Submitted:
22 July 2024
Posted:
24 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
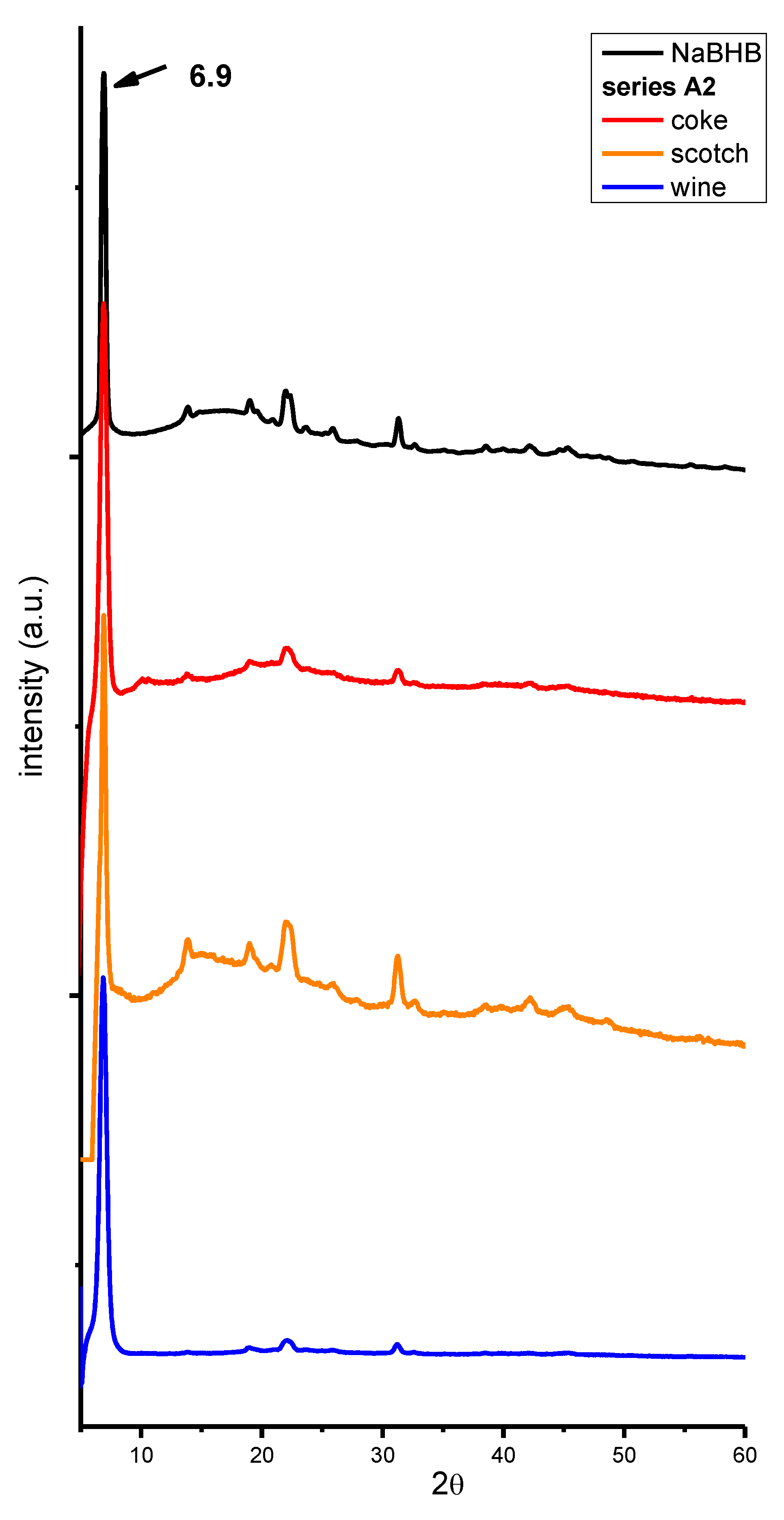
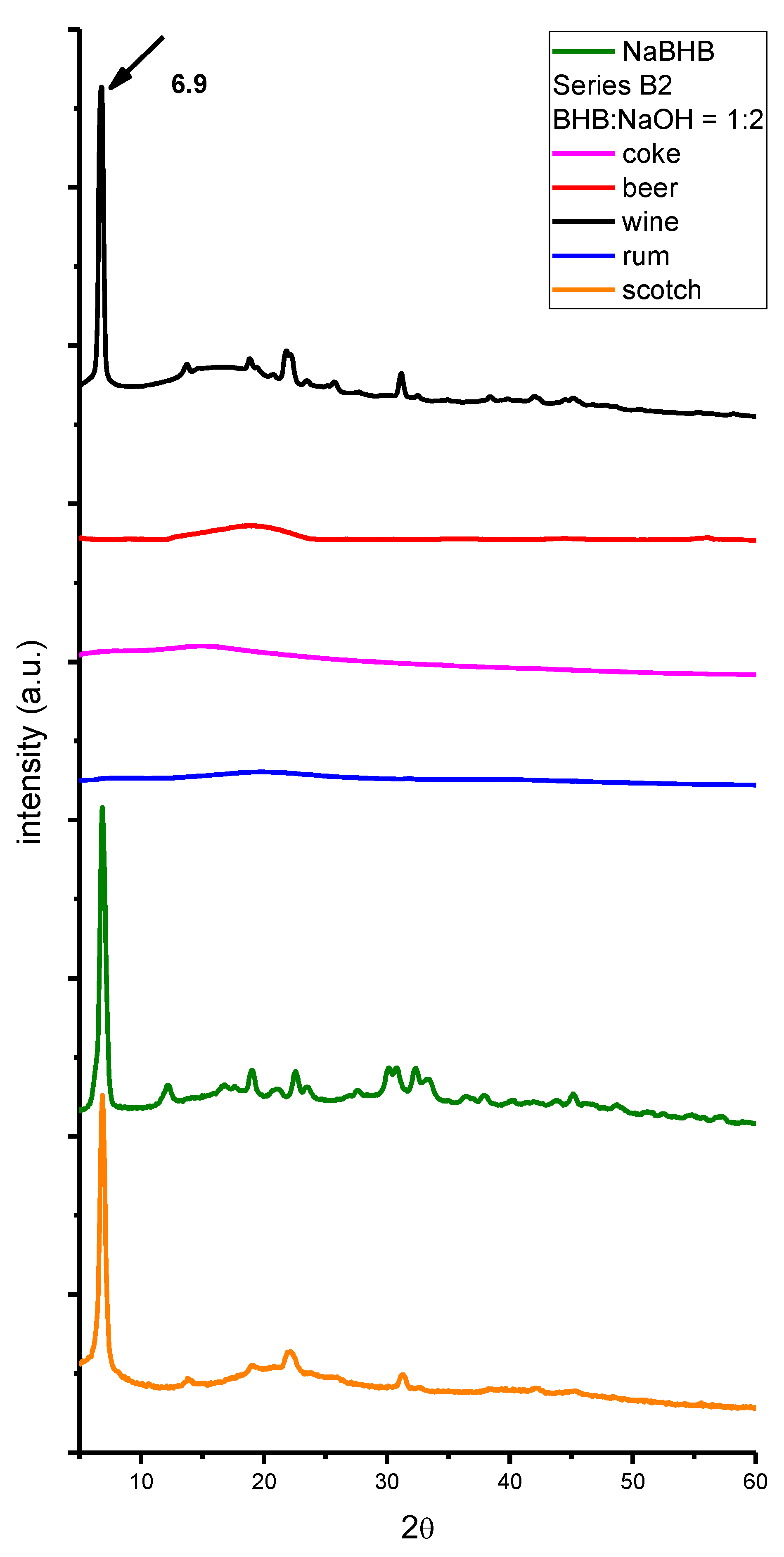
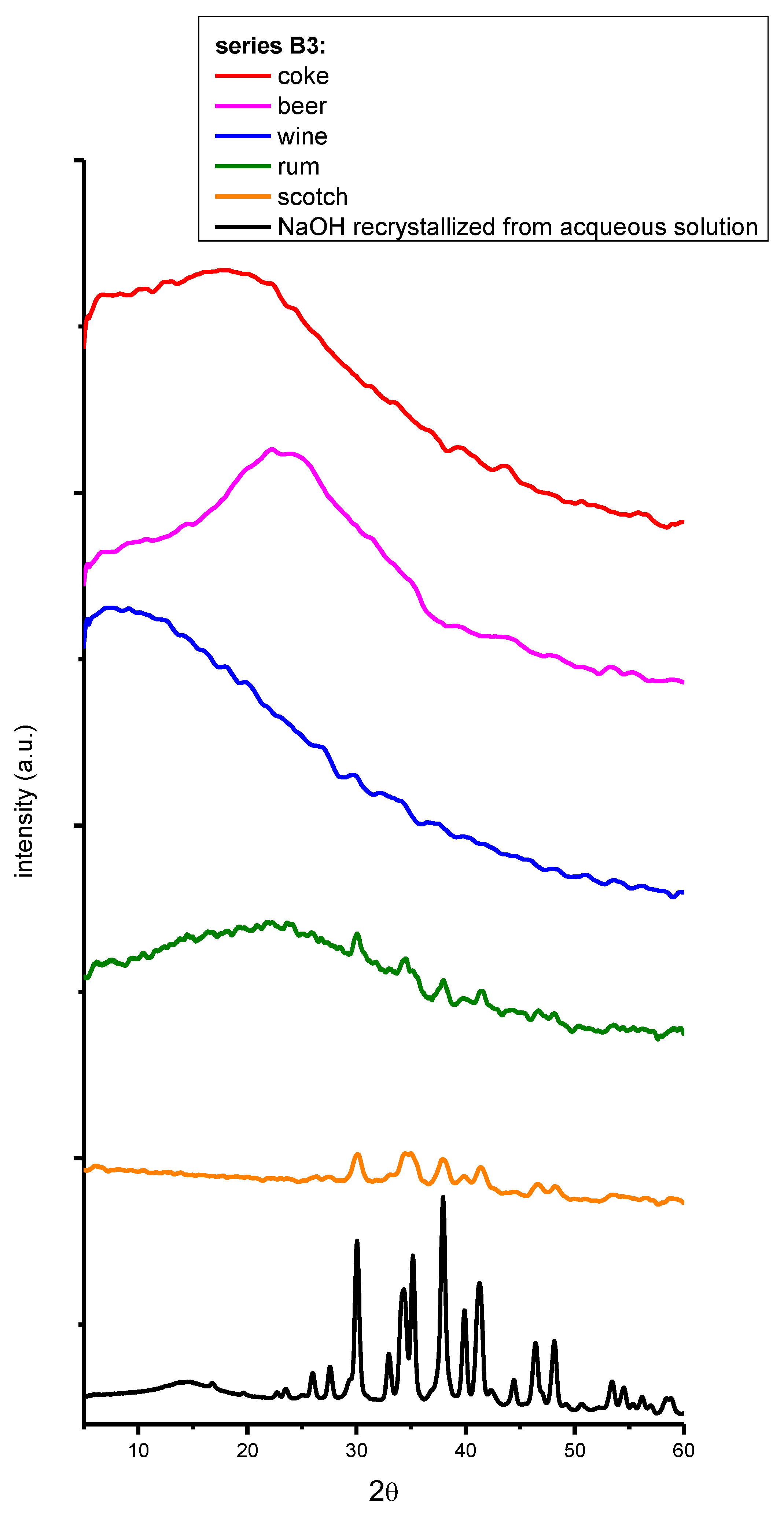
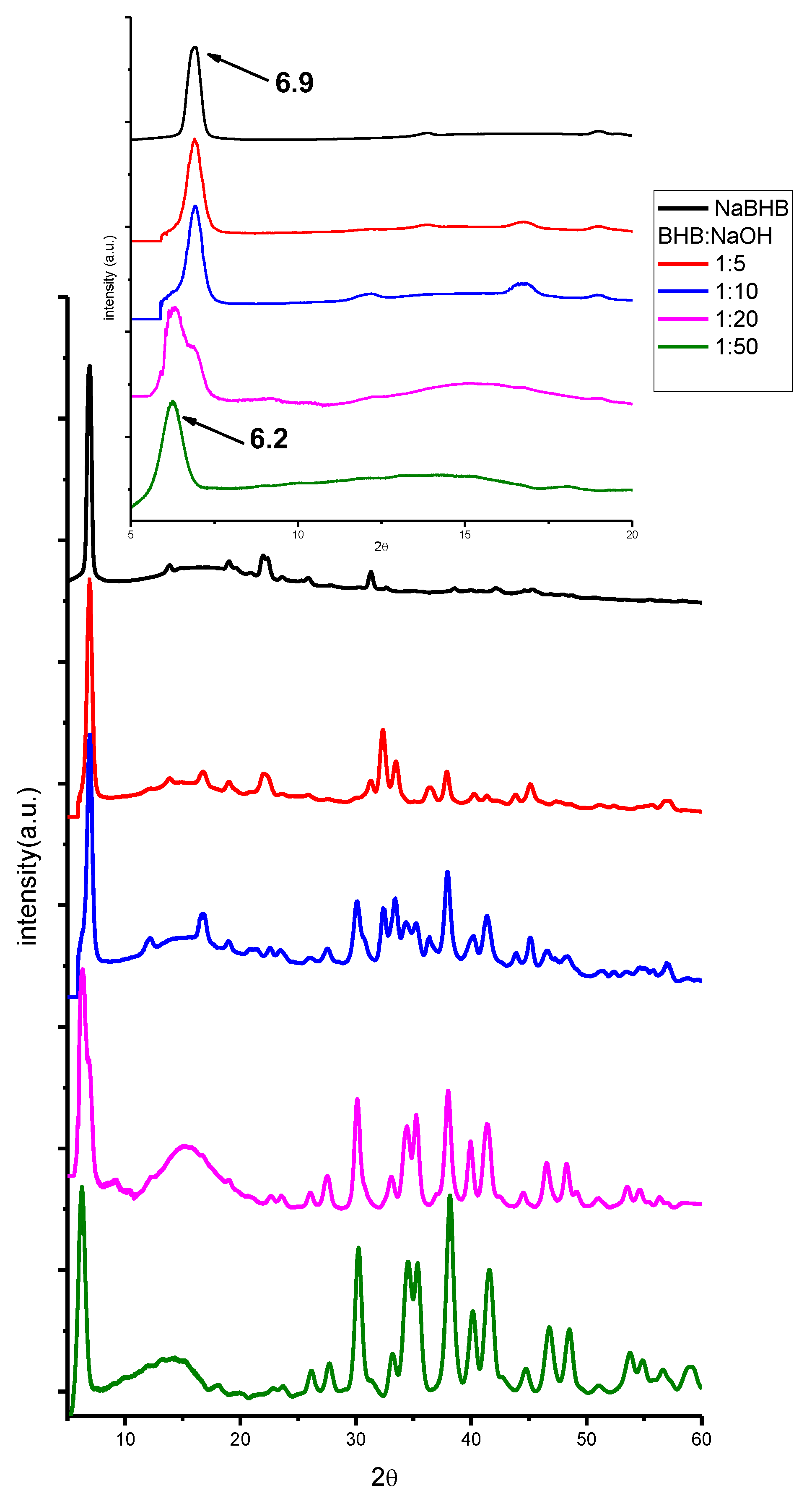
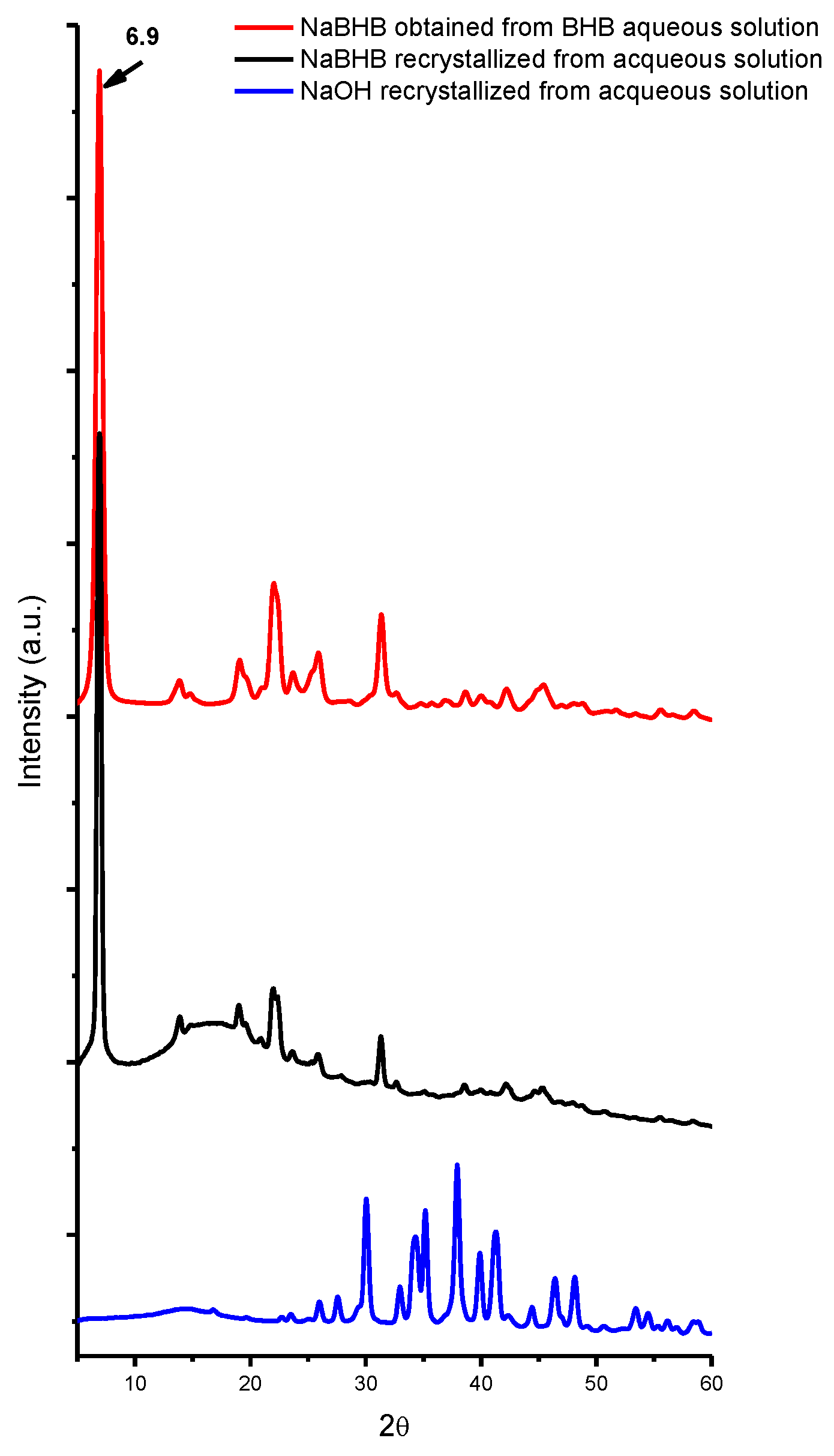
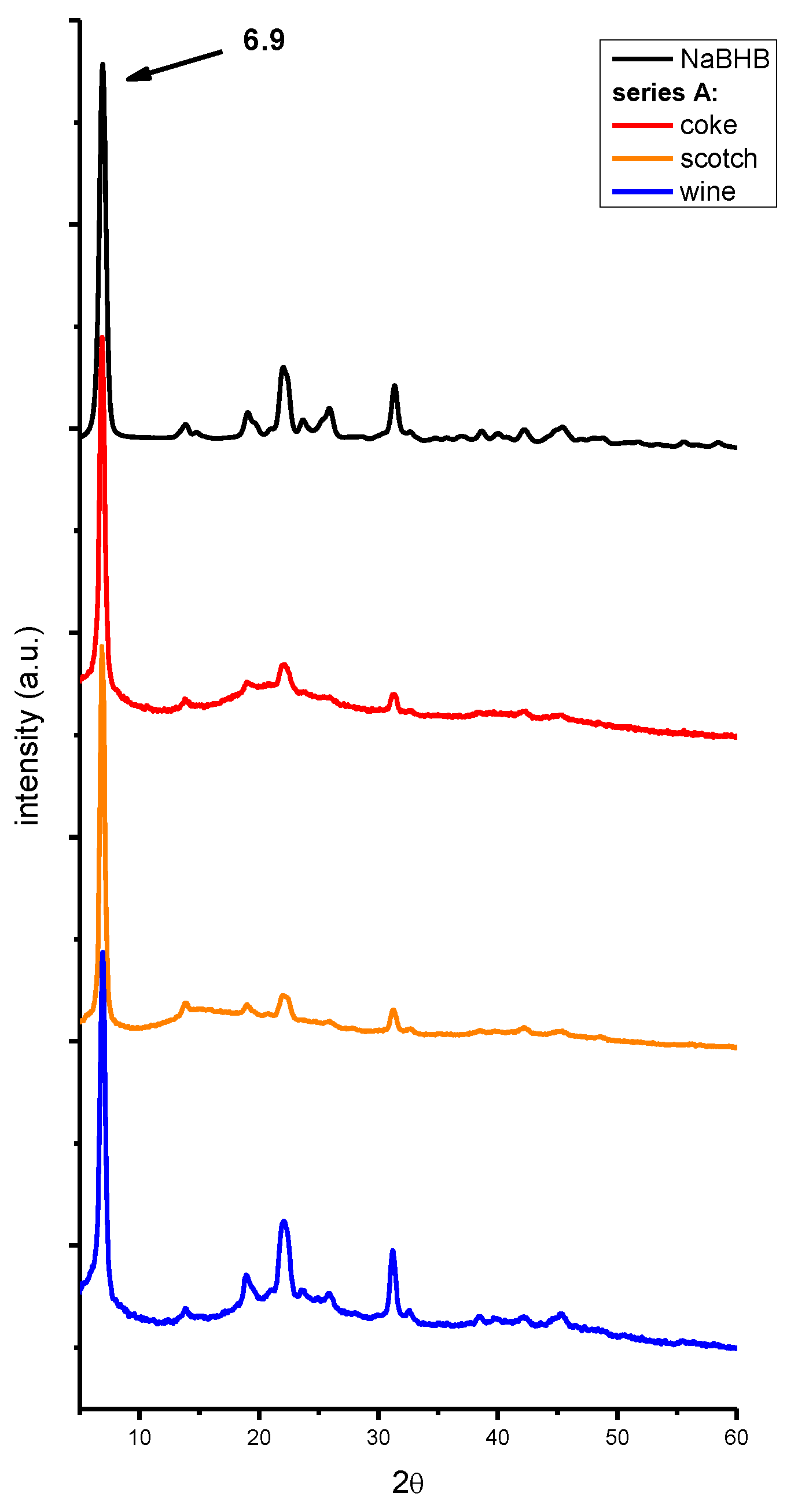
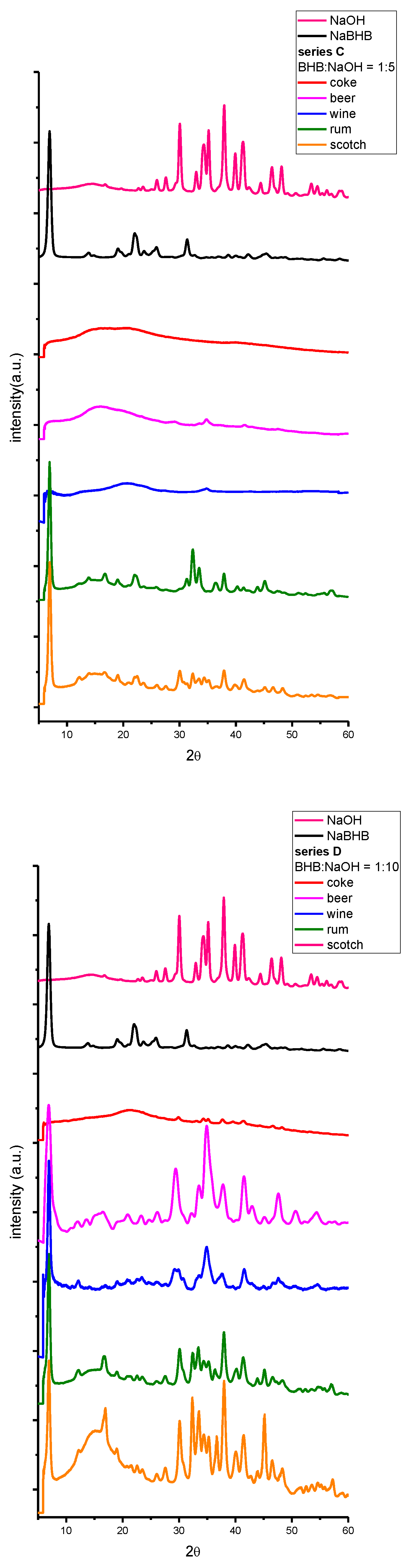
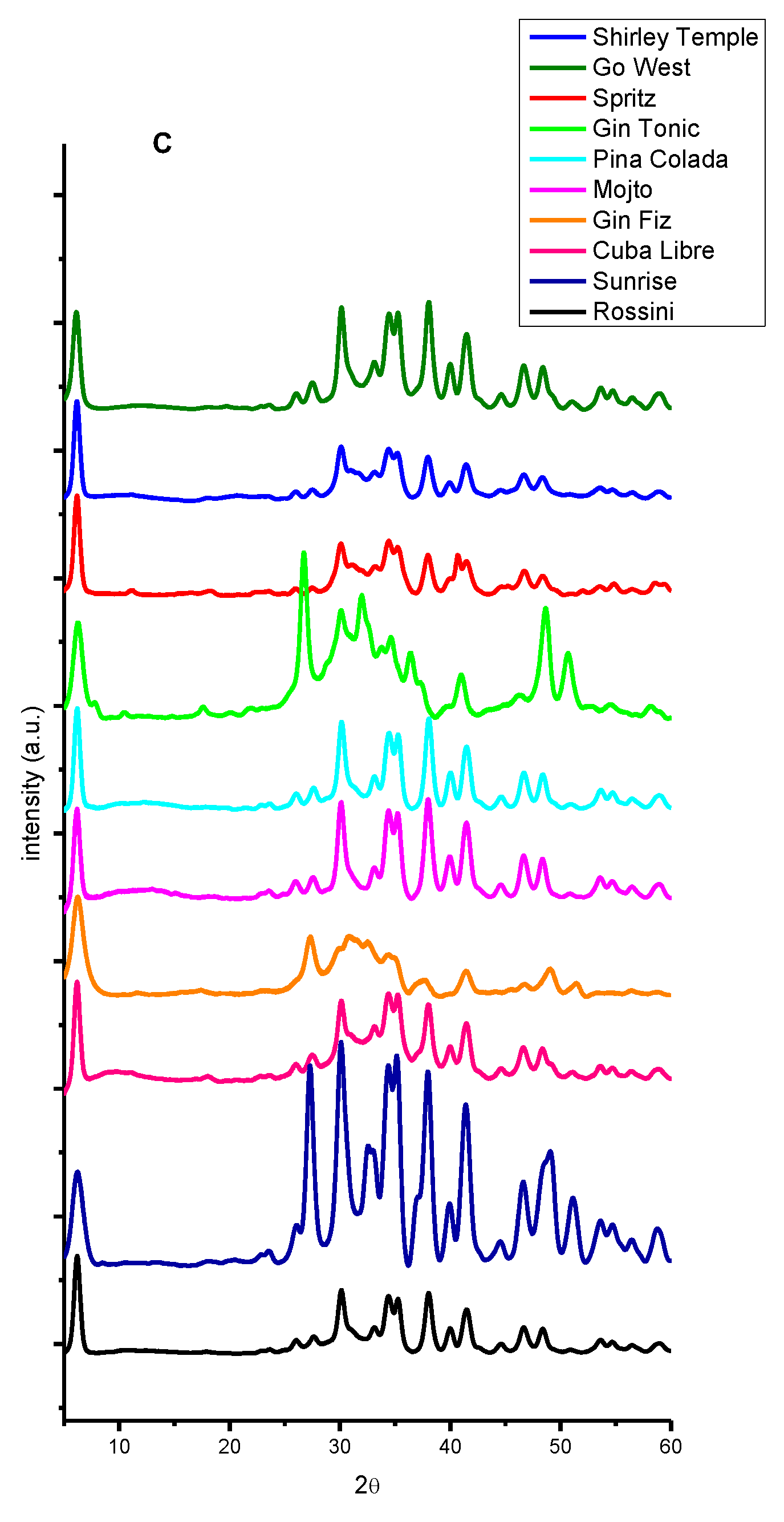
2. Results and Discussion
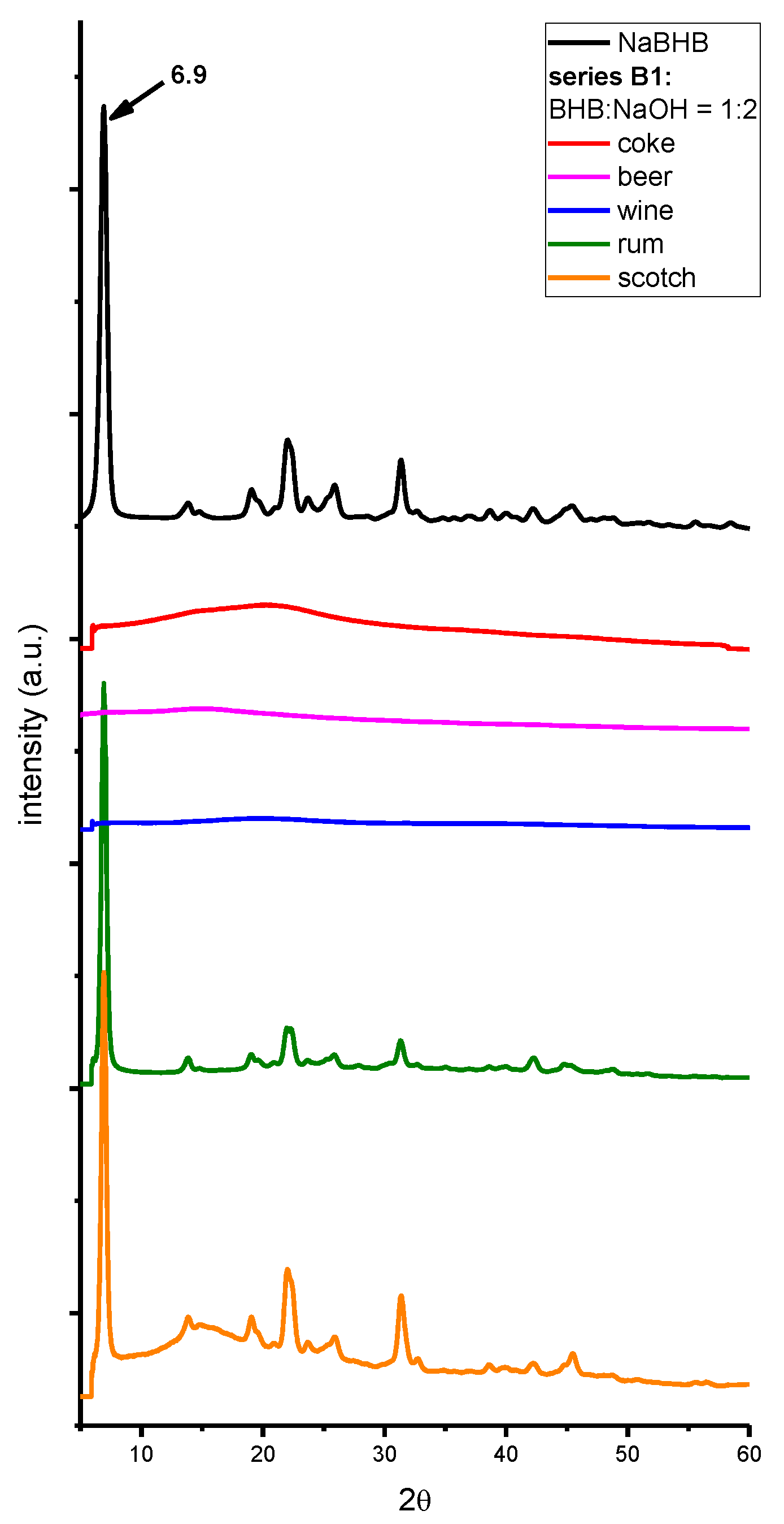
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Standard Preparation
3.3. Sample Preparation
3.4. X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD).
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- Cocktails recipes.
- Shirley Temple
- 20 ml grenadine
- 100 ml Ginger Ale
- 1 lemon slice
- ice cubes
- Go West
- 30 ml Limoncello
- 30 ml white wine
- 15 ml Hazelnut Irish Cream
- 15 ml simple syrup
- 15 ml lemon juice
- Aperol Spritz
- 60 ml Prosecco
- 1 splash club soda
- 44 ml Aperol
- 1 slice orange
- ice cubes
- Gin Tonic
- 50 ml gin
- 150 ml tonic water
- 1 lemon
- ice cubes
- Pina colada
- 50 ml White Rum
- 30 ml Coconut Cream
- 50 ml Fresh Pineapple Juice
- ice cubes
- Mojito
- 10 fresh mint leaves
- 44 ml white rum
- ½ medium lime
- 2 tablespoons white sugar
- 120 ml club soda
- ice cubes
- Gin Fizz
- 45 ml Gin
- 30 ml Fresh Lemon Juice
- 10 ml Simple Syrup
- Splash of Soda Water
- ice cubes
- Cuba libre
- 50 ml White Rum
- 120 ml Coca Cola
- 10 ml Fresh Lime Juice
- ice cubes
- Sunrise
- 90 ml orange juice
- 60 ml sparkling water
- 7 ml grenadine
- ice cubes
- Rossini
- 50 g strawberries
- 10 g sugar
- 100 ml prosecco
References
- Elliott, S.P. Gamma hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) concentrations in humans and factors affecting endogenous production. Forensic Sci. Int. 2003, 133, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brailsford, A.D.; Cowan, D.A.; Kicman, A.T. Pharmacokinetic properties of -hydroxybutyrate (GHB) in whole blood, serum, and urine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2012, 36, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.G.; Chan, K.F.; Gibson, K.M.; Snead, O.C. Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid: neurobiology and toxicology of a recreational drug. Toxicol. Rev. 2004, 23(1), 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.; Keatin, G.M. Sodium oxybate: A review of its use in the management of narcolepsy. CNS Drugs 2007, 21(4), 337–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscolo-Berto, R.; Viel, G.; Montagnese, S.; Raduazzo, D.I.; Ferrara, S.D.; Dauvilliers, Y. Narcolepsy and effectiveness of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB): a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sleep Med. Rev. 2012, 16, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chick, J.; Nutt, D.J. Substitution therapy for alcoholism: Time for a reappraisal? J. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 26(2), 205–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keating, G.M. Sodium oxybate: A review of its use in alcohol withdrawal syndrome and in the maintenance of abstinence in alcohol dependence. Clin. Drug. Investig. 2014, 34(1), 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, M.G.; Pérez-Cárceles, M. D-; Osuna E.; Legaz I. Drug-facilitated sexual assault and other crimes: A systematic review by countries. J. Forensic. Leg. Med. 2021, 79, 102151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapitány-Fövény, M.; Zacher, G.; Posta, J.; Demetrovics, Z. GHB-involved crimes among intoxicated patients. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 275, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, R.H.; Milteer, R.; LeBeau, M.A. Drug-facilitated sexual assault ('date rape'). South Med J. 2000, 93(6), 558–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shbair, M.K.; Lhermitte, M. Drug-facilitated crimes: definitions, prevalence, difficulties and recommendations. A review. Ann. Pharm. Fr. 2010, 68(3), 136–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Németh, Z.; Kun, B.; Demetrovics, Z. Review: The involvement of gamma-hydroxybutyrate in reported sexual assaults: a systematic review. J. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 24(9), 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skov, K.; Johansen, S.S.; Linnet, K.; Nielsen, M.K.K. A review on the forensic toxicology of global drug-facilitated sexual assaults. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol Sci. 2022, 26(1), 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, L.; Richards, B.; Mintzer, M.; Griffiths, R.R. Relative Abuse Liability of GHB in Humans: A Comparison of Psychomotor, Subjective, and Cognitive Effects of Supratherapeutic Doses of Triazolam, Pentobarbital, and GHB. Neuropsychopharmacol 2006, 31, 2537–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillebrand J.; Olszewski D.; Sedefov R. (2008). GHB and its precursor GBL : an emerging trend case study (European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction, Ed.). Lisbon: European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA).
- Corkery, J.M.; Loi, B.; Claridge, H.; Goodair, C.; Corazza, O.; Elliott, S.; Schifano, F. Gamma hydroxybutyrate (GHB), gamma butyrolactone (GBL) and 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BD; BDO): A literature review with a focus on UK fatalities related to non-medical use. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 53, 52–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey T.; Lesar C.T.; Decatur J.; Lukasiewicz E.; Champeil E. Report on the analysis of common beverages spiked with gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) and gamma-butyrolactone (GBL) using NMR and the PURGE solvent-suppression technique. Forensic Sci. Int. 2011, 212(1-3), e40-5. [CrossRef]
- Beynon, C.M.; McVeigh, C.; McVeigh, J.; Leavey, C.; Bellis, M.A. The involvement of drugs and alcohol in drug-facilitated sexual assault: a systematic review of the evidence. Trauma Violence Abuse 2008, 9(3), 178–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busardò, F.P.; Varì, M.R.; di Trana, A.; Malaca, S.; Carlier, J.; di Luca, N.M. Drug-facilitated sexual assaults (DFSA): a serious underestimated issue. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol Sci. 2019, 23(24), 10577–10587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djezzar S.; Gaulier J.M.; Gorgiard C.; Chèze M.; Alvarez J.C.; Martin C.; Dumestre-Toulet, V.; Lavit M.; Mathieu O.; Eysseric H.; Berland E.; Roussel C.; Gaillard Y.; Hurtel-Lemaire A.S.; Deveaux M.; Pion C. Assessment of 19 years of a prospective national survey on drug-facilitated crimes in France, Legal Medicine 2023, 65, 102297. [CrossRef]
- Hagemann C.T.; Helland A.; Spigset O.; Espnes K.A.; Ormstad K.; Schei B. Ethanol and drug findings in women consulting a Sexual Assault Center – Associations with clinical characteristics and suspicions of drug-facilitated sexual assault, J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2013, 20, 6, 777-784. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufayet L.; Bargel S.; Bonnet A.; Boukerma A.K.; Chevallier C.;, Evrard M.; Guillotin S.; Loeuillet E.; Paradis C.; Pouget A.M.; Reynoard J.; Vaucel J.A. Gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB), 1,4-butanediol (1,4BD), and gamma-butyrolactone (GBL) intoxication: A state-of-the-art review. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 142, 105435. [CrossRef]
- Ingels, A.S.M.E.; Wille, S.M.R.; Samyn, N.; Lambert, W.E.; Stove, C.P.S. Screening and confirmation methods for GHB determination in biological fluids. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 3553–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziadosz, M.; Klintschar, M.; Teske, J. Signal-Separated Quantification of γ-Hydroxybutyrate with Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Human Urine and Serum as an Improvement of the Analyte Adduct Ion-Based Quantification. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2022, 46(6), 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen L.K.; Hasselstrøm J.B. A hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography electrospray tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of γ-hydroxybutyrate and its precursors in forensic whole blood. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 222(1-3):352-9. [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Oh, S.M.; Chung, K.H.; Lee, S. A surrogate analyte-based LC-MS/MS method for the determination of γ-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) in human urine and variation of endogenous urinary concentrations of GHB. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 98, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanshuxian, L.; Yilei, F.; Zhongping, H.; Huijun, L.; Lili, W.; Zhenlu, S.; Ichi, W. Rapid determination of γ-hydroxybutyric acid in human hair by on-line pyrolytic methylation-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Appl Pyrol. 2020, 151, 104920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuer, A.E.; Bavato, F.; Schnider, L.K.; Dornbierer, D.A.; Bosch, O.G.; Quednow, B.B.; Seifritz, E. Steuer C. Kraemer T. Urinary concentrations of GHB and its novel amino acid and carnitine conjugates following controlled GHB administration to humans. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.E.; Hickey, L.D.; Goodpaster, J.V. Detection of ɣ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) and ɣ-butyrolactone (GBL) in alcoholic beverages via total vaporization solid-phase microextraction (TV-SPME) and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Forensic Sci. 2021, 66, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott S, Burgess V. The presence of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) and gamma-butyrolactone (GBL) in alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages. Forensic Sci Int. 2005, 151(2-3):289-92. [CrossRef]
- Grootveld M.; Algeo D.; Silwood C.J.; Blackburn J.C.; Clark A.D. Determination of the illicit drug gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) in human saliva and beverages by 1H NMR analysis. Biofactors 2006, 27(1-4), 21-36. [CrossRef]
- Chew, S.L.; Meyers, J.A. Identification and quantitation of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (NaGHB) by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Forensic Sci. 2003, 48(2), 292–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Signore, A.G.; McGregor, M.; Cho, B.P. 1H NMR analysis of GHB and GBL: further findings on the interconversion and a preliminary report on the analysis of GHB in serum and urine. J. Forensic Sci. 2005, 50(1), 81–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappell, J.S.; Meyn, A.W.; Ngim, K.K. The extraction and infrared identification of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) from aqueous solutions. J. Forensic Sci. 2004, 49(1), 52–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFrancesco J.V.; Witkowski M.R.; Ciolino L.A. GHB free acid: I. Solution formation studies and spectroscopic characterization by 1HNMR and FT-IR. J. Forensic Sci. 2006, 51(2), 321-9. [CrossRef]
- Ciolino, L.A; Mesmer, M.Z.; Satzger, R.D.; Machal, A.C.; McCauley, H.A.; Mohrhaus, A.S. The chemical interconversion of GHB and GBL: forensic issues and implications. J. Forensic Sci. 2001, 46(6), 1315–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, M.R; Ciolino, L.A.; Defrancesco, J.V. GHB free acid: II. Isolation and spectroscopic characterization for forensic analysis. J. Forensic Sci. 2006, 51(2), 330–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranenburg R.F.; Weesepoel Y.; Alewijn M.; Sap S.; Arisz P.W.F.; van Esch A.; Keizers P.H.J.; van Asten A.C. The importance of wavelength selection in on-scene identification of drugs of abuse with portable near-infrared spectroscopy, Forensic Chemistry, 2022, 30, 100437. [CrossRef]
- West, M.J.; Went, M.J. Detection of drugs of abuse by Raman spectroscopy. Drug Test. Anal. 2011, 3(9), 532–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewster, V.L.; Edwards, H.G.; Hargreaves, M.D.; Munshi, T. Identification of the date-rape drug GHB and its precursor GBL by Raman spectroscopy. Drug Test. Anal. 2009, 1(1), 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inscore, F.; Shende, C.; Sengupta, A.; Huang, H.; Farquharson, S. Detection of drugs of abuse in saliva by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). Appl. Spectrosc. 2011, 65(9), 1004–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alston W.C., 2nd; Ng, K. Rapid colorimetric screening test for gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (liquid X) in human urine. Forensic Sci Int. 2002, 126(2), 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, S.; Jain, U.; Chauhan, N. A systematic review on sensing techniques for drug- facilitated sexual assaults (DFSA) monitoring. Chinese J. Anal. Chem. 2021, 49, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhai, D.; Chang, Y.-T. , Chapter 49 - Detection of GHB by Optical Methods, in Neuropathology of Drug Addictions and Substance Misuse, Editor(s): Victor R. Preedy; Publisher: Academic Press, 2016; Volume 2, pp. 529–535. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Nuevalos, S.; Costero, A.M.; Parra, M.; Gil, S.; Arroyo, P.; Saez, J.A.; Gaviña, P.; Ceroni, P.; Fermi, A. Colorimetric and fluorescent hydrazone-BODIPY probes for the detection of γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) and cathinones. Dyes and Pigments 2022, 207, 110757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busardò F., P.; Jones, A.W. GHB pharmacology and toxicology: acute intoxication, concentrations in blood and urine in forensic cases and treatment of the withdrawal syndrome. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13(1), 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharf M.B.; Lai A.A.; Branigan B.; Stover R.; Berkowitz D.B. Pharmacokinetics of gammahydroxybutyrate (GHB) in narcoleptic patients. Sleep, 1998, 21, 507–514.
- Abanades, S.; Farré, M.; Segura, M.; Pichini, S.; Barral, D.; Pacifici, R.; Pellegrini, M.; Fonseca, F.; Langohr, K.; De La Torre, R. Gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) in humans: pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1074, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines for the Forensic analysis of drugs facilitating sexual assault and other criminal acts- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime; United Nations: New York, 2011, pp. 2011–300.
- Bennett, M.J.; Steiner, R.R. Detection of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in various drink matrices via AccuTOF-DART. J. Forensic Sci. 2009, 54(2), 370–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Chen, S.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, J.; Mei, Y.; Cao, J.; Zheng, K. Application of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and GC-MS/MS for the determination of GHB in beverages and hair. J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2020, 1144, 122058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junghyun R.; Youngmi K. Overcoming interferences in the colorimetric and fluorimetric detection of γ-hydroxybutyrate in spiked beverages. Sensors & Actuators B: Chemical 2022, 364, 131861.
- Jin S.; Ning X.; Cao J.; Wang Y. Simultaneous Quantification of γ-Hydroxybutyrate, γ-Butyrolactone, and 1,4-Butanediol in Four Kinds of Beverages. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2020, 8837743, pp.7. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Qian, M.; Qi, S.; Zhou, L.; Pu, Q. Concise analysis of γ-hydroxybutyric acid in beverages and urine by capillary electrophoresis with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection using 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid as background electrolyte. J. Chromatogr. A. 2022, 1675, 463191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, J.; Almirall, J.R. Analysis of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) in spiked water and beverage samples using solid phase microextraction (SPME) on fiber derivatization/gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC/MS). J. Forensic Sci. 2005, 50(1), 31–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munshi, T.; Brewster, V.L.; Edwards, H.G.; Hargreaves, M.; Jilani, S.K.; Scowen, I.J. Monitoring of the interconversion of gamma-butyrolactone (GBL) to gamma hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) by Raman spectroscopy. Drug Test. Anal. 2013, 5(8), 678–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kugler, W. X-ray diffraction analysis in the forensic science: The last resort in many criminal cases. Adv. X-ray Anal. 2003, 46, 1–16.
- Rendle D.F. Forensic applications of X-ray powder diffraction. International Tables for Crystallography 2019. vol H. ch. 7.2, pp. 737–751. [CrossRef]
- Cappelletti P.; Graziano S.F.; Bish D.L. (2023). X-ray Diffractometry in Forensic Science. In Mineralogical Analysis Applied to Forensics. Soil Forensics.; Mercurio M., Langella, A., Di Maggio, R.M., Cappelletti, P. Eds.; Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- Kotrlý, M. Using X-ray diffraction in forensic science Zeitschrift für Kristallographie - Crystalline Materials, 2007, 222(3-4), 193-198. [CrossRef]
- Abraham, J.T.; Shukla S., K.; Singh A., K. Application of X-Ray Diffraction Techniques in Forensic Science. Forensic Sci. Commun. 2007, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jurásek B.; Bartůněk V.; Huber Š.; Kuchař M. X-Ray powder diffraction – A non-destructive and versatile approach for the identification of new psychoactive substances, Talanta 2019, 195, 414–418. [CrossRef]
- Jurásek, B.; Bartůněk, V.; Huber, Š.; Fagan, P.; Setnička, V.; Králík, F.; Dehaen, W.; Svozil, D.; Kuchař, M. Can X-Ray Powder Diffraction Be a Suitable Forensic Method for Illicit Drug Identification? Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulska, E.; Bachliński, R.; Cyrański, M.K.; Michalska-Kacymirow, M.; Kośnik, W.; Małecki, P.; Grela, K.; Dobrowolski, M.A. Comprehensive Protocol for the Identification and Characterization of New Psychoactive Substances in the Service of Law Enforcement Agencies. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decreto del Presidente della Repubblica 9 ottobre, n. 309. Testo unico delle leggi in materia di disciplina degli stupefacenti e sostanze psicotrope, prevenzione, cura e riabilitazione dei relativi stati di tossicodipendenza.Gazzetta Ufficiale – Serie Generale n. 255 (Suppl. Ordinario n. 67), 31 ottobre 1990.
- Di Luca N.M.; Busardò F.P.; Pirani F.; Varì M.R. Evolution of Italian laws banning trafficking, use and abuse of psychotropic drugs. Ann. Ist. Supe.r Sanità 2020, 56(1), 76-89. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorecho E.N. Qualitative analysis of sodium gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) residue from plastic and glass containers using FT-IR ATR, thesis in Master of Science in Forensic Science in the Office of graduate studies of the University of California, UMI Number: 1502266, 2011.
- Ferris T.J.; Went M.J. Synthesis, characterisation and detection of γ-hydroxybutyrate salts. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012; 216(1-3):158-62. [CrossRef]
- Elliott, S.P.; Fais, P. Further evidence for GHB naturally occurring in common non-alcoholic beverages. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 277, e36–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucci M.; Stocchero G.; Pertile R.; Favretto D. Detection of GHB at low levels in non-spiked beverages using solid phase extraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, Toxicologie Analytique et Clinique 2017, 29, 225–233. [CrossRef]
- Payan, C.; Gancel, A.-L.; Jourdes, M.; Christmann, M.; Teissedre, P.-L. Wine acidification methods: a review. OENO One 2023, 57(3), 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemical Composition of Alcoholic Beverages, Additives and Contaminants. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Alcohol Drinking. Lyon (FR): International Agency for Research on Cancer; 1988. (IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, No. 44.). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531662/.
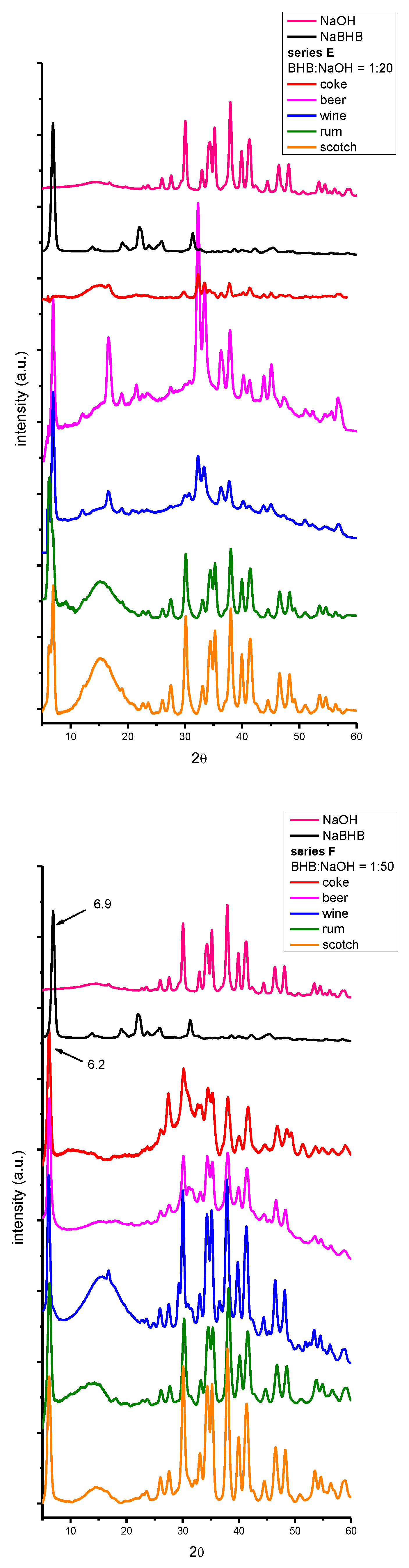
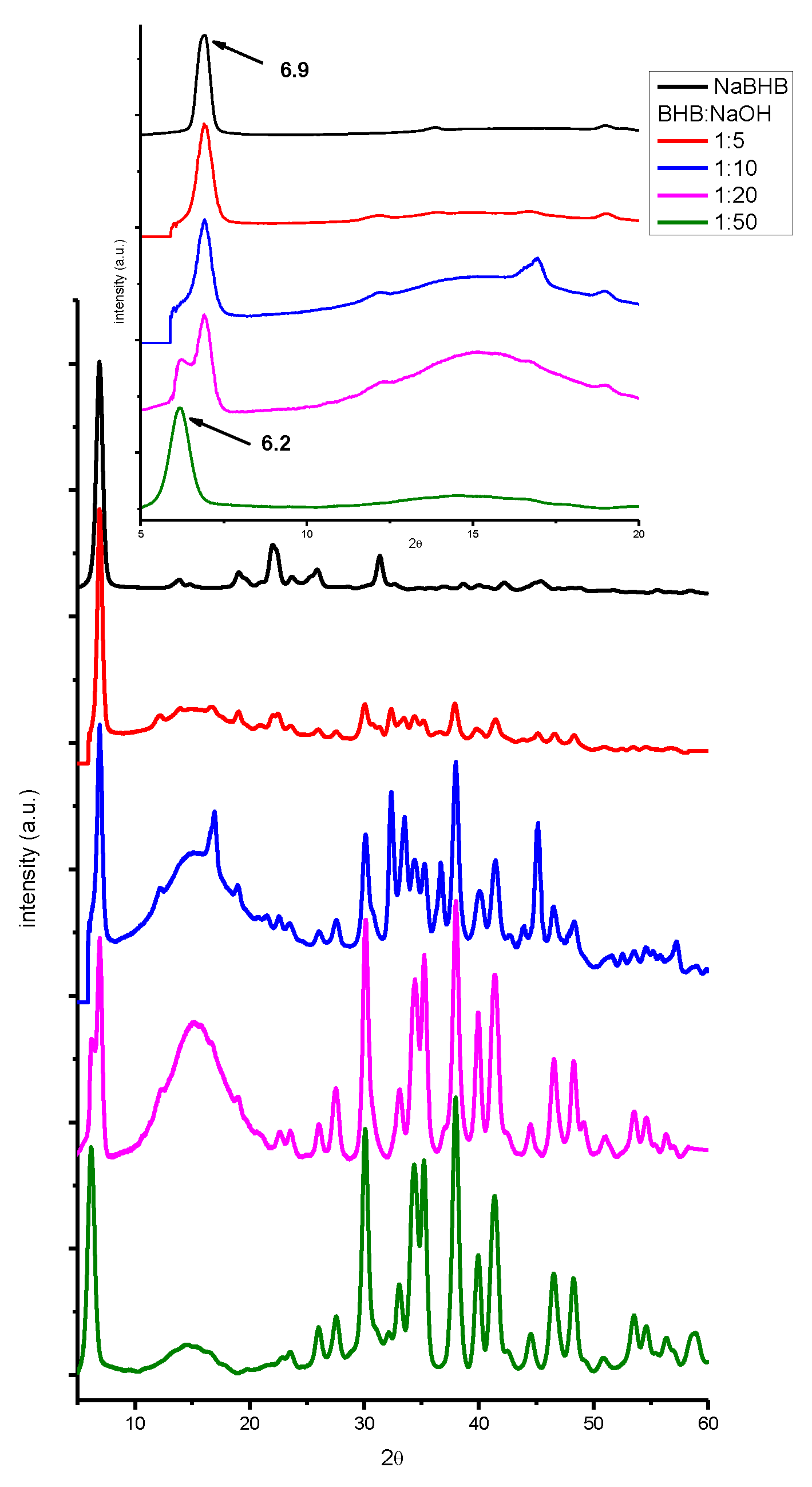
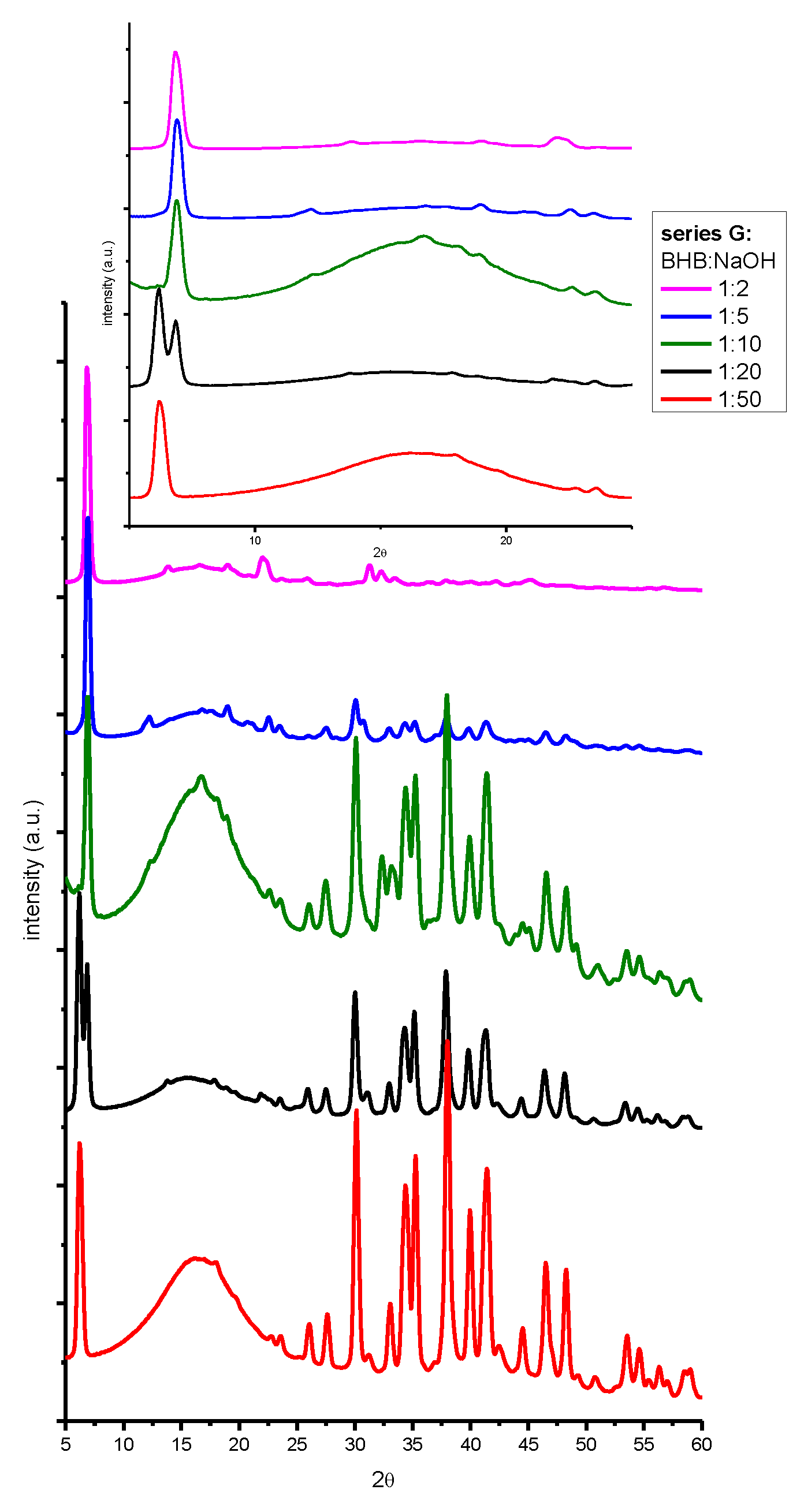
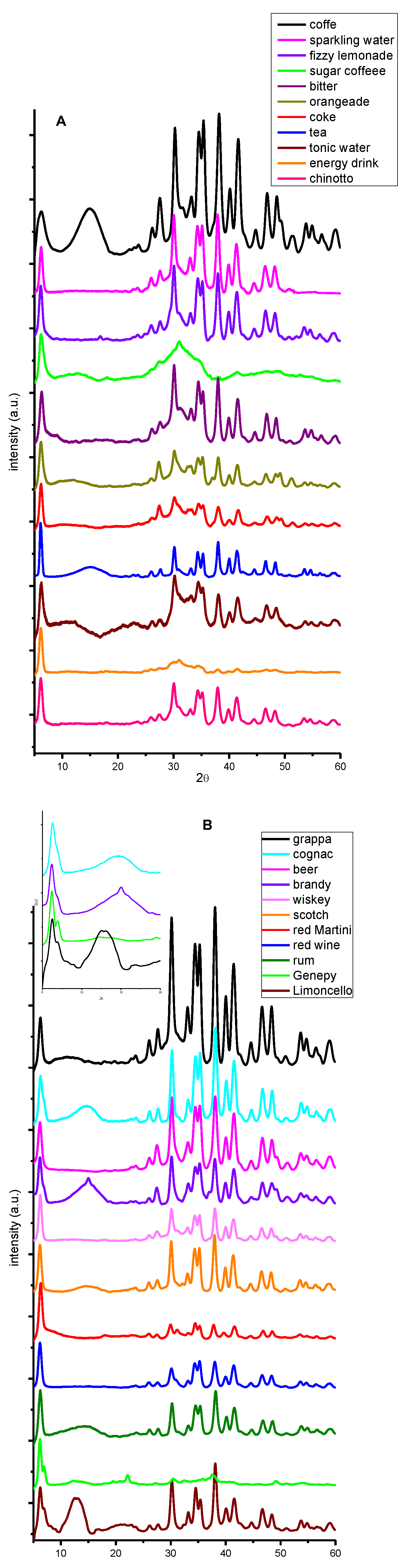
| beverage | dry residue (g/ml) (not spiked) |
NaBHB weight percentage (w/w) | ||
| BHB 1% v/v BHB:NaOH 1:2 |
BHB 20% v/v BHB:NaOH 1:1 |
BHB 1% v/v BHB:NaOH 1:50 |
||
| coke | 0.099 | 11.2 | 72.3 | 4.1 |
| beer | 0.037 | 23.9 | 5.2 | |
| red wine | 0.025 | 30.7 | 91.2 | 5.4 |
| rum | 0.002 | 67.8 | 5.5 | |
| scotch | 0.001 | 71.6 | 96.3 | 5.8 |
| analcoholic | alcoholic | cocktail |
|---|---|---|
| coffee (Nespresso ) | white wine schnapps (Candolini 40.0 ABV) | Shirley Temple |
| sparkling water (Sparea - Pontevecchio) | cognac (Couvoisier 40.0 ABV) | Go West |
| fizzy lemonade (Lemonsoda- Royal Unibrew) | beer (Carlsberg 5.0 ABV) | Aperol Spritz |
| sugary coffee (Nespresso) | brandy (Vecchia Romagna 37.2 ABV) | Gin Tonic |
| bitter (Crodino - Campari Group) | whiskey (Jack Daniel's 40.0 ABV) | Piña Colada |
| orangeade (Fanta - Coca-Cola HBC Italia) | schotch (J&B 40.0 ABV) | Mojto |
| coke (Coca Cola - Coca-Cola HBC Italia) | red Martini (14.4 ABV) | Gin Fiz |
| tea (Lipton) | red wine (Dolcetto 13.5 ABV) | Cuba libre |
| tonic water (Schweppes- San Benedetto) | rum (Havana Club 40,0 ABV) | Sunrise |
| energy drink (Red Bull – Rauch) | genepy (Alpe Herbetet 38,0 ABV) | Rossini cocktail |
| chinotto (Lurisia) | limoncello (Limoncè 25,0 ABV) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





