1. Introduction
Rosmarinus officinalis L. is one of the two species of the genus
Rosmarinus (along with
Rosmarinus eriocalix Jordan & Fourr.) present in the Mediterranean region of Europe [
1]. Rosemary is cultivated in various regions of Europe, including Romania, as an aromatic and ornamental plant. The leaves are used for their medicinal, aromatic, and insecticidal properties [
1,
2,
3,
4].
Rosemary has been known and used in the Mediterranean basin, its natural growing region, since antiquity, being mentioned in Egyptian, Greek, and Latin writings. In the ritual practices of ancient Egypt, rosemary was used for its aromatic properties, including in the mummification process [
5,
6]. Its presence on calcareous soils in the warm areas of the Mediterranean coast probably led to the choice of the Latin name for the genus, which translates to “dew of the sea” (
ros – dew,
marinus – sea) [
5].
Rosemary is a sempervirent subshrub that can reach a height of 250 cm under natural conditions [
1,
2,
7]. The species requires protection from wind and low temperatures, being fairly drought-resistant when cultivated in temperate regions [
1,
2,
7,
8]. The plant has acicular, sessile, and coriaceous leaves with revolute margins. The superior surface of the leaves is glabrous, while the inferior surface has protective and glandular hairs. The flowers have a bilabiate corolla, which is pale blue, white, or pink, and pubescent on the exterior. The corolla tube is longer than the calyx and lacks a hairy ring on the interior. The flowers are arranged in lax, spicate inflorescences. Flowering occurs during the spring-summer period [
1,
2,
7]. Depending on the color of the flowers and the shape of the leaves, various forms and varieties are mentioned, with some classifications also based on the chemical characteristics of plants from specific regions [
2,
5,
9,
10,
11,
12].
Rosmarini folium contains 1–2% essential oil, flavonoids (cirsimarin, cirsimaritin and derivatives), approx. 8% tannin, diterpenoids, triterpenoids (ursolic acid, oleanolic acid, betulinol, α-amirenol, β-amirenol, abietane-type derivatives), polyphenolic acids (caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid), lipids (seed oil), amino acids, carbohydrates, mineral salts [
10,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17]. The composition of tannin includes a depside called rosmarinic acid, dimer of caffeic acid conjugated with hydroxycaffeic acid [
13,
18,
19,
20,
21]. Diterpenoids (“bitter principles”) are abietane-type compounds represented mainly by rosmanol, carnosic acid and carnosol (picrosalvin), the latter component being identified for the first time in
Salvia carnosa Douglas ex Greene, purple sage (
Lamiaceae) [
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25]. Depending on the geographical origin and chemotype, rosemary essential oil contains up to 40% 1,8-cineole (eucalyptol), 25% borneol, 20% α- and β-pinene, 15% camphor [
26,
27,
28].
In ethnopharmacology, numerous properties and recommendations of rosemary leaves are mentioned for improving physical and mental state. Traditional uses of rosemary include enhancing memory capacity and treating rheumatic pains, migraines, stomach pains, dysmenorrhea, epilepsy, nervous disorders, and hysteria [
29].
Multiple studies have investigated the pharmacological actions of rosemary leaves extracts. The results report various properties, including antioxidant [
10,
18,
30,
31,
32,
33], anti-inflammatory [
31,
34,
35,
36], antidepressant [
37,
38], antibacterial [
31,
39,
40,
41,
42], antifungal [
43,
44,
45,
46], antiviral [
47,
48,
49,
50], and antiallergic [
51,
52], as well as neuroprotective [
53,
54,
55,
56], hepatoprotective [
52,
57,
58], nephroprotective [
52,
59,
60], antiproliferative and antitumor [
10,
19,
31,
61,
62,
63,
64,
65], immunomodulatory [
66], antihypertensive and anti-ischemic [
11,
67,
68,
69], hypolipidemic and hypocholesterolemic [
70,
71], hypoglycemic [
57,
67,
72,
73], antifibrotic [
74], radioprotective [
75,
76], and cutaneous texture restoration effects [
3,
40,
77,
78].
As a “rejuvenating remedy”, rosemary leaves or flowering tops exhibit choleretic-cholagogue and antihypercholesterolemic properties [
71]. As such or mixed with other herbal products, rosemary leaves are recommended for the antispastic action in the treatment of digestive colic, due to the content of polymethoxylated flavonoids of the cirsimarin type [
32,
79]. The flowering tops are used as a natural spice and preservative for some meat recipes [
32,
80,
81,
82].
Rosmarini aetheroleum is used against digestive cramps, as a spasmolytic, probably due to the content of borneol and not flavonoids (non-extractable with water vapor) [
83]. It also has antioxidant [
28], neuroprotective [
84], hepatoprotective [
85], antitumor [
86], radioprotective [
87], expectorant, bacteriostatic and epithelializing properties [
9,
27,
43,
88].
Rosemary leaves extracts and essential oil are the main components of some creams, antirheumatic ointments, cosmetic and perfumery products (soaps, cologne) [
3,
77,
78].
The aim of our paper was to report, for the first time, over a 12-month period, the identification and quantification of polyphenols and the investigation of the antioxidant and anticholinesterase activity of Rosmarinus officinalis L. species harvested at flowering from the flora of southwestern Romania (Oltenia Region).
2. Results
2.1. Total Phenolic Content
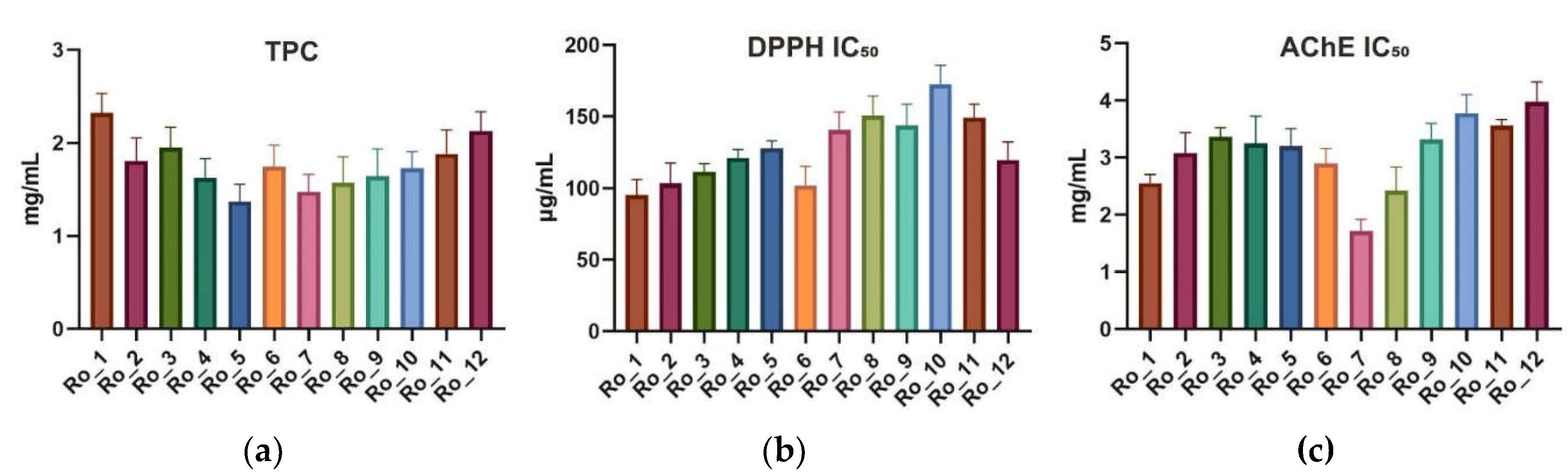
To determine the total phenolic content (TPC), the Folin–Ciocalteu assay was used. The mean TPC (mg/mL) across the months ranged from 1.372 to 2.323 mg/mL. The highest TPC was observed in February (Ro_1), while the lowest was in June (Ro_5). The standard deviations (SDs) indicated moderate variability throughout the 12-month period (
Table 1;
Figure 1a).
2.2. Antioxidant Activity (DPPH IC50)
The antioxidant activity of Ro_1 to Ro_12 samples was evaluated using the 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging assay. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC
50) values for DPPH ranged from 95.32 mL to 172.80 μg/mL. The lowest IC
50 value, indicating the highest antioxidant activity, was observed in February (Ro_1), while the highest IC
50 value was found in November (Ro_10) (
Table 1;
Figure 1b).
2.3. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activity (AChE IC50)
The acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitory activity was assessed, with IC
50 values ranging from 1.716 to 3.980 mg/mL. The strongest inhibitory activity was observed in August (Ro_7), while the weakest was in January (Ro_12) (
Table 1;
Figure 1c).
2.4. UHPLC/MS Analysis of Polyphenolic Acids
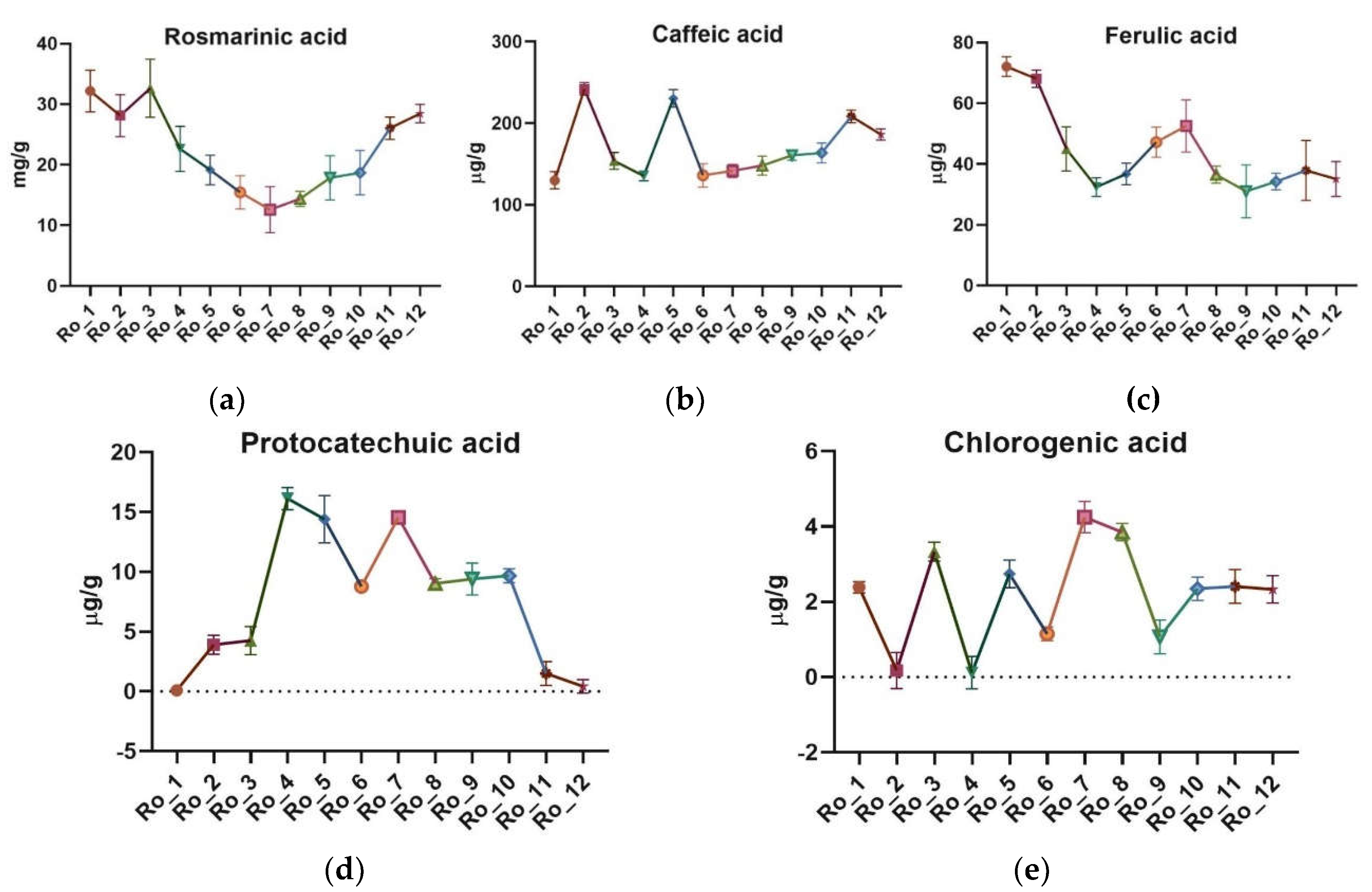
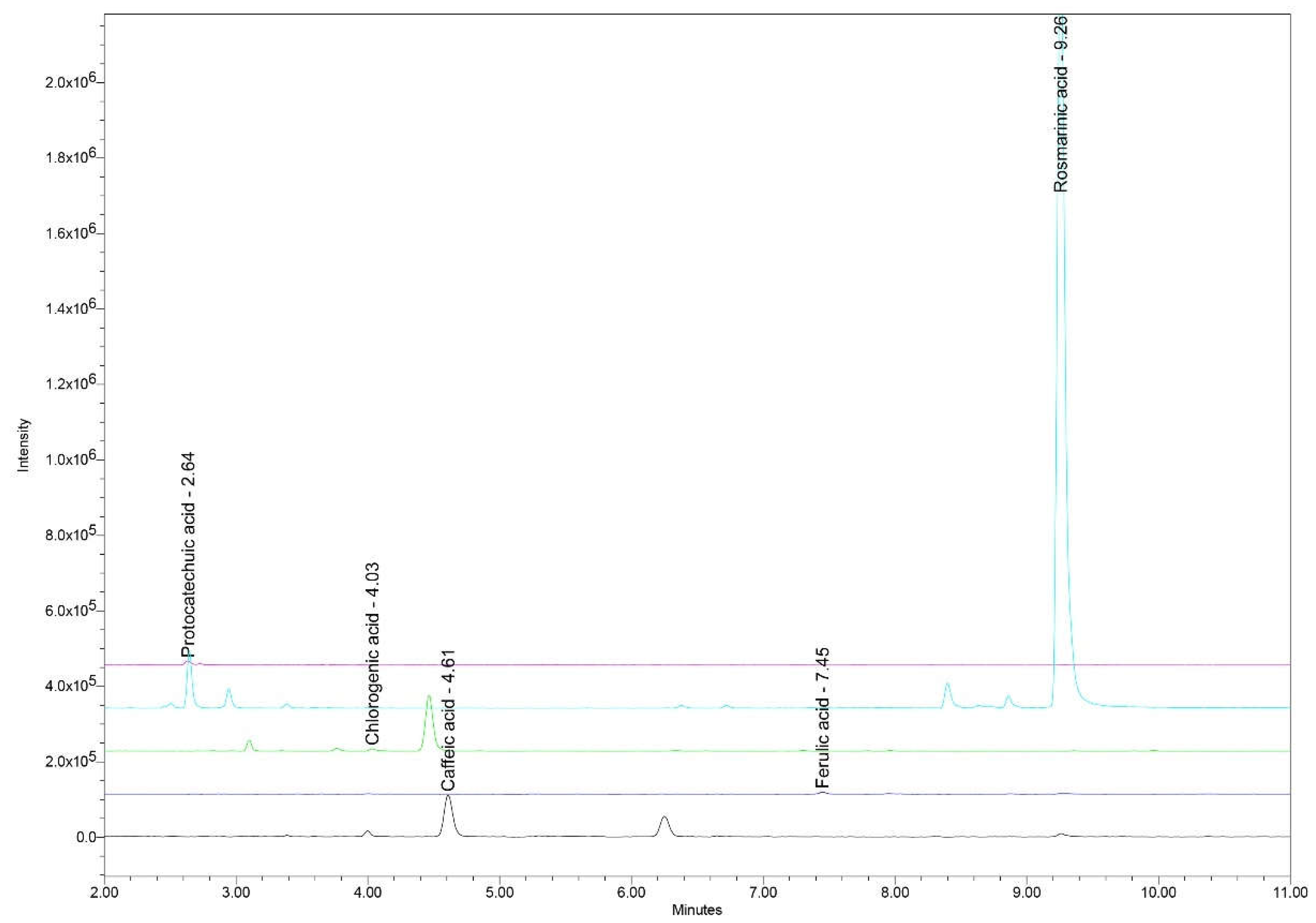
The ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (UHPLC/MS) analysis identified and quantified the main polyphenolic acids, including rosmarinic acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, protocatechuic acid, and chlorogenic acid. The mean concentrations of these compounds and variation across the 12-month period are highlighted in
Table 2 and
Figure 2 (a–e). A representative chromatogram was provided for the UHPLC/MS analysis results (
Figure 3).
Rosmarinic acid exhibited the highest amount in winter (32.179 mg/g, February) and the lowest in summer (12.585 mg/g, August). Caffeic acid concentrations were highest in spring (mean 176.41 μg/g) and lowest in summer (mean 132.31 μg/g). Ferulic acid amount peaked in winter (mean 56.35 μg/g) and were lowest in fall (mean 34.95 μg/g). Protocatechuic acid showed significant seasonal variation, with the highest concentration in summer (mean 12.11 μg/g) and the lowest in winter (mean 1.68 μg/g). Chlorogenic acid exhibited the highest concentration in fall (mean 2.42 μg/g) and the lowest in spring (mean 1.21 μg/g).
2.5. HPTLC–DPPH Analysis
Polyphenols separation on high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) plate were documented under ultraviolet (UV) light at 254 nm (
Figure 4) and at 365 nm (
Figure 5) without derivatization.
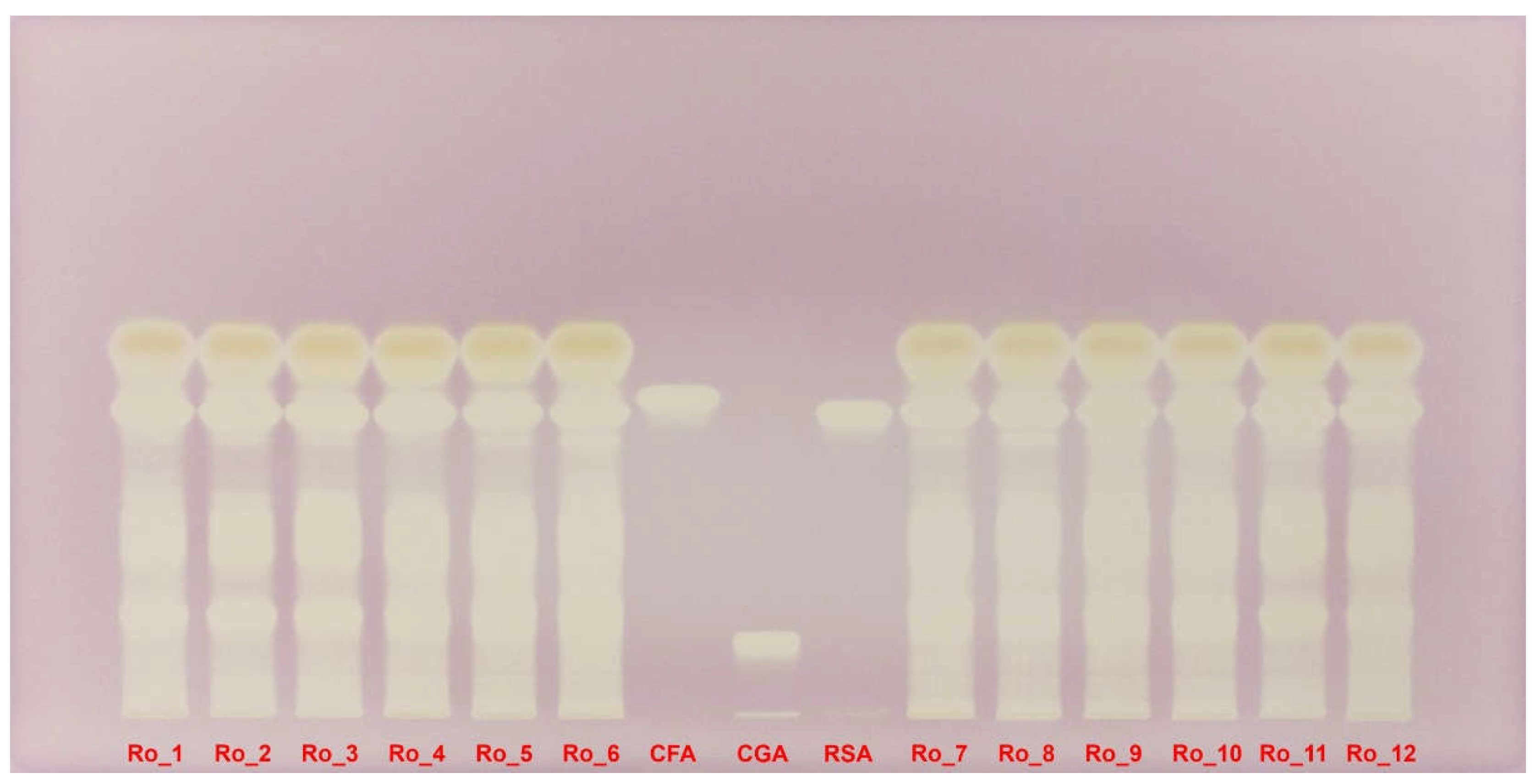
The DPPH-derivatized HPTLC plate under white light provides a clear visual representation of the antioxidant activity of the rosemary extracts. Yellow bands on a purple background indicate areas where the DPPH radical has been reduced, showcasing the antioxidant capacity of the compounds present (
Figure 6).
The first six columns (Ro_1 to Ro_6, representing February 2022 to July 2022) show varying intensities of yellow bands. Ro_1 sample exhibits multiple intense yellow bands, indicating strong antioxidant activity. This activity decreases gradually through the summer months, with Ro_6 sample showing less intense but still significant yellow bands. The less well-separated compounds for Ro_5 and Ro_6 samples suggest that multiple overlapping polyphenols contribute to the antioxidant activity, despite the lower overall intensity (
Figure 6).
Columns 7 to 9 serve as benchmarks, showing the antioxidant activity of three standards: caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid, and rosmarinic acid. The reference compounds confirm the presence of these specific polyphenolic acids in the extracts, as indicated by corresponding yellow bands (
Figure 6).
The last six columns (Ro_7 to Ro_12, representing August 2022 to January 2023) reveal increasing antioxidant activity as winter approaches. Ro_12 shows the highest intensity of yellow bands, aligning with the peak polyphenol concentrations observed in quantitative analyses. The summer extract (Ro_7) again displays less separation but substantial yellow bands, indicating high antioxidant potential due to the combined effects of overlapping polyphenols (
Figure 6).
The DPPH-derivatized HPTLC plate clearly illustrates the seasonal variations in antioxidant activity among the rosemary extracts. Winter months, particularly January, show the highest antioxidant activity, consistent with higher polyphenol content. Conversely, summer months (June–August), despite having less well-separated compounds, demonstrate significant antioxidant potential due to the presence of multiple overlapping polyphenols (
Figure 6).
2.6. Statistical Correlation Analysis
The statistical correlation analysis provided valuable insights into how different polyphenolic compounds contribute to the biological activities of rosemary by examining the relationships between TPC, antioxidant activity (DPPH IC
50), and AChE inhibitory activity (AChE IC
50) with the concentrations of individual polyphenolic compounds (
Table 3).
2.6.1. Total Phenolic Content
The TPC displayed a strong positive correlation with rosmarinic acid (
r=0.801), indicating that higher overall polyphenol levels are strongly associated with increased rosmarinic acid content. In contrast, protocatechuic acid showed a strong negative correlation with TPC (
r=−0.884), suggesting that higher levels of this compound are linked to lower overall polyphenol content. Additionally, ferulic acid had a moderately positive correlation with TPC (
r=0.447), indicating that it contributes to the overall polyphenolic profile. Caffeic acid and chlorogenic acid exhibited no significant correlation with TPC (
Table 3).
2.6.2. Antioxidant Activity (DPPH IC50)
The analysis revealed a moderately negative correlation between rosmarinic acid and DPPH IC
50 (
r=−0.533). This suggests that higher concentrations of rosmarinic acid are associated with stronger antioxidant activity, as indicated by lower DPPH IC
50 values. Similarly, ferulic acid exhibited a moderately negative correlation with DPPH IC
50 (
r=−0.642), indicating its significant role in enhancing antioxidant activity. Conversely, chlorogenic acid and protocatechuic acid showed a moderately positive correlation with DPPH IC
50 (
r=0.353 and
r=0.325, respectively), implying that higher concentrations of these compounds are associated with weaker antioxidant activity. Caffeic acid has a limited role in antioxidant activity, exhibiting no significant correlation with DPPH IC
50 (
Table 3).
2.6.3. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activity (AChE IC50)
In terms of AChE inhibitory activity, rosmarinic acid and caffeic acid demonstrated a moderately positive correlation with AChE IC
50 (
r=0.435 and
r=0.392, respectively), suggesting that higher concentrations of these two polyphenols are linked to weaker AChE inhibitory activity. On the other hand, protocatechuic acid showed a moderately negative correlation with AChE IC
50 (
r=−0.334), indicating stronger inhibitory activity at higher concentrations. Ferulic acid also had a moderately negative correlation with AChE IC
50 (
r=−0.480), reinforcing its role in enhancing AChE inhibition. Chlorogenic acid exhibited a similar moderately negative correlation with AChE IC
50 (
r=−0.405), further highlighting its contribution to AChE inhibitory activity (
Table 3).
2.6.4. Correlation of TPC with DPPH IC50 and AChE IC50
The analysis of the relationship between TPC and the in vitro activities measured by DPPH IC50 and AChE IC50 provided further insights into the overall impact of polyphenols on antioxidant and AChE inhibitory activities.
TPC demonstrated a moderately negative correlation with DPPH IC
50 (
r=−0.469). This negative correlation indicates that higher TPC is associated with lower DPPH IC
50 values, which in turn signifies stronger antioxidant activity. Essentially, as TPC increases, the plant’s ability to scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress improves. This relationship underscores the importance of polyphenolic compounds in enhancing the antioxidant capacity of rosemary (
Table 3).
In contrast, TPC exhibited a moderately positive correlation with AChE IC
50 (
r=0.293). This positive correlation suggests that higher TPC is associated with higher AChE IC
50 values, indicating weaker AChE inhibitory activity. In other words, as the overall TPC increases, the ability of the plant to inhibit AChE diminishes. This finding may reflect the complex interactions between different phenolic compounds, where certain polyphenols may enhance antioxidant activity while others contribute more significantly to AChE inhibition (
Table 3).
2.6.5. Overview
The statistical correlation results highlight the dual role of polyphenolic compounds in rosemary. Higher TPC is beneficial for enhancing antioxidant activity, as indicated by the strong negative correlation with DPPH IC
50. However, the relationship with AChE inhibitory activity is more nuanced, with higher TPC associated with weaker inhibition, as reflected by the positive correlation with AChE IC
50. This dual role emphasizes the need to consider the specific polyphenolic profile of the plant when evaluating its medicinal properties and potential therapeutic applications (
Table 3).
2.7. Seasonal Variability Comparison
The seasonal variation in polyphenolic content and their associated activities in rosemary was analyzed by categorizing the data into four seasons: winter, spring, summer, and fall. This analysis revealed significant differences in the concentrations of polyphenolic compounds and their biological activities across different seasons.
TPC was highest in winter, with an average of 2.112 mg/mL, and lowest in summer, averaging 1.524 mg/mL. This suggests that the polyphenolic compounds in R. officinalis are most abundant during the colder months, potentially due to the plant’s adaptive mechanisms to withstand harsh environmental conditions.
The antioxidant activity, as measured by the DPPH IC50, showed that the lowest IC50 values were in winter (average 111.73 μg/mL), indicating the strongest antioxidant activity. In contrast, the highest IC50 values were observed in fall (average 155.15 μg/mL), reflecting weaker antioxidant activity. This seasonal trend indicates that the antioxidant potential of the plant is maximized during winter, possibly correlating with the higher TPC observed in this season.
The AChE inhibitory activity, indicated by AChE IC50 values, was found to be the strongest in summer, with the lowest IC50 values averaging 2.605 mg/mL. Conversely, the weakest inhibitory activity was observed in winter, with an average IC50 value of 3.356 mg/mL. This suggests that specific polyphenolic compounds with strong AChE inhibitory properties are more concentrated in the plant during the summer months.
Rosmarinic acid content was highest in winter, averaging 28.23 mg/g, and significantly lower in summer, at 15.69 mg/g. This pattern aligns with the TPC and suggests that rosmarinic acid is a major contributor to the overall polyphenolic profile in winter. The concentration of protocatechuic acid was highest in summer (12.11 μg/g) and lowest in winter (1.68 μg/g). This inverse relationship with the TPC and rosmarinic acid indicates that protocatechuic acid might be synthesized or accumulated differently in the plant compared to other polyphenols. Ferulic acid showed the highest levels in winter (56.35 μg/g) and the lowest in fall (34.95 μg/g). This suggests a potential protective role of ferulic acid during the colder months, contributing to the plant’s overall resilience. Caffeic acid concentrations were highest in spring (176.41 μg/g) and lowest in summer (132.31 μg/g). The spring peak might be associated with the plant’s growth phase, where caffeic acid plays a significant role in plant development and defense. Chlorogenic acid was highest in fall (2.42 μg/g) and lowest in spring (1.21 μg/g). Although chlorogenic acid concentrations were relatively low compared to other polyphenols, its seasonal variation suggests it has specific roles or synthesis patterns in different environmental conditions.
3. Discussion
The present study focused, for the first time, on evaluating the polyphenolic content, antioxidant capacity, and AChE inhibitory activity of R. officinalis species from southwest Romania flora. The analysis was conducted over a 12-month period to understand seasonal variations and their impact on the plant’s bioactive properties. The results revealed significant correlations between specific polyphenolic compounds and the measured biological activities, providing insights into the optimal harvesting times and potential medicinal benefits of rosemary.
3.1. Total Phenolic Content
Polyphenols are critical secondary metabolites in plants, known for their antioxidant properties and health benefits. The TPC in rosemary exhibited seasonal variations, with the highest amount recorded in February (Ro_1 sample, 2.323 mg/mL) and the lowest in June (Ro_5 sample, 1.372 mg/mL). This seasonal trend suggests that environmental factors such as temperature, sunlight, and water availability significantly influence the synthesis and accumulation of polyphenols in rosemary.
Winter months, characterized by lower temperatures and reduced sunlight, seem to favor the accumulation of polyphenols. This could be a protective response to environmental stressors, enhancing the plant’s ability to scavenge free radicals and protect against oxidative damage. Conversely, the lower TPC in summer may result from higher temperatures and increased metabolic activity, which could lead to the utilization of polyphenolic compounds for growth and development [
30,
89].
3.2. Antioxidant Activity
The DPPH radical scavenging assay is a widely used method to assess the antioxidant capacity of plant extracts. The IC50 value, representing the concentration required to inhibit 50% of DPPH radicals, is inversely proportional to antioxidant activity. The results showed that the antioxidant activity was strongest in February (Ro_1 sample), with the lowest IC50 value of 95.32 μg/mL, and weakest in November (Ro_10 sample), with the highest IC50 value of 172.8 μg/mL.
The strong antioxidant activity in winter aligns with the higher TPC observed during this season. Polyphenols, such as rosmarinic acid and ferulic acid, are known for their potent antioxidant properties. The correlation analysis revealed a moderately negative correlation between TPC and DPPH IC50 (r=-0.469), confirming that higher polyphenol concentrations are associated with stronger antioxidant activity.
Rosmarinic acid, in particular, showed a significant contribution to the antioxidant capacity, with a moderately negative correlation (
r=-0.533) with DPPH IC
50. Ferulic acid also exhibited a strong negative correlation (
r=-0.642) with DPPH IC
50, highlighting its role in enhancing the antioxidant potential of rosemary. These findings underscore the importance of specific polyphenolic compounds in determining the antioxidant properties of rosemary extracts [
89,
90].
3.3. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitory Activity
AChE inhibitors are compounds that prevent the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter essential for memory and cognition. AChE inhibitors are therefore valuable in treating neurodegenerative injuries, such as Alzheimer’s disease. The study found that the AChE inhibitory activity of rosemary varied seasonally, with the strongest activity observed in August (Ro_7 sample, IC50 1.716 mg/mL) and the weakest in January (Ro_12 sample, IC50 3.98 mg/mL).
The TPC showed a moderately positive correlation with AChE IC
50 (
r=0.293), indicating that higher polyphenol levels are associated with weaker AChE inhibition. This positive correlation suggests that not all polyphenols contribute equally to AChE inhibitory activity. For instance, while rosmarinic acid exhibited a moderately positive correlation with AChE IC
50 (
r=0.435), indicating weaker inhibitory activity at higher concentrations, other polyphenols like ferulic acid and protocatechuic acid showed negative correlations (
r=-0.480 and
r=-0.334, respectively), suggesting stronger inhibitory effects [
91].
3.4. Correlation of Polyphenols Content with Antioxidant and Anticholinesterase Activities
The study identified and quantified several key polyphenolic compounds in rosemary, including rosmarinic acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, protocatechuic acid, and chlorogenic acid. Each of these compounds exhibited distinct seasonal variations and contributed differently to the plant’s bioactive properties.
Rosmarinic acid, a major polyphenol in rosemary, showed the highest concentration in winter (32.179 mg/g) and the lowest in summer (12.585 mg/g). This seasonal trend mirrors the total polyphenol content, suggesting that rosmarinic acid is a significant contributor to the overall polyphenol profile of rosemary. The strong positive correlation between rosmarinic acid and TPC (
r=0.801) supports this observation. In terms of antioxidant activity, rosmarinic acid exhibited a moderately negative correlation with DPPH IC
50, indicating that higher concentrations enhance the antioxidant capacity of rosemary. However, its contribution to AChE inhibitory activity was less straightforward, with a moderately positive correlation suggesting weaker inhibitory effects at higher concentrations. This dual role highlights the complexity of polyphenolic interactions in determining the bioactive properties of plant extracts [
30,
92].
Caffeic acid concentrations were highest in spring (176.41 μg/g) and lowest in summer (132.31 μg/g). Unlike other polyphenols, caffeic acid showed no significant correlation with DPPH IC
50, suggesting a limited role in antioxidant activity. However, it exhibited a moderately positive correlation with AChE IC
50 (
r=0.392), indicating weaker AChE inhibitory effects at higher concentrations. These results suggest that while caffeic acid is present in substantial amounts, its contribution to the bioactive properties of rosemary may be less pronounced compared to other polyphenols like rosmarinic acid and ferulic acid [
18,
30,
93].
Ferulic acid concentrations peaked in winter (56.35 μg/g) and were lowest in fall (34.95 μg/g). This polyphenol showed strong correlations with both antioxidant and AChE inhibitory activities. The negative correlation with DPPH IC
50 (
r=-0.642) highlights its significant contribution to the antioxidant potential of rosemary. Additionally, its moderately negative correlation with AChE IC
50 (
r=-0.480) indicates that ferulic acid also enhances the plant’s neuroprotective properties. These findings suggest that ferulic acid plays a crucial role in the bioactivity of rosemary, particularly during the winter months when its concentration is highest [
30,
93].
Protocatechuic acid showed significant seasonal variation, with the highest amount in summer (12.11 μg/g) and the lowest in winter (1.68 μg/g). Interestingly, its correlation with TPC was strongly negative (
r=-0.884), indicating that higher overall polyphenol levels are associated with lower concentrations of protocatechuic acid. Despite its lower amounts compared to other polyphenols, protocatechuic acid demonstrated notable biological activity. It exhibited a moderately negative correlation with AChE IC
50, suggesting strong AChE inhibitory effects at higher concentrations. This compound’s unique profile underscores the diverse functional roles of different polyphenols in rosemary [
30,
93].
Chlorogenic acid exhibited the highest concentration in fall (2.42 μg/g) and the lowest in spring (1.21 μg/g). Its correlation with DPPH IC
50 was moderately positive (
r=0.353), indicating weaker antioxidant activity at higher concentrations. In contrast, it showed a moderately negative correlation with AChE IC
50 (
r=-0.405), suggesting stronger AChE inhibitory effects. Although chlorogenic acid amounts were relatively low compared to other polyphenols, its significant correlations with both DPPH IC
50 and AChE IC
50 highlight its dual role in contributing to the antioxidant and neuroprotective properties of rosemary [
30,
41,
93].
In a study using three extracts of rosemary leaves (ethyl acetate, ethanol and water), only the ethyl acetate extract (250 µg/mL) exhibited a significant AChE inhibitory effect (75%) compared to galanthamine as a standard (88%). In addition, the highest TPC was highlighted for the ethyl acetate extract, which also presented the highest antioxidant capacity (DPPH IC
50 272 μg/mL) compared with the other two extracts: ethanol (DPPH IC
50 387 μg/mL) and aqueous (DPPH IC
50 534 μg/mL), respectively [
30,
94].
3.5. Importance of Seasonal Variations
The seasonal comparison revealed that winter is the optimal season for harvesting rosemary to maximize its polyphenolic content and antioxidant activity. The highest concentrations of total polyphenols, rosmarinic acid, and ferulic acid were observed in winter, coinciding with the strongest antioxidant activity (lowest DPPH IC50 values). This seasonal trend suggests that winter conditions favor the accumulation of polyphenolic compounds with potent antioxidant properties.
In contrast, summer showed the strongest AChE inhibitory activity, with the lowest AChE IC
50 values. The higher concentrations of protocatechuic acid and the significant presence of ferulic acid during this season likely contribute to this enhanced neuroprotective effect. These findings indicate that the optimal season for harvesting rosemary depends on the desired bioactive property—winter for antioxidant activity and summer for AChE inhibition [
30,
93].
3.6. Implications for Medicinal and Nutritional Use
The findings of this study have important implications for the medicinal and nutritional use of
R. officinalis species. Understanding the seasonal variations in polyphenolic content and biological activities can guide optimal harvesting times and monitoring the extraction process to maximize the plant’s health benefits [
95]. For instance, rosemary harvested in winter would be more suitable for products aimed at enhancing antioxidant capacity, such as dietary supplements or skincare products. Conversely, rosemary harvested in summer would be more effective for formulations targeting neuroprotective effects, such as supplements for cognitive health.
Additionally, the distinct profiles of individual polyphenols highlight the potential for selective breeding or cultivation practices to enhance specific bioactive compounds in rosemary. For example, cultivars with higher concentrations of rosmarinic acid and ferulic acid could be developed to boost antioxidant activity, while those with elevated levels of protocatechuic acid could enhance AChE inhibition.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material
The plant material (leaves) of R. officinalis cultivated species were collected over a 12-month period (February 2022 to January 2023) from southwest Romania flora (Cârcea Village, Dolj County, Oltenia Region). During the entire harvesting period, the plant remained in the flowering stage. All vegetal samples for analysis were collected in the middle of each month from the above-mentioned time interval and were deposited in the Herbarium of the Department of Pharmaceutical Botany, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova. The study did not involve endangered or protected species.
4.2. Chemicals and Reagents
The analysis of R. officinalis samples utilized a range of high-quality chemicals and reagents to ensure precise and reliable results.
Ultrapure water was produced using the HALIOS 12 lab water system (Neptec, Montabaur, Germany), providing the necessary purity for all aqueous solutions and dilutions.
Gradient grade acetonitrile, formic acid, ethyl acetate, methanol, and ethanol, all sourced from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany), were employed as solvents in the preparation of samples and mobile phases for UHPLC analysis.
The Folin–Ciocalteu reagent from Merck was essential for determining the total phenolic content, with anhydrous sodium carbonate, also from Merck, acting as a reagent in this assay. Gallic acid, prepared at a concentration of 10 mg/mL and sourced from Merck, served as a standard for calibrating phenolic content measurements.
The antioxidant activity of the samples was evaluated using DPPH, a stable free radical, and ascorbic acid from Sigma-Aldrich (Taufkirchen, Germany).
For the assessment of anticholinesterase activity, AChE from Electrophorus electricus, obtained from Sigma-Aldrich, was utilized, along with bovine serum albumin from Sigma-Aldrich and buffer components such as TRIS-hydrochloride and TRIS from Carl Roth (Karlsruhe, Germany). Fast Blue Salt (FBS), sourced from MP Biomedicals (Santa Ana, CA, USA), was used in chromogenic detection assays, with naphthyl acetate from Sigma-Aldrich serving as the substrate for esterase activity assays. Additionally, rivastigmine tartrate from Sigma-Aldrich was employed as a standard inhibitor in anticholinesterase activity assays, providing a benchmark for comparison. Disodium phosphate from Merck was used as a buffering agent in various biochemical assays to maintain the necessary pH stability.
All chemicals and reagents used in this study were of analytical grade and were utilized without further purification to ensure the integrity and accuracy of the experimental results.
HPTLC Silica gel 60 F254, 20×10 cm glass plates were purchased from Merck.
4.3. Sample Preparation
A precise amount of 0.1 g of plant material (rosemary leaves) was measured and added to 10 mL of 70% ethanol. The extraction process was conducted in a Bandelin Sonorex Digiplus DL 102H ultrasound bath (Bandelin electronic GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin, Germany) set at 50°C for 10 minutes to ensure efficient extraction of the compounds. Post extraction, the samples were centrifuged at 10,000 rpm using an Eppendorf 5804 centrifuge (Eppendorf SE, Hamburg, Germany) to separate the supernatant from the solid residues. The resulting supernatant was carefully decanted and then filtered through a Cytiva Whatman Uniflo syringe filter (Cytiva Europe GmbH, Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany) with a diameter of 13 mm and a pore size of 0.2 μm to ensure clarity and remove any particulate matter.
4.4. Total Phenolic Content
To determine the TPC, 20 μL of each 10 mg/mL plant extract in 70% ethanol was loaded into a 96-well microplate. Folin–Ciocalteu reagent was then added to each well and mixed thoroughly for 5 minutes. Subsequently, 80 μL of a 7.5% sodium carbonate solution was added and mixed well. The microplate was kept in the dark for 2 hours to allow the reaction to occur. Absorbance was measured at 620 nm using a FLUOstar Optima microplate reader (BMG Labtech, Ortenberg, Germany). The TPC was quantified using a standard curve obtained for gallic acid (10 mg/mL). All herbal extracts were analyzed in triplicate [
17].
4.5. Antioxidant Assay
For the antioxidant assay, 50 μL of each sample was added to a 96-well microplate. Then, 200 μL of 2 mM DPPH solution was added to each well. Serial dilutions were performed to obtain a range of concentrations for analysis. The reaction mixtures were incubated in the dark for 30 minutes at room temperature. The decrease in absorbance was measured at 517 nm using a FLUOstar Optima microplate reader (BMG Labtech). The antioxidant activity was calculated based on the reduction in DPPH absorbance compared to a control (ascorbic acid). The IC
50 value, representing the concentration of the sample required to inhibit 50% of the DPPH free radicals, was determined from the dose–response curve generated. All samples were assessed in triplicate [
17].
4.6. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition Assay
For the AChE inhibition assay, 10 μL of plant extract, 50 μL of naphthyl acetate, and 200 μL of AChE solution (3.33 U/mL) were loaded into a 96-well microplate. The mixture was then incubated at 4°C for 40 minutes to allow the reaction to proceed. Following incubation, 10 μL of FBS dissolved in water was added to each well. The absorbance was measured at 595 nm using a FLUOstar Optima microplate reader (BMG Labtech). The IC
50 value, indicating the concentration of the plant extract required to inhibit 50% of the AChE activity, was calculated from the dose–response curve generated during the assay. All samples were analyzed in triplicate [
96].
4.7. UHPLC/MS Analysis
The UHPLC/MS analysis employed a gradient elution system with two mobile phases: water containing 0.1% formic acid (mobile phase A) and acetonitrile containing 0.1% formic acid (mobile phase B). The flow rate was set at 0.8 mL/min. The gradient started with 98% mobile phase A, which was adjusted to 91% at 1.8 minutes and held constant until 4 minutes. At 10 minutes, the proportion of mobile phase A was reduced to 70%. By 15 minutes, mobile phase A was further decreased to 10% and maintained at this level until 16 minutes, before returning to the initial condition of 98% A by 17 minutes [
97].
To ensure stability and reproducibility, a 15-minute equilibration period with the initial mobile phase ratio was maintained between each injection. The column temperature was controlled at 28°C, while the sample temperature was kept at 10°C to maintain sample integrity and consistent results [
97].
MS was performed in negative ionization mode with a capillary voltage of 0.8 kV and a probe temperature of 400°C. Quantification was carried out in Selected Ion Recording (SIR) mode for specific compounds. Rosmarinic acid was monitored with an
m/z of 359 and a cone voltage of 20 V. Chlorogenic acid, ferulic acid, caffeic acid, and protocatechuic acid were monitored with
m/z values of 353, 193, 179, and 153, respectively, each with a cone voltage of 15 V [
97].
4.8. HPTLC–DPPH Analysis
All ethanolic extracts were applied as 15 µL, 8-mm bands on HPTLC plates using a CAMAG Linomat 5 applicator (CAMAG, Muttenz, Switzerland). The HPTLC plates were developed in a twin trough chamber using a solvent mixture of ethyl acetate–formic acid–water–methanol (15:1:1:0.1,
v/v/v/v) up to a migration distance of 70 mm. After development, the HPTLC plates were dried using a hair dryer for 5 minutes. The plates were then documented under UV light at 254 nm and 365 nm without derivatization, and under white light after DPPH derivatization, to visualize the antioxidant activity. Caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid and rosmarinic acid standards were added as 5 µL bands each of a 0.2 mg/mL concentration [
98].
4.9. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were conducted using GraphPad Prism version 8. The TPC, antioxidant activity (DPPH IC50), and AChE inhibitory activity (AChE IC50) data were analyzed for seasonal variations and correlations. Descriptive statistics, including means and SDs, were calculated for each month. To evaluate the relationships between the polyphenolic content and the biological activities, Pearson’s correlation coefficients (r) were computed. Specifically, Pearson’s r correlation was used to determine the strength and direction of the linear relationships between TPC and DPPH IC50 values, as well as between TPC and AChE IC50 values. Additionally, the IC50 values for DPPH and AChE were calculated using the log(inhibitor) vs. normalized response setting in GraphPad Prism. These statistical analyses provided insights into the potential interactions and synergistic effects of the polyphenolic compounds present in R. officinalis.
5. Conclusions
For the first time, the one year-long study of R. officinalis species from southwest Romania flora has illuminated significant seasonal variations in its polyphenolic content and related biological activities, which are crucial for optimizing its medicinal and nutritional uses. The TPC was found to be highest in winter, peaking in February at 2.323 mg/mL, and lowest in summer, with June recording 1.372 mg/mL. This suggests that colder, less sunny conditions enhance polyphenol accumulation, vital for the plant’s oxidative stress defense. Antioxidant activity, measured via DPPH IC50, was strongest in winter, with the lowest IC50 value of 95.32 μg/mL in February, indicating robust antioxidant activity that correlates with higher polyphenol levels. The moderate negative correlation between TPC and DPPH IC50 (r=-0.469) highlights the crucial role of polyphenols in enhancing antioxidant capacity. Conversely, AChE inhibitory activity was most potent in summer, with the lowest IC50 value of 1.716 mg/mL in August, suggesting a complex interplay of polyphenolic compounds influencing this activity. Higher polyphenol levels were associated with weaker AChE inhibition (r=0.293). Key polyphenols, including rosmarinic acid, ferulic acid, protocatechuic acid, caffeic acid, and chlorogenic acid, exhibited distinct seasonal patterns. Rosmarinic acid and ferulic acid, peaking in winter, significantly contributed to antioxidant activity, while protocatechuic acid, peaking in summer, enhanced AChE inhibitory activity. These findings suggest that winter-harvested rosemary is optimal for antioxidant applications, while summer-harvested rosemary is better for neuroprotective uses. Understanding these seasonal variations allows for maximizing rosemary’s health benefits, guiding optimal harvesting times, and enhancing its medicinal and nutritional value. In summary, this study advances our knowledge of rosemary’s bioactive potential, providing practical insights for its therapeutic and nutritional applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.E.B. and G.D.M.; methodology, A.B. and A.E.S.; validation, G.D.M. and A.E.S.; formal analysis, C.B.; investigation, A.B., A.R. and M.V.C.; resources, L.E.B. and A.B.; writing—original draft preparation, A.B. and G.D.M.; writing—review and editing, L.E.B. and G.D.M.; visualization, G.D.M., A.E.S. and C.B.; supervision, A.B. and G.D.M.; funding acquisition, L.E.B. and A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The manuscript does not contain experiments on laboratory animals.
Informed Consent Statement
The manuscript does not contain clinical studies or patient data.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Tutin, T.G.; Heywood, V.H.; Burges, N.A.; Moore, D.M.; Valentine, D.H.; Walters, S.M.; Webb, D.A. (Eds). Flora Europaea. Vol. 3: Diapensiaceae to Myoporaceae, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1972, p. 187.
- Săvulescu T (Ed). Flora R.P.R., 1st edition; Romanian Academy Publishing House: Bucharest, Romania, 1961; Volume VIII, pp. 108–109 (in Romanian).
- Li Pomi, F.; Papa, V.; Borgia, F.; Vaccaro, M.; Allegra, A.; Cicero, N.; Gangemi, S. Rosmarinus officinalis and Skin: Antioxidant Activity and Possible Therapeutical Role in Cutaneous Diseases. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 680. [https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12030680] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36978928/]. [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Al Kamaly, O.; Alanazi, A.S.; Noman, O. Phytochemical Analysis and Antimicrobial Activity of Rosmarinus officinalis L. Growing in Saudi Arabia: Experimental and Computational Approaches. Processes 2022, 10, 2422. [https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10112422]. [CrossRef]
- Begum, A.; Sandhya, S.; Shaffath Ali, S.; Vinod, K.R.; Reddy, S.; Banji, D. An in-depth review on the medicinal flora Rosmarinus officinalis (Lamiaceae). Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2013, 12, 61–73. [https://www.food.actapol.net/volume12/issue1/abstract-6.html] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24584866/].
- Teja, Y.S.C.; Jyothika, L.S.; Vasavi, N.; Reddy, K.S.S.; Sudheer, A. Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Rosemary: An In-depth Review of its Pharmacological Properties. Asian J. Adv. Med. Sci. 2024, 6, 19–31. [https://journalmedicals.com/index.php/AJOAIMS/article/view/141].
- Chatterjee, K.; Tamta, B.; Mukopadayay, S. A review on “pharmacological, phytochemical, and medicinal properties of Rosmarinus officinalis (Rosemary)”. Int. J. Health Sci. 2022, 6, 3491–3500. [https://doi.org/10.53730/ijhs.v6nS6.10184]. [CrossRef]
- Popescu, G.; Iancu, T.; Popescu, C.A.; Stanciu, S.M.; Luca, R.; Imbrea, F.; Radulov, I.; Sala, F.; Moatăr, M.M.; Camen, D.D. The influence of soil fertilization on the quality and extraction efficiency of rosemary essential oil (Rosmarinus officinalis L.). Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 25, 1961–1968. [https://doi.org/10.25083/rbl/25.5/1961.1968]. [CrossRef]
- Bernardes, W.A.; Lucarini, R.; Tozatti, M.G.; Flauzino, L.G.B.; Souza, M.G.M.; Turatti, I.C.C.; Andrade e Silva, M.L.; Martins, C.H.G.; da Silva Filho, A.A.; Cunha, W.R. Antibacterial activity of the essential oil from Rosmarinus officinalis and its major components against oral pathogens. Z. Naturforsch. C J. Biosci. 2010, 65, 588–593. [https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2010-9-1009] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21138060/]. [CrossRef]
- Kontogianni, V.G.; Tomic, G.; Nikolic, I.; Nerantzaki, A.A.; Sayyad, N.; Stosic-Grujicic, S.; Stojanovic, I.; Gerothanassis, I.P.; Tzakos, A.G. Phytochemical profile of Rosmarinus officinalis and Salvia officinalis extracts and correlation to their antioxidant and anti-proliferative activity. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 120–129. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.07.091] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23017402/]. [CrossRef]
- Fernández, L.F.; Palomino, O.M.; Frutos, G. Effectiveness of Rosmarinus officinalis essential oil as antihypotensive agent in primary hypotensive patients and its influence on health-related quality of life. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 509–516. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2013.11.006] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24269249/]. [CrossRef]
- Mersin, B.; Işcan, G.S. Rosmarinus officinalis L. In Novel Drug Targets with Traditional Herbal Medicines: Scientific and Clinical Evidence, 1st edition; Gürağaç Dereli, F.T., Ilhan, M., Belwal, T., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 525–541. [https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07753-1_34]. [CrossRef]
- Borrás-Linares, I.; Stojanović, Z.; Quirantes-Piné, R.; Arráez-Román, D.; Švarc-Gajić, J.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A. Rosmarinus officinalis Leaves as a Natural Source of Bioactive Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 20585–20606. [https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151120585] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25391044/]. [CrossRef]
- Quílez, M.; Ferreres, F.; López-Miranda, S.; Salazar, E.; Jordán, M.J. Seed Oil from Mediterranean Aromatic and Medicinal Plants of the Lamiaceae Family as a Source of Bioactive Components with Nutritional. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 510. [https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9060510] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32532110/]. [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, J.A.B.; Álvarez-Rivera, G.; Alves, R.C.; Costa, A.S.G.; Machado, S.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibáñez, E.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Comprehensive Phenolic and Free Amino Acid Analysis of Rosemary Infusions: Influence on the Antioxidant Potential. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 500. [https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030500] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33807074/]. [CrossRef]
- Kakouri, E.; Nikola, O.; Kanakis, C.; Hatziagapiou, K.; Lambrou, G.I.; Trigas, P.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C.; Tarantilis, P.A. Cytotoxic Effect of Rosmarinus officinalis Extract on Glioblastoma and Rhabdomyosarcoma Cell Lines. Molecules 2022, 27, 6348. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196348] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36234882/]. [CrossRef]
- Luţă, E.A.; Biţă, A.; Moroşan, A.; Mihaiescu, D.E.; Mihai, D.P.; Popescu, L.; Bejenaru, L.E.; Bejenaru, C.; Popovici, V.; Olaru, O.T.; et al. Implications of the Cultivation of Rosemary and Thyme (Lamiaceae) in Plant Communities for the Development of Antioxidant Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11670. [https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241411670] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37511428/]. [CrossRef]
- Elansary, H.O.; Szopa, A.; Kubica, P.; Ekiert, H.; El-Ansary, D.O.; Al-Mana, F.A.; Mahmoud, E.A. Saudi Rosmarinus officinalis and Ocimum basilicum L. Polyphenols and Biological Activities. Processes 2020, 8, 446. [https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8040446] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34885955/]. [CrossRef]
- Lamponi, S.; Baratto, M.C.; Miraldi, E.; Baini, G.; Biagi, M. Chemical Profile, Antioxidant, Anti-Proliferative, Anticoagulant and Mutagenic Effects of a Hydroalcoholic Extract of Tuscan Rosmarinus officinalis. Plants 2021, 10, 97. [https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10010097] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33418860/]. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Fan, Y.; Bai, X. A Green and Effective Polyethylene Glycols-Based Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Carnosic and Rosmarinic Acids from Rosmarinus officinalis Leaves. Foods 2023, 12, 1761. [https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12091761] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37174298/]. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Fan, Y.; Wu, H. The Selective Separation of Carnosic Acid and Rosmarinic Acid by Solid-Phase Extraction and Liquid–Liquid Extraction: A Comparative Study. Molecules 2023, 28, 5493. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28145493] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37513364/]. [CrossRef]
- Danisman, B.; Cicek, B.; Yildirim, S.; Bolat, I.; Kantar, D.; Golokhvast, K.S.; Nikitovic, D.; Tsatsakis, A.; Taghizadehghalehjoughi, A. Carnosic Acid Ameliorates Indomethacin-Induced Gastric Ulceration in Rats by Alleviating Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 829. [https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030829] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36979808/]. [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, S. Anti-Inflammatory Therapeutic Mechanisms of Natural Products: Insight from Rosemary Diterpenes, Carnosic Acid and Carnosol. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 545. [https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020545] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36831081/]. [CrossRef]
- Mirza, F.J.; Zahid, S.; Holsinger, R.M.D. Neuroprotective Effects of Carnosic Acid: Insight into Its Mechanisms of Action. Molecules 2023, 28, 2306. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052306] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36903551/]. [CrossRef]
- Kallimanis, P.; Magiatis, P.; Panagiotopoulou, A.; Ioannidis, K.; Chinou, I. Extraction Optimization and Qualitative/Quantitative Determination of Bioactive Abietane-Type Diterpenes from Three Salvia Species (Common Sage, Greek Sage and Rosemary) by 1H-qNMR. Molecules 2024, 29, 625. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030625] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38338370/]. [CrossRef]
- Vella, F.M.; Laratta, B. Rosemary Essential Oil Extraction and Residue Valorization by Means of Polyphenol Recovery. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2023, 26, 8. [https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2023-15024]. [CrossRef]
- Hendel, N.; Sarri, D.; Sarri, M.; Napoli, E.; Palumbo Piccionello, A.; Ruberto, G. Phytochemical Analysis and Antioxidant and Antifungal Activities of Powders, Methanol Extracts, and Essential Oils from Rosmarinus officinalis L. and Thymus ciliatus Desf. Benth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7989. [https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147989]. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, L.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, B.; Zhao, M. Optimization of Enzyme-Assisted Extraction of Rosemary Essential Oil Using Response Surface Methodology and Its Antioxidant Activity by Activating Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2024, 29, 3382. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29143382]. [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh Rahbardar, M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Therapeutic effects of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) and its active constituents on nervous system disorders. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 1100–1112. [https://doi.org/10.22038/ijbms.2020.45269.10541] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32963731/]. [CrossRef]
- Hcini, K.; Lozano-Pérez, A.A.; Luis Cenis, J.; Quílez, M.; José Jordán, M. Extraction and Encapsulation of Phenolic Compounds of Tunisian Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) Extracts in Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles. Plants 2021, 10, 2312. [https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10112312] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34834676/]. [CrossRef]
- Lešnik, S.; Bren, U. Mechanistic Insights into Biological Activities of Polyphenolic Compounds from Rosemary Obtained by Inverse Molecular Docking. Foods 2022, 11, 67. [https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010067] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35010191/]. [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, N.S.S.; Ramos, V.S.; Prado-Souza, L.F.L.; Lopes, R.M.; Arini, G.S.; Feitosa, L.G.P.; Silva, R.R.; Nantes, I.L.; Damasceno, D.C.; Lopes, N.P.; et al. Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) Glycolic Extract Protects Liver Mitochondria from Oxidative Damage and Prevents Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 628. [https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12030628] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36978874/]. [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Sui, X.; Jiang, L. Protection Function and Mechanism of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) Extract on the Thermal Oxidative Stability of Vegetable Oils. Foods 2023, 12, 2177. [https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112177] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37297422/]. [CrossRef]
- Amaral, G.P.; de Carvalho, N.R.; Barcelos, R.P.; Dobrachinski, F.; Portella, R.L.; da Silva, M.H.; Lugokenski, T.H.; Dias, G.R.M.; da Luz, S.C.A.; Boligon, A.A.; et al. Protective action of ethanolic extract of Rosmarinus officinalis L. in gastric ulcer prevention induced by ethanol in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 55, 48–55. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.12.038] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23279841/]. [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, C.; Fernandes, D.; Silva, I.; Mateus, V. Potential Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Rosmarinus officinalis in Preclinical In Vivo Models of Inflammation. Molecules 2022, 27, 609. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030609] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35163873/]. [CrossRef]
- Francolino, R.; Martino, M.; Caputo, L.; Amato, G.; Chianese, G.; Gargiulo, E.; Formisano, C.; Romano, B.; Ercolano, G.; Ianaro, A.; et al. Phytochemical Constituents and Biological Activity of Wild and Cultivated Rosmarinus officinalis Hydroalcoholic Extracts. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1633. [https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12081633] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37627628/]. [CrossRef]
- Machado, D.G.; Cunha, M.P.; Neis, V.B.; Balen, G.O.; Colla, A.R.; Grando, J.; Brocardo, P.S.; Bettio, L.E.; Dalmarco, J.B.; Rial, D.; et al. Rosmarinus officinalis L. hydroalcoholic extract, similar to fluoxetine, reverses depressive-like behavior without altering learning deficit in olfactory bulbectomized mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 143, 158–169. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2012.06.017] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22721880/]. [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.; Imran, M.; Aslam Gondal, T.; Imran, A.; Shahbaz, M.; Muhammad Amir, R.; Wasim Sajid, M.; Batool Qaisrani, T.; Atif, M.; Hussain, G.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Rosmarinic Acid: A Comprehensive Review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3139. [https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153139]. [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Hillebrand, G.G.; Nunez, G. Rosmarinus officinalis L. (Rosemary) Extracts Containing Carnosic Acid and Carnosol are Potent Quorum Sensing Inhibitors of Staphylococcus aureus Virulence. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 149. [https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040149] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32244277/]. [CrossRef]
- Gavan, A.; Colobatiu, L.; Hanganu, D.; Bogdan, C.; Olah, N.K.; Achim, M.; Mirel, S. Development and Evaluation of Hydrogel Wound Dressings Loaded with Herbal Extracts. Processes 2022, 10, 242. [https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10020242]. [CrossRef]
- Ielciu, I.; Niculae, M.; Pall, E.; Barbălată, C.; Tomuţă, I.; Olah, N.K.; Burtescu, R.F.; Benedec, D.; Oniga, I.; Hanganu, D. Antiproliferative and Antimicrobial Effects of Rosmarinus officinalis L. Loaded Liposomes. Molecules 2022, 27, 3988. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27133988] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35807229/]. [CrossRef]
- Iobbi, V.; Parisi, V.; Bernabè, G.; De Tommasi, N.; Bisio, A.; Brun, P. Anti-Biofilm Activity of Carnosic Acid from Salvia rosmarinus against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Plants 2023, 12, 3679. [https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12213679] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37960038/]. [CrossRef]
- Al Khoury, A.; El Khoury, A.; Rocher, O.; Hindieh, P.; Puel, O.; Maroun, R.G.; Atoui, A.; Bailly, J.D. Inhibition of Aflatoxin B1 Synthesis in Aspergillus flavus by Mate (Ilex paraguariensis), Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) and Green Tea (Camellia sinensis) Extracts: Relation with Extract Antioxidant Capacity and Fungal Oxidative Stress Response Modulation. Molecules 2022, 27, 8550. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238550] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36500642/]. [CrossRef]
- Corbu, V.M.; Gheorghe-Barbu, I.; Marinas, I.C.; Avramescu, S.M.; Pecete, I.; Geanǎ, E.I.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Eco-Friendly Solution Based on Rosmarinus officinalis Hydro-Alcoholic Extract to Prevent Biodeterioration of Cultural Heritage Objects and Buildings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11463. [https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911463] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36232763/]. [CrossRef]
- Meccatti, V.M.; Santos, L.F.; de Carvalho, L.S.; Souza, C.B.; Carvalho, C.A.T.; Marcucci, M.C.; Abu Hasna, A.; de Oliveira, L.D. Antifungal Action of Herbal Plants’ Glycolic Extracts against Candida Species. Molecules 2023, 28, 2857. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062857] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36985829/]. [CrossRef]
- Letsiou, S.; Pyrovolou, K.; Konteles, S.J.; Trapali, M.; Krisilia, S.; Kokla, V.; Apostolaki, A.; Founda, V.; Houhoula, D.; Batrinou, A. Exploring the Antifungal Activity of Various Natural Extracts in a Sustainable Saccharomyces cerevisiae Model Using Cell Viability, Spot Assay, and Turbidometric Microbial Assays. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1899. [https://doi.org/10.3390/app14051899]. [CrossRef]
- Nolkemper, S.; Reichling, J.; Stintzing, F.C.; Carle, R.; Schnitzler, P. Antiviral effect of aqueous extracts from species of the Lamiaceae family against Herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 in vitro. Planta Med. 2006, 72, 1378–1382. [https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-951719] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17091431/]. [CrossRef]
- Horváth, G.; Molnár, E.; Szabó, Z.; Kecskeméti, G.; Juhász, L.; Tallósy, S.P.; Nyári, J.; Bogdanov, A.; Somogyvári, F.; Endrész, V.; et al. Carnosic Acid Inhibits Herpes simplex Virus Replication by Suppressing Cellular ATP Synthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4983. [https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25094983] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38732202/]. [CrossRef]
- Karagianni, K.; Pettas, S.; Kanata, E.; Lioulia, E.; Thune, K.; Schmitz, M.; Tsamesidis, I.; Lymperaki, E.; Xanthopoulos, K.; Sklaviadis, T.; et al. Carnosic Acid and Carnosol Display Antioxidant and Anti-Prion Properties in In Vitro and Cell-Free Models of Prion Diseases. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 726. [https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11040726] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35453411/]. [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.; Trudler, D.; Oh, C.K.; Lipton, S.A. Potential Therapeutic Use of the Rosemary Diterpene Carnosic Acid for Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and Long-COVID through NRF2 Activation to Counteract the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 124. [https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11010124] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35052628/]. [CrossRef]
- Crozier, R.W.E.; Yousef, M.; Coish, J.M.; Fajardo, V.A.; Tsiani, E.; MacNeil, A.J. Carnosic acid inhibits secretion of allergic inflammatory mediators in IgE-activated mast cells via direct regulation of Syk activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 102867. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102867] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36608933/]. [CrossRef]
- Peno-Mazzarino, L.; Radionov, N.; Merino, M.; González, S.; Mullor, J.L.; Jones, J.; Caturla, N. Protective Potential of a Botanical-Based Supplement Ingredient against the Impact of Environmental Pollution on Cutaneous and Cardiopulmonary Systems: Preclinical Study. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 1530–1555. [https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46020099] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38392217/]. [CrossRef]
- Kayashima, T.; Matsubara, K. Antiangiogenic effect of carnosic acid and carnosol, neuroprotective compounds in rosemary leaves. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 115–119. [https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.110584] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22232247/]. [CrossRef]
- Mirza, F.J.; Zahid, S.; Amber, S.; Sumera; Jabeen, H.; Asim, N.; Ali Shah, S.A. Multitargeted Molecular Docking and Dynamic Simulation Studies of Bioactive Compounds from Rosmarinus officinalis against Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2022, 27, 7241. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27217241] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36364071/]. [CrossRef]
- Alrashdi, J.; Albasher, G.; Alanazi, M.M.; Al-Qahtani, W.S.; Alanezi, A.A.; Alasmari, F. Effects of Rosmarinus officinalis L. Extract on Neurobehavioral and Neurobiological Changes in Male Rats with Pentylenetetrazol-Induced Epilepsy. Toxics 2023, 11, 826. [https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100826] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37888677/]. [CrossRef]
- Kosmopoulou, D.; Lafara, M.-P.; Adamantidi, T.; Ofrydopoulou, A.; Grabrucker, A.M.; Tsoupras, A. Neuroprotective Benefits of Rosmarinus officinalis and Its Bioactives against Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6417. [https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156417]. [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, K.S.; Khalil, O.A.; Danial, E.N.; Alnahdi, H.S.; Ayaz, N.O. Hypoglycemic and hepatoprotective activity of Rosmarinus officinalis extract in diabetic rats. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 69, 779–783. [https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-013-0253-8] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23625639/]. [CrossRef]
- Ielciu, I.; Sevastre, B.; Olah, N.-K.; Turdean, A.; Chișe, E.; Marica, R.; Oniga, I.; Uifălean, A.; Sevastre-Berghian, A.C.; Niculae, M.; et al. Evaluation of Hepatoprotective Activity and Oxidative Stress Reduction of Rosmarinus officinalis L. Shoots Tincture in Rats with Experimentally Induced Hepatotoxicity. Molecules 2021, 26, 1737. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26061737] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33804618/]. [CrossRef]
- Azab, A.E.S.; Fetouh, F.A.; Albasha, M.O. Nephro-protective effects of curcumin, rosemary, and propolis against gentamicin induced toxicity in Guinea pigs: Morphological and biochemical study. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 2, 28–35. [https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajcem.20140202.14]. [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, J.R.; Camargo, S.E.A.; de Oliveira, L.D. Rosmarinus officinalis L. (rosemary) as therapeutic and prophylactic agent. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 5. [https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-019-0499-8] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30621719/]. [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; Yousef, M.; Tsiani, E. Anticancer Effects of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) Extract and Rosemary Extract Polyphenols. Nutrients 2016, 8, 731. [https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8110731] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27869665/]. [CrossRef]
- Allegra, A.; Tonacci, A.; Pioggia, G.; Musolino, C.; Gangemi, S. Anticancer Activity of Rosmarinus officinalis L.: Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Potentials. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1739. [https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12061739] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32532056/]. [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, E.J.; Moore, J.; Song, J.; Tsiani, E.L. Inhibition of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Proliferation and Survival by Rosemary Extract Is Associated with Activation of ERK and AMPK. Life 2022, 12, 52. [https://doi.org/10.3390/life12010052] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35054445/]. [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, E.J.; Sze, N.S.K.; MacPherson, R.E.K.; Tsiani, E. Carnosic Acid against Lung Cancer: Induction of Autophagy and Activation of Sestrin-2/LKB1/AMPK Signalling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1950. [https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25041950] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38396629/]. [CrossRef]
- Bouammali, H.; Zraibi, L.; Ziani, I.; Merzouki, M.; Bourassi, L.; Fraj, E.; Challioui, A.; Azzaoui, K.; Sabbahi, R.; Hammouti, B.; et al. Rosemary as a Potential Source of Natural Antioxidants and Anticancer Agents: A Molecular Docking Study. Plants 2024, 13, 89. [https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13010089] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38202397/]. [CrossRef]
- Alzahri, R.Y.; Al-Ghamdi, F.A.; Al-Harbi, S.S. Immunological and Histological Studies of Different Concentrations of Rosmarinus officinalis and Thymus vulgaris Extracts on Thymus Gland of Chick Embryos. Toxics 2023, 11, 625. [https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11070625] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37505590/]. [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.L.; Peng, C.H.; Chyau, C.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Wang, H.E.; Peng, R.Y. Low-density lipoprotein, collagen, and thrombin models reveal that Rosmarinus officinalis L. exhibits potent antiglycative effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 2884–2891. [https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0631833] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17385882/]. [CrossRef]
- Karthik, D.; Viswanathan, P.; Anuradha, C.V. Administration of rosmarinic acid reduces cardiopathology and blood pressure through inhibition of p22phox NADPH oxidase in fructose-fed hypertensive rats. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2011, 58, 514–521. [https://doi.org/10.1097/fjc.0b013e31822c265d] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21795992/]. [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Durán, R.E.; Medrano-Rodríguez, J.C.; Sánchez-Aguilar, M.; Soria-Castro, E.; Rubio-Ruíz, M.E.; Del Valle-Mondragón, L.; Sánchez-Mendoza, A.; Torres-Narvaéz, J.C.; Pastelín-Hernández, G.; Ibarra-Lara, L. Extracts of Crataegus oxyacantha and Rosmarinus officinalis Attenuate Ischemic Myocardial Damage by Decreasing Oxidative Stress and Regulating the Production of Cardiac Vasoactive Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2412. [https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112412] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29135932/]. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Adelakun, T.A.; Wang, S.; Ruan, J.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T. Inhibitory Effects of Constituents from the Aerial Parts of Rosmarinus officinalis L. on Triglyceride Accumulation. Molecules 2017, 22, 110. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010110] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28106756/]. [CrossRef]
- Madsen, S.; Bak, S.Y.; Yde, C.C.; Jensen, H.M.; Knudsen, T.A.; Bæch-Laursen, C.; Holst, J.J.; Laustsen, C.; Hedemann, M.S. Unravelling Effects of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) Extract on Hepatic Fat Accumulation and Plasma Lipid Profile in Rats Fed a High-Fat Western-Style Diet. Metabolites 2023, 13, 974. [https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13090974] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37755254/]. [CrossRef]
- El-Huneidi, W.; Anjum, S.; Saleh, M.A.; Bustanji, Y.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Taneera, J. Carnosic Acid Protects INS-1 β-Cells against Streptozotocin-Induced Damage by Inhibiting Apoptosis and Improving Insulin Secretion and Glucose Uptake. Molecules 2022, 27, 2102. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27072102] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35408495/]. [CrossRef]
- Kabubii, Z.N.; Mbaria, J.M.; Mathiu, P.M.; Wanjohi, J.M.; Nyaboga, E.N. Diet Supplementation with Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) Leaf Powder Exhibits an Antidiabetic Property in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Male Wistar Rats. Diabetology 2024, 5, 12–25. [https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology5010002]. [CrossRef]
- Boo, Y.C. Therapeutic Potential and Mechanisms of Rosmarinic Acid and the Extracts of Lamiaceae Plants for the Treatment of Fibrosis of Various Organs. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 146. [https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13020146] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38397744/]. [CrossRef]
- Del Baño, M.J.; Castillo, J.; Benavente-García, O.; Lorente, J.; Martín-Gil, R.; Acevedo, C.; Alcaraz, M. Radioprotective-antimutagenic effects of rosemary phenolics against chromosomal damage induced in human lymphocytes by gamma-rays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2064–2068. [https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0581574] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16536576/]. [CrossRef]
- Acharya, G.S.; Goyal, P.K. Role of Rosemary leaves extract against radiation-induced hematological and biochemical alterations in mice. Nucl. Technol. Radiat. Prot. 2008, 23, 72–78. [https://doi.org/10.2298/NTRP0802072A]. [CrossRef]
- de Macedo, L.M.; Santos, É.M.; Militão, L.; Tundisi, L.L.; Ataide, J.A.; Souto, E.B.; Mazzola, P.G. Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L., syn Salvia rosmarinus Spenn.) and Its Topical Applications: A Review. Plants 2020, 9, 651. [https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9050651] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32455585/]. [CrossRef]
- de Macedo, L.M.; Santos, É.M.; Ataide, J.A.; Silva, G.T.S.; Guarnieri, J.P.O.; Lancellotti, M.; Jozala, A.F.; Rosa, P.C.P.; Mazzola, P.G. Development and Evaluation of an Antimicrobial Formulation Containing Rosmarinus officinalis. Molecules 2022, 27, 5049. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27165049] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36014289/]. [CrossRef]
- Ventura-Martínez, R.; Rivero-Osorno, O.; Gómez, C.; González-Trujano, M.E. Spasmolytic activity of Rosmarinus officinalis L. involves calcium channels in the guinea pig ileum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 1528–1532. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2011.08.047] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21896322/]. [CrossRef]
- Nieto, G.; Ros, G.; Castillo, J. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis, L.): A Review. Medicines 2018, 5, 98. [https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines5030098] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30181448/]. [CrossRef]
- Zeraat Pisheh, F.; Falah, F.; Sanaei, F.; Vasiee, A.; Zanganeh, H.; Tabatabaee Yazdi, F.; Ibrahim, S.A. The Effect of Plasma-Activated Water Combined with Rosemary Extract (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) on the Physicochemical Properties of Frankfurter Sausage during Storage. Foods 2023, 12, 4022. [https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12214022] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37959142/]. [CrossRef]
- de Lima, A.F.; Leite, R.H.d.L.; Pereira, M.W.F.; Silva, M.R.L.; de Araújo, T.L.A.C.; de Lima Júnior, D.M.; Gomes, M.d.N.B.; Lima, P.d.O. Chitosan Coating with Rosemary Extract Increases Shelf Life and Reduces Water Losses from Beef. Foods 2024, 13, 1353. [https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13091353] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38731724/]. [CrossRef]
- Sagorchev, P.; Lukanov, J.; Beer, A.M. Investigations into the specific effects of rosemary oil at the receptor level. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 693–697. [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2009.09.012] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20034774/]. [CrossRef]
- Al-Tawarah, N.M.; Al-dmour, R.H.; Abu Hajleh, M.N.; Khleifat, K.M.; Alqaraleh, M.; Al-Saraireh, Y.M.; Jaradat, A.Q.; Al-Dujaili, E.A.S. Rosmarinus officinalis and Mentha piperita Oils Supplementation Enhances Memory in a Rat Model of Scopolamine-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease-like Condition. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1547. [https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15061547] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36986277/]. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.E.; Younis, N.S.; El-Beltagi, H.S.; Mohafez, O.M. The Synergistic Hepatoprotective Activity of Rosemary Essential Oil and Curcumin: The Role of the MEK/ERK Pathway. Molecules 2022, 27, 8910. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248910] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36558044/]. [CrossRef]
- Dolghi, A.; Coricovac, D.; Dinu, S.; Pinzaru, I.; Dehelean, C.A.; Grosu, C.; Chioran, D.; Merghes, P.E.; Sarau, C.A. Chemical and Antimicrobial Characterization of Mentha piperita L. and Rosmarinus officinalis L. Essential Oils and In Vitro Potential Cytotoxic Effect in Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 6106. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27186106] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36144839/]. [CrossRef]
- Zhaeintan, P.; Nickfarjam, A.; Shams, A.; Abdollahi-Dehkordi, S.; Hamzian, N. Radioprotective Effect of Rosmarinus officinalis L (Rosemary) Essential Oil on Apoptosis, Necrosis and Mitotic Death of Human Peripheral Lymphocytes (PBMCs). J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2022, 12, 245–256. [https://doi.org/10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.2105-1333] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35698543/]. [CrossRef]
- Salamatullah, A.M.; Hayat, K.; Arzoo, S.; Alzahrani, A.; Ahmed, M.A.; Yehia, H.M.; Alsulami, T.; Al-Badr, N.; Al-Zaied, B.A.M.; Althbiti, M.M. Boiling Technique-Based Food Processing Effects on the Bioactive and Antimicrobial Properties of Basil and Rosemary. Molecules 2021, 26, 7373. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26237373] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34885955/]. [CrossRef]
- Pontillo, A.R.N.; Papakosta-Tsigkri, L.; Lymperopoulou, T.; Mamma, D.; Kekos, D.; Detsi, A. Conventional and Enzyme-Assisted Extraction of Rosemary Leaves (Rosmarinus officinalis L.): Toward a Greener Approach to High Added-Value Extracts. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3724. [https://doi.org/10.3390/app11083724]. [CrossRef]
- Dhouibi, N.; Manuguerra, S.; Arena, R.; Messina, C.M.; Santulli, A.; Kacem, S.; Dhaouadi, H.; Mahdhi, A. Impact of the Extraction Method on the Chemical Composition and Antioxidant Potency of Rosmarinus officinalis L. Extracts. Metabolites 2023, 13, 290. [https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020290] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36837909/]. [CrossRef]
- Bencharif-Betina, S.; Benhamed, N.; Benabdallah, A.; Bendif, H.; Benslama, A.; Negro, C.; Plavan, G.; Abd-Elkader, O.H.; De Bellis, L. A Multi-Approach Study of Phytochemicals and Their Effects on Oxidative Stress and Enzymatic Activity of Essential Oil and Crude Extracts of Rosmarinus officinalis. Separations 2023, 10, 394. [https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10070394]. [CrossRef]
- Moliner, C.; López, V.; Barros, L.; Dias, M.I.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Langa, E.; Gómez-Rincón, C. Rosemary Flowers as Edible Plant Foods: Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Properties in Caenorhabditis elegans. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 811. [https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9090811] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32882905/]. [CrossRef]
- Athanasiadis, V.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Mantiniotou, M.; Kalompatsios, D.; Kotsou, K.; Makrygiannis, I.; Bozinou, E.; Lalas, S.I. Optimization of Four Different Rosemary Extraction Techniques Using Plackett–Burman Design and Comparison of Their Antioxidant Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7708. [https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147708]. [CrossRef]
- Kamli, M.R.; Sharaf, A.A.M.; Sabir, J.S.M.; Rather, I.A. Phytochemical Screening of Rosmarinus officinalis L. as a Potential Anticholinesterase and Antioxidant–Medicinal Plant for Cognitive Decline Disorders. Plants 2022, 11, 514. [https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11040514] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35214846/]. [CrossRef]
- Delueg, S.; Kirchler, C.G.; Meischl, F.; Ozaki, Y.; Popp, M.A.; Bonn, G.K.; Huck, C.W. At-Line Monitoring of the Extraction Process of Rosmarini Folium via Wet Chemical Assays, UHPLC Analysis, and Newly Developed Near-Infrared Spectroscopic Analysis Methods. Molecules 2019, 24, 2480. [https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24132480] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31284547/]. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.; Fagan, J.; Schaefer, J. In vitro Screening for Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition and Antioxidant Potential in Different Extracts of Sage (Salvia officinalis L.) and Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.). J. Biol. Act. Prod. Nat. 2020, 10, 59–69. [https://doi.org/10.1080/22311866.2020.1729239]. [CrossRef]
- Velamuri, R.; Sharma, Y.; Fagan, J.; Schaefer, J. Application of UHPLC–ESI–QTOF–MS in Phytochemical Profiling of Sage (Salvia officinalis) and Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis). Planta Med. Int. Open 2020, 7, e133–e144. [https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1272-2903]. [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.K.; Sostaric, T.; Lim, L.Y.; Hammer, K.; Locher, C. Antioxidant HPTLC–DPPH Fingerprinting of Honeys and Tracking of Antioxidant Constituents Upon Thermal Exposure. Foods 2021, 10, 357. [https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020357] [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33562382/]. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Variation of TPC [mg/mL] (a), antioxidant activity (DPPH IC50 [μg/mL]) (b), and AChE inhibitory activity (AChE IC50 [mg/mL]) (c) of Ro_1 to Ro_12 samples over the 12-month period (February 2022 to January 2023). AChE: Acetylcholinesterase; DPPH: 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl; IC50: Half maximal inhibitory concentration; Ro: Rosmarinus officinalis; TPC: Total phenolic content.
Figure 1.
Variation of TPC [mg/mL] (a), antioxidant activity (DPPH IC50 [μg/mL]) (b), and AChE inhibitory activity (AChE IC50 [mg/mL]) (c) of Ro_1 to Ro_12 samples over the 12-month period (February 2022 to January 2023). AChE: Acetylcholinesterase; DPPH: 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl; IC50: Half maximal inhibitory concentration; Ro: Rosmarinus officinalis; TPC: Total phenolic content.
Figure 2.
Seasonal variation of the main polyphenolic acids of Ro_1 to Ro_12 samples over the 12-month period (February 2022 to January 2023): (a) Rosmarinic acid [mg/g]; (b) Caffeic acid [μg/g]; (c) Ferulic acid [μg/g]; (d) Protocatechuic acid [μg/g]; (e) Chlorogenic acid [μg/g]. Ro: Rosmarinus officinalis.
Figure 2.
Seasonal variation of the main polyphenolic acids of Ro_1 to Ro_12 samples over the 12-month period (February 2022 to January 2023): (a) Rosmarinic acid [mg/g]; (b) Caffeic acid [μg/g]; (c) Ferulic acid [μg/g]; (d) Protocatechuic acid [μg/g]; (e) Chlorogenic acid [μg/g]. Ro: Rosmarinus officinalis.
Figure 3.
UHPLC chromatogram with RTs for the main polyphenolic acids identified and quantified in Ro_1 to Ro_12 samples: protocatechuic acid (RT 2.64 min), chlorogenic acid (RT 4.03 min), caffeic acid (RT 4.61 min), ferulic acid (RT 7.45 min), and rosmarinic acid (RT 9.26 min). Ro: Rosmarinus officinalis; RT: Retention time; UHPLC: Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography.
Figure 3.
UHPLC chromatogram with RTs for the main polyphenolic acids identified and quantified in Ro_1 to Ro_12 samples: protocatechuic acid (RT 2.64 min), chlorogenic acid (RT 4.03 min), caffeic acid (RT 4.61 min), ferulic acid (RT 7.45 min), and rosmarinic acid (RT 9.26 min). Ro: Rosmarinus officinalis; RT: Retention time; UHPLC: Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography.
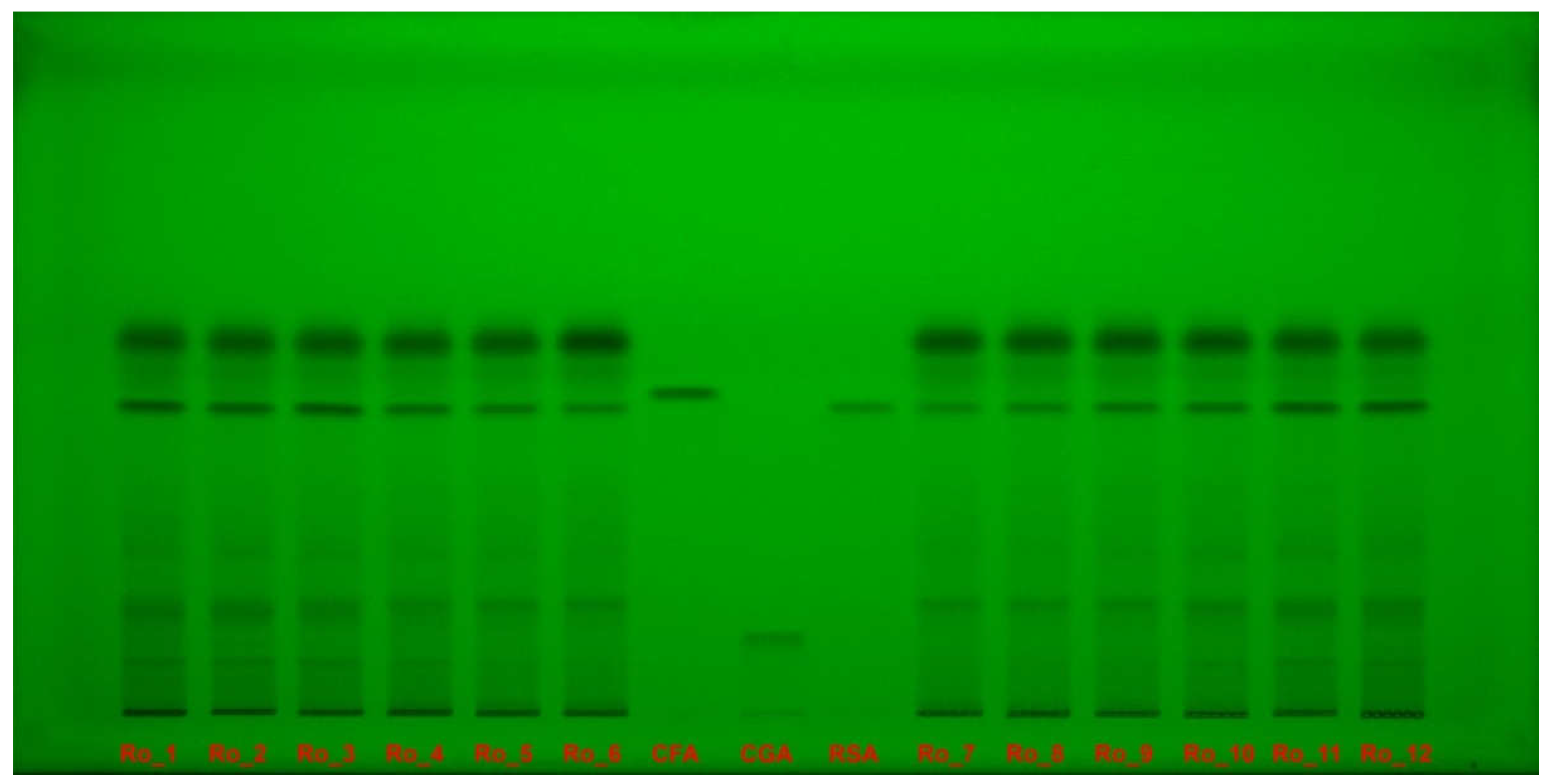
Figure 4.
Polyphenols separation on HPTLC plate, documented under UV light, at 254 nm, without derivatization, for Ro_1 to Ro_12 samples over the 12-month period (February 2022 to January 2023) compared with CFA, CGA and RSA reference compounds. CFA: Caffeic acid; CGA: Chlorogenic acid; HPTLC: High-performance thin-layer chromatography; Ro: Rosmarinus officinalis; RSA: Rosmarinic acid; UV: Ultraviolet.
Figure 4.
Polyphenols separation on HPTLC plate, documented under UV light, at 254 nm, without derivatization, for Ro_1 to Ro_12 samples over the 12-month period (February 2022 to January 2023) compared with CFA, CGA and RSA reference compounds. CFA: Caffeic acid; CGA: Chlorogenic acid; HPTLC: High-performance thin-layer chromatography; Ro: Rosmarinus officinalis; RSA: Rosmarinic acid; UV: Ultraviolet.
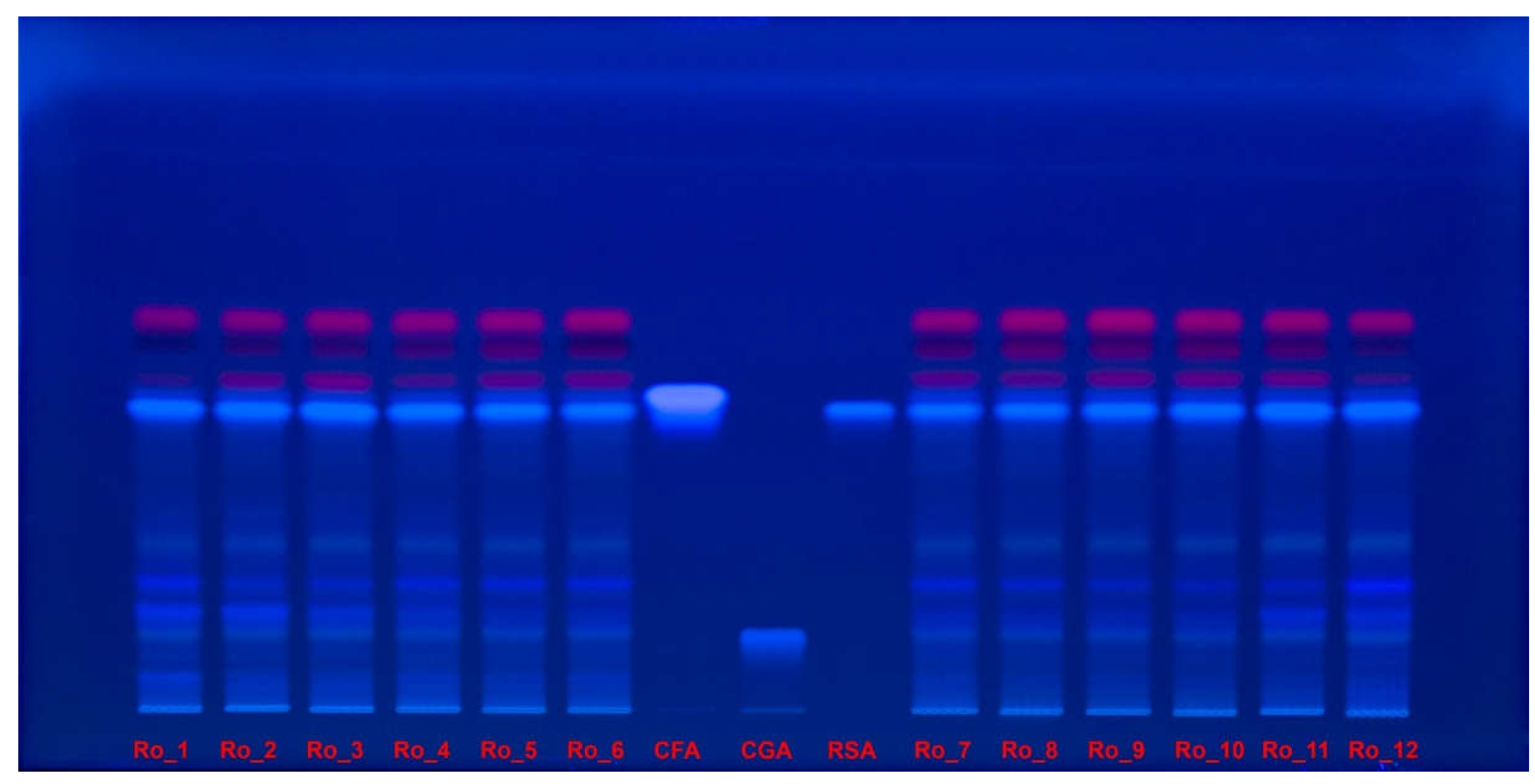
Figure 5.
Polyphenols separation on HPTLC plate, documented under UV light, at 365 nm, without derivatization, for Ro_1 to Ro_12 samples over the 12-month period (February 2022 to January 2023) compared with CFA, CGA and RSA reference compounds. CFA: Caffeic acid; CGA: Chlorogenic acid; HPTLC: High-performance thin-layer chromatography; Ro: Rosmarinus officinalis; RSA: Rosmarinic acid; UV: Ultraviolet.
Figure 5.
Polyphenols separation on HPTLC plate, documented under UV light, at 365 nm, without derivatization, for Ro_1 to Ro_12 samples over the 12-month period (February 2022 to January 2023) compared with CFA, CGA and RSA reference compounds. CFA: Caffeic acid; CGA: Chlorogenic acid; HPTLC: High-performance thin-layer chromatography; Ro: Rosmarinus officinalis; RSA: Rosmarinic acid; UV: Ultraviolet.
Figure 6.
DPPH-derivatized HPTLC plate under white light evidencing the antioxidant activity of Ro_1 to Ro_12 samples over the 12-month period (February 2022 to January 2023) compared with CFA, CGA and RSA reference compounds. CFA: Caffeic acid; CGA: Chlorogenic acid; DPPH: 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl; HPTLC: High-performance thin-layer chromatography; Ro: Rosmarinus officinalis; RSA: Rosmarinic acid.
Figure 6.
DPPH-derivatized HPTLC plate under white light evidencing the antioxidant activity of Ro_1 to Ro_12 samples over the 12-month period (February 2022 to January 2023) compared with CFA, CGA and RSA reference compounds. CFA: Caffeic acid; CGA: Chlorogenic acid; DPPH: 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl; HPTLC: High-performance thin-layer chromatography; Ro: Rosmarinus officinalis; RSA: Rosmarinic acid.
Table 1.
TPC and in vitro activities (antioxidant and anti-AChE) with SDs over the 12-month period.
Table 1.
TPC and in vitro activities (antioxidant and anti-AChE) with SDs over the 12-month period.
| Sample |
TPC [mg/mL] |
DPPH IC50 [μg/mL] |
AChE IC50 [mg/mL] |
| Ro_1 (February 2022) |
2.323±0.210 |
95.32±10.68 |
2.558±0.147 |
| Ro_2 (March 2022) |
1.810±0.243 |
103.30±14.26 |
3.083±0.356 |
| Ro_3 (April 2022) |
1.948±0.221 |
111.40±5.71 |
3.370±0.157 |
| Ro_4 (May 2022) |
1.623±0.209 |
121.10±5.87 |
3.250±0.478 |
| Ro_5 (June 2022) |
1.372±0.185 |
127.90±5.20 |
3.200±0.309 |
| Ro_6 (July 2022) |
1.748±0.229 |
101.90±13.33 |
2.900±0.266 |
| Ro_7 (August 2022) |
1.476±0.188 |
140.50±12.78 |
1.716±0.206 |
| Ro_8 (September 2022) |
1.572±0.278 |
150.70±13.70 |
2.425±0.410 |
| Ro_9 (October 2022) |
1.644±0.293 |
143.90±14.79 |
3.320±0.282 |
| Ro_10 (November 2022) |
1.731±0.177 |
172.80±12.99 |
3.780±0.327 |
| Ro_11 (December 2022) |
1.884±0.258 |
149.20±9.61 |
3.560±0.108 |
| Ro_12 (January 2023) |
2.130±0.206 |
119.50±12.81 |
3.980±0.347 |
Table 2.
Concentrations of the main polyphenolic acids with SDs over the 12-month period.
Table 2.
Concentrations of the main polyphenolic acids with SDs over the 12-month period.
| Sample |
Rosmarinic acid [mg/g] |
Caffeic acid [μg/g] |
Ferulic acid [μg/g] |
Protocatechuic acid [μg/g] |
Chlorogenic acid [μg/g] |
| Ro_1 (February 2022) |
32.179±3.448 |
129.960±10.666 |
72.079±4.907 |
0.100±0.699 |
2.387±0.150 |
| Ro_2 (March 2022) |
28.130±3.468 |
241.906±7.654 |
68.100±3.419 |
3.904±0.791 |
0.178±0.479 |
| Ro_3 (April 2022) |
32.629±4.775 |
153.950±10.232 |
44.962±3.957 |
4.251±1.183 |
3.333±0.251 |
| Ro_4 (May 2022) |
22.624±3.727 |
135.378±5.939 |
32.446±1.157 |
16.126±0.933 |
0.118±0.431 |
| Ro_5 (June 2022) |
19.138±2.438 |
230.384±10.759 |
36.758±2.131 |
14.400±1.978 |
2.743±0.365 |
| Ro_6 (July 2022) |
15.435±2.748 |
136.149±14.293 |
47.211±1.481 |
8.783±0.294 |
1.153±0.184 |
| Ro_7 (August 2022) |
12.585±3.791 |
141.502±8.186 |
52.560±2.185 |
14.554±0.497 |
4.251±0.416 |
| Ro_8 (September 2022) |
14.392±1.241 |
148.004±11.674 |
36.522±1.475 |
9.028±0.406 |
3.853±0.228 |
| Ro_9 (October 2022) |
17.857±3.667 |
160.610±6.318 |
31.060±2.272 |
9.407±1.341 |
1.070±0.446 |
| Ro_10 (November 2022) |
18.691±3.683 |
163.689±12.163 |
34.259±2.657 |
9.678±0.581 |
2.347±0.312 |
| Ro_11 (December 2022) |
26.042±1.842 |
208.323±7.894 |
37.923±1.257 |
1.502±0.986 |
2.409±0.447 |
| Ro_12 (January 2023) |
28.460±1.516 |
186.245±6.832 |
35.116±3.770 |
0.435±0.564 |
2.332±0.362 |
Table 3.
The correlation coefficient (r) between the phenolic compounds and the in vitro activities measured.
Table 3.
The correlation coefficient (r) between the phenolic compounds and the in vitro activities measured.
| Phenolic compound |
TPC [mg/mL] |
DPPH IC50 [μg/mL] |
AChE IC50 [mg/mL] |
| Rosmarinic acid [mg/g] |
0.801 |
-0.533 |
0.435 |
| Caffeic acid [μg/g] |
-0.140 |
0.030 |
0.392 |
| Ferulic acid [μg/g] |
0.447 |
-0.642 |
-0.480 |
| Protocatechuic acid [μg/g] |
-0.884 |
0.325 |
-0.334 |
| Chlorogenic acid [μg/g] |
-0.097 |
0.353 |
-0.405 |
| TPC [mg/mL] |
|
-0.469 |
0.293 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).