Submitted:
30 July 2024
Posted:
31 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
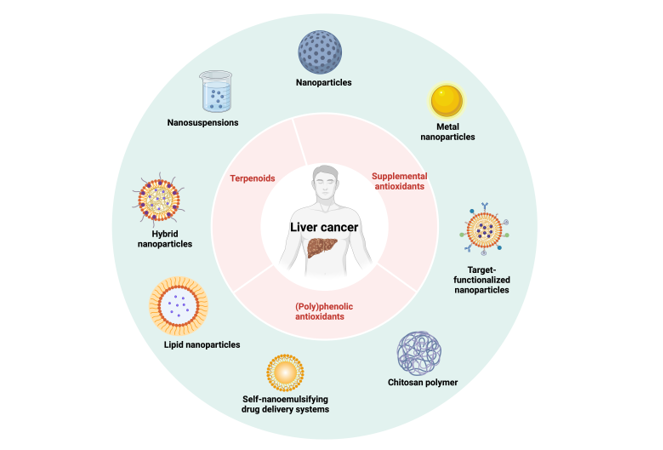
Keywords:
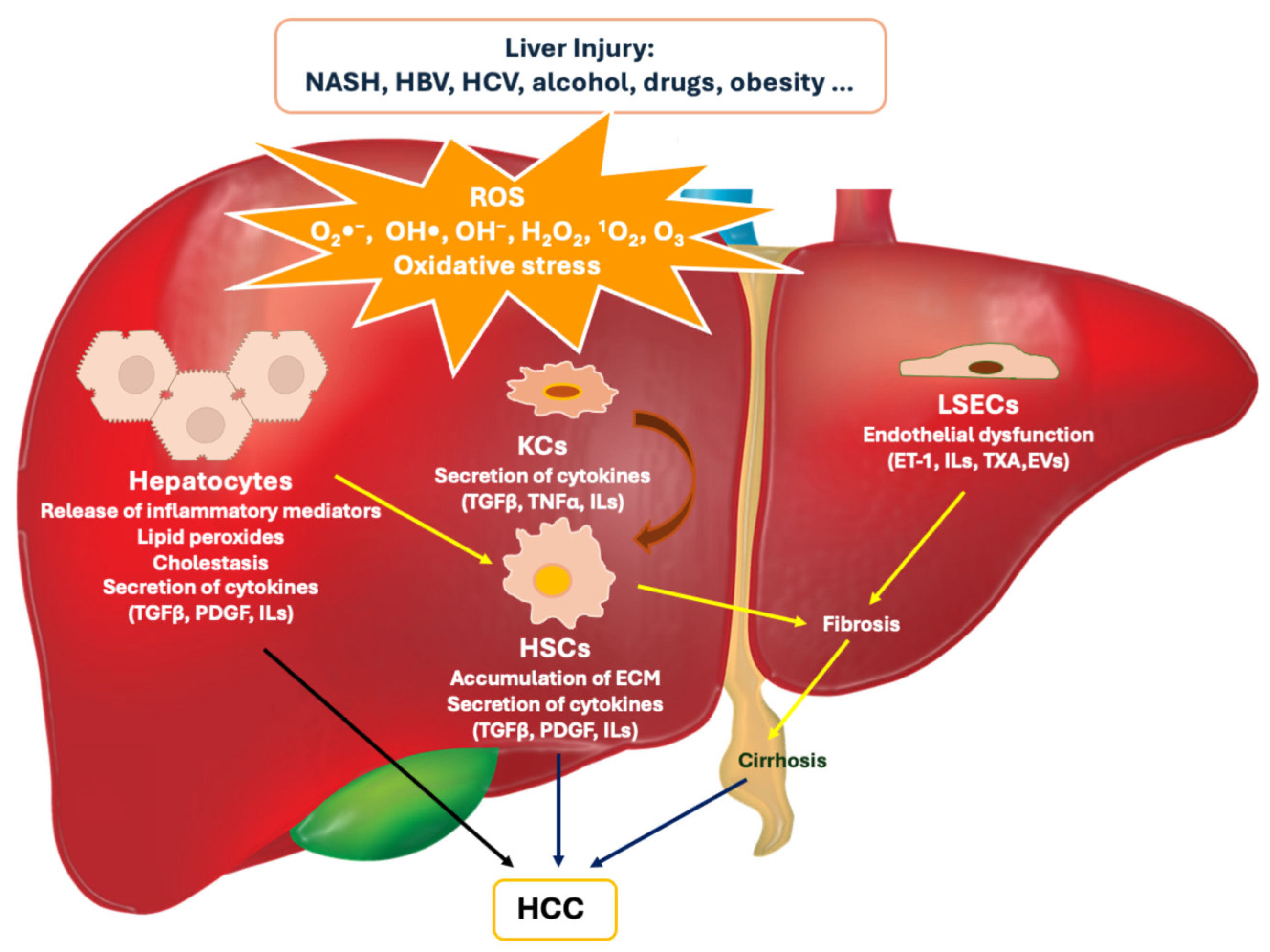
1. Introduction
2. Nano-Formulations Containing (Poly)Phenolic Antioxidants
3. Nano-Formulations Containing Terpenoid Antioxidants
4. Nano-Formulations Containing Supplemental Antioxidants
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oh, J.H.; Jun, D.W. The Latest Global Burden of Liver Cancer: A Past and Present Threat. Clin Mol Hepatol 2023, 29, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liver Cancer Statistics | World Cancer Research Fund International. WCRF International.
- Jiang, K.; Al-Diffalha, S.; Centeno, B.A. Primary Liver Cancers—Part 1: Histopathology, Differential Diagnoses, and Risk Stratification. Cancer Control 2018, 25, 107327481774462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Centeno, B.A. Primary Liver Cancers, Part 2: Progression Pathways and Carcinogenesis. Cancer Control 2018, 25, 107327481774465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilimigras, D.I.; Brodt, P.; Clavien, P.-A.; Muschel, R.J.; D’Angelica, M.I.; Endo, I.; Parks, R.W.; Doyle, M.; De Santibañes, E.; Pawlik, T.M. Liver Metastases. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, J.; Victor, D.; Asham, E.H.; Burroughs, S.G.; Boktour, M.; Saharia, A.; Li, X.; Ghobrial, M.; Monsour, H. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review. JHC 2016, Volume 3, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaranathan-Reghupaty, S.; Fisher, P.B.; Sarkar, D. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): Epidemiology, Etiology and Molecular Classification. In Advances in Cancer Research; Elsevier, 2021; Vol. 149, pp. 1–61 ISBN 978-0-12-824030-4.
- Bragazzi, M.C.; Venere, R.; Ribichini, E.; Covotta, F.; Cardinale, V.; Alvaro, D. Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Evolving Strategies in Management and Treatment. Digestive and Liver Disease 2024, 56, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlajoki, M.; Eloranta, K.; Nousiainen, R.; Väyrynen, V.; Soini, T.; Kyrönlahti, A.; Parkkila, S.; Kanerva, J.; Wilson, D.B.; Pakarinen, M.P.; et al. Biology of Childhood Hepatoblastoma and the Search for Novel Treatments. Advances in Biological Regulation 2024, 91, 100997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattovich, G.; Stroffolini, T.; Zagni, I.; Donato, F. Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhosis: Incidence and Risk Factors. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, S35–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, M.B.; Al Sbihi, A.; Chaudhary, A.J.; Haider, S.M.; Edhi, A.I. Heredity Hemochromatosis: Temporal Trends, Sociodemographic Characteristics, and Independent Risk Factor of Hepatocellular Cancer – Nationwide Population-Based Study. World J Hepatol 2022, 14, 1804–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Hajdu, C.H. Wilson Disease and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 2008, 4, 438–439. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Y.-J.; Yang, H.-I.; Wu, H.-C.; Lee, M.-H.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.-Y.; Lu, S.-N.; Jen, C.-L.; You, S.-L.; Santella, R.M.; et al. Aflatoxin B1 Exposure Increases the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Associated with Hepatitis C Virus Infection or Alcohol Consumption. European Journal of Cancer 2018, 94, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hino, K.; Yanatori, I.; Hara, Y.; Nishina, S. Iron and Liver Cancer: An Inseparable Connection. The FEBS Journal 2022, 289, 7810–7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machicado, C.; Machicado, J.D.; Maco, V.; Terashima, A.; Marcos, L.A. Association of Fasciola Hepatica Infection with Liver Fibrosis, Cirrhosis, and Cancer: A Systematic Review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2016, 10, e0004962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Ye, Y.; Xie, L.; Li, W. Oxidative Stress and Liver Cancer: Etiology and Therapeutic Targets. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liver Pathophysiology: Therapies and Antioxidants; Muriel, P. , Ed.; Academic Press, an imprint of Elsevier: London, United Kingdom, 2017; ISBN 978-0-12-804274-8. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Chung, F.-L. Oxidative Stress and Hepatocarcinogenesis. HR 2018, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, D.; Takaki, A.; Oyama, A.; Adachi, T.; Wada, N.; Onishi, H.; Okada, H. Oxidative Stress Management in Chronic Liver Diseases and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, S.M. Oxidative Stress in Hepatocarcinogenesis and Role of Antioxidant Therapy. In Handbook of Oxidative Stress in Cancer: Mechanistic Aspects; Chakraborti, S., Ray, B.K., Roychoudhury, S., Eds.; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2022; pp. 821–838. ISBN 9789811594106. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, R. Insights into the Role of Oxidative Stress in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed) 2023, 28, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allameh, A.; Niayesh-Mehr, R.; Aliarab, A.; Sebastiani, G.; Pantopoulos, K. Oxidative Stress in Liver Pathophysiology and Disease. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahma, M.K.; Gilglioni, E.H.; Zhou, L.; Trépo, E.; Chen, P.; Gurzov, E.N. Oxidative Stress in Obesity-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Sources, Signaling and Therapeutic Challenges. Oncogene 2021, 40, 5155–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, V.; Moliné, T.; Somoza, R.; Paciucci, R.; Kondoh, H.; LLeonart, M.E. Oxidative Stress and Cancer: An Overview. Ageing Research Reviews 2013, 12, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, A.J.P.O.; De Oliveira, J.C.P.L.; Da Silva Pontes, L.V.; De Souza Júnior, J.F.; Gonçalves, T.A.F.; Dantas, S.H.; De Almeida Feitosa, M.S.; Silva, A.O.; De Medeiros, I.A. ROS: Basic Concepts, Sources, Cellular Signaling, and Its Implications in Aging Pathways. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2022, 2022, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morry, J.; Ngamcherdtrakul, W.; Yantasee, W. Oxidative Stress in Cancer and Fibrosis: Opportunity for Therapeutic Intervention with Antioxidant Compounds, Enzymes, and Nanoparticles. Redox Biology 2017, 11, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arfin, S.; Jha, N.K.; Jha, S.K.; Kesari, K.K.; Ruokolainen, J.; Roychoudhury, S.; Rathi, B.; Kumar, D. Oxidative Stress in Cancer Cell Metabolism. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, C.; Jardim, J.K.B.; Zancanaro, V. Role of Antioxidants in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Integrative Review. RSD 2021, 10, e46310112028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zheng, J.; Li, S.; Li, H.-B. Dietary Natural Products for Prevention and Treatment of Liver Cancer. Nutrients 2016, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.B.; Lee, D.K.; Cheon, C.; Ribeiro, R.I.M.A.; Kim, B. Natural Products for Liver Cancer Treatment: From Traditional Medicine to Modern Drug Discovery. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, I.F.; Miranda, R.G.; Dorta, D.J.; Rolo, A.P.; Palmeira, C.M. Targeting Oxidative Stress with Polyphenols to Fight Liver Diseases. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrelli, M. Medicinal Plants. Plants 2021, 10, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lorenzo, C.; Colombo, F.; Biella, S.; Stockley, C.; Restani, P. Polyphenols and Human Health: The Role of Bioavailability. Nutrients 2021, 13, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J. Recent Advances on the Stability of Dietary Polyphenols. eFood 2022, 3, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanati, M.; Afshari, A.R.; Kesharwani, P.; Sukhorukov, V.N.; Sahebkar, A. Recent Trends in the Application of Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy: The Involvement of Oxidative Stress. Journal of Controlled Release 2022, 348, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, B.; Halim, S.A.; Farrukh, A.; Greish, Y.; Amin, A. Current Status of Nanomaterial-Based Treatment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2019, 116, 108852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escutia-Gutiérrez, R.; Sandoval-Rodríguez, A.; Zamudio-Ojeda, A.; Guevara-Martínez, S.J.; Armendáriz-Borunda, J. Advances of Nanotechnology in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. JCM 2023, 12, 6867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Su, D.; Shi, D.; Xiang, X. The Improving Strategies and Applications of Nanotechnology-Based Drugs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1272850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, I.; Yehye, W.A.; Etxeberria, A.E.; Alhadi, A.A.; Dezfooli, S.M.; Julkapli, N.B.M.; Basirun, W.J.; Seyfoddin, A. Nanoantioxidants: Recent Trends in Antioxidant Delivery Applications. Antioxidants 2019, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonda, A.; Zhao, N.; Shah, J.V.; Calvelli, H.R.; Kantamneni, H.; Francis, N.L.; Ganapathy, V. Engineering Tumor-Targeting Nanoparticles as Vehicles for Precision Nanomedicine. Med One 2019, 4, e190021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argenziano, M.; Arpicco, S.; Brusa, P.; Cavalli, R.; Chirio, D.; Dosio, F.; Gallarate, M.; Peira, E.; Stella, B.; Ugazio, E. Developing Actively Targeted Nanoparticles to Fight Cancer: Focus on Italian Research. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezgin-Bayindir, Z.; Losada-Barreiro, S.; Fernández-Bravo, S.; Bravo-Díaz, C. Innovative Delivery and Release Systems for Antioxidants and Other Active Substances in the Treatment of Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriagada, F.; Günther, G.; Nos, J.; Nonell, S.; Olea-Azar, C.; Morales, J. Antioxidant Nanomaterial Based on Core–Shell Silica Nanospheres with Surface-Bound Caffeic Acid: A Promising Vehicle for Oxidation-Sensitive Drugs. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micale, N.; Citarella, A.; Molonia, M.S.; Speciale, A.; Cimino, F.; Saija, A.; Cristani, M. Hydrogels for the Delivery of Plant-Derived (Poly)Phenols. Molecules 2020, 25, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.; Alhakamy, N.A.; Md, S.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Rizwanullah, Md.; Fatima, S.; Ahmed, N.; Alyazedi, F.M.; Karim, S.; Ahmad, J. Nanogels as Potential Delivery Vehicles in Improving the Therapeutic Efficacy of Phytopharmaceuticals. Polymers 2022, 14, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevanović, M.; Filipović, N. A Review of Recent Developments in Biopolymer Nano-Based Drug Delivery Systems with Antioxidative Properties: Insights into the Last Five Years. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awasthi, K.K.; John, P.J.; Awasthi, A.; Awasthi, K. Multi Walled Carbon Nano Tubes Induced Hepatotoxicity in Swiss Albino Mice. Micron 2013, 44, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noonan, D.M.; Principi, E.; Girardello, R.; Bruno, A.; Manni, I.; Gini, E.; Pagani, A.; Grimaldi, A.; Ivaldi, F.; Congiu, T.; et al. Systemic Distribution of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in a Novel Model: Alteration of Biochemical Parameters, Metabolic Functions, Liver Accumulation, and Inflammation in Vivo. IJN 2016, Volume 11, 4299–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Harpe, K.; Kondiah, P.; Choonara, Y.; Marimuthu, T.; Du Toit, L.; Pillay, V. The Hemocompatibility of Nanoparticles: A Review of Cell–Nanoparticle Interactions and Hemostasis. Cells 2019, 8, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, A.; Hedberg, J.; Blomberg, E.; Odnevall, I. Reactive Oxygen Species Formed by Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles in Physiological Media—A Review of Reactions of Importance to Nanotoxicity and Proposal for Categorization. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, Y.; Suminda, G.G.D.; Heo, Y.; Kim, M.; Ghosh, M.; Son, Y.-O. Metal-Based Nanoparticles and Their Relevant Consequences on Cytotoxicity Cascade and Induced Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Luan, J.; Chen, W.; Fan, J.; Nan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Meng, G.; Ju, D. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Induced Hepatotoxicity via NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Caspase-1-Dependent Pyroptosis. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 9141–9152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouey, B.; Boukholda, K.; Gargouri, B.; Bhatia, H.S.; Attaai, A.; Kebieche, M.; Bouchard, M.; Fetoui, H. Silica Nanoparticles Induce Hepatotoxicity by Triggering Oxidative Damage, Apoptosis, and Bax-Bcl2 Signaling Pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res 2022, 200, 1688–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulikemu, A.; Zhao, X.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Ma, R.; Yao, Q.; Wang, J.; Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, C. Silica Nanoparticles Aggravated the Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease through Disturbed Amino Acid and Lipid Metabolisms-Mediated Oxidative Stress. Redox Biology 2023, 59, 102569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, P.B.; Ha, S.E.; Vetrivel, P.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, G.S. Functions of Polyphenols and Its Anticancer Properties in Biomedical Research: A Narrative Review. Transl Cancer Res TCR 2020, 9, 7619–7631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duthie, G.; Crozier, A. Plant-Derived Phenolic Antioxidants: Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care 2000, 3, 447–451. 3. [CrossRef]
- Singla, R.K.; Dubey, A.K.; Garg, A.; Sharma, R.K.; Fiorino, M.; Ameen, S.M.; Haddad, M.A.; Al-Hiary, M. Natural Polyphenols: Chemical Classification, Definition of Classes, Subcategories, and Structures. j aoac int 2019, 102, 1397–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drago, L.; Ciprandi, G.; Brindisi, G.; Brunese, F.P.; Dinardo, G.; Gori, A.; Indolfi, C.; Naso, M.; Tondina, E.; Trincianti, C.; et al. Certainty and Uncertainty in the Biological Activities of Resveratrol. Food Frontiers 2024, 5, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, M.; Rizvi, A. The Pharmacological Properties of Red Grape Polyphenol Resveratrol: Clinical Trials and Obstacles in Drug Development. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micale, N.; Molonia, M.S.; Citarella, A.; Cimino, F.; Saija, A.; Cristani, M.; Speciale, A. Natural Product-Based Hybrids as Potential Candidates for the Treatment of Cancer: Focus on Curcumin and Resveratrol. Molecules 2021, 26, 4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosova, V.; Vesely, O.; Doskocil, I.; Tomisova, K.; Marsik, P.; Jaimes, J.D.; Smejkal, K.; Kloucek, P.; Havlik, J. Metabolism of Cis- and Trans-Resveratrol and Dihydroresveratrol in an Intestinal Epithelial Model. Nutrients 2020, 12, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarfraz, M.; Arafat, M.; Zaidi, S.H.H.; Eltaib, L.; Siddique, M.I.; Kamal, M.; Ali, A.; Asdaq, S.M.B.; Khan, A.; Aaghaz, S.; et al. Resveratrol-Laden Nano-Systems in the Cancer Environment: Views and Reviews. Cancers 2023, 15, 4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annaji, M.; Poudel, I.; Boddu, S.H.S.; Arnold, R.D.; Tiwari, A.K.; Babu, R.J. Resveratrol-loaded Nanomedicines for Cancer Applications. Cancer Reports 2021, 4, e1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
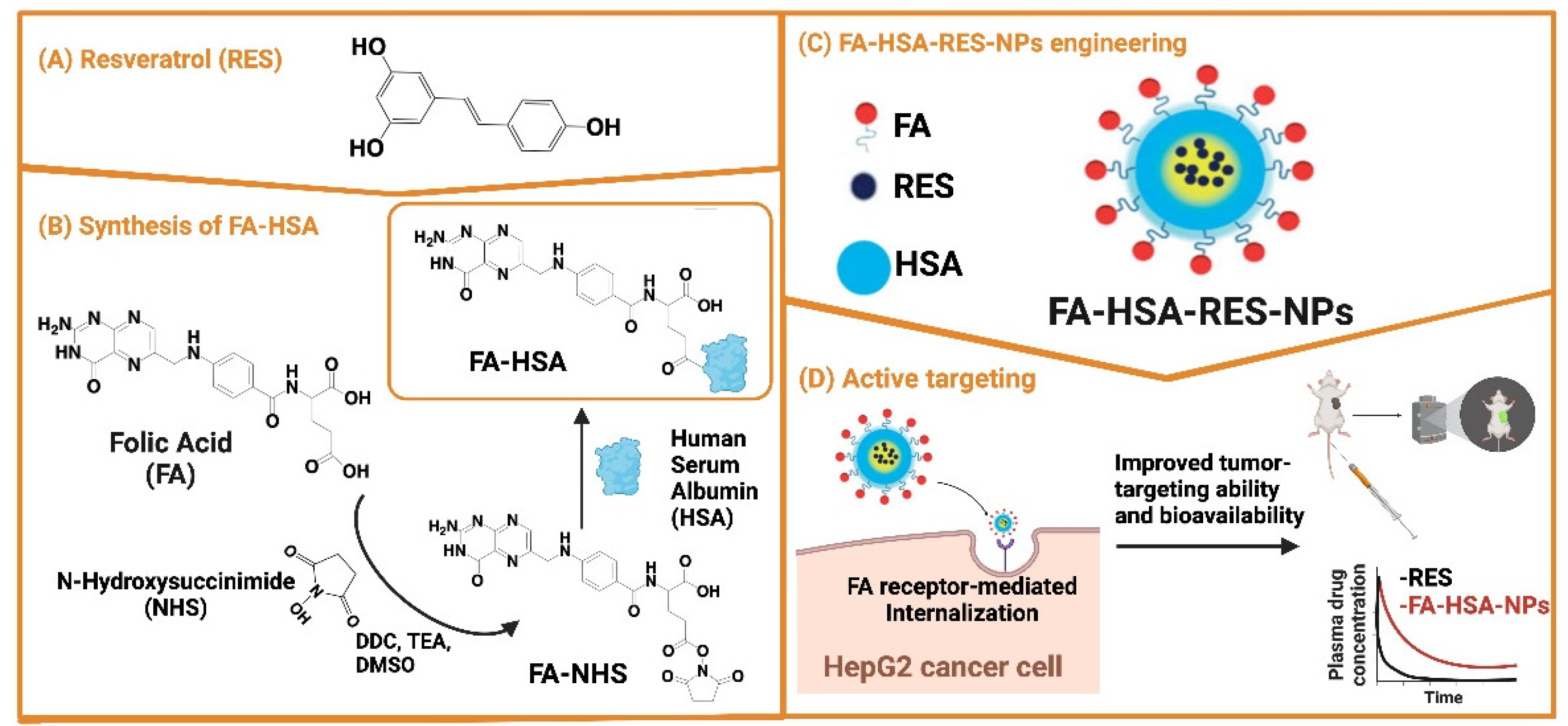
- Lian, B.; Wu, M.; Feng, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zhong, C.; Zhao, X. Folate-Conjugated Human Serum Albumin-Encapsulated Resveratrol Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization, Bioavailability and Targeting of Liver Tumors. Artificial Cells, Nanomedicine, and Biotechnology 2019, 47, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Lian, B.; Deng, Y.; Feng, Z.; Zhong, C.; Wu, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zu, C.; Zhao, X. Resveratrol-Loaded Glycyrrhizic Acid-Conjugated Human Serum Albumin Nanoparticles Wrapping Resveratrol Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization, and Targeting Effect on Liver Tumors. J Biomater Appl 2017, 32, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Cao, H.; Liu, P.; Cheng, G.; Sun, M. Glycyrrhizic Acid in the Treatment of Liver Diseases: Literature Review. BioMed Research International 2014, 2014, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Li, G.; Li, H.; Zhong, W.; Jiang, G.; Cai, J.; Xiong, Q.; Wu, C.; Su, K.; Huang, R.; et al. Glycyrrhetinic Acid as a Hepatocyte Targeting Ligand-Functionalized Platinum(IV) Complexes for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy and Overcoming Multidrug Resistance. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 8020–8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sheng, Z.; Xiao, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Jia, J.; Zeng, X.; Li, L. Advances in the Roles of Glycyrrhizic Acid in Cancer Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1265172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Wu, M.; Zeng, M.; Li, C.; Liu, F.; Liao, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, J. Development of Glycyrrhetinic Acid Ligand-Functionalized Liposomes for Targeting Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Synthesis, Preparation, Characterization, and Evaluation. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2023, 16, 105131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, J.; Li, Z.; Zuo, H.; Huang, C.; Zhao, X. Nano-Gold Loaded with Resveratrol Enhance the Anti-Hepatoma Effect of Resveratrol In Vitro and In Vivo. j biomed nanotechnol 2019, 15, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztandera, K.; Gorzkiewicz, M.; Klajnert-Maculewicz, B. Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Treatment. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2019, 16, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vines, J.B.; Yoon, J.-H.; Ryu, N.-E.; Lim, D.-J.; Park, H. Gold Nanoparticles for Photothermal Cancer Therapy. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urošević, M.; Nikolić, L.; Gajić, I.; Nikolić, V.; Dinić, A.; Miljković, V. Curcumin: Biological Activities and Modern Pharmaceutical Forms. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Rayess, Y.E.; Rizk, A.A.; Sadaka, C.; Zgheib, R.; Zam, W.; Sestito, S.; Rapposelli, S.; Neffe-Skocińska, K.; Zielińska, D.; et al. Turmeric and Its Major Compound Curcumin on Health: Bioactive Effects and Safety Profiles for Food, Pharmaceutical, Biotechnological and Medicinal Applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 01021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalraj, A.; Pius, A.; Gopi, S.; Gopi, S. Biological Activities of Curcuminoids, Other Biomolecules from Turmeric and Their Derivatives – A Review. Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine 2017, 7, 205–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Duan, W.; Xu, Q.; Li, X.; Han, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Z.; Lei, J. Curcumin Suppresses Hepatic Stellate Cell-Induced Hepatocarcinoma Angiogenesis and Invasion through Downregulating CTGF. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2019, 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Liao, L.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, X.; Zheng, P.; Guo, Y.; Deng, T.; Tian, X. Curcumin Inhibits the Growth of Liver Cancer by Impairing Myeloid-derived Suppressor Cells in Murine Tumor Tissues. Oncol Lett 2021, 21, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Bu, G. Curcumin Inhibits the Growth of Liver Cancer Stem Cells through the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Signaling Pathway. Exp Ther Med 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
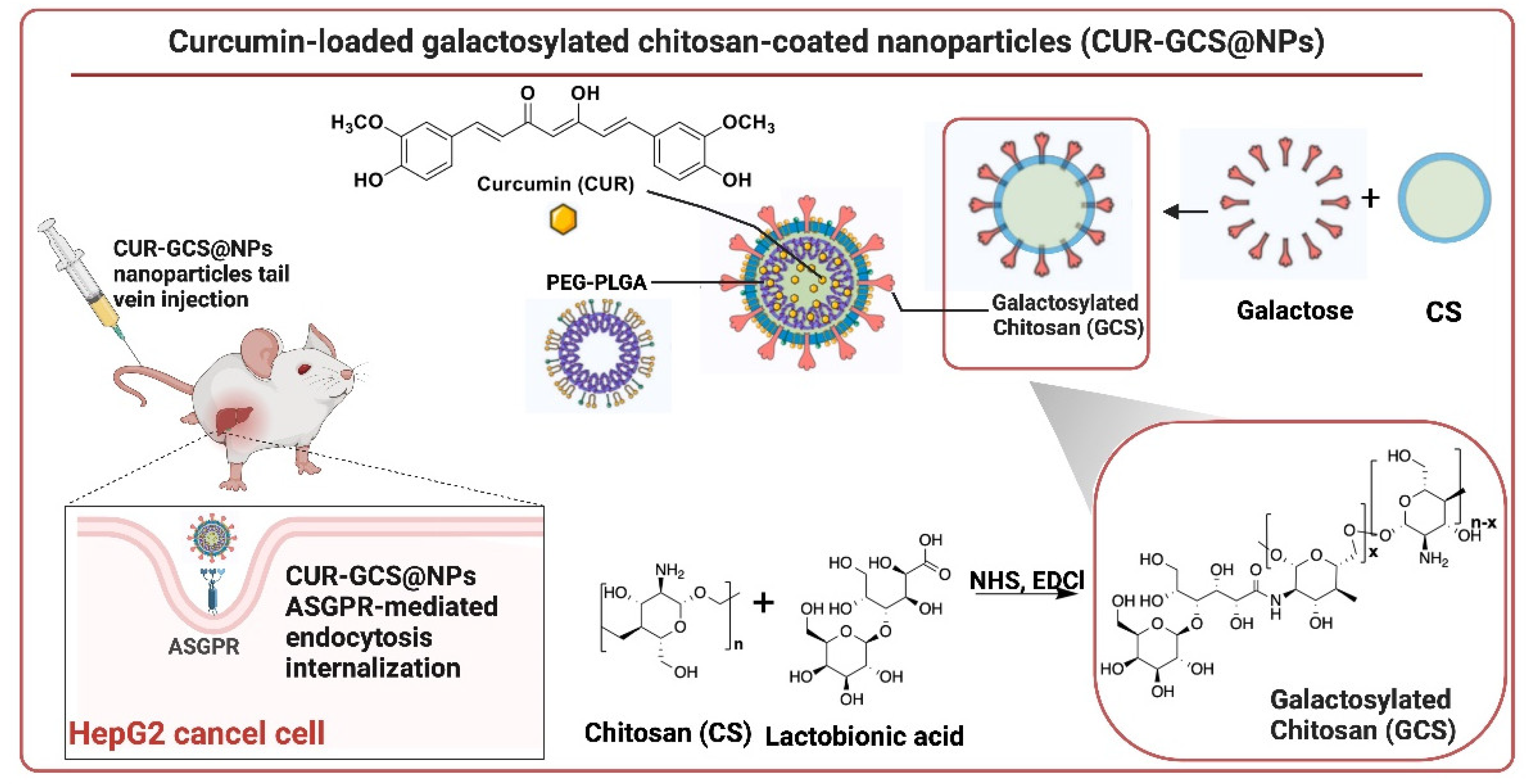
- Huang, M.; Liu, J.; Fan, Y.; Sun, J.; Cheng, J.-X.; Zhang, X.-F.; Zhai, B.-T.; Guo, D.-Y. Development of Curcumin-Loaded Galactosylated Chitosan-Coated Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2023, 253, 127219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaab, H.O.; Alharbi, F.D.; Alhibs, A.S.; Alanazi, N.B.; Alshehri, B.Y.; Saleh, M.A.; Alshehri, F.S.; Algarni, M.A.; Almugaiteeb, T.; Uddin, M.N.; et al. PLGA-Based Nanomedicine: History of Advancement and Development in Clinical Applications of Multiple Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, M.; Tang, S.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Peng, H.; Wang, Q. Effects of Polyethylene Glycol on the Surface of Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 10748–10764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, B.; Abrams, M.; Sepp-Lorenzino, L. Expression of Asialoglycoprotein Receptor 1 in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J Histochem Cytochem. 2013, 61, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anter, H.M.; Aman, R.M.; Othman, D.I.A.; Elamin, K.M.; Hashim, I.I.A.; Meshali, M.M. Apocynin-Loaded PLGA Nanomedicine Tailored with Galactosylated Chitosan Intrigue Asialoglycoprotein Receptor in Hepatic Carcinoma: Prospective Targeted Therapy. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2023, 631, 122536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savla, S.R.; Laddha, A.P.; Kulkarni, Y.A. Pharmacology of Apocynin: A Natural Acetophenone. Drug Metabolism Reviews 2021, 53, 542–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshtam, M.; Kouhpayeh, S.; Amini, F.; Azizi, Y.; Najaflu, M.; Shariati, L.; Khanahmad, H. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Apocynin: A Narrative Review of the Evidence. All Life 2021, 14, 997–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hu, L.; Huang, S.; Xu, W.; Wan, J.; Wang, D.; Zheng, G.; Xia, Z. Curcumin-Loaded Galactosylated BSA Nanoparticles as Targeted Drug Delivery Carriers Inhibit Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Proliferation and Migration. IJN 2018, Volume 13, 8309–8323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiu, B.; Assenat, E. Doxorubicin for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: GAME OVER! Ann Transl Med 2020, 8, 1693–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Tang, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, X. Doxorubicin and Curcumin Co-Delivery by Lipid Nanoparticles for Enhanced Treatment of Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Mice. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 2015, 93, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbinta-Patrascu, M.-E.; Gorshkova, Y.; Ungureanu, C.; Badea, N.; Bokuchava, G.; Lazea-Stoyanova, A.; Bacalum, M.; Zhigunov, A.; Petrovic, S. Characterization and Antitumoral Activity of Biohybrids Based on Turmeric and Silver/Silver Chloride Nanoparticles. Materials 2021, 14, 4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwahab, T.; Abdelhamed, R.; Ali, E.; Mansour, N.; Abdalla, M. Evaluation of Silver Nanoparticles Caffeic Acid Complex Compound as New Potential Therapeutic Agent against Cancer Incidence in Mice. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2021, 22, 3189–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espíndola, K.M.M.; Ferreira, R.G.; Narvaez, L.E.M.; Silva Rosario, A.C.R.; Da Silva, A.H.M.; Silva, A.G.B.; Vieira, A.P.O.; Monteiro, M.C. Chemical and Pharmacological Aspects of Caffeic Acid and Its Activity in Hepatocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Munir, S.; Badshah, S.L.; Khan, N.; Ghani, L.; Poulson, B.G.; Emwas, A.-H.; Jaremko, M. Important Flavonoids and Their Role as a Therapeutic Agent. Molecules 2020, 25, 5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand David, A.; Arulmoli, R.; Parasuraman, S. Overviews of Biological Importance of Quercetin: A Bioactive Flavonoid. Phcog Rev 2016, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishayee, K.; Khuda-Bukhsh, A.R.; Huh, S.-O. PLGA-Loaded Gold-Nanoparticles Precipitated with Quercetin Downregulate HDAC-Akt Activities Controlling Proliferation and Activate P53-ROS Crosstalk to Induce Apoptosis in Hepatocarcinoma Cells. Molecules and Cells 2015, 38, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.-W.; Li, Y.-H.; Wu, G.; Ren, J.-Z.; Lu, H.-B.; Li, Z.-M.; Han, X.-W. Quercetin Nanoparticles Display Antitumor Activity via Proliferation Inhibition and Apoptosis Induction in Liver Cancer Cells. International Journal of Oncology 2017, 50, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Dong, H.; Wang, W.; Xing, B.; Liu, X. Comparison of Flavonoid O-Glycoside, C-Glycoside and Their Aglycones on Antioxidant Capacity and Metabolism during In Vitro Digestion and In Vivo. Foods 2022, 11, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, P.; Rahman, M.; Bhatt, P.C.; Beg, S.; Paul, B.; Hafeez, A.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Nadeem, M.S.; Baothman, O.; Anwar, F.; et al. Implication of Nano-Antioxidant Therapy for Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using PLGA Nanoparticles of Rutin. Nanomedicine (Lond.) 2018, 13, 849–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gokuladhas, K.; Jayakumar, S.; Rajan, B.; Elamaran, R.; Pramila, C.S.; Gopikrishnan, M.; Tamilarasi, S.; Devaki, T. Exploring the Potential Role of Chemopreventive Agent, Hesperetin Conjugated Pegylated Gold Nanoparticles in Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Male Wistar Albino Rats. Ind J Clin Biochem 2016, 31, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.P.; Lee, W.L.; Tang, Y.Q.; Yap, W.H. Honokiol: A Review of Its Anticancer Potential and Mechanisms. Cancers 2019, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banik, K.; Ranaware, A.M.; Deshpande, V.; Nalawade, S.P.; Padmavathi, G.; Bordoloi, D.; Sailo, B.L.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Fan, L.; Arfuso, F.; et al. Honokiol for Cancer Therapeutics: A Traditional Medicine That Can Modulate Multiple Oncogenic Targets. Pharmacological Research 2019, 144, 192–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, P.; Sun, Q.; Yang, H.; Tang, B.; Pu, H.; Li, H. Honokiol Nanoparticles Based on Epigallocatechin Gallate Functionalized Chitin to Enhance Therapeutic Effects against Liver Cancer. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2018, 545, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piekarska, K.; Sikora, M.; Owczarek, M.; Jóźwik-Pruska, J.; Wiśniewska-Wrona, M. Chitin and Chitosan as Polymers of the Future—Obtaining, Modification, Life Cycle Assessment and Main Directions of Application. Polymers 2023, 15, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Bhatt, P.; Rahman, M.; Kaithwas, G.; Choudhry, H.; Al-Abbasi, F.; Anwar, F.; Verma, A. Fabrication, Optimization, and Characterization of Umbelliferone β-D-Galactopyranoside-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles in Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. IJN 2017, Volume 12, 6747–6758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.-M.; Hu, D.-H.; Zhang, J.-J. Umbelliferone Exhibits Anticancer Activity via the Induction of Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in HepG2 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Molecular Medicine Reports 2015, 12, 3869–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, S.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X. Advances in Pharmacological Activities of Terpenoids. Natural Product Communications 2020, 15, 1934578X2090355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, S.; Sinniah, A.; Abdulghani, M.A.M.; Alshawsh, M.A. Therapeutic Potential of Certain Terpenoids as Anticancer Agents: A Scoping Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikanth, P.; Maxton, A.; Masih, S.A.; Sofo, A.; Khan, N.A. Isoprene: An Antioxidant to Guard Plants against Stress. IJPB 2024, 15, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollastri, S.; Baccelli, I.; Loreto, F. Isoprene: An Antioxidant Itself or a Molecule with Multiple Regulatory Functions in Plants? Antioxidants 2021, 10, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoppil, R.J. Terpenoids as Potential Chemopreventive and Therapeutic Agents in Liver Cancer. WJH 2011, 3, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, N.P.; Rawal, U.M.; Patel, B.P. Hepatoprotective Effect of Andrographolide Against Hexachlorocyclohexane-Induced Oxidative Injury. Integr Cancer Ther 2007, 6, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Pradhan, G.K.; Das, S.; Nath, D.; Das Saha, K. Enhanced Protective Activity of Nano Formulated Andrographolide against Arsenic Induced Liver Damage. Chemico-Biological Interactions 2015, 242, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.W.; Zhao, P.; Khan, A.; Raza, F.; Raza, S.M.; Sarfraz, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, T.; Ma, X.; et al. Synergism of Cisplatin-Oleanolic Acid Co-Loaded Calcium Carbonate Nanoparticles on Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells for Enhanced Apoptosis and Reduced Hepatotoxicity. IJN 2019, Volume 14, 3753–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Xu, S.; Shi, F.; Klaassen, C.D. Oleanolic Acid Reprograms the Liver to Protect against Hepatotoxicants, but Is Hepatotoxic at High Doses. Liver International 2019, 39, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.-Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.-T.; Ma, X.-D.; Tang, Z.-Y. Anticancer Activity of Oleanolic Acid and Its Derivatives: Recent Advances in Evidence, Target Profiling and Mechanisms of Action. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2022, 145, 112397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, M.; Afzal, A.; Raza, S.M.; Bashir, S.; Madni, A.; Khan, M.W.; Ma, X.; Xiang, G. Liposomal Co-Delivered Oleanolic Acid Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Multi-Organ Toxicity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 47136–47153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Žiberna, L.; Šamec, D.; Mocan, A.; Nabavi, S.; Bishayee, A.; Farooqi, A.; Sureda, A.; Nabavi, S. Oleanolic Acid Alters Multiple Cell Signaling Pathways: Implication in Cancer Prevention and Therapy. IJMS 2017, 18, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Gao, M.; Xu, H.; Liu, K.-X.; Zhang, C.-H.; Jiang, N.; Chu, Q.-C.; Guan, X.; Tian, Y. A Novel Oleanolic Acid-Loaded PLGA-TPGS Nanoparticle for Liver Cancer Treatment. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy 2015, 41, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumbhar, P.S.; Nadaf, S.; Manjappa, A.S.; Jha, N.K.; Shinde, S.S.; Chopade, S.S.; Shete, A.S.; Disouza, J.I.; Sambamoorthy, U.; Kumar, S.A. D-ɑ-Tocopheryl Polyethylene Glycol Succinate: A Review of Multifarious Applications in Nanomedicines. OpenNano 2022, 6, 100036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dintaman, J.M.; Silverman, J.A. Inhibition of P-Glycoprotein by D-Alpha-Tocopheryl Polyethylene Glycol 1000 Succinate (TPGS). Pharmaceutical Research 1999, 16, 1550–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sztiller-Sikorska, M.; Czyz, M. Parthenolide as Cooperating Agent for Anti-Cancer Treatment of Various Malignancies. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrani, H.M.H.; Ghobeh, M.; Homayouni Tabrizi, M. The Anticancer, Anti-Oxidant, and Antibacterial Activities of Chitosan-Lecithin-Coated Parthenolide/Tyrosol Hybrid Nanoparticles. Journal of Biomaterials Science, Polymer Edition 2023, 34, 1603–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covas, M.I.; Miró-Casas, E.; Fitó, M.; Farré-Albadalejo, M.; Gimeno, E.; Marrugat, J.; De La Torre, R. Bioavailability of Tyrosol, an Antioxidant Phenolic Compound Present in Wine and Olive Oil, in Humans. Drugs Exp Clin Res 2003, 29, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Padayatty, S.J.; Katz, A.; Wang, Y.; Eck, P.; Kwon, O.; Lee, J.-H.; Chen, S.; Corpe, C.; Dutta, A.; Dutta, S.K.; et al. Vitamin C as an Antioxidant: Evaluation of Its Role in Disease Prevention. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 2003, 22, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traber, M.; Packer, L. Vitamin E: Beyond Antioxidant Function. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1995, 62, 1501S–1509S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljuhr, S.A.; Abdelaziz, G.; Essa, B.M.; Zaghary, W.A.; Sakr, T.M. Hepatoprotective, Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Potentials of Vit-E/C@SeNPs in Rats: Synthesis, Characterization, Biochemical, Radio-Biodistribution, Molecular and Histopathological Studies. Bioorganic Chemistry 2021, 117, 105412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinggi, U. Selenium: Its Role as Antioxidant in Human Health. Environ Health Prev Med 2008, 13, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, T.M.; Korany, M.; Katti, K.V. Selenium Nanomaterials in Biomedicine—An Overview of New Opportunities in Nanomedicine of Selenium. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 2018, 46, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tupal, A.; Sabzichi, M.; Bazzaz, R.; Fathi Maroufi, N.; Mohammadi, M.; Pirouzpanah, S.M.; Ramezani, F. Application of Ɑ-Tocotrienol-Loaded Biocompatible Precirol in Attenuation of Doxorubicin Dose-Dependent Behavior in HUH-7 Hepatocarcinoma Cell Line. Nutrition and Cancer 2020, 72, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- German-Cortés, J.; Vilar-Hernández, M.; Rafael, D.; Abasolo, I.; Andrade, F. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Multitasking Nano-Carriers for Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantle, D.; Lopez-Lluch, G.; Hargreaves, I.P. Coenzyme Q10 Metabolism: A Review of Unresolved Issues. IJMS 2023, 24, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eftekhari, A.; Ahmadian, E.; Azami, A.; Johari-Ahar, M.; Eghbal, M.A. Protective Effects of Coenzyme Q10 Nanoparticles on Dichlorvos-induced Hepatotoxicity and Mitochondrial/Lysosomal Injury. Environmental Toxicology 2018, 33, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quagliariello, V.; Vecchione, R.; De Capua, A.; Lagreca, E.; Iaffaioli, R.V.; Botti, G.; Netti, P.A.; Maurea, N. Nano-Encapsulation of Coenzyme Q10 in Secondary and Tertiary Nano-Emulsions for Enhanced Cardioprotection and Hepatoprotection in Human Cardiomyocytes and Hepatocytes During Exposure to Anthracyclines and Trastuzumab. IJN 2020, Volume 15, 4859–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonin, D.; Pochkaeva, E.; Zhuravskii, S.; Postnov, V.; Korolev, D.; Vasina, L.; Kostina, D.; Mukhametdinova, D.; Zelinskaya, I.; Skorik, Y.; et al. Biological Safety and Biodistribution of Chitosan Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, A.R.; Racine, R.R.; Hennig, M.J.P.; Lokeshwar, V.B. The Role of CD44 in Disease Pathophysiology and Targeted Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, M.; Baker, K.; Postovit, L.; Field, C. A Critical Review on the Effect of Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA) on Cancer Cell Cycle Progression. IJMS 2017, 18, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Freitas Rodrigues, J.; Philippsen, H.K.; Dolabela, M.F.; Nagamachi, C.Y.; Pieczarka, J.C. The Potential of DHA as Cancer Therapy Strategies: A Narrative Review of In Vitro Cytotoxicity Trials. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, L.; Mulik, R.S.; Wen, X.; Dilip, A.; Corbin, I.R. Low-Density Lipoprotein-Mediated Delivery of Docosahexaenoic Acid Selectively Kills Murine Liver Cancer Cells. Nanomedicine (Lond.) 2014, 9, 2123–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, L.R.; Mulik, R.S.; Van Treuren, T.; Kim, S.Y.; Corbin, I.R. Investigation into the Distinct Subcellular Effects of Docosahexaenoic Acid Loaded Low-Density Lipoprotein Nanoparticles in Normal and Malignant Murine Liver Cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects 2016, 1860, 2363–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
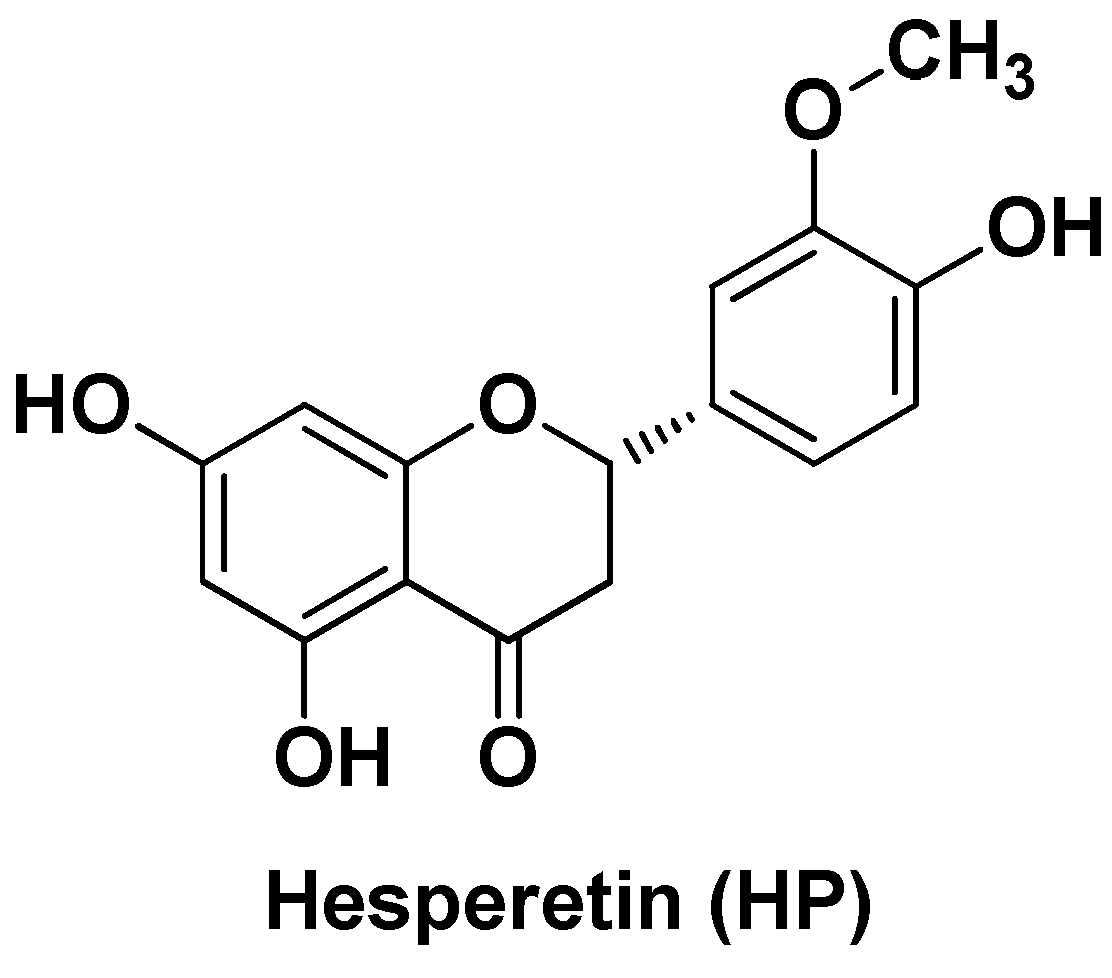
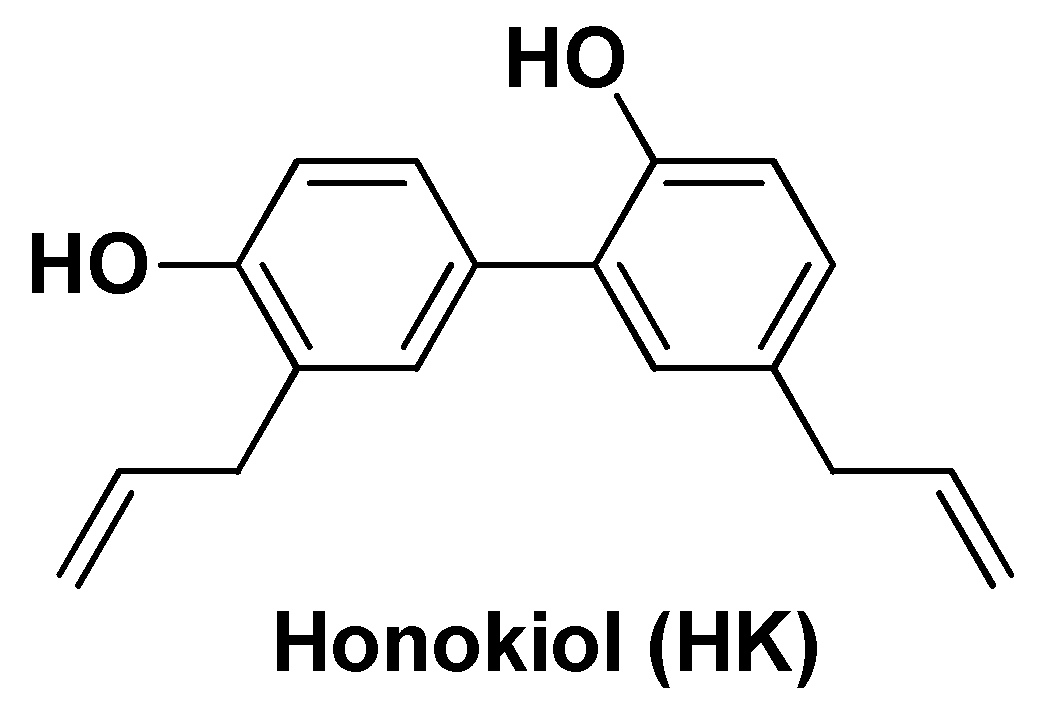
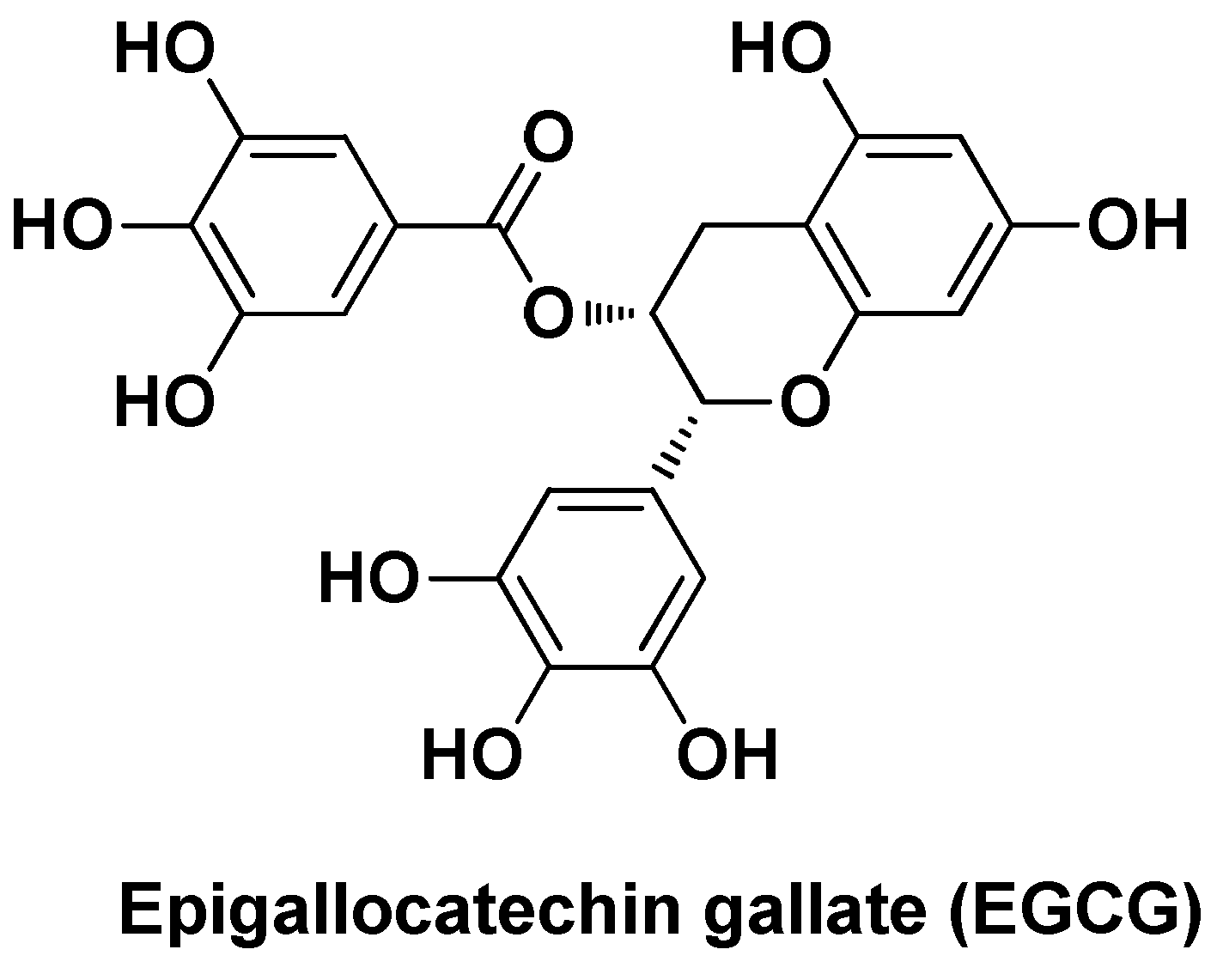
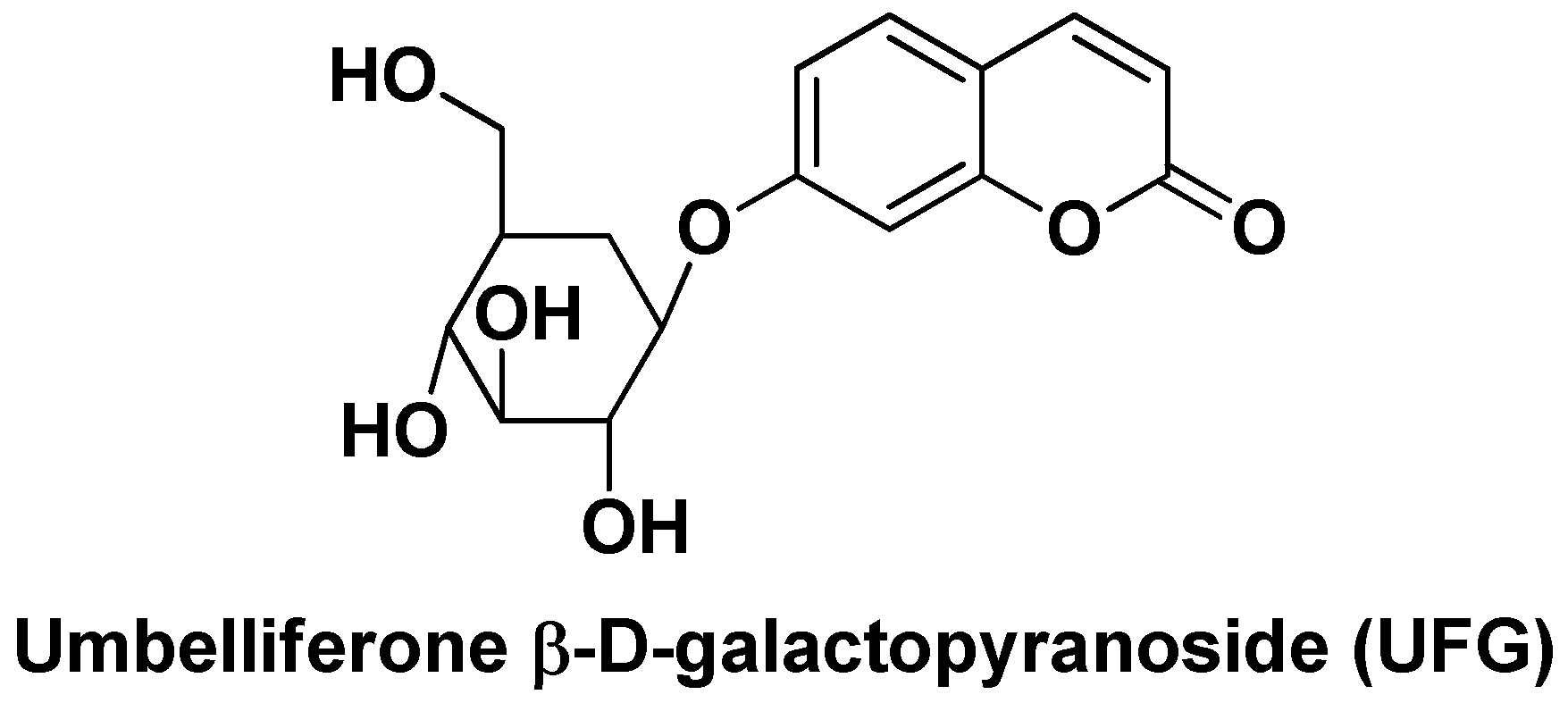
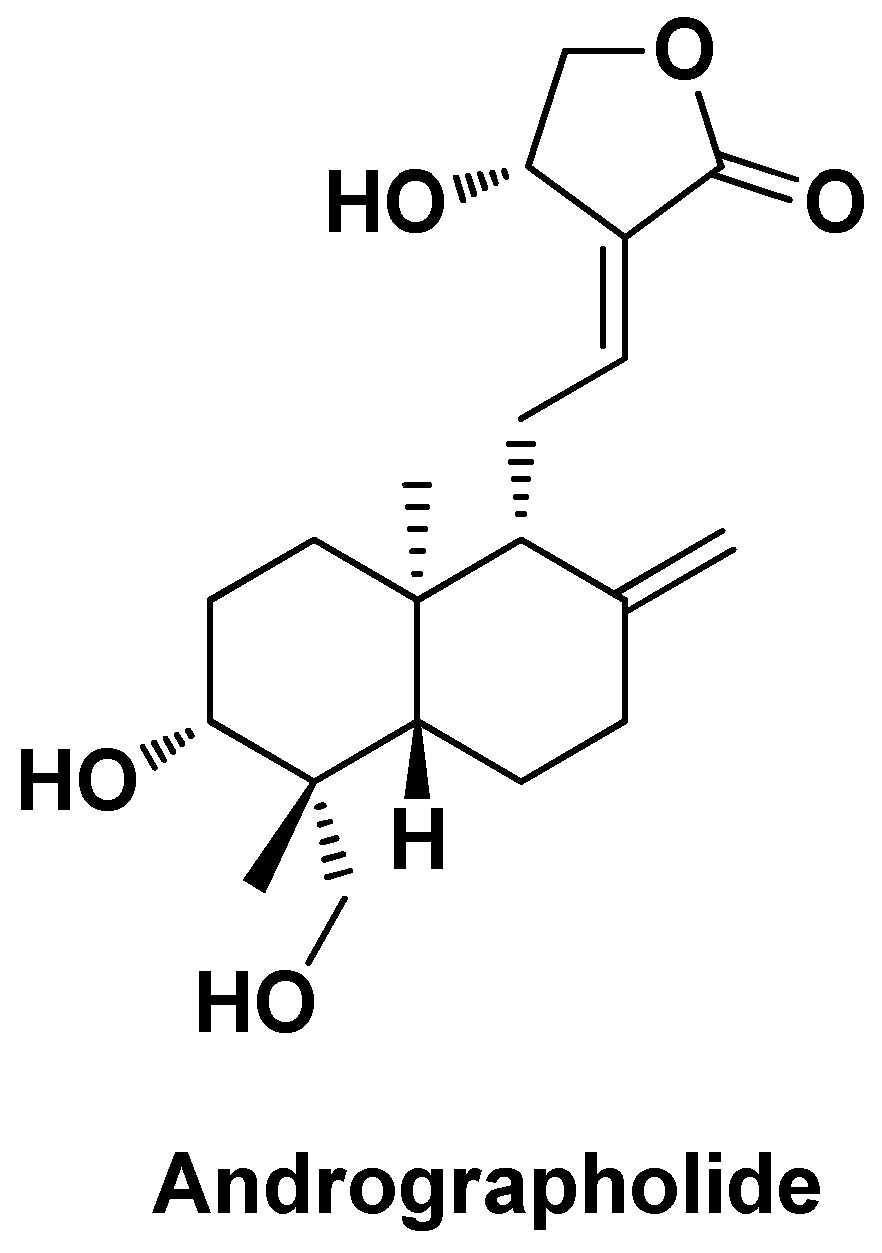
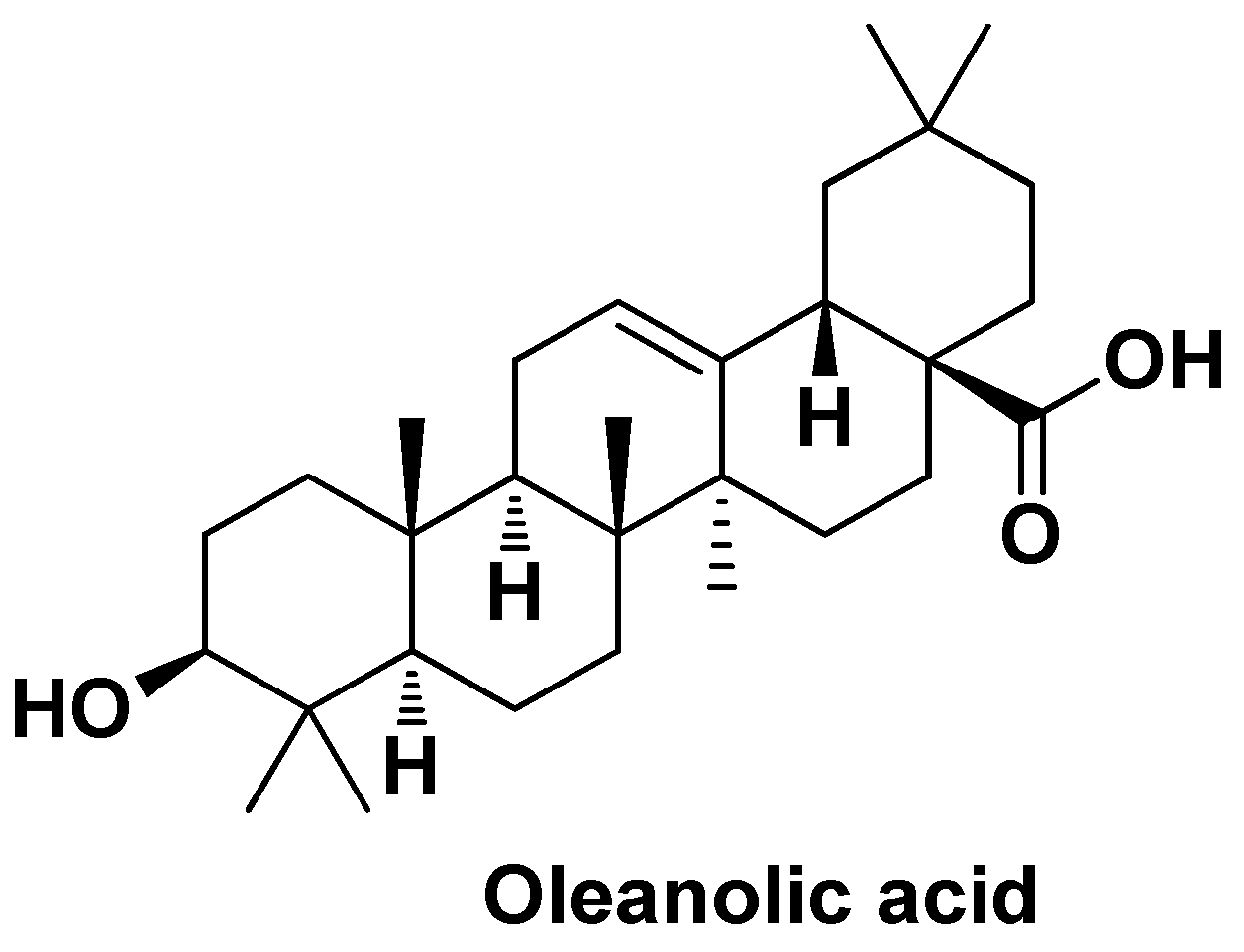
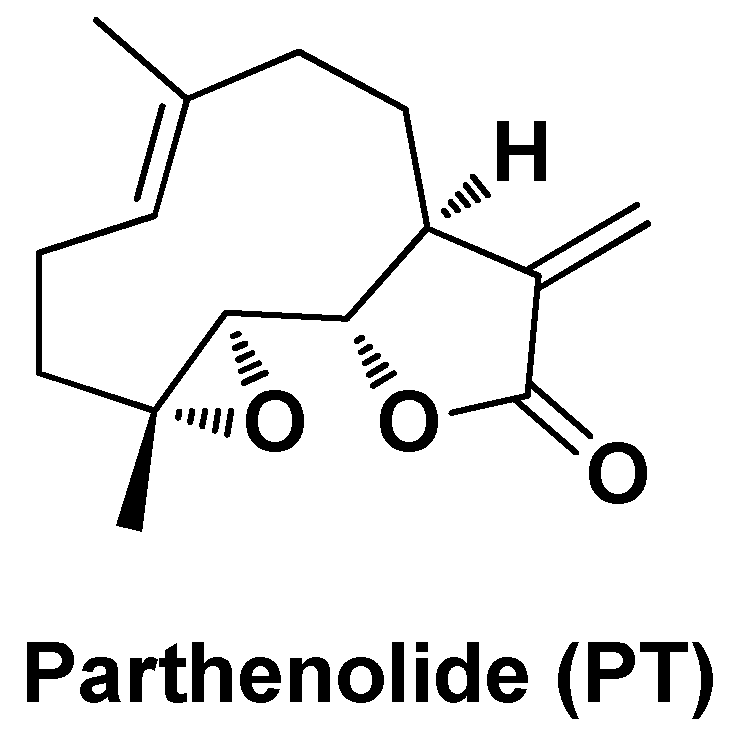
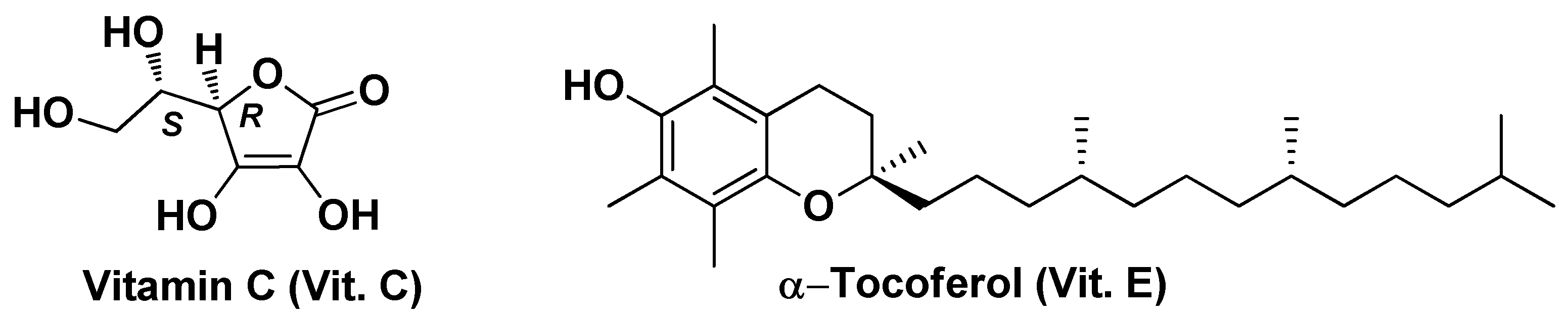
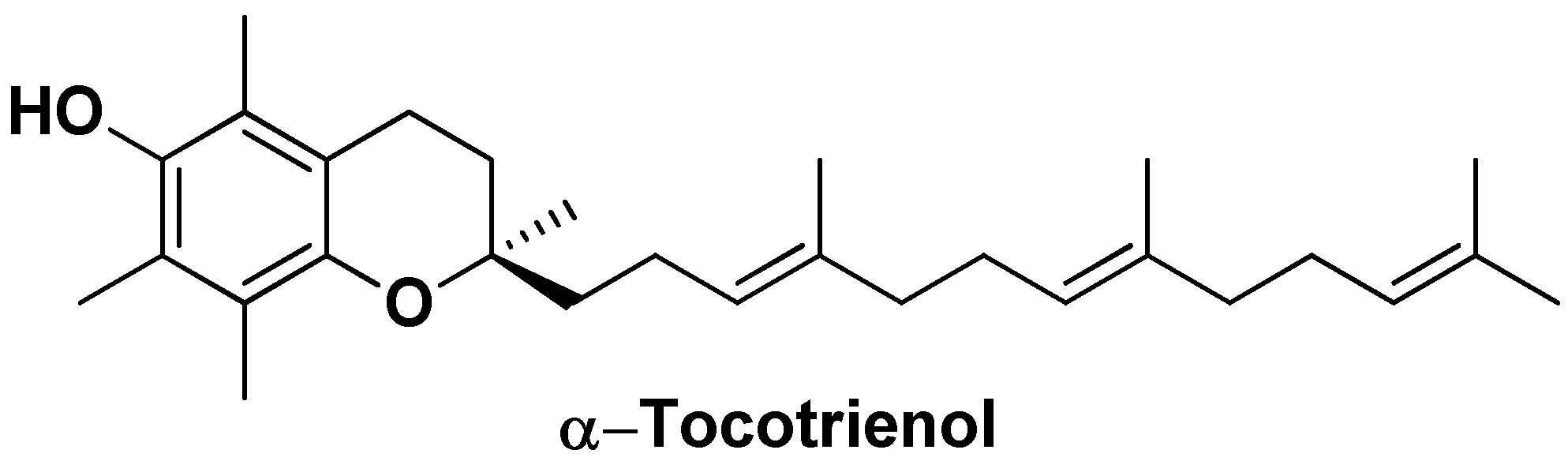
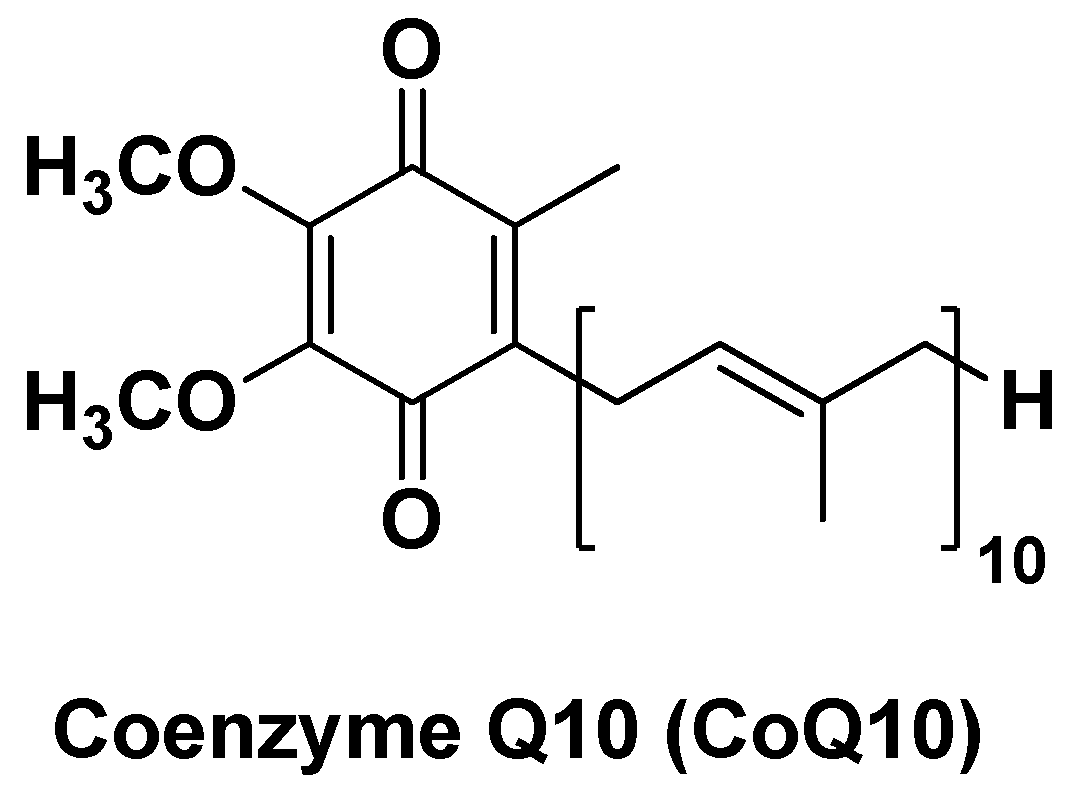
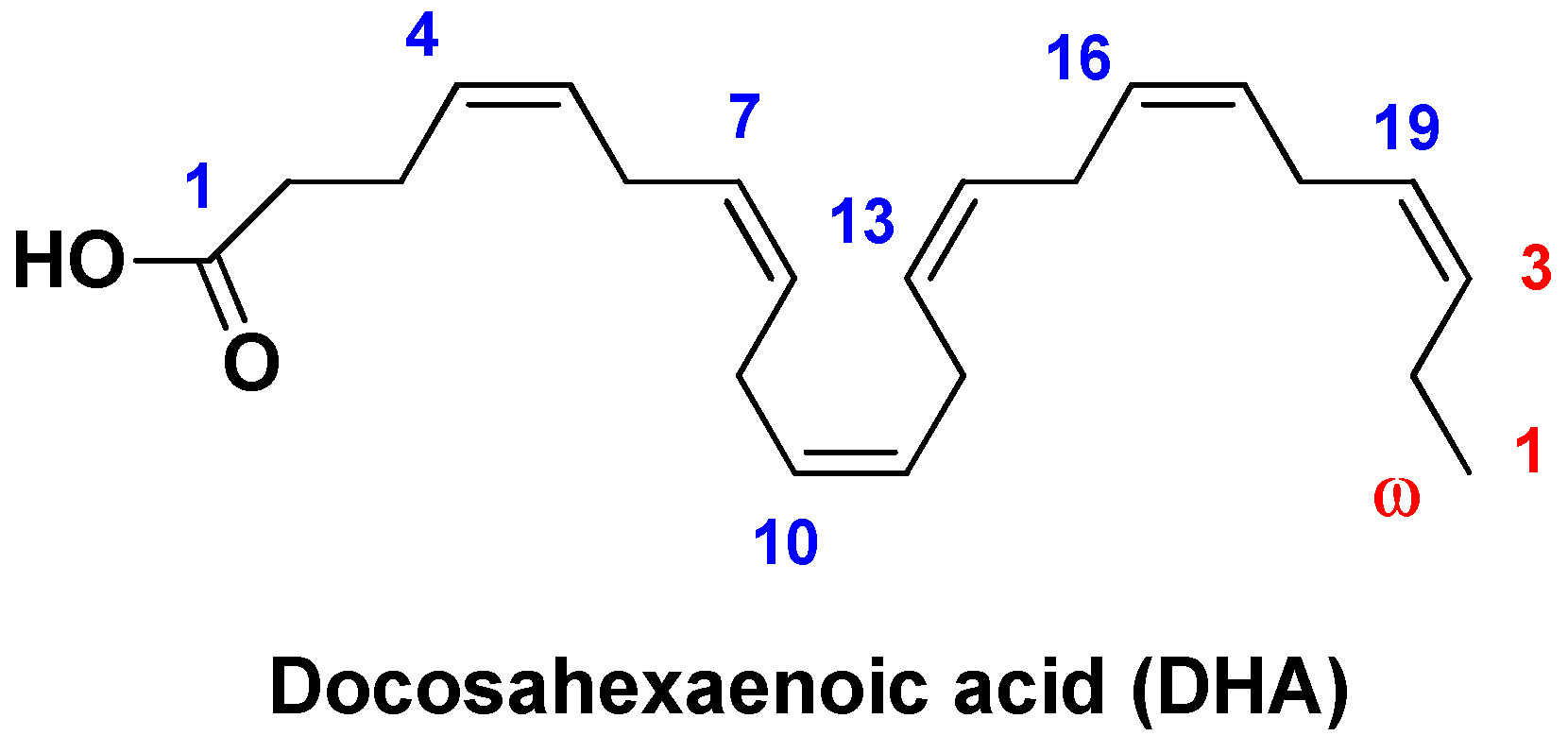
| Nano-formulation | API | Excipients | Physical characteristics | Biological Activity | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FA-HSA-RES-NPs | Resveratrol | Folic acid, human serum albumin | Spherical shape (~102 nm), high EE (~98%) and DL (~15%) | Enhanced cell uptake and antiproliferative activity in vitro and improved biodistribution | [64] | |||
| GA-HSA-RES-NPs | Resveratrol | Glycyrrhizic acid, human serum albumin | Nearly spherical (~108 nm), high EE (83.6%) and DL (11.5%) | Enhanced antiproliferative activity in HepG2 cells and better biodistribution via EPR effect and ASGPR-mediated endocytosis | [65] | |||
| RES-AuNPs | Resveratrol | Gold nanoparticles | Spherical shape (~39-1110 nm) and zeta potential (ζ) = -32.5 mV | Stronger apoptosis induction via down-regulation of pro-caspase-9, pro-caspse-8, PI3K and Akt and up-regulation of caspase-8 and Bax, tumor growth suppression. | [70] | |||
| CUR-GCS@NPs | Curcumin | PLGA-PEG, galactosylated chitosan | Particle size ~100 nm, EE = ~94%, DL = 4.56%, ζ = -9.82 mV, Polydispersity index (PDI) = 0.25 | Targeted delivery to liver tumor tissues, enhanced biocompatibility | [79] | |||
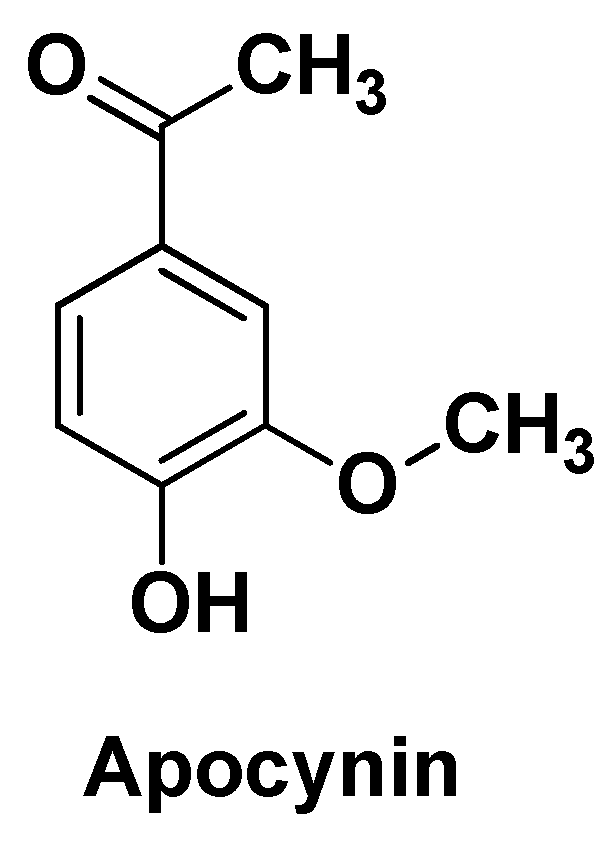
| APO-GCS@NPs | Apocynin | PEG-PLGA, galactosylated chitosan | Particle size 224-232 nm, EE = 34%, pH-dependent drug release (31-60% after 72h) | Significant improvement in antiproliferative activity against HepG2 cells | [83] | |||
| CUR-G-BSA-NPs | Curcumin | bovine serum albumin, galactosyl units | Spherical shape (~116 nm), high drug release rate | Better antiproliferative activity against HepG2 cells (~5,6-fold compared to the free drug) | [86] | |||
| Dox/CUR-NPs | Doxorubicin, Curcumin | Glyceril distearate, soybean lecithin, Polyoxyl 40 Hydrogenated Castor Oil, glycerin, triglycerides medium chain | Spherical shape (~89 nm), high EE (Dox = 97.1% and CUR = 99.8%), ζ = -14.3 mV, PDI = 0.22, sustained release profile (Dox = 55% and CUR = 40% after 48 h) | Synergistic antiproliferative effects in HCC models, modulation on apoptosis, proliferation-, angiogenesis-, MDR- and hypoxia-related mRNAs and proteins | [88] | |||
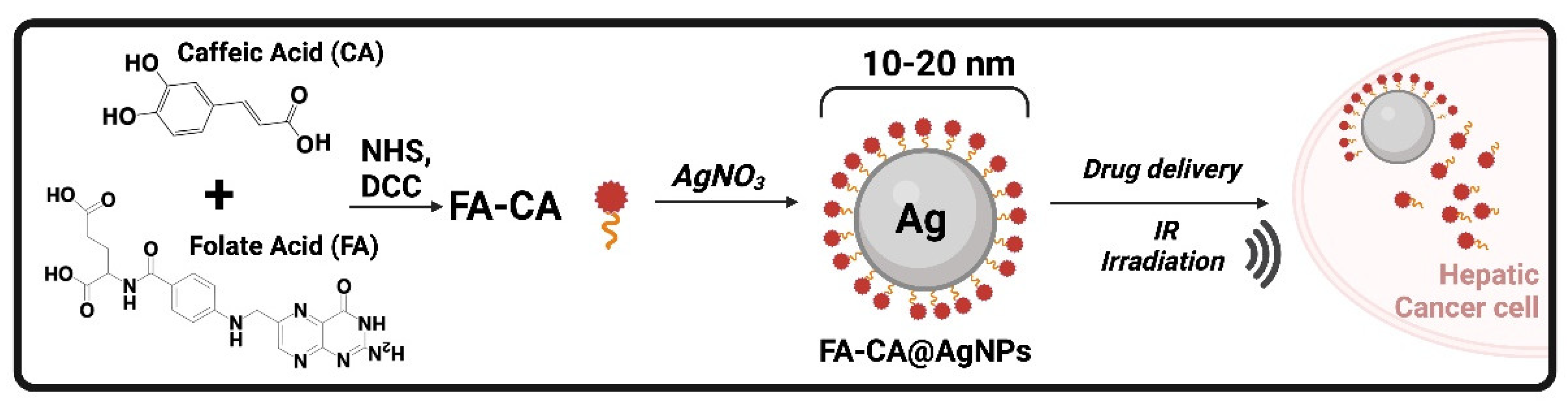
| FA-CA@AgNPs | Folic acidCaffeic Acid | Silver nanoparticles | Small particle size (10–20 nm) | Higher antiproliferative effects, apoptosis induction by caspase-8, caspase-3, and TNF-α pathways | [90] | |||
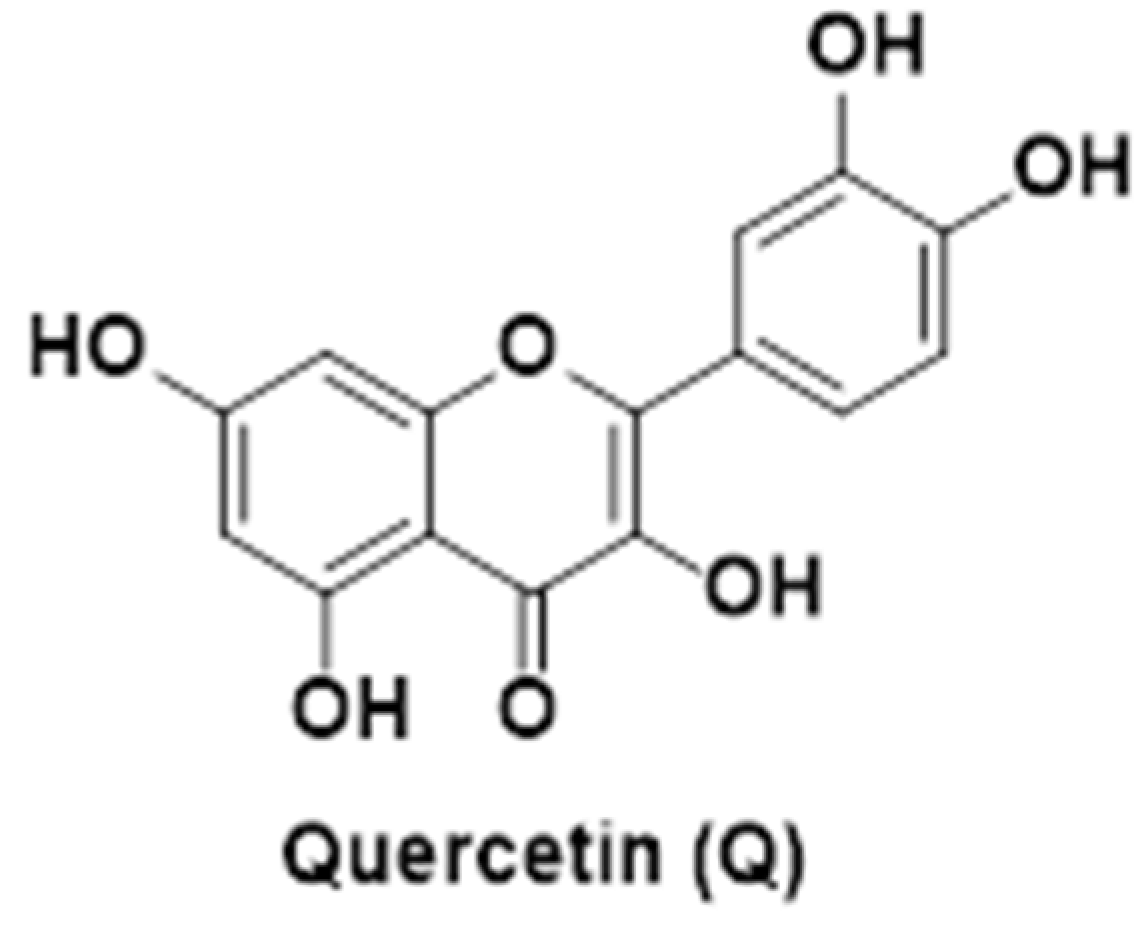
| Q-AuNPs | Quercetin | Gold nanoparticles | Spherical shape (~114 nm) | Higher cellular uptake and apoptosis induction via p53-ROS pathway | [94] | |||
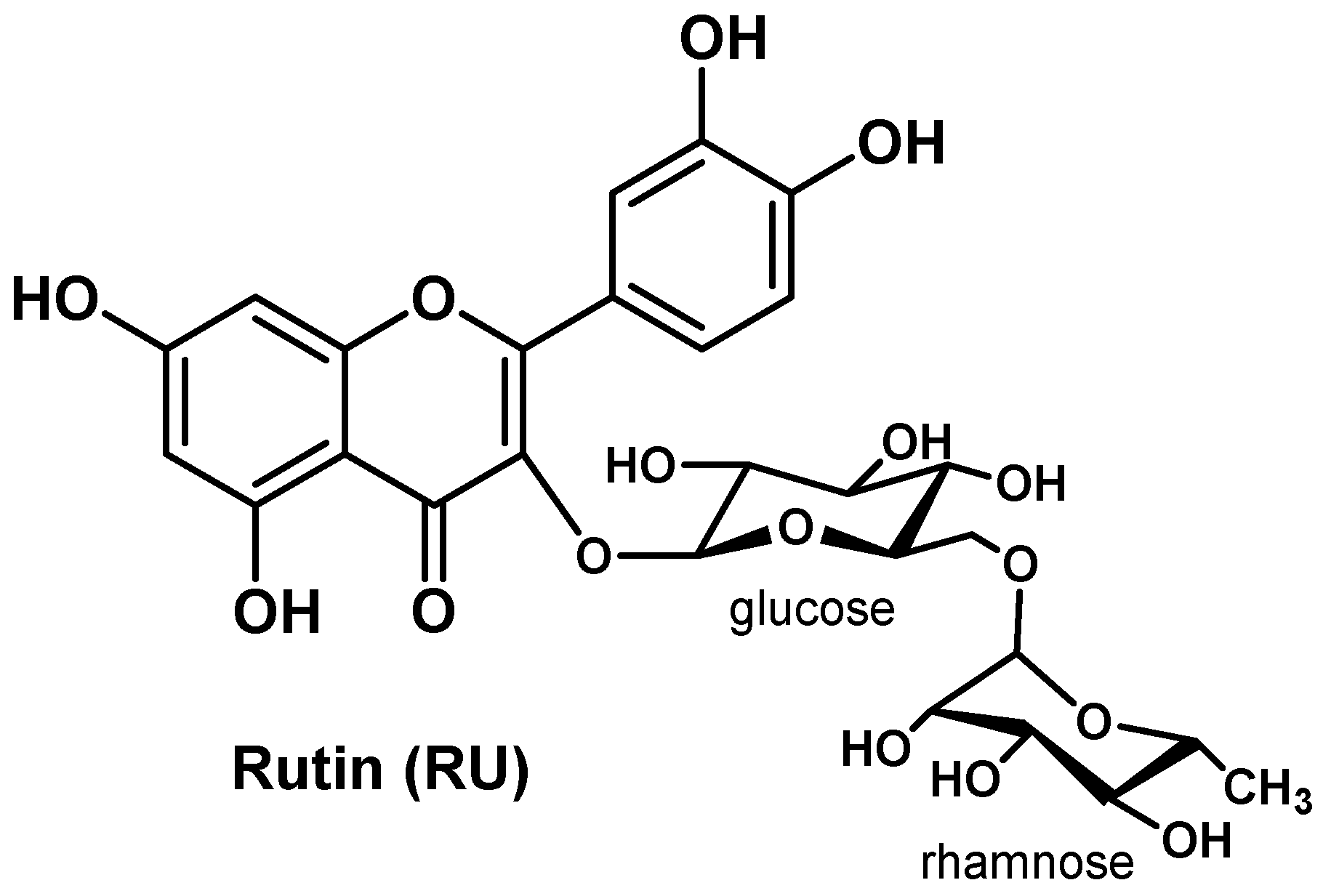
| RU-PLGA-NPs | Rutin | PLGA | Particle size ~211 nm, high EE (77.83%) and DL (6.39%), sustained release (71% after 48h) | Over expression of GPx, GTS, MPO, CAT and SOD, down-regulation of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and NF-κB, and improvement on membrane-bound enzyme activity (Ca2+-ATPase, Na+/K+-ATPase, and Mg2+-ATPase) | [97] | |||
| HP-mPEG5000-S-AuNPs | Hesperetin | mPEG5000-SH, gold nanoparticles | Spherical, triangular and pentagon in shape (110–120 nm), ζ = -4.38 mV, sustained release (80% after 72h) | High antioxidant activity, improved hepatic parameters in HCC models, inhibition of inflammatory markers, antioxidant enzymes and ATPase activity related to liver damage | [98]. | |||
| CE-HK-NPs | Honokiol | Chitin, epigallocatechin-3- gallate | Spherical shape (~80 nm), sustained release (80% after 24h) | Extended antiproliferative activity in vitro and reduction of tumor growth (~84%)after inter-tumoral injection (3 x week) | [101] | |||
| UFG-PLGA-NPs | Umbelliferone β-d-galactopyranoside | PLGA | Uniform size distribution (~187 nm), EE = 60–90%, sustained in vitro DR (82.5% after 48 h) | Reduced liver/body weight ratio and liver nodules in DEN-treated rats, inhibition of HCC cell proliferation in vitro. | [103] | |||
| AG-PLGA-NPs | Andrographolide | PLGA | Particle size ~66 nm, EE = 64% | Decreased serum levels of ALT, AST and ALP, arsenic deposition in liver, SOD, CAT and GSH | [111] | |||
| CDDP/OA-LCC@NPs | Oleanolic Acid, Cisplatin | Mono-methoxy polyethylene glycol 2000-distearoyl phosphatidylethanolamine (PEG-DSPE 2000) 1,2-dioleoyl-in-glycerol-3-phosphate (DOPA), dehydrogenated soya phosphatidylcholine (HSPC), Calcium carbonate | Particle size ~206 nm, EE = ~64%, pH-dependent drug release (70% of CDDP at pH = 5.5 and 28% of CDDP at pH = 7.4) | Induction of apoptosis via downregulation of P13K/AKT/mTOR pathway and upregulation of p53 proapoptotic pathway, inhibition of drug resistance by downregulating the proteins like XIAP and Bcl-2 via NK-κB pathway | [116] | |||
| OA-PLGA-TPGS-NPs | Oleanolic Acid | PLGA, d-α-tocopheryl PEG1000 succinate | Spherical shape (~200 nm), DL = ~28%, EE = ~92 % | Increased in vitro cytotoxicity against HepG2 cells compared to the free drug, and higher growth inhibition rate in volume | [117] | |||
| PLT/TYR-CSL@NPs | Parthenolide, Tyrosol | Chitosan, Lecithin | Particle size ~38 nm; PLT EE = 93% | Cancer-selective cytotoxicity in vitro assessed on HepG2 cells and potent antioxidant activity. Apoptotic effects by up-regulating the expression of the apoptotic genes Bax and caspase-8 and down-regulating the expression of the anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-2 | [121] | |||
| Vit. E/C@SeNPs | Vitamin C, Vitamin E | Selenium nanoparticles | Particle size ~50 nm, high antioxidant capacity (~76% DPPH scavenging), improved liver function markers | Higher antioxidant capacity (~76% DPPH scavenging), improved ALT, AST, ALP, total bilirubin and GGT, increased in GSH concentration and CAT activity | [125] | |||
| Precirol® ATO5 | α-Tocotrienol | Precirol ATO5 Glyceryl distearate, miglyol, poloxamer 407 | Particle size ~78 nm,ζ = -11 mV, PDI = 0.24 | Increased cytotoxicity in vitro (IC50 = 15 µM compared to IC50 = 10 µM of the free drug), decreased in the expression of the anti-apoptotic genes survivin and Bcl-2 and increased of theproapoptotic genes Bid and Bax | [128] | |||
| CoQ10-CS/HA@NPs | Coenzyme Q10 | Hyaluronic acid, Chitosan | Monodispersed, average diameter ~54 nm | Hepatoprotective effects against OS and xenobiotics, enhanced cellular antioxidant capacity | [131] | |||
| DHA-LDL-NPs | Docosahexaenoic acid | LDL | Particle size ~20 nm | Selective cytotoxicity against liver cancer cells, modulation of oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage | [138] | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





