Submitted:
07 August 2024
Posted:
08 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Magnetic (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles
2.3. Synthesis of Fe3O4@SiO2
2.4. Synthesis of Graphene Oxide
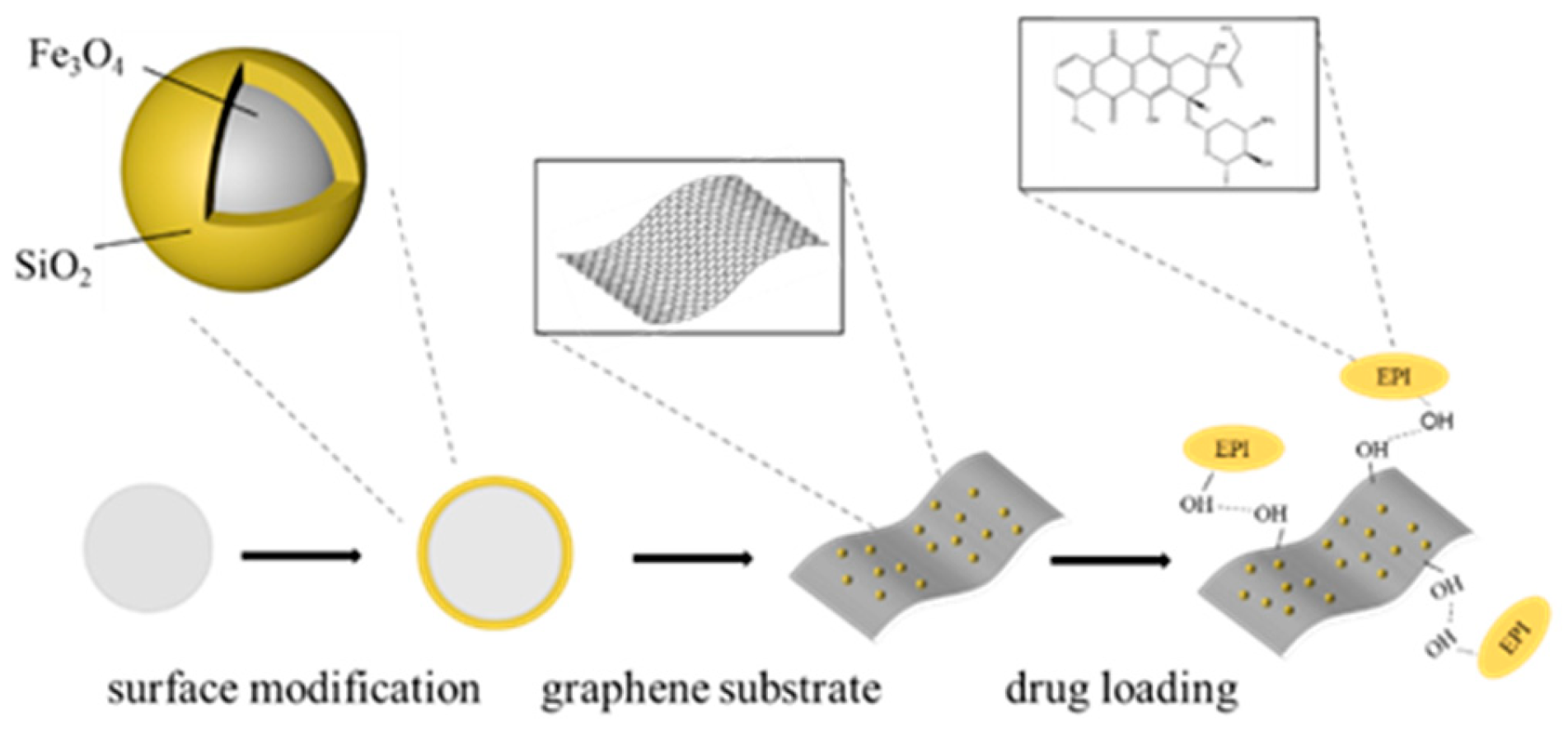
2.5. Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2/N–rGO
2.6. Drug Loading Preparation of EPI–Loaded Fe3O4@SiO2/rGO
2.7. Drug Release
3. Results and Discussion
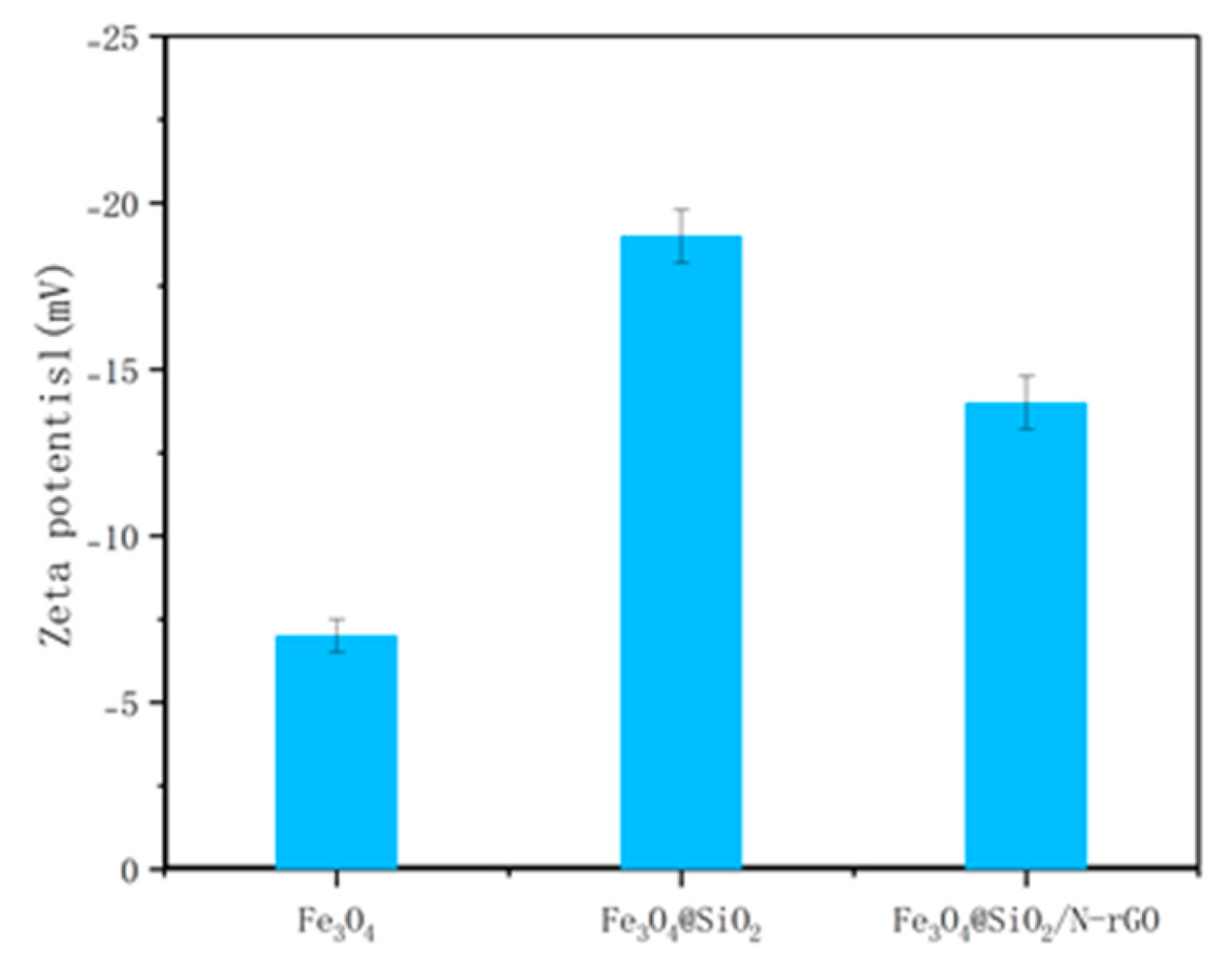
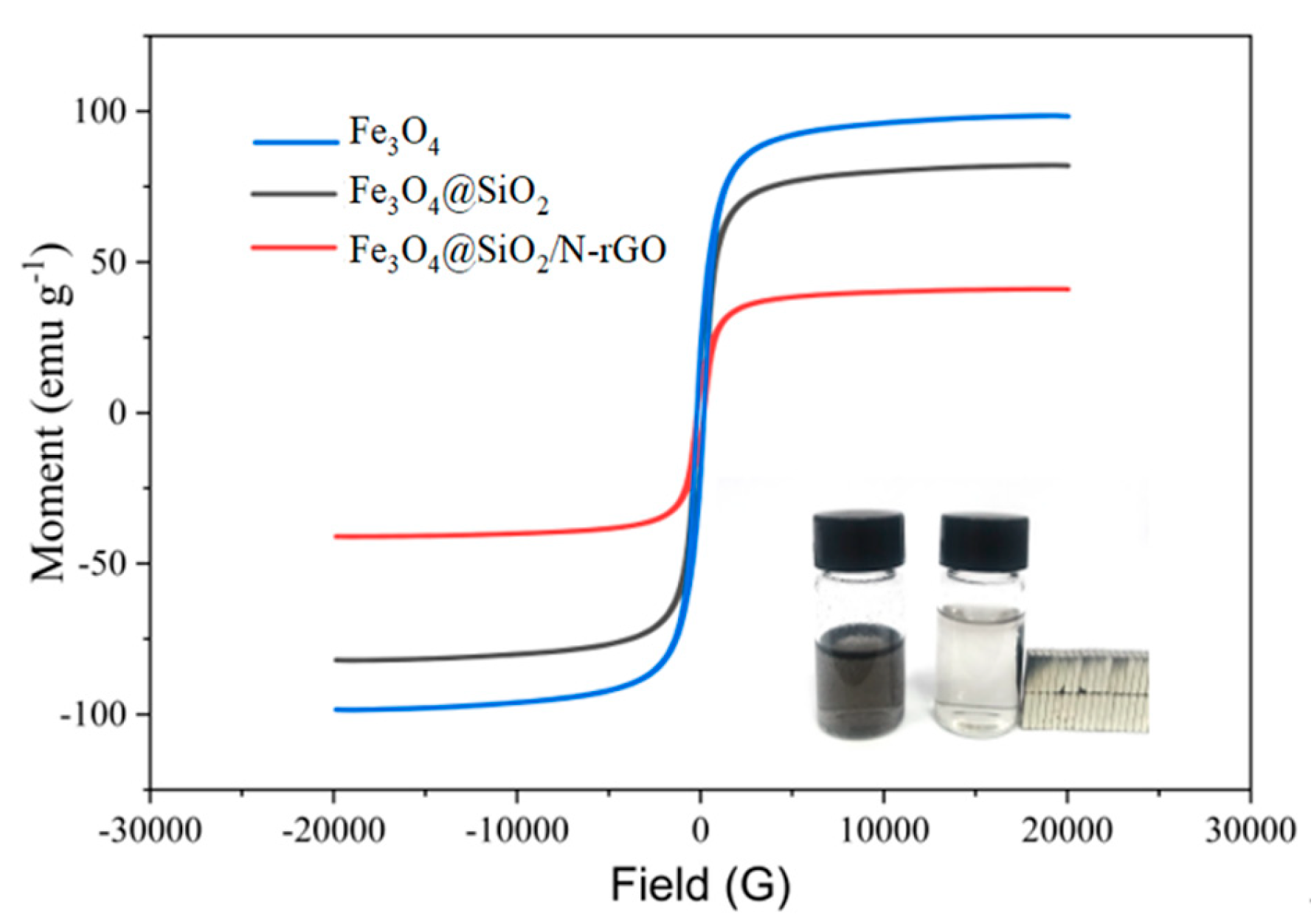
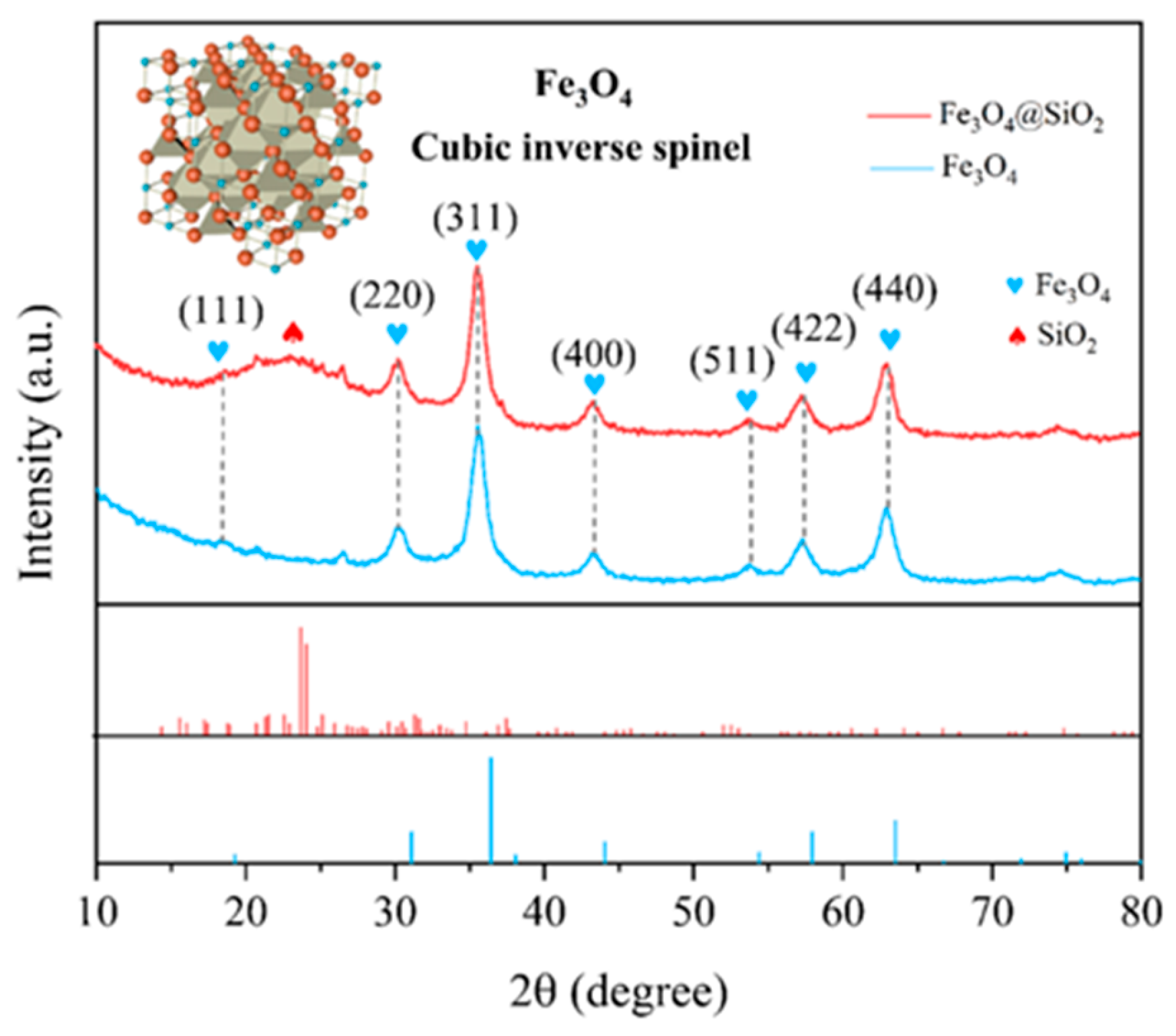
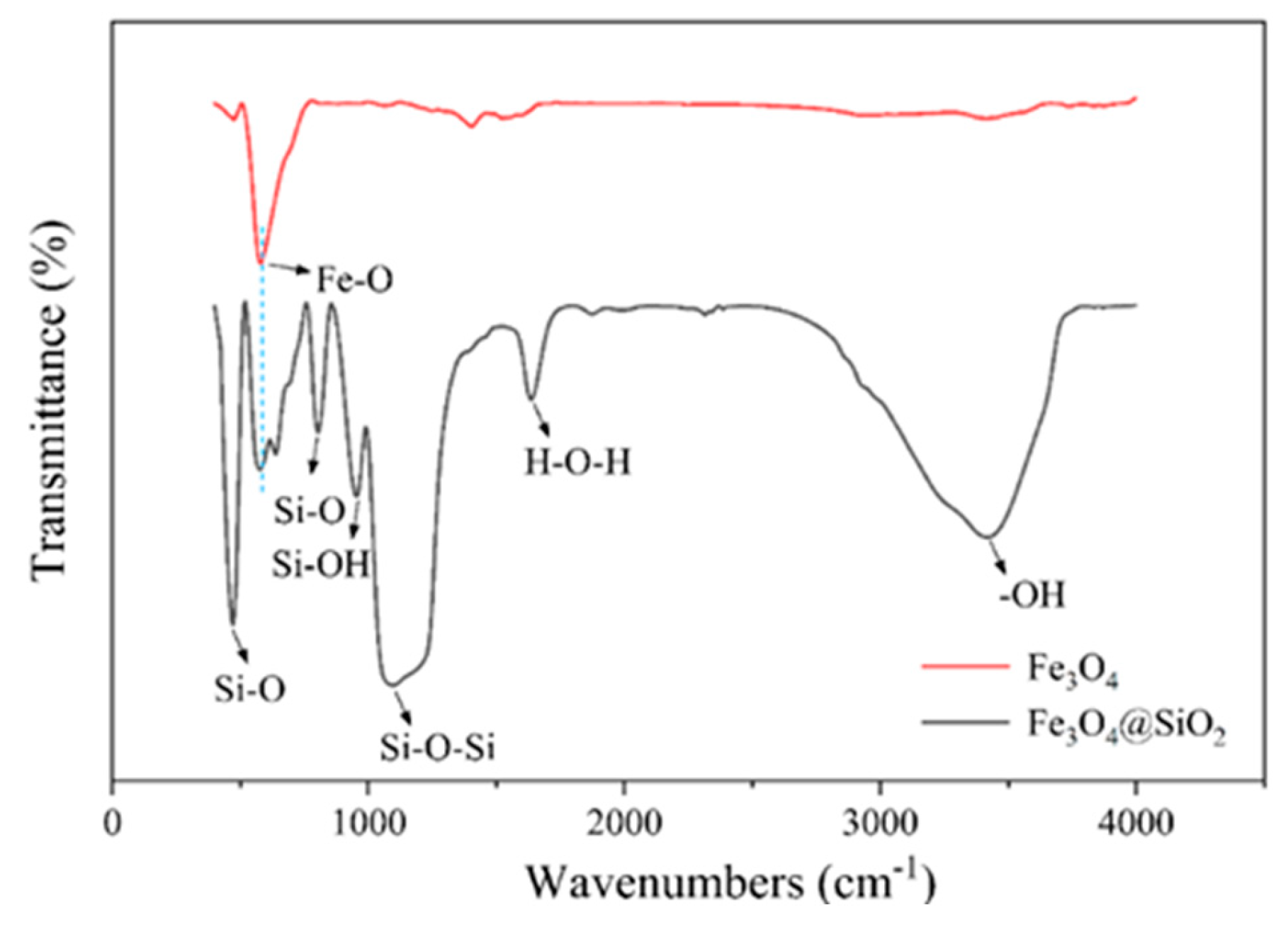
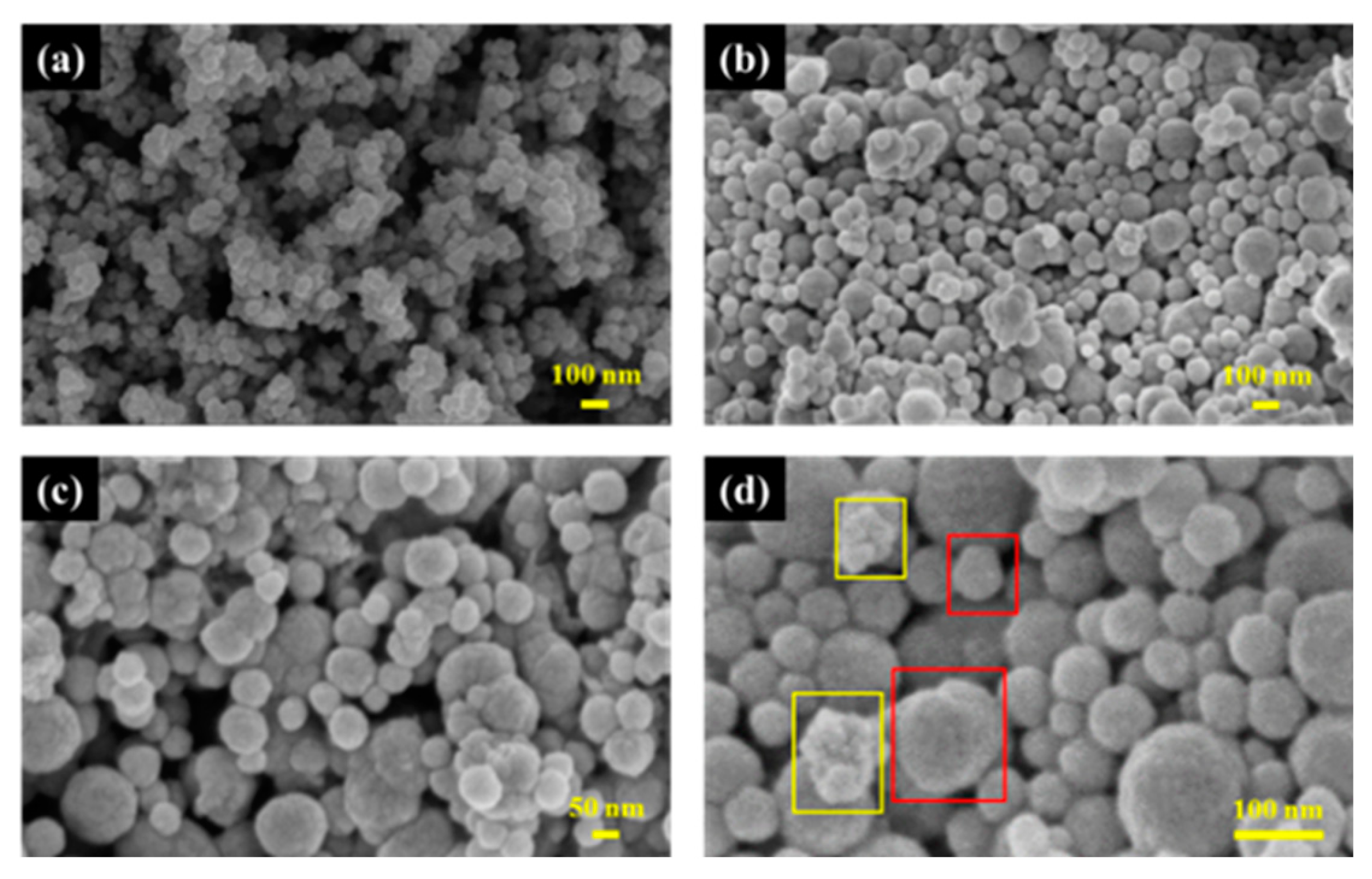
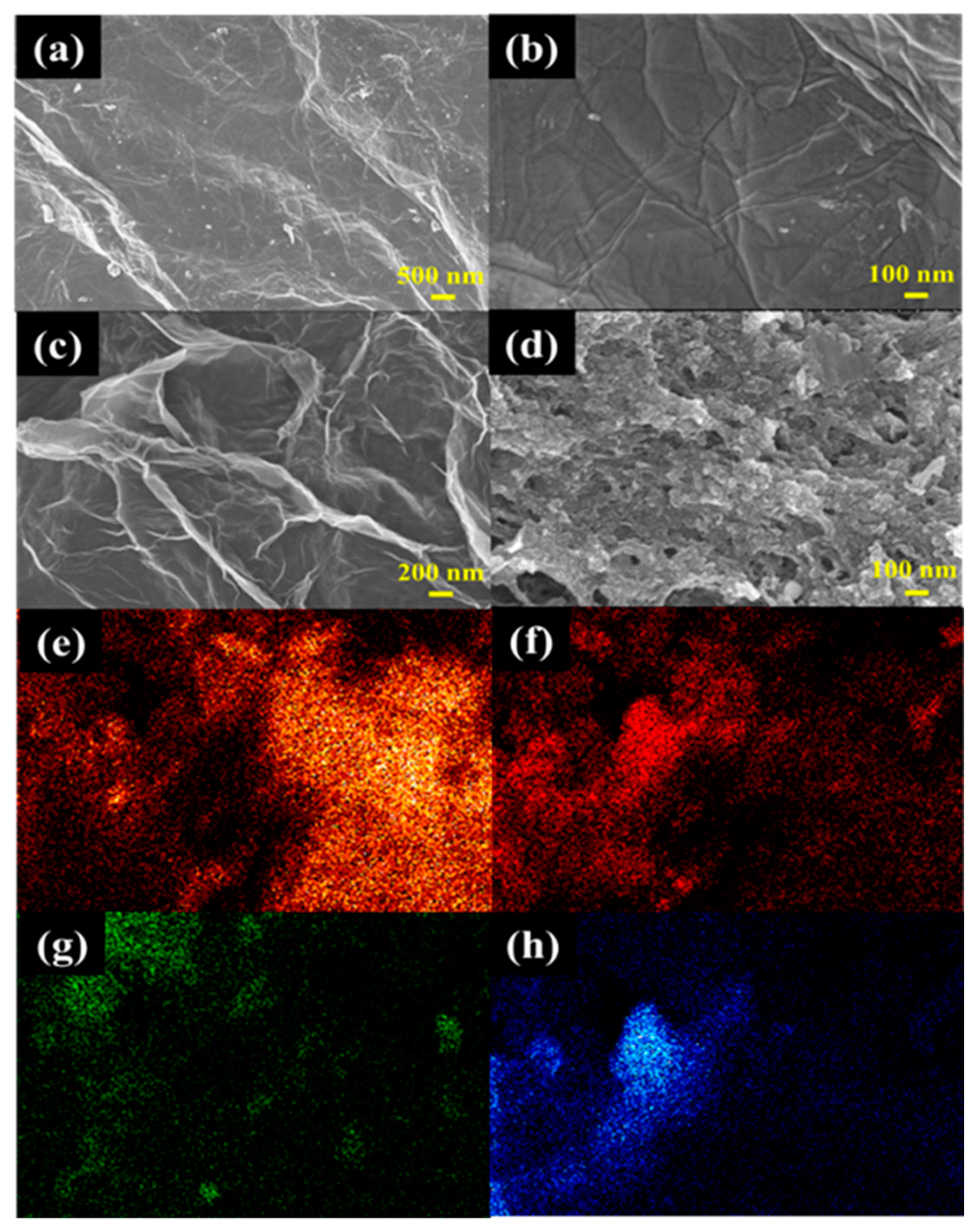
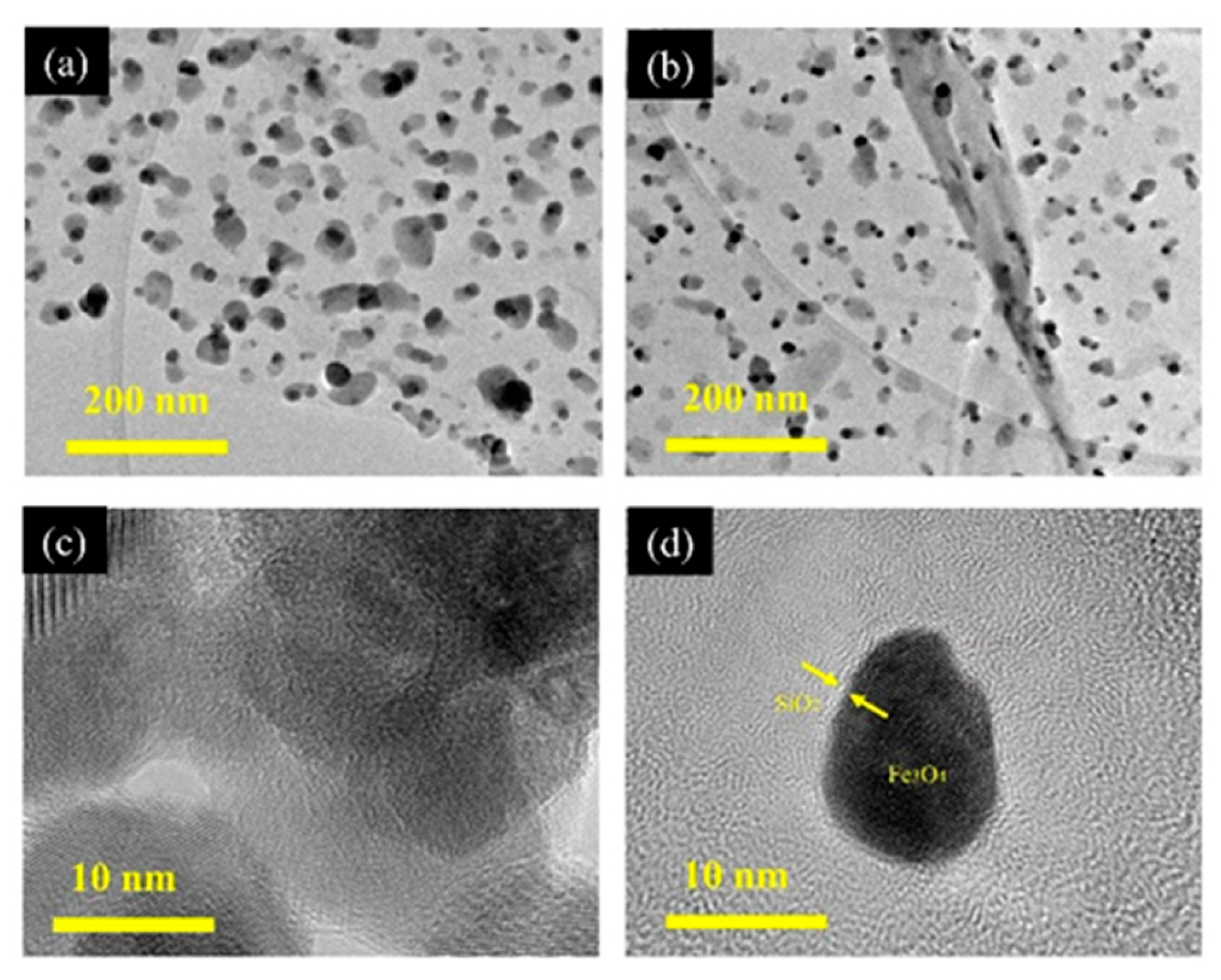
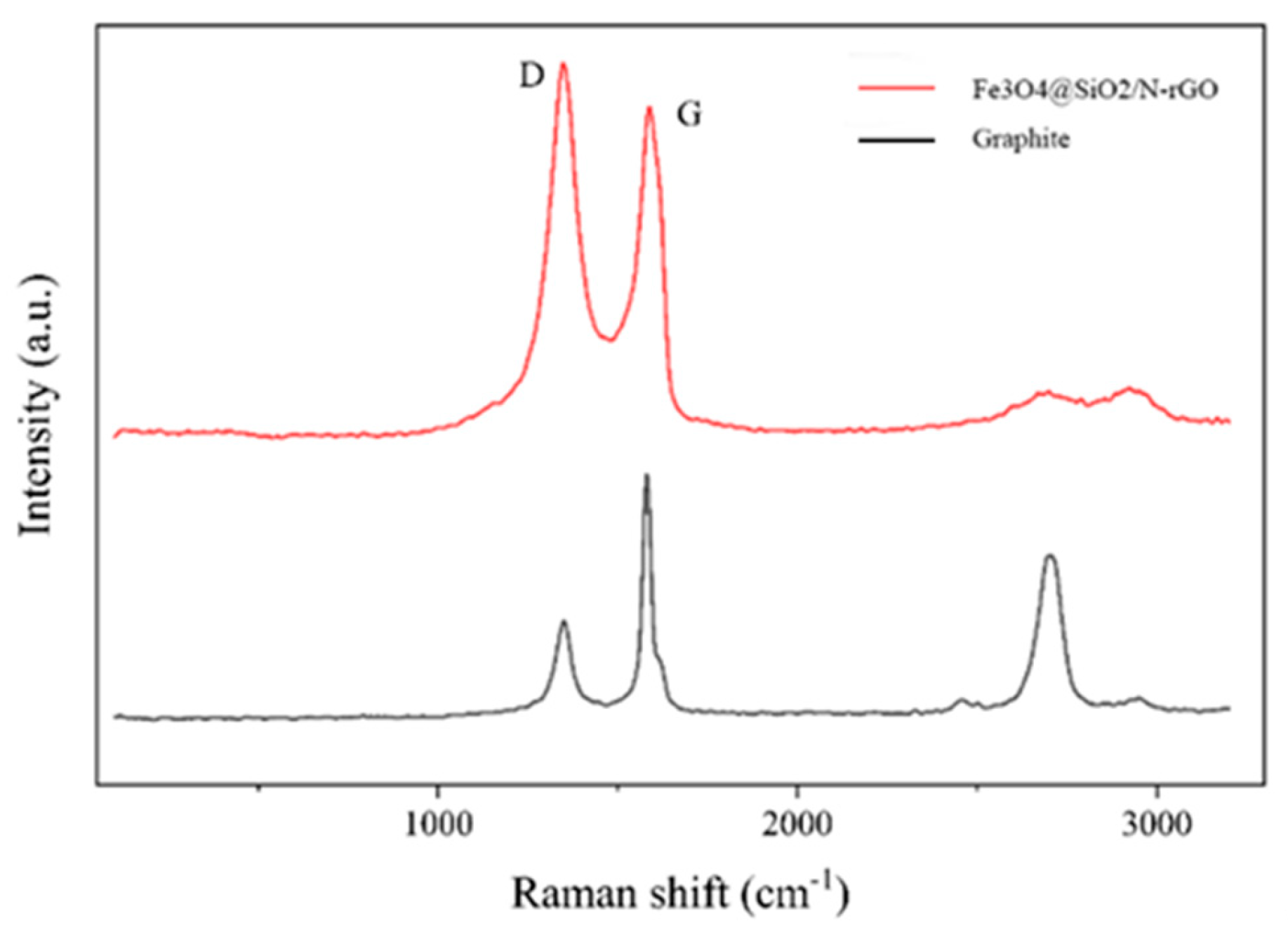
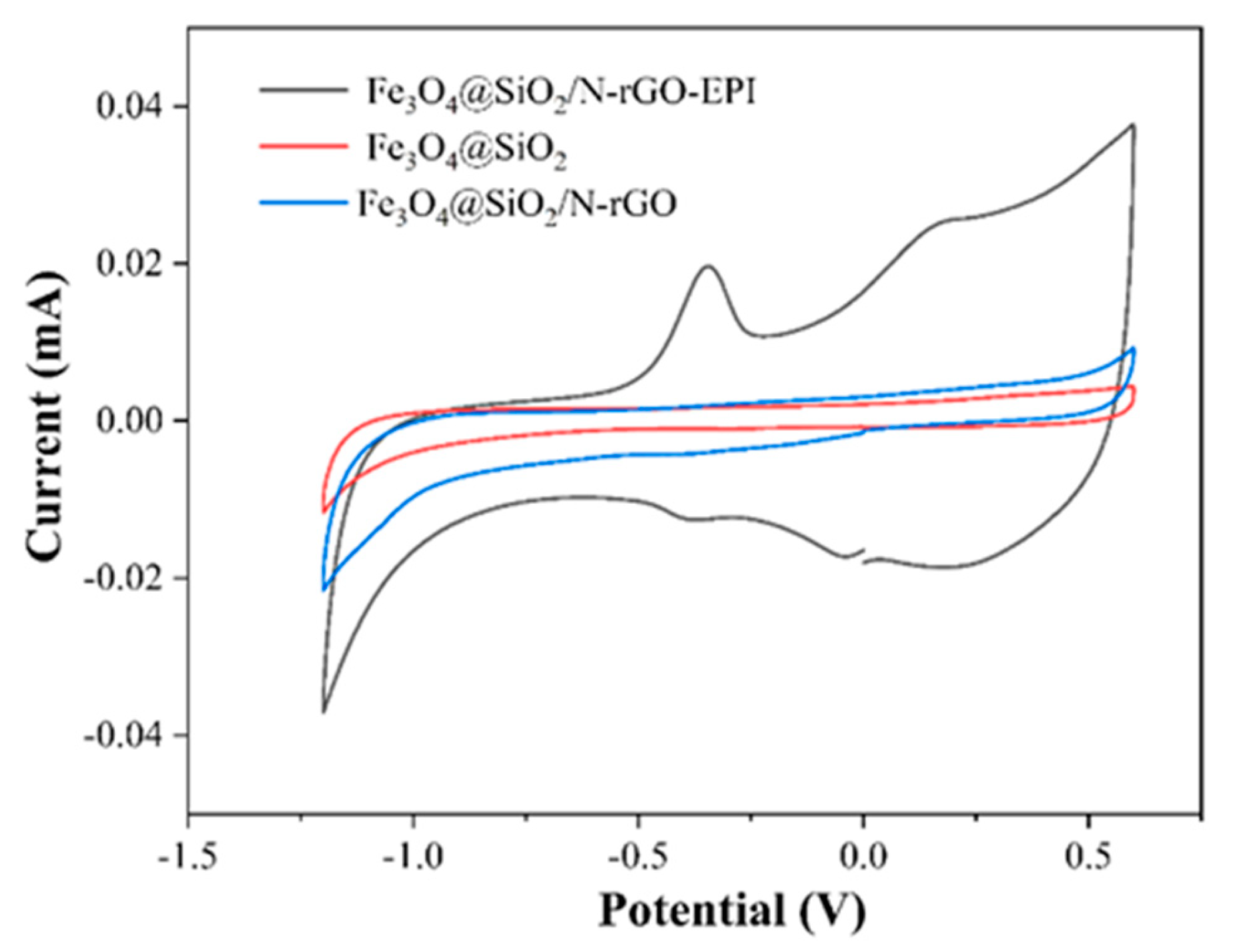
3.1. Structural Characterization
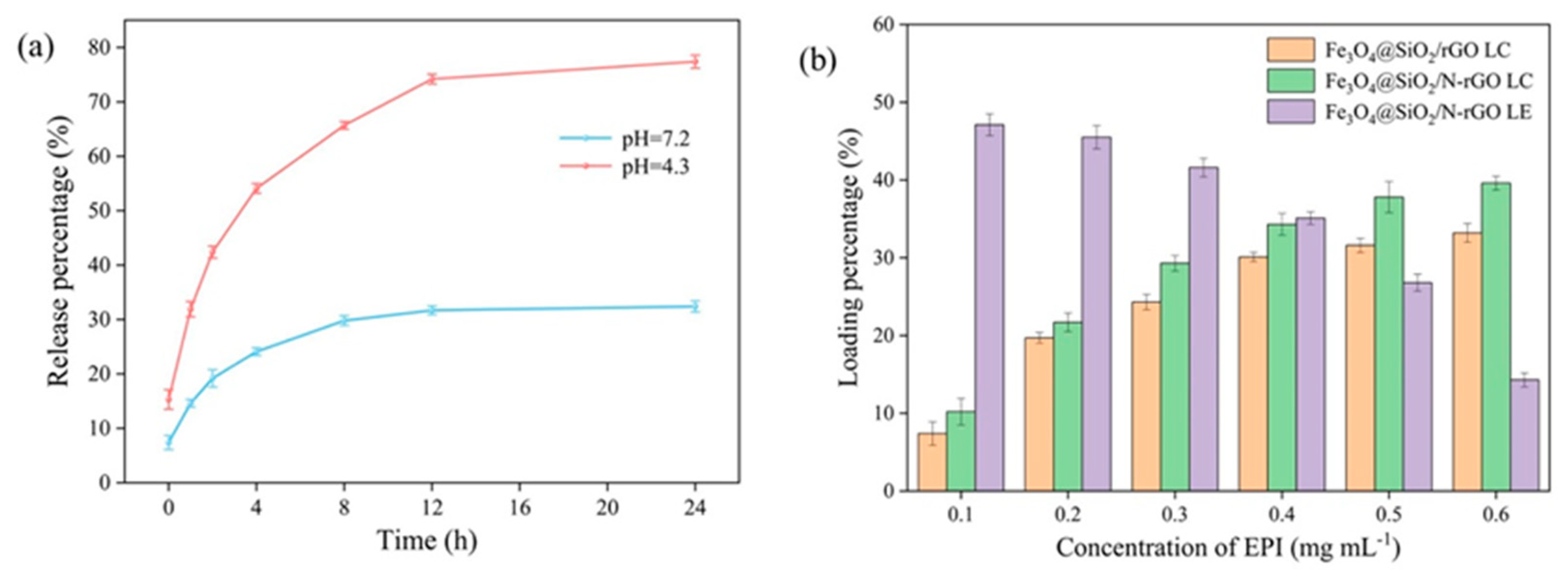
3.1. Performance of Drug Carrier
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weng, N.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, X.; Zhu, Q. Repurposing antifungal drugs for cancer therapy. Journal of Advanced Research 2023, 48, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Ahmed, A.; Wang, Q.; Cong, H.; Shen, Y.; Yu, B. Preparation and chromatographic application of β-cyclodextrin modified poly (styrene-divinylbenzene) microspheres. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e53180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, N.; Mohammadi-Manesh, E.; Ahmadvand, N.; Danafar, H.; Ghiasvand, S. Curcumin-Loaded by Fe3O4/GO and Fe3O4/ZnO/GO Nanocomposites for Drug Delivery Applications: Synthesis, Characterization and Anticancer Assessment. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials 2024, 34, 1256–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Xue, D. Green immobilized Ag NPs over magnetic Fe3O4 NPs using Pomegranate juice induces apoptosis via P53 and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathways in human gastric cancer cells. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 146, 110159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; You, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, J. Green synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4/Ag nanocomposite using Pomegranate peel extract for the treatment of ovarian cancer. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2024, 17, 105394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; An, Q.; Li, M.; Lv, X. Chitosan-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the oral delivery of Norcantharidin: In vitro and in vivo assessment. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2024, 369, 113013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangra, N.; Kawatra, A.; Datten, B.; Gupta, S.; Gulati, P. Recent trends in targeted delivery of smart nanocarrier-based microbial enzymes for therapeutic applications. Drug Discovery Today 2024, 29, 103915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothini, K.; Dhilip Kumar, S.S.; Abrahamse, H.; Rajan, M. Synergistic effect of polymer functionalized graphene oxide system for breast cancer treatment. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 632, 122556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Xie, B. Ultrasmall graphene oxide for combination of enhanced chemotherapy and photothermal therapy of breast cancer. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2023, 225, 113288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.-J.; Xue, S.-J.; Mei, Z.-H.; Li, T.-T.; Li, H.-F.; Zhuang, X.-F.; Pan, L.-M. Synthesis, characterization, and efficacy evaluation of a PH-responsive Fe-MOF@GO composite drug delivery system for the treating colorectal cancer. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-J.; Wu, W.-C.; Lin, Y.-H. Magnetic graphene oxide nanoflakes for dual RNA interfering delivery and gene knockdown in prostate and liver cancers. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2023, 253, 127357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca, S.; Leclercq, L.; Gonzalez, P.; Dhellemmes, L.; Boiteau, L.; Rydzek, G.; Cottet, H. Modifying last layer in polyelectrolyte multilayer coatings for capillary electrophoresis of proteins. Journal of Chromatography A 2023, 1692, 463837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utatsu, K.; Kogo, T.; Taharabaru, T.; Onodera, R.; Motoyama, K.; Higashi, T. Supramolecular polymer-based transformable material for reversible PEGylation of protein drugs. Materials Today Bio 2021, 12, 100160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad-Beigi, H.; Morshedi, D.; Shojaosadati, S.A.; Pedersen, J.N.; Marvian, A.T.; Aliakbari, F.; Christiansen, G.; Pedersen, J.S.; Otzen, D.E. Gallic acid loaded onto polyethylenimine-coated human serum albumin nanoparticles (PEI-HSA-GA NPs) stabilizes α-synuclein in the unfolded conformation and inhibits aggregation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 85312–85323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Du, K.; Yuan, X.; Xiao, W.; Tao, Y.; Xu, D.; Hu, H. A comparative study of the in vitro antitumor effect of mannose-doxorubicin conjugates with different linkers. Drug Dev. Res. 2022, 83, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Kaur, A.; Jain, U.K.; Chandra, R.; Madan, J. Stealth recombinant human serum albumin nanoparticles conjugating 5-fluorouracil augmented drug delivery and cytotoxicity in human colon cancer, HT-29 cells. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2017, 155, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, I.; Wiesen, M.H.J.; Albert, V.; Bobylev, I.; Joshi, A.R.; Müller, C.; Lehmann, H.C. Impact of drug formulations on kinetics and toxicity in a preclinical model of paclitaxel-induced neuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2021, 26, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zuo, G.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, F.; Wan, Y. Encapsulating doxorubicin-intercalated lamellar nanohydroxyapatite into PLGA nanofibers for sustained drug release. CAP 2019, 19, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawas-Qalaji, M.M.; Werdy, S.; Rachid, O.; Simons, F.E.R.; Simons, K.J. Sublingual Diffusion of Epinephrine Microcrystals from Rapidly Disintegrating Tablets for the Potential First-Aid Treatment of Anaphylaxis: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Study. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, Z.; Dehghan, R.; Nejabat, M.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Hadizadeh, F. Dual-targeting CD44 and mucin by hyaluronic acid and 5TR1 aptamer for epirubicin delivery into cancer cells: Synthesis, characterization, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.S.; Hekmatara, H. MWCNT decorated Magnetic/Ceramic/Polymer (Fe2O3/Fe3O4/SiO2/PANI) nanocomposite with enhanced microwave absorption at an entire X and Ku frequency bands. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 11795–11803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lan, G.; Liu, Y.; Xue, S.; Xu, B.; Qiu, H.; Pu, K. Synthesis of a composite Fe3O4@SiO2/poly(SMA-co-BA-co-BZMA-co-DMC) and evaluation of its oil-water separation performance. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2024, 686, 133311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerami, S.E.; Pourmadadi, M.; Fatoorehchi, H.; Yazdian, F.; Rashedi, H.; Nigjeh, M.N. Preparation of pH-sensitive chitosan/polyvinylpyrrolidone/α-Fe2O3 nanocomposite for drug delivery application: Emphasis on ameliorating restrictions. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2021, 173, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liao, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, D.; Yuan, M.; Fu, X. Synergistic Chemo-Photothermal Therapy of Breast Cancer Based on Mesoporous Polydopamine Nanoparticles Decorated with Atovaquone. ACS Applied Nano Materials 2024, 7, 4555–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanrıverdi, V.; Gençer, N.G. Induced Current Electro-Thermal Imaging for Breast Tumor Detection: A Numerical and Experimental Study. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 52, 1078–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusefi, M.; Lee-Kiun, M.S.; Shameli, K.; Teow, S.-Y.; Ali, R.R.; Siew, K.-K.; Chan, H.-Y.; Wong, M.M.-T.; Lim, W.-L.; Kuča, K. 5-Fluorouracil loaded magnetic cellulose bionanocomposites for potential colorectal cancer treatment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussien, N.A.; Işıklan, N.; Türk, M. Aptamer-functionalized magnetic graphene oxide nanocarrier for targeted drug delivery of paclitaxel. Materials Chemistry and Physics 2018, 211, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiyani, M.; Rana, A.; Pal, M.; Rana, S.; Melkani, A.B.; Sahoo, N.G. Polymer grafted magnetic graphene oxide as a potential nanocarrier for pH-responsive delivery of sparingly soluble quercetin against breast cancer cells. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 2574–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tao, Y.; Mao, H.; Kong, Y.; Shen, J.; Deng, L.; Yang, L. Construction of magnetic-targeted and NIR irradiation-controlled drug delivery platform with Fe3O4@Au@SiO2 nanospheres. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 5061–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Yang, C.; Lin, H.; Qu, F. P(EO-co-LLA) functionalized Fe3O4@mSiO2 nanocomposites for thermo/pH responsive drug controlled release and hyperthermia. DTr 2014, 43, 18056–18065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Carrier name | Surface modification | Substrate | Ms / emu g–1 | Drug | LC/% | LE/% | RE/% | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC | —— | Cellulose | 34.8 | 5–FU | 12.0 | 62.5 | 93 | [26] |
| MGO | —— | GO | 32.5 | PAC | 19.4 | 95.8 | 67.6 | [27] |
| GO–PVP–Fe3O4 | —— | GO–PVP | —— | QSR | 62.8 | —— | 35.4 | [28] |
| Fe3O4@Au@SiO2 | Au/SiO2 | —— | 18.3 | VP16 | 74.3 | —— | 67.3 | [29] |
| Fe3O4@mSiO2–P(EO–co–LLA) | mSiO2–P(EO–co–LLA) | —— | 48.7 | DOX | 6.8 | —— | 92.7 | [30] |
| Fe3O4@SiO2/N–rGO | SiO2 | N–rGO | 40.9 | EPI | 39.6 | 47.1 | 77.4 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





