Submitted:
30 July 2024
Posted:
31 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Purification of Endolysin
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. NMR Spectroscopy
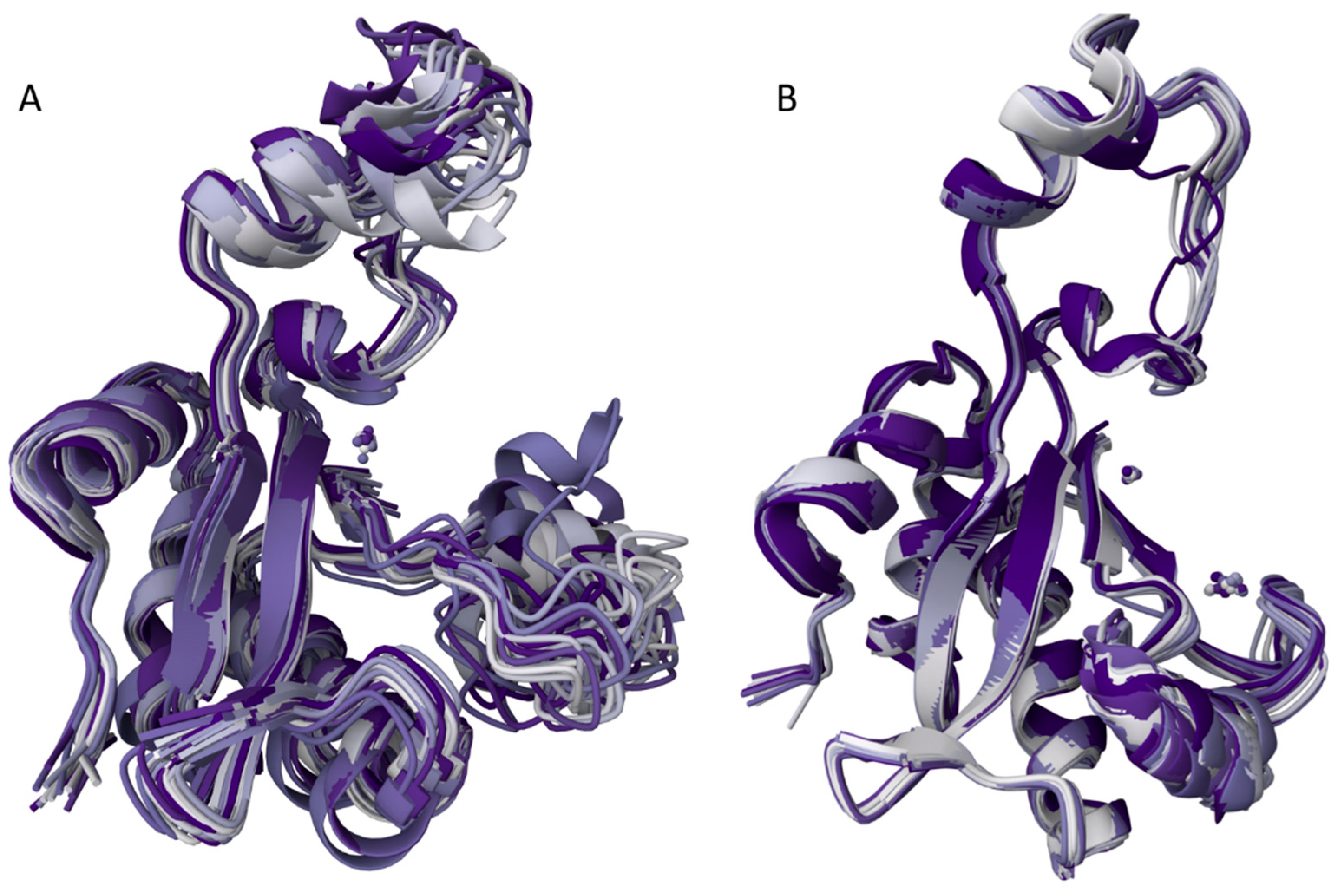
2.4. Calculation of Spatial Structure
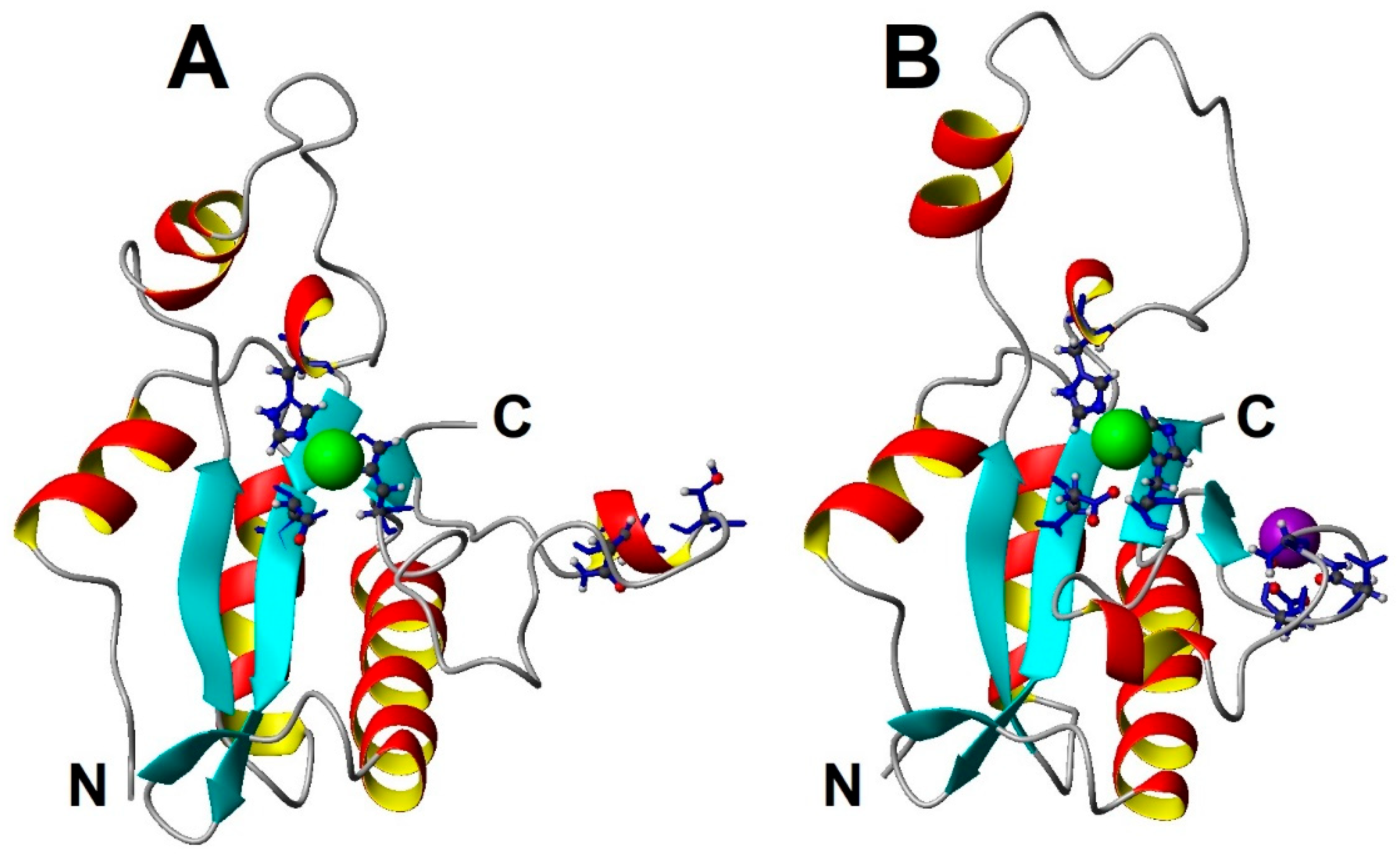
2.5. Overall Structure of EndoT5-Zn2+Ca2+[M1]
3. Results and Discussion
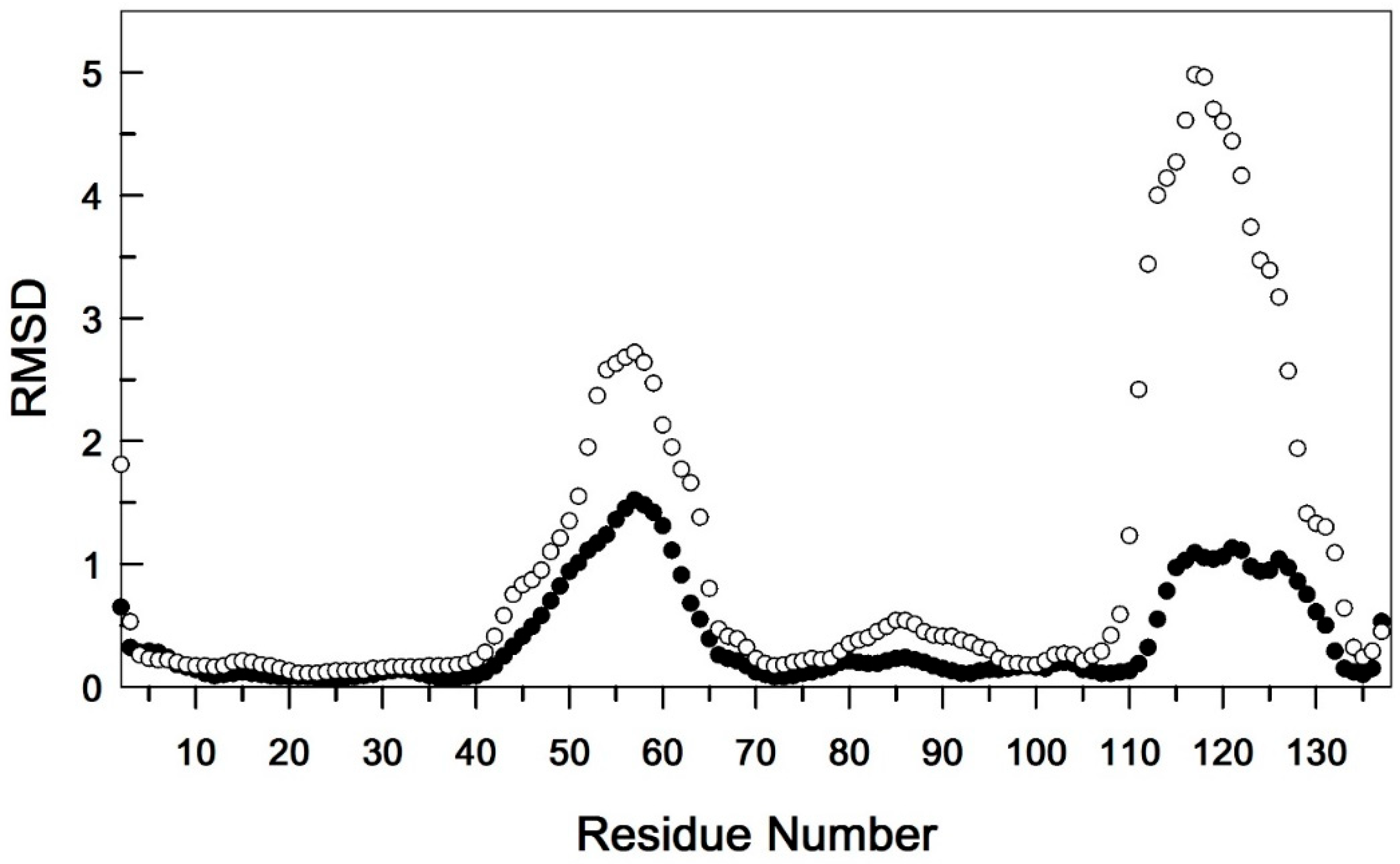
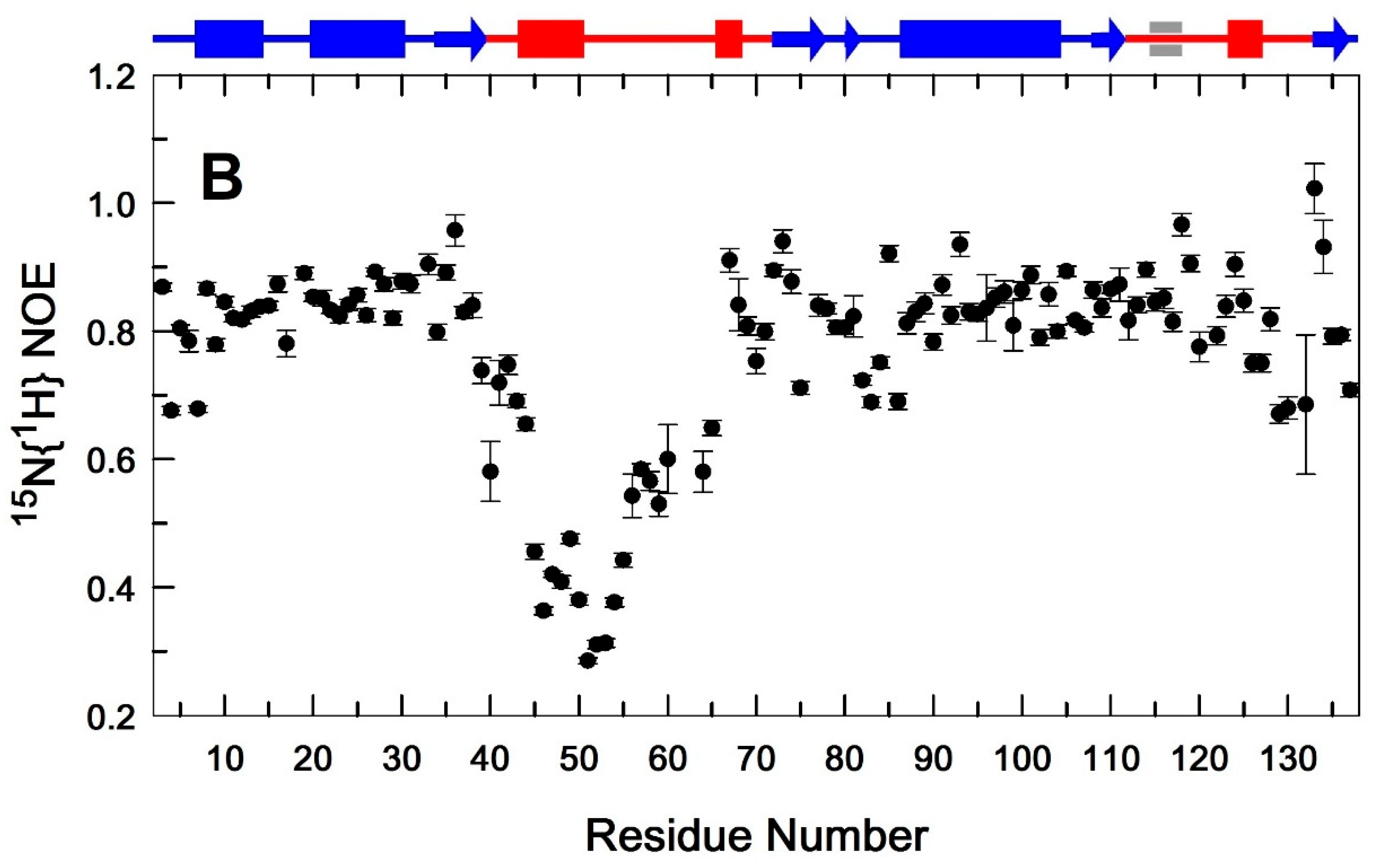
3.1. Comparative Analysis of the Secondary Structure of Single and Dual Ion Forms of EndoT5
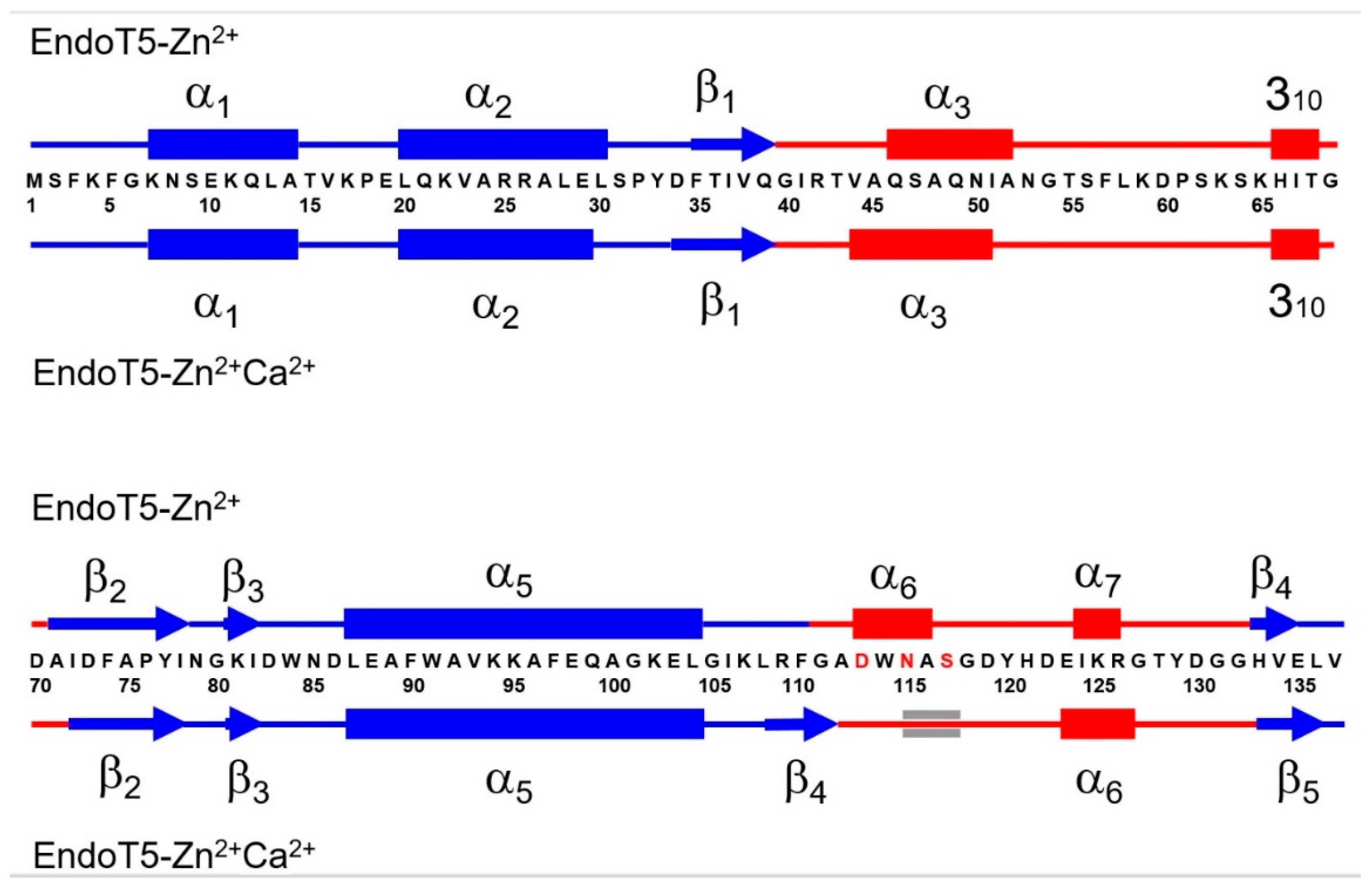
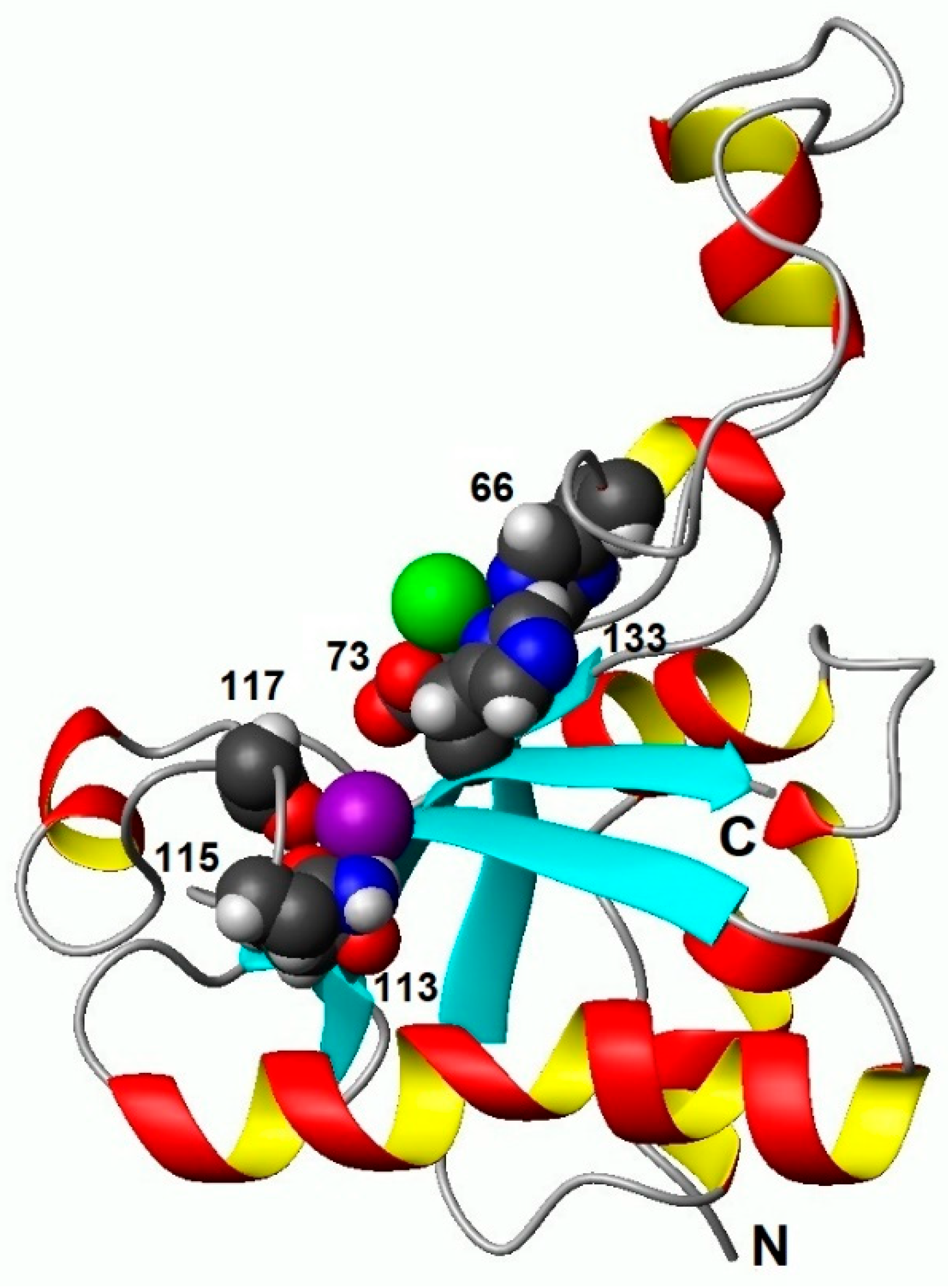
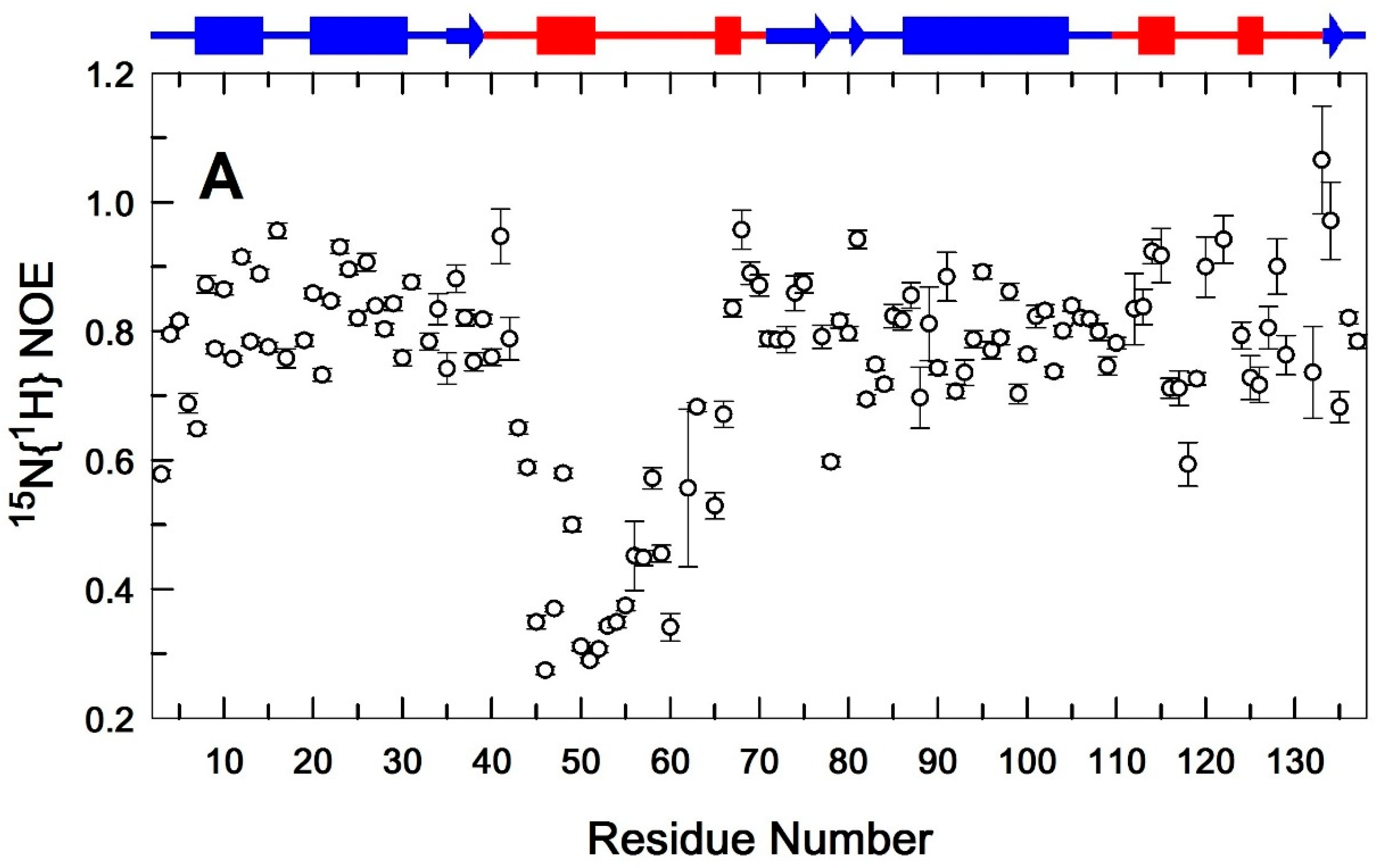
3.2. Binding of Ca2+ Ion by the Regulatory Loop and Its Effect on Intramolecular Mobility
3.3. Structural Basis of Activation of EndoT5 by Regulatory Ca2+
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bonhivers, M.; Letellier, L. Calcium controls phage T5 infection at the level of the Escherichia coli cytoplasmic membrane. FEBS Lett 1995, 374, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, R.W.; Buchanan, J.M. Effect of calcium ions on synthesis of T5-specific ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem 1970, 245, 5904–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, R.W.; Buchanan, J.M. Effect of calcium ions on synthesis of T5-specific proteins. J Biol Chem 1970, 245, 5897–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huet, A.; Conway, J.F.; Letellier, L.; Boulanger, P. In vitro assembly of the T=13 procapsid of bacteriophage T5 with its scaffolding domain. J Virol 2010, 84, 9350–9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikoulinskaia, G.V.; Odinokova, I.V.; Zimin, A.A.; Lysanskaya, V.Y.; Feofanov, S.A.; Stepnaya, O.A. Identification and characterization of the metal ion-dependent L-alanoyl-D-glutamate peptidase encoded by bacteriophage T5. FEBS J 2009, 276, 7329–7342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokhorov, D.A.; Mikoulinskaia, G.V.; Molochkov, N.V.; Uversky, V.N.; Kutyshenko, V.P. High-resolution NMR structure of a Zn 2+-containing form of the bacteriophage T5 L-alanyl-D-glutamate peptidase. RSC advances 2015, 5, 41041–41049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalenko, A.O.; Chernyshov, S.V.; Kutyshenko, V.P.; Molochkov, N.V.; Prokhorov, D.A.; Odinokova, I.V.; Mikoulinskaia, G.V. Investigation of the calcium-induced activation of the bacteriophage T5 peptidoglycan hydrolase promoting host cell lysis. Metallomics 2019, 11, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, H.; Nakayama, S.; Kretsinger, R.H. Classification and evolution of EF-hand proteins. Biometals 1998, 11, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, D.C.; Guragain, M.; Patrauchan, M. Calcium binding proteins and calcium signaling in prokaryotes. Cell Calcium 2015, 57, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, R. The computer aided resonance assignment tutorial; CANTINA verlag: 2004.
- Masse, J.E.; Keller, R. AutoLink: automated sequential resonance assignment of biopolymers from NMR data by relative-hypothesis-prioritization-based simulated logic. J Magn Reson 2005, 174, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markley, J.L.; Bax, A.; Arata, Y.; Hilbers, C.W.; Kaptein, R.; Sykes, B.D.; Wright, P.E.; Wuthrich, K. Recommendations for the presentation of NMR structures of proteins and nucleic acids--IUPAC-IUBMB-IUPAB Inter-Union Task Group on the standardization of data bases of protein and nucleic acid structures determined by NMR spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem 1998, 256, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Bigam, C.G.; Yao, J.; Abildgaard, F.; Dyson, H.J.; Oldfield, E.; Markley, J.L.; Sykes, B.D. 1H, 13C and 15N chemical shift referencing in biomolecular NMR. J Biomol NMR 1995, 6, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, N.A.; Muhandiram, R.; Singer, A.U.; Pascal, S.M.; Kay, C.M.; Gish, G.; Shoelson, S.E.; Pawson, T.; Forman-Kay, J.D.; Kay, L.E. Backbone dynamics of a free and phosphopeptide-complexed Src homology 2 domain studied by 15N NMR relaxation. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 5984–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharchenko, V.; Nowakowski, M.; Jaremko, M.; Ejchart, A.; Jaremko, L. Dynamic (15)N(1)H NOE measurements: a tool for studying protein dynamics. J Biomol NMR 2020, 74, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornilescu, G.; Delaglio, F.; Bax, A. Protein backbone angle restraints from searching a database for chemical shift and sequence homology. J Biomol NMR 1999, 13, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzesiek, S.; Bax, A. Improved 3D triple-resonance NMR techniques applied to a 31 kDa protein. Journal of Magnetic Resonance (1969) 1992, 96, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenkarev, Z.O.; Balashova, T.A.; Yakimenko, Z.A.; Ovchinnikova, T.V.; Arseniev, A.S. Peptaibol zervamicin IIb structure and dynamics refinement from transhydrogen bond J couplings. Biophys J 2004, 86, 3687–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stickle, D.F.; Presta, L.G.; Dill, K.A.; Rose, G.D. Hydrogen bonding in globular proteins. J Mol Biol 1992, 226, 1143–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korndorfer, I.P.; Kanitz, A.; Danzer, J.; Zimmer, M.; Loessner, M.J.; Skerra, A. Structural analysis of the L-alanoyl-D-glutamate endopeptidase domain of Listeria bacteriophage endolysin Ply500 reveals a new member of the LAS peptidase family. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 2008, 64, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Vysotski, E.S.; Markova, S.V.; Liu, Z.J.; Lee, J.; Rose, J.; Wang, B.C. All three Ca2+-binding loops of photoproteins bind calcium ions: the crystal structures of calcium-loaded apo-aequorin and apo-obelin. Protein Sci 2005, 14, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntert, P. Automated NMR structure calculation with CYANA. Methods Mol Biol 2004, 278, 353–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koradi, R.; Billeter, M.; Wuthrich, K. MOLMOL: a program for display and analysis of macromolecular structures. J Mol Graph 1996, 14, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fersht, A. Structure and mechanism in protein science: a guide to enzyme catalysis and protein folding; Macmillan: 1999.
- Koshland, D.E. Application of a Theory of Enzyme Specificity to Protein Synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1958, 44, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.J.; Kumar, S.; Ma, B.; Nussinov, R. Folding funnels, binding funnels, and protein function. Protein Sci 1999, 8, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, R.A.; Fyfe, P.K.; Lodge, A.; Biboy, J.; Vollmer, W.; Hunter, W.N.; Sargent, F. Structure and activity of ChiX: a peptidoglycan hydrolase required for chitinase secretion by Serratia marcescens. Biochem J 2018, 475, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Son, B.; Ryu, S.; Ha, N.C. Crystal Structure of LysB4, an Endolysin from Bacillus cereus-Targeting Bacteriophage B4. Mol Cells 2019, 42, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Gaitero, M.; Keary, R.; Garcia-Doval, C.; Coffey, A.; van Raaij, M.J. Crystal structure of the lytic CHAP(K) domain of the endolysin LysK from Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage K. Virol J 2014, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Feng, Y.; Feng, X.; Sun, C.; Lei, L.; Ding, W.; Niu, F.; Jiao, L.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; et al. Structural and biochemical characterization reveals LysGH15 as an unprecedented "EF-hand-like" calcium-binding phage lysin. PLoS Pathog 2014, 10, e1004109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikoulinskaia, G.V.; Prokhorov, D.A.; Chernyshov, S.V.; Sitnikova, D.S.; Arakelian, A.G.; Uversky, V.N. Conservative Tryptophan Residue in the Vicinity of an Active Site of the M15 Family l,d-Peptidases: A Key Element in the Catalysis. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehr, D.D.; Nussinov, R.; Wright, P.E. The role of dynamic conformational ensembles in biomolecular recognition. Nat Chem Biol 2009, 5, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henzler-Wildman, K.A.; Thai, V.; Lei, M.; Ott, M.; Wolf-Watz, M.; Fenn, T.; Pozharski, E.; Wilson, M.A.; Petsko, G.A.; Karplus, M.; et al. Intrinsic motions along an enzymatic reaction trajectory. Nature 2007, 450, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehr, D.D.; McElheny, D.; Dyson, H.J.; Wright, P.E. The dynamic energy landscape of dihydrofolate reductase catalysis. Science 2006, 313, 1638–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, S.; Wang, C. Calcium Signaling Mechanisms Across Kingdoms. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2021, 37, 311–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbino, A.; Colella, M. The Different Facets of Extracellular Calcium Sensors: Old and New Concepts in Calcium-Sensing Receptor Signalling and Pharmacology. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.E.; Holland, I.B.; Campbell, A.K. Direct measurement of free Ca(2+) shows different regulation of Ca(2+) between the periplasm and the cytosol of Escherichia coli. Cell Calcium 2002, 32, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.M.; Kelleher, N.L.; Consortium for Top Down, P. Proteoform: a single term describing protein complexity. Nat Methods 2013, 10, 186–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlen, M.; Bjorling, E.; Agaton, C.; Szigyarto, C.A.; Amini, B.; Andersen, E.; Andersson, A.C.; Angelidou, P.; Asplund, A.; Asplund, C.; et al. A human protein atlas for normal and cancer tissues based on antibody proteomics. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 2005, 4, 1920–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrah, T.; Deutsch, E.W.; Omenn, G.S.; Sun, Z.; Watts, J.D.; Yamamoto, T.; Shteynberg, D.; Harris, M.M.; Moritz, R.L. State of the Human Proteome in 2013 as Viewed through PeptideAtlas: Comparing the Kidney, Urine, and Plasma Proteomes for the Biology- and Disease-Driven Human Proteome Project. Journal of Proteome Research 2014, 13, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrah, T.; Deutsch, E.W.; Hoopmann, M.R.; Hallows, J.L.; Sun, Z.; Huang, C.Y.; Moritz, R.L. The State of the Human Proteome in 2012 as Viewed through PeptideAtlas. Journal of Proteome Research 2013, 12, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.J.; Ray, S.; Srivastava, S. The Quest of the Human Proteome and the Missing Proteins: Digging Deeper. Omics-a Journal of Integrative Biology 2015, 19, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Pinto, S.M.; Getnet, D.; Nirujogi, R.S.; Manda, S.S.; Chaerkady, R.; Madugundu, A.K.; Kelkar, D.S.; Isserlin, R.; Jain, S.; et al. A draft map of the human proteome. Nature 2014, 509, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uversky, V.N. p53 Proteoforms and Intrinsic Disorder: An Illustration of the Protein Structure-Function Continuum Concept. Int J Mol Sci 2016, 17, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uversky, V.N. Unusual biophysics of intrinsically disordered proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013, 1834, 932–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uversky, V.N. p53 Proteoforms and Intrinsic Disorder: An Illustration of the Protein Structure-Function Continuum Concept. Int J Mol Sci 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uversky, V.N. Protein intrinsic disorder and structure-function continuum. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 2019, 166, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uversky, V.N. Intrinsically disordered proteins and their “mysterious” (meta)physics. Frontiers in Physics 2019, 7, Article 10 (18 pages). [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N. Dancing Protein Clouds: The Strange Biology and Chaotic Physics of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. J Biol Chem 2016, 291, 6681–6688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N. Functional roles of transiently and intrinsically disordered regions within proteins. FEBS J 2015, 282, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonin, A.V.; Darling, A.L.; Kuznetsova, I.M.; Turoverov, K.K.; Uversky, V.N. Multi-functionality of proteins involved in GPCR and G protein signaling: making sense of structure-function continuum with intrinsic disorder-based proteoforms. Cell Mol Life Sci 2019, 76, 4461–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.N.; Uversky, V.N. Protein structure-function continuum model: Emerging nexuses between specificity, evolution, and structure. Protein Sci 2024, 33, e4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.; Leite, V.B.P.; Roy, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Mohanty, A.; Achuthan, S.; Singh, D.; Appadurai, R.; Rangarajan, G.; Weninger, K.; et al. Intrinsically disordered proteins: Ensembles at the limits of Anfinsen's dogma. Biophys Rev (Melville) 2022, 3, 011306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N. Functional unfoldomics: Roles of intrinsic disorder in protein (multi)functionality. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol 2024, 138, 179–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, S.B.; Trach, S.O. Estimation of macromolecule concentrations and excluded volume effects for the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 1991, 222, 599–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, B.; Ellis, R.J.; Dobson, C.M. Effects of macromolecular crowding on protein folding and aggregation. The EMBO journal 1999, 18, 6927–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, G.; Ferrone, F.; Herzfeld, J. Life in a crowded world. EMBO reports 2004, 5, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, R.J.; Minton, A.P. Cell biology: join the crowd. Nature 2003, 425, 27–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, S.B.; Minton, A.P. Macromolecular crowding: biochemical, biophysical, and physiological consequences. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1993, 22, 27–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulton, A.B. How crowded is the cytoplasm? Cell 1982, 30, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, A.P. Influence of excluded volume upon macromolecular structure and associations in 'crowded' media. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1997, 8, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, R.J. Macromolecular crowding: obvious but underappreciated. Trends Biochem Sci 2001, 26, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, A.P. Protein folding: Thickening the broth. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, R97–R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Used restrictions b | |
|---|---|
| Spatial nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE) restrictions | |
| Intra-residual (i-j = 0) | 491 |
| Sequential (|i-j| = 1) | 667 |
| Mid-range (1<|i-j|≤4) | 417 |
| Long-range (|i-j|≥5) | 965 |
| Total number of NOE restrictions | 2540 |
| Restrictions on dihedral angles | |
| Torsion angle (φ/ψ) | 102/103 |
| Restrictions on hydrogen bonds (upper/lower) | 40/40 |
| Restrictions on coordination links | |
| with Zn2+ ion in the active site (upper / lower) | 6/6 |
| with Ca2+ ion in the regulatory loop (upper / lower) | 6/6 |
| Violations of the NOE restrictions | |
| at distances >0.1Å | 46 |
| at distances >0.2Å | 8 |
| to dihedral angles >5° | 0 |
| RMSD (Å) in (residues 5-137) c | |
| main chain atoms | 0.52±0.27 |
| all heavy atoms | 0.96±0.21 |
| Ramachandran Map Analysis d | |
| % of residues in the most preferred regions | 76.3 |
| % of residues in additional allowed regions | 20.9 |
| % of residues in conditionally permitted regions | 2.8 |
| % of residues in prohibited regions | 0.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





