Submitted:
23 July 2024
Posted:
24 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
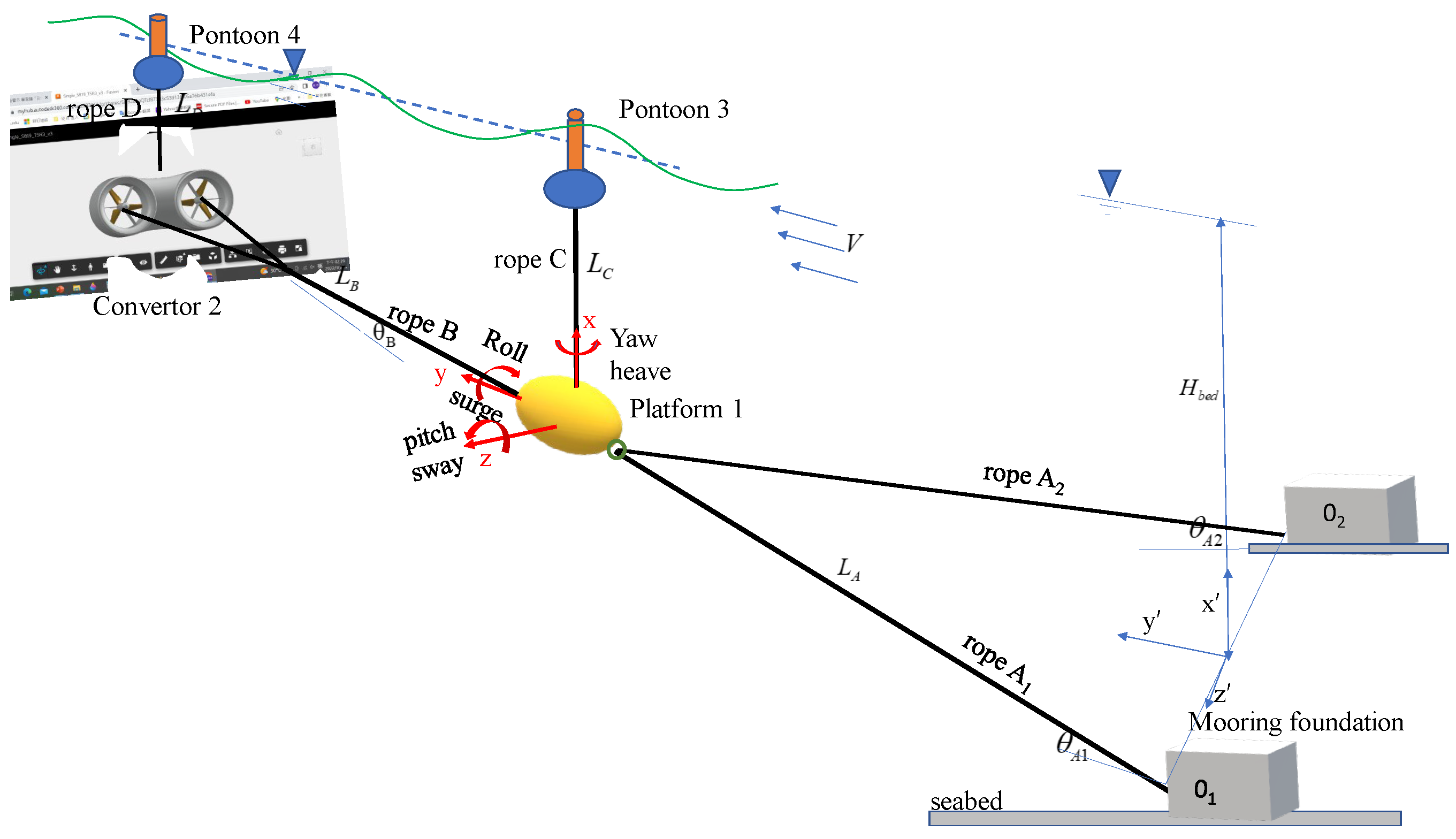
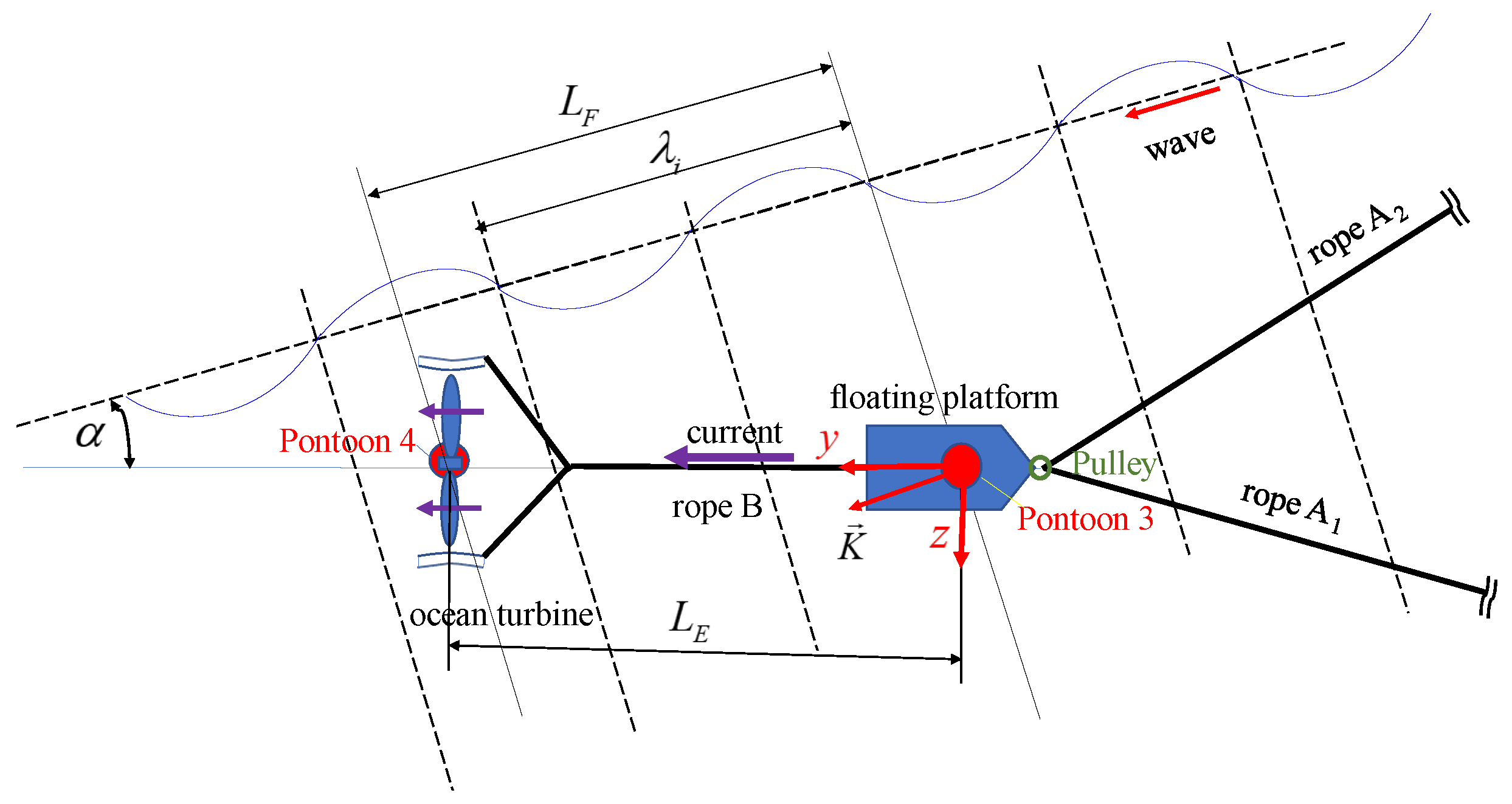
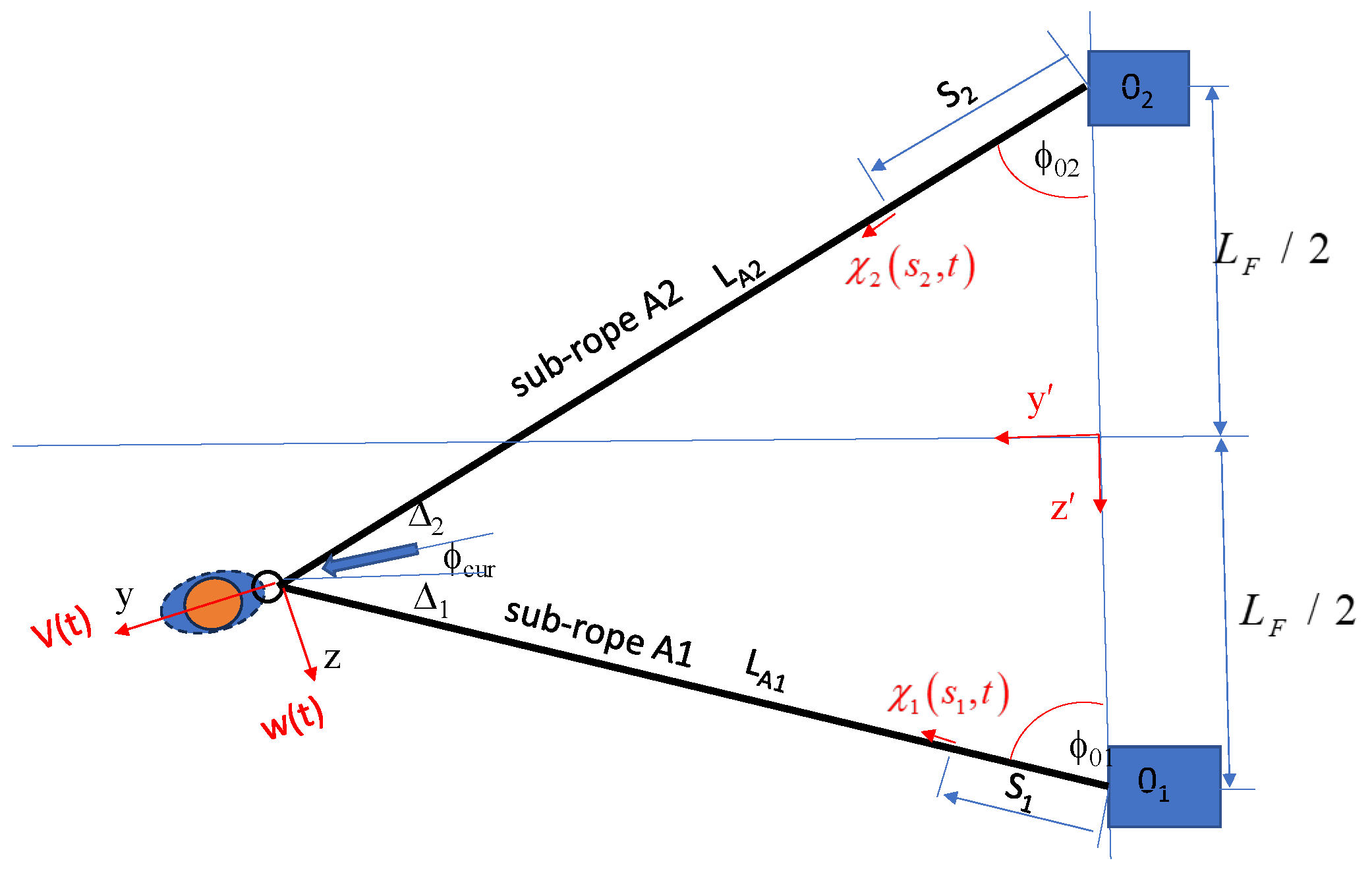
2. Mathematical Model
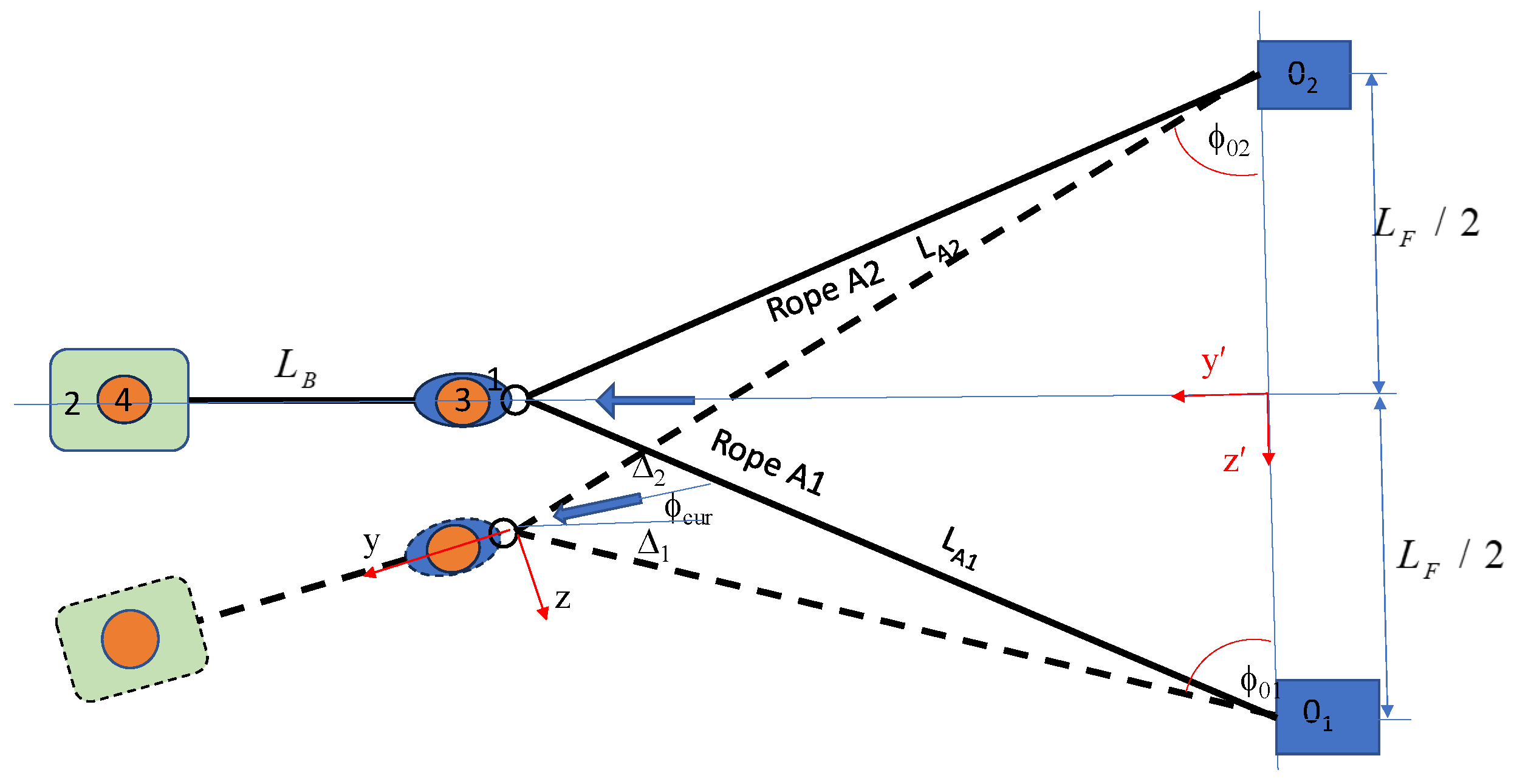
3. Static Displacements and Equilibrium under the Steady Current only
3.1. Static Displacements
3.2. Static Force Equilibrium
3.3. Solution Method of Static Equilibrium and Displacements
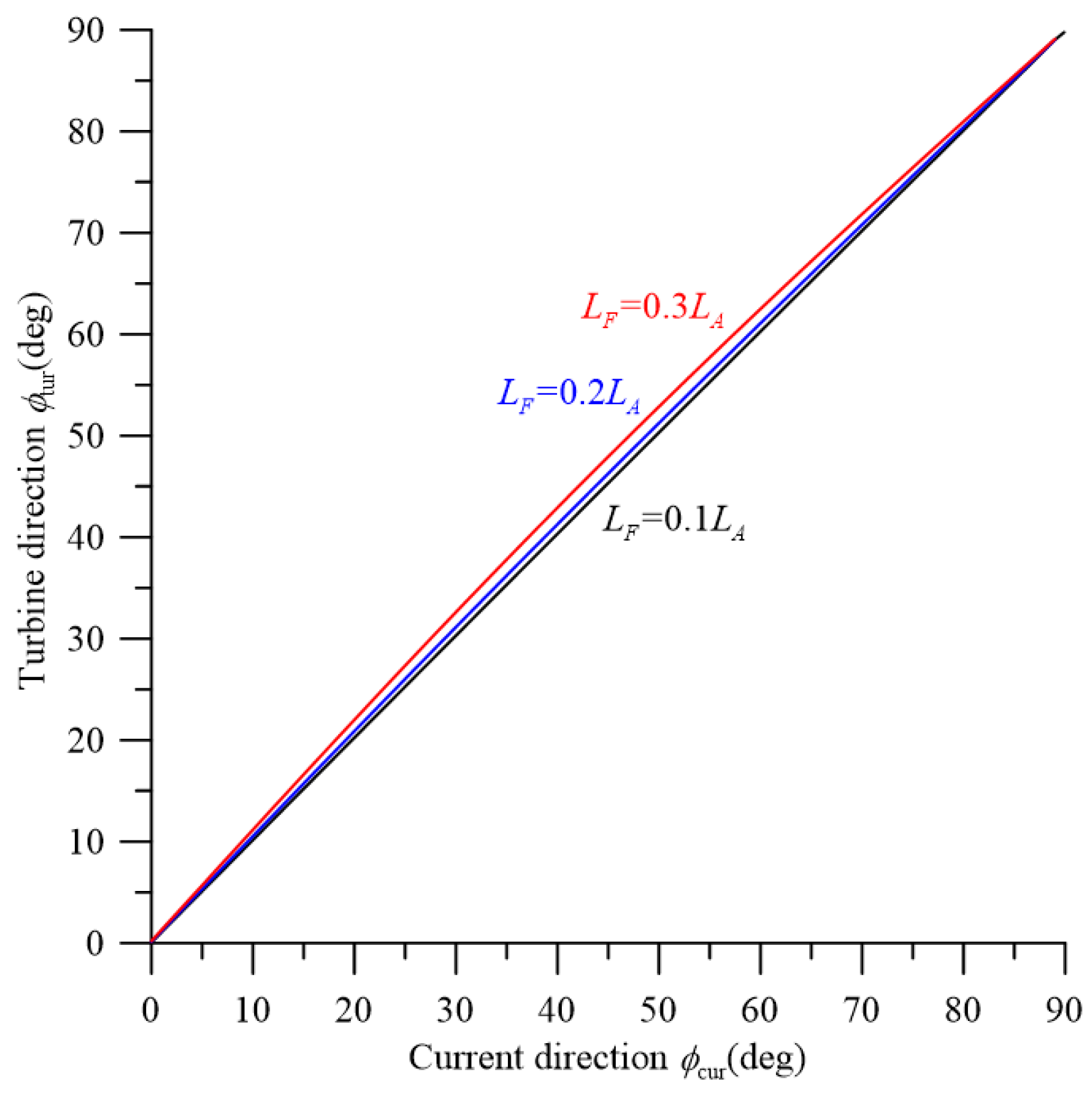
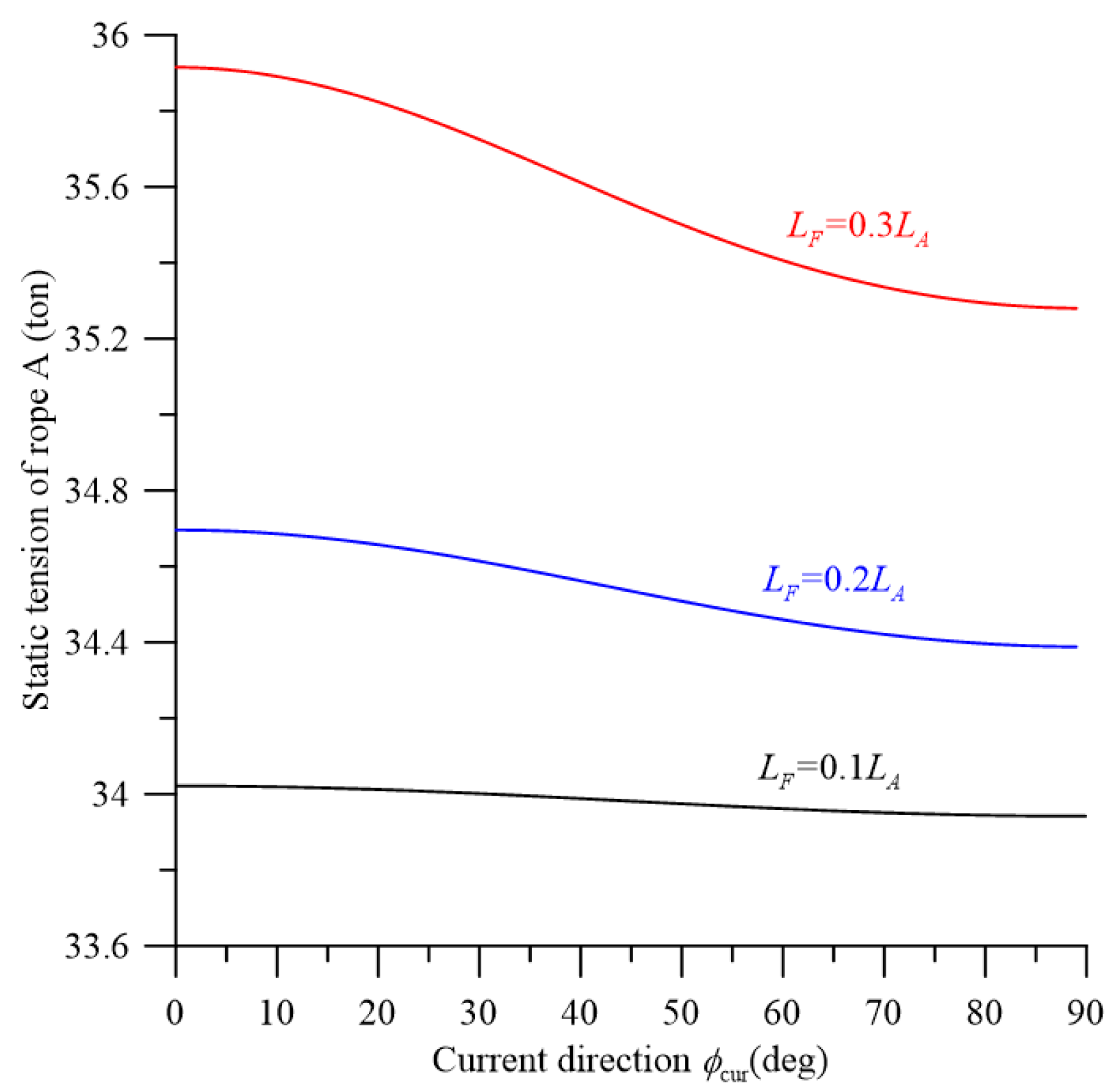
3.4. Static Numerical Results
4. Dynamic Analysis
4.1. Similarity of System
4.1.1. Hydrodynamic Similarity of Convertor
4.1.2. Hydrodynamic Similarity of Platform
4.1.3. Geometrical Inertia and Buoyance Similarities
4.2. Translational Motion in the x-Axis Direction
4.2.1. Equation of Heaving Motion for Pontoon 3
4.2.2. Equation of Heaving Motion for Pontoon 4
4.2.3. Equation of Heaving Motion of the Platform
4.2.4. Equation of Heaving Motion for the Convertor
4.3. Translational motion in the y-direction
4.3.1. Equation of Surging Motion of Platform
4.3.2. Equation of Surging Motion of Convertor in the y-direction
4.3.3. Equation of Surging Motion of Pontoon 3 in the y-direction
4.3.4. Equation of Surging Motion of Pontoon 4 in the y-direction
4.4. Translational motion in the z-direction
4.4.1. Equation of Swaying Motion of Platform
4.4.2. Equation of Swaying Motion of Convertor
4.4.3. Equation of Swaying Motion for Pontoon 3
4.4.4. Equation of Swaying Motion of Pontoon 4
4.5. Rotational motion
4.5.1. Equation of Yawing Motion of Convertor
4.5.2. Equation of Rolling Motion of Convertor
4.5.3. Equation of Pitching Motion of Convertor
4.5.4. Equation of Yawing Motion of Platform
4.5.5. Equation of Rolling Motion of Platform
4.5.6. Equation of Pitching Motion of Platform
4.6. Solution Method of Dynamic Displacements
4.8. Dynamic Tensions of Ropes
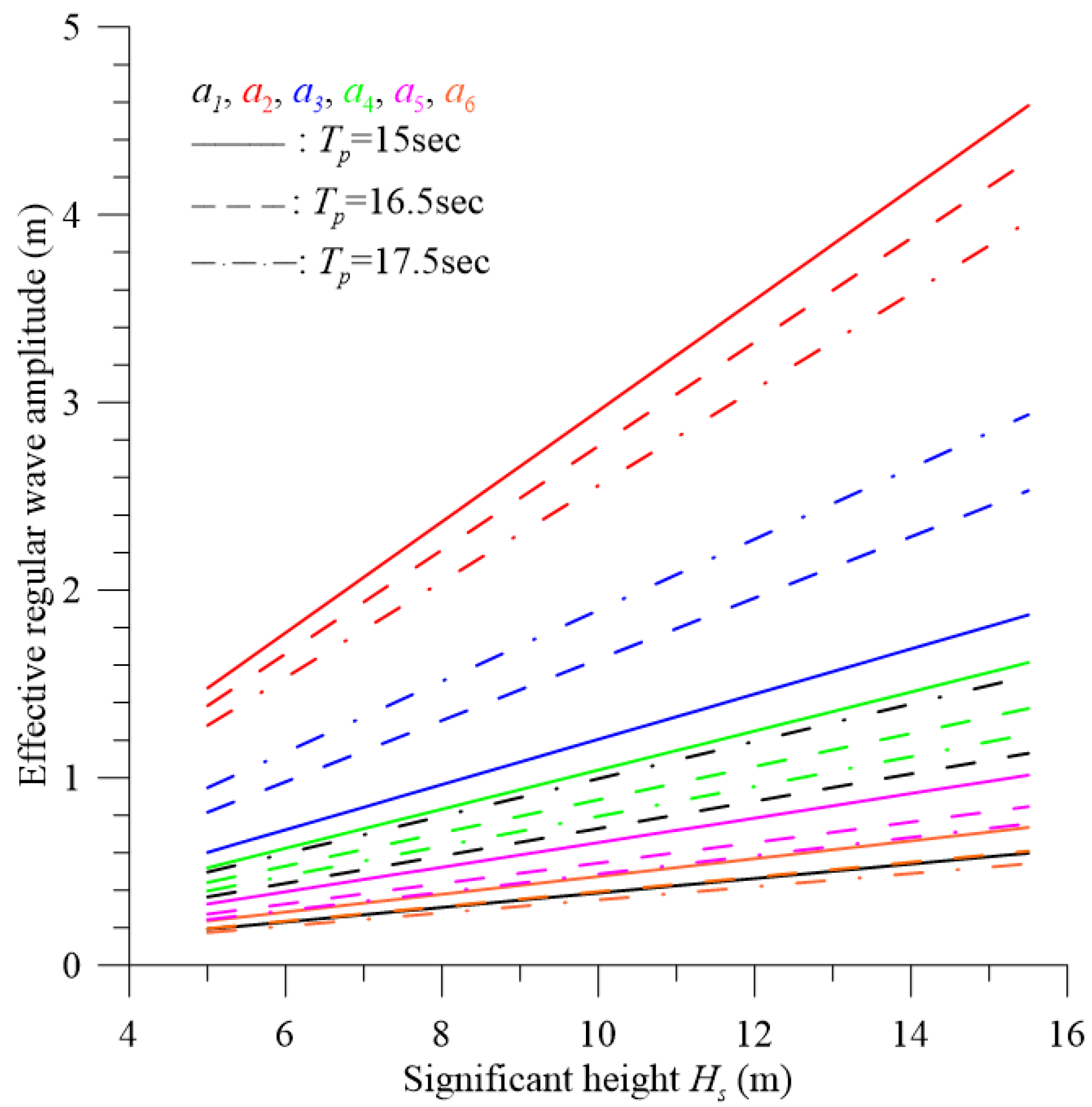
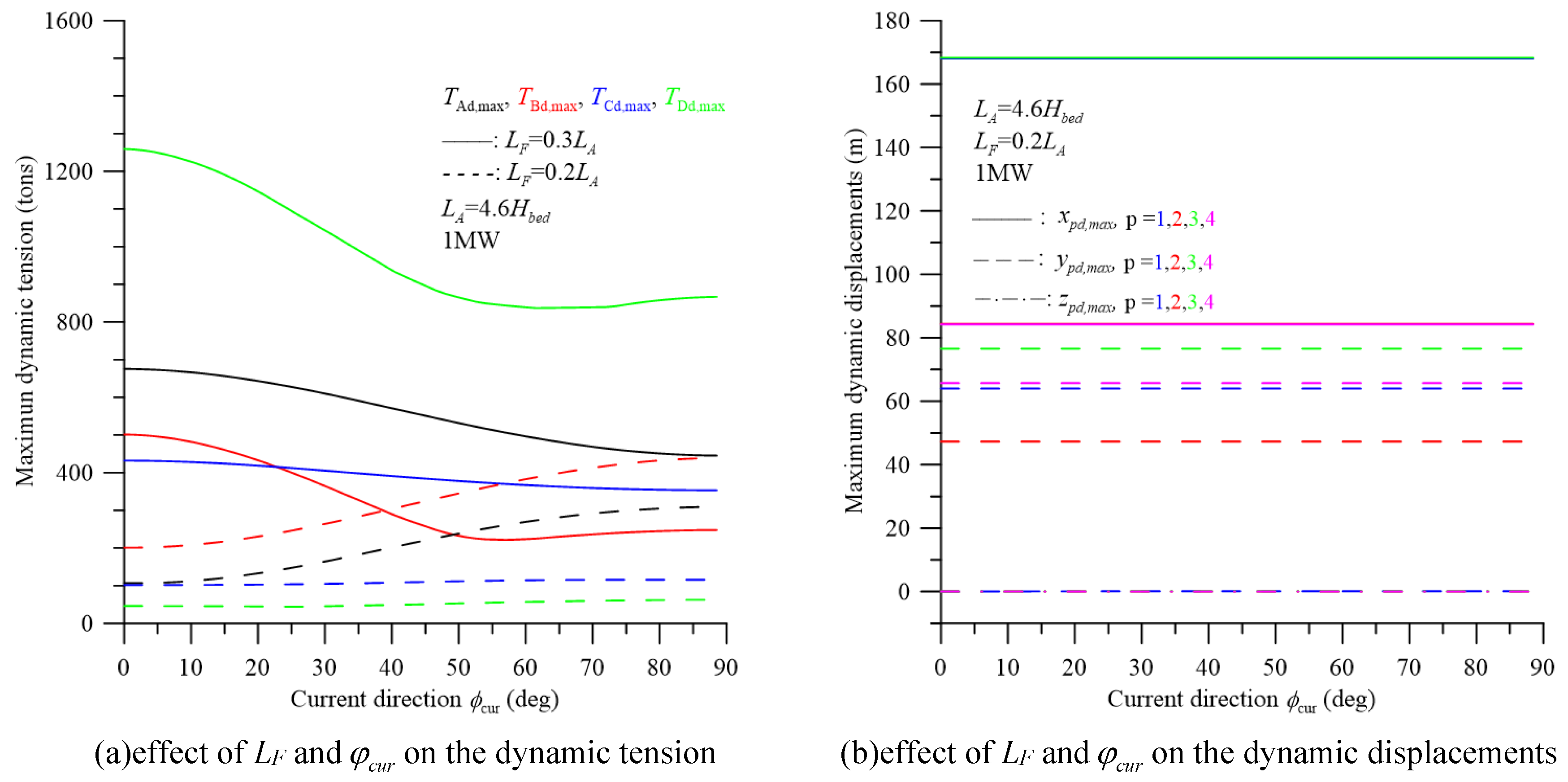
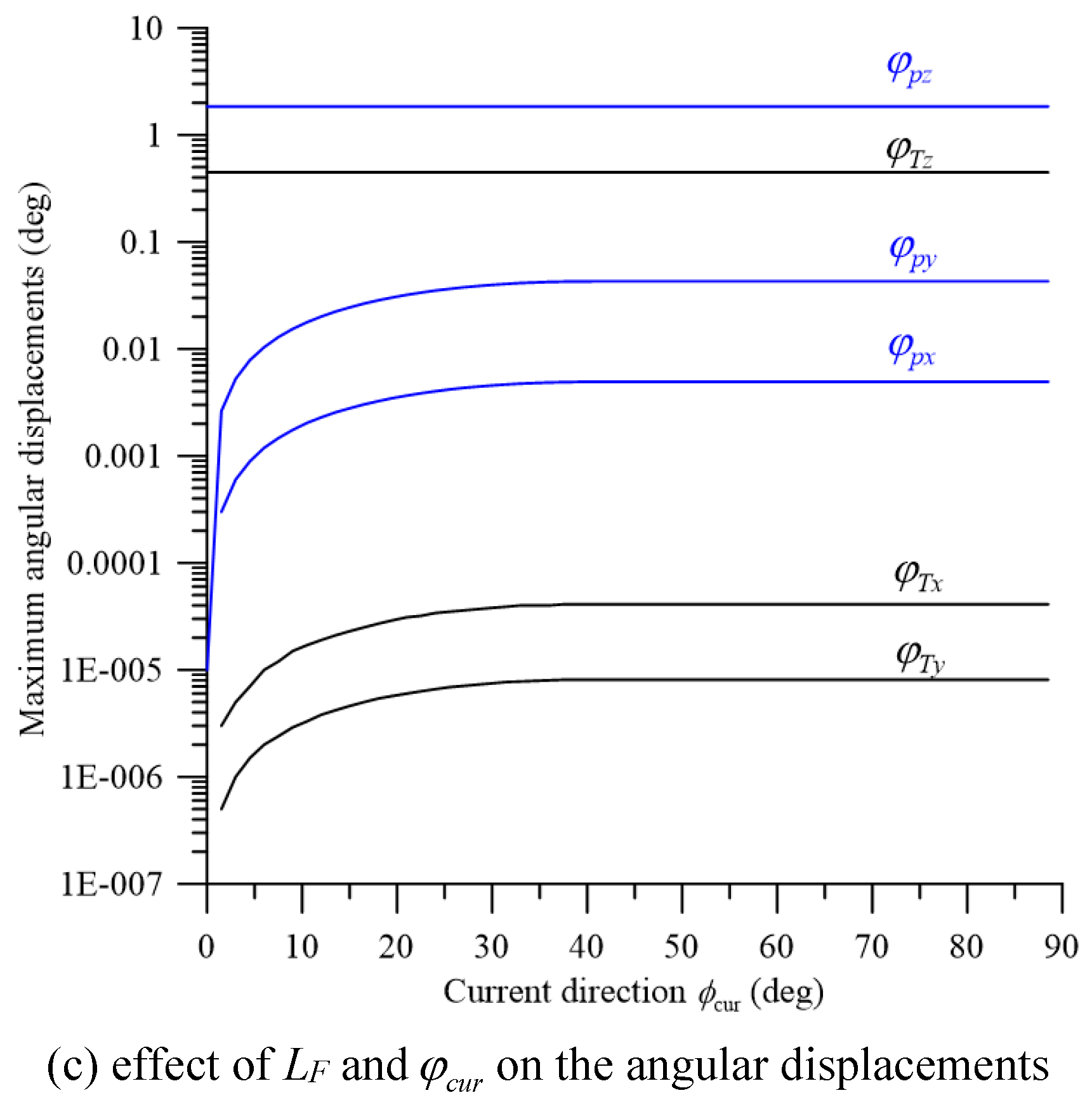
5. Dynamic Response and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Nomenclature
| ai | amplitude of the ith regular wave |
| ABX: ABT | cross-sectional area of surfaced cylinder of pontoons 3 and 4, respectively |
| ABY, ATY | damping area of platform and convertor under current, respectively |
| damping coefficient of floating platform and convertor | |
| Ei | Young’s modulus of rope i, i = A, B, C, D |
| FB | buoyance |
| fp | significant frequency |
| fkj | hydrodynamic force of element k in the j-direction |
| , | the drag of the floating platform and the convertor under steady current |
| Hbed | depth of seabed |
| Hs | significant wave height |
| mass moment of inertia of the convertor and the platform about the j-axis. | |
| g | gravity |
| Kid | effective spring constant of rope i, |
| wave vector of the i-th regular wave | |
| Li | length of rope i |
| LE | horizontal distance between the convertor and platform, |
| Mi | mass of element i |
| effective mass of rope A in the i-direction | |
| hydrodynamic moment of convertor or platform about the i-axis | |
| coordinate | |
| distance between the center of gravity of invertor and the rope B, about the x-axis. | |
| distance between the center of gravity of invertor and the rope D, about the y-axis. | |
| distance between the center of gravity of invertor and the rope B, about the z-axis | |
| , | distances in the y-z plane from the center of gravity to the rope A and B, respectively |
| , | distances in the x-z plane from the center of gravity to the rope A and C, respectively |
| ,, | distances in the x-y plane from the center of gravity to the ropes A, B and C, respectively |
| Ti | tension force of rope i |
| t | time variable |
| V | ocean current velocity |
| Wi | weight of component i |
| wPE | weight per unit length of HMPE |
| xi, yi, zi | displacements of component i |
| xw | sea surface elevation |
| α | relative angle between the directions of wave and current |
| ρ | density of sea water |
| ωΤ | angular speed of turbine |
| Ω | angular frequency of wave |
| angular displacement of convertor or platform about the j-axis | |
| phase delay of wave, | |
| θi | angles of rope i |
| λ | length of wave |
| δi | elongation of rope i |
| Subscript: | |
| 0~4 | mooring foundation, floating platform, convertor, and two pontoons, respectively |
| A, B, C, D | Ropes A, B, C, and D, respectively |
| mod | model |
| iα, iβ | component α, β of rope i = A, B, C, and D |
| frac | fracture |
| s, d | static and dynamic, respectively |
| PE | PE dyneema rope |
| P | platform |
| pro | ptototype |
| T | convertor |
References
- Chen, Y. Y.; Hsu, H. C.; Bai, C. Y., Yang Y., Lee C. W., Cheng H. K., Shyue S. W., Li M. S. Evaluation of test platform in the open sea and mounting test of KW Kuroshio power-generating pilot facilities. In Proceedings of the 2016 Taiwan Wind Energy Conference, Keelung, Taiwan, 24–25 November 2016.
- IHI; NEDO. The demonstration experiment of the IHI ocean current turbine located off the coast of Kuchinoshima Island, Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan, 14 August 2017. Available online: https://tethys.pnnl.gov/project-sites/ihi-ocean-current-turbine (accessed on 28 August 2021).
- Guo et al. Manufacture and sea trial of 20 kW Floating Kuroshio Turbine. (2021) NAMR110050; Ocean Affairs Council: Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 2021. (In Chinese).
- Lin, S.M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Hsu, H.C.; Li, M.S. Dynamic Stability of an Ocean Current Turbine System. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.M.; Chen, Y.Y. Dynamic stability and protection design of a submarined floater platform avoiding Typhoon wave impact. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Liauh, C.T. Dynamic stability of the coupled pontoon-ocean turbine-floater platform-rope system under harmonic wave excitation and steady ocean current. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 01425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.M.; Liauh, C.T.; Utama, D.W. Design and dynamic stability analysis of a submersible ocean current generator-platform mooring system under typhoon irregular wave. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.M. , Utama D.W.; Liauh C.T. Coupled translational-rotational stability analysis of a submersible ocean current converter-platform mooring system under typhoon wave. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.M. , Wang W.R.and Yuan H. Transient translational-rotational motion of an ocean current converter mooring system with initial conditions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, W.J., Jr.; Moskowitz, L. A proposed spectral form for fully developed wind seas based on the similarity theory of S. A. Kitaigorodskii. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1964, 69, 5181–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, S.A. Dynamic response of offshore platforms to extreme waves including fluid-structure interaction. Engineering Structures, 1982,4(3): 179-185.
- Belibassakis, K. A. A boundary element method for the hydrodynamic analysis of floating bodies in variable bathymetry regions. Engineering analysis with boundary elements, 2008, 32(10): 796-810.
- Geuzaine, P.; Farhat, C.; Brown, G. Application of a three-field nonlinear fluid-structure formulation to the prediction of the aeroelastic parameters of an f-16 fighter. Computers and Fluids,2003, 32:3–29.
- Bathe, K.J.; Nitikitpaiboon, C.; Wang, X. A mixed displacement-based finite element formulation for acoustic fluid-structure interaction. Computers and Structures, 1995, 56(2-3):225–237.
- Lin, S.M.; Wang W., R.; Lee, S. Y.; Chen C., W.; Hsiao, Y.C.; Teng, M.J. Wave modes of a pre-stressed thick tube conveying blood on the viscoelastic foundation. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2015, 39: 466–482.
- Tsui,Y.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Huang, C.L.; Lin, S.W. A finite-volume-based approach for dynamic fluid-structure interaction. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part B: Fundamentals, 2013, 64(4): 326-349.
- Hasanpour, A.; Istrati, D.; Buckle, I. Coupled SPH–FEM Modeling of Tsunami-Borne Large Debris Flow and Impact on Coastal Structures. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2021, 9(10), 1068. [CrossRef]
- Shyue, S.W. Development and Promotion of Key Technologies of Ocean Current Energy; OAC108001; Ocean Affairs Council, Kaohsiung, Taiwan: 2019; pp. 4–103. (in Chinese).
- Aggarwal, A.; Pákozdi, C.; Bihs, H.; Myrhaug, D.; Chella, M.A. Free Surface Reconstruction for Phase Accurate Irregular Wave Generation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
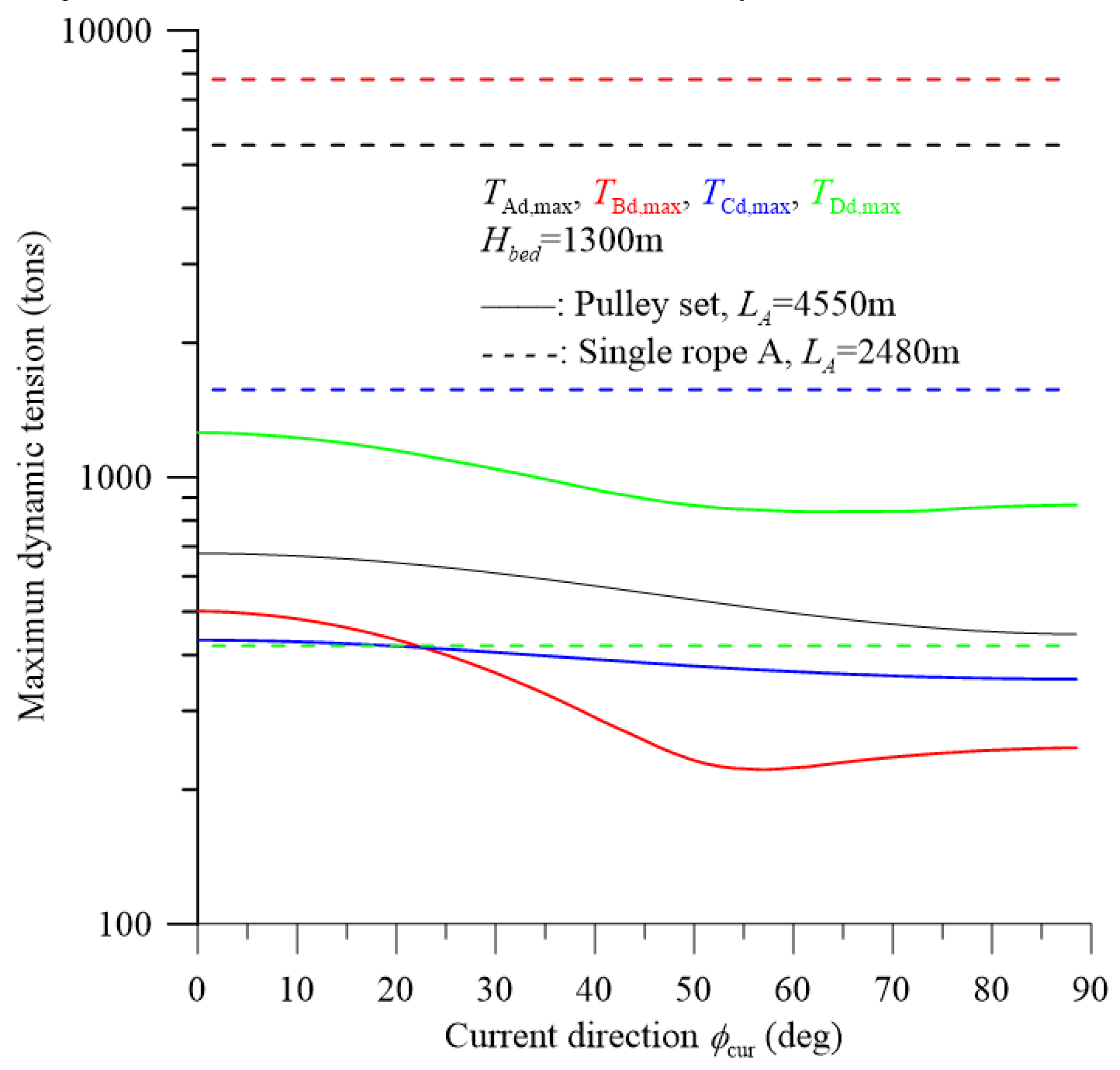
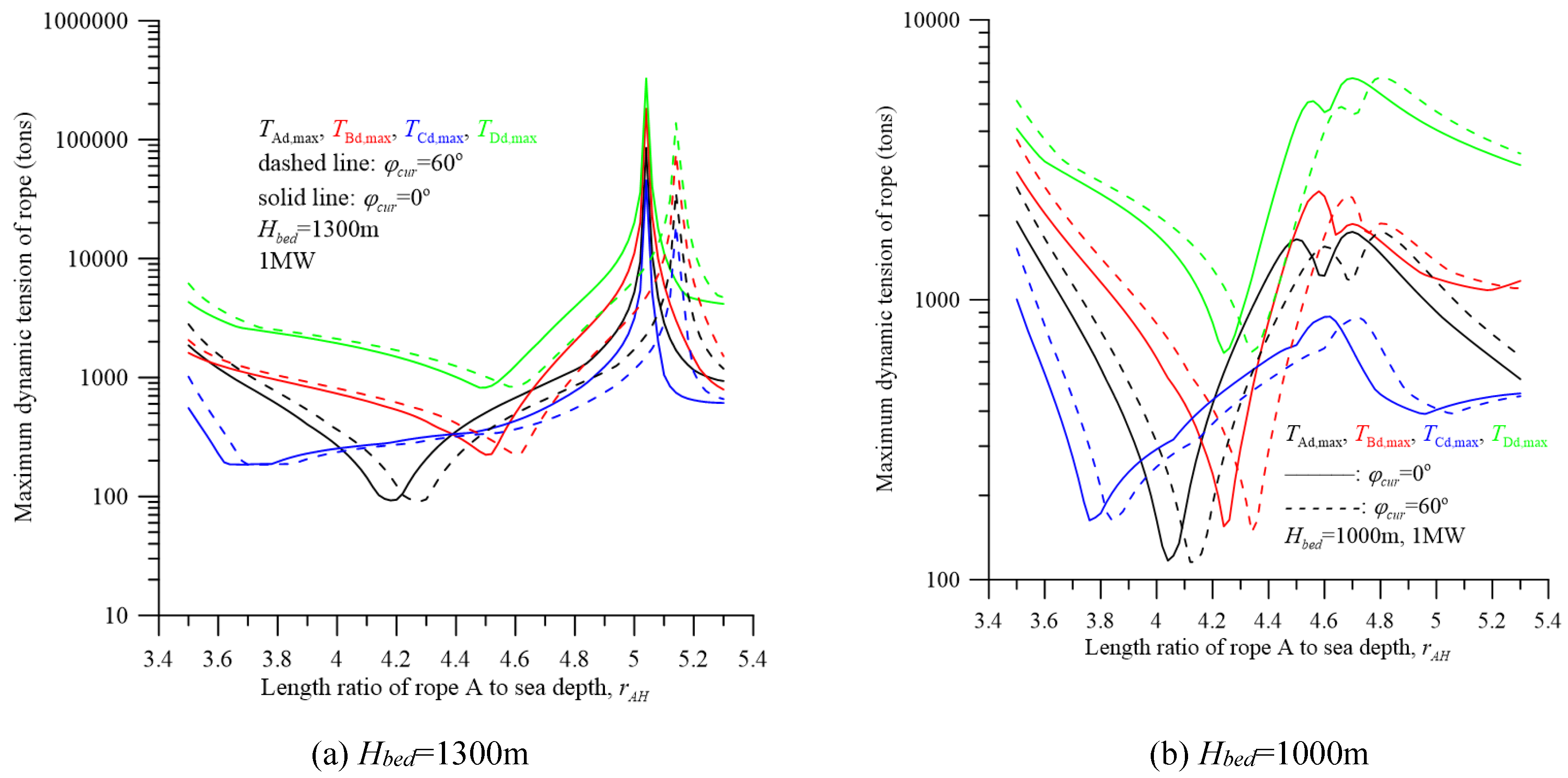
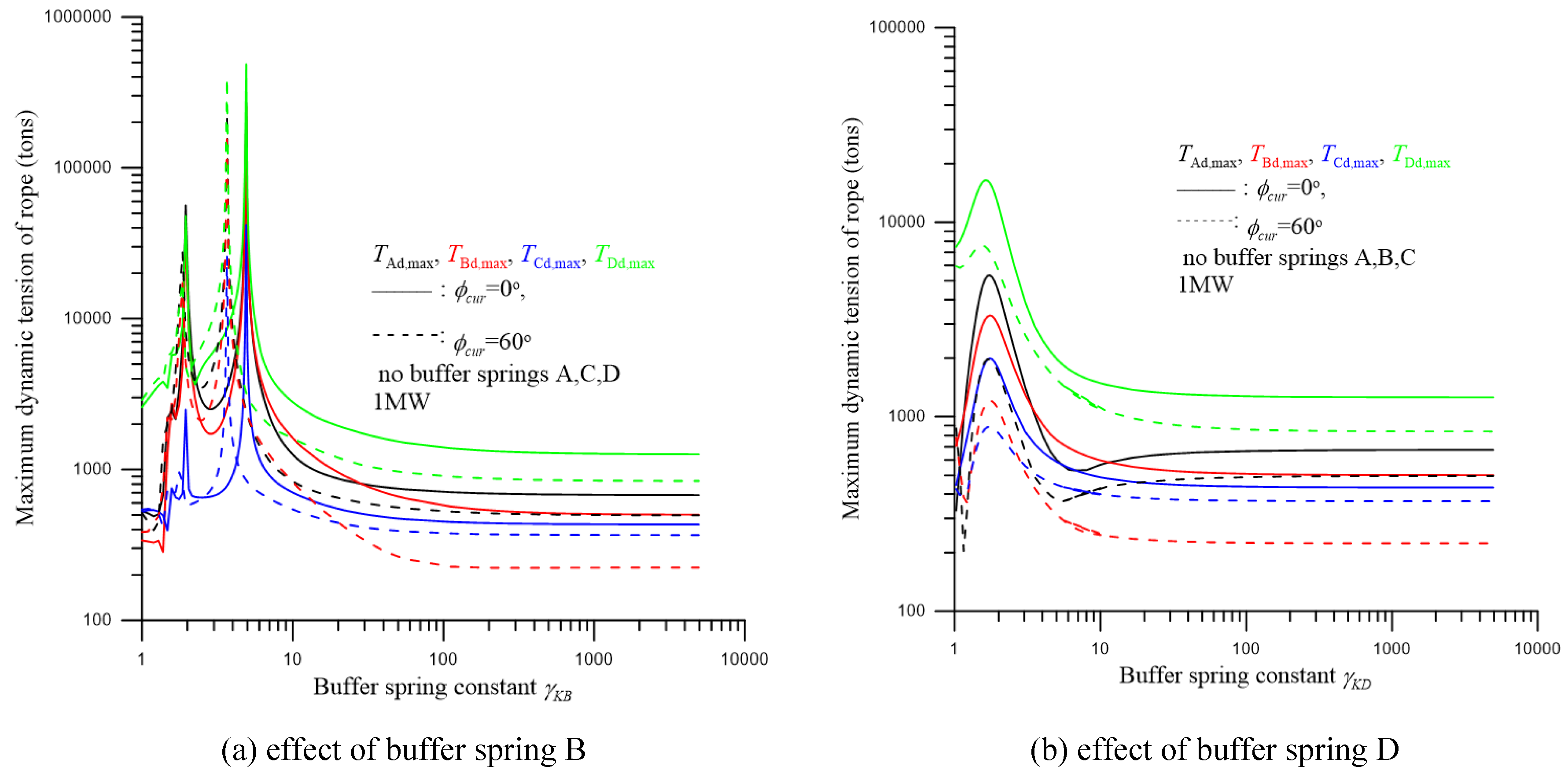
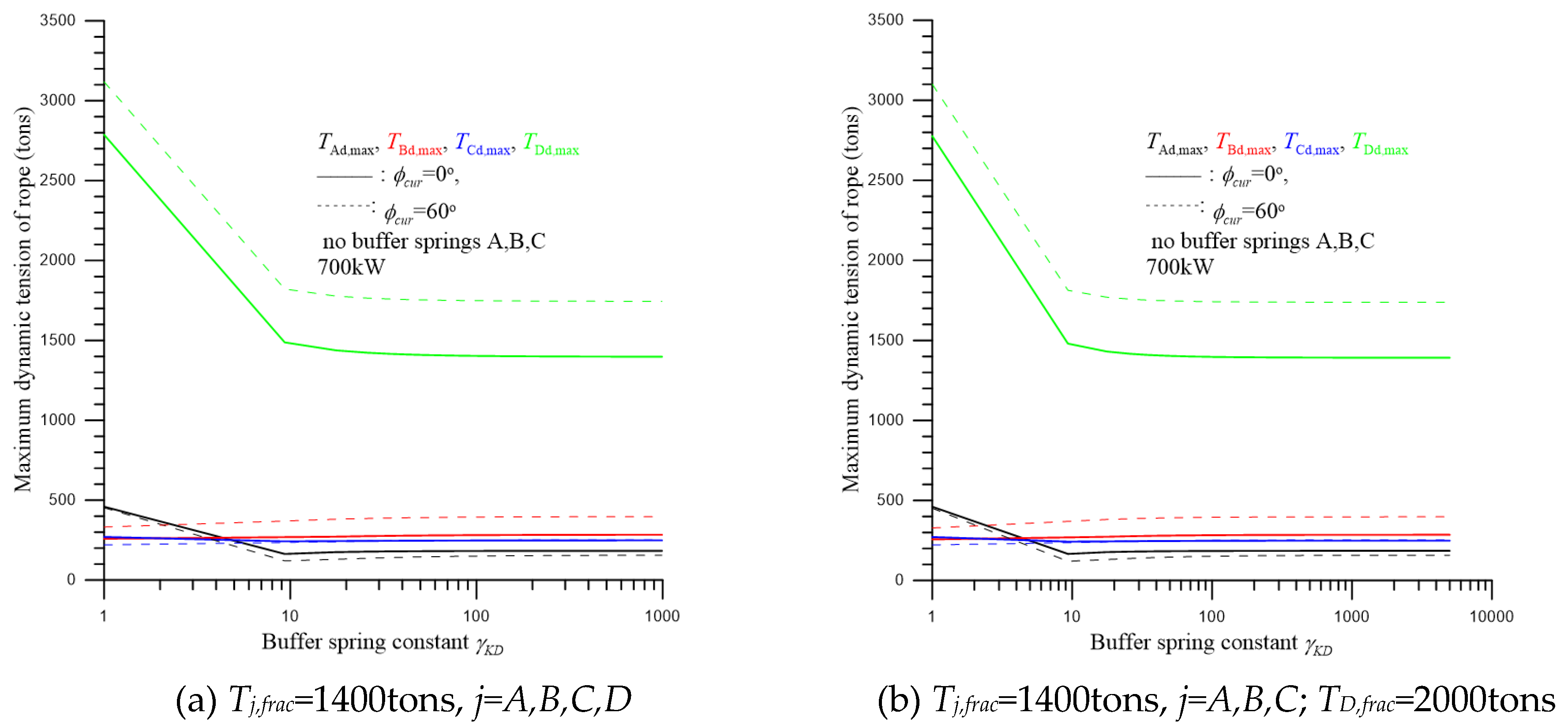
| parameter | dimension | parameter | dimension |
|---|---|---|---|
| depth of seabed Hbed | 1300m | current velocity V | 1.5m/s |
| length of rope A, LA | 5200m | length of rope B, LB | 170m |
| length of rope C, LC | 60m | length of rope D, LD | 140m |
| Static drag of the invertor FDT | 59.35 tons | Static drag of the platform FDB | 0.077 tons |
| Significant frequency | Parameter | Regular wave | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
|
Tp =15.0s, fp =0.067Hz |
fi(Hz) | 0.043 | 0.067 | 0.092 | 0.115 | 0.150 | 0.267 |
| ki(1/m) | 0.0073 | 0.0179 | 0.0339 | 0.0533 | 0.0906 | 0.2861 | |
| li(m) | 863.6 | 350.9 | 185.6 | 117.9 | 69.3 | 22.0 | |
|
Tp =16.5s, fp =0.061Hz |
fi(Hz) | 0.043 | 0.061 | 0.086 | 0.115 | 0.150 | 0.267 |
| ki(1/m) | 0.0073 | 0.0148 | 0.0295 | 0.0533 | 0.0906 | 0.2861 | |
| li(m) | 863.6 | 424.7 | 212.8 | 117.9 | 69.3 | 22.0 | |
|
Tp=17.5s, fp=0.057Hz |
fi(Hz) | 0.043 | 0.057 | 0.082 | 0.115 | 0.150 | 0.267 |
| ki(1/m) | 0.0073 | 0.0132 | 0.0272 | 0.0533 | 0.0906 | 0.2861 | |
| li(m) | 863.6 | 477.6 | 231.2 | 117.9 | 69.3 | 22.0 | |
| (o) | 30 | 60 | 90 | 120 | 170 | 300 | |
| Parameter | Dimension | Parameter | Dimension | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| depth of seabed Hbed | 1300m | length of rope A, LA | 5980m | |
| length of rope B, LB | 152.97m | length of rope C, LC | 100m | |
| length of rope D, LD | 70m | distance between two foundations, LF | 1196m | |
| current velocity V | 1.5m/s | net buonyance of invertor and platform FBNT/ FBNB | 1543.6/689.2tons | |
| static drag of the invertor FDT | 148.3 tons | static drag of the platform FDB | 0.192 tons | |
| mass of the platform M1 | 790.6 tons | mass of the invertor M2 | 2126.6 tons | |
| mass of the pontoon 3, M3 | 395.3tons | mass of the pontoon 4, M4 | 474.3tons | |
| cross-sectional area of surfaced cylinder of pontoon 3, ABX | 5.75m2 | mass moment of inertia of the convertor about the x, y, z-axis, |
/ |
|
| cross-sectional area of surfaced cylinder of pontoon 4, ABT | 5.75m2 | mass moment of inertia of the platform about the x,y,z-axis, | / | |
| significant wave height Hs | 15.4m | significant period Tp | 16.5s | |
| relative angle between current and wave a | 30o | phase angles of six regular simulating the irregular wave | 30/60/90/120/170 /300o | |
| HMPE / Dyneema® SK75 |
Young’s modulus EPE | 116GPa, | distance from gravities of platform and convertor |
|
| weight per unit length wPE | 24.47kg/m | |||
| diameter DPE | 178.9mm | |||
| cross sectional area APE | 0.0251m2 | |||
| fracture strength Tfrac | 2000tons | |||
| Parameter | Dimension | Parameter | Dimension | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| depth of seabed Hbed | 1300m | length of rope A, LA | 5980m | |
| length of rope B, LB | 152.97m | length of rope C, LC | 100m | |
| length of rope D, LD | 70m | distance between two foundations, LF | 1196m | |
| current velocity V | 1.5m/s | net buonyance of invertor and platform FBNT/ FBNB | 907.4/407.9tons | |
| static drag of the invertor FDT | 103.9 tons | static drag of the platform FDB | 0.134 tons | |
| mass of the platform M1 | 463.0 tons | mass of the invertor M2 | 1245.5 tons | |
| mass of the pontoon 3, M3 | 213.5tons | mass of the pontoon 4, M4 | 277.8tons | |
| cross-sectional area of surfaced cylinder of pontoon 3, ABX | 4.03m2 | mass moment of inertia of the convertor about the x, y, z-axis, |
/ |
|
| cross-sectional area of surfaced cylinder of pontoon 4, ABT | 4.03m2 | mass moment of inertia of the platform about the x,y,z-axis, | / | |
| significant wave height Hs | 15.4m | significant period Tp | 16.5s | |
| relative angle between current and wave a | 30o | phase angles of six regular simulating the irregular wave | 30/60/90/120/170 /300o | |
| HMPE / Dyneema® SK75 |
Young’s modulus EPE | 116GPa, | distance from gravities of platform and convertor |
|
| weight per unit length wPE | 17.16kg/m | |||
| diameter DPE | 149.7mm | |||
| cross sectional area APE | 0.0176m2 | |||
| fracture strength Tfrac | 1400tons | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





