Submitted:
23 July 2024
Posted:
23 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
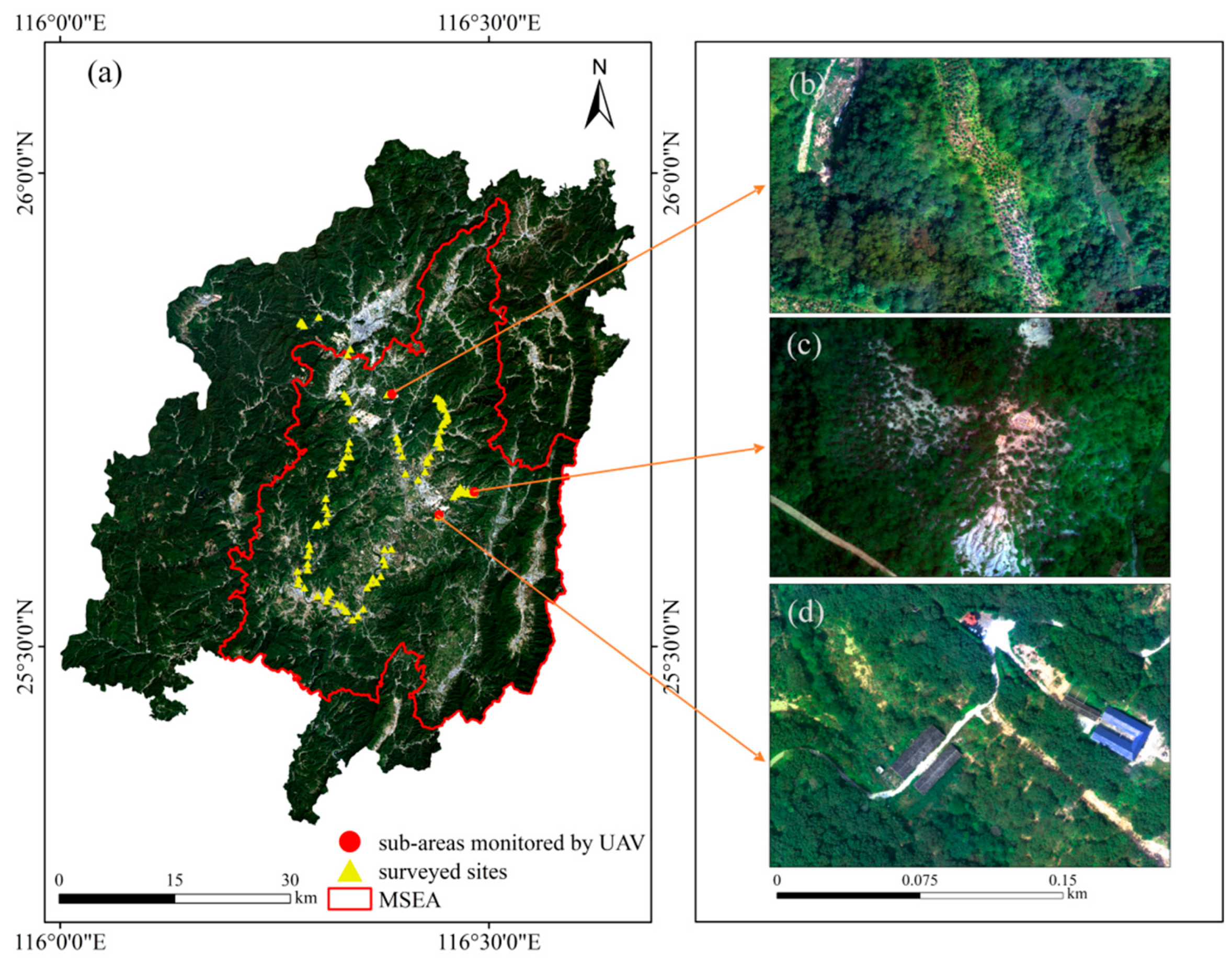
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
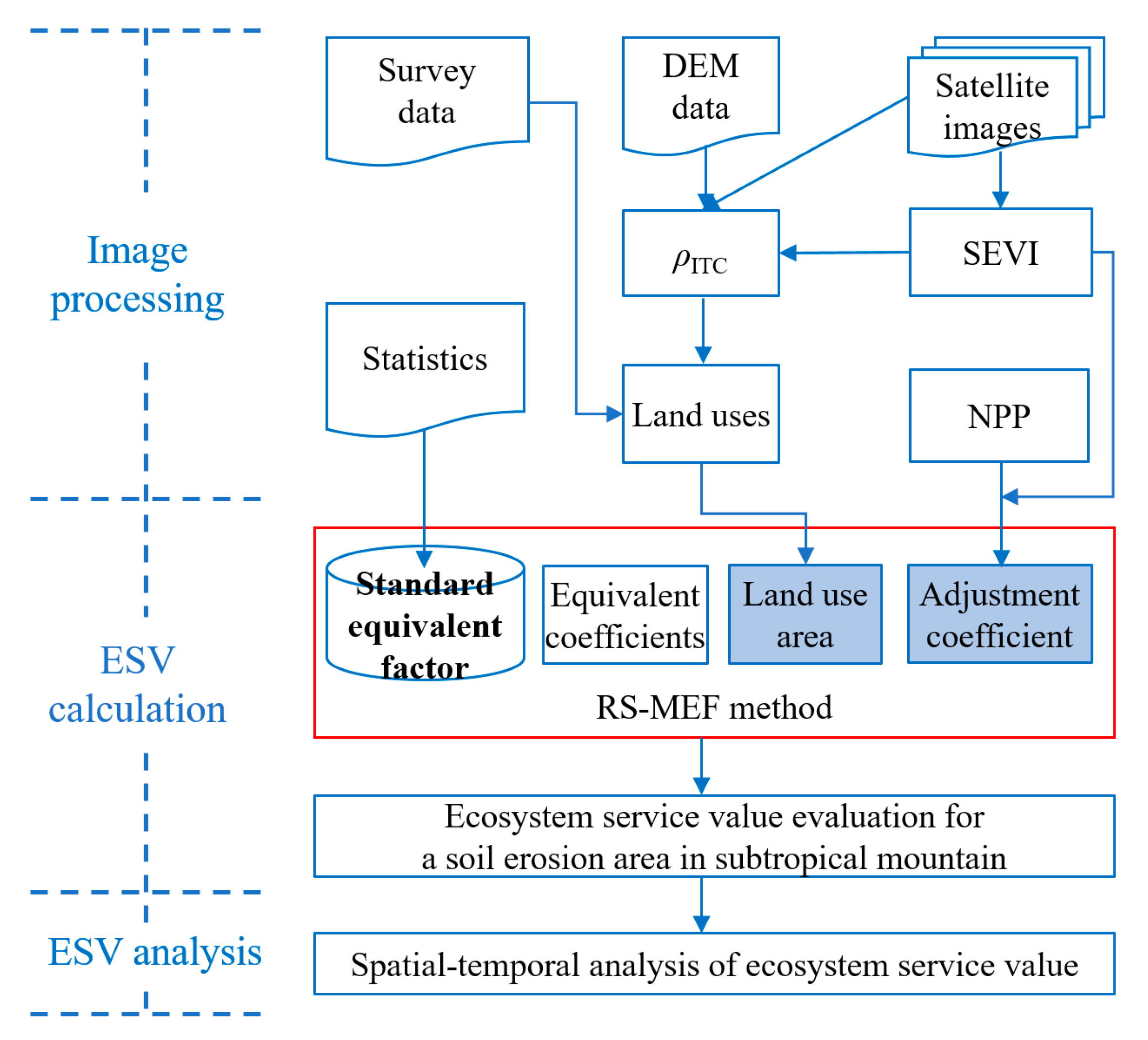
3. Methods
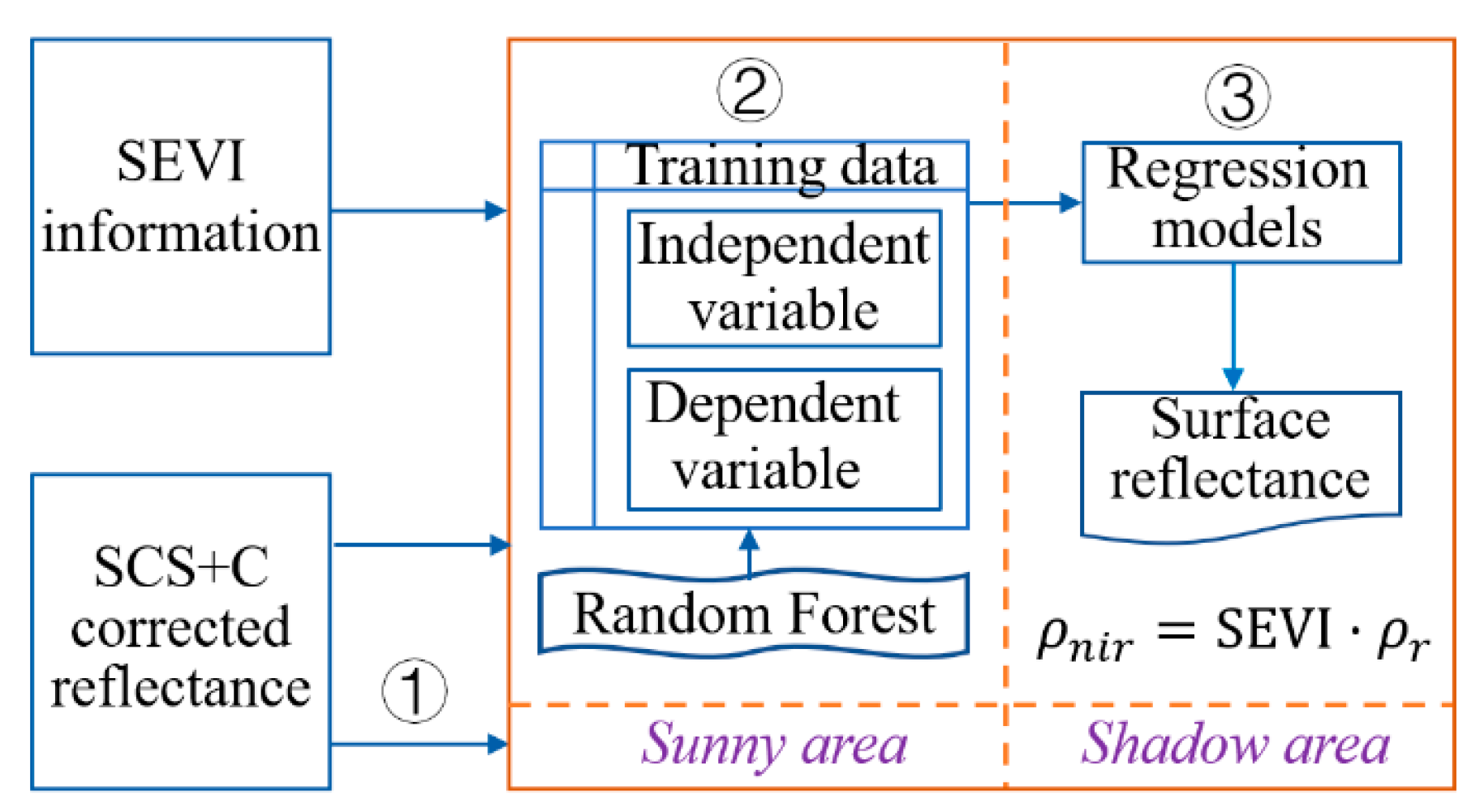
3.1. Image Processing
3.2. ESV Calculation
- (1)
- Standard equivalent factor
- (2)
- Equivalent coefficients
- (3)
- Land uses
- (4)
- Spatial adjustment coefficient
- (5)
- ESV calculation
3.3. ESV Analysis
4. Results
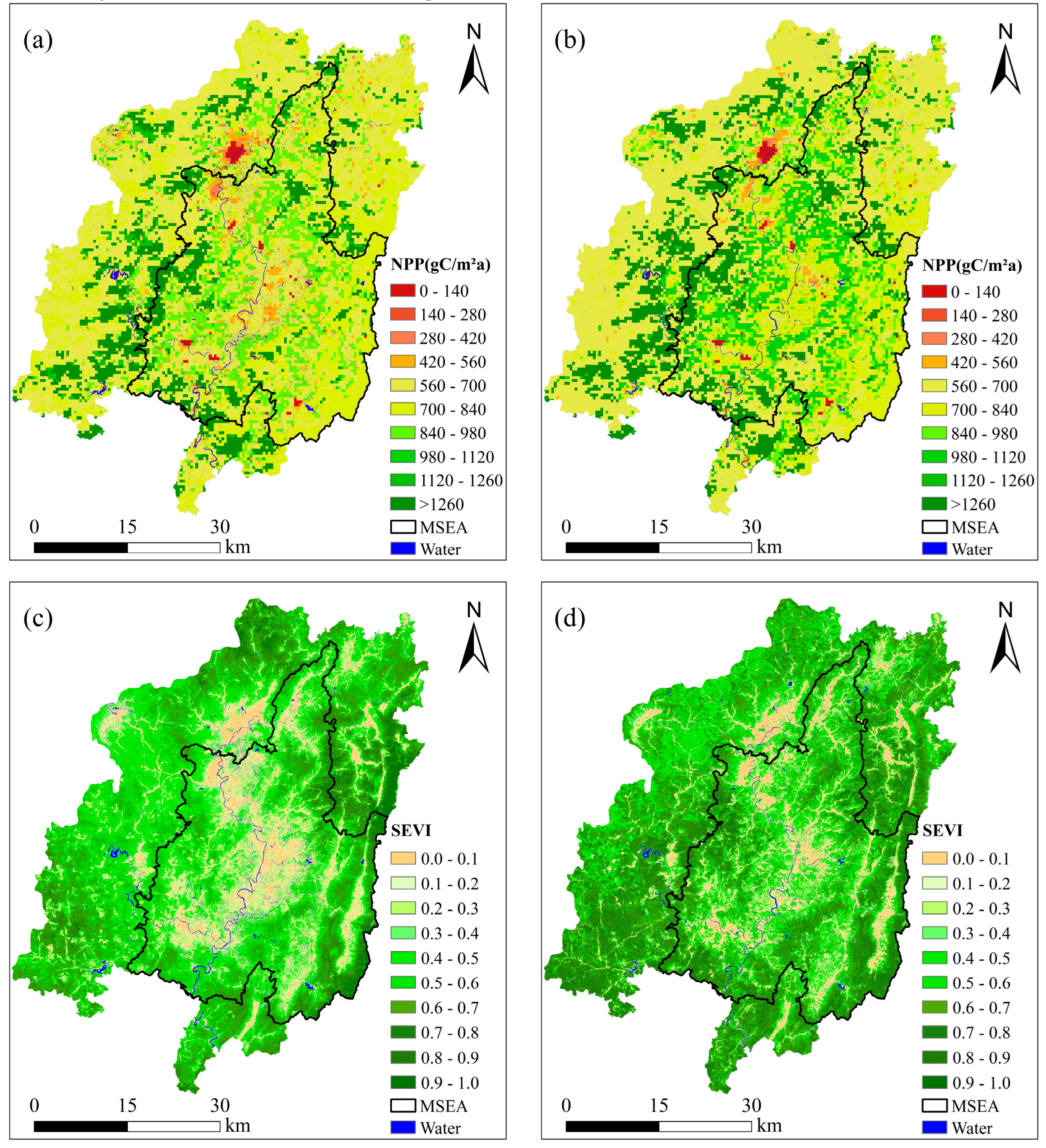
4.1. Standard Equivalent Factor
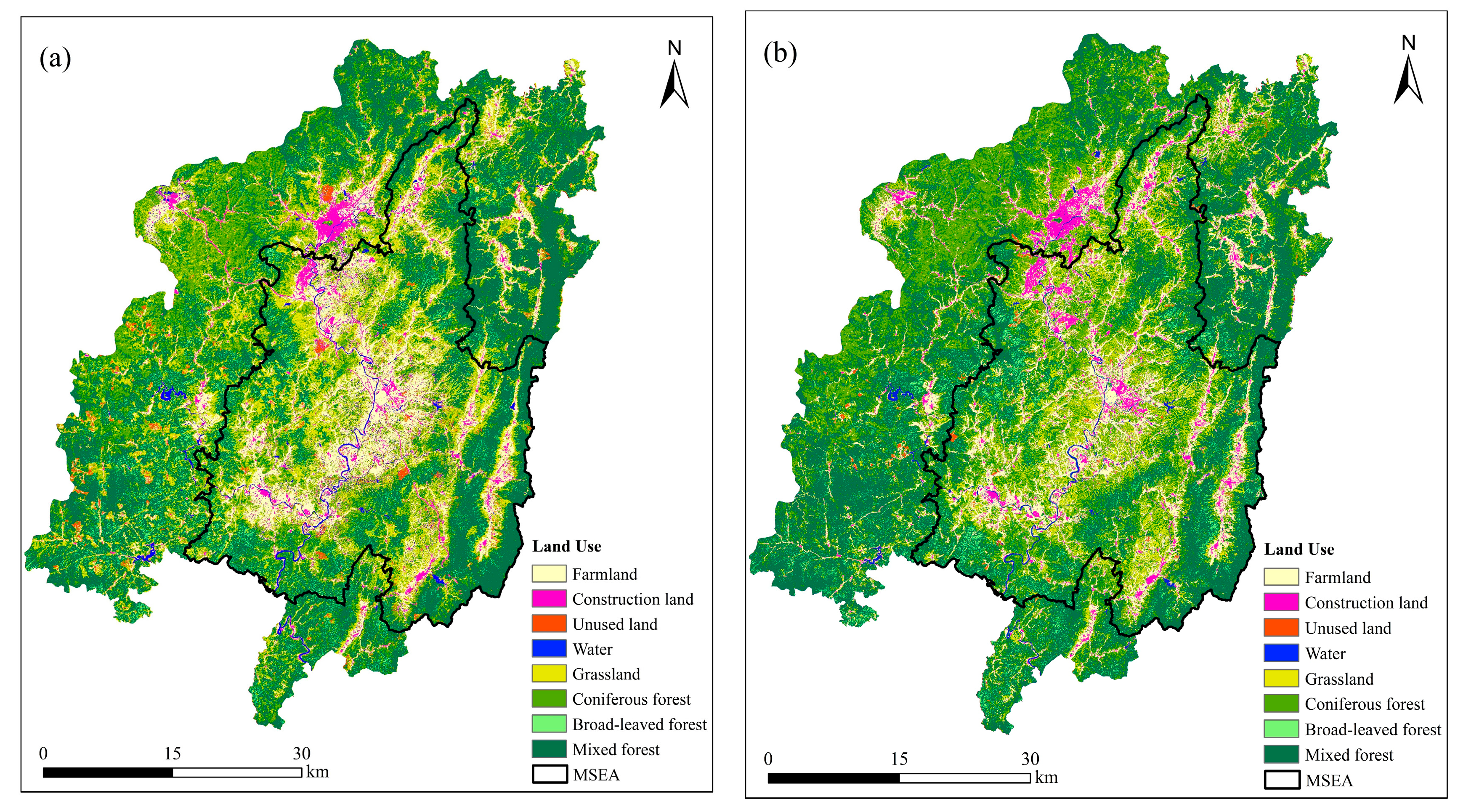
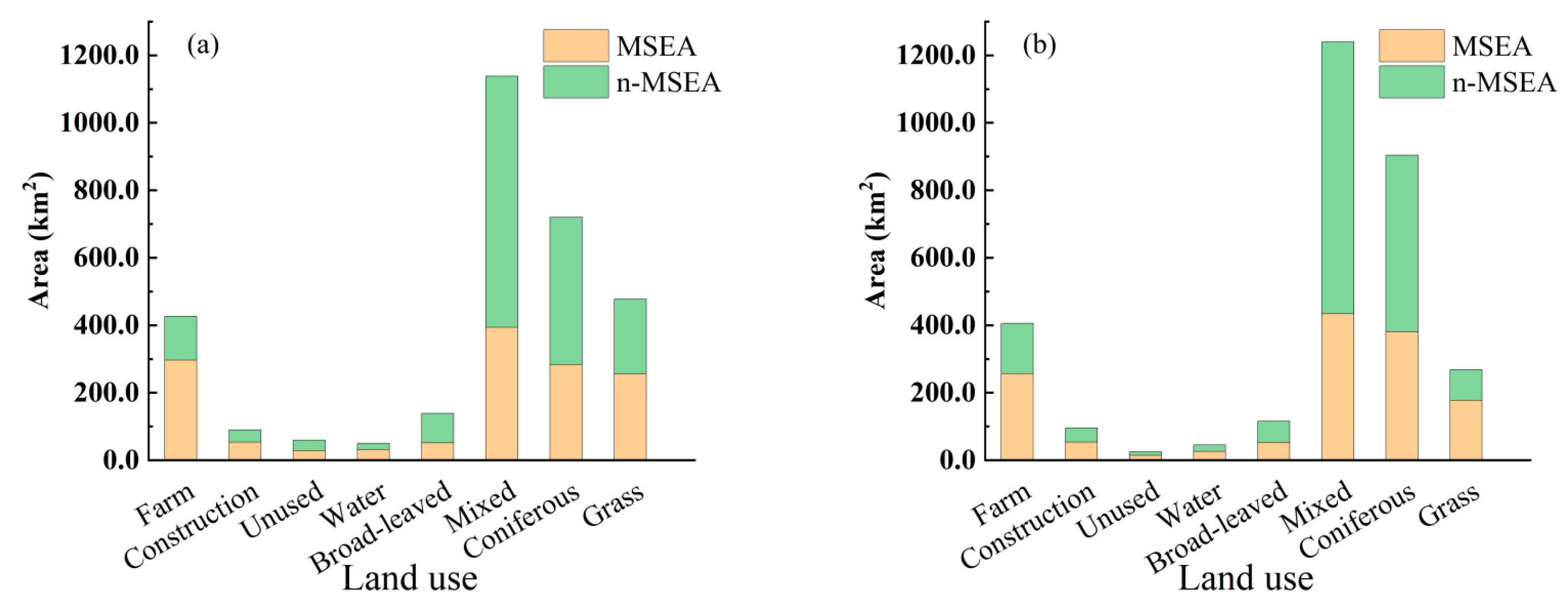
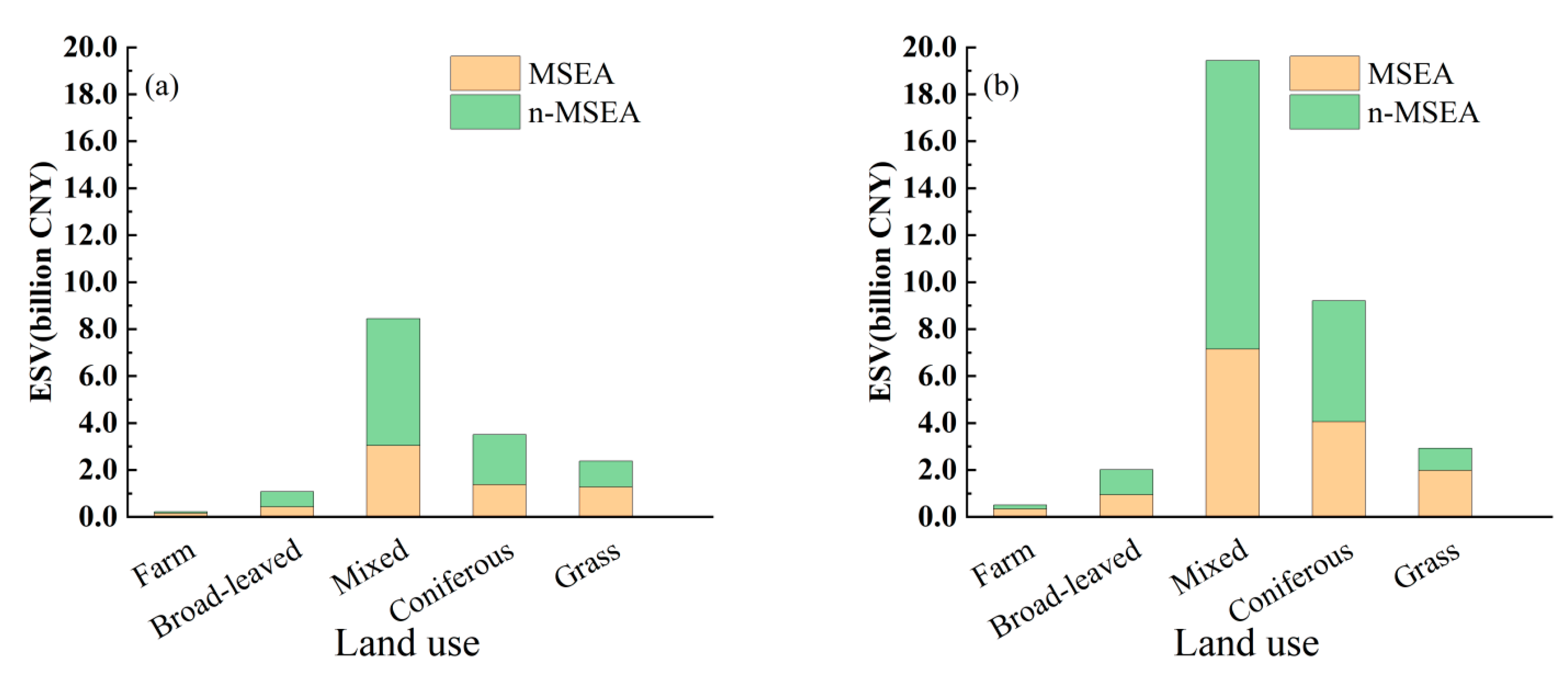
4.2. Land Uses
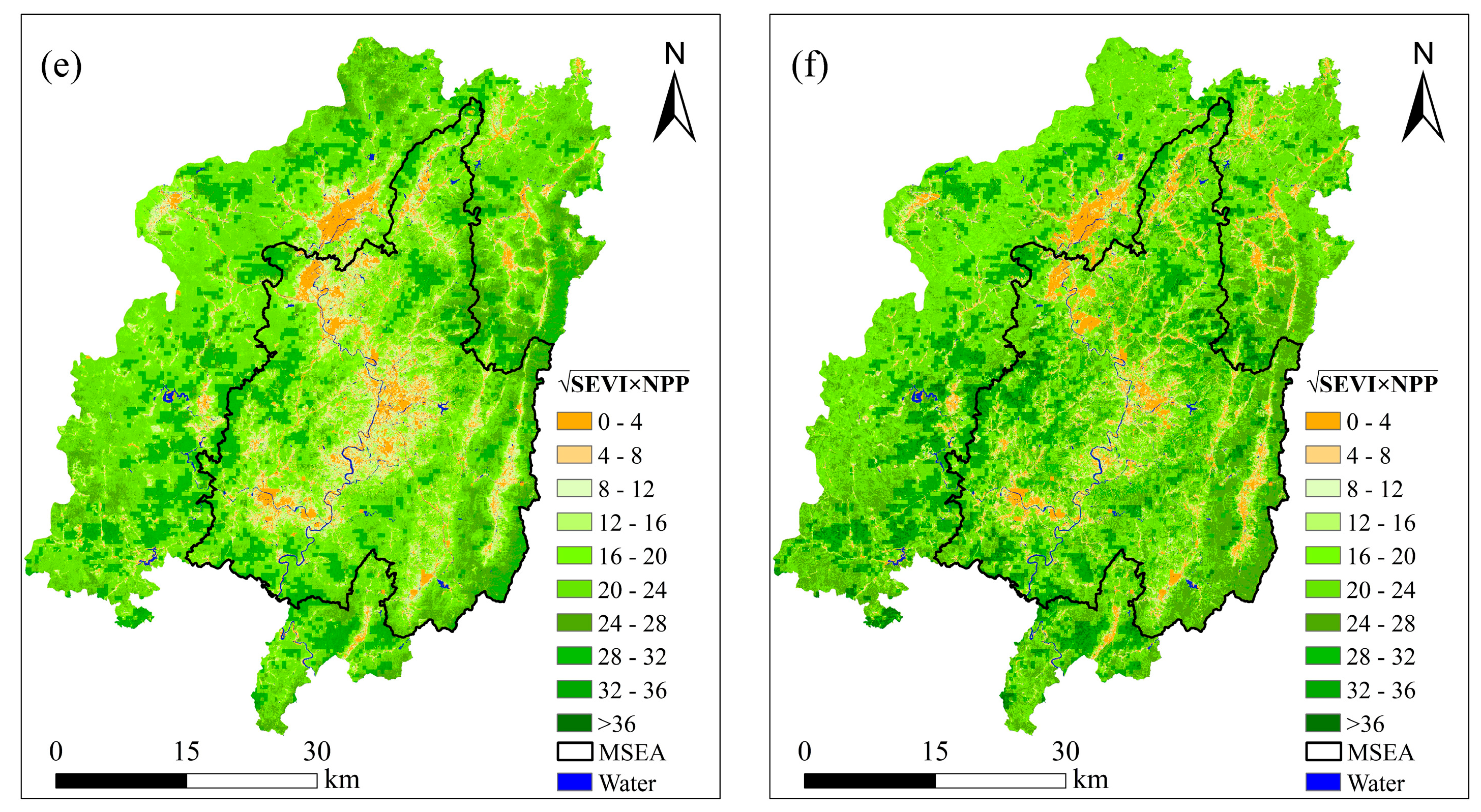
4.3. Spatial Adjustment Coefficients
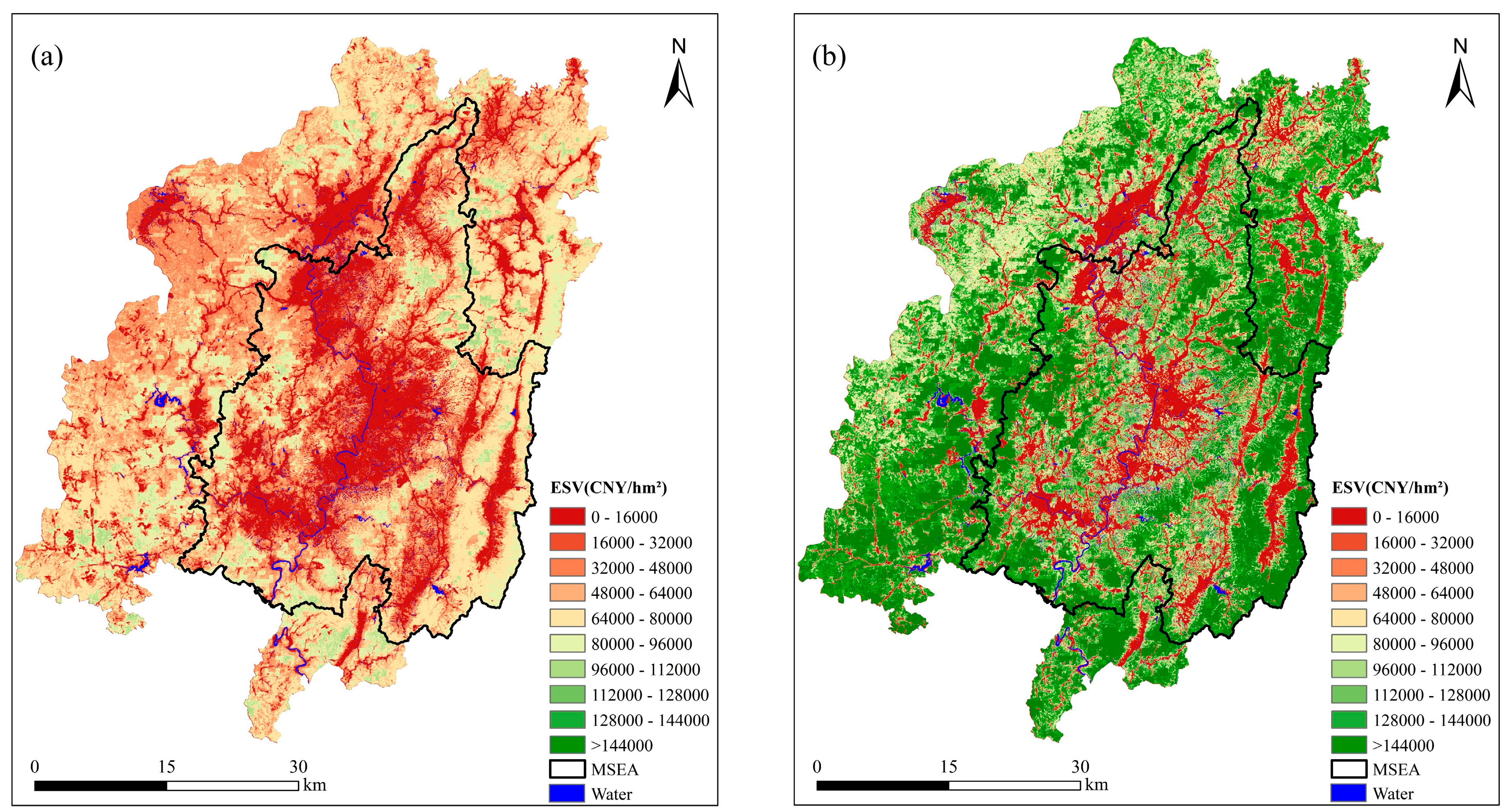
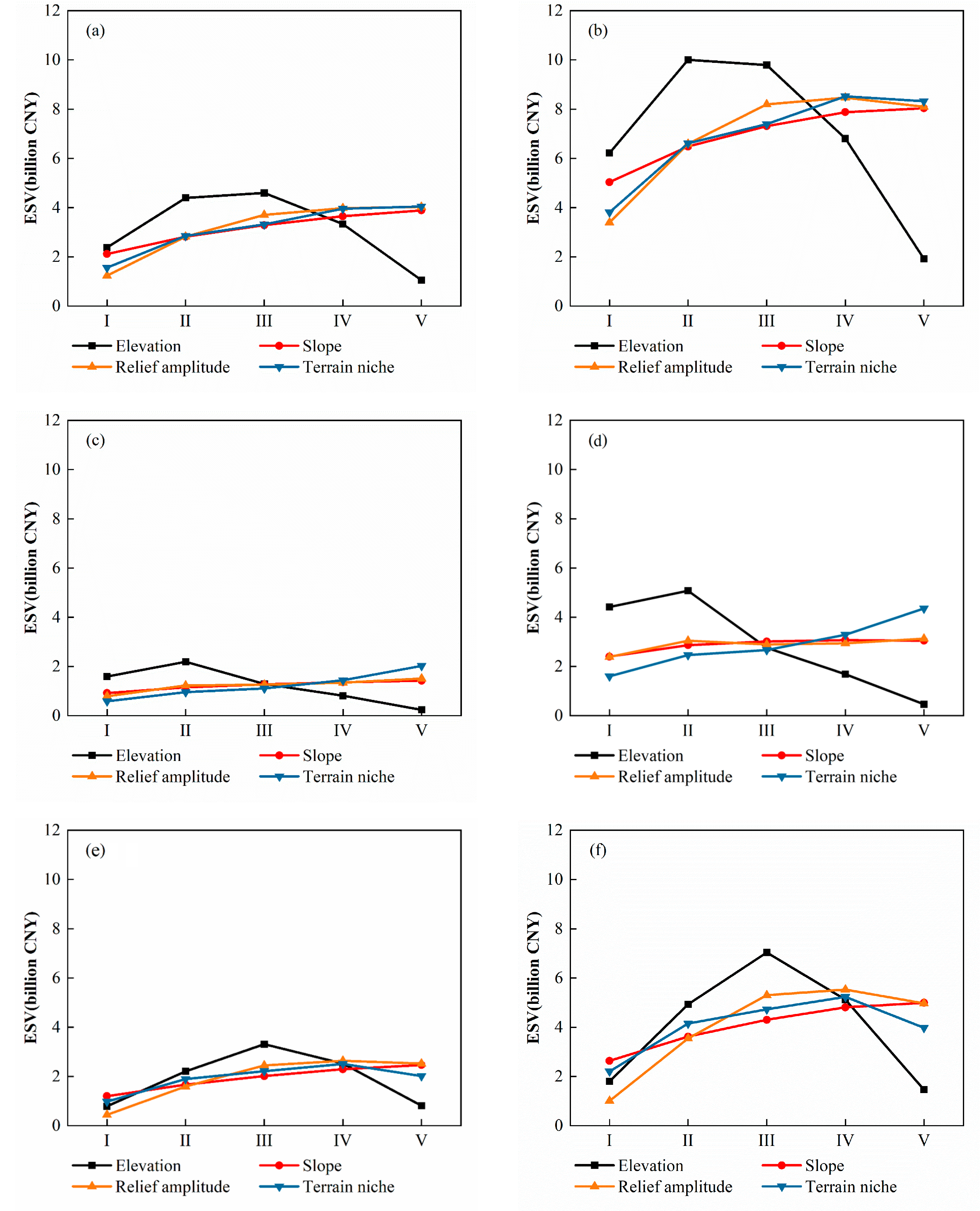
4.4. ESV and Distribution Characteristics
5. Discussion
5.1. ESV of Soil Erosion Area
5.2. Pros and Cons of the RS-MEF Method
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Declaration of Competing Interest
References
- Wuepper, D.; Borrelli, P., Finger, R. Countries and the global rate of soil erosion. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3(1), 51–55. [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Standardi, G.; Borrelli, P.; Lugato, E.; Montanarella, L.; Bosello, F. Cost of agricultural productivity loss due to soil erosion in the European Union: From direct cost evaluation approaches to the use of macroeconomic models. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 471–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D. A.; Fraser, I.; Dominati, E. J.; Davísdóttir, B.; Jónsson, J. O. G.; Jones, L.; Jones, S. B.; Tuller, M.; Lebron, I.; Bristow, K. L.; Souza, D. M.; Banwart, S.; Clothier, B. E. On the value of soil resources in the context of natural capital and ecosystem service delivery. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78(3), 685–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (MEA). Ecosystems and human wellbeing: Synthesis. Island Press, Washington, DC, 2005.
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; deGroot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; Oneill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; Raskin, R.G.; Sutton, P.; VandenBelt, M. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387(6630), 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, G. C.; Alexander, S. V.; Ehrlich, P. R.; Goulder, L. H.; Lubchenco, J.; Matson, P. A.; Woodwell, G. M. Ecosystem services: Benefits supplied to human societies by natural ecosystems. Ecology 1997, 1, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Rao, E. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016, 352(6292), 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braat, L.C.; De Groot, R. The ecosystem services agenda: bridging the worlds of natural science and economics, conservation and development, and public and private policy. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 1(1), 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A. V.; Tiwari, C.; Atkinson, S. F. Progress in ecosystem services research: A guide for scholars and practitioners. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 49, 101267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W. Ecosystem services research in China: A critical review. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; deGroot, R.; Sutton, P.; Van der Ploeg, S.; Anderson, S. J.; Kubiszewski, I.; Turner, R. K. Changes in the global value of ecosystem services. Glob. Environ. Change 2014, 26, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K. G.; Anderson, S.; Gonzales-Chang, M.; Costanza, R.; Courville, S.; Dalgaard, T.; Porfirio, L. A review of methods, data, and models to assess changes in the value of ecosystem services from land degradation and restoration. Ecol. Model. 2016, 319, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Min, Q.; Liu, M.; Cheng, S. Ecosystem service tradeoff between traditional and modern agriculture: A case study in Congjiang County, Guizhou Province, China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2012, 6, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Dong, S.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y. Effect of degradation intensity on grassland ecosystem services in the alpine region of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. PloS one 2013, 8(3), e58432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arowolo, A.O.; Deng, X.; Olatunji, O.A.; Obayelu, A.E. Assessing changes in the value of ecosystem services in response to land-use/land-cover dynamics in Nigeria. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sannigrahi, S.; Bhatt, S.; Rahmat, S.; Paul, S. K. Sen, S. Estimating global ecosystem service values and its response to land surface dynamics during 1995–2015. J. Environ. Manage. 2018; 223, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Das, M.; Houqe, R.; Pereira, P. Mapping ecosystem services for ecological planning and management: a case from a tropical planning region, Eastern India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30(3), 7543–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhen, L.; Zhang, L. Dynamic changes in the value of China’s ecosystem services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Tang, G.; Li, B.; Han, R. Spatial and temporal variations of ecosystem service values in relation to land use pattern in the Loess Plateau of China at town scale. PLoS One 2014, 9(10), e110745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Zhang, W. A comparison of Markov model-based methods for predicting the ecosystem service value of land use in Wuhan, central China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2014, 7, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, L.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Bu, K.; Wang, Q.; Tang, J.; Chang, L. The effects of population density changes on ecosystem services value: A case study in Western Jilin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Li, D.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, Y. Spatially non-stationary response of ecosystem service value changes to urbanization in Shanghai, China. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Deng, X. Land-use/land-cover change and ecosystem service provision in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Cost-effective targeting soil and water conservation: A case study of Changting county in southeast China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhan, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, M. Response of ecosystem services to land use and cover change: A case study in Chengdu City. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 132, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Fu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhai, J.; Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Yang, M. Progress and perspectives of ecosystem assets management. Sheng Tai XueBao 2020, 40(24), 8851–8860. [Google Scholar]
- Su, K.; Wei, D.Z.; Lin, W.X. Evaluation of ecosystem services value and its implications for policy making in China–A case study of Fujian province. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Xiong, K.; Zhang, Z. Ecosystem services and ecological compensation of world heritage: A literature review. J. Nat. Conserv. 2021, 60, 125968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, L.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L. A general variational framework considering cast shadows for the topographic correction of remote sensing imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2016, 117, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Chen, A.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chi, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Vegetation monitoring for mountainous regions using a new integrated topographic correction (ITC) of the SCS+ C Correction and the shadow-eliminated vegetation index. Remote Sens. 2022a, 14(13), 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Yin, G.; Zhao, W.; Yan, K.; Wu, S.; Hao, D.; Liu, G. Topographic correction of optical remote sensing images in mountainous areas: A systematic review. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, S.; Cao, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X. A shadow-eliminated vegetation index (SEVI) for removal of self and cast shadow effects on vegetation in rugged terrains. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2019, 12(9), 1013–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zuo, X.; Xie, W.; Li, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhang, H. A correction method of NDVI topographic shadow effect for rugged terrain. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 8456–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zha, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, L. Evaluation of soil erosion vulnerability on the basis of exposure, sensitivity, and adaptive capacity: A case study in the Zhuxi watershed, Changting, Fujian Province, Southern China. Catena 2019, 177, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhu, C.; Yu, J.; Zhai, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, K.; Hou, X. Ecological vulnerability in the red soil erosion area of Changting under continuous ecological restoration: Spatiotemporal dynamic evolution and prediction. Forests 2022, 13, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Yao, M.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, W.; Mao, Z. Vegetation monitoring of protected areas in rugged mountains using an improved shadow-eliminated vegetation index (SEVI). Remote Sens. 2022b, 14(4), 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J. R. Remote sensing of the environment: An earth resource perspective, 2nd ed.; Publisher: Person Education, Upper Saddle River, Inc. 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Zheng, X.; Yue, H.; Chen, Y. Developing a new red band–SEVI–blue band (RSB) enhancement method for recognition the extra-high-voltage transmission line corridor in green mountains. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2023, 16(1), 806–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Rodríguez, V.; Melo, F. P.; Martínez-Ramos, M.; Bongers, F.; Chazdon, R. L.; Meave, J. A.; Tabarelli, M. Multiple successional pathways in human-modified tropical landscapes: new insights from forest succession, forest fragmentation and landscape ecology research. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92(1), 326–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Xia, C.; Yue, H.; Ma, H.; Lin, G. Targeted control measures for ecological restoration in Western Fujian, China. Land Use Policy 2018, 76, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Zhou, S.L.; Wu, S.H.; Liao, F.Q. Relationships between intensity gradation and evolution of soil erosion: A case study of Changting in Fujian Province, China. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Li, Y.; Yin, B.; Wu, N.; Ye, R.; Liu, G. Spatiotemporal variation of net primary productivity and its response to drought in Inner Mongolian desert steppe. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 33, e01991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shen, Y.; Pei, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Revegetation projects significantly improved ecosystem service values in the agro-pastoral ecotone of northern China in recent 20 years. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. Cost-benefit analysis of ecological restoration based on land use scenario simulation and ecosystem service on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 34, e02006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data | Resolution | Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| Landsat images Digital elevation model Net primary productivity UAV images Crop sown area and Production Crop price Equivalent coefficients |
30 m 30 m 500 m 4 cm — — — — |
http://www.gscloud.cn/ http://www.gscloud.cn/ https://apeears.earthdatacloud.nasa.gov/ Field survey Changting Statistical Yearbook 2023 Changting Statistical Yearbook 2023 Compilation of National Agricultural Cost-benefit Data 2023 Xie et al., 2017 |
| Ecosystem Services | Farm | Grass | Forest | Construction Land | Unused Land | Water | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Secondary | Coniferous | Broad-Leaved | Mixed | |||||
| Provisioning services | Food | 1.36 | 0.38 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0 | 0 | 0.80 |
| Materials | 0.09 | 0.56 | 0.52 | 0.66 | 0.71 | 0 | 0 | 0.23 | |
| Water | -2.63 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.34 | 0.37 | 0 | 0 | 8.29 | |
| Regulating services | Air quality regulation | 1.11 | 1.97 | 1.70 | 2.17 | 2.35 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.77 |
| Climate regulation | 0.57 | 5.21 | 5.07 | 6.50 | 7.03 | 0 | 0 | 2.29 | |
| Waste treatment | 0.17 | 1.72 | 1.49 | 1.93 | 1.99 | 0 | 0.10 | 5.55 | |
| Hydrological regulation | 2.72 | 3.82 | 3.34 | 4.74 | 3.51 | 0 | 0.03 | 102.24 | |
| Support services | Erosion prevention | 0.01 | 2.40 | 2.06 | 2.65 | 2.86 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.93 |
| Maintenance of soil fertility | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0 | 0 | 0.07 | |
| Biodiversity protection | 0.21 | 2.18 | 1.88 | 2.41 | 2.60 | 0 | 0.02 | 2.55 | |
| Cultural services | Aesthetic landscape | 0.09 | 0.96 | 0.82 | 1.06 | 1.14 | 0 | 0.01 | 1.89 |
| Land Use | Landsat 9 OLI | Field photo | Google Earth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coniferous forest |  |
 |
 |
| Broad-leaved forest |  |
 |
 |
| Mixed forest |  |
 |
 |
| Grassland |  |
 |
 |
| Farmland |  |
 |
 |
| Construction land |  |
 |
 |
| Unused land |  |
 |
 |
| Water |  |
 |
 |
| Grade | Elevation (m) | Slope (°) | Relief amplitude (m) | Terrain niche |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | ≤385 | ≤8.62 | ≤15 | ≤0.09 |
| II | 385 ~ 513 | 8.62 ~ 13.61 | 15 ~ 22 | 0.09 ~ 0.32 |
| III | 513 ~ 658 | 13.61 ~ 18.64 | 22 ~ 29 | 0.32 ~ 0.47 |
| IV | 658 ~ 854 | 18.64 ~ 24.92 | 29 ~ 39 | 0.47 ~ 0.63 |
| V | >854 | >24.92 | >39 | >0.63 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





