Submitted:
12 July 2024
Posted:
15 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
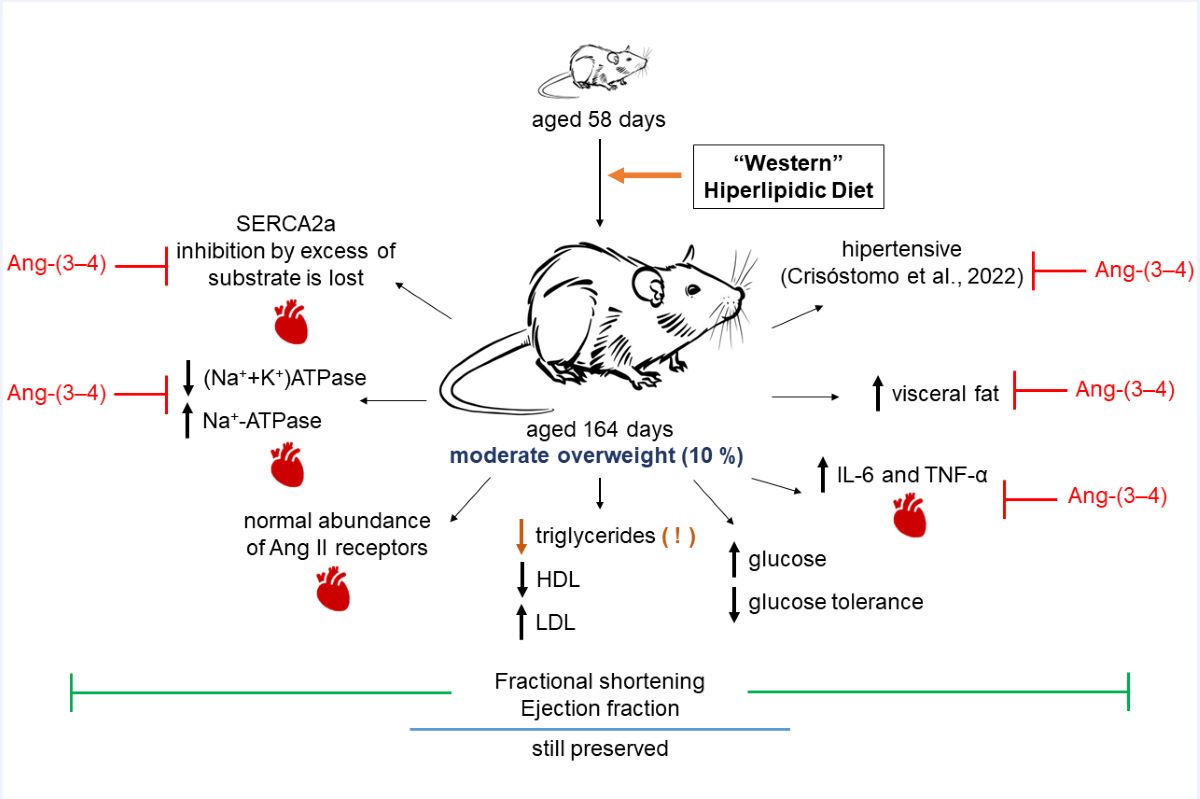
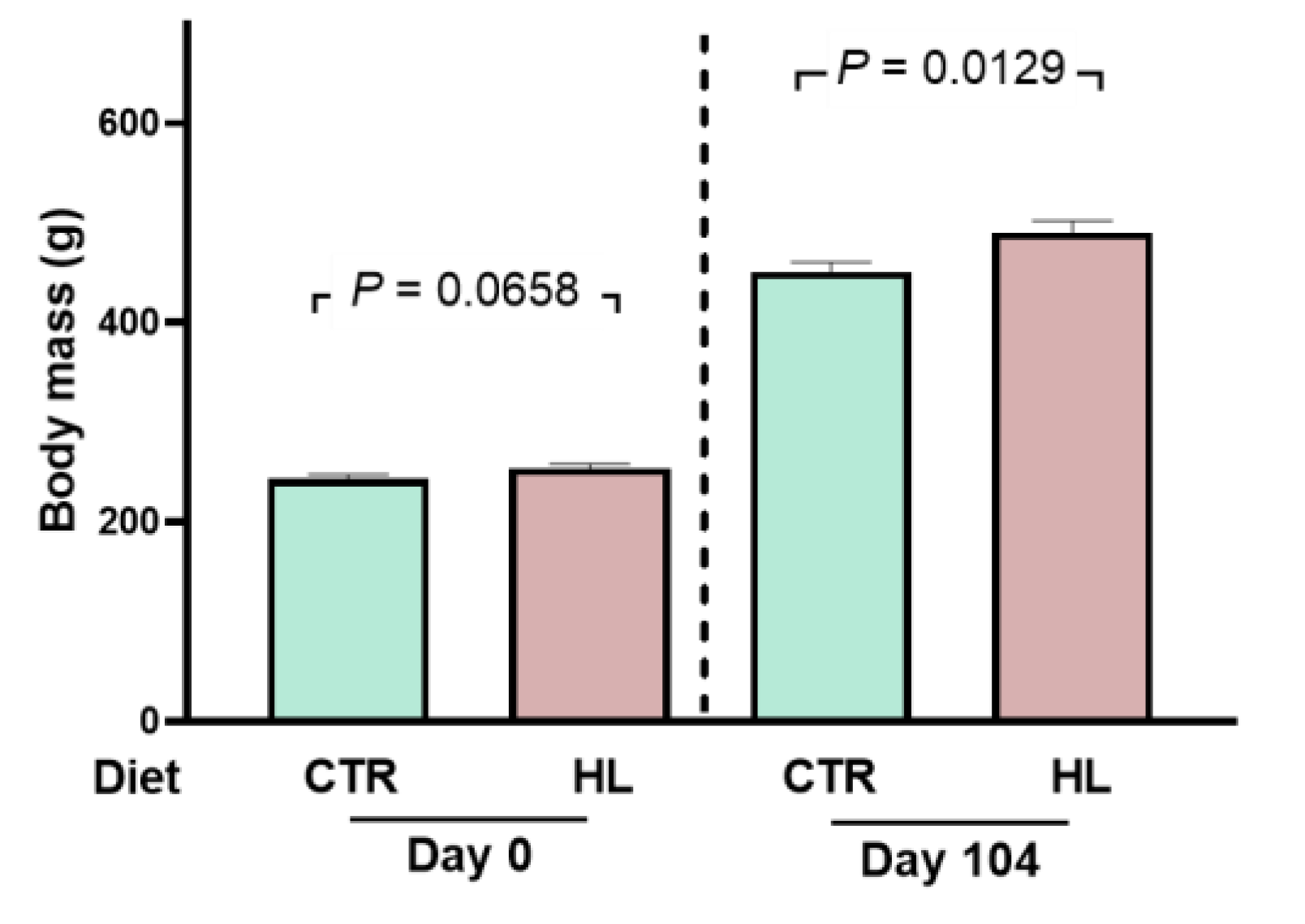
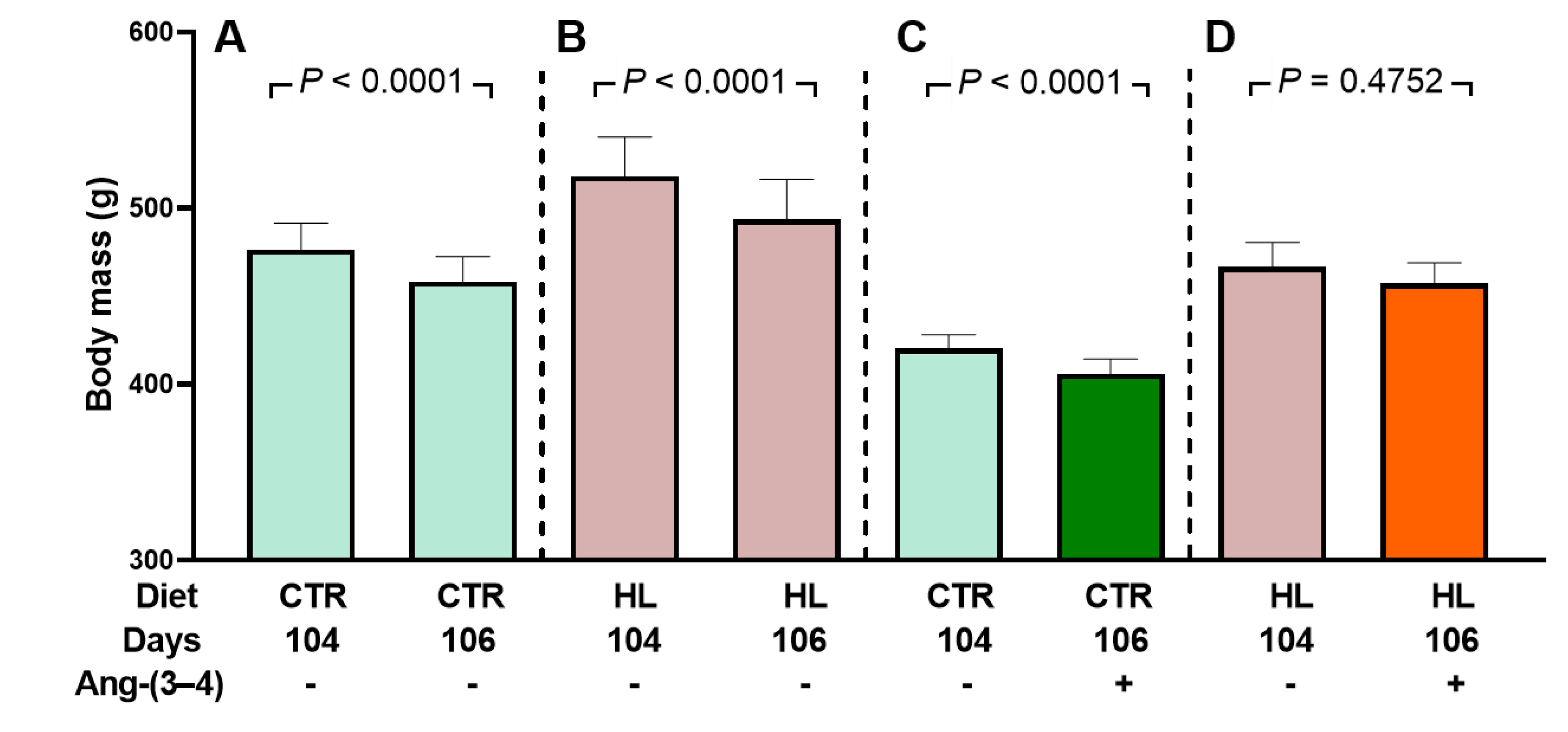
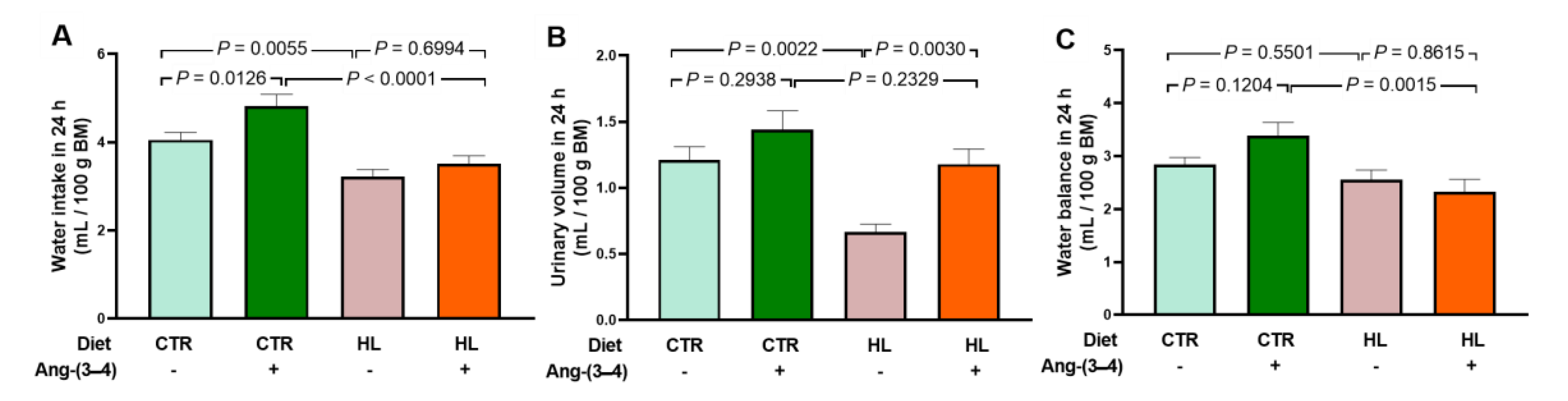
2.1. Development of Moderate Overweight in Rats that Received the High-fat Diet
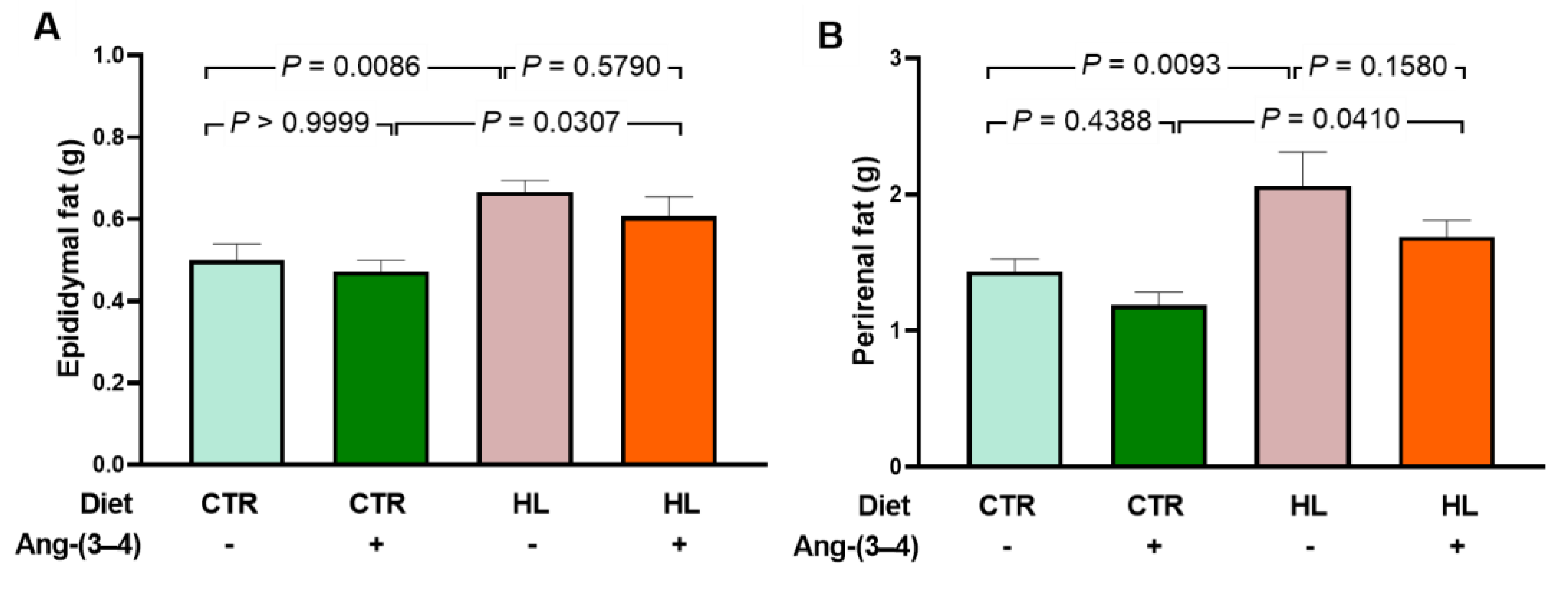
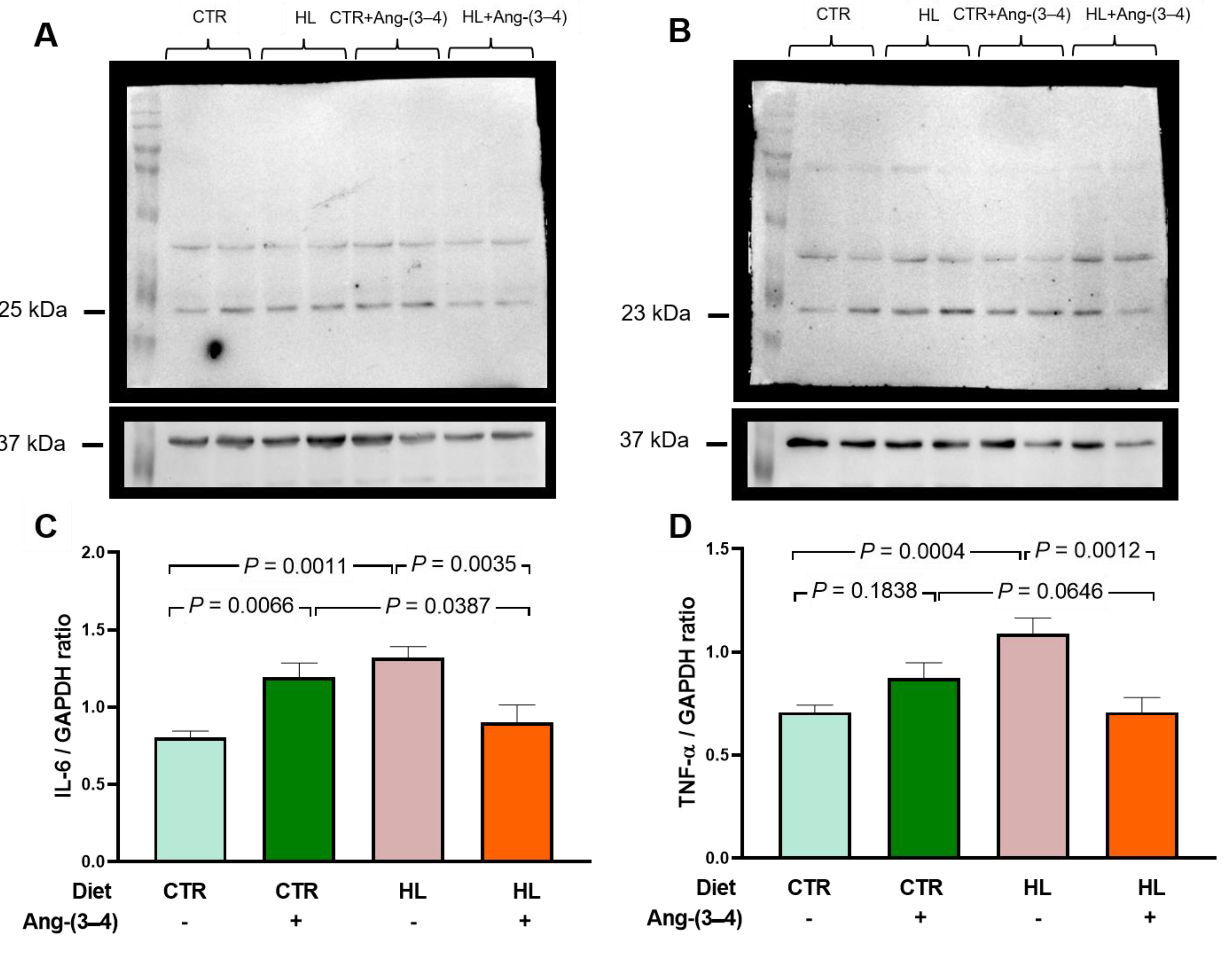
2.2. Biomarkers of Metabolic Alterations and Inflammatory Processes in HL Overweight Rats
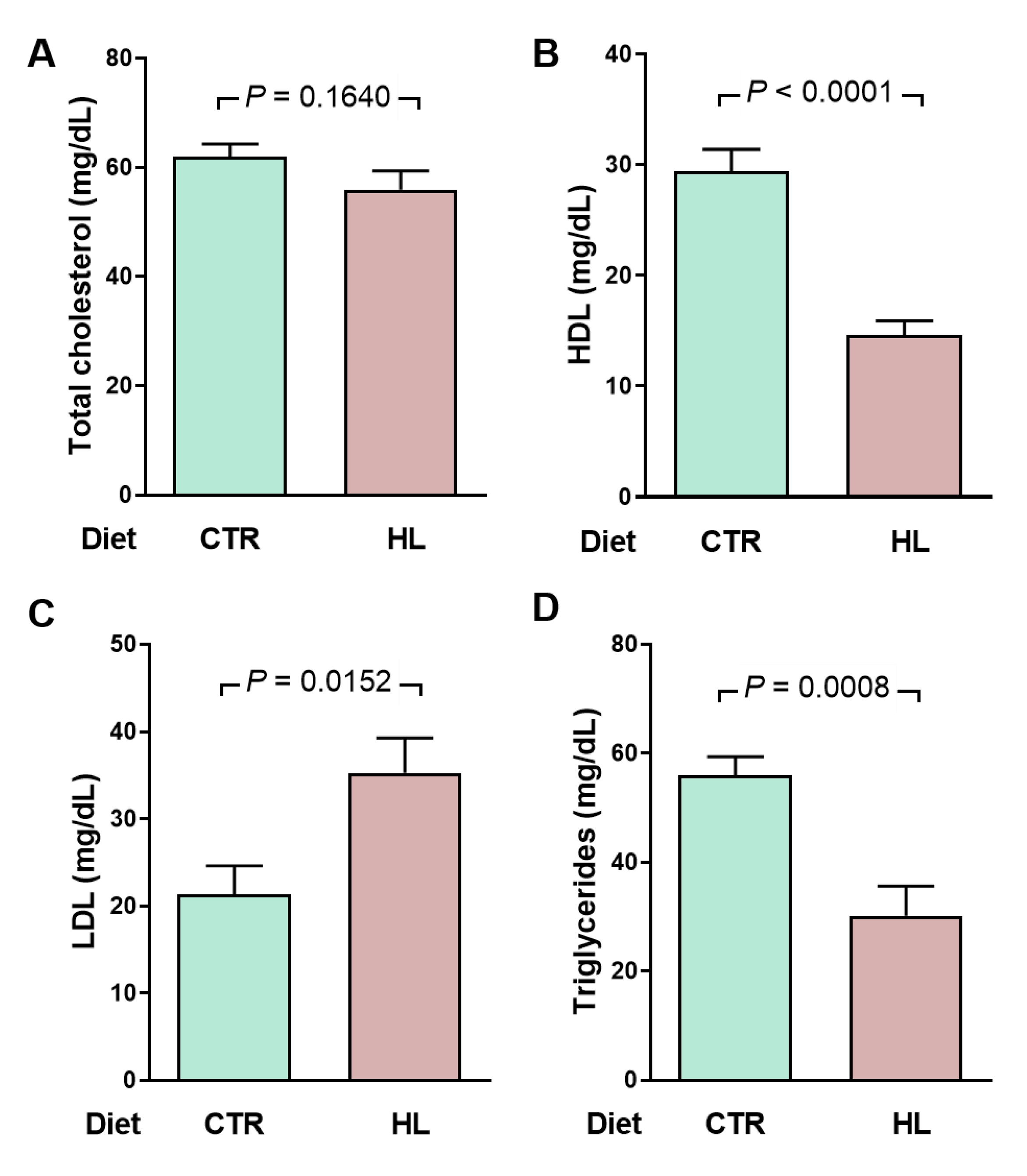
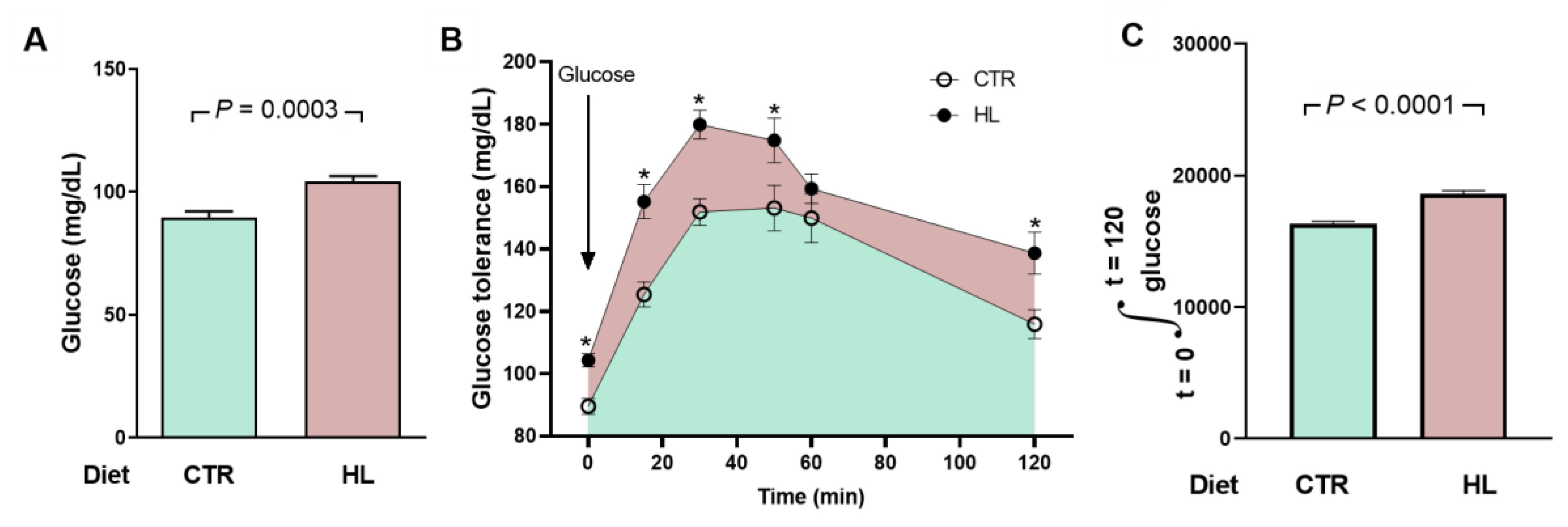
2.3. Atypical Metabolic Syndrome in HL Overweight Rats
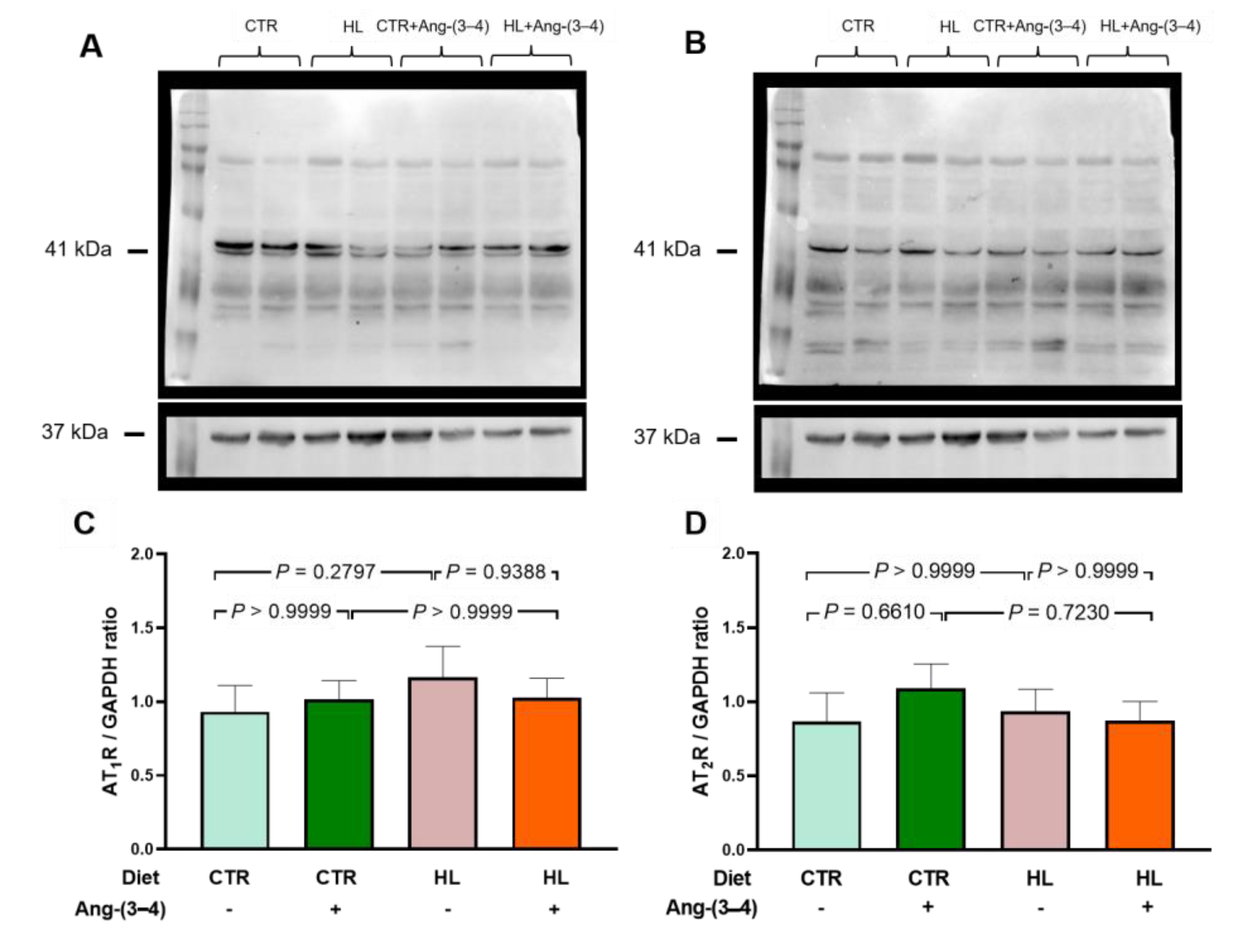
2.4. Unmodified Angiotensin II Receptors in Left Ventricle Microsomes from HL Rats
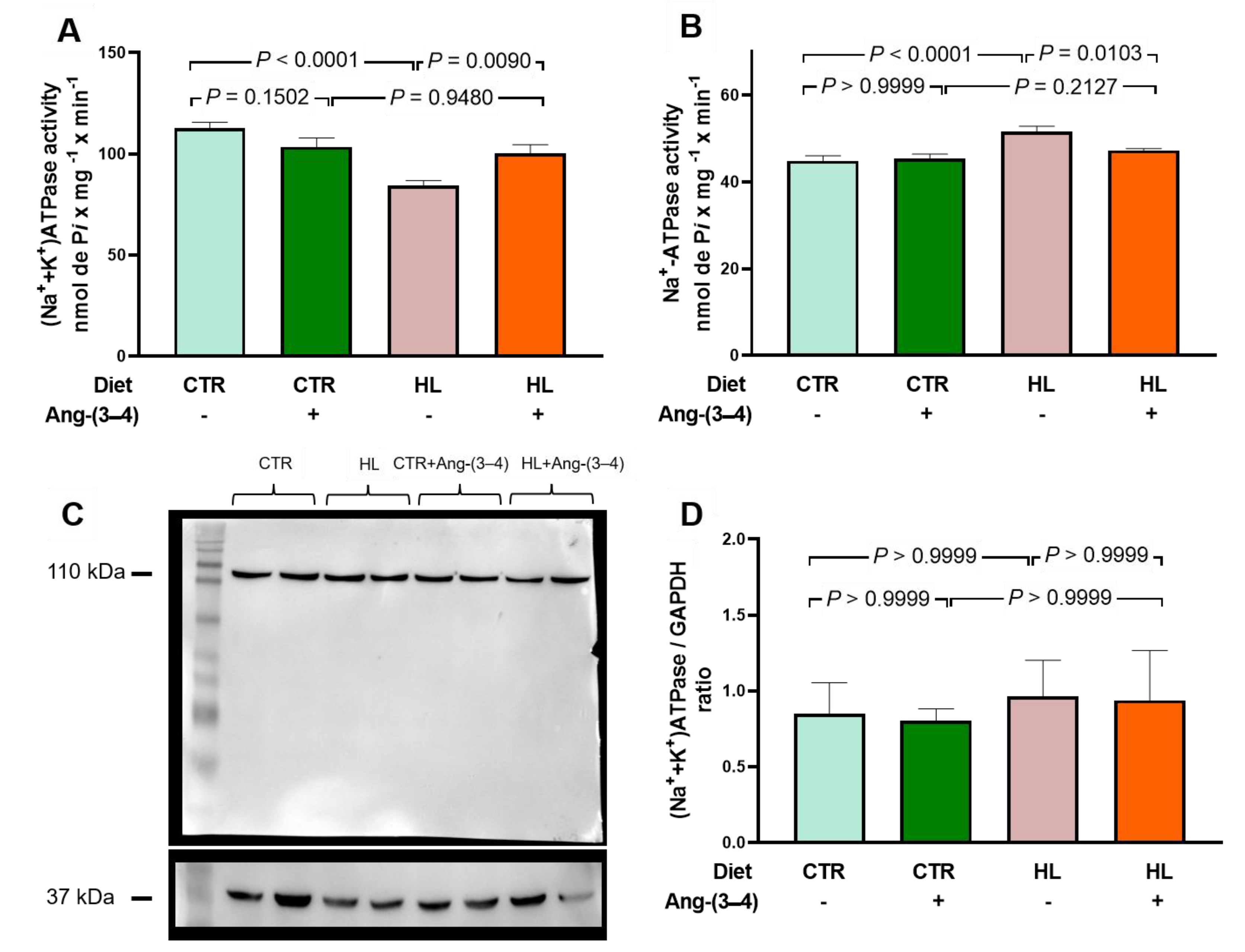
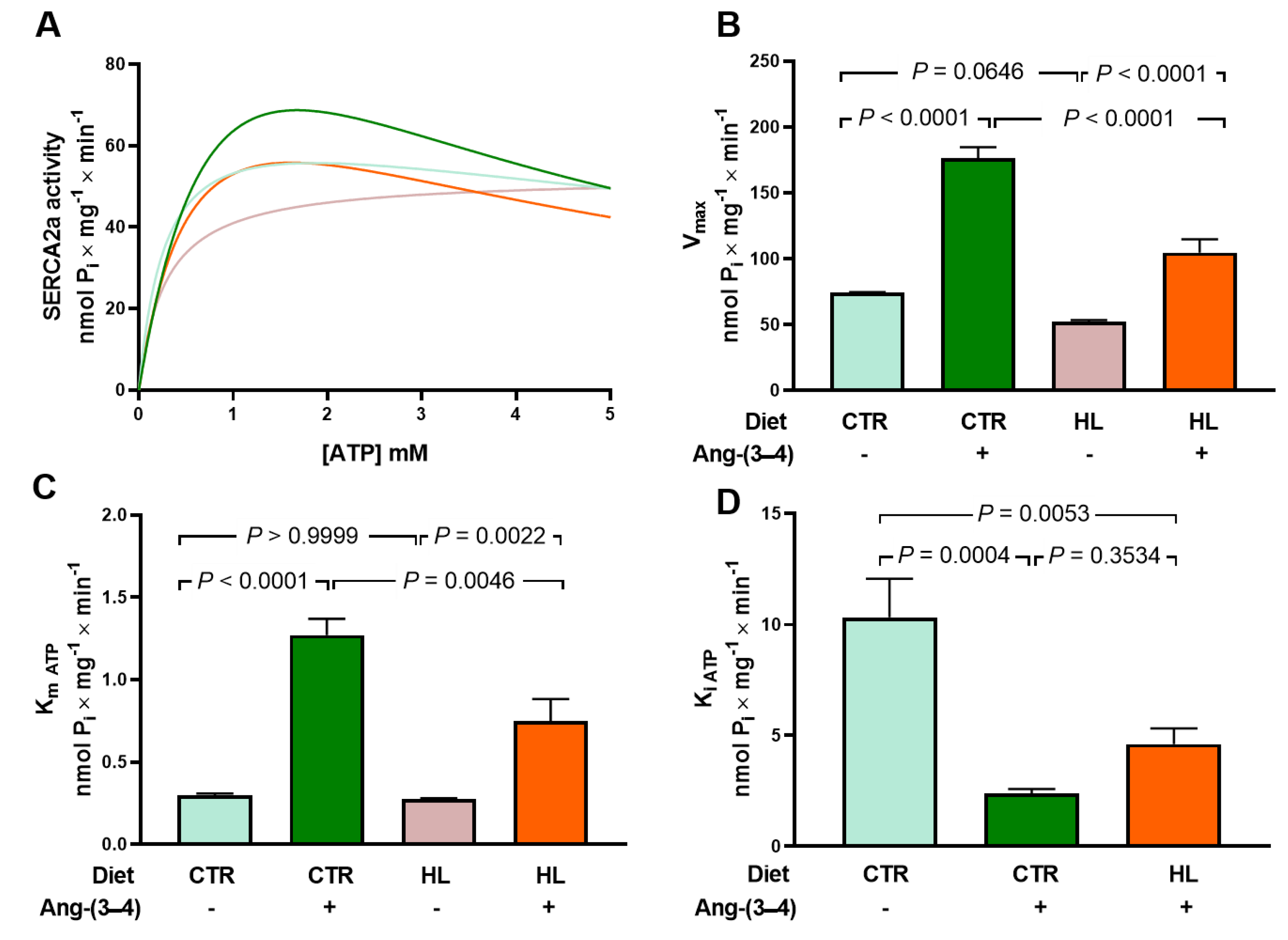
2.5. Overweight Rats Present Alterations in the Active Transport of Na+ and Ca2+ in Left Ventricle that Are Reverted by Ang-(3–4)
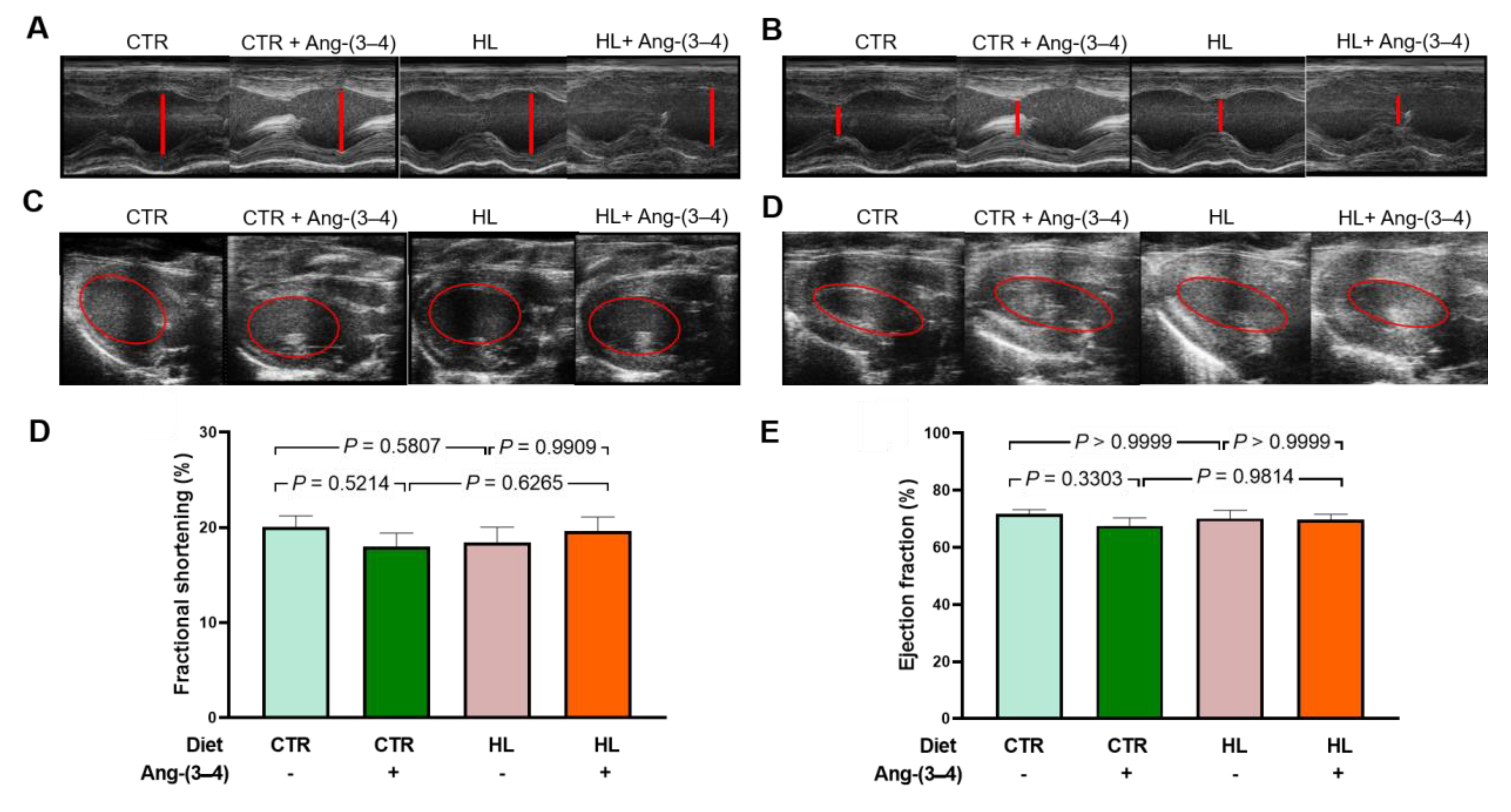
2.6. There Is no Structural Remodeling in Overweight Rats at Juvenile Age
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Considerations
4.2. Experimental Groups and Diets
4.3. Lipidogram
4.4. Glycemia Determination and Oral Glucose Tolerance Curve
4.5. Preparation of Left Ventricle Microsomes
4.6. SDS PAGE and Western Blotting
4.7. Measurement of Left Ventricle Na+-transporting ATPases Activity
4.8. Measurement of Left Ventricle Sarco-Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase/SERCA2a Activity
4.9. Echocardiographic Images
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swinburn, B.A.; Kraak, V.I.; Allender, S.; Atkins, V.J.; Baker, P.I.; Bogard, J.R.; Brinsden, H.; Calvillo, A.; De Schutter, O.; Devarajan, R.; Ezzati, M.; Friel, S.; Goenka, S.; Hammond, R.A.; Hastings, G.; Hawkes, C.; Herrero, M.; Hovmand, P.S.; Howden, M.; Jaacks, L.M.; Kapetanaki, A.B.; Kasman, M.; Kuhnlein, H.V.; Kumanyika, S.K.; Larijani, B.; Lobstein, T.; Long, M.W.; Matsudo, V.K.R.; Mills, S.D.H.; Morgan, G.; Morshed, A.; Nece, P.M.; Pan, A.; Patterson, D.W.; Sacks, G.; Shekar, M.; Simmons, G.L.; Smit, W.; Tootee, A.; Vandevijvere, S.; Waterlander, W.E.; Wolfenden, L.; Dietz, W.H. The global syndemic of obesity, undernutrition, and climate change: the lancet commission report. Lancet. 2019, 393, 791−846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity and overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (acessed on june 26, 2024).
- United Nations (UN). World population to reach 8 billion on 15 November 2022. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/desa/world-population-reach-8-billion-15-november-2022 (acessed on June 26, 2024).
- Xu, H.; Cupples, L.A.; Stokes, A.; Liu, C.T. Association of obesity with mortality over 24 years of weight history: findings from the framingham heart study. JAMA Netw. Open. 2018, 1, e184587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.S.; Mulder, C.; Twisk, J.W.; van Mechelen, W.; Chinapaw, M.J. Tracking of childhood overweight into adulthood: a systematic review of the literature. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, A.G.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Barreira, T.V.; Broyles, S.T.; Chaput, J.P.; Church, T.S.; Fogelholm, M.; Harrington, D.M.; Hu, G.; Kuriyan, R.; Kurpad, A.; Lambert, E.V.; Maher, C.; Maia, J.; Matsudo, V.; Olds, T.; Onywera, V.; Sarmiento, O.L.; Standage, M.; Tudor-Locke, C.; Zhao, P.; Tremblay, M.S. and ISCOLE Research Group. Correlates of total sedentary time and screen time in 9–11 year-old children around the world: the international study of childhood obesity, lifestyle and the environment. PLoS One. 2015, 10, e0129622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goran, M.I. Energy metabolism and obesity. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2000, 84, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, W. How Western diet and lifestyle drive the pandemic of obesity and civilization diseases. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2019, 12, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkin, B.M.; Richards, M.K.; Montiero, C.A. Stunting is associated with overweight in children of four nations that are undergoing the nutrition transition. J. Nutr. 1996, 126, 3009–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, B.; Rubinstein, S. Environmental factors affecting nutritional status in urban areas of developing countries. Arch. Latinoam. Nutr. 1997, 47, 3−8. [Google Scholar]
- Mill, J.G.; Malta, D.C.; Machado, I.E.; PateI, A.; Pereira, C.A.; Jaime, P.C.; Szwarcwald, C.L.; Rosenfeld, L.G. Estimation of salt intake in the Brazilian population: results from the 2013 National Health Survey. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2019, 22, e190009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzes, R.; Crisóstomo, T.; Silva, P.A.; Iack, R.; de Abreu, V.G.; Francischetti, E.A.; Vieyra, A. Angiotensin-(3–4) normalizes blood pressure, decreases Na+ and energy intake, but preserves urinary Na+ excretion in overweight hypertensive rats. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, R. Comparing rat’s to human’s age: how old is my rat in people years? Nutrition. 2005, 21, 775–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touati, S.; Meziri, F.; Devaux, S.; Berthelot, A.; Touyz, R.M.; Laurant, P. Exercise reverses metabolic syndrome in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, M., Mehr. A.P., Kreutz R. Physiology of local renin-angiotensin systems. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 747–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelband, F.; Dias, J.; Miranda, F.; Ferrão, F.M.; Reis, R.I.; Costa-Neto, C.M.; Lara, L.S.; Vieyra, A. Angiotensin-(3–4) counteracts the Angiotensin II inhibitory action on renal Ca2+-ATPase through a cAMP/PKA pathway. Regul. Pept. 2012, 177, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, J.; Ferrão, F.M.; Axelband, F.; Carmona, A.K.; Lara, L.S.; Vieyra, A. ANG-(3–4) inhibits renal Na+-ATPase in hypertensive rats through a mechanism that involves dissociation of ANG II receptors, heterodimers, and PKA. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2014, 306, F855–F863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, J.; Axelband, F.; Lara, L.S.; Muzi-Filho, H.; Vieyra, A. Is angiotensin-(3–4) (Val-Tyr). the shortest angiotensin II-derived peptide. opening new vistas on the renin-angiotensin system? J. Renin. Angiotensin. Aldosterone Syst. 2017, 18, 1470320316689338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, P.G. Components of the AIN-93 diets as improvements in the AIN-76A diet. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 838S–841S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, A.A.; Grobe, C.C.; Reho, J.J.; Jensen, E.S.; Thulin, J.D.; Segar, J.L.; Grobe, J.L. Short-term housing in metabolic caging on measures of energy and fluid balance in male C57BL/6J mice (Mus musculus). J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2022, 61, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chughtai, H.L.; Morgan, T.M.; Rocco, M.; Stacey, B.; Brinkley, T.E.; Ding, J.; Nicklas, B.; Hamilton, C.; Hundley, W.G. Renal sinus fat and poor blood pressure control in middle-aged and elderly individuals at risk for cardiovascular events. Hypertension. 2010, 56, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chusyd, D.E.; Wang, D.; Huffman, D.M.; Nagy, T.R. Relationships between rodent white adipose fat pads and human white adipose fat depots. Front. Nutr. 2016, 3, 10−22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Park, T. Genes are differentially expressed in the epididymal fat of rats rendered obese by a high-fat diet. Nutr. Res. 2008, 28, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, P.A.; Ranganathan, S.; Li, C.; Wood, L.; Ranganathan, G. Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 280, E745–E751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.Y.; Choi, W.J.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.W. Relationship between inflammatory markers and visceral obesity in obese and overweight Korean adults: An observational study. Medicine. 2019, 98, e14740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H. Obese visceral fat tissue inflammation: from protective to detrimental? BMC Med. 2022, 20, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisóstomo, T.; Pardal, M.A.E.; Herdy, S.A.; Muzi-Filho, H.; Mello, D.B.; Takiya, C.M.; Luzes, R.; Vieyra, A. Liver steatosis, cardiac and renal fibrosis, and hypertension in overweight rats: Angiotensin-(3–4)-sensitive hepatocardiorenal syndrome. Metabol. Open. 2022, 14, 100176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedewald, W.T.; Levy, R.I.; Fredrickson, D.S. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 499−502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinz, I.; Tian, R.; Belke, D.; Swanson, E.; Dillmann, W.; Ingwall, J.S. Compromised myocardial energetics in hypertrophied mouse hearts diminish the beneficial effect of overexpressing SERCA2a. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 10163–10168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, M.; Murakami, K. Analysis of the substrate inhibition of complete and partial types. SpringerPlus. 2015, 4, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailova, A.; McCulloch, A. Model study of ATP and ADP buffering, transport of Ca2+ and Mg2+, and regulation of ion pumps in ventricular myocyte. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Iwai, M.; Wu, L.; Shiuchi, T.; Jinno, T.; Cui, T.X.; Horiuchi, M. Role of AT2 receptor in the brain in regulation of blood pressure and water intake. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2003, 284, H116–H121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellen, K.E.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Torres, I.; Gutiérrez-Alvarez, Y.; Guarner-Lans, V.; Díaz-Díaz, E.; Manzano Pech, L.; Caballero-Chacón, SDC. Intra-abdominal fat adipocyte hypertrophy through a progressive alteration of lipolysis and lipogenesis in metabolic syndrome rats. Nutrients. 2019, 11, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Fu, M.; Li, M.D.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Ni, W.; Ong, Q.; Mi, J.; Yang, X. O-GlcNAc transferase inhibits visceral fat lipolysis and promotes diet-induced obesity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langin, D.; Dicker, A.; Tavernier, G.; Hoffstedt, J.; Mairal, A.; Rydén, M.; Arner, E.; Sicard, A.; Jenkins, C. M.; Viguerie, N.; van Harmelen, V.; Gross, R.W.; Holm, C.; Arner, P. Adipocyte lipases and defect of lipolysis in human obesity. Diabetes. 2005, 54, 3190–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clementi, A.; Brocca, A.; Virzì, G.M.; de Cal, M.; Giavarina, D.; Carta, M.; Muciño-Bermejo, M.J.; Hinna, D.T.; Salvador, L.; Ronco, C. Procalcitonin and interleukin-6 levels: are they useful biomarkers in cardiac surgery patients? Blood Purif. 2017, 43, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerrschmid, C.; Crawford, J.R.; Reineke, E.; Taffet, G.E.; Trial, J.; Entman, M.L.; Haudek, S.B. TNF receptor 1 signaling is critically involved in mediating angiotensin-II-induced cardiac fibrosis. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2013, 57, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradham, W.S.; Bozkurt, B.; Gunasinghe, H.; Mann, D.; Spinale, F.G. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and myocardial remodeling in progression of heart failure: a current perspective. Cardiovasc. Res. 2002, 53, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster, J.J.; Walsh, K. The good, the bad, and the ugly of interleukin-6 signaling. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 1425–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forcina, L.; Franceschi, C.; Musarò, A. The hormetic and hermetic role of IL-6. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 80, 101697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauer, J. , Chaurasia, B., Goldau, J., Vogt, M.C., Ruud, J., Nguyen, K.D., Theurich, S., Hausen, A.C., Schmitz, J., Brönneke, H.S., Estevez, E., Allen, T.L., Mesaros, A., Partridge, L., Febbraio, M.A., Chawla, A., Wunderlich, F.T., Brüning, J.C. Signaling by IL-6 promotes alternative activation of macrophages to limit endotoxemia and obesity-associated resistance to insulin. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A. , Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011, 1813, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mello, W.C. Local renin angiotensin aldosterone systems and cardiovascular diseases. Med. Clin. North Am. 2017, 101, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.C.; Barrett, P.H.; Watts, G.F. Lipoprotein kinetics in the metabolic syndrome: pathophysiological and therapeutic lessons from stable isotope studies. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2004, 25, 31–48. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, M.; Berneis, K. An update on the role of the quality of LDL in cardiovascular risk: the contribution of the universities of Palermo and Zurich. Recent Pat. Cardiovasc. Drug Discov. 2007, 2, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, S.; Genest, J. Effect of obesity on high-density lipoprotein metabolism. Obesity. 2007, 15, 2875–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbarino, J.; Sturley, S.L. Saturated with fat: new perspectives on lipotoxicity. Curr Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care. 2009, 12, 110−116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caër, C.; Rouault, C.; Le Roy, T.; Poitou, C.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Torcivia, A.; Bichet, J.C.; Clément, K.; Guerre-Millo, M.; André, S. Immune cell-derived cytokines contribute to obesity-related inflammation, fibrogenesis and metabolic deregulation in human adipose tissue. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strazzullo, P.; Barbab, G.; Cappuccioc, F.P.; Sianib, A.; Trevisand, M.; Farinaroe, E.; Paganoa, E.; Barbatoa, A.; Iaconea, R.; Galletti, F. Altered renal sodium handling in men with abdominal adiposity: a link to hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2001, 19, 2157−2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeau, K.J.; Maahs, D.M.; Daniels, S.R.; Eckel, R.H. Childhood obesity and cardiovascular disease: links and prevention strategies. Nat. Ver. Cardiol. 2011, 8, 513−525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.K.; Griendling, K.K. Angiotensin II cell signaling: physiological and pathological effects in the cardiovascular system. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C82–C97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjit, A.; Khajehpour, S.; Aghazadeh-Habashi, A. Update on angiotensin II subtype 2 receptor: focus on peptide and nonpeptide agonists. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 99, 469–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, P. A.; Monnerat-Cahli, G.; Pereira-Acácio, A.; Luzardo, R.; Sampaio, L.S.; Luna-Leite, M.A.; Lara, L.S.; Einicker-Lamas, M.; Panizzutti, R.; Madeira, C.; Vieira-Filho, L.D.; Castro-Chaves, C.; Ribeiro, V.S.; Paixão, A.D.O.; Medei, E.; Vieyra, A. Mechanisms Involving Ang II and MAPK/ERK1/2 signaling pathways underlie cardiac and renal alterations during chronic undernutrition. PLoS One. 2014, 9, e100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, P.A.; Muzi-Filho, H.; Pereira-Acácio, A.; Dias, J.; Martins, J.F.; Landim-Vieira, M.; Verdoorn, K.S.; Lara, L.S.; Vieira-Filho, L.D.; Cabral, E.V.; Paixão, A.D.; Vieyra, A. Altered signaling pathways linked to angiotensin II underpin the upregulation of renal Na+-ATPase in chronically undernourished rats. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014, 1842, 2357–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obradovic, M.; Sudar-Milovanovic, E.; Gluvic, Z.; Banjac, K.; Rizzo, M.; Isenovic, E.R. The Na+/K+-ATPase: A potential therapeutic target in cardiometabolic diseases. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2023, 14, 1150171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Bai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sottejeau, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Lingrel, J.B.; Malhotra, D.; Cooper, C.J; Shapiro, J.I.; Xie, Z.J.; Tian, J. Reduction of Na/K-ATPase potentiates marinobufagenin-induced cardiac dysfunction and myocyte apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 16390–16398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, F.; Wu, Z.; Yan, X.; Zheng, J.; Sun, H.; Cao, X.; Bian, J.S. DR region of Na+-K+-ATPase is a new target to protect heart against oxidative injury. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cat, A.N.D.; Montezano, A.C.; Burger, D.; Touyz, R.M. Angiotensin II, NADPH oxidase, and redox signaling in the vasculature. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camejo, J.L.; Proverbio, T.; Proverbio, F. Ouabain-insensitive, Na+-stimulated ATPase activity in rabbit cardiac sarcolemma. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 110, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, M.; Cain, P.; Holmqvist, C.; Stahlberg, F.; Lundback, S.; Arheden, H. Total heart volume variation throughout the cardiac cycle in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004, 287, H243–H250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.J.; Oh, J.G. SERCA2a: a prime target for modulation of cardiac contractility during heart failure. BMB Rep. 2013, 46, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.C. Control of respiration and ATP synthesis in mammalian mitochondria and cells. Biochem. J. 1992, 284, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, C.J.; Bright, N.A.; Rutter, G.A.; Griffiths, E.J. ATP regulation in adult rat cardiomyocytes: time-resolved decoding of rapid mitochondrial calcium spiking imaged with targeted photoproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 28058–28067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Li, Y.; Xiao, C.; Du, J. Angiotensin II induces inflammation leading to cardiac remodeling. Front. Biosci. 2012, 17, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, N.; Scott, I. In the heart and beyond: Mitochondrial dysfunction in Heart Failure with preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF). Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2024, 76, 102461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasenfuss, G.; Reinecke, H.; Studer, R.; Meyer, M.; Pieske, B.; Holtz, J.; Holubarsch, C.; Posival, H.; Just, H.; Drexler, H. Relation between myocardial function and expression of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase in failing and nonfailing human myocardium. Circ. Res. 1994, 75, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisner, D.; Caldwell, J.; Trafford, A. Sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase and heart failure 20 years later. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 958–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, T.E. Phosphofructokinase activity in skeletal muscle extracts following administration of epinephrine. J. Biol. Chem. 1972, 247, 6059–6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.Y.; Storey, K.B. Regulation of phosphofructokinase from muscle and liver of rainbow trout by protein phosphorylation. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1994, 33, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reed, M.C.; Lieb, A.; Nijhout, H.F. The biological significance of substrate inhibition: a mechanism with diverse functions. Bioessays. 2010, 32, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharov, V.S.; Dremina, E.S.; Galeva, N.A.; Williams, T.D.; Schöneich, C. Quantitative mapping of oxidation-sensitive cysteine residues in SERCA in vivo and in vitro by HPLC-electrospray-tandem MS: selective protein oxidation during biological aging. Biochem. J. 2006, 394, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horáková, L.; Strosova, M.K.; Spickett, C.M.; Blaskovic, D. Impairment of calcium ATPases by high glucose and potential pharmacological protection. Free Radic. Res. 2013, 47, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlaug, B.A.; Jensen, M.D.; Kitzman, D.W.; Lam, C.S.P.; Obokata, M.; Rider, O.J. Obesity and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: new insights and pathophysiological targets. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 118, 3434–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouton, A.J.; Li, X.; Hall, M.E.; Hall, J.E. Obesity, hypertension, and cardiac dysfunction: novel roles of immunometabolism in macrophage activation and inflammation. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 789–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, W.J.; Zile, MR. From systemic inflammation to myocardial fibrosis: the heart failure with preserved ejection fraction paradigm revisited. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 1451–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Tuttle, K.R.; Chow, S.L.; Mathew, R.O.; Khan, S.S.; Coresh, J.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Carnethon, M.R.; Després, J.P.; Ho, J.E.; Joseph, J.J.; Kernan, W.N.; Khera. A.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Lekavich, C.L.; Lewis, E.F.; Lo, K.B.; Ozkan, B.; Palaniappan, L.P.; Patel, S.S.; Pencina, M.J.; Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Sperling, L.S.; Virani, S.S.; Wright, J.T.; Rajgopal Singh, R.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Rangaswami, J.; American Heart Association. A Synopsis of the Evidence for the Science and Clinical Management of Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2023, 148, 1636–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robotham, J.L.; Takata, M.; Berman, M.; Harasawa, Y. Ejection fraction revisited. Anesthesiology. 1991, 74, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, I.S.; Liu, D.; Chugh, S.S.; Prahash, A.J.; Gupta, S.; John, R.; Popescu, F.; Chandrashekhar, Y. Isolated myocyte contractile function is normal in postinfarct remodeled rat heart with systolic dysfunction. Circulation. 1997, 96, 3974–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaraju, A.; Goyal, A.; Grigorova, Y.; Makaryus, A.N. Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2023.
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; Emerson, M.; Garner, P.; Holgate, S.T.; Howells, D.W.; Karp, N.A.; Lazic, S.E.; Lidster, K.; MacCallum, C.J.; Macleod, M.; Pearl, E.J.; Petersen, O.H.; Rawle, F.; Reynolds, P.; Rooney, K.; Sena, E.S.; Silberberg, S.D.; Steckler, T.; Würbel, H. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: updated guidelines for reporting animal research. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 3617–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, K.E.; Kane, C.J.; Pierce, D.R.; Jenkins, D. Ge,Y.; Brown, G.; Yang, H.; Nyamweya, N. Intragastric intubation: important aspects of the model for administration of ethanol to rat pups during the postnatal period. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1998, 22, 1600−1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, H.; Moss, T.J.; Gatford, K.L.; Moritz, K.M.; Akison, L.; Fullston, T.; Hryciw, D.H.; Maloney, C.A.; Morris, M.J.; Wooldridge, A.L.; Schjenken, J.E.; Robertson, S.A.; Waddell, B.J.; Mark, P.J.; Wyrwoll, C.S.; Ellery, S.J.; Thornburg, K.L.; Muhlhausler, B.S.; Morrison, J.L. A review of fundamental principles for animal models of DOHaD research: an Australian perspective. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2016, 7, 449–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostanic, I.; Schultz Jel, J.; Lorenz, J.N.; Lingrel, J.B. The α1 isoform of Na,K-ATPase regulates cardiac contractility and functionally interacts and co-localizes with the Na/Ca exchanger in heart. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 54053–54061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebroug, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taussky, H.H.; Shorr, E. A microcolorimetric method for the determination of inorganic phosphorus. J. Biol. Chem. 1953, 202, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorenson, M.M.; Coelho, H.S.; Reuben, J.P. Caffeine inhibition of calcium accumulation by the sarcoplasmic reticulum in mammalian skinned fibers. J. Membr. Biol. 1986, 90, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, R.M.; Bierig, M.; Devereux, R.B.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Foster, E.; Pellikka, P.A.; Picard, M.H.; Roman, M.J.; Seward, J.; Shanewise, J.S.; Solomon, S.D.; Spencer, K.T.; Sutton, M.S.; Stewart, W.J.; Chamber Quantification Writing Group; American Society of Echocardiography's Guidelines and Standards Committee; European Association of Echocardiography. Recommendations for chamber quantification: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography's Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Chamber Quantification Writing Group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, a branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2005, 18, 1440–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




