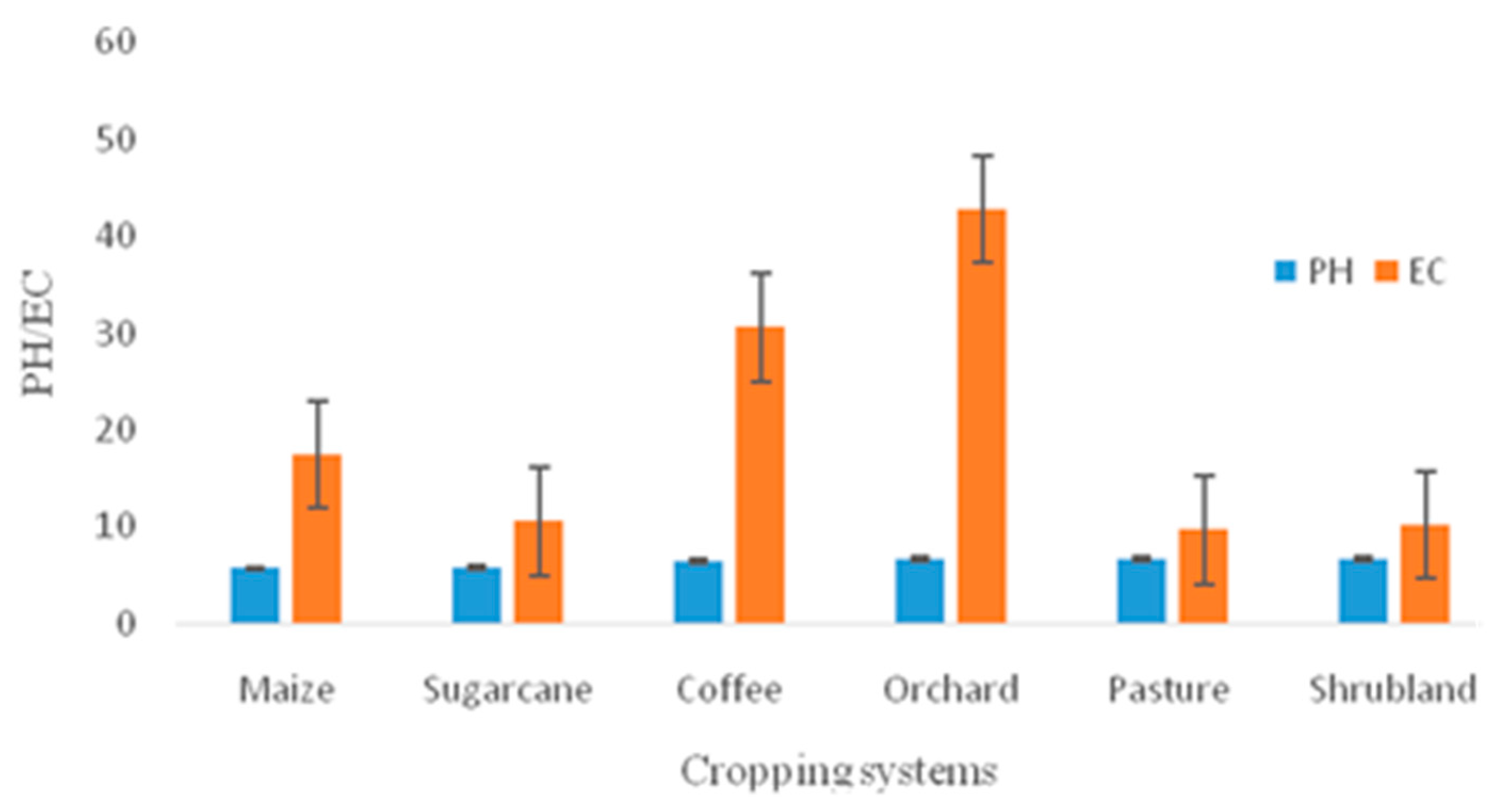
3.1.1. Variation in PH and Electrical Conductivity
3.1.2. Heavy Metal Concentrations under Various Cropping Systems
3.1.3. Namerow’s Pollution Index/Row’s Pollution Index (NPI) per Cropping System
3.1.4. Correlation between the Analyzed Physicochemical Parameters
| Parameters | PH | EC | Total N | Na | K | Ca | Mg | Cu | Pb | Cr (III) | Cd | Zn | Fe | TOC |
| PH | 1.00 | |||||||||||||
| EC | -0.510 0.000* |
1.00 | ||||||||||||
| Total N | +0.03 0.967 |
+0.256* 0.000 |
1.00 | |||||||||||
| Na | -0.149 0.033 |
+0.204* 0.000 |
+0.118 0.094 |
1.00 | ||||||||||
| K | -0.096 0.180 |
+0.066 0.340 |
-0.161* 0.022 |
0.034 0.626 |
1.00 | |||||||||
| Ca | -0.066 0.370 |
+0.059 0.403 |
-0.089 0.210 |
0.005 0.938 |
+0.512* 0.000 |
1.00 | ||||||||
| Mg | +0.119 0.090 |
-0.098 0.165 |
-0.191* 0.010 |
-0.054 0.447 |
+0.354* 0.000 |
+0.446* 0.000 |
1.00 | |||||||
| Cu | -0.542** 0.000 |
+0.150* 0.030 |
-0.091 0.199 |
+0.013 0.849 |
+0.066 0.351 |
+0.033 0.638 |
-0.145* 0.039 |
1.00 | ||||||
| Pb | -0.414** 0.000 |
+0.326* 0.000 |
0.012 0.870 |
+0.007 0.917 |
+0.060 0.093 |
+0.141* 0.046 |
-0.178* 0.011 |
+0.528* 0.000 |
1.00 | |||||
| Cr (III) | -0.316** 0.000 |
+0.280* 0.000 |
-0.059 0.401 |
-0.013 0.853 |
+0.232* 0.000 |
+0.301* 0.000 |
+0.157* 0.000 |
+0.398* 0.000 |
0.335** 0.000 |
1.00 | ||||
| Cd | -0.284* 0.000 |
+0.200* 0.000 |
0.109 0.120 |
+0.081 0.251 |
+0.255* 0.000 |
+0.221* 0.000 |
+0.243* 0.000 |
+0.321* 0.000 |
0.292** 0.000 |
0.427** 0.000 |
1.00 | |||
| Zn | -0.310* 0.000 |
+0.347* 0.000 |
-0.043 0.544 |
+0.019 0.787 |
+0.375* 0.000 |
+0.645* 0.000 |
+0.234* 0.001 |
+0.257* 0.000 |
0.458 0.000 |
0.561** 0.000 |
0.345** 0.000 |
1.00 | ||
| Fe | -0.091 0.190 |
+0.159* 0.023 |
0.076 0.283 |
+0.027 0.702 |
+0.040 0.570 |
+0.153 0.030 |
+0.030 0.666 |
+0.068 0.335 |
0.142 0.044 |
0.000 0.055 |
0.090 0.020 |
0.181** 0.010 |
1.00 | |
| TOC | -0.103 0.143 |
+0.160* 0.022 |
0.347** 0.000 |
+0.072 0.307 |
-0.094 0.182 |
-0.031 0.665 |
-0.040 0.569 |
+0.106 0.132 |
0.185 0.080 |
0.146* 0.037 |
0.402** 0.000 |
0.124 0.079 |
0.016 0.816 |
1.00 |
4. Discussion
4.1. Variations in pH, EC and Base Cation Concentrations
4.2. Soil Heavy Metal Pollution due to Agriculture
5. Conclusions
6. Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Preira, V.; Martinho, D. Exploring the Topics of Soil Pollution and Agricultural Economics: Highlighting Good Practices. Agriculture. 2020, 10, 24. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, X.; Meng,W.; Liu, N.; and Wu, P. Accumulation and source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils based on GIS, SOM and PMF: A case study in superposition areas of geochemical anomalies and zinc smelting, Southwest China. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159: 964–977.
- Sidhu, G.P. Heavy metal toxicity in soils: sources, remediation technologies and challenges. Adv. Plants Agric. Res. 2016, 5:445‒446.
- Weissmannová, H.D.; Dolezalova, P. Indices of soil contamination by heavy metals: methodology of calculation for pollution assessment (mini review). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189: 616.
- Zheng, S.; Chen, B.; Qui, X.; Chen, M.; Ma, Z.; Yu, X. Distribution and risk assessment of 82 pesticides in Jiulong River and estuary. Chemosphere, 2016, 144, 1177–1192.
- Srivastava, V.; Sarkar, A.; Singh, S.; Singh, P.; de Araujo, A.S.; Singh, R.P. Agroecological Responses of Heavy Metal Pollution with Special Emphasis on Soil Health and Plant Performances. Front. Environ. Sci. 2017, 5: 64-71. [CrossRef]
- Wanjala, F.O..; Hashim, N.; Otwoma, O.D.; Nyambura, C.; Kebwaro, J.; Ndege, M.; Bartilol, S. Environmental assessment of heavy metal pollutants in soils and water from Ortum, Kenya Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192:11. [CrossRef]
- Alengebawy, A; Abdelkhalek, S.T.; Qureshi, S.R..; Wang, M.Q..; 2021. Heavy metals and pesticides toxicity in agricultural soil and plants: Ecological risks and human health implications. Toxics, 2021, 9: 42. [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Muhammad, M.; Muhammad, J.K.; Khadim, M.D.; Dost, M.; Ishaq, A.; Mian, W.A.; Shah, F.; Shah, S.; Zafar, H.; Taufiq, N.; Shah, A.; Khan, S.; Beenish, A.; Jan, B.; Sagher, A.; Sidra, M.; Subhan, D.; Rahu, D.; Abdallah, M.; Raf, D. Heavy metals immobilization and improvement in maize (Zea mays L.) growth amended with biochar and compost. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11:18416. [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Han, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, R.; Xia, L.; Fan, Y.. Assessment of Soil-Heavy Metal Pollution and the Health Risks in a Mining Area from Southern Shaanxi Province, China. Toxics, 2022, 10: 385.
- Dong, H.; Zhao, J.; Xie, M. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Orchard Soils with Different Cultivation Durations and Their Potential Ecological Risks in Shaanxi Province, Northwest China. Sustainability, 2021.13, 4741. 741. [CrossRef]
- Raven, P.H.; Wgner, D.L. Agricultural intensification and climate change are rapidly decreasing insect biodiversity. PNAS, 2020, 118 No. 2. [CrossRef]
- Mekuria, W. The link between agricultural production and population dynamics in Ethiopia: A review. Adv. Plants Agric. Res. 2018, 8:349‒353.
- Food and Agriculture Organization. How to feed the world in 2050. Expert Papers, Rome, Italy, 2019, pp 1-35.
- Garcia, A. The environmental impacts of agricultural intensification, Technical note no. 9. CGIAR. 2020, pp 4–13.
- De Vries, W.; Römkens, P.F.; Kros, J.; Voogd, J.C.; Schulte-Uebbing, L.F. Impacts of nutrients and heavy metals in European agriculture: Current and critical inputs in relation to air, soil and water quality. ETC-DI, 2022, pp 72. ISBN: 978-3-200-08327-1.
- Nicolopoulou, S.P.; Maipas, S.; Kotampasi, C.; Stamatis, P.; Hens, L. Chemical pesticides and human health: The urgent need for a new concept in agriculture. Front. Public Health, 2016, 4, 148. [CrossRef]
- Jallow, M.F.A.; Dawood, G.A.; Mohammed, S.A.; Vimala, Y.D.; Binson, M.T. Pesticide Knowledge and Safety Practices among Farm Workers in Kuwait: Results of a Survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2017, 14, 340. [CrossRef]
- Akashe, M.M.; Uday, V.P.; Ashwin, V.N.; Classification of pesticides: A review. Int. J. Res. Ayurveda Pharm. 2018, 9: 144-152. [CrossRef]
- Kole, R.K.; Roy, K.; Panja, B.N.; Sankarganesh, E.; Mandal, T.; Worede, R.E. Use of pesticides in agriculture and emergence of resistant pests. Indian J. Anim. Hlth. 2019, 58: 53-70. [CrossRef]
- Yawson, D.O. Pesticide use culture among food crop farmers: Implications for subtle exposure and management in Barbados. Agriculture, 2022, 12, 288. [CrossRef]
- Al-Kazafy, H.S. Synthetic fertilizers, roles and hazards. Fertil. Technol. 2015, 1: 111–133.
- Du Jardin, P. Plant biostimulants: Definition, concept, main categories and regulation. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196: 3–14. [CrossRef]
- Minase, N.A.; Masafu, M.M.; Geda, A.E.; Wolde, A.T. Heavy metals in agricultural soils of Central Ethiopia: The contribution of land use types and organic sources to their variability. Open Sci. J. 2016, 6: 99-112. [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Fazio, F.; Habib, S.S.; Nawaz, G.; Attaullah, S.; Ullah, M.; Hayat, A.; Ahmed, I.. Incidence of Heavy Metals in the Application of Fertilizers to Crops (Wheat and Rice), a Fish (Common carp) Pond and a Human Health Risk Assessment. Sustainability, 2022, 14, 13441. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, J. Geochemical behavior and potential health risk of heavy metals in basalt-derived agricultural soil and crops: A case study from Xuyi County, eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729: 139058. [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Ji, J.; Yang, Z.; Han, H.; Zhang, W. Cadmium risk in the soil-plant system caused by weathering of carbonate bedrock. Chemosphere, 2020, 254, 126799. [CrossRef]
- Inna, D.; Yury, M.; Evgeny, D.; Tatiana, G. Impact of drainage on heavy metal pollution of soils and land usage regulation. 16th International Scientific Conference: Engineering for Rural Development, Jelgava, Latvia, 24th-26th May, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jia, J.; Bao, X. Heavy metals and lead isotopes in soils, road dust and leafy vegetables and health risks via vegetable consumption in the industrial areas of Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 620: 1349–1357. [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.; Fan, W.; Chen, J.; Jiang, S.; Huang, S.; Peng, L.; Zeng, Q.; Luo, S. Annual input and output fluxes of heavy metals to paddy fields in four types of contaminated areas in Hunan Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634: 67–76. [CrossRef]
- Mungai, T.M.; Jun, W. Heavy metal pollution in suburban topsoil of Nyeri, Kapsabet, Voi, Ngong and Juja towns, in Kenya. SN App. Sci. 2019, 1: 960. [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Niu, Z.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, J.; Xiang, P. Soil heavy metal pollution and food safety in China: Effects, sources and removing technology. Chemos. 2022, 267, 129205. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, N.; Meng, W.; He, J.; Wu, P. 2022. Accumulation and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal(loid)s in Soil-Crop Systems from Central Guizhou, Southwest China. J. Agric. 2022, 12, 981. [CrossRef]
- Sayadi, M.H.; Mehri, S.; Najmeh, A. Pollution Index and Ecological Risk of Heavy Metals in the Surface Soils of Amir-Abad Area in Birjand City, Iran. Health Scope, 2015, 4:e2113.
- Akenga, T.; Ayabei, K.; Kerich, E.; Sudoi, V.; Kuya, C. Evaluation of levels of selected heavy metals in kales, soils and water collected from irrigated farms along River Moiben, Uasin-Gishu County, Kenya. J. Geosci. Environ. Protec. 2020, 8: 144-155. ISSN 2327-4336.
- Sharma, A.; Vinod, K.; Babar, S.; Mohsin, T.; Gagan, P.; Singh, S.; Neha, H.; Sukhmeen, K.; Poonam, Y.; Aditi, S.; et al. Worldwide pesticide usage and its impacts on ecosystem. App. Sci. 2019, 1, 1446. [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Yulong, R.; Shijie, W.; Xiuming, L.; Bin, L. Effects of organic mineral fertilizer on heavy metal migration and potential carbon sink in soils in a karst region. Acta Geochim, 2017, 36: 539–543. 543. [CrossRef]
- Kinuthia, G.K.; Ngure, V.; Dunstone, B.; Lugalia, R.; Agnes, W.; Kamau, L. Levels of heavy metals in wastewater and soil samples from open drainage channels in Nairobi, Kenya: Community health implication. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10: 8434. [CrossRef]
- Angelone, M.; and Bini, C. Trace element concentrations in soils and plants of Western Europe. Biogeochemistry of trace metals. CRC Press. 2017. pp. 31–72.
- Hu, Z.C.; Li, J.W.; Wang, H.L.; Ye, Z.Q.; Wang, X.D.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, D.; Song, Z.L. Soil Contamination with Heavy Metals and Its Impact on Food Security in China. J. Geosci. Environ. Protec. 2019, 7:168-183.
- Tomno, R.M.; Kitulu, L.; Nzeve, J.K.; Waswa, F.; Mailu, S.N.; Shitanda, D. Heavy Metal Concentrations in Vegetables Cultivated and Sold in MachakosMunicipality, Kenya. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manage. 2020, 24: 2027-2034. ISSN 1119-8362.
- González, H.; Ghneim-Herrera, T. Heavy Metals in Soils and the Remediation Potential of Bacteria Associated With the Plant Microbiome. Fron. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9: 604216. [CrossRef]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Naseri, K.; Tahergorabi, Z.; Khazdair, M.; Sadeghi, M. Toxic mechanisms of five heavy metals: mercury, lead, chromium, cadmium, and arsenic. Fron. Pharm. 2021, 12; 643972. [CrossRef]
- Omwoma, S.L.; Joseph, O.L.; Ongeri, D.M.; Wanyonyi, B.M. Impact of fertilizers on heavy metals loads in Nzoia nucleus estate sugarcane farms in Western Kenya. Bull. Environ. Cont. Toxicol. 2010, 85: 602-608. [CrossRef]
- Limo, E.; Kipkemboi, P.K.; Kipkemei A.S.; Kituyi, L. Concentration, partitioning and enrichment of heavy metals in water, soil and sediments in River Kapsabet micro-watershed scale, Kenya. Int. J. of Sci. Eng. Res. 2015, 6; 1404-1427. ISSN 2229-5518.
- Nyika, J.; Megersa, O.D. Heavy metal pollution in soils and vegetables from suburban regions of Nairobi, Kenya and their community health implications. Pollut. 2022, 8: 1434-1447. [CrossRef]
- Onyando, Z.O.; Omukunda, E.; Okoth, P.; Khatiebi, S.; Omwoma, S.; Otieno, P.; Osano, O.; Lalah, J. 2023. Screening and Prioritization of Pesticide Application for Potential Human Health and Environmental Risks in Largescale Farms in Western Kenya. Agriculture, 2023, 13, 1178. [CrossRef]
- Government of Kenya. Trans Nzoia County Integrated Development Plan 2018–2022 Indicator Handbook; Government Printer: Nairobi, Kenya, 2018. pp. 1–13.
- Okalebo, J.R.; Gathua, K.W.; Woomer, P.L. Laboratory methods for soil and plant analysis: A working manual. TSBF, Nairobi, Kenya. 2002.
- Kowalska, J.B.; Mazurek, R.; Gąsiorek, M. Pollution indices as useful tools for the comprehensive evaluation of the degree of soil contamination–A review. Environ Geochem Health. 2018. 40, 2395–2420. [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, J.; Subash, S.; Krishna, P.T.; Sudeep, S.; Meena, P.; Aakriti, S.; Sajina, S.; Mohammad, A.H. Sustainable Intensification in Agriculture: An Approach for Making Agriculture Greener and Productive. J. Nepal Agric. Res. Council, 2021. 7: 133-150.
- Bacar, T.S.; Cheng, Y.B.; Wang, Y.Q.; Kaboul, K.; Lopes, N.D. The Effect of Vegetation Restoration in Soil Organic Carbon Storage. Open J. Soil Sci. 2022, 12: 427-445. [CrossRef]
- Zajícová, K.; Chuman, T. Effect of land use on soil chemical properties after 190 years of forest to agricultural land conversion. Soil Water Res. 2019, 14: 121–131. [CrossRef]
- Bato, Y.; Bekele, T.; Demissew, S. Effect of different land use systems and soil depths on soil chemical properties alteration in Yerer forests and its surrounding area, at the central highland of Ethiopia. Research Square, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2020.
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Standard operating procedure for soil pH determination. Rome, Italy, 2021.
- Läuchli, A.; Grattan, S.R. Soil PH extremes. Plant Stres. Phys. 2012, 3: 194-209. [CrossRef]
- Lake, B. 2000. Understanding soil PH. South wales.
- Shapkota, J.; Kafle, G.; Variation in Soil Organic Carbon under Different Forest Types in Shivapuri Nagarjun National Park, Nepal. Scientifica, 2021, 1382687. [CrossRef]
- Tesfahunegn, G.B.; Gebru, T.A. Variation in soil properties under different cropping and other land-use systems in Dura catchment, Northern Ethiopia. PLoS ONE, 2020, 15: 2. [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Standard operating procedure for soil Total Carbon. Rome, Italy, 2019.
- Upadhyay, P.; Vaishampayan, A.; Jaiswal, S.K. Soil Pollution Caused by Agricultural Practices and Strategies to Manage It. In: Plant Responses to Soil Pollution. Singh, P., Singh, S.K., Prasad, S.M. (eds). Springer, Singapore, 2020. Pp. 119–132. [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, A.; Emmaverdian, A.; Pehlivan, N.; Zargar, M.; Razavi, S.M.; Chen, M. Nano enabled agrochemicals mitigating heavy metal toxicity and enhancing crop adaptability for sustainable production. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 191. [CrossRef]
- Adriano DC. 2001. Trace Elements in Terrestrial Environments: Biogeochemistry, Bioavailability, and Risks of Metals. Springer, New York, NY, USA.
- Li, X.; Liu, H.; Meng,W.; Liu, N.; Wu, P. Accumulation and source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils based on GIS, SOM and PMF: A case study in superposition areas of geochemical anomalies and zinc smelting, Southwest China. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159: 964–977.
- Saha, J.K.; Selladurai, R.; Coumar, M.V.; Dotaniya, M.L.; Kundu, S.; Patra, A.K. Assessment of Heavy Metals Contamination in Soil. In: Soil Pollution-An Emerging Threat to Agriculture. Environ. Chem. Sust. World. 2017, vol 10. Springer, Singapore. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xinbin, F.; Christopher, W.N.; Erson, X.; Guangle, Q.; Zhengduo, B.Y.; Lihai, S. Effect of cropping systems on heavy metal distribution and mercury fractionation in the Wanshan Mining District, China: Implications for environmental management. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 2147-2155. [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Yu, H. Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil in Dehui, Northeast China. Chemos. 2013 92: 517–523. [CrossRef]
- Kelepertzis, E. Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Mediterranean: insights from Argolida Basin, Peloponnese, Greece. Geoderma, 2014, 221: 82–90. [CrossRef]
- Guo J.; Yue T.; Li, X.; Yuan, Y. Heavy metal levels in Kiwifruit orchard soils and trees and its potential health risk assessment in Shaanxi, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 14: 14560-14566. [CrossRef]
- Haider, F.U.; Liqun, C.; Coulter, J.A.; Cheema, S.A.; Wu, J.; Zhang, R.; Wenjun, M., and Farooq M. Cadmium toxicity in plants: Impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. saf. 2021, 211: 111887. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Danyang, Y.; Yanhong, W.; Xueli, D.; Guochen, L.; Bo, L.; Yujie, Z.; Yinghui, W.; Shuang, X. Source analysis of heavy metalpollution in agricultural soil irrigated with sewage in Wuqing, Tianjin. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11:17816. [CrossRef]
- Fishel, F.M. Pesticide Toxicity Profile: Copper-based Pesticides. EDIS, University of Florida, 2014. 5. 2005. [CrossRef]
- Tóth, G.; Hermann, T.; Da Silva, M.R.; Montanarella, L. Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environ. Int. 2016, 88: 299–309. [CrossRef]
| Cropping systems | |||||||
| Parameters | N | Maize (MF) | Orchard (OF) | Sugarcane (SF) | Coffee (CF) | Pasture land (PL) | Shrub land (CS) |
| PH | 204 | 5.699±0.390 | 6.636±0.241 | 5.760±0.279 | 6.491±0.317 | 6.648±0.179 | 6.640±0.133 |
| EC (µS cm-1) | 204 | 17.467±6.610 | 42.766±15.210 | 10.533±7.401 | 30.645±18.170 | 9.700±4.864 | 10.187±7.600 |
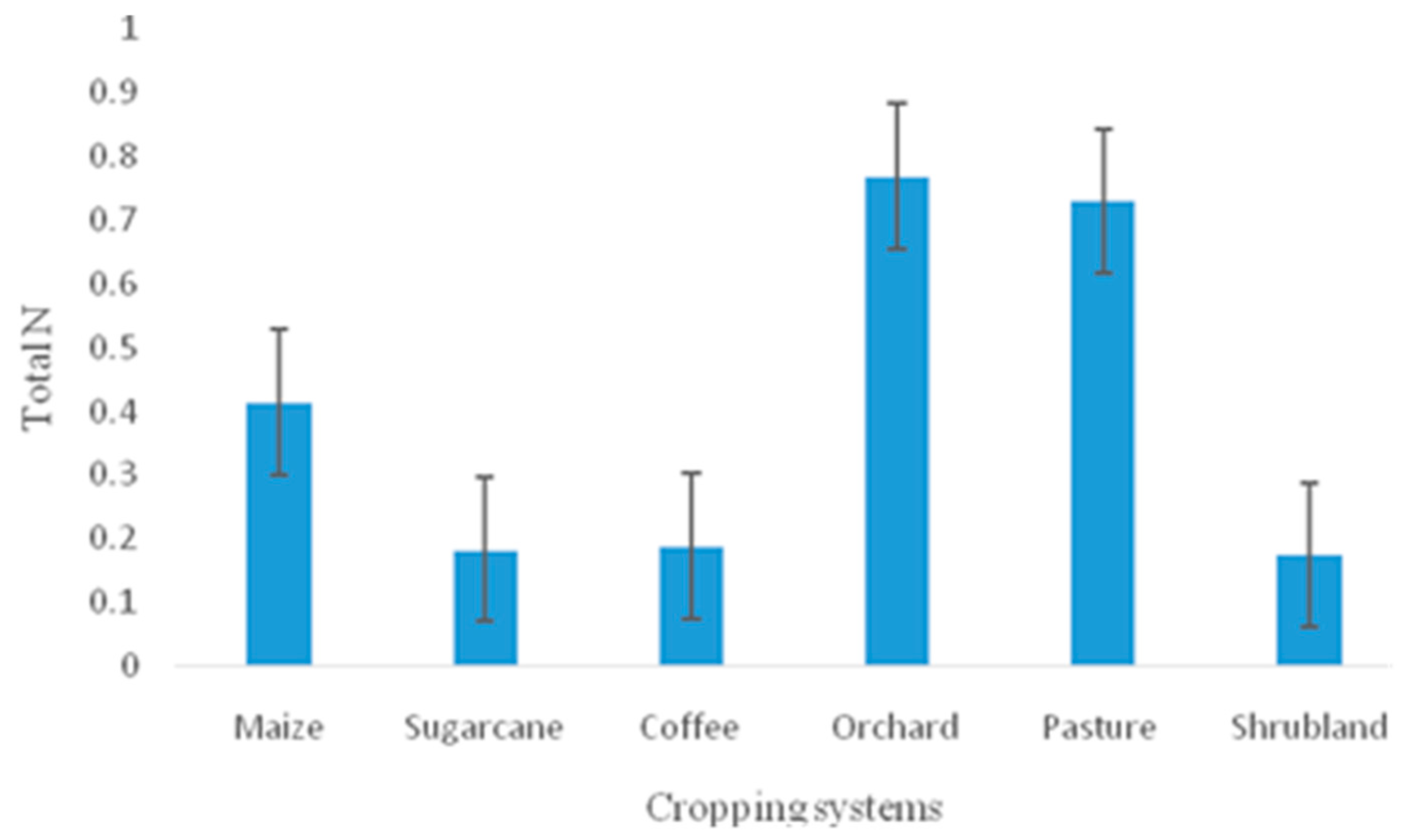
| Total N(MgL1) | 204 | 0.415±0. 362 | 0.769±0.295 | 0.183±0.024 | 0.188±0. 087 | 0.730±0.268 | 0.174±0.189 |
| Na+ (MgKg-1) | 204 | 549.748±31.073 | 425.71±107.038 | 450.260±54.456 | 533.540±91.057 | 583.798±24.515 | 433.290±96.874 |
| K+ (MgKg-1) | 204 | 359.059±74.505 | 246.18±23.729 | 301.594±54.456 | 320.051±42.2458 | 271.069±15.411 | 234.941±82.533 |
| Ca2+ (MgKg-1) | 204 | 683.094±29.657 | 372.73±43.053 | 439.669±99.284 | 526.749±90.814 | 363.954±22.951 | 389.770±166.840 |
| Mg2+ (MgKg-1) | 204 | 353.145±22.778 | 255.39±44.621 | 371.607±67.731 | 401.313±84.577 | 367.795±367.795 | 259.621±47.814 |
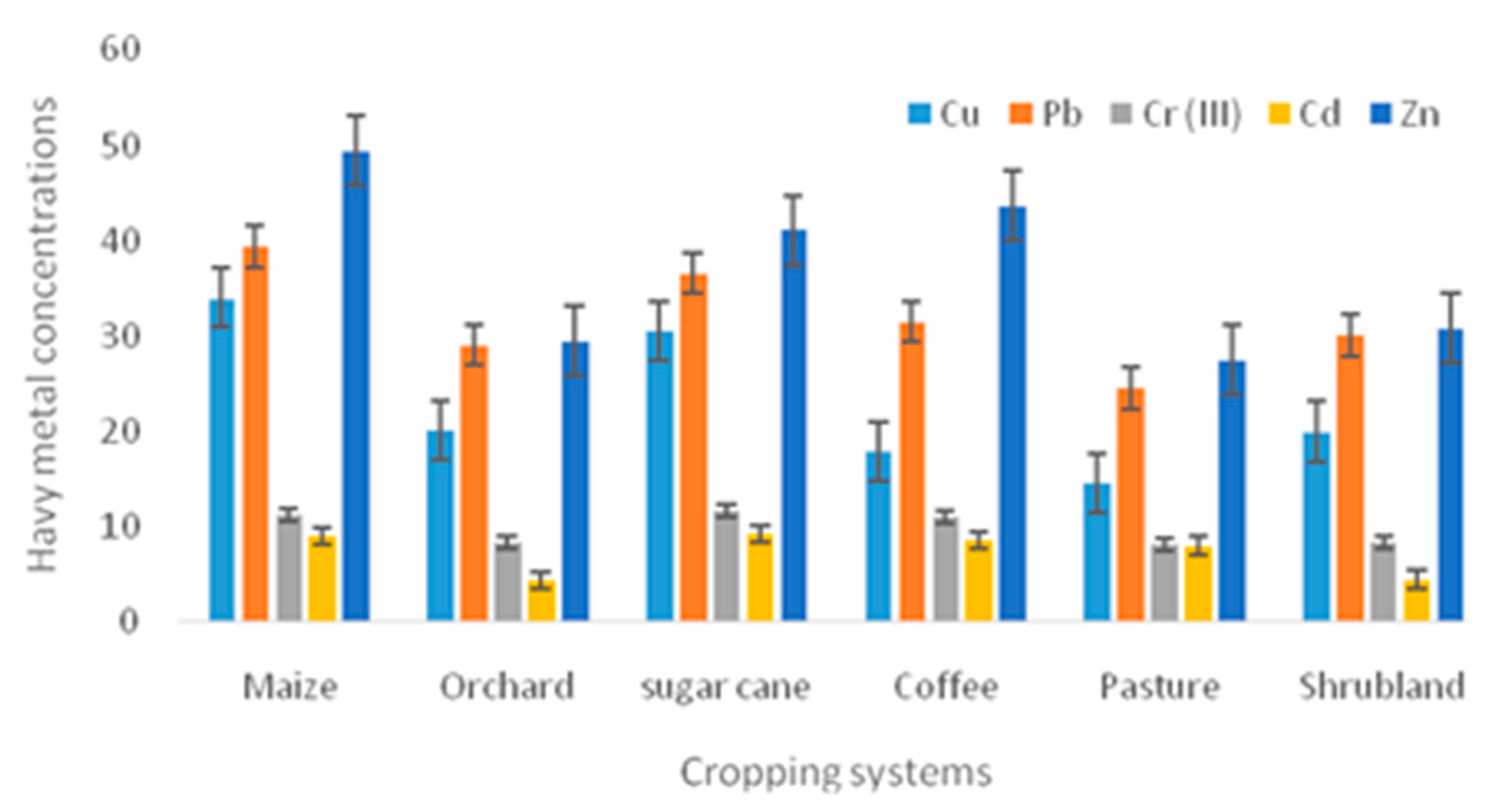
| Cu (MgKg-1) | 204 | 33.985±1.731 | 20.152±5.0748 | 30.503±11.531 | 17.855±3.344 | 14.587±2.647 | 20.010±4.414 |
| Pb (MgKg-1) | 204 | 39.389±3.455 | 29.077±5.6342 | 36.634±8.528 | 31.544±7.604 | 24.532±3.902 | 30.105±7.298 |
| Cr (MgKg-1) | 204 | 11.251±0. 604 | 8.311±1.155 | 11.656±1.542 | 11.095±2.661 | 8.255±1.005 | 8.494±2.010 |
| Cd (MgKg-1) | 204 | 9.042±0.582 | 4.475±0.531 | 9.347±1.827 | 8.644±1.325 | 8.032±1.064 | 4.535±0.992 |
| Zn (MgKg-1) | 204 | 49.478±2.588 | 29.488±1.880 | 41.134±5.255 | 43.663±6.306 | 27.543±3.927 | 30.776±9.471 |
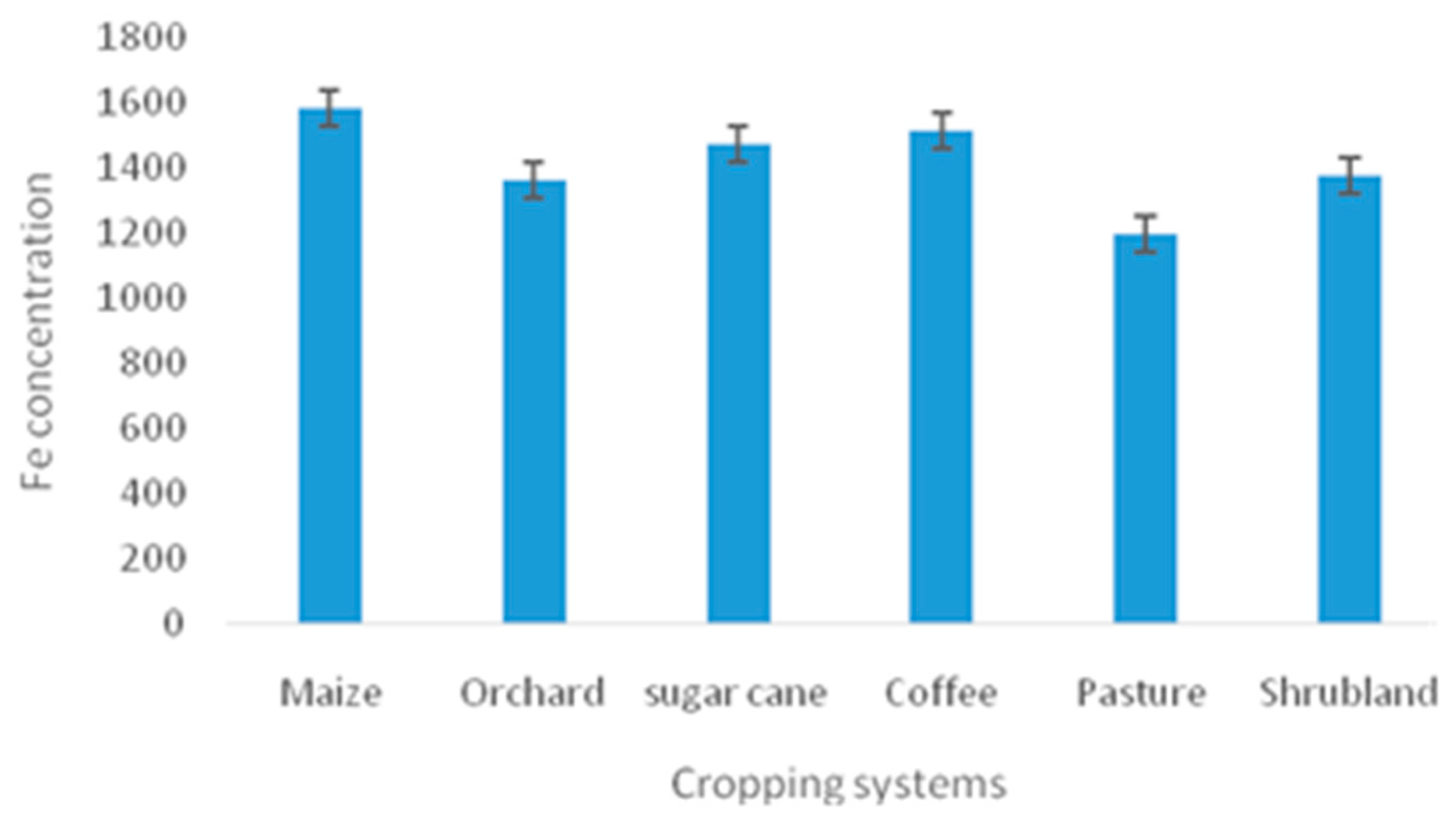
| Fe (MgKg-1) | 204 | 1583.833±77.953 | 1365.9±39.638 | 1474.104±77.142 | 1519.611±115.022 | 1201.513±70.629 | 1377.254±136.205 |
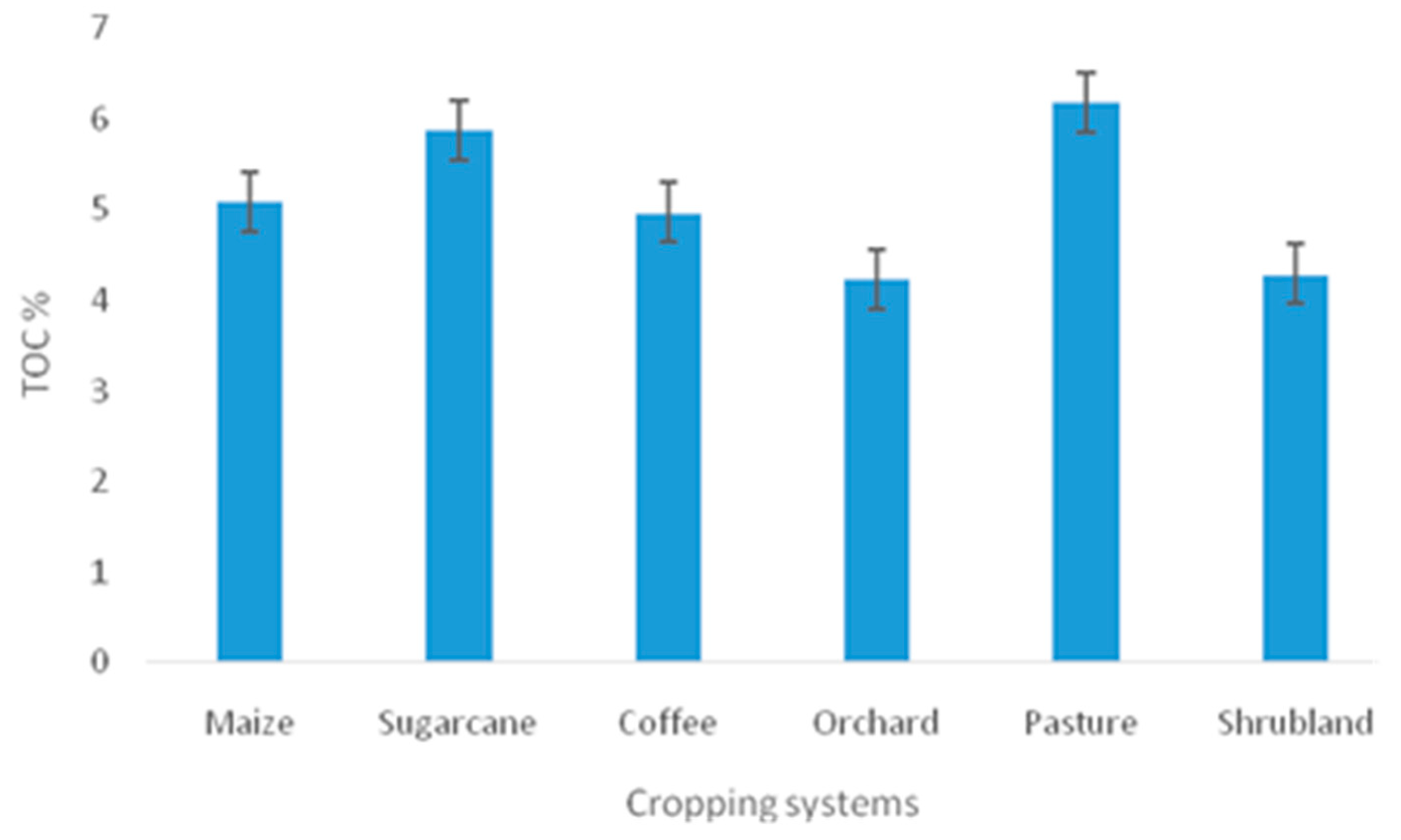
| TOC (%) | 204 | 5.089±0. 596 | 4.233±0.525 | 5.877±1.262 | 4.970±1.295 | 6.195±0.687 | 4.287±2.048 |
| Cropping system | Metal (Mg/Kg) |
WHO permitted soil limit (Mg/Kg) | Bn (Mg/Kg) |
Cn (Mg/Kg) |
NPI | Pollution class interpretation |
| Maize | Cu | 36.000 | 20.010 | 33.985 | 0.944 | Tending towards pollution |
| Pb | 85.000 | 30.105 | 39.389 | 0.463 | Less chances of pollution | |
| Cr (III) | 100.000 | 8.494 | 11.251 | 0.112 | Less chances of pollution | |
| Cd | 0.800 | 4.535 | 9.042 | 11.303 | Surplus levels hence pollution | |
| Zn | 50.000 | 30.776 | 49.478 | 0.990 | Tending towards pollution | |
| Fe | 5000.000 | 1377.254 | 1583.833 | 0.317 | Less chances of pollution | |
| Orchard | Cu | 36.000 | 20.010 | 20.152 | 0.560 | Tending towards pollution |
| Pb | 85.000 | 30.105 | 29.077 | 0.342 | Less chances of pollution | |
| Cr (III) | 100.000 | 8.494 | 8.311 | 0.083 | Less chances of pollution | |
| Cd | 0.800 | 4.535 | 4.475 | 5.594 | Surplus levels hence pollution | |
| Zn | 50.000 | 30.776 | 29.488 | 0.590 | Tending towards pollution | |
| Fe | 5000.000 | 1377.254 | 1365.9 | 0.273 | Less chances of pollution | |
| Sugar cane | Cu | 36.000 | 20.01 | 30.503 | 0.847 | Tending towards pollution |
| Pb | 85.000 | 30.105 | 36.634 | 0.431 | Less chances of pollution | |
| Cr (III) | 100.000 | 8.494 | 11.656 | 0.117 | Less chances of pollution | |
| Cd | 0.800 | 4.535 | 9.347 | 11.684 | Surplus levels hence pollution | |
| Zn | 50.000 | 30.776 | 41.134 | 0.823 | Tending towards pollution | |
| Fe | 5000.000 | 1377.254 | 1474.104 | 0.295 | Tending towards pollution | |
| Coffee | Cu | 36.000 | 20.01 | 17.855 | 0.496 | Less chances of pollution |
| Pb | 85.000 | 30.105 | 31.544 | 0.371 | Less chances of pollution | |
| Cr (III) | 100.000 | 8.494 | 11.095 | 0.111 | Less chances of pollution | |
| Cd | 0.800 | 4.535 | 8.644 | 10.805 | Surplus levels hence pollution | |
| Zn | 50.000 | 30.776 | 43.663 | 0.873 | Tending towards pollution | |
| Fe | 5000.000 | 1377.254 | 1519.611 | 0.304 | Less chances of pollution | |
| Pastureland | Cu | 36.000 | 20.01 | 14.587 | 0.405 | Less chances of pollution |
| Pb | 85.000 | 30.105 | 24.532 | 0.289 | Less chances of pollution | |
| Cr (III) | 100.000 | 8.494 | 8.255 | 0.083 | Less chances of pollution | |
| Cd | 0.800 | 4.535 | 8.032 | 10.04 | Surplus levels hence pollution | |
| Zn | 50.000 | 30.776 | 27.543 | 0.551 | Tending towards pollution | |
| Fe | 5000.000 | 1377.254 | 1201.513 | 0.240 | Less chances of pollution | |
| Shrubland | Cu | 36.000 | 20.01 | 20.010 | 0.556 | Tending towards pollution |
| Pb | 85.000 | 30.105 | 30.105 | 0.354 | Less chances of pollution | |
| Cr (III) | 100.000 | 8.494 | 8.494 | 0.085 | Less chances of pollution | |
| Cd | 0.800 | 4.535 | 4.535 | 5.669 | Surplus levels hence pollution | |
| Zn | 50.000 | 30.776 | 30.776 | 0.616 | Tending towards pollution | |
| Fe | 5000.000 | 1377.254 | 1377.254 | 0.275 | Less chances of pollution |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





