Submitted:
19 July 2024
Posted:
24 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
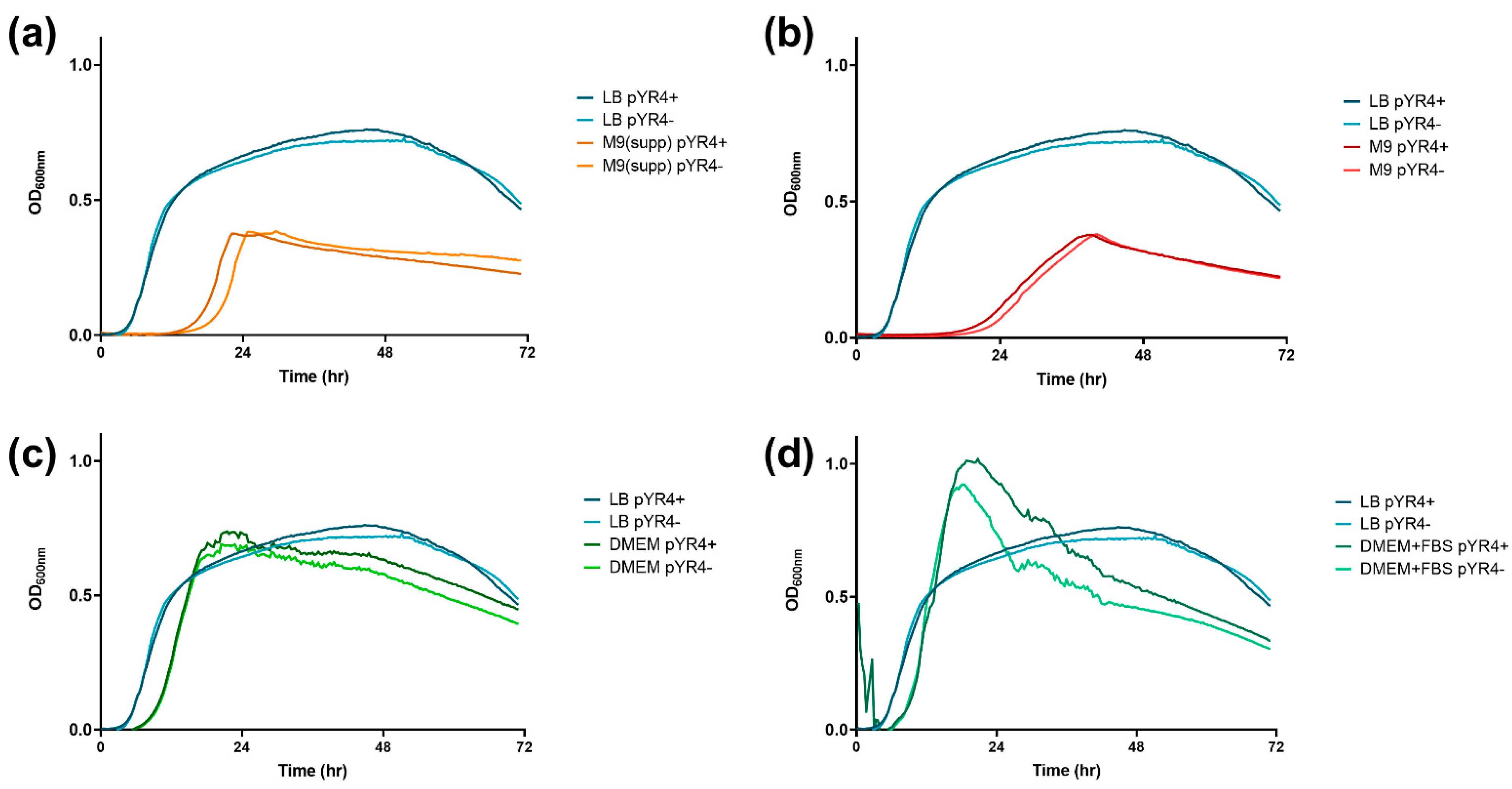
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
2.2. Cloning
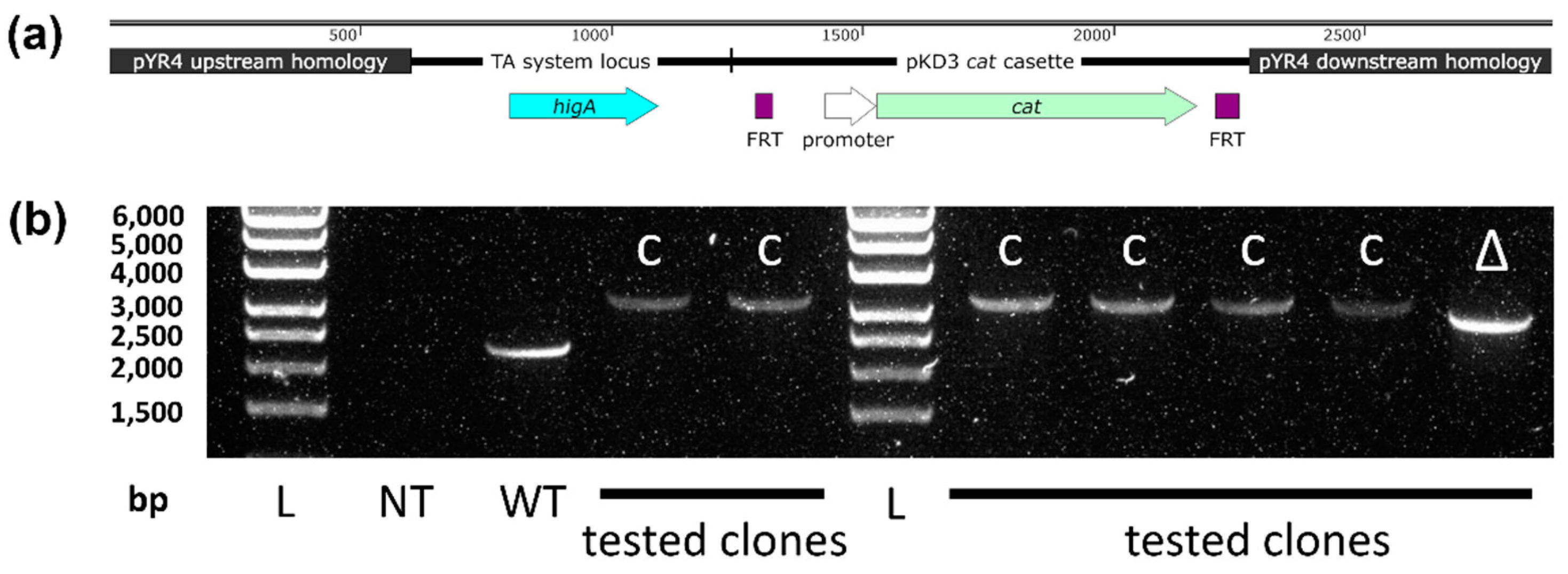
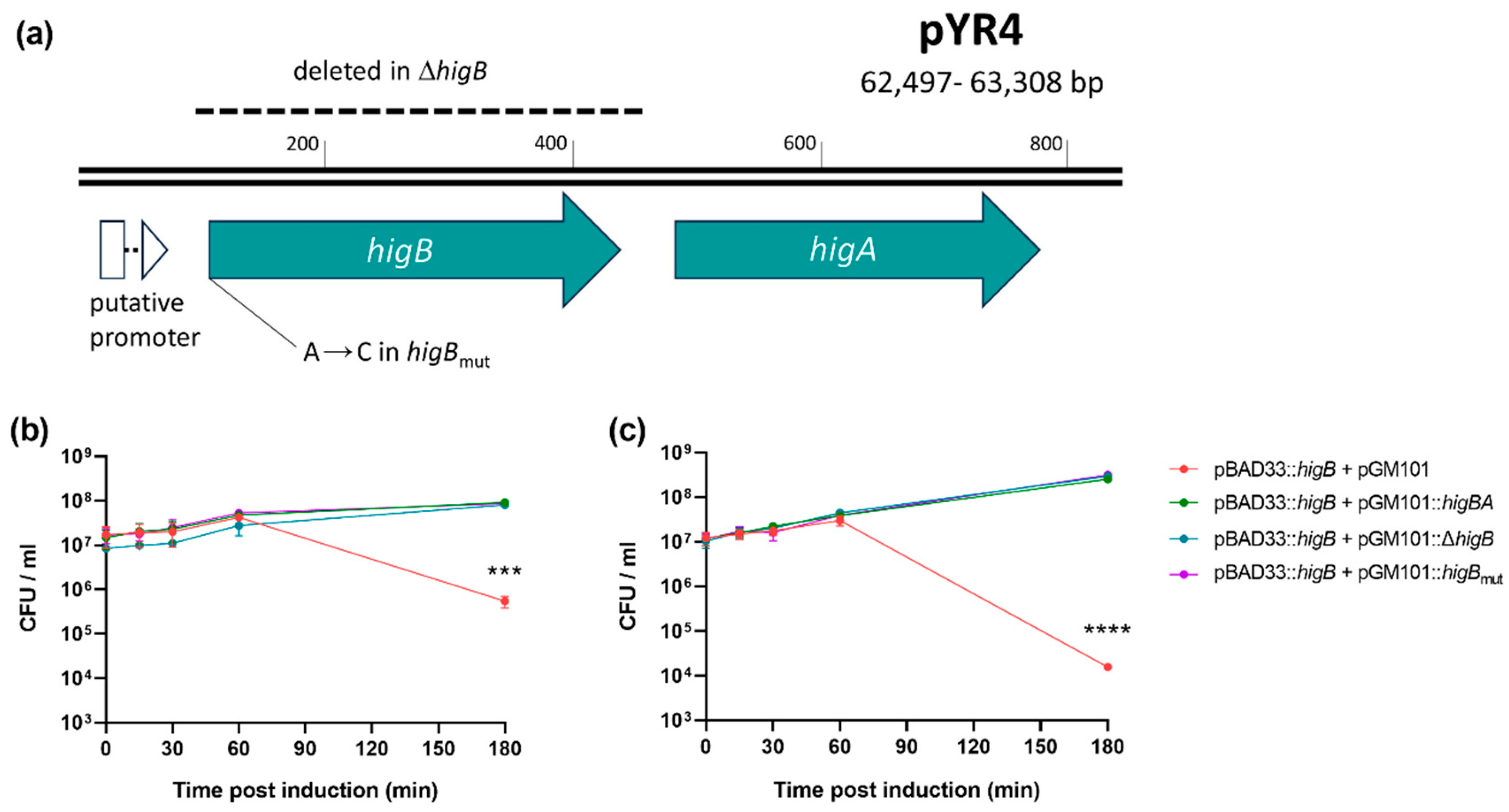
2.3. Creating a higB Knockout and Introducing a Selection Marker into pYR4
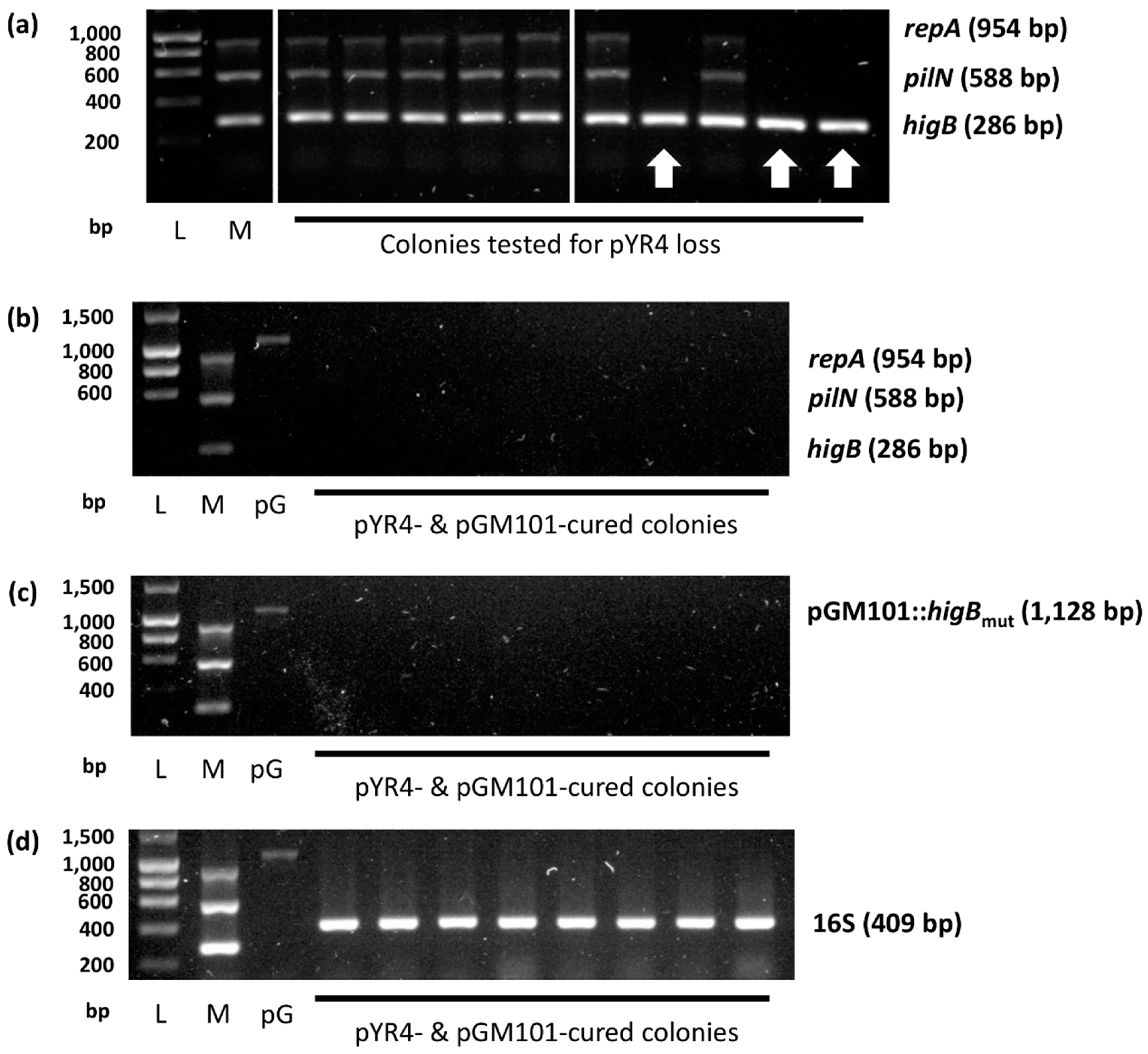
2.3. Plasmid Curing and Plasmid Loss Experiments
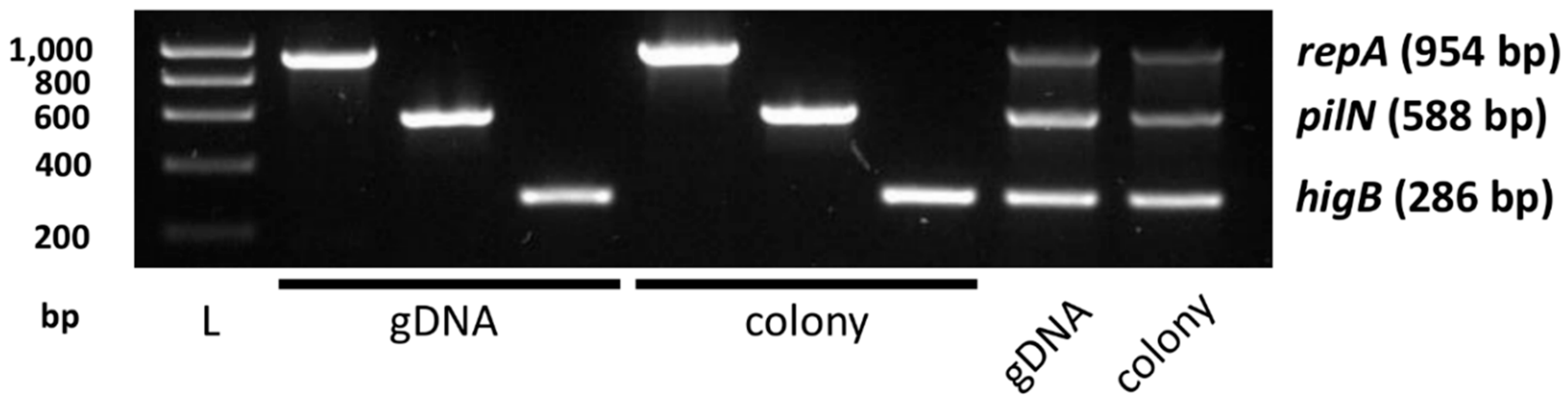
2.4. Conjugation
2.5. Toxicity Assays
2.6. Twitching Motility Assays
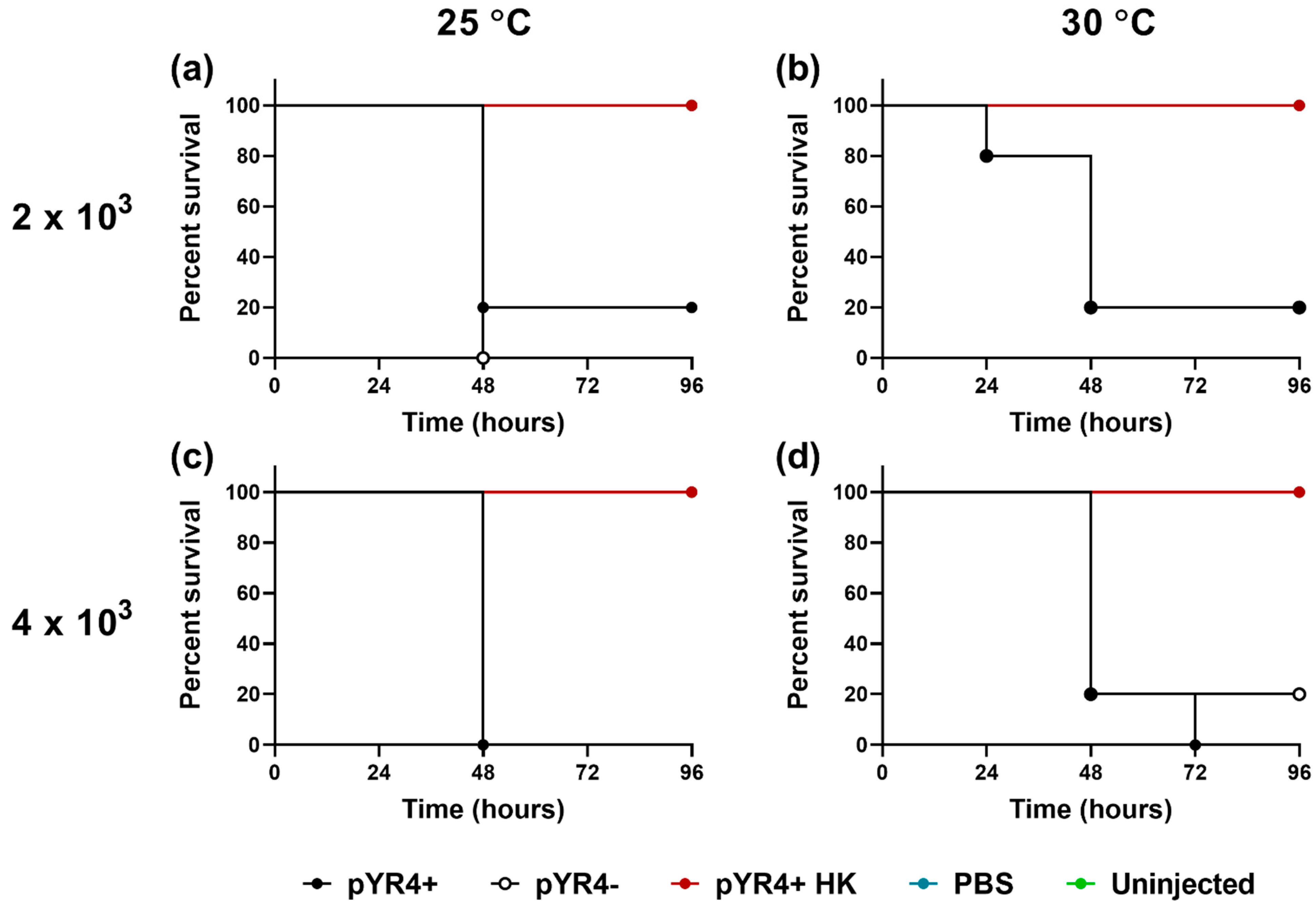
2.7. Galleria Infection Assays
3. Results
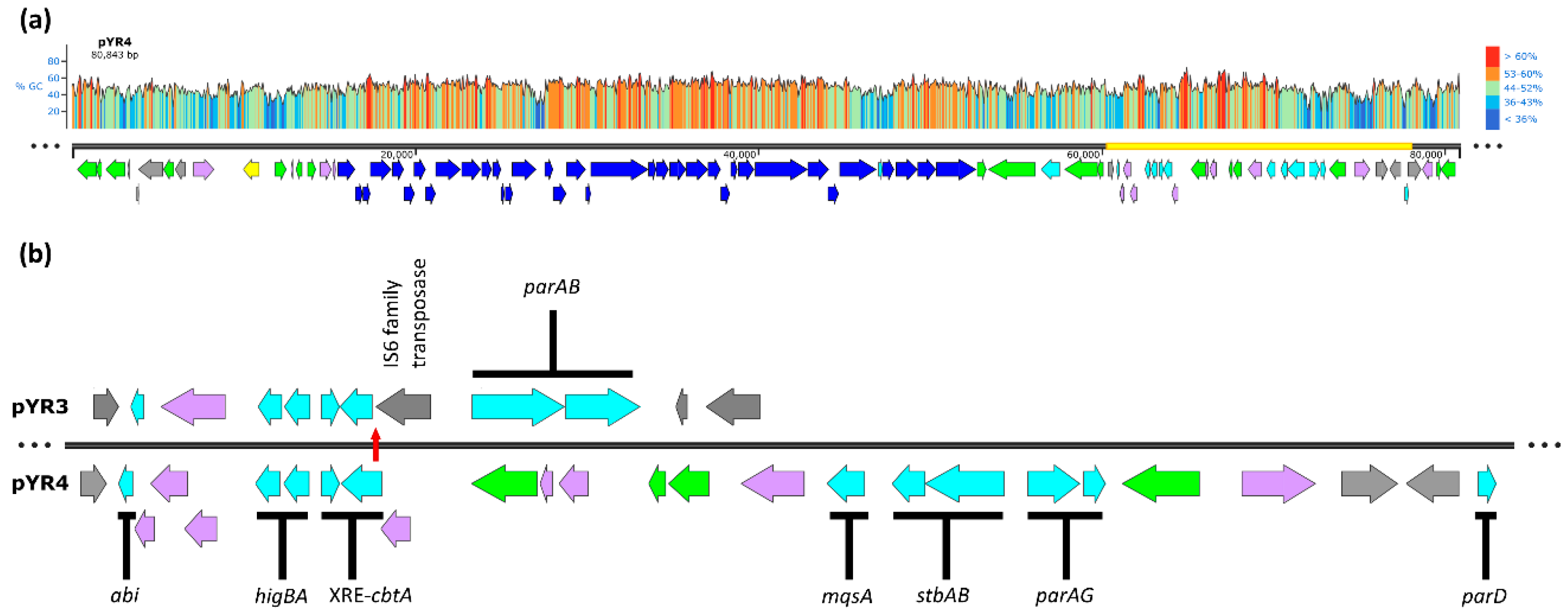
3.1. pYR4 Carries Several Putative TA-Related Genes
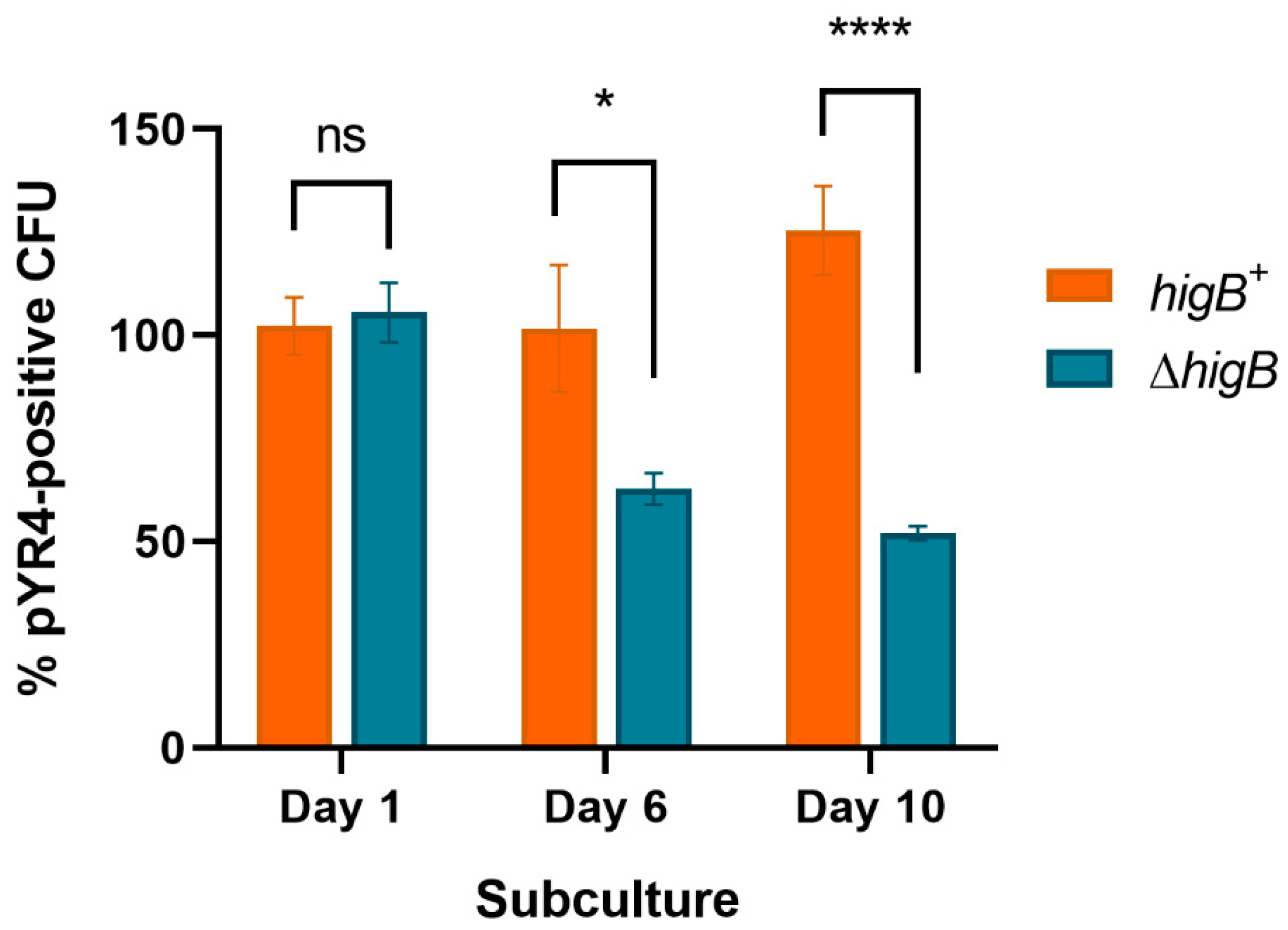
3.2. pYR4 HigBA Is a Functional Postsegregational Killing System
3.3. Qualitative Evidence of pYR4 Conjugation
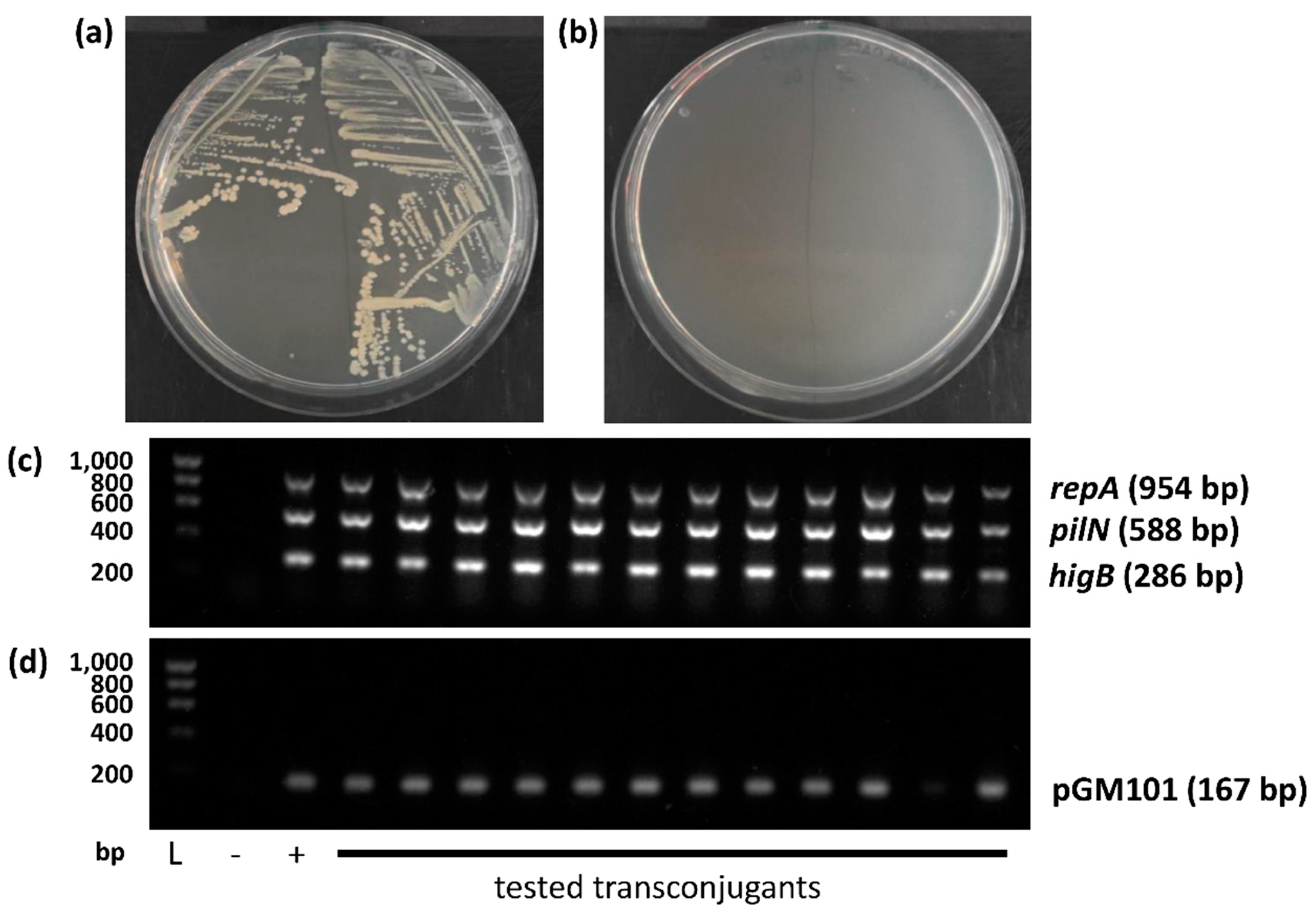
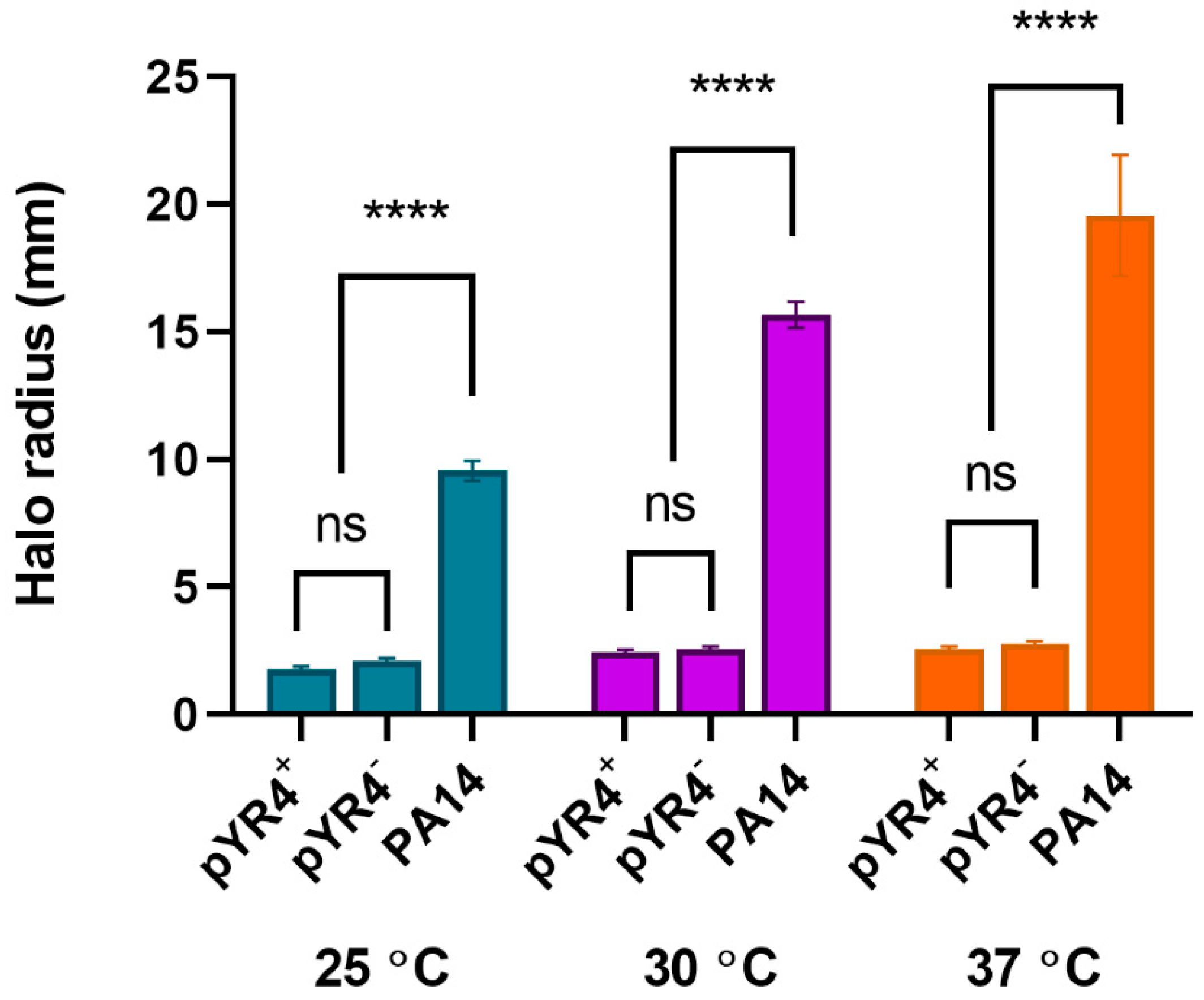
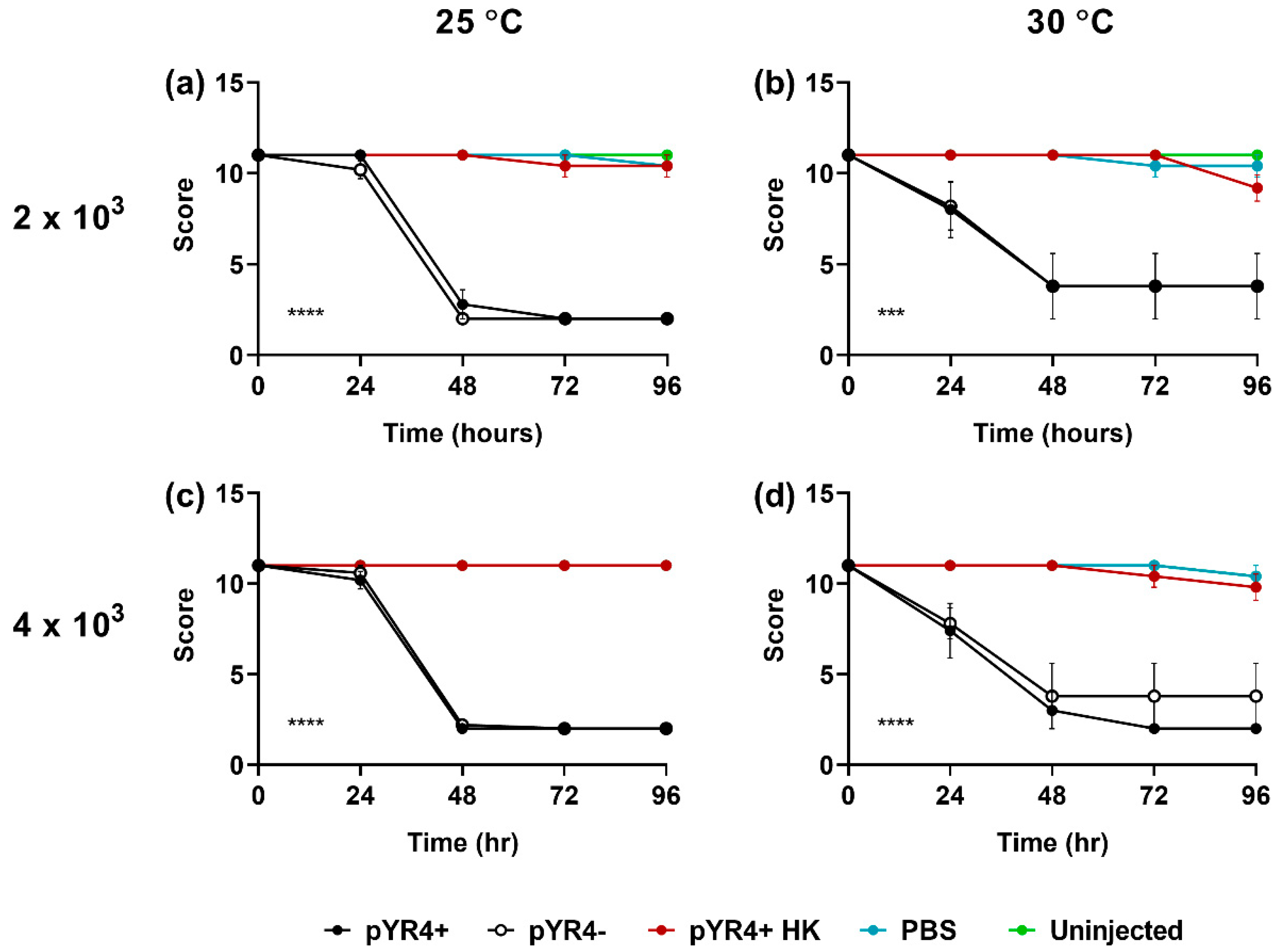
3.4. Virulence-Related Phenotypes Encoded by pYR4
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Primer | Sequence (5’->3’) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GMntu043 | GCATTTTTATCCATAAGATTAGCGG | pBAD33 MCS (forward) |
| GMntu044 | GCGTTCTGATTTAATCTGTATCAGG | pBAD33 MCS (reverse) |
| GMntu045 | CACCGTCATCACCGAAACG | pGM101 insert site (forward) |
| GMntu046 | CTGTTTTATCAGACCGCTTCTGC | pGM101 insert site (reverse) |
| GMmbiol057 | GGATCCTCTAGAGTCGACGCAAGGGACGAGCGTTAATGG | higB with pBAD33 overlap (forward) |
| GMmbiol058 | AAGCTTGCATGCCTGCAGCGGGGGCTTGTTATTCGATTTG | higB with pBAD33 overlap (reverse) |
| GMmbiol059 | AATCGAATAACAAGCCCCCGCTGCAGGCATGCAAGCTT | pBAD33 with higB overlap (forward) |
| GMmbiol060 | CATTAACGCTCGTCCCTTGCGTCGACTCTAGAGGATCC | pBAD33 with higB overlap (reverse) |
| GMmbiol061 | GCATGGCGGCTAAAGTTGTG | pYR4 repA (forward) |
| GMmbiol062 | GCTAGATTATGCCTGCTCGC | pYR4 repA (reverse) |
| GMmbiol063 | CCATGAGCAAGGGCGAATTGCT | pYR4 pilN (forward) |
| GMmbiol064 | GCTTCAGTCATCACGCTGACAT | pYR4 pilN (reverse) |
| GMmbiol065 | CCCGTATTTAGCAGGCGAAGAG | pYR4 higB (forward) |
| GMmbiol066 | GCTGACTTATCGATTTCAGGAC | pYR4 higB (reverse) |
| GMmbiol067 | CAGCGGAAAGTAGCTTG | Y. ruckeri 16S rDNA (forward) |
| GMmbiol068 | TGTTCAGTGCTATTAACACTTAA | Y. ruckeri 16S rDNA (reverse) |
| GMmbiol069 | CGCCCACAGGGTGCGCCGCTCGAAGCGGCATGCATTTACG | pGM101 with higBA overlap (forward) |
| GMmbiol070 | TTGCACTTTTTGAGATGATTCCTTCGCGCGCGAATTGATC | pGM101 with higBA overlap (reverse) |
| GMmbiol071 | GATCAATTCGCGCGCGAAGGAATCATCTCAAAAAGTGCAATTATTGC | higBA with pGM101 overlap (forward) |
| GMmbiol072 | CGTAAATGCATGCCGCTTCGAGCGGCGCACCCTGTGG | higBA with pGM101 overlap (reverse) |
| GMmbiol073 | TCAGCAAGGGACGAGCGTTACAAGCCCCCGCACTGCG | ΔhigB variant (forward) |
| GMmbiol074 | CCCCGCAGTGCGGGGGCTTGTAACGCTCGTCCCTTGCTGA | ΔhigB variant (reverse) |
| GMmbiol075 | GCAAGGGACGAGCGTTATACGAGTATCTAGAATTCATTGAG | higB mutation variant (forward) |
| GMmbiol076 | ATGAATTCTAGATACTCGTATAACGCTCGTCCCTTGCTGACCG | higB mutation variant (reverse) |
| MS103 | GGGAGAGCTCAAAAAAGCGACTTTAGCC | Upstream higBA (forward) |
| MS104 | TGAGATGATTATGACAGGTTATGAATTGC | Upstream higBA (reverse) |
| MS105 | AACCTGTCATAATCATCTCAAAAAGTGCAATTATTGCACTATTTTATATTTTTATTTAGCGAGCGTATACC | ΔhigA (forward) |
| MS106 | TAATTCCCATGAGCGGCGCACCCTGTGG | ΔhigA (reverse) |
| MS107 | TGCGCCGCTCATGGGAATTAGCCATGGTCC | Chloramphenicol cassette (forward) |
| MS108 | TGGCCAGTAAGTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTC | Chloramphenicol cassette (reverse) |
| MS109 | CAGCCTACACTTACTGGCCACTTCCGTG | Downstream higBA (forward) |
| MS110 | TACCGCATGCAGCCGAAGCATATGTTTTG | Downstream higBA (reverse) |
References
- FAO Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics – Yearbook 2021, FAO Yearbook of Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics: Rome, 2024.
- OECD/FAO. Fish. In OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2023-2032OECD Publishing: Paris, 2023; pp. 214-224.
- Segner, H.; Sundh, H.; Buchmann, K.; Douxfils, J.; Sundell, K.S.; Mathieu, C.; Ruane, N.; Jutfelt, F.; Toften, H.; Vaughan, L. Health of farmed fish: its relation to fish welfare and its utility as welfare indicator. Fish Physiol Biochem 2011, 38, 85-105, DOI 10.1007/s10695-011-9517-9. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10695-011-9517-9.
- Stentiford, G.D.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Flegel, T.W.; Williams, B.A.P.; Withyachumnarnkul, B.; Itsathitphaisarn, O.; Bass, D. New paradigms to help solve the global aquaculture disease crisis. PLoS Pathog 2017, 13, e1-e1006160, DOI 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006160. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28152043.
- Kumar, G.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Saleh, M.; El-Matbouli, M. Yersinia ruckeri, the causative agent of enteric redmouth disease in fish. Vet Res 2015, 46, 103, DOI 10.1186/s13567-015-0238-4. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26404907.
- Fernandez-espinel, C.; Medina-morillo, M.; Irgang, R.; Sotil, G.; Araya-león, H.; Flores-dominick, V.; Romalde, J.L.; Avendaño-herrera, R.; Yunis-aguinaga, J. Co-existence of two Yersinia ruckeri biotypes and serotype O1a retrieved from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) farmed in Puno, Peru. J Fish Dis 2022, 46, 157-163, DOI 10.1111/jfd.13730. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jfd.13730.
- Riborg, A.; Colquhoun, D.J.; Gulla, S. Biotyping reveals loss of motility in two distinct Yersinia ruckeri lineages exclusive to Norwegian aquaculture. J Fish Dis 2022, 45, 641-653, DOI 10.1111/jfd.13590. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jfd.13590.
- Fouz, B.; Zarza, C.; Amaro, C. First description of non-motile Yersinia ruckeri serovar I strains causing disease in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), cultured in Spain. J Fish Dis 2006, 29, 339-346, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2761.2006.00723.x. Available online: https://api.istex.fr/ark:/67375/WNG-03SWBFVW-X/fulltext.pdf.
- Wrobel, A.; Leo, J.C.; Linke, D. Overcoming fish defences: the virulence factors of Yersinia ruckeri. Genes 2019, 10, 700, DOI 10.3390/genes10090700. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31514317.
- Carniel Arniel, E. Plasmids and Pathogenicity Islands of Yersinia. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 2002, 264, 89-108, DOI 10.1007/978-3-642-56031-6_6. Available online: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-642-56031-6_6.
- Andreopoulos, W.B.; Geller, A.M.; Lucke, M.; Balewski, J.; Clum, A.; Ivanova, N.N.; Levy, A. Deeplasmid: deep learning accurately separates plasmids from bacterial chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 50, e17, DOI 10.1093/nar/gkab1115. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/34871418.
- Riborg, A.; Gulla, S.; Fiskebeck, E.Z.; Ryder, D.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; Colquhoun, D.J.; Welch, T.J. Pan-genome survey of the fish pathogen Yersinia ruckeri links accessory- and amplified genes to virulence. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285257, DOI 10.1371/journal.pone.0285257. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37167256.
- Wrobel, A.; Ottoni, C.; Leo, J.C.; Linke, D. pYR4 from a Norwegian isolate of Yersinia ruckeri is a putative virulence plasmid encoding both a type IV pilus and a type IV secretion system. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2018, 8, 373, DOI 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00373. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2018.00373/full.
- Pelicic, V. Type IV pili: e pluribus unum? Mol Microbiol 2008, 68, 827-837, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06197.x. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06197.x.
- Costa, T.R.D.; Patkowski, J.B.; Macé, K.; Christie, P.J.; Waksman, G. Structural and functional diversity of type IV secretion systems. Nat Rev Microbiol 2023, 22, 170-185, DOI 10.1038/s41579-023-00974-3. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37814112.
- Méndez, J.; Fernández, L.; Menéndez, A.; Reimundo, P.; Pérez-Pascual, D.; Navais, R.; Guijarro, J.A. A chromosomally located traHIJKCLMN operon encoding a putative type IV secretion system is involved in the virulence of Yersinia ruckeri. Appl Environ Microbiol 2009, 75, 937-945, DOI 10.1128/AEM.01377-08. Available online: http://aem.asm.org/content/75/4/937.abstract.
- Qiu, J.; Zhai, Y.; Wei, M.; Zheng, C.; Jiao, X. Toxin–antitoxin systems: Classification, biological roles, and applications. Microbiol Res 2022, 264, 127159, DOI 10.1016/j.micres.2022.127159. Available online: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2022.127159.
- Harms, A.; Brodersen, D.E.; Mitarai, N.; Gerdes, K. Toxins, targets, and triggers: An overview of toxin-antitoxin biology. Mol Cell 2018, 70, 768-784, DOI 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.01.003. Available online: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.01.003.
- Chan, W.T.; Espinosa, M.; Yeo, C.C. Keeping the wolves at bay: Antitoxins of prokaryotic type II toxin-antitoxin systems. Front Mol Biosci 2016, 3, 9, DOI 10.3389/fmolb.2016.00009. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/molecular-biosciences/articles/10.3389/fmolb.2016.00009/full.
- Tian, Q.B.; Ohnishi, M.; Murata, T.; Nakayama, K.; Terawaki, Y.; Hayashi, T. Specific protein–DNA and protein–protein interaction in the hig gene system, a plasmid-borne proteic killer gene system of plasmid Rts1. Plasmid 2001, 45, 63-74, DOI 10.1006/plas.2000.1506. Available online: https://dx.doi.org/10.1006/plas.2000.1506.
- Christensen-Dalsgaard, M.; Gerdes, K. Two higBA loci in the Vibrio cholerae superintegron encode mRNA cleaving enzymes and can stabilize plasmids. Mol Microbiol 2006, 62, 397-411, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05385.x. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05385.x.
- Wrobel, A.; Ottoni, C.; Leo, J.C.; Gulla, S.; Linke, D. The repeat structure of two paralogous genes, Yersinia ruckeri invasin (yrInv) and a “Y. ruckeri invasin-like molecule”, (yrIlm) sheds light on the evolution of adhesive capacities of a fish pathogen. Journal of structural biology 2018, 201, 171-183, DOI 10.1016/j.jsb.2017.08.008. Available online: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2017.08.008.
- Wasteson, U.; Hvaal, A.; Serum, H.; Myhr, E.; Fossum, K. Antibacterial spectrum and some other characteristics of an antimicrobial factor produced by Yersinia ruckeri. Acta Vet Scand 1989, 30, 253-257, DOI 10.1186/BF03548029. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2629502.
- Bertani, G. Studies on lysogenesis. I. The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. Journal of bacteriology 1951, 62, 293-300, DOI 10.1128/jb.62.3.293-300.1951. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14888646.
- AnonymousM9 minimal medium (standard). Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2010, 2010, pdb.rec12295, DOI 10.1101/pdb.rec12295. Available online: https://cshprotocols.cshlp.org/content/2010/8/pdb.rec12295.
- Gibson, D.G.; Chuang, R.; Hutchison, C.A.; Venter, J.C.; Smith, H.O.; Young, L. Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat Methods 2009, 6, 343-345, DOI 10.1038/nmeth.1318. Available online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1318.
- Guzman, L.M.; Belin, D.; Carson, M.J.; Beckwith, J. Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose PBAD promoter. J Bacteriol 1995, 177, 4121-4130, DOI 10.1128/jb.177.14.4121-4130.1995. Available online: http://jb.asm.org/content/177/14/4121.abstract.
- Mcvicker, G.; Tang, C.M. Deletion of toxin–antitoxin systems in the evolution of Shigella sonnei as a host-adapted pathogen. Nat Microbiol 2016, 2, 16204, DOI 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.204. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/nmicrobiol2016204.
- Datsenko, K.A.; Wanner, B.L. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000, 97, 6640-6645, DOI 10.1073/pnas.120163297. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/122690.
- Hossain, M.J.; Thurlow, C.M.; Sun, D.; Nasrin, S.; Liles, M.R. Genome modifications and cloning using a conjugally transferable recombineering system. Biotechnol Rep 2015, 8, 24-35, DOI 10.1016/j.btre.2015.08.005. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2215017X15000478.
- Turnbull, L.; Whitchurch, C.B. Motility assay: Twitching motility. Methods Mol Biol 2014, 1149, 73-86, DOI 10.1007/978-1-4939-0473-0_9. Available online: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-1-4939-0473-0_9.
- Serrano, I.; Verdial, C.; Tavares, L.; Oliveira, M. The virtuous Galleria mellonella model for scientific experimentation. Antibiotics 2023, 12, DOI 10.3390/antibiotics12030505.
- Schureck, M.A.; Meisner, J.; Hoffer, E.D.; Wang, D.; Onuoha, N.; Ei Cho, S.; Lollar, P.; Dunham, C.M. Structural basis of transcriptional regulation by the HigA antitoxin. Mol Microbiol 2019, 111, 1449-1462, DOI 10.1111/mmi.14229. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/mmi.14229.
- Overgaard, M.; Borch, J.; Jørgensen, M.G.; Gerdes, K. Messenger RNA interferase RelE controls relBE transcription by conditional cooperativity. Mol Microbiol 2008, 69, 841-857, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06313.x. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06313.x.
- Robertson, J.; Nash, J.H.E. MOB-suite: software tools for clustering, reconstruction and typing of plasmids from draft assemblies. Microb Genom 2018, 4, e000206, DOI 10.1099/mgen.0.000206. Available online: https://search.datacite.org/works/10.6084/m9.figshare.6177188.
- Tian, Q.B.; Ohnishi, M.; Tabuchi, A.; Terawaki, Y. A new plasmid-encoded proteic killer gene system: cloning, sequencing, and analyzing hig locus of plasmid Rts1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996, 220, 280-284, DOI 10.1006/bbrc.1996.0396. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8645296.
- Christensen-Dalsgaard, M.; Gerdes, K. Two higBA loci in the Vibrio cholerae superintegron encode mRNA cleaving enzymes and can stabilize plasmids. Mol Microbiol 2006, 62, 397-411, DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05385.x. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05385.x.
- Pandey, D.P.; Gerdes, K. Toxin-antitoxin loci are highly abundant in free-living but lost from host-associated prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 2005, 33, 966-976, DOI 10.1093/nar/gki201. Available online: https://api.istex.fr/ark:/67375/HXZ-H200PTKH-F/fulltext.pdf.
- Yang, Y.; Mei, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Yang, A. Legionella pneumophila-mediated host posttranslational modifications. J Mol Cell Biol 2023, 15, mjad032, DOI 10.1093/jmcb/mjad032. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/37156500.
- Allard, N.; Neil, K.; Grenier, F.; Rodrigue, S. The type IV pilus of plasmid TP114 displays adhesins conferring conjugation specificity and is important for DNA transfer in the mouse gut microbiota. Microbiol Spectr 2022, 10, e0230321, DOI 10.1128/spectrum.02303-21. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/35293798.
- Carter, M.Q.; Chen, J.; Lory, S. The Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenicity island PAPI-1 is transferred via a novel type IV pilus. J Bacteriol 2010, 192, 3249-3258, DOI 10.1128/jb.00041-10.
- Ishiwa, A.; Komano, T. PilV adhesins of plasmid R64 thin pili specifically bind to the lipopolysaccharides of recipient cells. Journal of Molecular Biology 2004, 343, 615-625, DOI 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.08.059. Available online: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.08.059. [CrossRef]
- Guijarro, J.A.; Cascales, D.; García-Torrico, A.I.; García-Domínguez, M.; Méndez, J. Temperature-dependent expression of virulence genes in fish-pathogenic bacteria. Front Microbiol 2015, 6, 700, DOI 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00700.
- Mendez, J.; Cascales, D.; Garcia-Torrico, A.I.; Guijarro, J.A. Temperature-dependent gene expression in Yersinia ruckeri: Tracking specific genes by bioluminescence during in vivo colonization. Front Microbiol 2018, 9, 1098, DOI 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01098. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29887855.
- Wrobel, A.; Saragliadis, A.; Pérez-Ortega, J.; Sittman, C.; Göttig, S.; Liskiewicz, K.; Spence, M.H.; Schneider, K.; Leo, J.C.; Arenas, J.; Linke, D. The inverse autotransporters of Yersinia ruckeri, YrInv and YrIlm, contribute to biofilm formation and virulence. Environ Microbiol 2020, 22, 2939-55, DOI 10.1111/1462-2920.15051. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32372498.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





