Submitted:
17 July 2024
Posted:
18 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Protocol and Research Question
Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
Selection of Studies
Analysis of Risk of Bias
Extraction of Data
3. Results
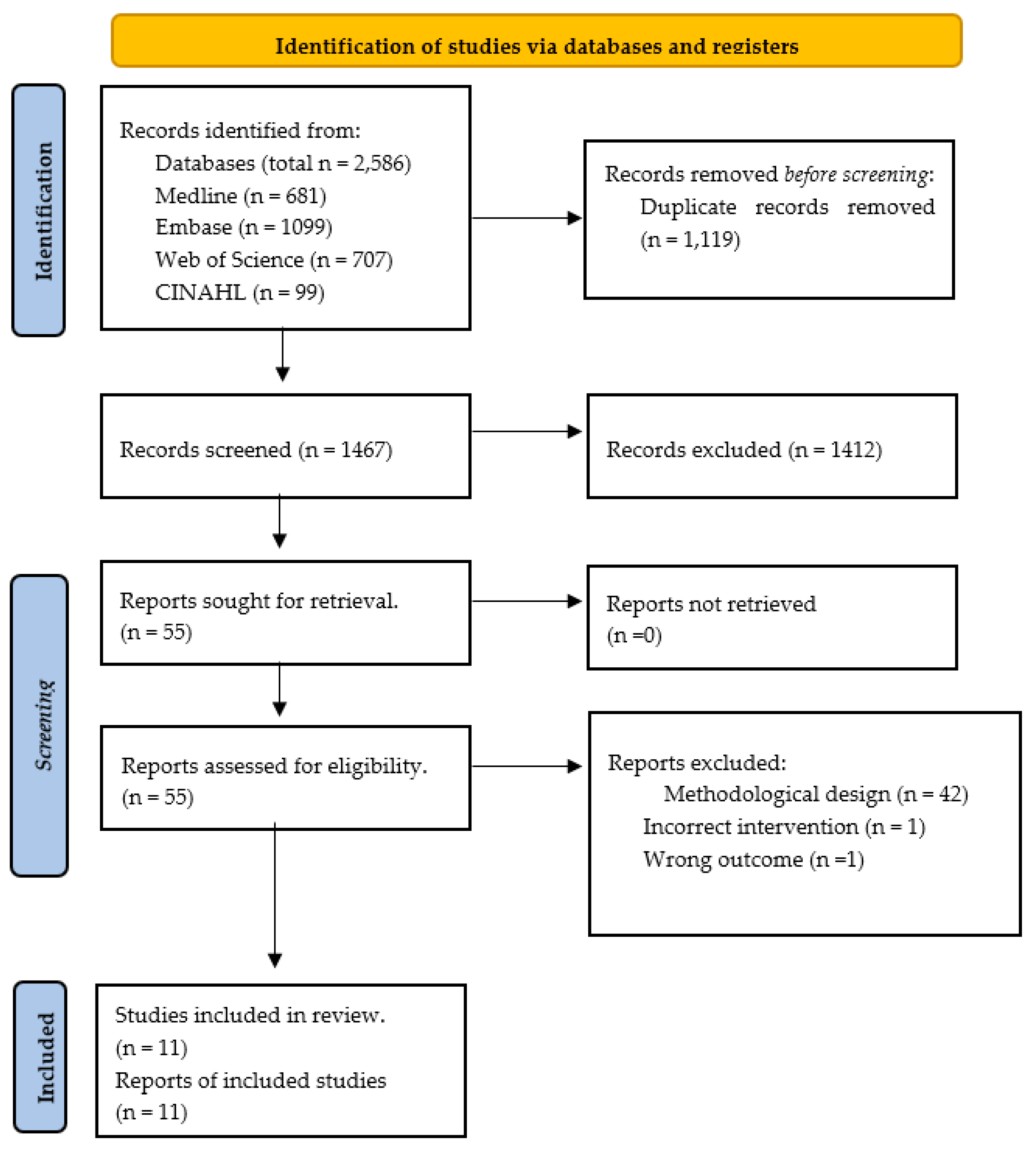
Literature Search Outflow
Studies Results
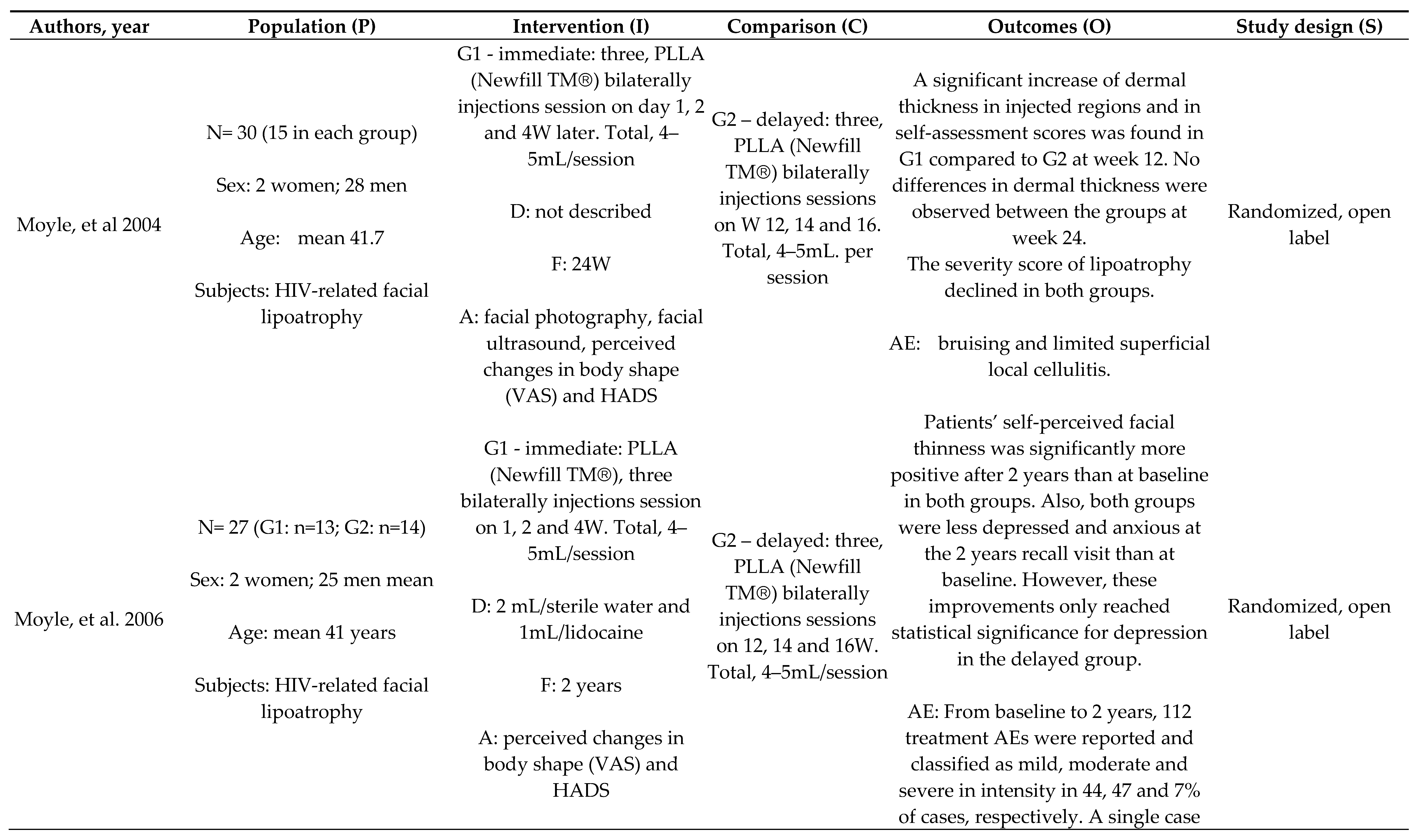
Efficacy and Durability of PLLA: Immediate x Delayed Protocol
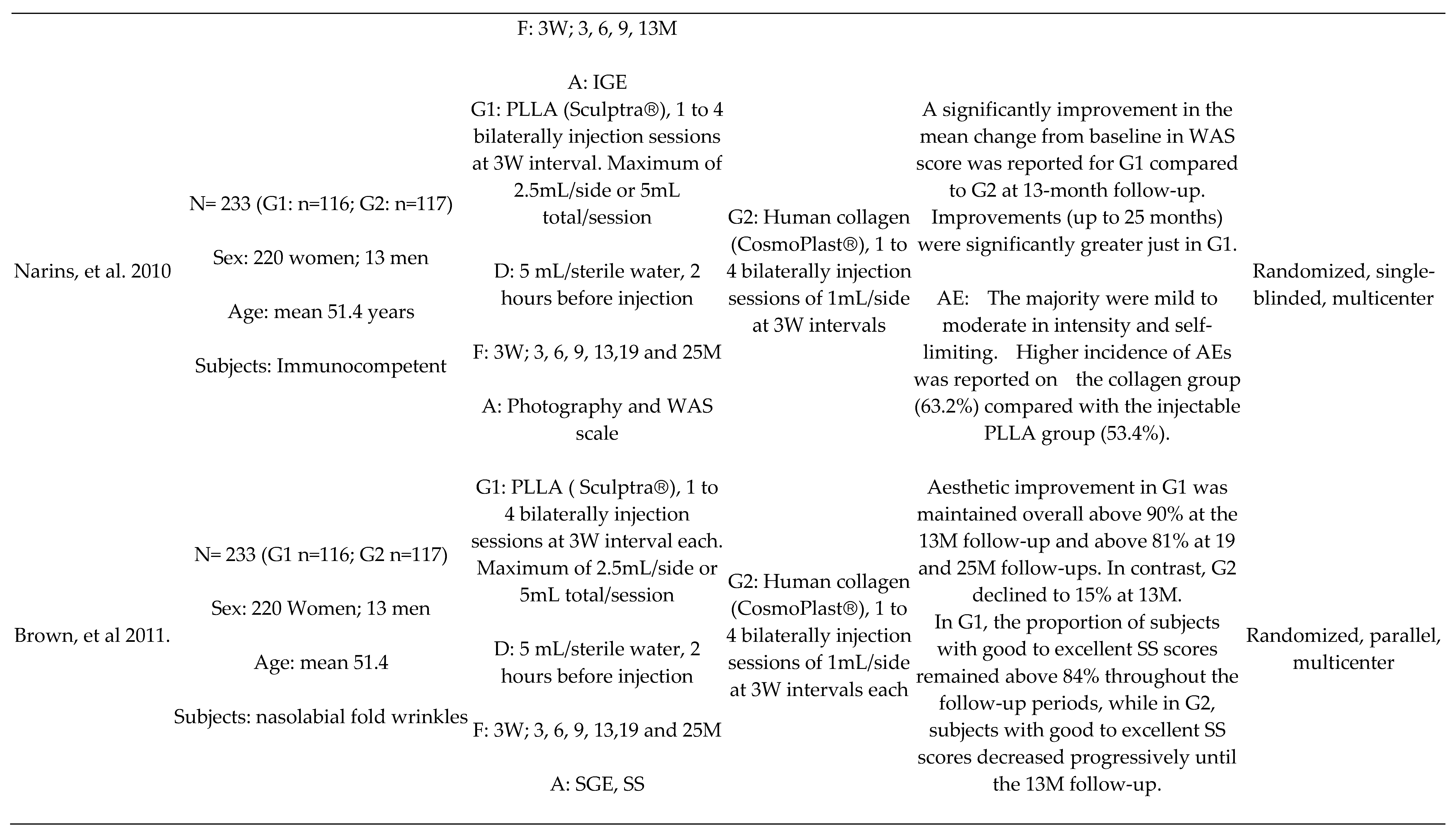
PLLA x Human Collagen
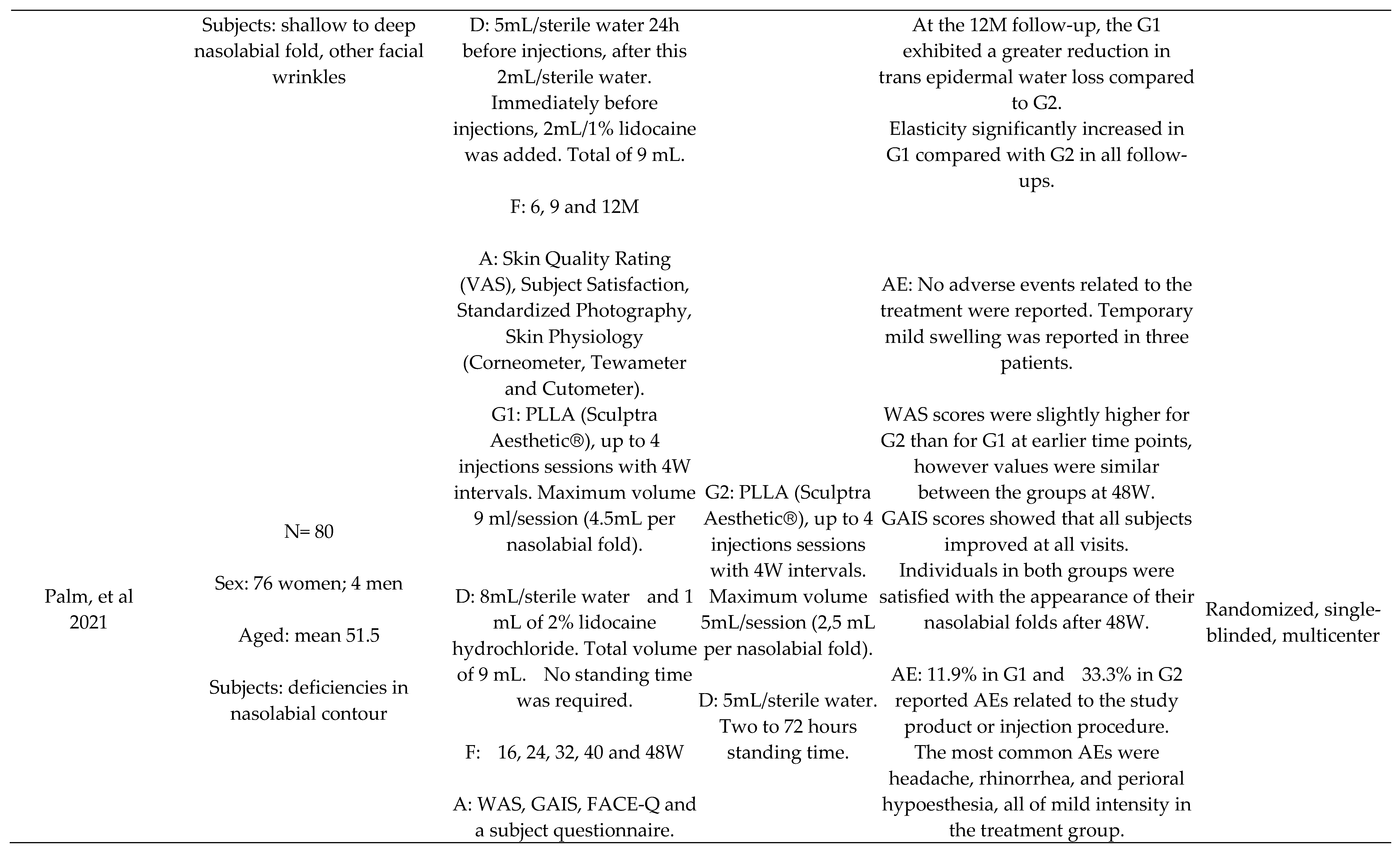
Other Comparisons
Adverse Events
Dilution Protocol
Quality Assessment
4. Discussion
Study Strengths and Limitations
Clinical Implications and Generalizability
Future Applications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christen, M.-O. Collagen stimulators in body applications: a review focused on poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA). Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology, 1019. [Google Scholar]
- Narins, R.S.; Baumann, L.; Brandt, F.S.; Fagien, S.; Glazer, S.; Lowe, N.J.; Monheit, G.D.; Rendon, M.I.; Rohrich, R.J.; Werschler, W.P. A randomized study of the efficacy and safety of injectable poly-L-lactic acid versus human-based collagen implant in the treatment of nasolabial fold wrinkles. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2010, 62, 448–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnert, K.; Dorizas, A.; Lorenc, P.; Sadick, N.S. Randomized, controlled, multicentered, double-blind investigation of injectable poly-L-lactic acid for improving skin quality. Dermatologic Surgery 2019, 45, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, R.; Vleggaar, D. Facial volume restoration of the aging face with poly-l-lactic acid. Dermatologic therapy 2011, 24, 2–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, D.L.; Baker, D.; Rogers, G.D.; Petoumenos, K.; Chuah, J.; Easey, N.; Machon, K.; Cooper, D.A.; Emery, S.; Carr, A. A randomized, multicenter, open-label study of poly-L-lactic acid for HIV-1 facial lipoatrophy. JAIDS Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes 2007, 46, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyle, G.; Lysakova, L.; Brown, S.; Sibtain, N.; Healy, J.; Priest, C.; Mandalia, S.; Barton, S. A randomized open-label study of immediate versus delayed polylactic acid injections for the cosmetic management of facial lipoatrophy in persons with HIV infection. HIV medicine 2004, 5, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.M.; Azizzadeh, B.; Graivier, M. Injectable poly-L-lactic acid (Sculptra): technical considerations in soft-tissue contouring. Plastic and reconstructive surgery 2006, 118, 55S–63S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabi, S.; Hamilton, T.; LaTowsky, B.; Kazin, R.; Marcus, K.; Mayoral, F.; Joseph, J.; Hooper, D.; Shridharani, S.; Hicks, J. Effectiveness and Safety of Sculptra Poly-L-Lactic Acid Injectable Implant in the Correction of Cheek Wrinkles. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology: JDD 2024, 23, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration FDA (2023). Summary of Safety and effectiveness Data (SSES). Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf16/P160035B.pdf.
- Brandt, F.S.; Cazzaniga, A.; Baumann, L.; Fagien, S.; Glazer, S.; Kenkel, J.M.; Lowe, N.J.; Monheit, G.D.; Narins, R.S.; Rendon, M.I. Investigator global evaluations of efficacy of injectable poly-L-lactic acid versus human collagen in the correction of nasolabial fold wrinkles. Aesthetic surgery journal 2011, 31, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, A.; Kadunc, B.V.; Guarnieri, C.; Noviello, J.S.; da Cunha, M.G.; Parada, M.B. Conceitos atuais no uso do ácido poli-l-láctico para rejuvenescimento facial: revisão e aspectos práticos. Surgical & cosmetic dermatology 2017, 9, 60–71. [Google Scholar]
- Akinbiyi, T.; Othman, S.; Familusi, O.; Calvert, C.; Card, E.B.; Percec, I. Better results in facial rejuvenation with fillers. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery–Global Open 2020, 8, e2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterwick, K.; Lowe, N.J. Injectable poly-L-lactic acid for cosmetic enhancement: learning from the European experience. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology 2009, 61, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, J.J.; Malik, K.M.; Burnie, S.J.; Endicott, A.R.; Busse, J.W. What is your research question? An introduction to the PICOT format for clinicians. The Journal of the Canadian Chiropractic Association 2012, 56, 167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Annals of internal medicine 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.M.; Sanders, S.; Carter, M.; Honeyman, D.; Cleo, G.; Auld, Y.; Booth, D.; Condron, P.; Dalais, C.; Bateup, S. Improving the translation of search strategies using the Polyglot Search Translator: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the Medical Library Association: JMLA 2020, 108, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramer, W.M.; Giustini, D.; de Jonge, G.B.; Holland, L.; Bekhuis, T. De-duplication of database search results for systematic reviews in EndNote. Journal of the Medical Library Association: JMLA 2016, 104, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Systematic reviews 2016, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Hoboken: Wiley 2019.
- Moyle, G.J.; Brown, S.; Lysakova, L.; Barton, S.E. Long-term safety and efficacy of poly-L-lactic acid in the treatment of HIV-related facial lipoatrophy. HIV Med 2006, 7, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.A.; Rohrich, R.J.; Baumann, L.; Brandt, F.S.; Fagien, S.; Glazer, S.; Kenkel, J.M.; Lowe, N.J.; Monheit, G.D.; Narins, R.S.; et al. Subject global evaluation and subject satisfaction using injectable poly-L-lactic acid versus human collagen for the correction of nasolabial fold wrinkles. Plast Reconstr Surg 2011, 127, 1684–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafaurie, M.; Dolivo, M.; Girard, P.M.; May, T.; Bouchaud, O.; Carbonnel, E.; Madelaine, I.; Loze, B.; Porcher, R.; Molina, J.M. Polylactic acid vs. polyacrylamide hydrogel for treatment of facial lipoatrophy: a randomized controlled trial [Agence Nationale de Recherches sur le SIDA et les Hépatites Virales (ANRS) 132 SMILE]. HIV Med 2013, 14, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, M.; Weinkle, S.; Cho, Y.; LaTowsky, B.; Prather, H. A Randomized Study on PLLA Using Higher Dilution Volume and Immediate Use Following Reconstitution. J Drugs Dermatol 2021, 20, 760–766. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kwon, R.; Kang, S.M.; Yon, D.K. Safety and efficacy of Poly-L-Lactic acid filler (Gana V vs. Sculptra) injection for correction of the nasolabial fold: a double-blind, non-inferiority, randomized, split-face controlled trial. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery 2023, 47, 1796–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.M.; Batsukh, S.; Sung, M.J.; Lim, T.H.; Lee, M.H.; Son, K.H.; Byun, K. Poly-L-lactic acid fillers improved dermal collagen synthesis by modulating m2 macrophage polarization in aged animal skin. Cells 2023, 12, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedush, N.G.; Kalinin, K.T.; Azarkevich, P.N.; Gorskaya, A.A. Physicochemical characteristics and hydrolytic degradation of polylactic acid dermal fillers: A comparative study. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, K.; Alm, J.; Norberg, M.; Ejehorn, M. Immediate Use After Reconstitution of a Biostimulatory Poly-L-Lactic Acid Injectable Implant. Journal of Drugs in Dermatology: JDD 2020, 19, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Kumar, V. New emerging trends in synthetic biodegradable polymers–Polylactide: A critique. European polymer journal 2007, 43, 4053–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddhesh, D. Global Poly-L-lactic Acid (PLLA) Filler Market. 2023. Available online: https://dataintelo.com/report/global-poly-l-lactic-acid-plla-filler-market/.




| Author, year |
Randomization Process |
Deviations from Intended Interventions |
Missing Outcome Data |
Measurement of the Outcome |
Selection of the Reported Results | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moyle et al., 2004 | Some concerns | High risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Moyle et al., 2006 | Some concerns | High risk | Some concerns | Some concerns | Some concerns | High risk |
| Carey et al., 2007 | Some concerns | High risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Brandt et al., 2010 | Some concerns | Low risk | Some concerns | Some concerns | Some concerns | Some concerns |
| Narins et al., 2010 | Some concerns | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | Some concerns |
| Brown et al., 2011 | Low risk | Some concerns | Some concerns | Some concerns | Some concerns | Some concerns |
| Lafaurie et al., 2013 | Low risk | Some concerns | Some concerns | Some concerns | Some concerns | Some concerns |
| Bohnert et al., 2019 | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | Low risk | Some concerns | Some concerns |
| Palm et al., 2021 | Some concerns | High risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Han et al., 2023 | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | Low risk | Some concerns | Some concerns |
| Fabi et al., 2024 | Some concerns | High risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





