Submitted:
05 August 2024
Posted:
05 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Health Literacy Questionnaire - HLQ
- Mental Health Literacy Scale - MHLS
- Rapid Estimate of Adult Literacy in Medicine - REALM
- Test of Functional Health Literacy in Adults - TOFHLA
- Health Literacy Survey - HLS
- The Newest Vital Sign - NVS
- eHealth Literacy Scale - eHeals
2. Materials and Methods
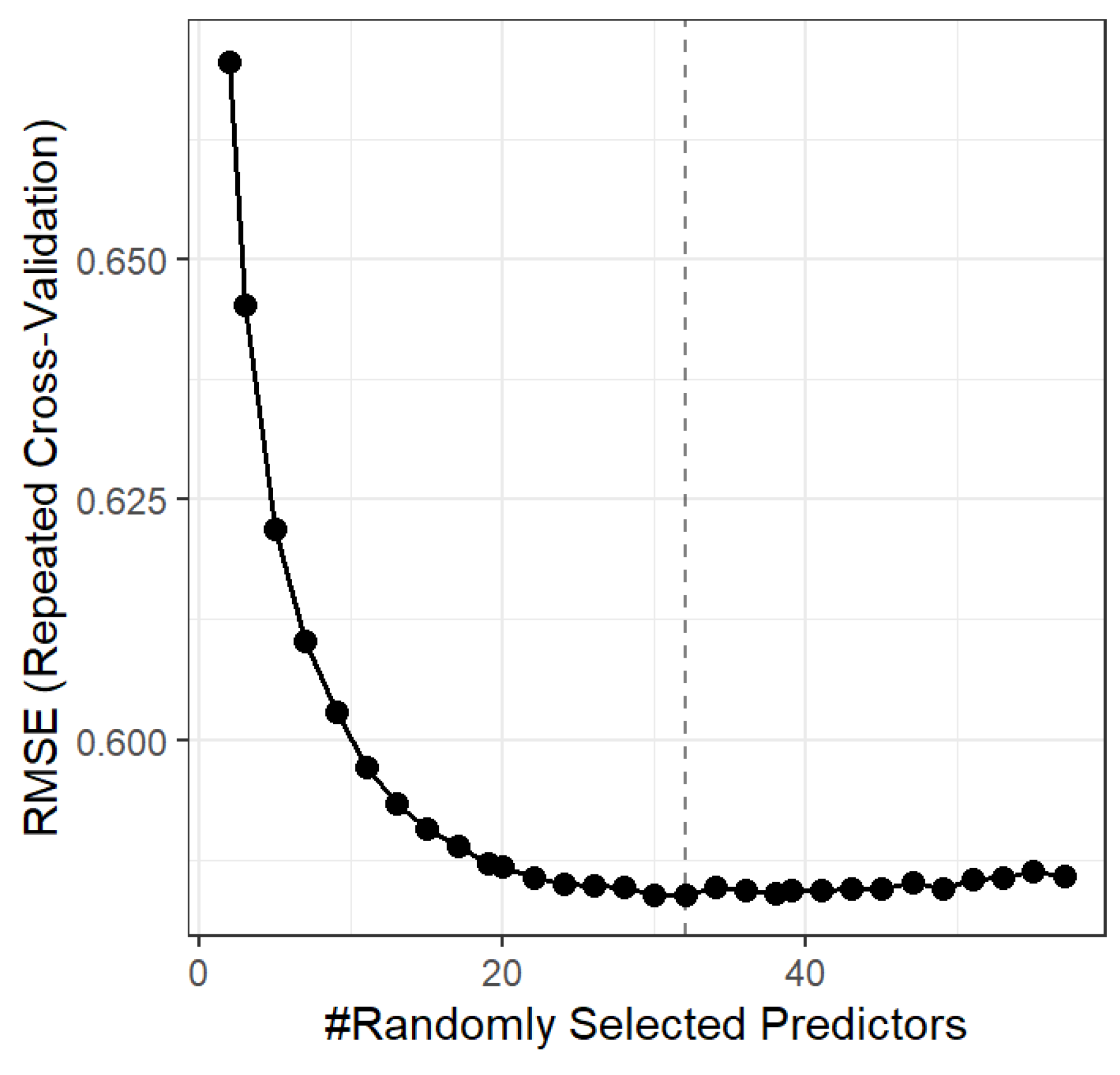
2.1. Structural Topic Modeling
2.2. Citation Dynamics
3. Results
3.1. Instruments
3.2. Structural Topic Modeling Results
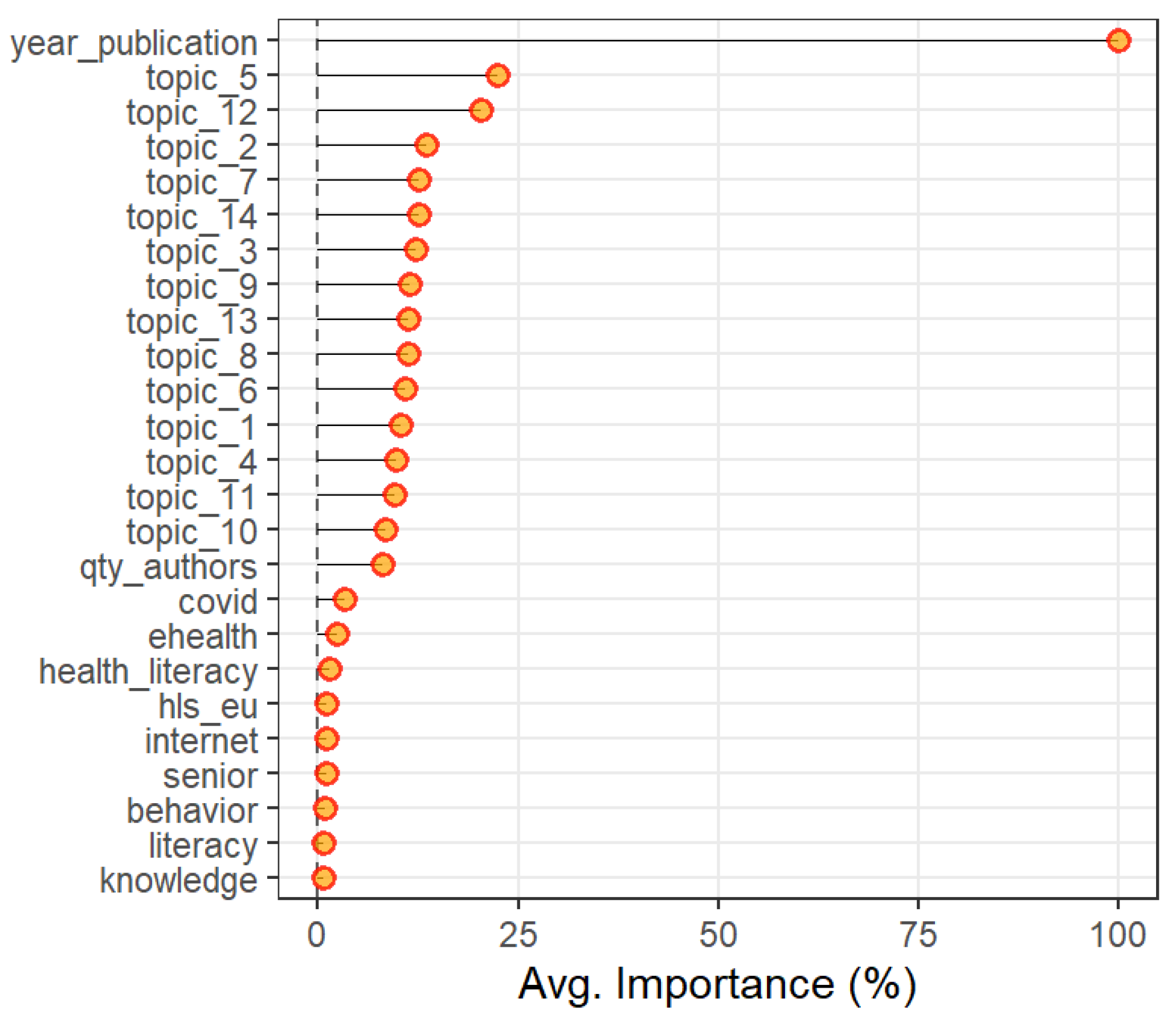
3.3. Citation Dynamics
4. Discussion
4.1. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| eHeals | eHealth Literacy Scale |
| HLS-EU-Q | The European Health Literacy Survey Questionnaire |
| MHLS | Mental Health Literacy Scale |
| TOFHLA | Test of Functional Health Literacy in Adults |
| REALM | Rapid Estimate of Adult Literacy in Medicine |
| NVS | Newest Vital Signt |
| HLQ | Health Literacy Questionnaire |
References
- Tabak, B.M.; Froner, M.B.; Corrêa, R.S.; Silva, T.C. The Intersection of Health Literacy and Public Health: A Machine Learning-Enhanced Bibliometric Investigation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2023, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.L.; Chiang, C.H.; Yang, S.C.; Wu, F.Z. The Associations among Gender, Age, eHealth Literacy, Beliefs about Medicines and Medication Adherence among Elementary and Secondary School Teachers. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19, 6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabricius, P.K.; Aharaz, A.; Stefánsdóttir, N.T.; Houlind, M.B.; Steffensen, K.D.; Andersen, O.; Kirk, J.W. Shared Decision Making with Acutely Hospitalized, Older Poly-Medicated Patients: A Mixed-Methods Study in an Emergency Department. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19, 6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Suh, D.; Barone, J.A.; Jung, S.Y.; Wu, W.; Suh, D.C. Health literacy level and comprehension of prescription and nonprescription drug information. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19, 6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, F.; Al-Kumaim, N.H.; Alzahrani, A.I.; Fazea, Y. The impact of social media shared health content on protective behavior against COVID-19. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2023, 20, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrdelja, M.; Vrbovšek, S.; Klopčič, V.; Dadaczynski, K.; Okan, O. Facing the growing COVID-19 infodemic: digital health literacy and information-seeking behaviour of university students in Slovenia. International journal of environmental research and public health 2021, 18, 8507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okan, O.; Bollweg, T.M.; Berens, E.M.; Hurrelmann, K.; Bauer, U.; Schaeffer, D. Coronavirus-related health literacy: a cross-sectional study in adults during the COVID-19 infodemic in Germany. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2020, 17, 5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickles, K.; Copp, T.; Meyerowitz-Katz, G.; Dodd, R.H.; Bonner, C.; Nickel, B.; Steffens, M.S.; Seale, H.; Cvejic, E.; Taba, M.; others. COVID-19 vaccine misperceptions in a community sample of adults aged 18–49 years in Australia. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19, 6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelodar, H.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, C.; Feng, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L. Latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) and topic modeling: models, applications, a survey. Multimedia Tools and Applications 2019, 78, 15169–15211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent dirichlet allocation. Journal of machine Learning research 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Blei, D.M.; Lafferty, J.D. Topic models. In Text mining; Chapman and Hall/CRC, 2009; pp. 101–124.
- Roberts, M.E.; Stewart, B.M.; Tingley, D.; Lucas, C.; Leder-Luis, J.; Gadarian, S.K.; Albertson, B.; Rand, D.G. Structural topic models for open-ended survey responses. American journal of political science 2014, 58, 1064–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.E.; Stewart, B.M.; Tingley, D. Stm: An R package for structural topic models. Journal of Statistical Software 2019, 91, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, T.; Draxler, R.R. Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE). Geoscientific model development discussions 2014, 7, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Koehler, A.B. Another look at measures of forecast accuracy. International journal of forecasting 2006, 22, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabak, B.M.; Silva, T.C.; Fiche, M.E.; Braz, T. Citation likelihood analysis of the interbank financial networks literature: A machine learning and bibliometric approach. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications 2021, 562, 125363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, P.W.; Davis, T.C.; Long, S.W.; Jackson, R.H.; Decker, B.C. Rapid estimate of adult literacy in medicine (REALM): a quick reading test for patients. Journal of reading 1993, 37, 124–130. [Google Scholar]
- Batterham, R.W.; Buchbinder, R.; Beauchamp, A.; Dodson, S.; Elsworth, G.R.; Osborne, R.H. The OPtimising HEalth LIterAcy (Ophelia) process: Study protocol for using health literacy profiling and community engagement to create and implement health reform. BMC Public Health 2014, 14. Cited by: 116; All Open Access, Gold Open Access, Green Open Access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchamp, A.; Batterham, R.W.; Dodson, S.; Astbury, B.; Elsworth, G.R.; McPhee, C.; Jacobson, J.; Buchbinder, R.; Osborne, R.H. Systematic development and implementation of interventions to OPtimise Health Literacy and Access (Ophelia). BMC Public Health 2017, 17. Cited by: 67; All Open Access, Gold Open Access, Green Open Access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, R.H.; Batterham, R.W.; Elsworth, G.R.; Hawkins, M.; Buchbinder, R. The grounded psychometric development and initial validation of the Health Literacy Questionnaire (HLQ). BMC public health 2013, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, K.; Van den Broucke, S.; Pelikan, J.M.; Fullam, J.; Doyle, G.; Slonska, Z.; Kondilis, B.; Stoffels, V.; Osborne, R.H.; Brand, H. Measuring health literacy in populations: illuminating the design and development process of the European Health Literacy Survey Questionnaire (HLS-EU-Q). BMC public health 2013, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, K.; Pelikan, J.M.; Röthlin, F.; Ganahl, K.; Slonska, Z.; Doyle, G.; Fullam, J.; Kondilis, B.; Agrafiotis, D.; Uiters, E.; others. Health literacy in Europe: comparative results of the European health literacy survey (HLS-EU). The European journal of public health 2015, 25, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfizer Inc. Newest Vital Sign: A Health Literacy Assessment Tool, 2011. Accessed: 2023-07-28.
- Parker, R.M.; Baker, D.W.; Williams, M.V.; Nurss, J.R. The test of functional health literacy in adults: a new instrument for measuring patients’ literacy skills. J Gen Intern Med 1995, 10, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, C.D.; Skinner, H.A. eHEALS: the eHealth literacy scale. Journal of medical Internet research 2006, 8, e507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, M.; Casey, L. The Mental Health Literacy Scale (MHLS): A new scale-based measure of mental health literacy. Psychiatry Research 2015, 229, 511–516, Cited by: 187; All Open Access, Green Open Access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Airoldi, E.M.; Bischof, J.M. Improving and evaluating topic models and other models of text. Journal of the American Statistical Association 2016, 111, 1381–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischof, J.; Airoldi, E.M. Summarizing topical content with word frequency and exclusivity. Proceedings of the 29th international conference on machine learning (icml-12), 2012, pp. 201–208.
- Taddy, M. Multinomial inverse regression for text analysis. Journal of the American Statistical Association 2013, 108, 755–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
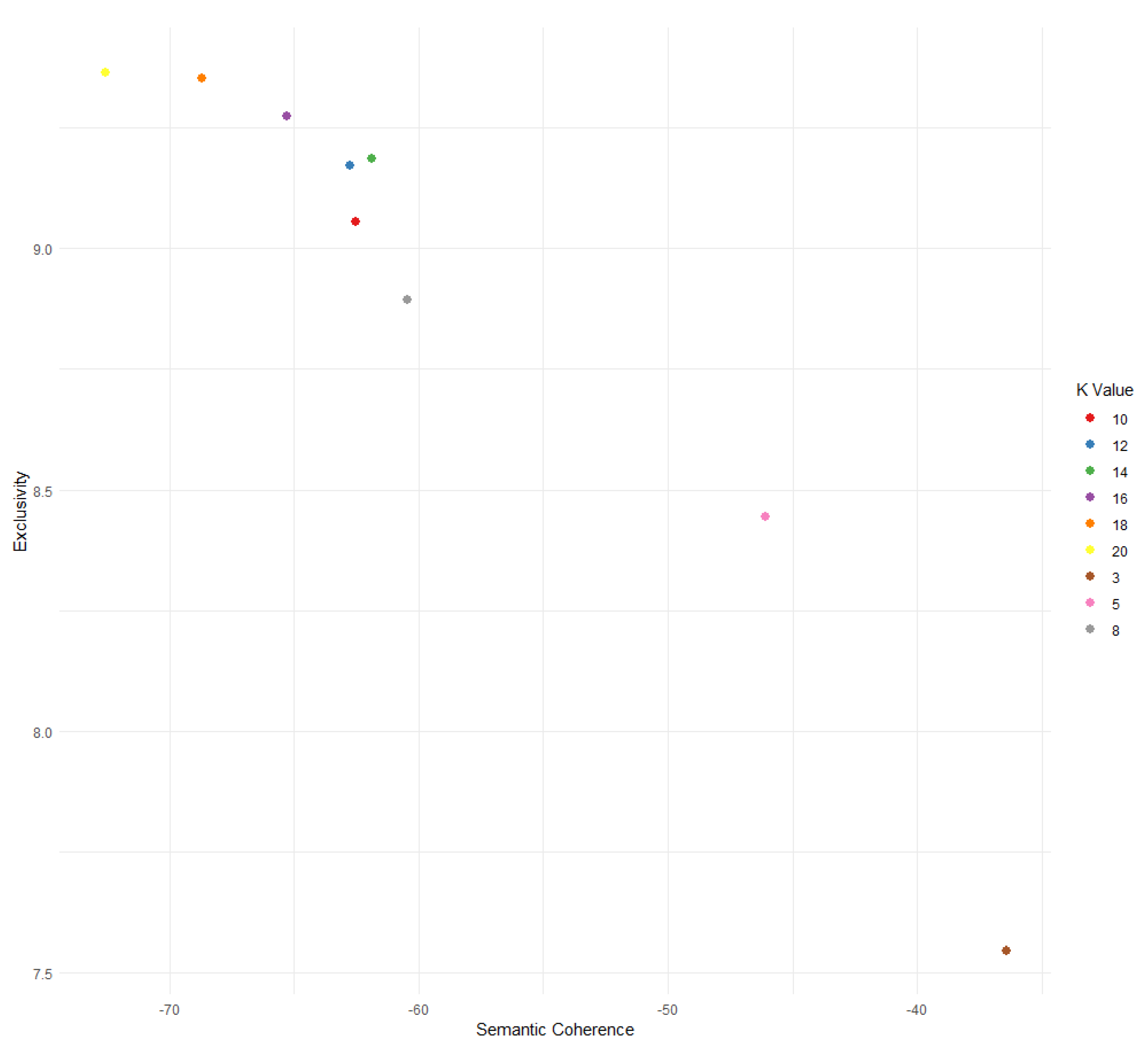
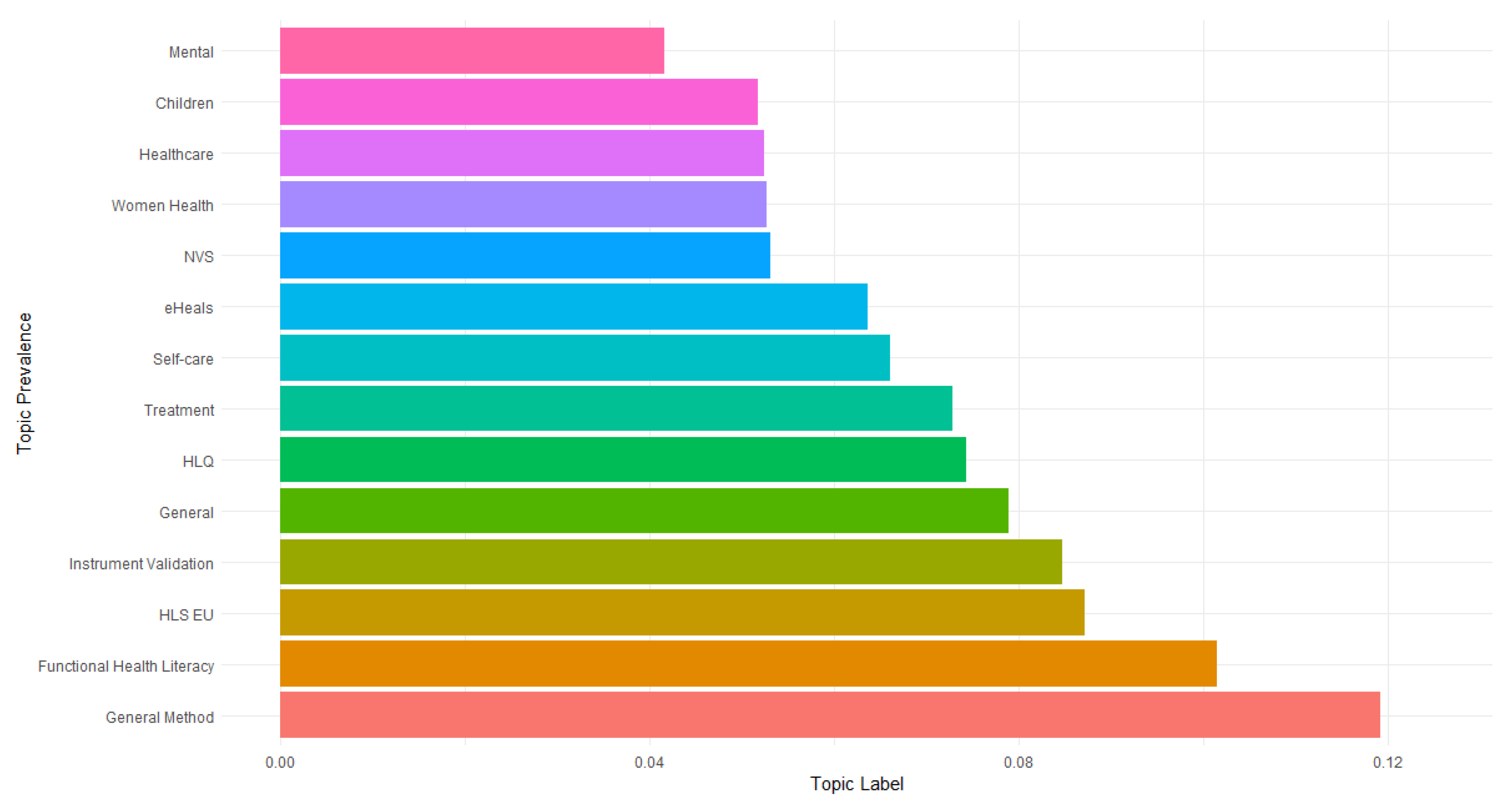
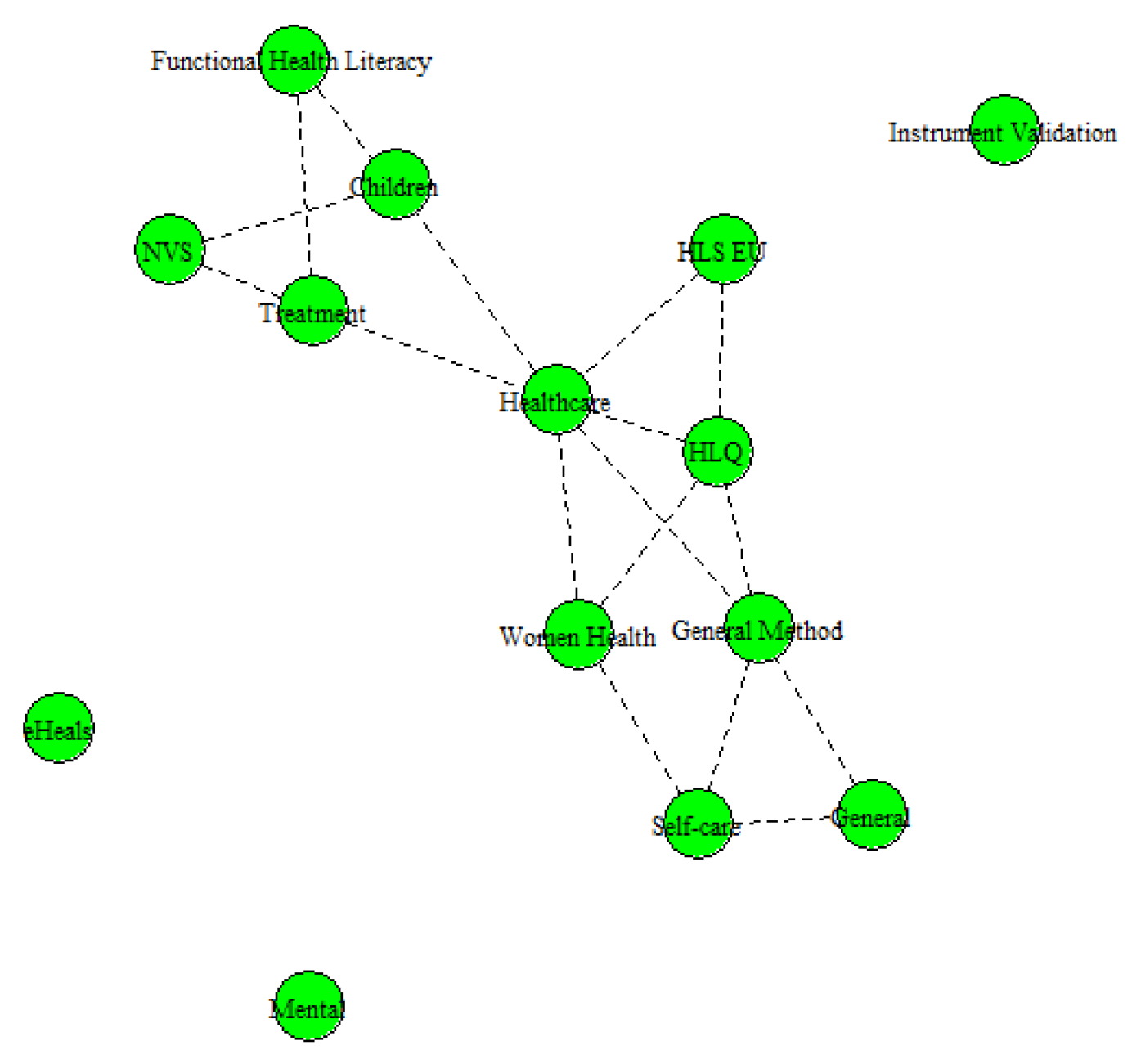
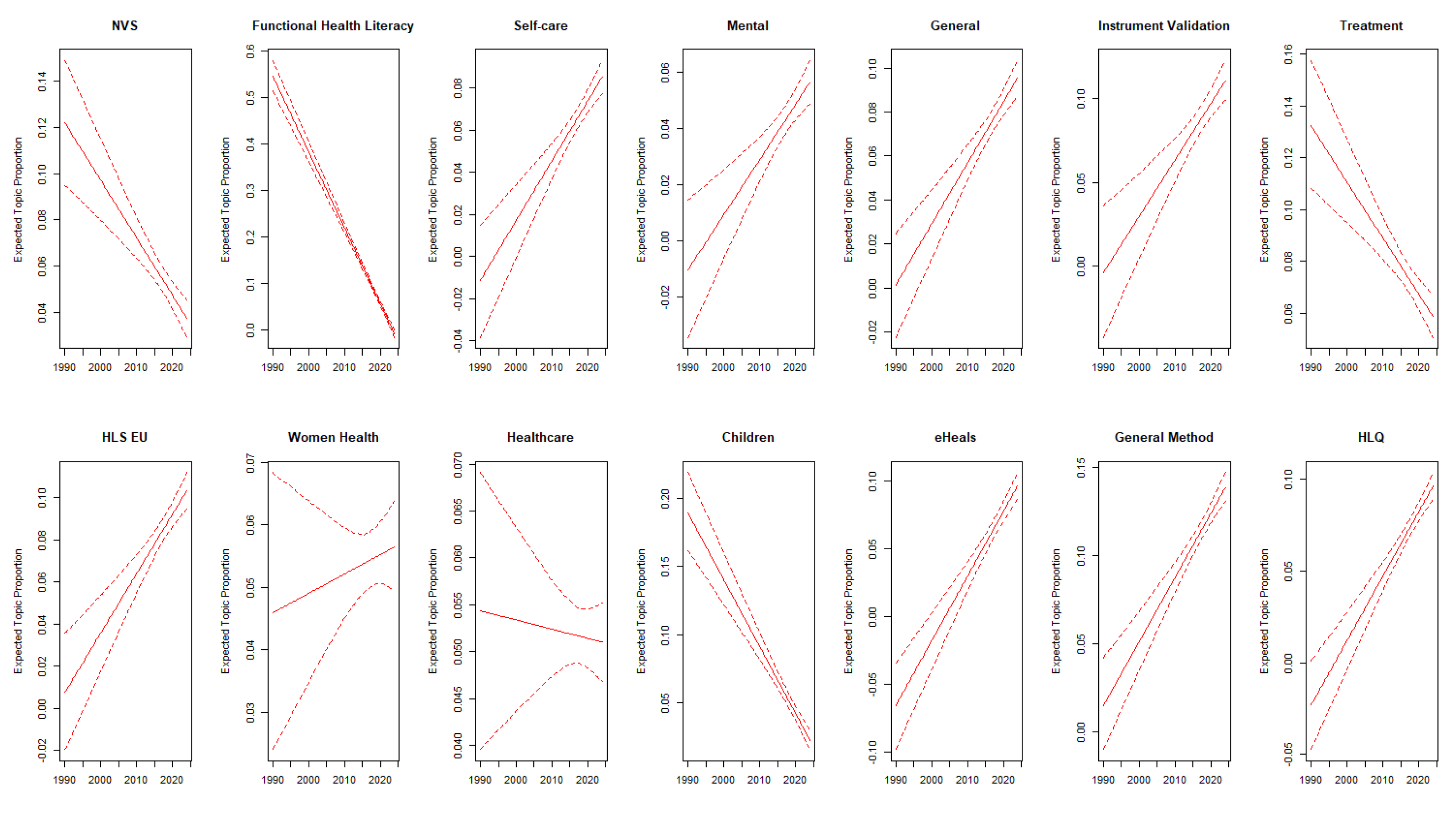
| Topic Number | Topic Label | Main Words |
|---|---|---|
| Topic 1 | NVS | Highest Prob: patient, nvs, sign, vital, newest, visit, use FREX: nvs, hrc, sign, heart, vital, visit, physician |
| Topic 2 | Functional Health Literacy | Highest Prob: literaci, health, adult, function, test, measur, tofhla FREX: tofhla, realm, read, function, numeraci, mmse, stofhla |
| Topic 3 | Self-care | Highest Prob: health, behavior, diabet, control, literaci, intervent, knowledg FREX: diabet, selfcar, behavior, glycem, control, spss, diet |
| Topic 4 | Mental | Highest Prob: mental, health, depress, mhl, scale, asthma, ill FREX: mental, mhl, disord, mhls, wellb, asthma, helpseek |
| Topic 5 | General | Highest Prob: health, literaci, score, studi, level, correl, signific FREX: dental, oral, univers, pearson, adolesc, correl, reserv |
| Topic 6 | Instrument Validation | Highest Prob: valid, item, reliabl, measur, factor, instrument, scale FREX: psychometr, cronbach, properti, alpha, confirmatori, converg, cfa |
| Topic 7 | Treatment | Highest Prob: patient, medic, adher, diseas, hospit, associ, literaci FREX: adher, nonadher, transplant, hiv, kidney, hemodialysi, ckd |
| Topic 8 | HLS EU | Highest Prob: health, literaci, studi, use, research, popul, need FREX: european, will, project, migrant, compet, hls, review |
| Topic 9 | Women Health | Highest Prob: women, health, literaci, cancer, qualiti, inform, life FREX: cancer, breast, women, decisionmak, life, pregnant, pregnanc |
| Topic 10 | Healthcare | Highest Prob: low, group, particip, literaci, caregiv, care, intervent FREX: caregiv, vaccin, franci, taylor, low, llc, aor |
| Topic 11 | Children | Highest Prob: parent, screen, use, children, comprehens, question, particip FREX: parent, label, dose, children, screen, child, instruct |
| Topic 12 | eHeals | Highest Prob: ehealth, inform, use, literaci, eheal, internet, student FREX: ehealth, internet, digit, ehl, mhealth, eheal, onlin |
| Topic 13 | General Method | Highest Prob: health, literaci, associ, level, age, factor, educ FREX: resid, status, regress, incom, logist, sociodemograph, age |
| Topic 14 | HLQ | Highest Prob: health, literaci, inform, use, healthcar, activ, hlq FREX: hlq, domain, healthcar, engag, profil, navig, rehabilit |
| Dependent variable: | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Citation per year | ||||
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| Paper’s Age | 0.581*** | 0.590*** | ||
| (0.032) | (0.033) | |||
| Topic 1 (NVS) | −6.255*** | −6.338*** | −4.837*** | −4.825*** |
| (1.396) | (1.376) | (1.438) | (1.415) | |
| Topic 2 (Functional Health Literacy) | −6.726*** | −4.788*** | −6.489*** | −4.513*** |
| (1.573) | (1.564) | (1.597) | (1.582) | |
| Topic 3 (Self-care) | −1.542 | −1.546 | −1.236 | −1.376 |
| (1.571) | (1.535) | (1.598) | (1.558) | |
| Topic 4 (Mental) | −2.602* | −2.358 | −0.623 | −0.445 |
| (1.470) | (1.435) | (1.550) | (1.511) | |
| Topic 5 (General) | −7.133*** | −6.947*** | −6.574*** | −6.358*** |
| (1.661) | (1.619) | (1.682) | (1.636) | |
| Topic 6 (Instrumental Validation) | −0.629 | −0.424 | −0.113 | 0.118 |
| (1.193) | (1.169) | (1.214) | (1.189) | |
| Topic 7 (Treatment) | −3.735** | −3.533** | −2.731* | −2.475 |
| (1.542) | (1.513) | (1.568) | (1.536) | |
| Topic 8 (HLS EU) | −1.952 | −2.052 | −1.787 | −1.768 |
| (1.456) | (1.424) | (1.459) | (1.425) | |
| Topic 9 (Women Health) | −7.150*** | −6.370*** | −5.834*** | −4.929*** |
| (1.713) | (1.679) | (1.732) | (1.695) | |
| Topic 10 (Healthcare) | −3.694 | −3.608 | −3.970 | −3.900 |
| (2.727) | (2.665) | (2.741) | (2.673) | |
| Topic 11 (Children) | −4.233*** | −3.781** | −3.154** | −2.552 |
| (1.578) | (1.560) | (1.600) | (1.579) | |
| Topic 12 (eHeals) | 2.987** | 3.397** | 3.173** | 3.559** |
| (1.357) | (1.328) | (1.603) | (1.565) | |
| Topic 14 (HLQ) | 0.559 | 0.758 | 1.458 | 1.728 |
| (1.653) | (1.613) | (1.674) | (1.629) | |
| Amount of Authors | 0.156*** | 0.161*** | 0.146*** | 0.151*** |
| (0.037) | (0.036) | (0.037) | (0.036) | |
| Single Author | −0.805 | −0.916 | −0.835 | −0.941 |
| (0.738) | (0.723) | (0.734) | (0.717) | |
| Keyword Covid | 1.861*** | 2.075*** | ||
| (0.616) | (0.605) | |||
| Keyword eHealth | 0.452 | 0.348 | ||
| (0.482) | (0.469) | |||
| Keyword Health Literacy | 0.966*** | 0.919*** | ||
| (0.285) | (0.281) | |||
| Keyword HLS EU | 1.333** | 1.310** | ||
| (0.597) | (0.582) | |||
| Keyword Internet | 0.483 | 0.520 | ||
| (0.651) | (0.634) | |||
| Keyword Senior | 0.414 | 0.506 | ||
| (0.548) | (0.536) | |||
| Keyword Behavior | 0.120 | 0.253 | ||
| (0.478) | (0.465) | |||
| Keyword Literacy | 1.207** | 1.799*** | ||
| (0.525) | (0.526) | |||
| Keyword Knowledge | −0.684 | 0.119 | ||
| (0.783) | (0.780) | |||
| Constant | 1.448 | −0.074 | ||
| (1.048) | (1.116) | |||
| Fixed Effects | None | Paper’s Age | None | Paper’s Age |
| Observations | 1,857 | 1,857 | 1,857 | 1,857 |
| R2 | 0.211 | 0.267 | 0.224 | 0.282 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.204 | 0.248 | 0.213 | 0.260 |
| Residual Std. Error | 4.886 (df = 1840) | 4.748 (df = 1811) | 4.858 (df = 1831) | 4.710 (df = 1802) |
| Note: | *p<0.1; **p<0.05; ***p<0.01 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





