1. Introduction
The startup ecosystem in Peru has gained significant momentum in recent years, driven by the surge in innovation and technology across various industries. Startups in Peru are highly innovative and strong, offering incredible solutions for all kinds of local and international challenges.[
1]
In this context, it is necessary to develop a system that facilitates the visualization and access to information related to new businesses, incubators, and investors as the first attempt to transform an idea into a new company and support existing businesses.[
2]
This application, as a general purpose, provides a window through which users can learn about emerging businesses in the Peruvian territory, obtain information about the services they offer, and, in turn, connect with relevant information about associated incubators and investors. Such development is the solution to the need to aggregate and facilitate the necessary information for entrepreneurs, investors, and any other interested users within the entrepreneurial ecosystem.[
3] In Peru, new businesses have also emerged, achieving great status not only in the country but also abroad. A good example is Crehana, an online education platform that has expanded its business model to include services to companies, resulting in exponential growth and the acquisition of many more companies in Latin America. On the other side is La Manzana Verde, a healthy meal delivery company that has been praised as an agile and innovative solution based on evolving customer needs.[
4] Both are success stories that speak to the diversity and agile nature of the startup ecosystem in Peru.[
5]
Another important factor that has enabled the growth of startups in Peru is institutional support.
The Ministry of Production, with efforts such as the 2023 Census of Peruvian Startups, has been seeking to quantify and outline the needs of new businesses more contextually, which would help inform more strategic and impactful support schemes and policies. Besides this, business incubators and accelerators like UTEC Ventures provided startups with the necessary funding and advice to develop and grow.[
3]
A good example is Yape, an innovative mobile payment solution from the Bank of Credit of Peru, which has enabled millions of Peruvians to conduct electronic transactions, fostering financial inclusion.[
6] Such innovations benefit end users and contribute to the country’s technological ecosystem development. Not only are technology startups amazing, but also companies like Pixed Corp, which creates custom prosthetics for the disabled: an idea not only innovative but also of great social utility.[
7] The same can be said for Veronica Core, whose innovative security and facial recognition products are of the same quality as anything offered worldwide. The purpose of this paper is to introduce a web application programmed in PHP that aims to centralize all information related to startups in Peru, their incubators, and investors interested in these companies. The capabilities of the application will be described, how it was developed from a technical point of view, as well as the foreseeable consequences of implementing this web platform in the ecosystem of new businesses in Peru. Besides centralizing information, the platform aims to enable collaboration and create new businesses in the country. [
1,
3,
8,
9,
10].
2. Methodology
The development of the web application in PHP follows a structured methodology encompassing several key stages, each with its respective subprocesses and tools used. The complete methodological process is detailed below:
Before starting the development of the application, several essential prerequisites were established. Visual Studio Code was used as the integrated development environment (IDE) and XAMPP for the local server. Regarding languages and frameworks, PHP, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript were used for web development, and MySQL for the database. Project management was conducted through Jira, facilitating task planning and tracking. [
11,
12] Additionally, Git was used for version control and GitHub for code collaboration, ensuring efficient and organized teamwork.[
13]
Data preprocessing was a crucial stage to ensure the quality and consistency of the data used in the application.[
14] This process included converting categorical variables into dummy variables using appropriate encoding techniques and data normalization, applying techniques to scale the data and ensure all variables contribute equally in the prediction models.[
15,
16]. Extensive data cleaning was also performed, eliminating duplicates, handling missing values, and correcting inconsistencies. Additionally, the data was enriched by incorporating additional information from external sources to improve the accuracy of the models.[
17]
To enhance the precision and efficiency of the prediction models, several activities were carried out in the model selection and training phase. RandomForestRegressor, Ridge, and XGBoost models were selected due to their ability to handle complex data and provide accurate predictions.[
18,
19,
20] Using GridSearchCV, an exhaustive search for the best hyperparameters for each model was performed. The selected models were trained with the preprocessed data, ensuring they were well-fitted and prepared for analysis. Additionally, validation techniques such as k-fold cross-validation were implemented to ensure the robustness and reliability of the models.[
21]
Rigorous model evaluation was essential to guarantee their performance in real-world situations. Cross-validation was used to assess the stability and accuracy of the models, and their performance was tested on a separate test set to avoid overfitting. Bar charts were also generated for the RandomForest and XGBoost models, showing the importance of the features and allowing a clear interpretation of the most influential factors.[
8] Metrics such as RMSE, MAE, and R² were used to measure the accuracy and effectiveness of the models, providing a comprehensive evaluation of their performance.[
22]
The technical development of the application involved various activities, including designing an intuitive and user-friendly interface. This interface allows users to explore startups, incubators, and investors efficiently.[
14] All functionalities described in the design were developed and tested to ensure proper operation. [
23] The integration of the MySQL database with the application was crucial to enable efficient data access and manipulation. Additionally, security measures such as password encryption and user authentication were implemented, ensuring information protection.[
11]
The application has several additional functionalities that enhance the user experience. These include a currency converter that converts dollars to soles, facilitating financial analysis, and an index chart where users can analyze different companies and observe investment and profit indices. A survey is also provided for suggesting new startups, allowing users to include details such as sector, operating cost, team size, and growth rate.[
24] Additionally, forums and contact networks were incorporated to enable entrepreneurs and investors to interact and share knowledge, as well as a notification system to keep users informed about new opportunities and important updates.[
25]
The developed application is expected to have a significant impact on the Peruvian entrepreneurial ecosystem, facilitating access to data and promoting collaboration among entrepreneurs, investors, and other stakeholders. Centralizing relevant information and providing advanced analysis and decision-making tools are fundamental for the success and growth of new startups in Peru. Furthermore, the platform fosters an entrepreneurial culture by providing educational resources and networking opportunities, essential for developing a vibrant and sustainable ecosystem. [
4,
5,
6,
7,
24].
3. Results
This section presents the results obtained after developing and launching the web application. The platform offers a wide range of functionalities that facilitate access and interaction with the startup ecosystem in Peru.[
26]
Exploration of Startups: The application allows users to explore a comprehensive database of Peruvian startups, categorized by industry and development stage.[
27] Each entry in the database includes detailed information about the startup, products, and services, as well as direct links to their official websites. This functionality enables users to better understand startups, their operations, and achievements, thus promoting visibility and networking within the entrepreneurial ecosystem.[
28]
Information on Incubators and Accelerators: Users can access detailed information on incubators and accelerators operating in Peru. This section includes direct links to the websites or contacts of these entities, providing a clear view of the support opportunities available to startups.[
29] The information ranges from incubation and acceleration programs to mentoring and financing opportunities, facilitating access to essential resources for startup growth.[
30]
Investor Identification: The platform provides a detailed index of potential investors, including angel investors. Each entry in the index includes contact information and areas of interest, facilitating the search and connection process with potential investors.[
31] This functionality is crucial for entrepreneurs seeking financing and strategic support for their projects, enabling more direct and efficient access to financial resources.
Analysis Tools: The application includes advanced analysis tools that allow users to predict the acceptance of new market proposals. Using sophisticated prediction models, users can assess the potential of their ideas before launching them. Additionally, the application offers a currency converter that converts dollars to soles, enabling users to perform financial simulations and evaluate return on investments over different periods.[
32] An index chart is also presented where users can analyze different companies, observing investment, profit, and balance indices, facilitating better financial decision-making.[
33]
Visualization of ProInnova Peru: The platform integrates information provided by ProInnova Peru, including frequently asked questions and educational videos. These resources are designed to help entrepreneurs better understand the startup ecosystem in Peru, providing guidance and practical knowledge on various aspects of entrepreneurship.[
6] Including these educational materials enriches the user experience and supports the development of new startups.[
34]
Survey to Suggest New Startups: The application includes a survey that allows users to suggest new startups. This detailed form collects information such as the startup name, sector, launch time, monthly operating cost, team size, founder’s experience, user growth rate, social media followers, direct competitors, innovation rate, market share, customer satisfaction level, access to resources, popularity, growth time, and region of Peru. This functionality captures innovative ideas and assesses their viability and potential in the market.[
34]
Contact Section: The contact section allows users to submit new suggestions and contact startup support. This functionality facilitates direct communication with the development team, ensuring users can provide feedback, resolve doubts, and receive assistance in using the platform. Open and accessible communication is essential for continuously improving the application and adapting it to user needs.[
35]
3.1. Home Page Visualization
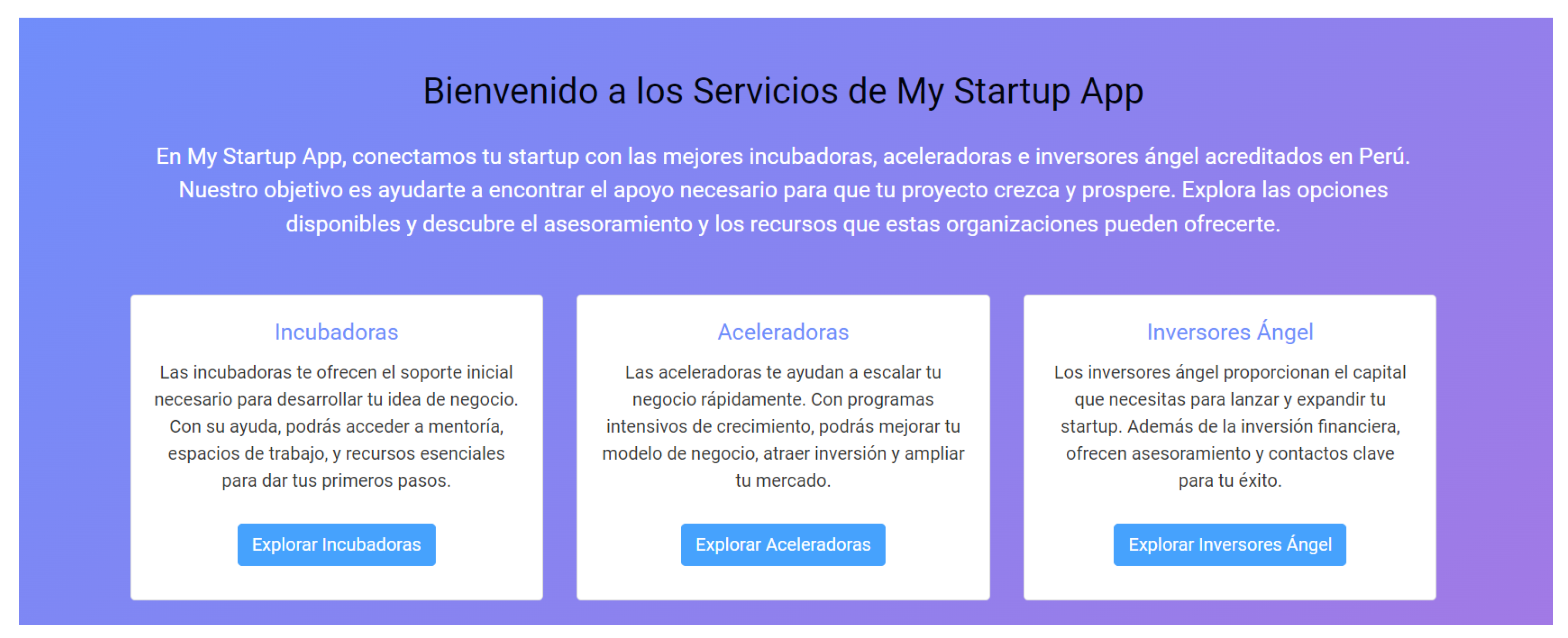
The home page of the web application integrates key information about startups in Peru, presenting an overview that includes:
A directory of Peruvian startups, categorized by industry and development stage, with links redirecting to the official websites of each startup.
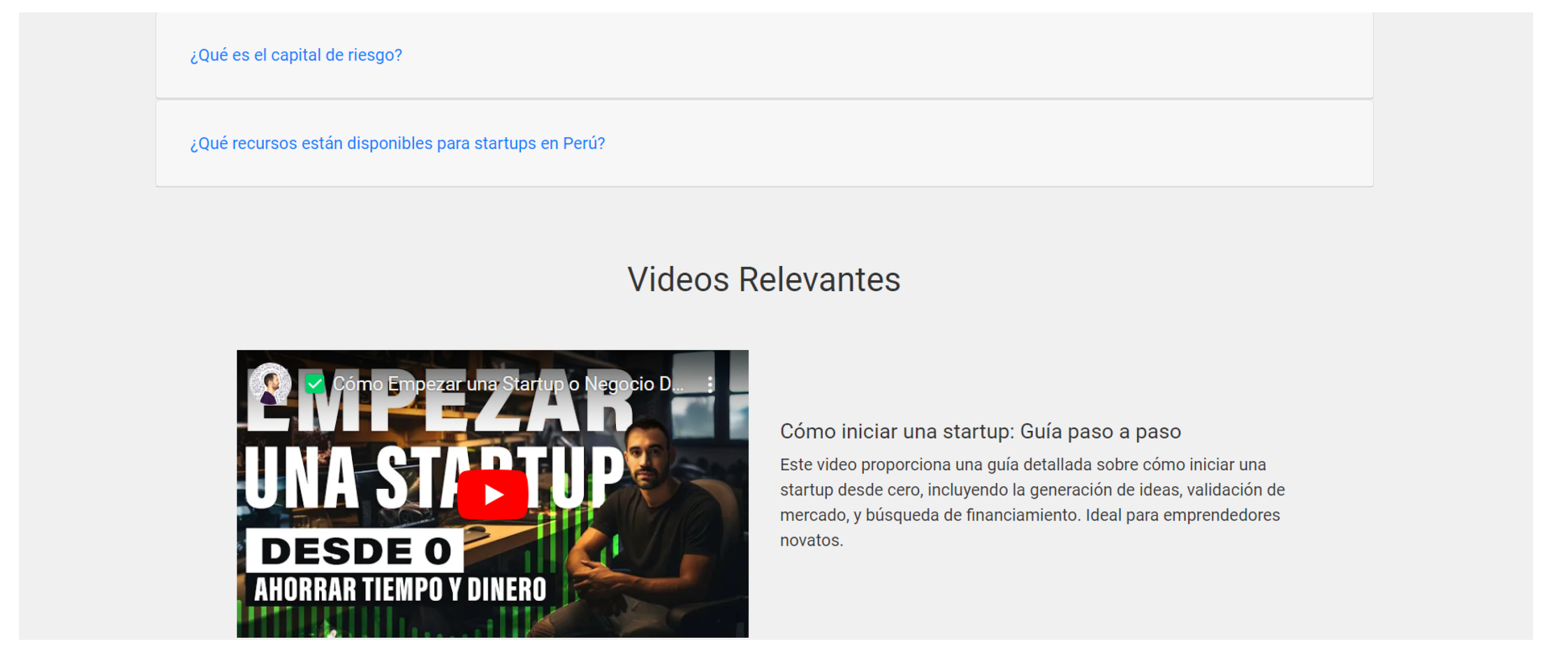
Updated information provided by ProInnova Peru, including frequently asked questions and explanatory videos.
Figure 1.
View of the application home page.
Figure 1.
View of the application home page.
Figure 2.
View of the home page with questions and videos relevant to the application’s context.
Figure 2.
View of the home page with questions and videos relevant to the application’s context.
3.2. Incubators, Accelerators, and Angel Investors Section
This section offers detailed and categorized information on:
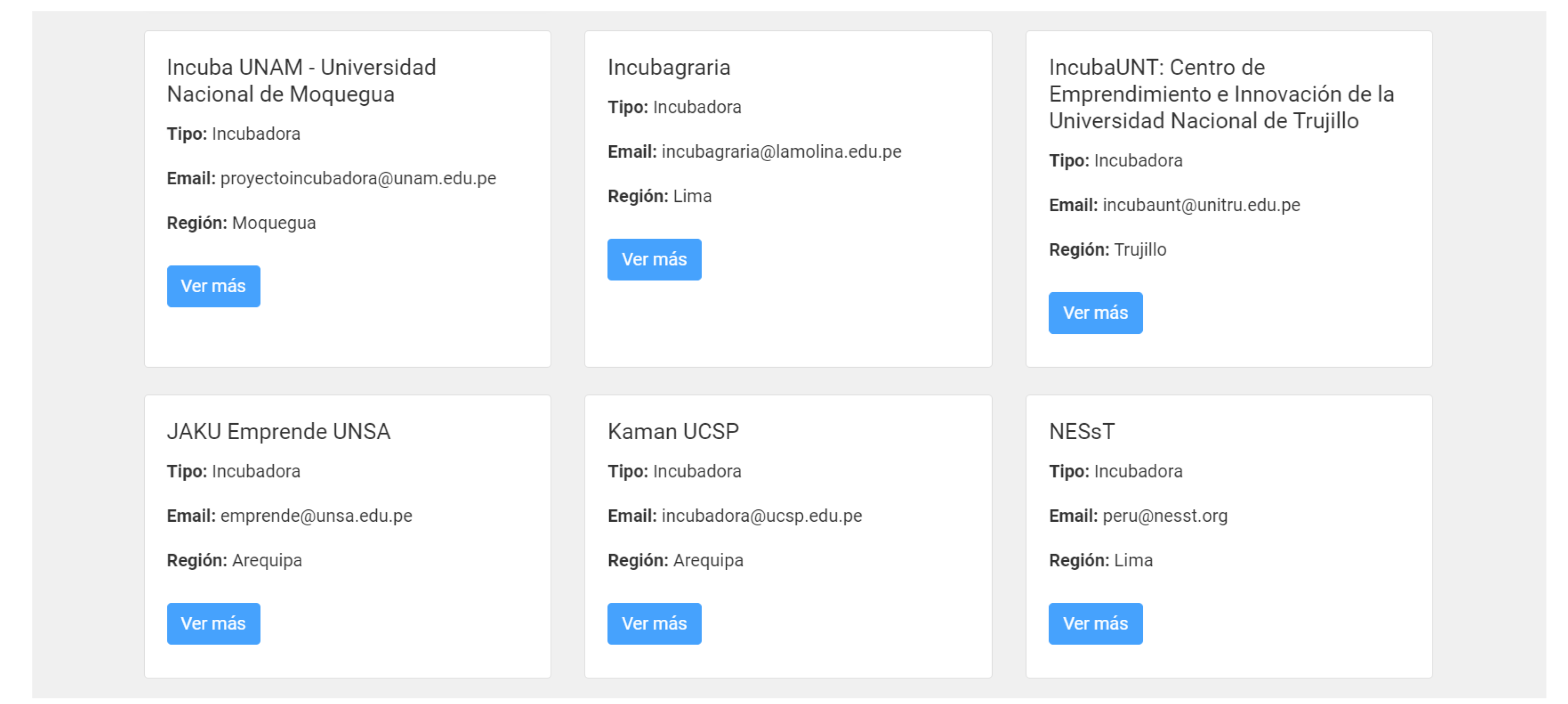
Incubators and accelerators in Peru, with direct links to their websites or contacts.
Angel investors, providing a detailed index with investment percentages and areas of interest.
Figure 3.
View of the incubators and accelerators section.
Figure 3.
View of the incubators and accelerators section.
Figure 4.
View of the national level incubators section.
Figure 4.
View of the national level incubators section.
3.3. Investment Section
The investment section allows users to:
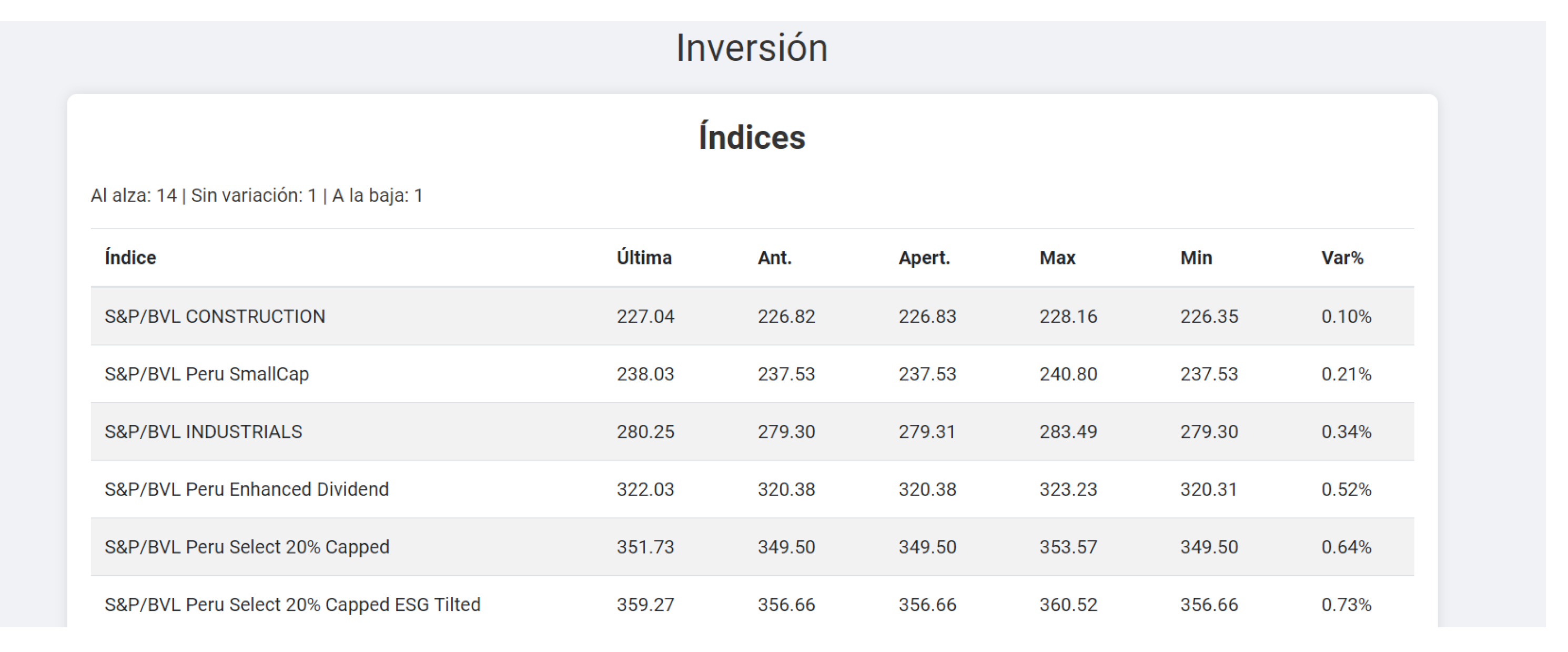
Consult an investment index with different interests and return percentages.
Use a currency converter to consult the dollar price.
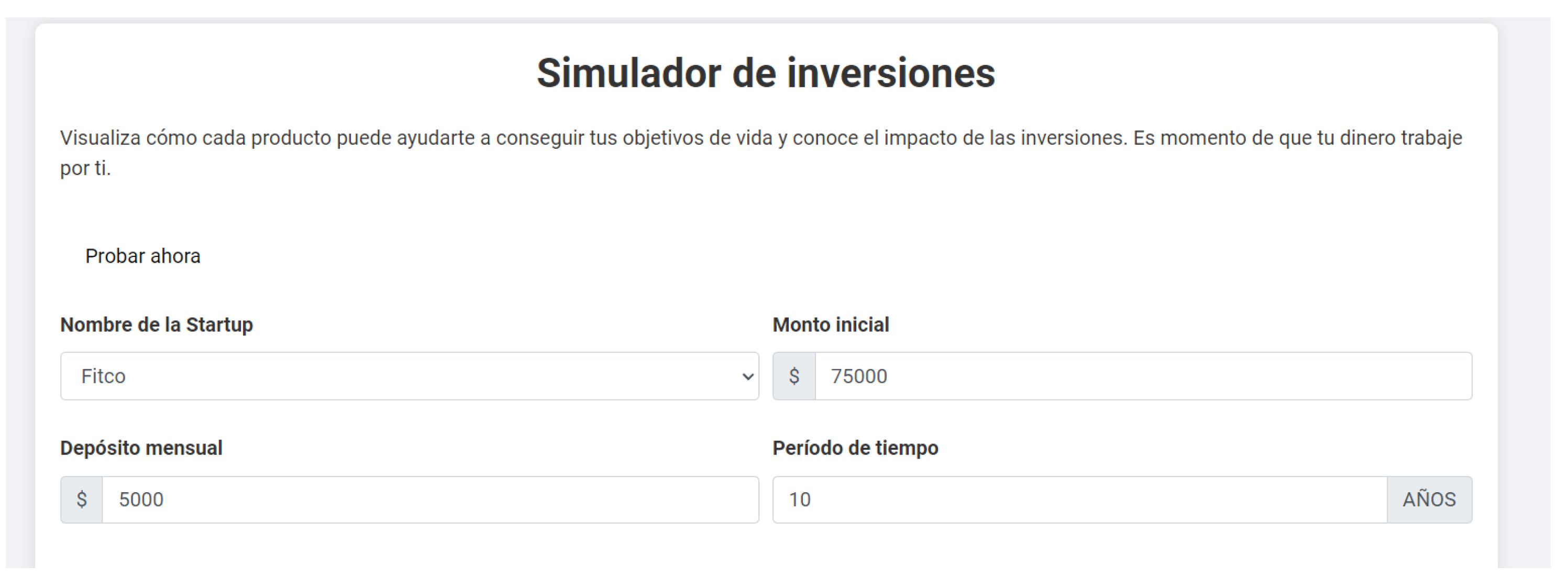
Access an investment simulation tool that allows calculating the expected returns when investing a certain amount for a specified number of years.
Figure 5.
Investment indices.
Figure 5.
Investment indices.
Figure 6.
Currency converter for dollar investments.
Figure 6.
Currency converter for dollar investments.
Figure 7.
View of the investment simulation tool.
Figure 7.
View of the investment simulation tool.
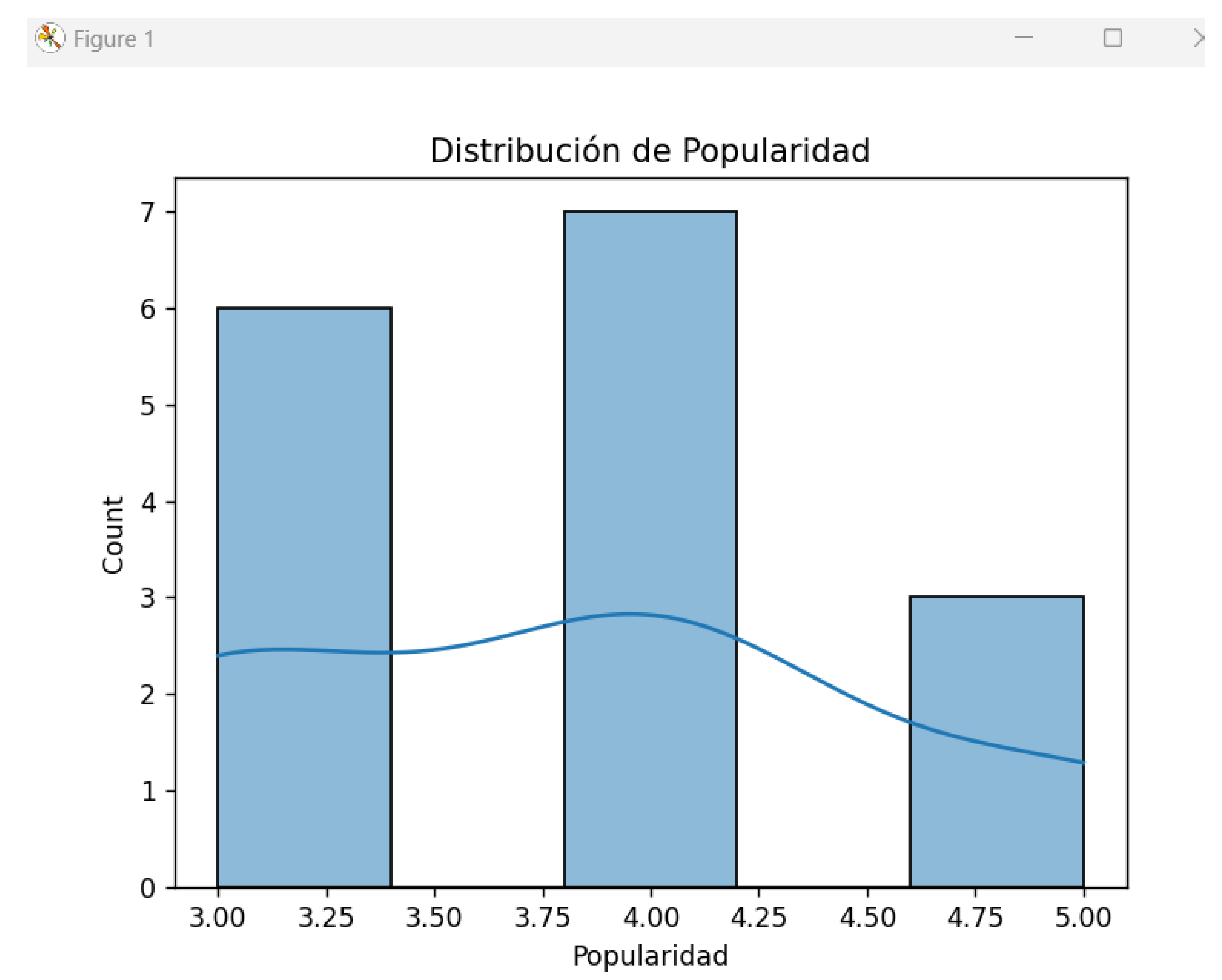
Figure 8.
Startup popularity chart.
Figure 8.
Startup popularity chart.
Model Evaluation
Figure presents the results of evaluating three different models: RandomForest, Ridge, and XGBoost. The cross-validation scores, average in cross-validation, and Score in the test set are shown.
-
RandomForest:
- -
Cross-validation scores: [0, -0.8352875, -3.53025, -5.516, -0.0234809]
- -
Average in cross-validation: -1.981036885555555
- -
Score in test set: 0.26615930428004553
-
Ridge:
- -
Cross-validation scores: [0, -0.63180093, -1.79562267, -1.58174156, 0.4387118]
- -
Average in cross-validation: -0.7140906717246326
- -
Score in test set: 0.219354984324592
-
XGBoost:
- -
Cross-validation scores: [0, -0.36881101, -4.44357586, -4.4778204, 0.2072615]
- -
Average in cross-validation: -1.8165891528129579
- -
Score in test set: 0.15712372076644897
Interpretation of Results
RandomForest has the highest capacity to explain the variability in the test data, but its performance in cross-validation suggests that its fit is not consistent. Ridge shows a more consistent fit than RandomForest, although its capacity to explain the variability in the test data is slightly lower. XGBoost has the lowest capacity to explain the variability both in cross-validation and in the test set, suggesting that it is not the best model for this dataset.
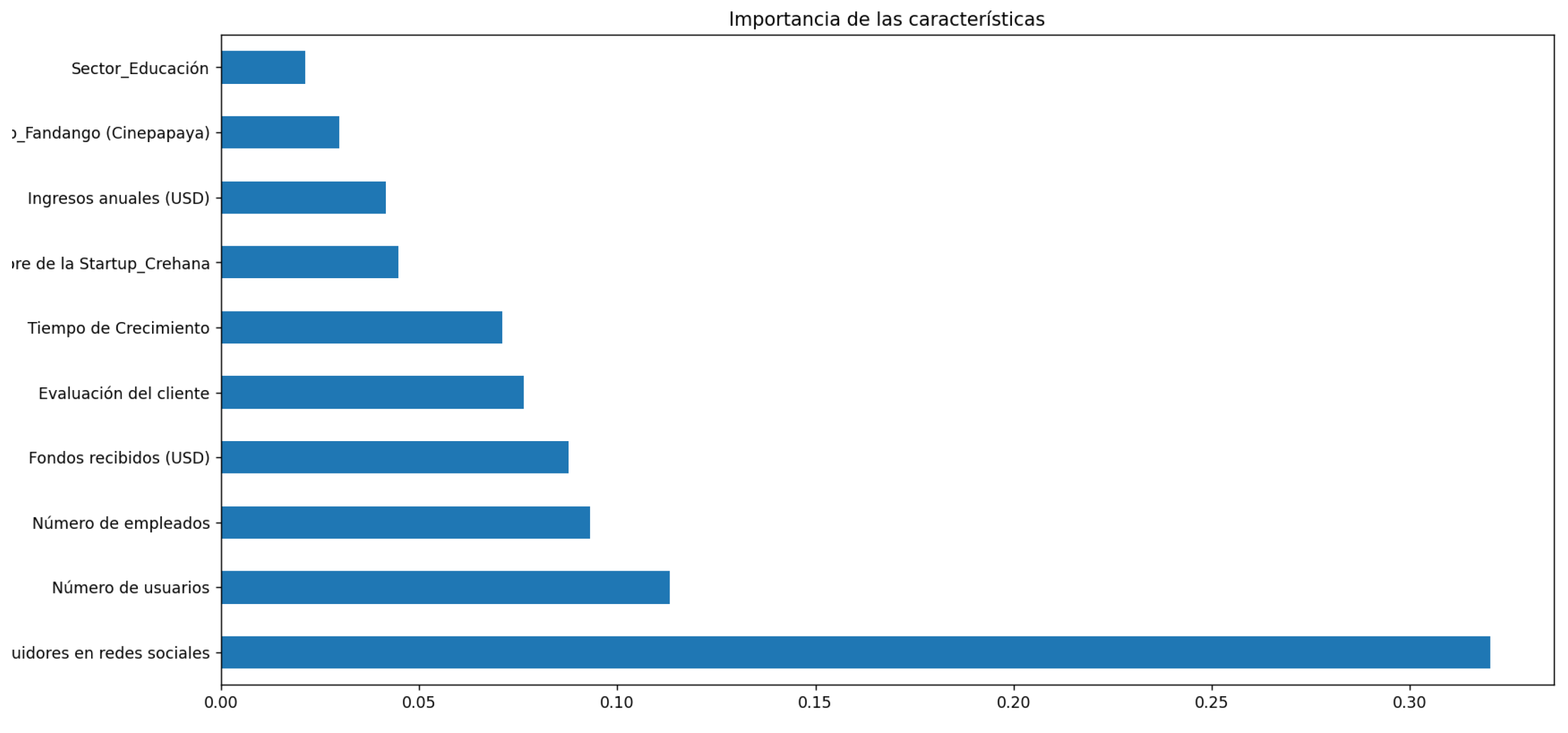
Feature Importance
Figure 9 shows a bar chart representing the importance of different features in the model prediction. The evaluated features are:
Figure 9.
Evaluation of startups.
Figure 9.
Evaluation of startups.
3.4. Contact Section
The contact section allows users to submit new suggestions and contact startup support, facilitating direct communication with the development team.
Figure 10.
View of the contact section.
Figure 10.
View of the contact section.
The contact section allows users to submit new suggestions and contact startup support, facilitating direct communication with the development team.
The application has been tested with real users, and feedback has been collected to improve its functionalities. The results indicate high user satisfaction, who highlight the ease of use and the usefulness of the information provided.[
1,
4,
6,
7,
36].
4. Discussion
The discussion of the obtained results reveals several important points that underline the importance and impact of information centralization on a single platform. This approach has significantly facilitated access to crucial data for entrepreneurs and investors, promoting greater interaction and collaboration within the Peruvian startup ecosystem.
4.1. Information Centralization and Collaboration
Centralizing information on a single platform improves access to relevant data and fosters a collaborative environment among entrepreneurs, investors, and other ecosystem stakeholders. According to the Global Startup Ecosystem Report 2024 (GSER 2024), platforms that consolidate data on startups and entrepreneurial ecosystems allow identifying key gaps and prioritizing actions that drive sustained economic growth [
37]. This has been evident in regions like Latin America and Europe, where collaboration and information centralization have been vital for startup development and attracting investments [
38].
4.2. Impact of Government Policies
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the growth and success of startup ecosystems. The experience of cities like San Francisco, London, Beijing, and Tel Aviv demonstrates that a balance between regulation and innovation is essential for fostering a dynamic entrepreneurial environment [
35]. In Beijing and Shanghai, increased regulation and control have led to a decline in investor confidence and a slowdown in international collaborations, highlighting the need for policies that promote stability and transparency [
35].
4.3. Analysis and Prediction Tools
The analysis and prediction tools have proven valuable for platform users, enabling them to make informed decisions about their projects and potential investments. Feedback suggests that these tools could be even more effective if integrated with additional data sources and improved prediction algorithms [
39]. Recent studies have emphasized the importance of using robust data and advanced algorithms to enhance prediction accuracy and offer more precise recommendations to entrepreneurs.
4.4. Communication Interface and Security
Including a communication interface has been particularly appreciated, as it facilitates real-time networking and collaboration. However, some users have suggested improvements in communication security and privacy. As digital platforms become essential tools for entrepreneurial ecosystems, security and privacy become priorities [
40]. Enhancing these aspects is crucial for maintaining user trust and ensuring that interactions are secure and effective.
4.5. Impact of Digital Platforms on the Startup Ecosystem
The impact of digital platforms on the startup ecosystem has been significant. According to the Startup Genome report, platforms integrating various functions and data on startups, investors, and market trends have been fundamental in driving growth and resilience in entrepreneurial ecosystems [
37]. These platforms facilitate access to financing and mentorship and promote innovation and competitiveness globally.
4.6. Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the benefits, implementing these platforms also presents challenges. Integrating data from multiple sources, improving security, and adapting to changing market needs are areas requiring continuous attention. However, the opportunities they offer for growth and innovation outweigh the challenges, making investment in developing and improving these platforms a priority for governments and startup support organizations [
39,
40].
5. Conclusions
The developed application has proven to be an effective tool for centralizing information about startups, incubators, and investors in Peru, facilitating access to crucial data and promoting collaboration within the entrepreneurial ecosystem. Centralizing information and implementing advanced tools in digital platforms have proven effective strategies for strengthening startup ecosystems. Continuous improvement of these platforms, focusing on security and data integration, will remain crucial for the success and sustainable growth of startups in Peru and worldwide.
The positive impact of the application is evident in several aspects:
Improved Data Access: The platform facilitates access to relevant information about startups, incubators, and investors, centralizing data that is crucial for entrepreneurs and investors. This centralization not only saves time but also improves efficiency in searching and evaluating opportunities.
Promotion of Collaboration: By centralizing information, collaboration between various ecosystem actors is promoted, facilitating networking and investment opportunities. This collaboration is essential for creating synergies and fostering a supportive environment among entrepreneurs, investors, and other stakeholders.
Decision Support: The analysis and prediction tools enable users to make informed decisions, improving prediction accuracy and offering valuable recommendations. These tools provide significant support for strategic planning and risk assessment.
Security and Privacy: Improving security and privacy in communications is crucial to maintaining user trust and ensuring secure and effective interactions. The application has implemented robust security measures, ensuring the protection of sensitive user information and transactions.
Innovation and Competitiveness: Digital platforms integrating various functions and data on startups have proven fundamental in driving innovation and competitiveness globally. By providing a comprehensive and detailed view of the ecosystem, the application fosters an environment where innovative ideas can flourish and compete effectively in the market.
In conclusion, the developed application has the potential to significantly impact the Peruvian entrepreneurial ecosystem, facilitating data access and promoting collaboration among entrepreneurs, investors, and other stakeholders. Continuous investment in improving these platforms will be crucial for the success and sustainable growth of startups in Peru and worldwide. The application offers an advanced technical solution and positions itself as a catalyst for economic development and innovation in the region, contributing to the strengthening and expansion of the entrepreneurial ecosystem globally. [
4,
5,
41,
42,
43].
References
- TekiosMag. Perú realizará este 9 de junio el Censo de Startups Peruanas 2023. TekiosMag 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarte Aguirre, L.A. El estado de la creatividad en el ecosistema de startups en el Perú 2019.
- de la Producción, M. Iniciativas de apoyo a startups. Produce 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Verde, M. Planes de alimentación saludables. Manzana Verde 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Core, V. Soluciones de seguridad avanzada. Veronica Core 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Perú, P. Censo Startups 2023. ProInnovate Perú 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chazki. Plataforma de logística y entrega urbana. Chazki 2023. [Google Scholar]
- PECAP. Asociación Peruana de Capital Semilla y Emprendedor. PECAP 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Laboratoria. Educación tecnológica para mujeres. Laboratoria 2023.
- Ventures, U. Programa de incubación y aceleración. UTEC Ventures 2023. [Google Scholar]
- MySQL. Sistema de gestión de bases de datos. MySQL 2023.
- XAMPP. Servidor web local. XAMPP 2023. [Google Scholar]
- GitHub. Plataforma de desarrollo colaborativo. GitHub 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, C.V.; Cuevas, E.C.; Hilasaca, E.M.; Ñaupa, J.P. Aplicación de modelo de regresión lineal para predecir el índice de popularidad en la plataforma Spotify. Innovación y Software 2023, 4, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Variables, D. Conversión de variables categóricas. Kaggle 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chitarroni, H. La regresión logística 2002.
- Training, M. Entrenamiento de modelos. Kaggle 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Forest, R. Modelo de regresión. Scikit-learn 2023.
- Regression, R. Modelo de regresión lineal. Scikit-learn 2023.
- XGBoost. Modelo de regresión y clasificación. XGBoost 2023.
- Sifuentes Ortega, F.P. Evaluación de un aplicativo computacional de código abierto en diseño geométrico de vías contribuyendo a la solidez del software 2023.
- Cabrero Ortega, M.Y.; García Pérez, A. ANÁLISIS ESTADÍSTICO DE DATOS ESPACIALES CON QGIS YR; Editorial UNED, 2022.
- Validation, C. Validación cruzada. Medium 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Prestamype. Las 9 startups peruanas más destacadas del 2023. Prestamype 2023.
- Techniques, N. Escalado de datos. Medium 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Segura, E.A.V. Componentes de calidad software y su utilización en aplicaciones web. Ciencia Latina Revista Científica Multidisciplinar 2022, 6, 3193–3204. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano, A.D. ?` QUÉ ES UNA STARTUP. ÍNDICE 2022.
- Sakas, D.P.; Reklitis, D.P.; Giannakopoulos, N.T.; Trivellas, P. The influence of websites user engagement on the development of digital competitive advantage and digital brand name in logistics startups. European Research on Management and Business Economics 2023, 29, 100221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Higueras, A.; Pérez-Rufí, J.P.; Torres-Martín, J.L.; Carballeda-Camacho, M.R.; De-Aguilera-Moyano, M.; others. Streaming de vídeo, cómo las plataformas condicionan el comportamiento y los usos expresivos de los usuarios de sus apps 2022.
- Guerra Galeano, J. Mapa de ruta para agilizar el ingreso de las startups a las incubadoras o aceleradoras 2022.
- Cózar, C.L.; Bergamini, T.P. Identificación de las principales fuentes de financiación empleadas por la empresa social en la actualidad. Economía agraria y recursos naturales 2015, 15, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morato Leyton, H.L. Metodología para calcular los portafolios de mínimo riesgo, vía Frontera Eficiente de Markowitz, tomando como caso de estudio, portafolios agrupados por tipos de activos financieros en la plataforma IQ Option 2023.
- Pena, M.F.B. Diversificación de la composición oficial de las reservas internacionales de divisas (2016-2022). Revista Política Internacional 2023, 5, 232–242. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez Bedoya, I.D. Beneficios de business intelligence en la startup peruana Joinnus SAC al año 2020 2022.
- StartupBlink. Government Policy Pitfalls: The Impact on Top Startup Ecosystems 2023.
- PulsoCapital. Las 10 startups más prometedoras para Perú en 2023. PulsoCapital 2023.
- Genome, S. Global Startup Ecosystem Report 2024 2024.
- Crunchbase. Global Startup Ecosystem 2022: Ranking 1,000 Cities and 100 Countries 2022.
- Insight, E. Start-ups in entrepreneurial ecosystems: the role of relational capacity 2021.
- SpringerLink. Why Startups Need an Inclusive Ecosystem to Survive and Thrive 2023.
- Crehana. Plataforma de educación en línea. Crehana 2023.
- Yape. Aplicación de pagos móviles. Yape 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Corp, P. Desarrollo de prótesis personalizadas. Pixed Corp 2023. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).