1. Introduction
An integral part of the Mediterranean diet, extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) is high in monounsaturated fatty acids, which are regarded as advantageous for protection against diseases [
1]. It is also a good source of antioxidants, including polyphenols and vitamin E, which may help protect against oxidative damage in the body, the cause of several chronic degenerative diseases [
2,
3]. EVOO reduces the risk of cardiovascular pathologies, type 2 diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases, and some cancers by displaying anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant effects [5]. Olive trees can produce useful metabolites in a variety of tissues, including the leaves. Olive mill wastewater (OMWW) is a large-scale liquid waste product released during olive oil extraction. It is an environmental concern on the one hand, but on the other, it is a rich source of phytochemicals that may have beneficial effects [5,6,7]. Hydroxytyrosol is the most common polyphenol in OMWW extracts however, verbascoside and oleuropein are also abundant [8]. It has been shown that polyphenols control inflammation and oxidative stress [9], regulate gene expression in metabolic pathways, and have the potential to improve insulin sensitivity [10]. In this way, polyphenols could play an important role in the prevention of metabolic syndrome, which is characterized by hypertension, hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, dyslipidemia, and obesity [11,12]. Thanks to pharmacometabolomics [13], the personalization of drug therapy is possible through the comprehensive analysis of metabolites in a patient’s biological fluids. Metabolomics can provide important information on the effect of clinical treatments on the metabolism, and therefore, mass spectrometry (MS) has taken a central role in personalized and precision medicine [14].
In this work, we report the application of a dietary strategy to study the effects of an OMWW-derived supplement, Oliphenolia® (OMWW-OL), on different serum parameters at distinct time points. Our aim was to measure hematochemical, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anthropometric parameters and to assess metabolic pathways before initiation (T0), after 30 days of nutritional intervention (T1), and 30 days after the end of the nutritional intervention (T2).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
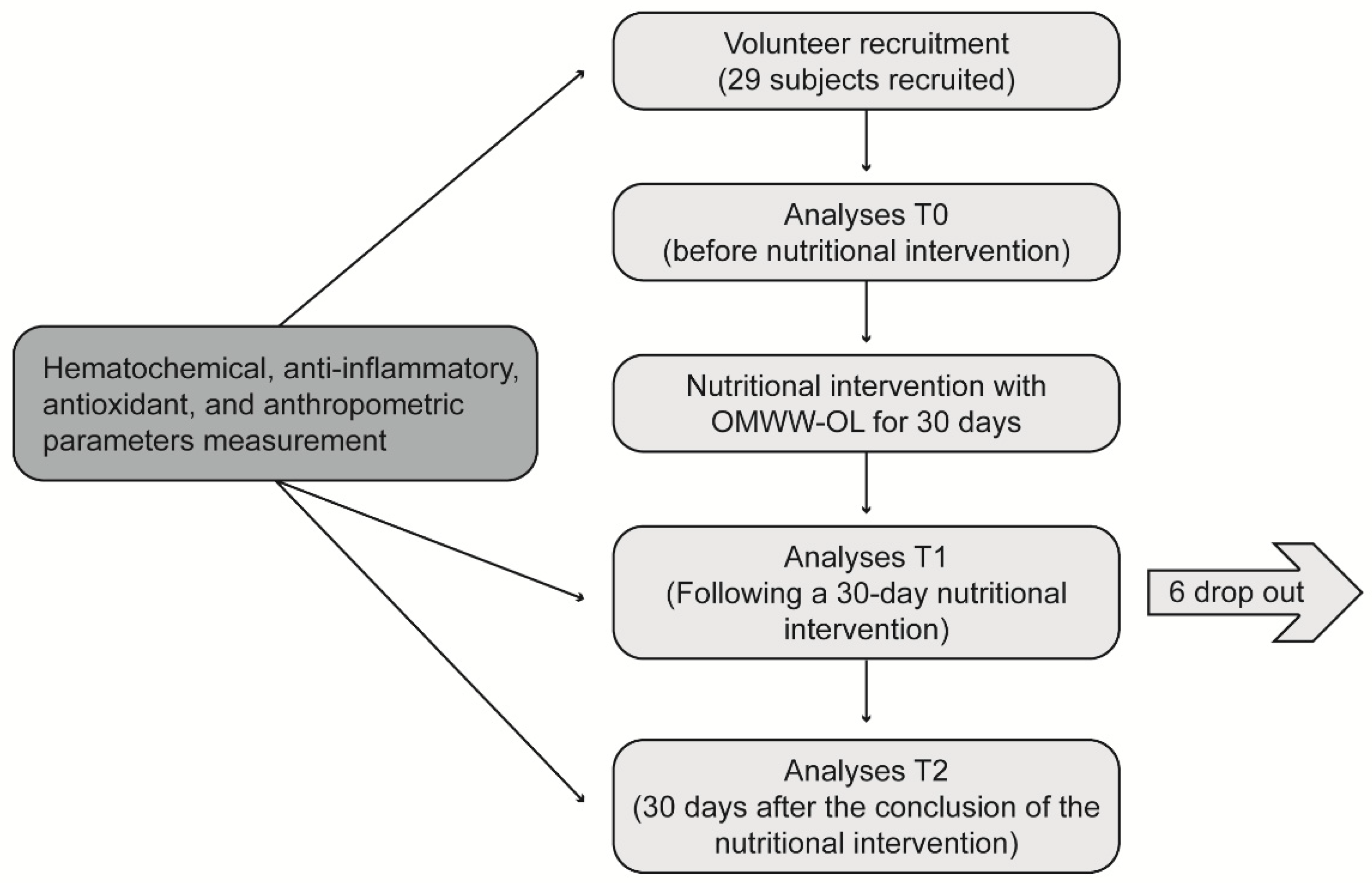
This was a single-arm longitudinal interventional study to evaluate the effect of OMWW-OL on a cohort of volunteers with characteristics close to metabolic syndrome as a pilot study. Participants were enrolled in western Sicily within the project “Nutraceutical effects of olive products: Role in the achievement of longevity”. The dietary intervention consisted in the consumption of 25 mL of OMWW-OL twice a day, 30 minutes before the main meals (lunch and dinner) for 30 days. Before starting the nutritional intervention, a 7-day washout period was carried out, during which the participants were required to abstain from EVOO and food supplements containing polyphenols. The flowchart of the study design is reported in
Figure 1.
2.2. Study Participants
The subjects enrolled had at least one of the following inclusion criteria: slight dyslipidemia (TC 190–240 mg/dL, triglyceride level ≥150 mg/dL); waist circumference ≥102 cm in men and ≥88 cm in women; altered glucose tolerance (fasting blood glucose ≥100 mg/dL). Exclusion criteria were: any treatment for specific diseases, including drugs to treat metabolic disorders; diagnosis of severe systemic disease; history of treatment with statins or similar drugs or other liposoluble or hypoglycemic drugs; restrictive dietary requirements (e.g., gluten-free diet). The onset of gastrointestinal disorders during the intervention determined the prompt exclusion from the study. No restriction related to gender was considered.
2.3. Ethical Considerations
Before enrollment, each recruited subject was fully informed about the purposes and procedures of the experiment, and their informed consent was obtained. To respect privacy, patients’ names were anonymized by assigning each one an encoded alpha-numeric identification code in accordance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR, EU Regulation 2016/679) concerning the protection of individuals with regard to the processing of personal data, as well as the free circulation of such data. The study protocol was conducted in accordance with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments, and the institutional Ethics Committee (Policlinico Paolo Giaccone, University Hospital) approved the study protocol (Nutrition and Longevity, No. 032017).
2.4. Data Collection
A group of well-trained biologists and physicians from the University of Palermo administered a questionnaire to the participants to collect demographic, clinical, and anamnestic data. Additionally, a weekly food diary was provided to record data on their dietary intake. A database in Excel was created to collect and handle all participants’ data and information. To obtain informative and reproducible analyses, anthropometric measures were obtained while participants wore light clothes and no shoes. Body weight was measured using an electronic scale calibrated in kilograms. Height was measured with the subject in the supine position with a stadiometer. The bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) was also performed in the supine position, wearing light clothes and barefoot. The resistance and the reactance, both in Ohm and the phase angle, were reported; the body compartment measurements (in percentage by weight and kg/m2) were estimated using regression equations by Bodygram® Plus 1.1.4.4 software (AKERN® Pisa, Italy). Body mass index (BMI, kg/m2) was calculated using anthropometric measurements, such as height (m) and weight (kg).
2.5. Analysis of Hematochemical Parameters
Overnight fasting blood samples were collected in the morning. The blood was collected in specific tubes without additives in order to separate the serum samples obtained after centrifugation at 2,500 rpm for 15 minutes at 4°C, rapidly frozen, and stored at -80°C for further tests. All hematochemical analyses were measured by standard biochemical assays. The concentration of serum low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol was calculated by using the Friedewald equation: LDL=total cholesterol-high-density lipoproteins (HDL)-(triglycerides/5). We also collected samples before initiation (T0), after 30 days of nutritional intervention (T1), and 30 days after the end of the nutritional intervention (T2) for spectrometry analysis.
2.6. Evaluation of the Anti-Oxidative Effect
Serum samples from patients were also used for the determination of human oxidized LDL (oxLDL) quantity, using a specific ELISA kit (Cusabio, Houston, TX, USA) following manufacturer instructions. The competitive inhibition enzyme immunoassay method was used in this assay. The microtiter plate was pre-coated with oxLDL. Standards or samples were added to the appropriate microtiter plate wells with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated antibody preparation specific for oxLDL. Pre-coated oxLDL and oxLDL in samples were used to start a competitive inhibition reaction. The absorption was determined with a microplate spectrophotometer (Tecan, Switzerland) at 450 nm. Results were interpreted by constructing a dose/response curve according to the standards provided in the kit.
2.7. Liquid Chromatography SANIST Mass Spectrometry
Serum metabolites were measured with an untargeted liquid chromatography (LC)-MS SANIST platform. Preliminary MS biomarker identification was obtained based on the accuracy of the derived molecular-mass data (m/z, mass error: 10 ppm), and the ratios of the relative abundance of the different metabolites (i.e., “metabolite ratio”) were calculated [16,17]. Thanks to the calculated ratios, metabolites were classified using an unsupervised method [16]. At 300 μL of serum, 600 μL of acetonitrile (CH3CN, Sigma Aldrich, Milan, Italy) was added to precipitate proteins, and centrifuged at 13,000 g for 10 minutes at room temperature. An aliquot of supernatant (600 μL) was collected and spiked with 100 μL of Ultramark polymer solution (10 ng/mL) to check the stability of the LC-MS signal during analysis. A SpeedVac (ThermoFisher, San Jose, CA, USA) was used to dry the remaining 300 μL; 100 μL of doubly distilled water/methanol (1:1, v/v; Sigma Aldrich, Milan, Italy) (1:1, v/v) solution was used to resuspend each sample, and 10 µL was added at internal standard reserpine (10 μL, final concentration 10 ng/mL, Sigma Aldrich, Milan, Italy). The samples were directly injected into the LC-MS apparatus. A reverse-phase C-18 LC column (50 × 2.1 mm; particle size, 5 µm; pore size, 100 Å; Phenomenex, [Torrance, CA OR San Jose], USA) was employed. The mobile phases consisted of A) water (containing 0.2% formic acid (HCOOH, Sigma Aldrich, Milan, Italy), v/v), and B) CH3CN (100%) and the separation was achieved using an elution gradient. The flow rate was 0.25 mL/min, and the injection volume was 15 µL. Full-scan spectra were acquired in the mass range m/z 40–800. Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) experiments on serum samples were performed with collision-induced dissociation using helium as collision gas. The precursor ions were isolated and fragmented (isolation windows, ±0.3 m/z; collision energy, 30% of its maximum value, which was 5 V peak to peak), and then product ions were obtained and analyzed by Orbitrap mass analyzer with a highly accurate m/z ratio (mass resolution m/z 15000; mass error <10 ppm). Compound identification was made based on fragmentation patterns and mass search database (NIST14) library following the European Union database match mode (EU directive 2002/657/EC) [18]. The chromatographic data were elaborated using the Xcalibur Quan Browser (Version 4.1.31.9). The SANIST data elaboration tool was used to predict the metabolomic pathways altered in the serum samples of participating subjects [19].
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Graphics and statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism Software. The Figures show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM. Significance was calculated from mean±SD and analyzed through GraphPad Prism Software, using the Student’s t-test, and one-way Anova. A value of p<0.05 was considered statistically significant. *p <0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p<0.0001.
3. Results
3.1. Anthropometric, Hematochemical, Inflammatory and Oxidative Parameters
A total of 29 participants were enrolled in this study; 17 were men, and the mean age was 57 years (ranging from 30 to 72 years). Six participants dropped out of the study after the 30-day time point for personal reasons, and 23 completed the study (average age: 59 years). For better visualization the parameters that showed significant differences, as well as those with an interesting trend, upon the intervention are reported in graphics (
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4,
Figure 5,
Figure 6,
Figure 7,
Figure 8 and
Figure 9;
Figures S1–S3).
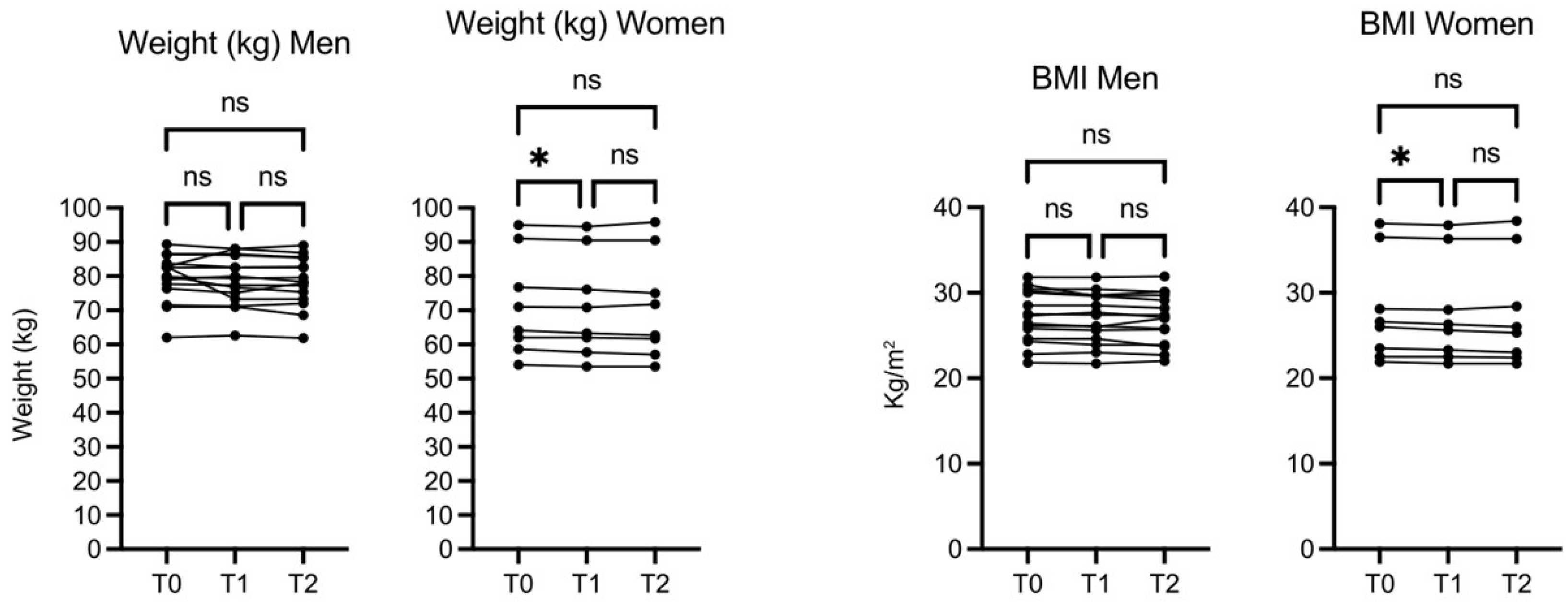
The weight (kg) and BMI of participant did not increase and actually in female subjects decreased slightly but significantly both at 30 days (T1) and 60 days (T2), while no significant changes were observed in men’s weight and BMI (
Figure 2).
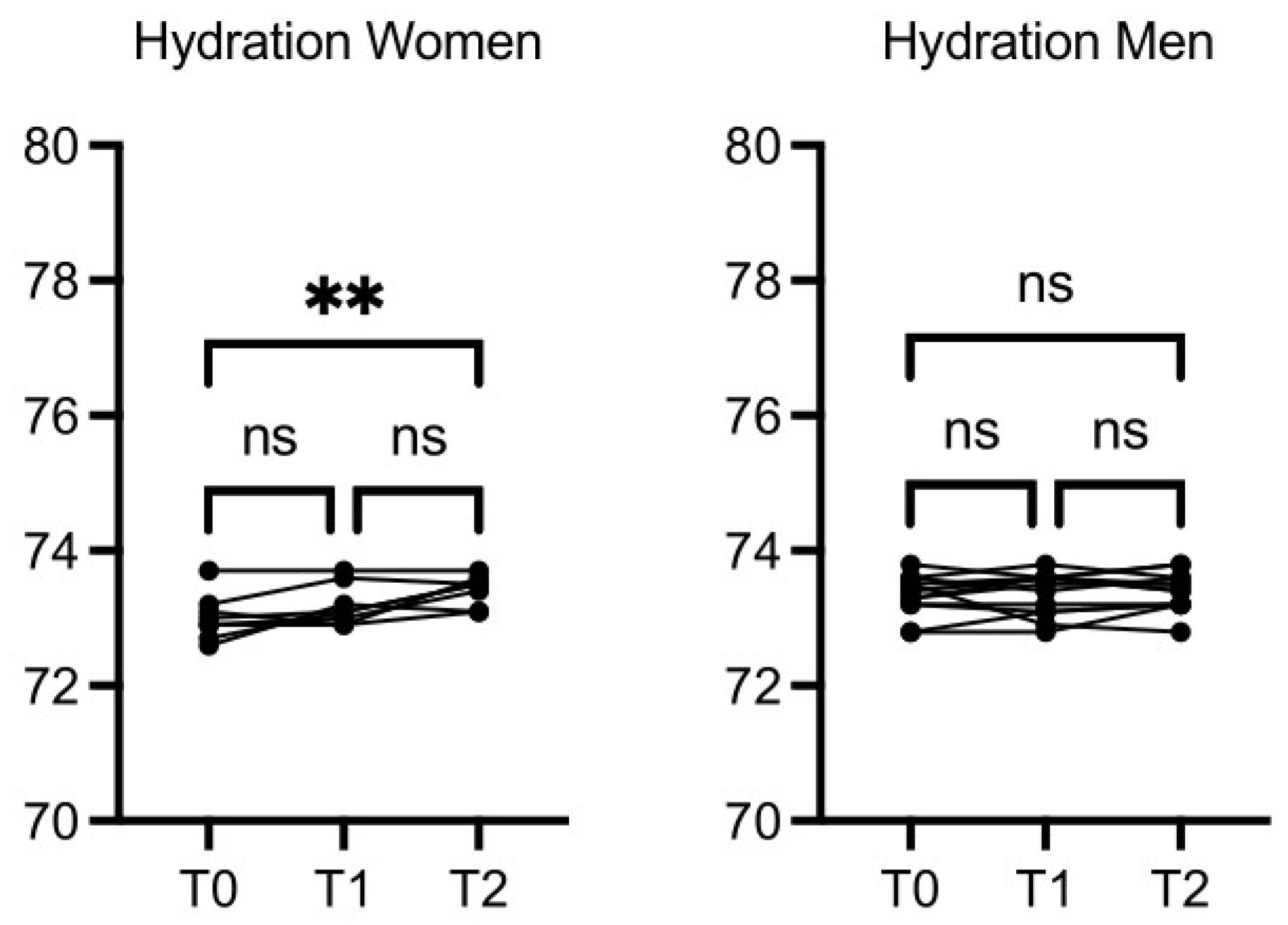
The circumference of the chest, wrist, arm, hip, calf, and abdomen did not change significantly after the intervention (data not shown). Women hydration was increased at T2
vs T0 (p≤0.01), while hydration in men was increased slightly but not in a statistically significant manner (
Figure 3).
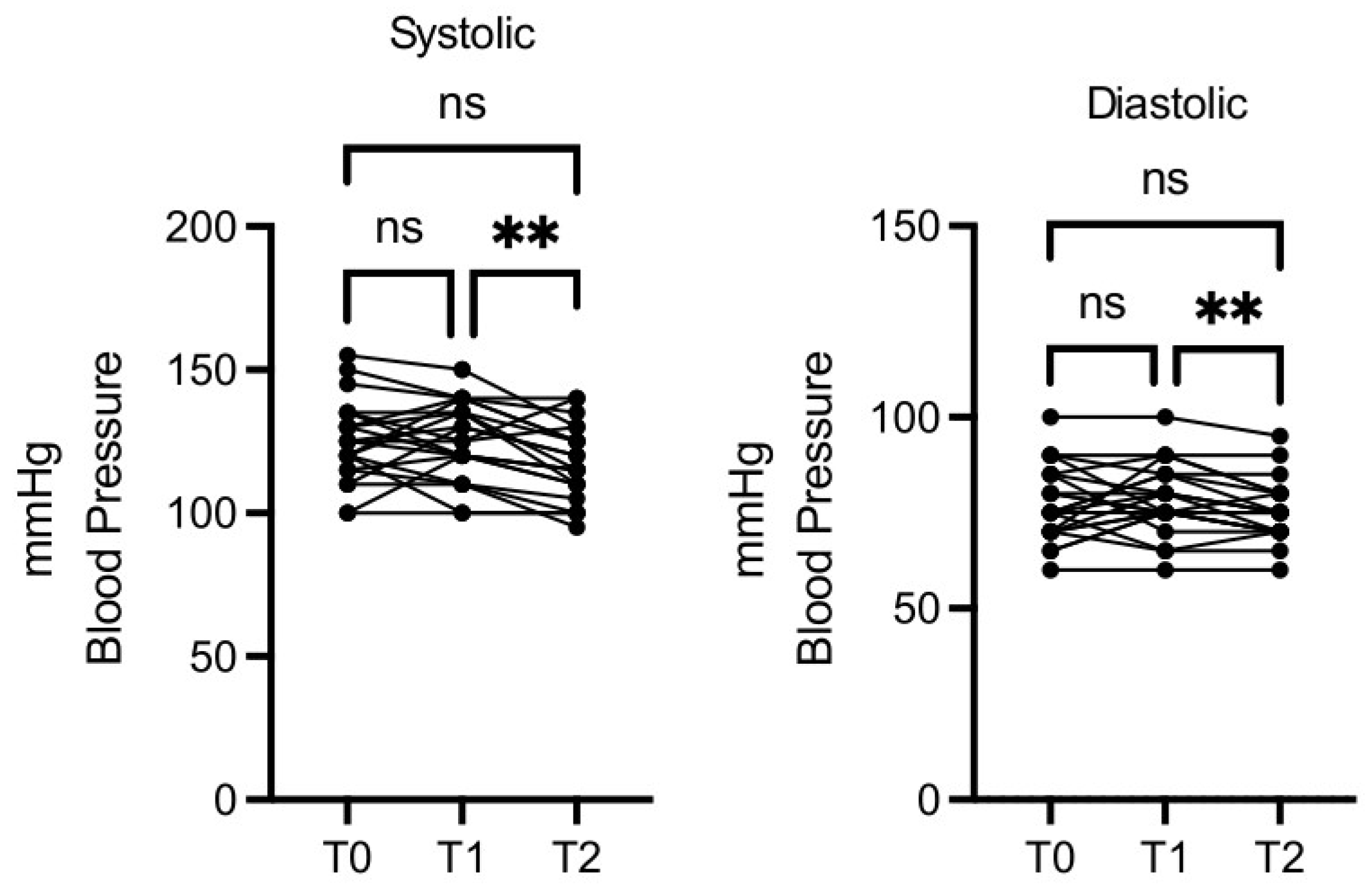
Blood pressure decreased in a statistically significant manner, both for minimum and maximum values, at T2
vs T1, while T1
vs T0 and T2
vs T0 differences were not significant (
Figure 4).
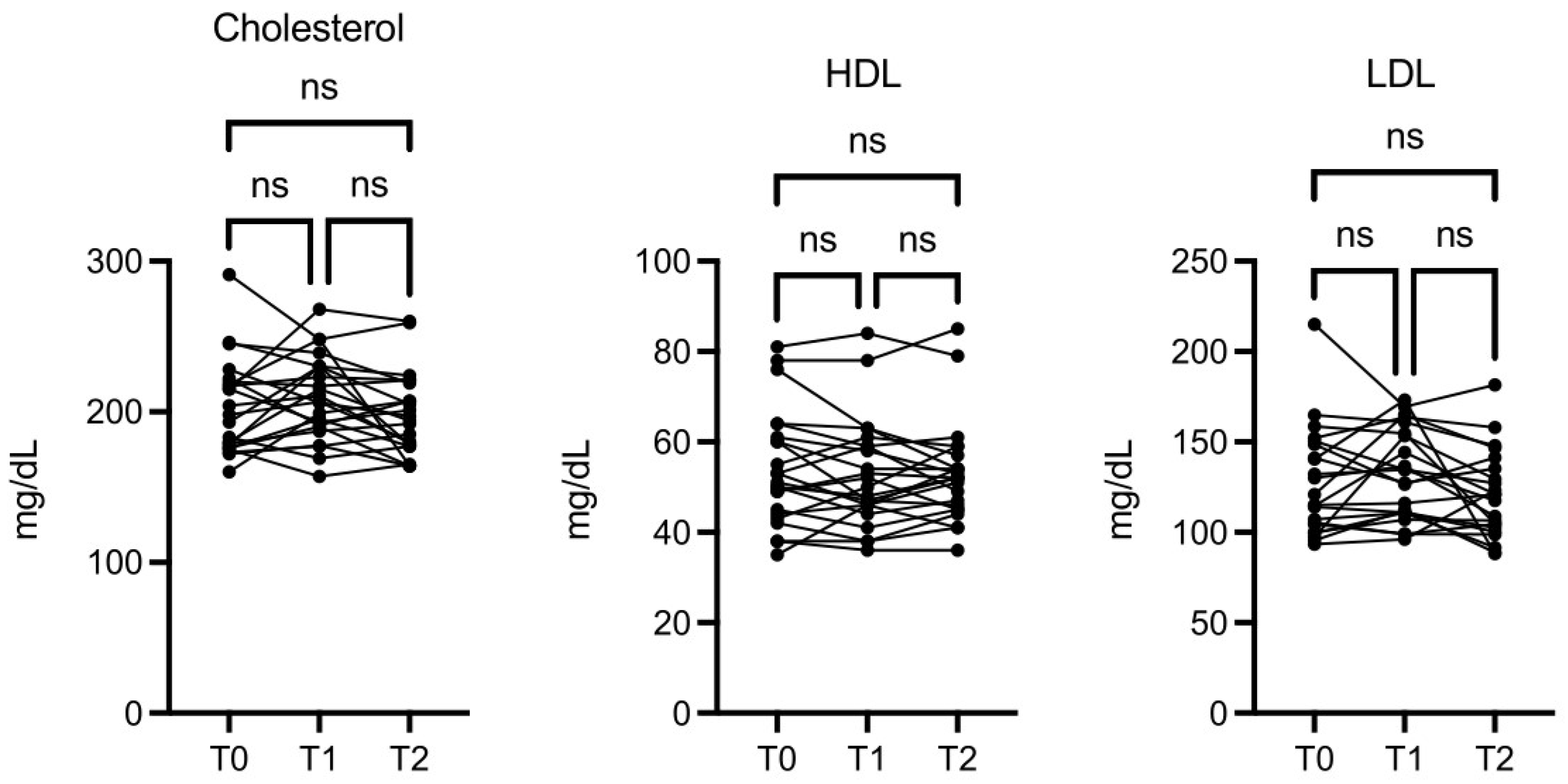
There was also an interesting, although not significant, change in levels of LDL, HDL, and total cholesterol (
Figure 5).
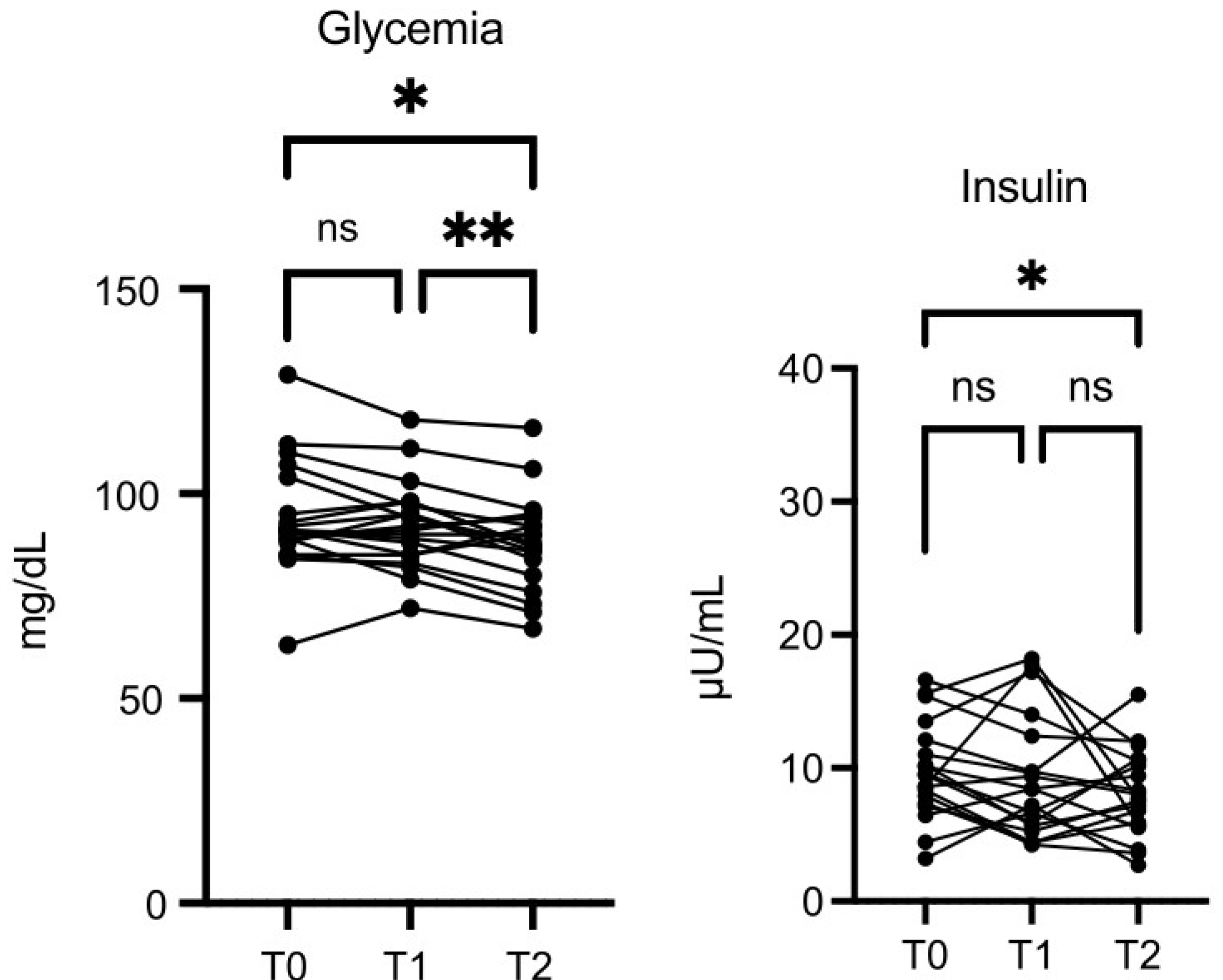
Glycemia values were lower at T2
vs T0 (p≤0.05), and the decrease was more significant at T2
vs T1 (p≤0.01) (
Figure 6). Insulin was also decreased at T2
vs T0 (p=0.05) (
Figure 6).
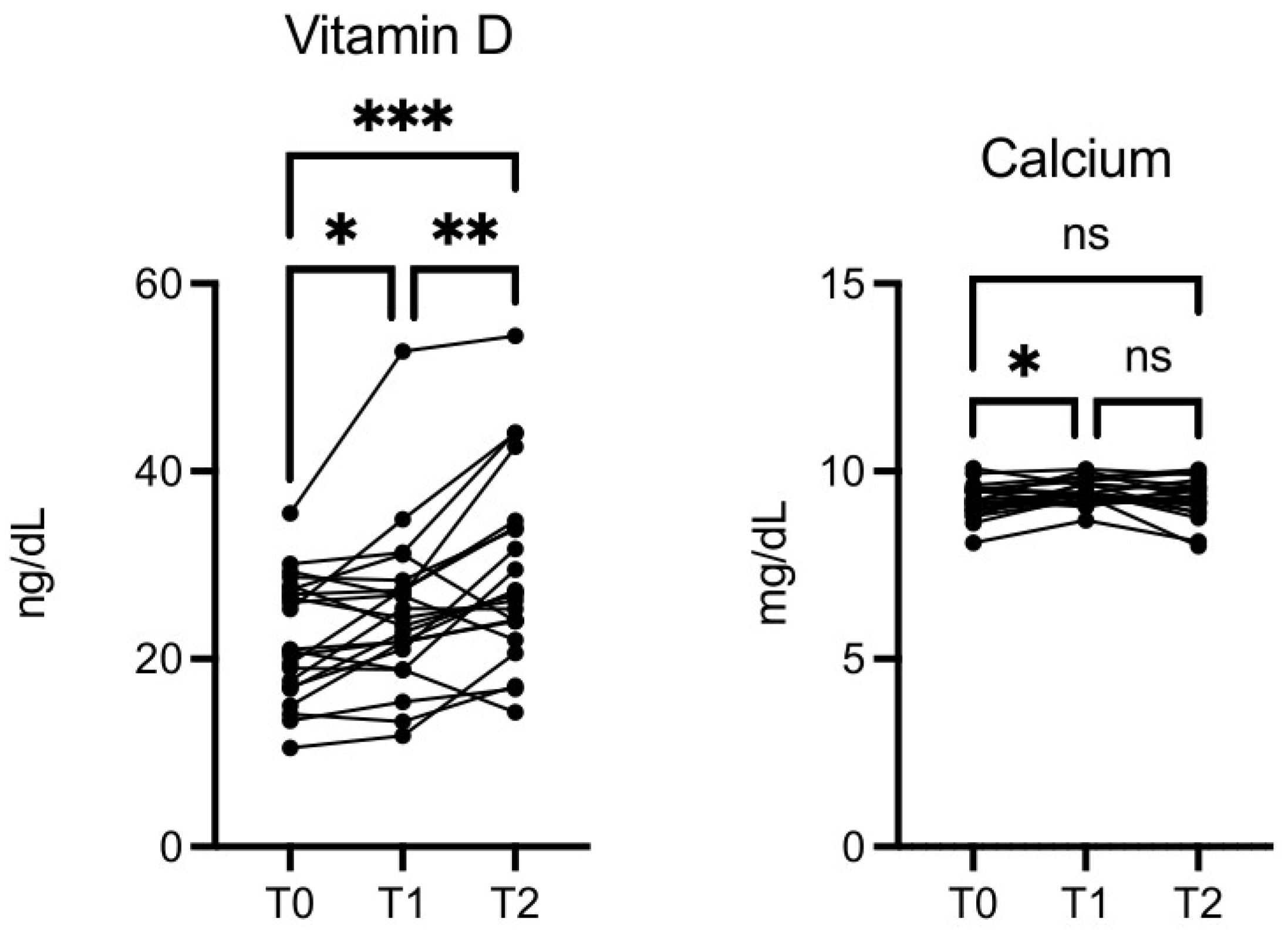
Vitamin D level was significantly increased at T1
vs T0 (p≤0.05), T2
vs T0 (p≤0.001), and T2
vs T1 (p≤0.01) (
Figure 7). This was not due to seasonal variation. Calcium was also increased at T1
vs T0 (p≤0.05,
Figure 7).
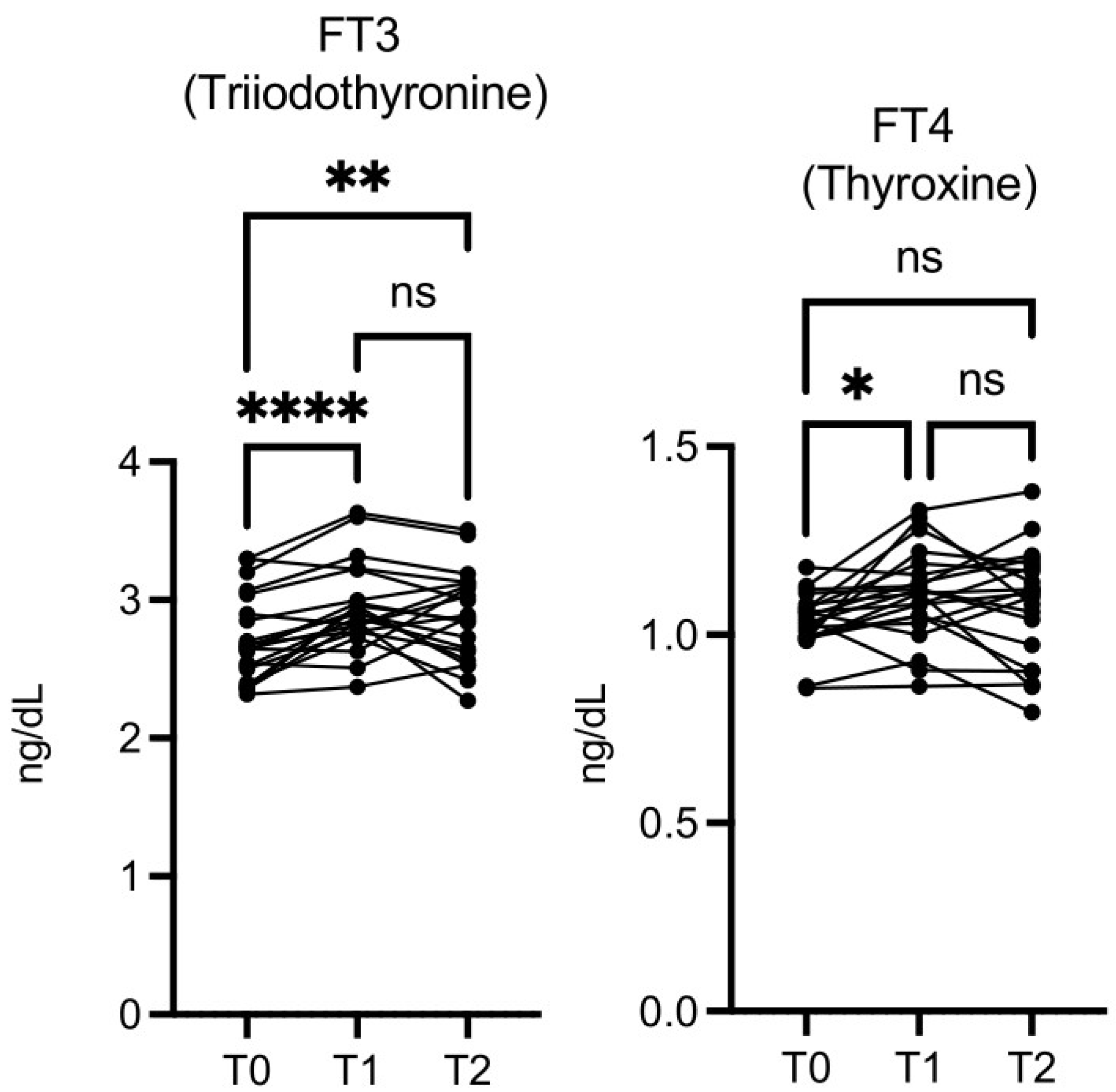
The free triiodothyronine (FT3) level was significantly higher at T1
vs T0 and at T2
vs T0, while free thyroxine (FT4) was significantly higher only at T1 vs T0 (
Figure 8). Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels did not change significantly (data not shown).
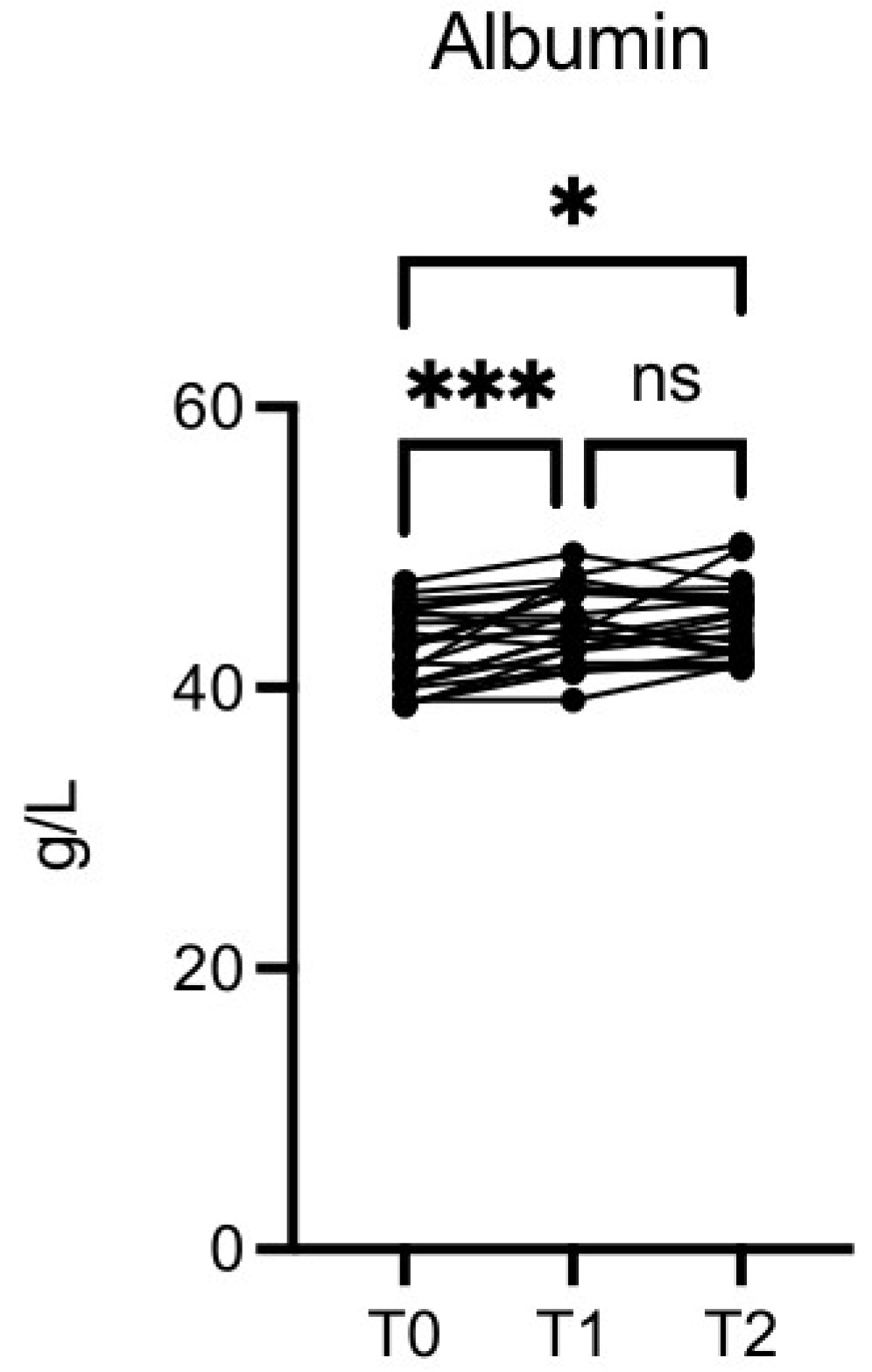
The albumin level was significantly increased at T1
vs T0 (p≤0.001) and T2
vs T0 (p≤0.01) (
Figure 9).
Sarcopenia associated markers such as, skeletal muscle index (SMI), skeletal muscle mass (SMM), fat mass index (FMI), fat-free mass index (FFMI), apendicular skeletal muscle mss (ASMM) and basal metabolism (Mbasal), although not in a significant manner, showed a trend toward improvements (
Figure S1). In our investigation transferrin, ferritin, and sideremia showed no significant differences (
Figure S2). At the end of the intervention, liver enzymes, including alkaline phosphatase, and markers of kidney function (creatinine, urea, uric acid, osteocalcin) (data not shown), and magnesium (
Figure S3) did not show variations. Potassium significantly decreased at T2
vs T1 (
Figure S3).
The values of oxidative stress parameters (TEAC, MDA and PSH) were not significantly different between the time points considered (data not shown).
In general the data show that the vital parameters remain in the standard range, there is no detrimental effect with some positive encouraging trends to health benefit.
3.2. Mass Spectrometry Serum Characterization
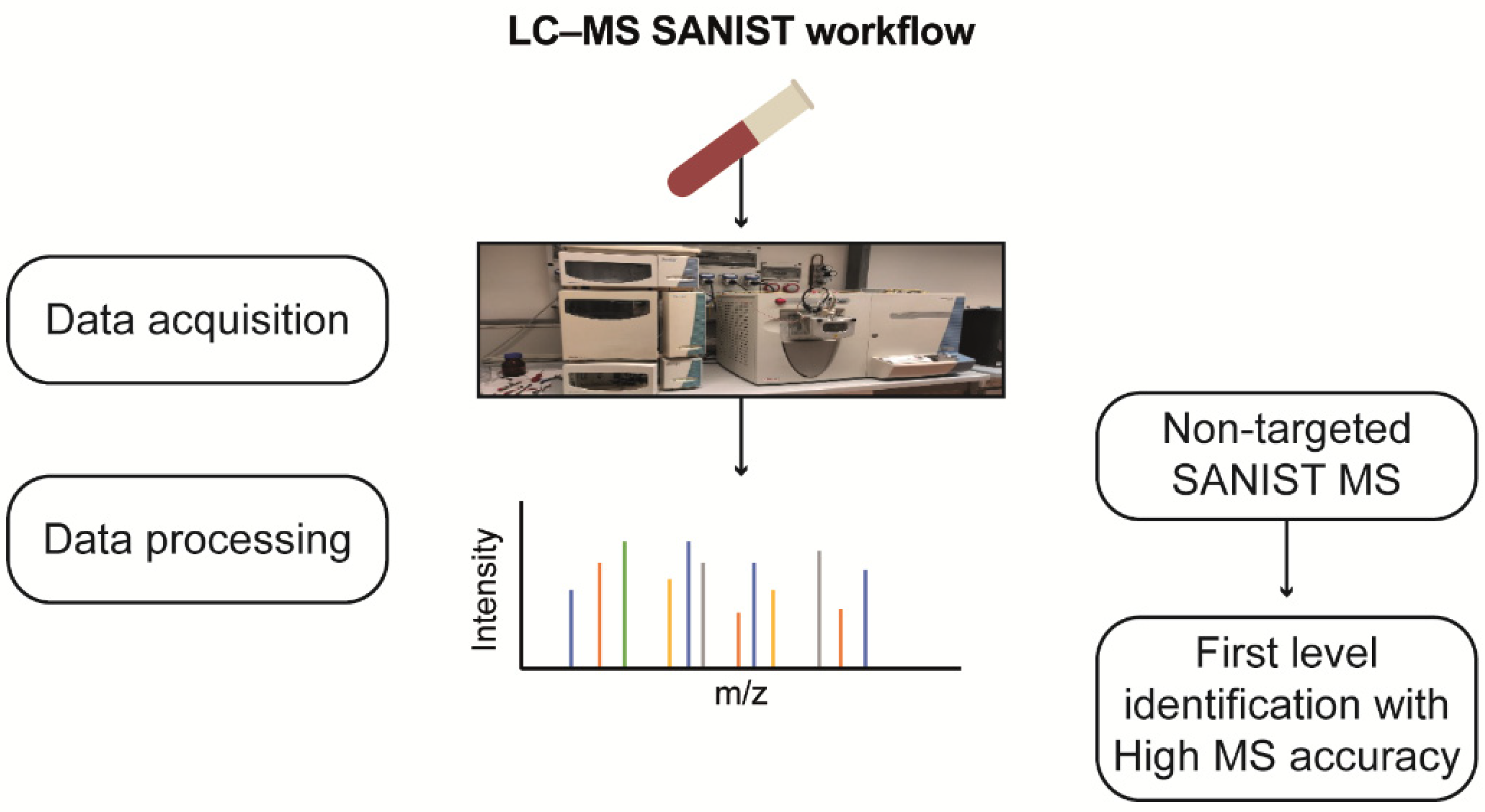
SANIST profiling revealed three chromatographic peak-area ratios, correlating them with enzyme functionality alteration. The detected potential biomarkers were identified using the approach shown in
Figure 10.
Mass spectra comparisons for LC-MS data obtained with the NIST library are shown in
Figure 11. SANIST technology [16] was used to obtain and compare metabolomics profiles. An Ultimate 3000 UPLC (ThermoFisher) LC system fitted with an Orbitrap mass spectrometer (ThermoFisher) coupled to a surface-activated chemical ionization (SACI)/ESI source was used to analyze metabolic profiling in both ESI-positive and ESI-negative ion modes.
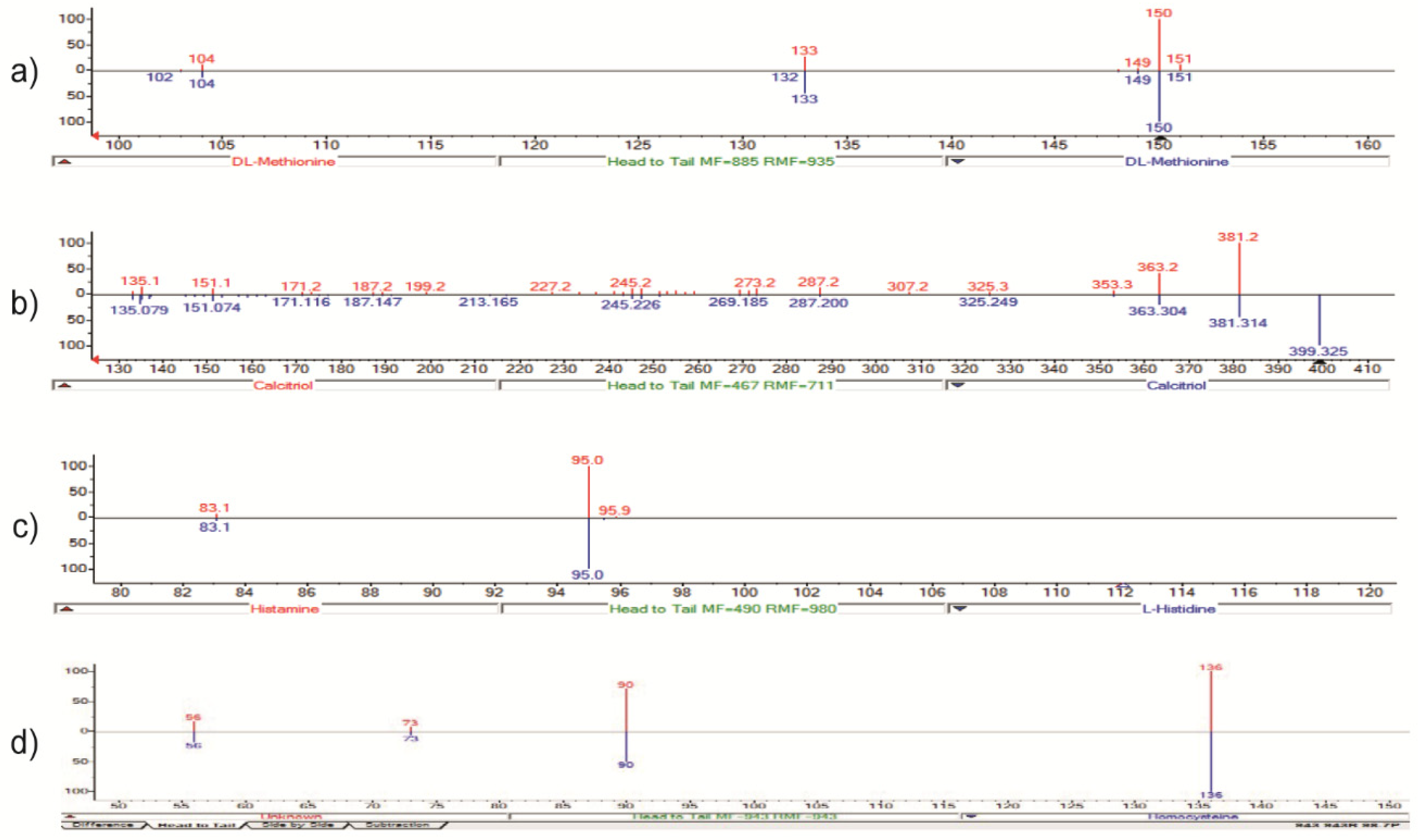
The ion at m/z 150 → 133 (loss of a –OH group) (red) was identified by NIST as methionine (C5H11NO2S) present in the library spectrum (blue), with a 92% identification score (direct match factor: 885; reverse match factor: 935) (
Figure 11A). Methionine was confirmed by comparison to LC and MS/MS data acquired for the certified analytical standard, following the EU directive (EU directive 2002/657/EC). The ions m/z 4.0 → 381 and 112 → 95 were identified using the same approach and corresponding to calcitriol and histamine, respectively (
Figure 11B and C). We also identified homocysteine with ion at m/z 136 → 90 (
Figure 11D).
Furthermore, we observed a peak at m/z 371 (data not shown), but the corresponding metabolite was not identified using both an MS and an MS/MS database search. However, this unknown metabolite is very interesting because the similarity approach in MS/MS search appears to be highly similar to a peptide molecule. Due to the absence of a commercial internal standard, verifying the data using EU Directive 2002/657/EC was not possible. In order to determine whether the metabolite at m/z 371 was present in the dietary supplement, OMWW-OL was analyzed using the LC-SANIST-MS/MS method. Nonetheless, it was evidently absent from the analysis of 10 OMWW-OL samples.
We observed a 10-fold increase in the homocysteine/methionine ratio (m/z 134/150) (p=4 × 10–5), the vitamin 25 (OH) D3/histamine ratio (m/z 401/112) (p=5 × 10–5) and the vitamin 25 (OH) D3/not identified metabolite ratio (m/z 401/371) (p=6 × 10–5) with respect to T0.
The mass spectrometry data show very promising beneficial effects on metabolites with the discovery of a new molecule induced during treatment.
4. Discussion
EVOO is an essential Mediterranean diet component rich in bioactive compounds [20]. Several studies suggest the role of its consumption in reducing the incidence of different diseases, such as cancer, cardiovascular pathologies, type 2 diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders [21,22,23,24,25]. Every year, olive tree cultivation and oil extraction generate a large amount of byproducts, primarily OMWW, which can have a negative environmental impact. However, OMWW is rich in phenolic compounds displaying potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, vascular protective, and anti-aging properties [26,27,28,29] and could potentially be useful in the pharmaceutical and food industries [20,28,30,31,32,33,34,35].
Here, we analyzed the effects of OMWW in the dietary supplement preparation [Oliphenolia®, OMWW-OL) on a cohort of volunteers with characteristics close to metabolic syndrome. Our data showed that OMWW-OL intake for 30 days had no negative effects on liver and kidney function and did not affect magnesium levels and iron absorption, transport, and storage. Several studies observed that diets, including daily EVOO, are effective for weight loss [36,37,38]; however, data on women were still lacking. Interestingly, our work found that OMWW-OL was associated with a small decrease in female participants’ weight and BMI even in a short time. Furthermore, the finding that hydration was significantly increased in females is a very promising result, as dehydration can significantly impair cognitive and physical abilities and has been associated with obesity, chronic diseases, and decreased longevity [39,40]. OMWW-OL might have the potential to ameliorate the state of hydration and, consequently, improve the metabolism, weight, BMI, and aging process, especially in females. Interestingly, hydration, weight, and BMI are more regulated in women than men, and in accordance with recent literature, including from our group, gender differences in aging parameters were revealed [41].
In agreement with several researches, we found that OMWW-OL reduces blood pressure. This effect is probably related to its high polyphenol content [42,43], which would also confer potential cardioprotective properties, as observed for EVOO [44]. We also observed a glycemia decrease after OMWW-OL supplementation in our population. This is consistent with the results obtained by Violi et al. [45], who showed that supplementation of EVOO at lunch is linked to lower post-prandial glycemic levels. Although at a non-significant level, cholesterol and LDL showed a decreasing trend while insulin decreased significantly. Besides its role in diabetes, insulin increases cancer risk by promoting the proliferation of normal, preneoplastic, and neoplastic cells [46]. By decreasing glycemia and insulin levels, OMWW-OL could play a role in preventing metabolic syndrome and cancer.
After nutritional intervention with OMWW-OL, we observed an increase in the FT3 and FT4 serum levels while TSH levels remained stable. Since low FT3 levels are associated with aging [47], the ability of OMWW-OL to increase FT3 and FT4 supports the potential anti-aging effect shown in a previous publication of one of our institutions [48]. In this study, we also observed a significant increase in albumin values. Albumin is involved in many bioactive functions, such as extracellular antioxidant defenses [49] and the transport of various ligands [50,51]. Decreases in albumin levels are associated with an inflammatory state [52] and are observed in cancer, infections, malnutrition, liver illness, and kidney disease [53]. Conversely, high albumin concentrations may protect against early glycemic deterioration and type 2 diabetes progression [54]. Therefore, the increased albumin levels observed with OMWW-OL intake may correlate to the anti-inflammatory activity of this olive byproduct and may contribute to metabolic syndrome prevention.
Since we observed a potassium reduction, patients with chronic kidney disease, who are typically recommended to reduce potassium consumption or eliminate it from their blood [55,56,57], might find this result especially significant. Given the absence of any relevant kidney toxicity in the short time of supplementation, OMWW might contribute to maintaining safe potassium levels in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Several works have observed that vitamin D appears to be effective therapeutic agents to prevent the production of reactive oxygen species and stop cytokine-mediated inflammation [58,59,60,61]. However, the literature does not provide much information on the impact of natural compounds on endogenous vitamin D levels. Our finding that a significant increase in vitamin D is achieved by supplementing with OMWW-OL supports a previous observation that in vitro digestion using olive oil resulted in higher absorption of the vitamin D precursor, calcifediol, than using other types of edible oils [62]. Since the nutritional intervention also led to increased calcium levels, our results suggest that OMWW-OL may promote calcium balance either by promoting calcium absorption directly or by increasing vitamin D. Calcium is essential for preserving physiological functions and preventing aging by promoting bone mineralization and sustaining heartbeat, blood clotting, and muscle and neuron function [63,64,65,66]. Naturally, calcium levels decline as we age, and calcium deficiency has been increasingly linked to aging [64,65].
Sarcopenia, which is an age-related reduction in muscle mass, muscle strength, and/or diminished physical function [67], could also be controlled from the intervention with OMWW-OL. The supplementation with OMWW-OL was able to modulate, although at a non-significant level, a decrease in the sarcopenia-associated marker, FM, FFM and ASMM.
Further insights into the dietary intervention were achieved through MS, and differences were observed in the methionine cycle, which involves the regeneration of methionine from homocysteine [68]. The low homocysteine/methionine ratio found in our metabolomic analysis could be associated with active homocysteine metabolism, which is involved in the effective prevention of both oxidative stress and infectious diseases [69]. Elevated homocysteine levels increase the frequency of cardiovascular disease [70,71,72,73,74] with which metabolic syndrome is associated [75]. Therefore, also according to the decrease cardiovascular risk previously observed for olive oil [76], OMWW-OL could reduce cardiovascular risk by lowering homocysteine levels.
The absence of the metabolite at m/z 371.192 in OMWW-OL suggests that the detection of this metabolite in vivo is due to reduced vitamin D25 oxidation. Therefore, the potential antioxidant activity of OMWW-OL may preserve vitamin D25 and its functionality. Interestingly, the vitamin D/histamine ratio is also high, suggesting a decrease in histamine, an inflammatory mediator [77,78,79]. Since vitamin D regulates the immune system, particularly mast cells that carry histamine, the decrease in histamine observed with OMWW-OL intervention could be a secondary effect of the vitamin D increase [80,81].
5. Conclusions
Here, we have shown that OMWW-OL has no detrimental effect on a variety of parameters, and also that in a preliminary way the study indicates the potential to improve biological parameters in volunteers at risk for metabolic syndrome, according to a trend towards a favorable modulation of several biological parameters. The absence of significant variations in most hematochemical parameters indicates that regular Oliphenolia® ingestion has no adverse effects on lipid levels, liver or kidney function.
Some aging-associated parameters were modulated favorably. In addition to extending the period without needing treatment and slowing the aging process, it could be hypothesized that OMWW-OL could help prevent or postpone the onset of age-related disorders, improving quality of life and reducing healthcare costs. MS data revealed improved vitamin D/histamine, homocysteine/methionine, and vitamin D/unknown metabolite ratios.
One of the study’s limitations is the limited sample size; therefore, the information must be considered preliminary, although encouraging, and needs to be strengthened in further research. Our data suggest that OMWW-OL may also have a promising effect in protecting cells from reactive oxygen species-induced injuries due to its high polyphenol content and vitamin D-boosting effect. The possibility of targeting aging instead of treating age-related pathologies is very attractive, as it can improve the quality of life and ensure longevity. This approach would align with positive biology, which researches the biological mechanisms involved in well-being [82]. Some of these parameters could also be relevant in cancer prevention or interception.
Future studies are needed to better elucidate the structure of the potential new metabolite and to investigate biological correlates.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Figure S1: Effects of OMWW-OL assumption on muscle and sarcopenia parameters in volunteers, Figure S2: Effects of OMWW-OL assumption on iron parameters in volunteers, Figure S3: Effects of OMWW-OL assumption on potassium and magnesium values in volunteers.
Author Contributions
A Aiello: clinical studies, LC: mass spectrometry, LC, DMN, PC: manuscript editing and illustration, SN: data analysis and editing, SC: mass spectrometry and metabolites identification, GA, GC, CC, AZ: study design and clinical studies, A Albini: manuscript drafting, and coordination.
Funding
This work has been supported by the Italian Ministry of Health Ricerca Corrente-IRCCS IEO and IRCCS MultiMedica. The dietary supplement was provided at no cost by“Fattoria La Vialla di Gianni, Antonio e Bandino Lofranco- SAS” (Castiglion Fibocchi Arezzo Italy).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Lara Vecchi, Valentina Attanasio, and Aashni Shah (Polistudium srl, Milan Italy) for editorial assistance and Massimiliano Pianta (Polistudium, srl, Milan, Italy) for graphic support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Jimenez-Lopez C, Carpena M, Lourenço-Lopes C, Gallardo-Gomez M, Lorenzo JM, Barba FJ, et al. Bioactive Compounds and Quality of Extra Virgin Olive Oil. Foods. (2020) 9(8):1014. [CrossRef]
- Lanza B, Ninfali P. Antioxidants in Extra Virgin Olive Oil and Table Olives: Connections between Agriculture and Processing for Health Choices. Antioxidants (Basel) (2020) 9(1):41. [CrossRef]
- Flynn MM, Tierney A, Itsiopoulos C. Is Extra Virgin Olive Oil the Critical Ingredient Driving the Health Benefits of a Mediterranean Diet? A Narrative Review. Nutrients (2023) 15(13):2916. [CrossRef]
- Rossi M, Caruso F, Kwok L, Lee G, Caruso A, Gionfra F, et al. Protection by extra virgin olive oil against oxidative stress in vitro and in vivo. Chemical and biological studies on the health benefits due to a major component of the Mediterranean diet. PLoS One (2017) 12(12):e0189341. [CrossRef]
- Cuffaro D, Bertolini A, Bertini S, Ricci C, Cascone MG, Danti S, et al. Olive Mill Wastewater as Source of Polyphenols with Nutraceutical Properties. Nutrients (2023) 15(17):3746. [CrossRef]
- Caponio F, Piga A, Poiana M. Valorization of Food Processing By-Products. Foods. 2022;11(20):3246. Published 2022 Oct 18. [CrossRef]
- Dini I, Graziani G, Fedele FL, Sicari A, Vinale F, Castaldo L, Ritieni A. An Environmentally Friendly Practice Used in Olive Cultivation Capable of Increasing Commercial Interest in Waste Products from Oil Processing. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Jun 1;9(6):466. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bellumori M, Cecchi L, Romani A, Mulinacci N, Innocenti M. Recovery and Stability over Time of Phenolic Fractions by an Industrial Filtration System of Olive Mill Wastewaters: A Three-Year Study. J Sci Food Agric (2018) 98:2761–2769.
- Krawczyk M, Burzynska-Pedziwiatr I, Wozniak LA, Bukowiecka-Matusiak M. Impact of Polyphenols on Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Factors in Diabetes Mellitus: Nutritional Antioxidants and Their Application in Improving Antidiabetic Therapy. Biomolecules (2023) 13(9):1402. [CrossRef]
- Williamson G, Sheedy K. Effects of Polyphenols on Insulin Resistance. Nutrients (2020) 12(10):3135. [CrossRef]
- Cho AR, Kwon YJ, Kim JK. Pre-Metabolic Syndrome and Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes and Hypertension: From the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study. J Pers Med (2021) 11(8):700. [CrossRef]
- Vona R, Gambardella L, Cittadini C, Straface E, Pietraforte D. Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Metabolic Syndrome and Associated Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev (2019) 2019:1–19. [CrossRef]
- Cristoni S, Rossi Bernardi L, Larini M, Natale G, Didomenico N, Varelli M, Conti M, Dorna I, Puccio G. Predicting and preventing intestinal dysbiosis on the basis of pharmacological gut microbiota metabolism. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2019 Jul 30;33(14):1221-1225. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang MY, Low TY, Lee PY, Wan Mohamad Nazarie WF, Guryev V, Jamal R. Proteogenomics: From next-generation sequencing (NGS) and mass spectrometry-based proteomics to precision medicine. Clin Chim Acta (2019) 498:38-46. [CrossRef]
- Zinellu E, Zinellu A, Fois AG, Carru C, Pirina P. Circulating biomarkers of oxidative stress in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review. Respir Res (2016) 17(1):150. [CrossRef]
- Albini A, Briga D, Conti M, Bruno A, Farioli D, Canali S, et al. SANIST: a rapid mass spectrometric SACI/ESI data acquisition and elaboration platform for verifying potential candidate biomarkers. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom (2015) 29(19):1703-10. [CrossRef]
- Albini A, Bruno A, Bassani B, D’Ambrosio G, Pelosi G, Consonni P, et al. Serum Steroid Ratio Profiles in Prostate Cancer: A New Diagnostic Tool Toward a Personalized Medicine Approach. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) (2018) 9:110. [CrossRef]
- Cristoni S, Dusi G, Brambilla P, Albini A, Conti M, Brambilla M, et al. SANIST: optimization of a technology for compound identification based on the European Union directive with applications in forensic, pharmaceutical and food analyses. J Mass Spectrom (2017) 52(1):16-21. [CrossRef]
- Cristoni S, Molin L, Lai A, Bernardi LR, Pucciarelli S, Agostini M, et al. MALDI-MS-NIST library approach for colorectal cancer diagnosis. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom (2009) 23(17):2839-45. [CrossRef]
- Albini A, Albini F, Corradino P, Dugo L, Calabrone L, Noonan DM. From antiquity to contemporary times: how olive oil by-products and waste water can contribute to health. Front Nutr (2023) 10:1254947. [CrossRef]
- Peri S, Ruzzolini J, Urciuoli S, Versienti G, Biagioni A, Andreucci E, Peppicelli S, Bianchini F, Bottari A, Calorini L, Nediani C, Magnelli L, Papucci L. An Oleocanthal-Enriched EVO Oil Extract Induces the ROS Production in Gastric Cancer Cells and Potentiates the Effect of Chemotherapy. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 7;11(9):1762. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lăcătușu CM, Grigorescu ED, Floria M, Onofriescu A, Mihai BM. The Mediterranean Diet: From an Environment-Driven Food Culture to an Emerging Medical Prescription. Int J Environ Res Public Health (2019) 16(6):942. [CrossRef]
- Santangelo C, Vari R, Scazzocchio B, De Sanctis P, Giovannini C, D’Archivio M, et al. Anti-inflammatory Activity of Extra Virgin Olive Oil Polyphenols: Which Role in the Prevention and Treatment of Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases? Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets (2018) 18(1):36-50. [CrossRef]
- Nocella C, Cammisotto V, Fianchini L, D’Amico A, Novo M, Castellani V, et al. Extra Virgin Olive Oil and Cardiovascular Diseases: Benefits for Human Health. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets (2018) 18(1):4-13. [CrossRef]
- Billingsley HE, Carbone S, Lavie CJ. Dietary Fats and Chronic Noncommunicable Diseases. Nutrients (2018) 10(10):1385. [CrossRef]
- Tsao, R. Chemistry and biochemistry of dietary polyphenols. Nutrients (2010) 2(12):1231-46. [CrossRef]
- Stagos, D. Antioxidant Activity of Polyphenolic Plant Extracts. Antioxidants (Basel) (2019) 9(1):19. [CrossRef]
- Rudrapal M, Khairnar SJ, Khan J, Dukhyil AB, Ansari MA, Alomary MN, et al. Dietary Polyphenols and Their Role in Oxidative Stress-Induced Human Diseases: Insights Into Protective Effects, Antioxidant Potentials and Mechanism(s) of Action. Front Pharmacol (2022) 13:806470. [CrossRef]
- Upasana Bhuyan, Jyotirekha G. Handique, Chapter 6 - Plant polyphenols as potent antioxidants: Highlighting the mechanism of antioxidant activity and synthesis/development of some polyphenol conjugates, Editor(s): Atta-ur-Rahman, Studies in Natural Products Chemistry, Elsevier, Volume 75, 2022, Pages 243-266, ISSN 1572-5995, ISBN 9780323912501. [CrossRef]
- Selim S, Albqmi M, Al-Sanea MM, Alnusaire TS, Almuhayawi MS, AbdElgawad H, et al. Valorizing the usage of olive leaves, bioactive compounds, biological activities, and food applications: A comprehensive review. Front Nutr (2022) 9:1008349. [CrossRef]
- Otero C, Miranda-Rojas S, Llancalahuén FM, Fuentes JA, Atala C, González-Silva G, et al. Biochemical characterization of Peumus boldus fruits: Insights of its antioxidant properties through a theoretical approach. Food Chem (2022) 370:131012. [CrossRef]
- Khwaldia K, Attour N, Matthes J, Beck L, Schmid M. Olive byproducts and their bioactive compounds as a valuable source for food packaging applications. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf (2022) 21(2):1218-1253. [CrossRef]
- Vauzour D, Rodriguez-Mateos A, Corona G, Oruna-Concha MJ, Spencer JP. Polyphenols and human health: prevention of disease and mechanisms of action. Nutrients (2010) 2(11):1106-31. [CrossRef]
- Bahadoran Z, Mirmiran P, Azizi F. Dietary polyphenols as potential nutraceuticals in management of diabetes: a review. J Diabetes Metab Disord (2013) 12(1):43. [CrossRef]
- Cory H, Passarelli S, Szeto J, Tamez M, Mattei J. The Role of Polyphenols in Human Health and Food Systems: A Mini-Review. Front Nutr (2018) 5:87. [CrossRef]
- Castañer O, Covas MI, Khymenets O, Nyyssonen K, Konstantinidou V, Zunft HF, et al. Protection of LDL from oxidation by olive oil polyphenols is associated with a downregulation of CD40-ligand expression and its downstream products in vivo in humans. Am J Clin Nutr. (2012) 95(5):1238-44. [CrossRef]
- Estruch R, Martínez-González MA, Corella D, Salas-Salvadó J, Fitó M, Chiva-Blanch G, et al. Effect of a high-fat Mediterranean diet on bodyweight and waist circumference: a prespecified secondary outcomes analysis of the PREDIMED randomised controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol (2019) 7(5):e6-e17. [CrossRef]
- Flynn MM, Reinert SE. Comparing an olive oil-enriched diet to a standard lower-fat diet for weight loss in breast cancer survivors: a pilot study. J Womens Health (Larchmt) (2010) 19(6):1155-61. [CrossRef]
- Nishi SK, Babio N, Paz-Graniel I, Serra-Majem L, Vioque J, Fitó M, et al. Water intake, hydration status and 2-year changes in cognitive performance: a prospective cohort study. BMC Med (2023) 21:82. [CrossRef]
- Li S, Xiao X, Zhang X. Hydration Status in Older Adults: Current Knowledge and Future Challenges. Nutrients (2023) 15(11):2609. [CrossRef]
- Caruso C, Accardi G, Virruso C, Candore G. Sex, gender and immunosenescence: a key to understand the different lifespan between men and women? Immun Ageing (2013) 10(1):20. [CrossRef]
- de Brito Alves JL, de Sousa VP, Cavalcanti Neto MP, Magnani M, Braga VA, da Costa-Silva JH, et al. New Insights on the Use of Dietary Polyphenols or Probiotics for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. Front Physiol (2016) 7:448. [CrossRef]
- Barona J, Jones JJ, Kopec RE, Comperatore M, Andersen C, Schwartz SJ, et al. A Mediterranean-style low-glycemic-load diet increases plasma carotenoids and decreases LDL oxidation in women with metabolic syndrome. J Nutr Biochem (2012) 23(6):609-15. [CrossRef]
- Sarapis K, Thomas CJ, Hoskin J, George ES, Marx W, Mayr HL, et al. The Effect of High Polyphenol Extra Virgin Olive Oil on Blood Pressure and Arterial Stiffness in Healthy Australian Adults: A Randomized, Controlled, Cross-Over Study. Nutrients (2020) 12(8):2272. [CrossRef]
- Violi F, Loffredo L, Pignatelli P, Angelico F, Bartimoccia S, Nocella C, et al. Extra virgin olive oil use is associated with improved post-prandial blood glucose and LDL cholesterol in healthy subjects. Nutr Diabetes (2015) 5(7):e172. [CrossRef]
- Vigneri R, Sciacca L, Vigneri P. Rethinking the relationship between insulin and cancer. Trends Endocrinol Metab (2020) 31:551–560.
- Bertoli A, Valentini A, Cianfarani MA, Gasbarra E, Tarantino U, Federici M. Low FT3: a possible marker of frailty in the elderly. Clin Interv Aging (2017) 12:335–41.
- Alì S, Davinelli S, Accardi G, Aiello A, Caruso C, Duro G, et al. Healthy ageing and Mediterranean diet: A focus on hormetic phytochemicals. Mech Ageing Dev (2021) 200:111592. [CrossRef]
- Roche M, Rondeau P, Singh NR, Tarnus E, Bourdon E. The antioxidant properties of serum albumin. FEBS Lett. 2008 Jun 11;582(13):1783-7. Epub 2008 May 12. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belinskaia DA, Voronina PA, Shmurak VI, Jenkins RO, Goncharov NV. Serum Albumin in Health and Disease: Esterase, Antioxidant, Transporting and Signaling Properties. Int J Mol Sci (2021) 22(19):10318. [CrossRef]
- Sitar ME, Aydin S, Cakatay U. Human serum albumin and its relation with oxidative stress. Clin Lab (2013) 59(9-10):945-52.
- Eckart A, Struja T, Kutz A, Baumgartner A, Baumgartner T, Zurfluh S, et al. Relationship of Nutritional Status, Inflammation, and Serum Albumin Levels During Acute Illness: A Prospective Study. Am J Med (2020) 133(6):713-722.e7. [CrossRef]
- Rozga J, Piątek T, Małkowski P. Human albumin: old, new, and emerging applications. Ann Transplant (2013) 18:205-17. [CrossRef]
- Jun JE, Lee SE, Lee YB, Jee JH, Bae JC, Jin SM, et al. Increase in serum albumin concentration is associated with prediabetes development and progression to overt diabetes independently of metabolic syndrome. PLoS One (2017) 12(4):e0176209. [CrossRef]
- Morris A, Krishnan N, Kimani PK, Lycett D. Effect of Dietary Potassium Restriction on Serum Potassium, Disease Progression, and Mortality in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Ren Nutr. 2020 Jul;30(4):276-285. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Erratum in: J Ren Nutr. 2022 Jan;32(1):e1-e10. 10.1053/j.jrn.2021.07.001. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picard K, Barreto Silva MI, Mager D, Richard C. Dietary Potassium Intake and Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease Progression in Predialysis Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review. Adv Nutr. 2020 Jul 1;11(4):1002-1015. Erratum in: Adv Nutr. 2023 Nov;14(6):1657. 10.1016/j.advnut.2023.09.014. PMCID: PMC7360460. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourafshar S, Sharma B, Kranz S, Mallawaarachchi I, Kurland E, Ma JZ, Scialla JJ. Patterns of Fruit and Vegetable Intake in Adults With and Without Chronic Kidney Disease in the United States. J Ren Nutr. 2023 Jan;33(1):88-96. Epub 2022 Jul 5. PMCID: PMC10001204. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berridge, M.J. Vitamin D, reactive oxygen species and calcium signalling in ageing and disease. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci (2016) 371(1700):20150434. [CrossRef]
- Della Nera G, Sabatino L, Gaggini M, Gorini F, Vassalle C. Vitamin D Determinants, Status, and Antioxidant/Anti-inflammatory-Related Effects in Cardiovascular Risk and Disease: Not the Last Word in the Controversy. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Apr 18;12(4):948. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Masjedi F, Keshtgar S, Zal F, Talaei-Khozani T, Sameti S, Fallahi S, et al. Effects of vitamin D on steroidogenesis, reactive oxygen species production, and enzymatic antioxidant defense in human granulosa cells of normal and polycystic ovaries. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol (2020) 197:105521. [CrossRef]
- Quigley M, Rieger S, Capobianco E, Wang Z, Zhao H, Hewison M, et al. Vitamin D Modulation of Mitochondrial Oxidative Metabolism and mTOR Enforces Stress Adaptations and Anticancer Responses. JBMR Plus. (2021) 6(1):e10572. [CrossRef]
- McCourt AF, O’Sullivan AM. Using food fortification to improve vitamin D bioaccessibility and intakes. Proc Nutr Soc (2022) 81(1):99-107. [CrossRef]
- Pu F, Chen N, Xue S. Calcium intake, calcium homeostasis and health. Food Sci Hum Wellness (2016) 5(1):8-16. [CrossRef]
- Beto, J.A. The role of calcium in human aging. Clin Nutr Res (2015) 4(1):1-8. [CrossRef]
- Veldurthy V, Wei R, Oz L, Dhawan P, Jeon YH, Christakos S. Vitamin D, calcium homeostasis and aging. Bone Res (2016) 4:16041. [CrossRef]
- Wicher SA, Roos BB, Teske JJ, Fang YH, Pabelick C, Prakash YS. Aging increases senescence, calcium signaling, and extracellular matrix deposition in human airway smooth muscle. PLoS One (2021) 16(7):e0254710. [CrossRef]
- Li ML, Zhang F, Luo HY, et al. Improving sarcopenia in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of whey protein supplementation with or without resistance training. J Nutr Health Aging. 2024;28(4):100184. [CrossRef]
- Shen W, Gao C, Cueto R, Liu L, Fu H, Shao Y, et al. Homocysteine-methionine cycle is a metabolic sensor system controlling methylation-regulated pathological signaling. Redox Biol (2020) 28:101322. [CrossRef]
- Cristoni S, Bernardi LR, Malvandi AM, Larini M, Longhi E, Sortino F, et al. A case of personalized and precision medicine: Pharmacometabolomic applications to rare cancer, microbiological investigation, and therapy. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom (2021) 35(2):e8976. [CrossRef]
- Brattström L, Wilcken DE. Homocysteine and cardiovascular disease: cause or effect? Am J Clin Nutr (2000) 72(2):315-23. [CrossRef]
- Dinavahi R, Falkner B. Relationship of homocysteine with cardiovascular disease and blood pressure. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) (2004) 6(9):494-8; quiz 499-500. [CrossRef]
- Yuan S, Mason AM, Carter P, Burgess S, Larsson SC. Homocysteine, B vitamins, and cardiovascular disease: a Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med (2021) 19(1):97. [CrossRef]
- Guieu R, Ruf J, Mottola G. Hyperhomocysteinemia and cardiovascular diseases. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) (2022) 80(1):7-14. [CrossRef]
- Kumar A, Palfrey HA, Pathak R, Kadowitz PJ, Gettys TW, Murthy SN. The metabolism and significance of homocysteine in nutrition and health. Nutr Metab (Lond) (2017) 14:78. [CrossRef]
- Nagayama D, Watanabe Y, Yamaguchi T, Suzuki K, Saiki A, Fujishiro K, et al. Issue of Waist Circumference for the Diagnosis of Metabolic Syndrome Regarding Arterial Stiffness: Possible Utility of a Body Shape Index in Middle-Aged Nonobese Japanese Urban Residents Receiving Health Screening. Obes Facts (2022) 15(2):160-169. [CrossRef]
- Branco ACCC, Yoshikawa FSY, Pietrobon AJ, Sato MN. Role of Histamine in Modulating the Immune Response and Inflammation. Mediators Inflamm (2018) 2018:9524075. [CrossRef]
- Mehmood A, Usman M, Patil P, Zhao L, Wang C. A review on management of cardiovascular diseases by olive polyphenols. Food Sci Nutr. 2020 Aug 13;8(9):4639-4655. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Thangam EB, Jemima EA, Singh H, Baig MS, Khan M, Mathias CB, et al. The Role of Histamine and Histamine Receptors in Mast Cell-Mediated Allergy and Inflammation: The Hunt for New Therapeutic Targets. Front Immunol (2018) 9:1873. [CrossRef]
- Carthy E, Ellender T. Histamine, Neuroinflammation and Neurodevelopment: A Review. Front Neurosci (2021) 15:680214. [CrossRef]
- Murdaca G, Allegra A, Tonacci A, Musolino C, Ricciardi L, Gangemi S. Mast Cells and Vitamin D Status: A Clinical and Biological Link in the Onset of Allergy and Bone Diseases. Biomedicines (2022) 10(8):1877. [CrossRef]
- Mehrani Y, Morovati S, Tieu S, Karimi N, Javadi H, Vanderkamp S, et al. Vitamin D Influences the Activity of Mast Cells in Allergic Manifestations and Potentiates Their Effector Functions against Pathogens. Cells (2023) 12(18):2271. [CrossRef]
- Caruso C, Passarino G, Puca A, Scapagnini G. “Positive biology”: the centenarian lesson. Immun Ageing (2012) 9(1):5. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
The flowchart of the study design. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee. During a 7-day washout period, the participants were required to abstain from extra virgin olive oil and food supplements containing polyphenols. The nutritional intervention consisted of the consumption of the OliphenoliaⓇ dietary supplement preparation (25 mL) twice a day, 30 minutes before the main meals (lunch and dinner), for 30 days, with no other restriction from the usual diet.
Figure 1.
The flowchart of the study design. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee. During a 7-day washout period, the participants were required to abstain from extra virgin olive oil and food supplements containing polyphenols. The nutritional intervention consisted of the consumption of the OliphenoliaⓇ dietary supplement preparation (25 mL) twice a day, 30 minutes before the main meals (lunch and dinner), for 30 days, with no other restriction from the usual diet.
Figure 2.
OMWW-OL assumption effects on weight and BMI in volunteers. The images show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM.
Figure 2.
OMWW-OL assumption effects on weight and BMI in volunteers. The images show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM.
Figure 3.
OMWW-OL assumption effects on hydration in volunteers. The images show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM.
Figure 3.
OMWW-OL assumption effects on hydration in volunteers. The images show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM.
Figure 4.
OMWW-OL assumption effects on blood pressure in volunteers. The images show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM.
Figure 4.
OMWW-OL assumption effects on blood pressure in volunteers. The images show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM.
Figure 5.
OMWW-OL assumption effects on cholesterol in volunteers. The images show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM.
Figure 5.
OMWW-OL assumption effects on cholesterol in volunteers. The images show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM.
Figure 6.
OMWW-OL assumption effects on glycemia and insulin in volunteers. The images show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM.
Figure 6.
OMWW-OL assumption effects on glycemia and insulin in volunteers. The images show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM.
Figure 7.
OMWW-OL assumption effects on vitamin D and calcium in volunteers. The images show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM.
Figure 7.
OMWW-OL assumption effects on vitamin D and calcium in volunteers. The images show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM.
Figure 8.
OMWW-OL assumption effects on thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) in volunteers. The images show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM.
Figure 8.
OMWW-OL assumption effects on thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) in volunteers. The images show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM.
Figure 9.
OMWW-OL assumption effects on albumin in volunteers. The images show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM.
Figure 9.
OMWW-OL assumption effects on albumin in volunteers. The images show the single values at T0, T1 and T2. Y-axis reports the values of the analysed biomarker. Statistics are performed on comparison between the average of T0/T1 ± SEM, T1/T2 ± SEM T0/T2 ± SEM.
Figure 10.
Workflow for non-targeted LC-MS SANIST metabolites profiling.
Figure 10.
Workflow for non-targeted LC-MS SANIST metabolites profiling.
Figure 11.
Biomarkers detected by NIST MS Search Program.
Figure 11.
Biomarkers detected by NIST MS Search Program.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).