Submitted:
04 August 2024
Posted:
06 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
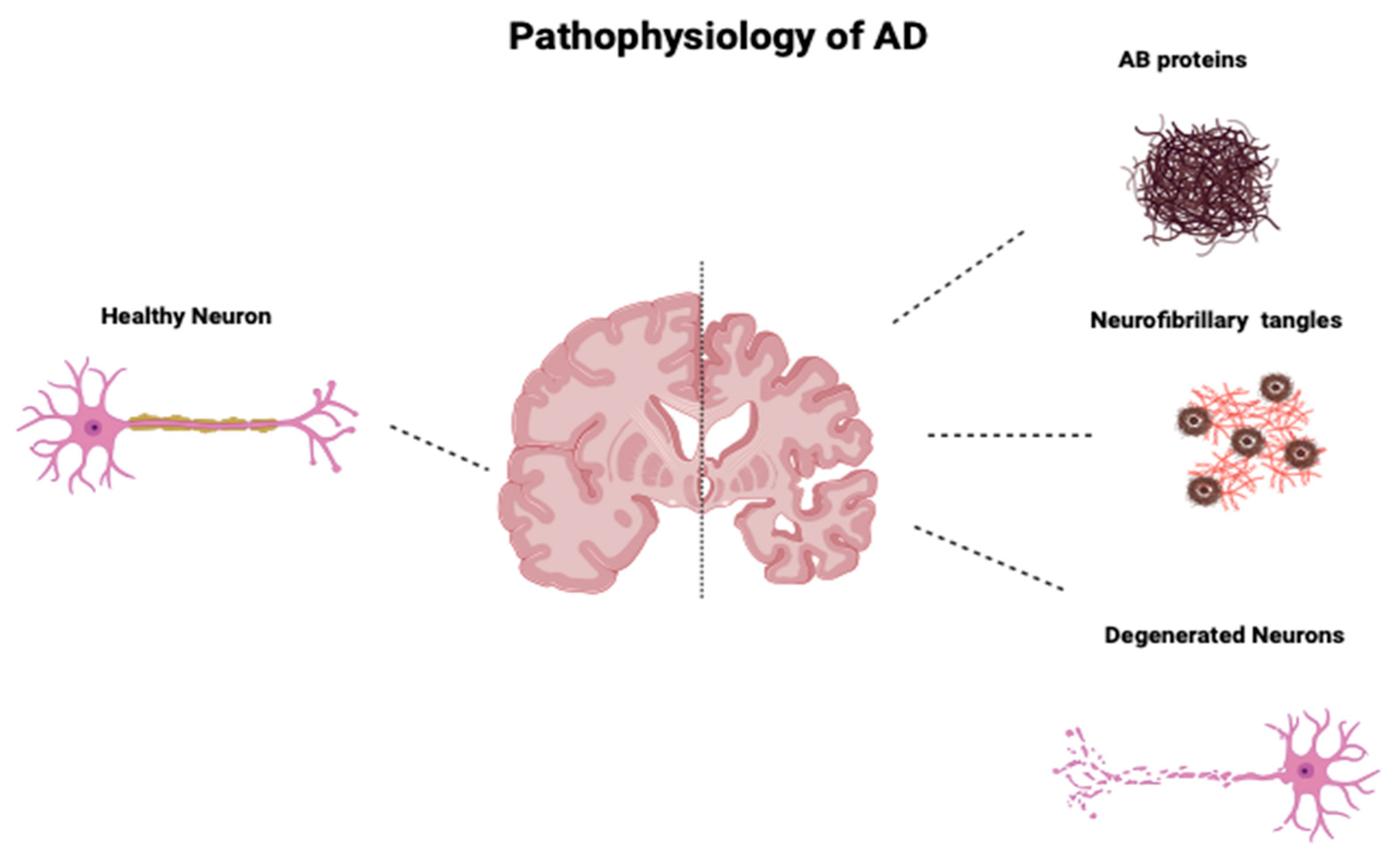
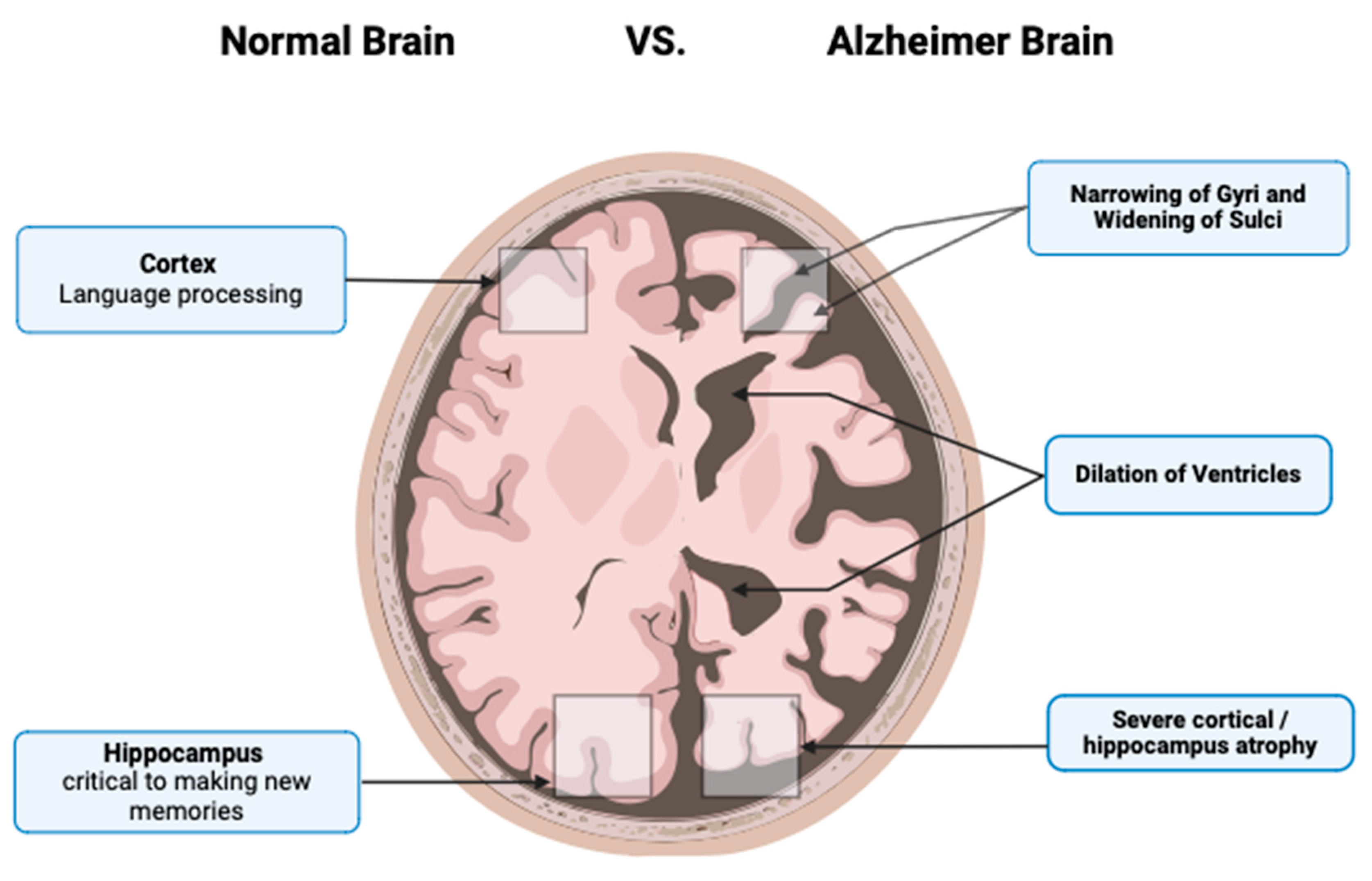
2. Pathophysiology of AD
Braak and Braak Staging
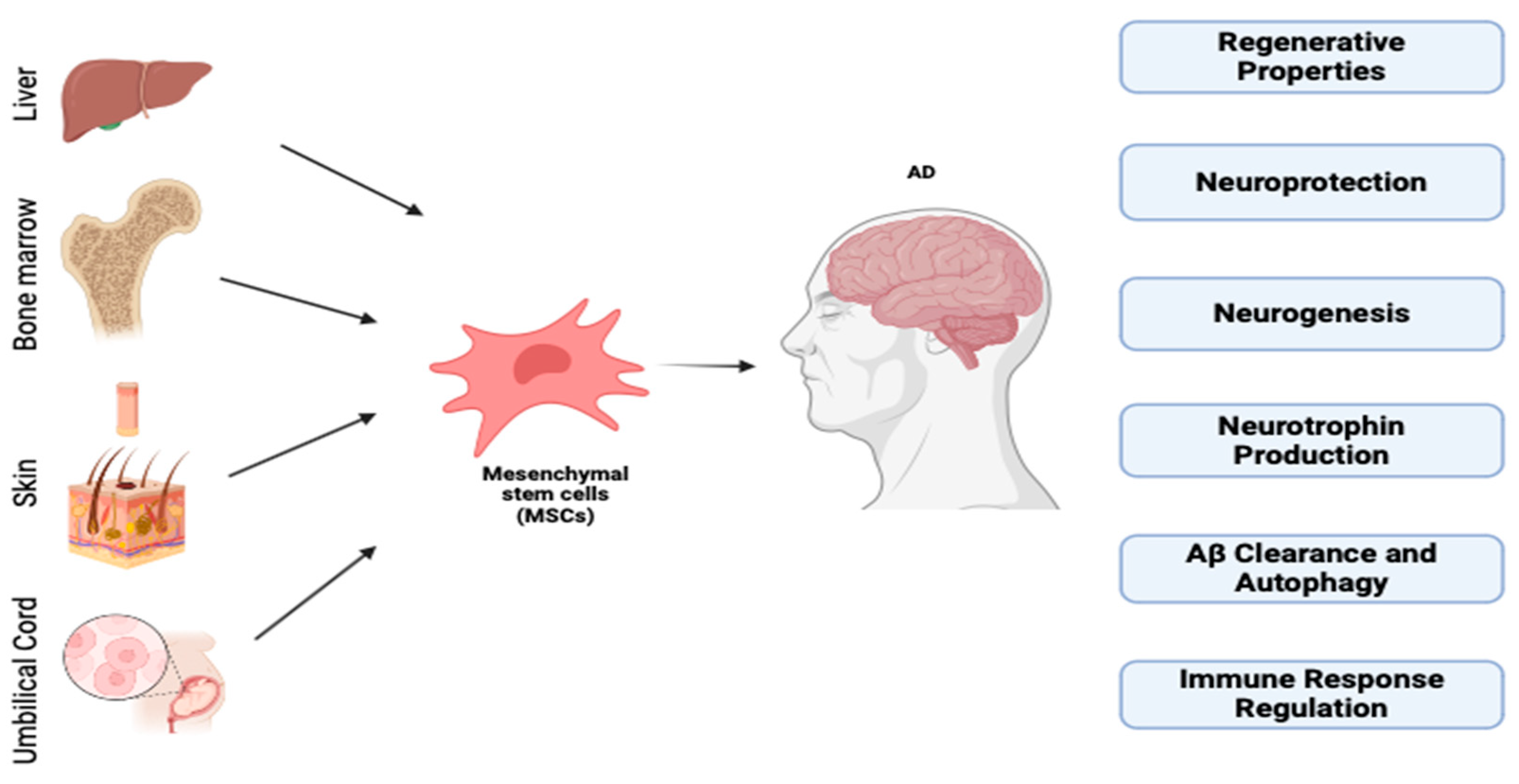
3. Neuroregeneration Therapy
Stem Cells
3.2. Exosomes
3.2.1. Isolation of Exosomes
3.2.2. Cell Culture
3.2.3. Working Model Biogenesis, Secretion, and Uptake
4. Exosomes as AD Biomarkers
| Source | Sample | Biomarker Protein Change |
|---|---|---|
| Neural | Plasma | P-T181-tau, P-S396-tau, and Aβ1–42 ↑, NRGN, REST ↓ compared to CNC and stable MCI patients [48]. |
| Neural | Plasma or serum | Total Tau, P-T181-tau, P-S396-tau and Aβ1–42 ↑compared to controls[49] |
| Neural | Plasma | cathepsin D, LAMP-1, ubiquitinylated proteins ↑, and HSP70 ↓ compared to controls and FTD[50] |
| Neuronal | Plasma or serum | Aβ42, T-tau, and P-T181-tau ↑ compared to aMCI and control groups[51] |
| Neuronal | Plasma | synaptophysin, synaptopodin, synaptotagmin-2, and neurogranin ↓ compared to controls[52] |
| Neuronal | Plasma | NPTX2, NRXN2α, AMPA4, NLGN1 ↓[53] |
| Astrocyte | Plasma | complement proteins, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β ↑; complement regulatory proteins (CD59, CD46, DAF), complement receptor type 1 ↓ compared to controls[54] |
| Astrocyte | Plasma | BACE-1, (s)APPβ ↑, GDNF ↓ compared to controls[55] |
5. Therapeutic Properties of Exosomes and Application in Alzheimer’s Disease
6. Clinical Trials
| Number | Therapy | Source | Status | Pathway | N= | Study location | |
| 1 | NCT02600130 | Cells | Bone marrow | Completed | Intravenous | 33 | USA |
| 2 | NCT03117738 | Cells | Adipose tissue | Completed | Intravenous | 21 | USA |
| 3 | NCT02054208; NCT03172117 (Kim et al., 2021) | Cells | UCB | Completed; Unknown | Intracerebroventricular | 45 | South Korea |
| 4 | NCT01297218 | Cells | UCB | Completed | Intracerebral | 9 | South Korea |
| 5 | NCT02833792 | Cells | Bone marrow | Recruiting | Intravenous | 40 | USA |
| 6 | NCT04040348 | Cells | Umbilical cord | Active, not recruiting | Intravenous | 6 | USA |
| 7 | NCT04482413 | Cells | Adipose tissue | Not yet recruiting | Intravenous | 80 | USA |
| 8 | NCT04954534 | Cells | UCB | Not yet recruiting | Intracerebroventricular | 9 | South Korea |
| 9 | NCT02672306 | Cells | Umbilical cord | Unknown | Intravenous | 16 | China |
| 10 | NCT01547689 | Cells | UCB | Unknown | Intravenous | 30 | China |
| 11 | NCT01696591 | Cells | UCB | Unknown | Intracerebroventricular | 9 | South Korea |
| 12 | NCT04228666 [65,66] | Cells | Adipose tissue | WithdrawnџDue to covid-19 pandemic | iv | 24 | USA |
| 13 | NCT04855955 | Cells | Adipose tissue | completed | N/A | 1 | USA |
| 14 | NCT04388982 | Cells | Adipose tissue | recruiting | Nasal drip | 9 | China |
| 15 | NCT02899091 | Cells | N/A | recruiting | iv | 24 | South Korea |
| 16 | NCT04684602 | Cells | N/A | recruiting | N/A | 5000 | USA |
7. Advantages and Challenges
8. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kochanek KD, Xu J, Murphy SL, Miniño AM, Kung H-C. Deaths: final data for 2009. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2011;60: 1–116. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24974587.
- de Jong, O.G.; Van Balkom, B.W.M.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Bouten, C.V.C.; Verhaar, M.C. Extracellular Vesicles: Potential Roles in Regenerative Medicine. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Yang, X.; Han, Z.-P.; Qu, F.-F.; Shao, L.; Shi, Y.-F. Mesenchymal stem cells: a new trend for cell therapy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, K.O.; Ornellas, F.L.M.; Martin, P.K.M.; Patti, C.L.; Mello, L.E.; Frussa-Filho, R.; Han, S.W.; Longo, B.M. Therapeutic effects of the transplantation of VEGF overexpressing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the hippocampus of murine model of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, A.M.; Ahmed, H.H.; Atta, H.M.; Ghazy, M.A.; Aglan, H.A. RETRACTED: Potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in management of Alzheimer's disease in female rats. Cell Biol. Int. 2014, 38, 1367–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urdzíková, L.M.; Růžička, J.; Labagnara, M.; Kárová, K.; Kubinová, Šárka; Jiráková, K.; Murali, R.; Syková, E.; Jhanwar-Uniyal, M.; Jendelová, P. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Modulate Inflammatory Cytokines after Spinal Cord Injury in Rat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 11275–11293. [CrossRef]
- Kumar A, Sidhu J, Lui F, Tsao JW. Alzheimer Disease. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29763097.
- Andreasson, K.I.; Bachstetter, A.D.; Colonna, M.; Ginhoux, F.; Holmes, C.; Lamb, B.; Landreth, G.; Lee, D.C.; Low, D.; Lynch, M.A.; et al. Targeting innate immunity for neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system. J. Neurochem. 2016, 138, 653–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzheimer's Association. 2016 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimer's Dement. 2016, 12, 459–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, J.; Lucas, J.J.; Pérez, M.; Hernández, F. Role of Tau Protein in Both Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 361–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paroni, G.; Bisceglia, P.; Seripa, D. Understanding the Amyloid Hypothesis in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 2019, 68, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Thal, D.R.; Ghebremedhin, E.; Del Tredici, K. Stages of the pathologic process in Alzheimer disease: Age categories from 1 to 100 years. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 70, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, G.S. Amyloid-β and Tau: The Trigger and Bullet in Alzheimer Disease Pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, S.M., et al., Cerebral amyloid angiopathy and Alzheimer disease - one peptide, two pathways. Nat Rev Neurol, 2020. 16(1): p. 30-42. [CrossRef]
- Parmar, M. Towards stem cell based therapies for Parkinson's disease. Development 2018, 145, dev156117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, M.; Grealish, S.; Henchcliffe, C. The future of stem cell therapies for Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 21, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.J.; Yanshree; Roy, J.; Tipoe, G.L.; Fung, M.-L.; Lim, L.W. Therapeutic Potential of Human Stem Cell Implantation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, N.; Annett, G.; Wirthlin, L.; Olson, S.; Bauer, G.; A Nolta, J. Mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of neurodegenerative disease. Regen. Med. 2010, 5, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, X.; Leak, R.K.; Chen, F.; Cao, G. Stem cell therapies in age-related neurodegenerative diseases and stroke. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 34, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cone, A.S.; Yuan, X.; Sun, L.; Duke, L.C.; Vreones, M.P.; Carrier, A.N.; Kenyon, S.M.; Carver, S.R.; Benthem, S.D.; Stimmell, A.C.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate Alzheimer's disease-like phenotypes in a preclinical mouse model. Theranostics 2021, 11, 8129–8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecerska-Heryć, E.; Pękała, M.; Serwin, N.; Gliźniewicz, M.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Michalczyk, A.; Heryć, R.; Budkowska, M.; Dołęgowska, B. The Use of Stem Cells as a Potential Treatment Method for Selected Neurodegenerative Diseases: Review. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 43, 2643–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glat, M.J.; Offen, D. Cell and Gene Therapy in Alzheimer's Disease. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 1490–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ager, R.R.; Davis, J.L.; Agazaryan, A.; Benavente, F.; Poon, W.W.; LaFerla, F.M.; Blurton-Jones, M. Human neural stem cells improve cognition and promote synaptic growth in two complementary transgenic models of Alzheimer's disease and neuronal loss. Hippocampus 2015, 25, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huber, C.C.; Wang, H. Disrupted blood-brain barrier in 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease can be mimicked and repaired in vitro with neural stem cell-derived exosomes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 525, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, B.; Tan, K.L.; Chan, H.H.; Looi, Q.H.D.; Lim, M.N.; How, C.W.; Law, J.X.; Foo, J.B. A Simple Benchtop Filtration Method to Isolate Small Extracellular Vesicles from Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, e64106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, L.; Ouandaogo, Z.G.; Anakor, E.; Connolly, O.; Browne, G.B.; Laine, J.; Duddy, W.; Duguez, S. Optimized method for extraction of exosomes from human primary muscle cells. Skelet. Muscle 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Rau, C.; Wu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wu, C.; Tsai, C.; Lin, C.; Lu, T.; Hsieh, C. Identification and characterization of hADSC-derived exosome proteins from different isolation methods. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 7436–7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Rhim, W.-K.; Seo, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, C.G.; Han, D.K. Comparative Analysis of MSC-Derived Exosomes Depending on Cell Culture Media for Regenerative Bioactivity. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2021, 18, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abels, E.R.; Breakefield, X.O. Introduction to Extracellular Vesicles: Biogenesis, RNA Cargo Selection, Content, Release, and Uptake. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futter, C.; Collinson, L.; Backer, J.; Hopkins, C. Human VPS34 is required for internal vesicle formation within multivesicular endosomes. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 1251–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, T.; Fürthauer, M. Biogenesis and function of ESCRT-dependent extracellular vesicles. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 74, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Théry, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, C.; Heuser, J.; Stahl, P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin and recycling of the transferrin receptor in rat reticulocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1983, 97, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janas, A.M.; Sapoń, K.; Janas, T.; Stowell, M.H.; Janas, T. Exosomes and other extracellular vesicles in neural cells and neurodegenerative diseases. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, F.; Perrotta, C.; Novellino, L.; Francolini, M.; Riganti, L.; Menna, E.; Saglietti, L.; Schuchman, E.H.; Furlan, R.; Clementi, E.; et al. Acid sphingomyelinase activity triggers microparticle release from glial cells. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Jiao, L.; Zhong, X.; Yao, W.; Du, K.; Lu, S.; Wu, Y.; Ma, T.; Tong, J.; Xu, M.; et al. Platelet Activating Factor Receptor Exaggerates Microglia-Mediated Microenvironment by IL10-STAT3 Signaling: A Novel Potential Biomarker and Target for Diagnosis and Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 856628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokar, S.; Marques, I.A.; Khazaei, S.; Martins-Marques, T.; Girao, H.; Laranjo, M.; Botelho, M.F. The Footprint of Exosomes in the Radiation-Induced Bystander Effects. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Wang, H.; Shi, Y.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J. Changes in the Morphology, Number, and Pathological Protein Levels of Plasma Exosomes May Help Diagnose Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 2020, 73, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Mu, D.; Ma, X.; Wang, D.; Zhong, J.; Gao, J.; Yu, S.; Qiu, L. Review on the roles of specific cell-derived exosomes in Alzheimer's disease. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 936760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.E.; Honoré, B.; Vestergård, K.; Maltesen, R.G.; Christiansen, G.; Bøge, A.U.; Kristensen, S.R.; Pedersen, S. Shotgun-based proteomics of extracellular vesicles in Alzheimer’s disease reveals biomarkers involved in immunological and coagulation pathways. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Cortez, L.; Kamali-Jamil, R.; Sim, V.; Wille, H.; Kar, S. Implications of exosomes derived from cholesterol-accumulated astrocytes in Alzheimer's disease pathology. Dis. Model. Mech. 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Rustam, Y.H.; Masters, C.L.; Makalic, E.; McLean, C.A.; Hill, A.F.; Barnham, K.J.; Reid, G.E.; Vella, L.J. Characterization of brain-derived extracellular vesicle lipids in Alzheimer's disease. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugli, G.; Cohen, A.M.; Bennett, D.A.; Shah, R.C.; Fields, C.J.; Hernandez, A.G.; Smalheiser, N.R. Plasma Exosomal miRNAs in Persons with and without Alzheimer Disease: Altered Expression and Prospects for Biomarkers. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0139233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-D.; Liu, W.-L.; Lin, H.-W.; Lin, M.-R.; Yu, Y.; Liu, H.-H.; Dai, Y.-L.; Chen, L.-W.; Jia, W.-W.; He, X.-J.; et al. Emerging blood exosome-based biomarkers for preclinical and clinical Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 2381–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gámez-Valero, A.; Campdelacreu, J.; Vilas, D.; Ispierto, L.; Reñé, R.; Álvarez, R.; Armengol, M.P.; Borràs, F.E.; Beyer, K. Exploratory study on microRNA profiles from plasma-derived extracellular vesicles in Alzheimer’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Transl. Neurodegener. 2019, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winston, C.N.; Goetzl, E.J.; Akers, J.C.; Carter, B.S.; Rockenstein, E.M.; Galasko, D.; Masliah, E.; Rissman, R.A. Prediction of conversion from mild cognitive impairment to dementia with neuronally derived blood exosome protein profile. Alzheimer's Dementia: Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2016, 3, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiandaca, M.S.; Kapogiannis, D.; Mapstone, M.; Boxer, A.; Eitan, E.; Schwartz, J.B.; Abner, E.L.; Petersen, R.C.; Federoff, H.J.; Miller, B.L.; et al. Identification of preclinical Alzheimer's disease by a profile of pathogenic proteins in neurally derived blood exosomes: A case-control study. Alzheimer's Dement. 2015, 11, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetzl, E.J.; Boxer, A.; Schwartz, J.B.; Abner, E.L.; Petersen, R.C.; Miller, B.L.; Kapogiannis, D. Altered lysosomal proteins in neural-derived plasma exosomes in preclinical Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2015, 85, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Qiu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chu, L.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C.; Liang, F.; Shi, S.; Wang, S.; et al. Concordance between the assessment of Aβ42, T-tau, and P-T181-tau in peripheral blood neuronal-derived exosomes and cerebrospinal fluid. Alzheimer's Dement. 2019, 15, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetzl, E.J.; Kapogiannis, D.; Schwartz, J.B.; Lobach, I.V.; Goetzl, L.; Abner, E.L.; Jicha, G.A.; Karydas, A.M.; Boxer, A.; Miller, B.L. Decreased synaptic proteins in neuronal exosomes of frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer's disease. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 4141–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetzl, E.J.; Abner, E.L.; Jicha, G.A.; Kapogiannis, D.; Schwartz, J.B. Declining levels of functionally specialized synaptic proteins in plasma neuronal exosomes with progression of Alzheimer's disease. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 888–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetzl, E.J.; Schwartz, J.B.; Abner, E.L.; Jicha, G.A.; Kapogiannis, D. High complement levels in astrocyte-derived exosomes of Alzheimer disease. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetzl, E.J.; Mustapic, M.; Kapogiannis, D.; Eitan, E.; Lobach, I.V.; Goetzl, L.; Schwartz, J.B.; Miller, B.L. Cargo proteins of plasma astrocyte-derived exosomes in Alzheimer's disease. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 3853–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooshabadi, V.T.; Mardpour, S.; Yousefi-Ahmadipour, A.; Allahverdi, A.; Izadpanah, M.; Daneshimehr, F.; Ai, J.; Banafshe, H.R.; Ebrahimi-Barough, S. The extracellular vesicles-derived from mesenchymal stromal cells: A new therapeutic option in regenerative medicine. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 8048–8073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regmi, S.; Liu, D.D.; Shen, M.; Kevadiya, B.D.; Ganguly, A.; Primavera, R.; Chetty, S.; Yarani, R.; Thakor, A.S. Mesenchymal stromal cells for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Strategies and limitations. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1011225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, V.K.; Faroqui, R.; Vyshkina, T.; Sadiq, S.A. Characterization of Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Neural Progenitors as a Feasible Source of Stem Cells for Central Nervous System Applications in Multiple Sclerosis. STEM CELLS Transl. Med. 2012, 1, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Velthoven, C.T.; Kavelaars, A.; Heijnen, C.J. Mesenchymal stem cells as a treatment for neonatal ischemic brain damage. Pediatr. Res. 2012, 71, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza-Zaldivar, E.E.; Hernández-Sapiéns, M.A.; Minjarez, B.; Gutiérrez-Mercado, Y.K.; Márquez-Aguirre, A.L.; Canales-Aguirre, A.A. Potential Effects of MSC-Derived Exosomes in Neuroplasticity in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.Y.; Park, H.J.; Na Kim, H.; Oh, S.H.; Bae, J.-S.; Ha, H.-J.; Lee, P.H. Mesenchymal stem cells enhance autophagy and increase β-amyloid clearance in Alzheimer disease models. Autophagy 2013, 10, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokokawa, K.; Iwahara, N.; Hisahara, S.; Emoto, M.C.; Saito, T.; Suzuki, H.; Manabe, T.; Matsumura, A.; Matsushita, T.; Suzuki, S.; et al. Transplantation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improves Amyloid-β Pathology by Modifying Microglial Function and Suppressing Oxidative Stress. J. Alzheimer's Dis. 2019, 72, 867–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, D.-S.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Jeon, H.B.; Lee, E.H.; Yang, Y.S.; Oh, W.; Chang, J.W. Galectin-3 secreted by human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduces amyloid-β42 neurotoxicity in vitro. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3601–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.K.; Park, S.E.; Kwon, S.J.; Shim, S.; Byeon, Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Na, D.L.; Chang, J.W. Agouti Related Peptide Secreted Via Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Upregulates Proteasome Activity in an Alzheimer’s Disease Model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.E.; García, E. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease. Stem Cells Int. 2021, 2021, 7834421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, R.; Li, A.; Datta, T.; Jha, N.K.; Talukder, S.; Jha, S.K.; Chen, Z.-S. Advances in stromal cell therapy for management of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 955401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.R.; Imhoff, F.M.; Baird, S.K. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit breast cancer cell migration and invasion through secretion of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 and -2. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 54, 1214–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musiał-Wysocka, A.; Kot, M.; Majka, M. The Pros and Cons of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapies. Cell Transplant. 2019, 28, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, S.; Collino, F.; Iavello, A.; Camussi, G. Effects of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on Tumor Growth. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, P.S.; Messina, D.J.; Hirsh, E.L.; Chi, N.; Goldman, S.N.; Lo, D.P.; Harris, I.R.; Popma, S.H.; Sachs, D.H.; Huang, C.A. Immunogenicity of umbilical cord tissue–derived cells. Blood 2008, 111, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrzejewska, A.; Lukomska, B.; Janowski, M. Concise review: Mesenchymal stem cells: From roots to boost. Stem Cells 2019, 37, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





