Submitted:
10 July 2024
Posted:
11 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
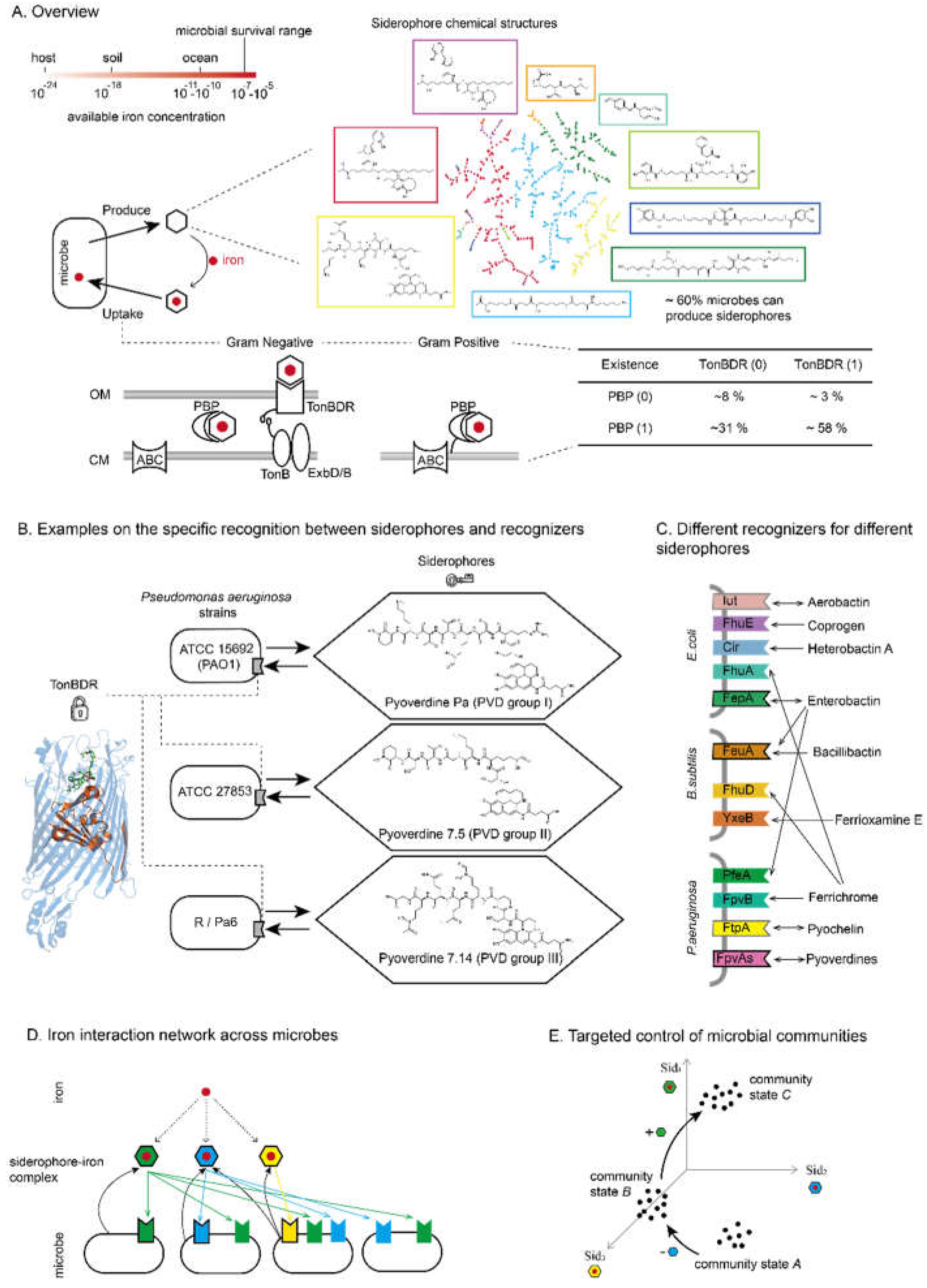
1. Poking Into the Microbial Community by Siderophore-Mediated Iron Interaction Network
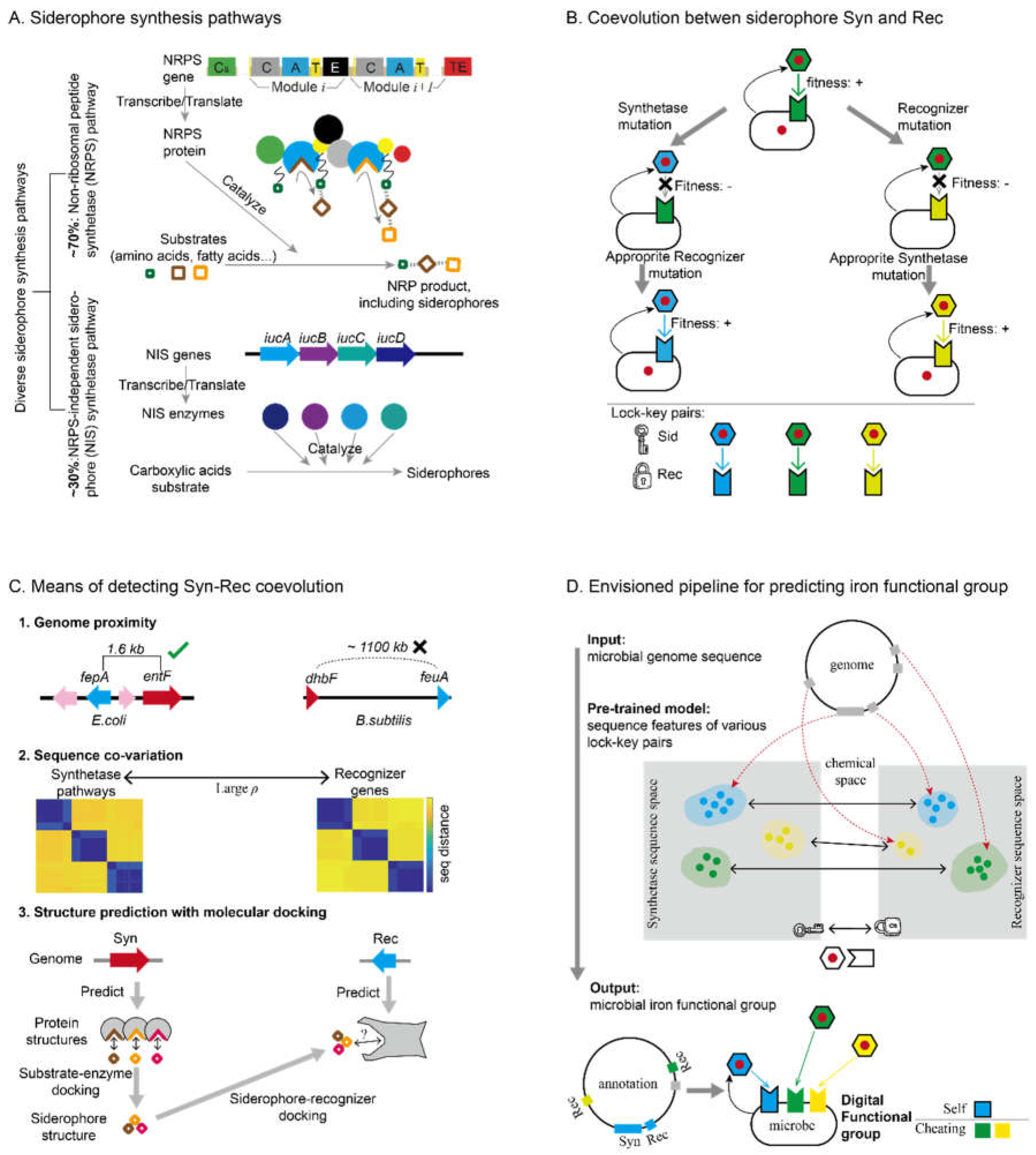
2. From Sequence to Ecology: Harness the Molecular Coevolution to Predict Siderophore-Mediated Interactions
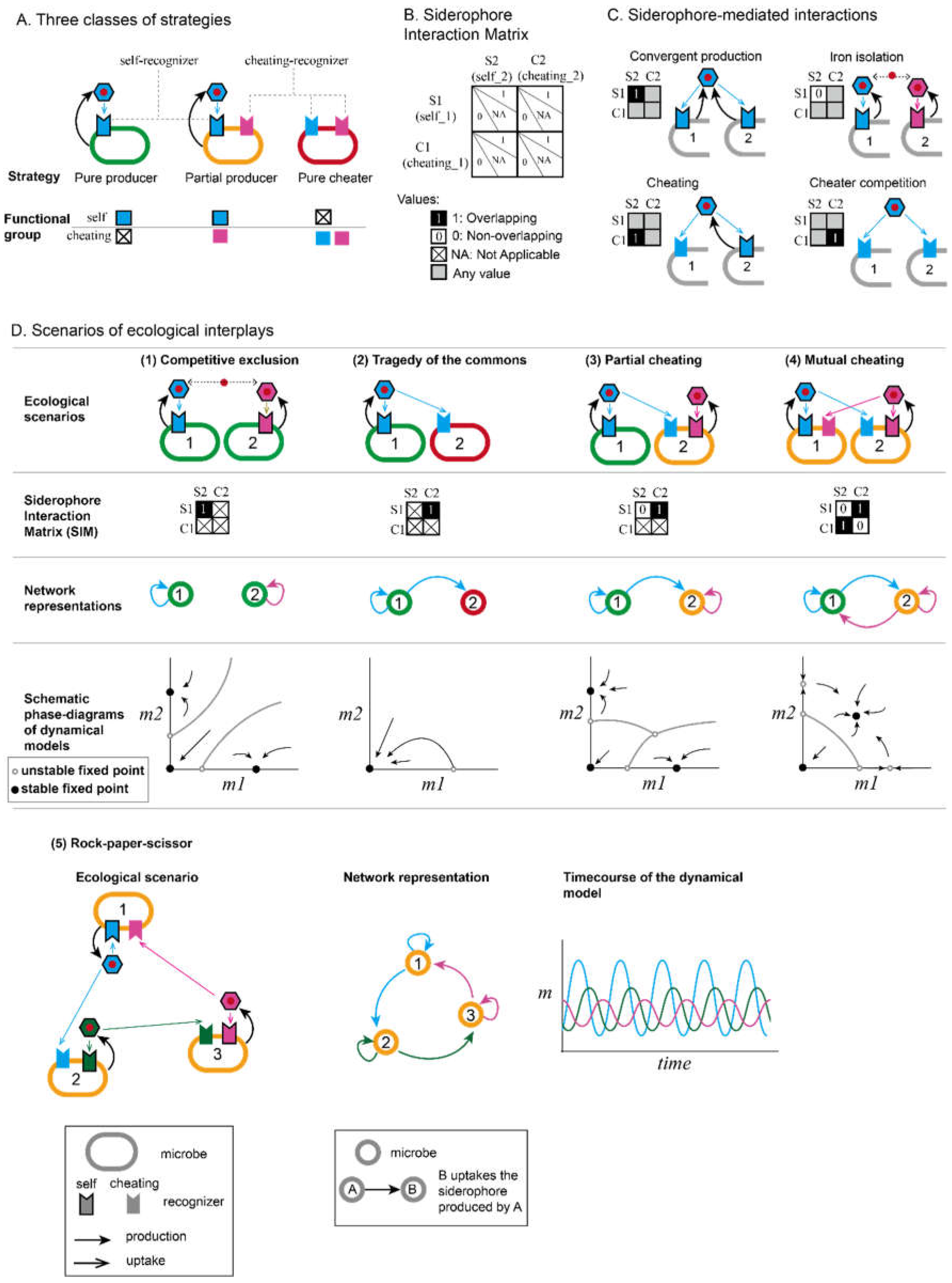
3. The Iron Interactions Network as a Playground for Microbial Game Theories
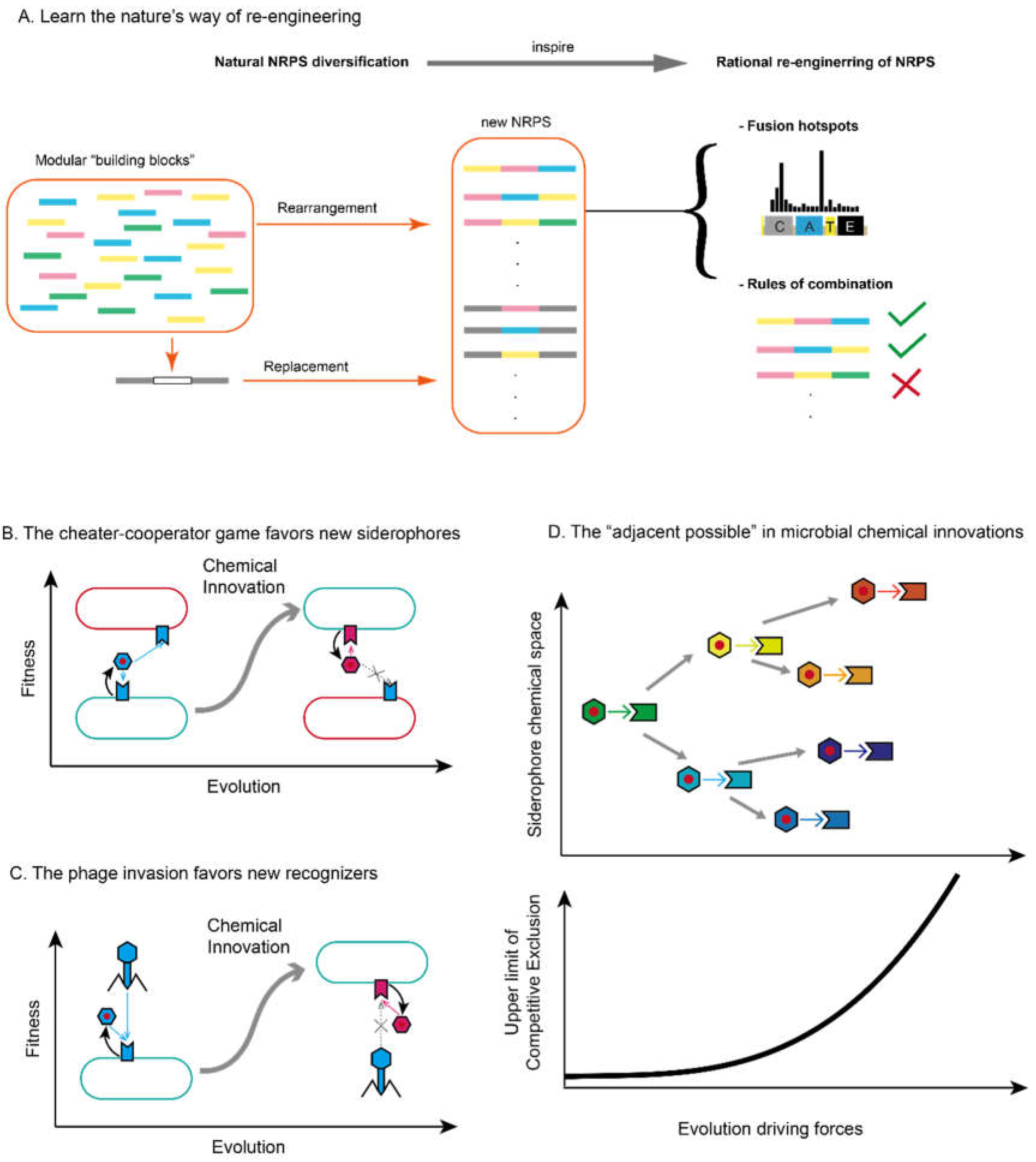
4. Fighting for Diversity: The Eco-Evolutionary Implications of Microbial Chemical Innovations via Secondary Metabolism
5. Discussion
Author Contribution
Ethics Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrews SC, Robinson AK, Rodríguez-Quiñones F: Bacterial iron homeostasis. FEMS microbiology reviews 2003, 27:215-237. [CrossRef]
- Ilbert M, Bonnefoy V: Insight into the evolution of the iron oxidation pathways. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics 2013, 1827:161-175. [CrossRef]
- Boyd PW, Ellwood MJ: The biogeochemical cycle of iron in the ocean. Nature Geoscience 2010, 3:675-682. [CrossRef]
- Boguta P, D’Orazio V, Senesi N, Sokołowska Z, Szewczuk-Karpisz K: Insight into the interaction mechanism of iron ions with soil humic acids. The effect of the pH and chemical properties of humic acids. Journal of Environmental Management 2019, 245:367-374. [CrossRef]
- Seyoum Y, Baye K, Humblot C: Iron homeostasis in host and gut bacteria–a complex interrelationship. Gut Microbes 2021, 13:1874855. [CrossRef]
- Hider RC, Kong X: Chemistry and biology of siderophores. Natural product reports 2010, 27:637-657. [CrossRef]
- Krewulak KD, Hans J. Vogel: Structural biology of bacterial iron uptake. 2008, 1778:1781-1804. [CrossRef]
- Siderophore Information Database (SIDERTE). 2024.
- He R, Gu S, Xu J, Li X, Chen H, Shao Z, Wang F, Shao J, Yin WB, Qian L: SIDERITE: Unveiling hidden siderophore diversity in the chemical space through digital exploration. iMeta 2024, 3:e192. [CrossRef]
- Gu Shaohua SY, Rehm Karoline, Bigler Laurent, Zhang Di, He Ruolin, Xu Ruichen, Shao Jiqi, Jousset Alexandre, Friman Ville-Petri, Bian Xiaoying, Wei Zhong, Kümmerli Rolf, Li Zhiyuan: From sequence to molecules: Feature sequence-based genome mining uncovers the hidden diversity of bacterial siderophore pathways eLife 13:RP96719. eLife 2024, 13:RP96719. [CrossRef]
- He R, Zhang J, Shao Y, Gu S, Song C, Qian L, Yin W-B, Li Z: Knowledge-guided data mining on the standardized architecture of NRPS: Subtypes, novel motifs, and sequence entanglements. PLOS Computational Biology 2023, 19:e1011100. [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva AM, Galyamova MR, Sedykh SE: Bacterial siderophores: Classification, biosynthesis, perspectives of use in agriculture. Plants 2022, 11:3065. [CrossRef]
- Schalk IJ, Mislin GL, Brillet K: Structure, function and binding selectivity and stereoselectivity of siderophore–iron outer membrane transporters. Current topics in membranes 2012, 69:37-66. [CrossRef]
- Clarke TE, Ku S-Y, Dougan DR, Vogel HJ, Tari LW: The structure of the ferric siderophore binding protein FhuD complexed with gallichrome. Nature structural biology 2000, 7:287-291. [CrossRef]
- Fukushima T, Allred BE, Sia AK, Nichiporuk R, Andersen UN, Raymond KN: Gram-positive siderophore-shuttle with iron-exchange from Fe-siderophore to apo-siderophore by Bacillus cereus YxeB. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2013, 110:13821-13826. [CrossRef]
- Grigg JC, Cheung J, Heinrichs DE, Murphy ME: Specificity of Staphyloferrin B recognition by the SirA receptor from Staphylococcus aureus. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2010, 285:34579-34588. [CrossRef]
- Meyer J-M, Stintzi A, De Vos D, Cornelis P, Tappe R, Taraz K, Budzikiewicz H: Use of siderophores to type pseudomonads: the three Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyoverdine systems. Microbiology 1997, 143:35-43. [CrossRef]
- De Chial M, Ghysels B, Beatson SA, Geoffroy V, Meyer JM, Pattery T, Baysse C, Chablain P, Parsons YN, Winstanley CJM: Identification of type II and type III pyoverdine receptors from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 2003, 149:821-831. [CrossRef]
- Greenwald J, Nader M, Celia H, Gruffaz C, Geoffroy V, Meyer JM, Schalk IJ, Pattus F: FpvA bound to non-cognate pyoverdines: molecular basis of siderophore recognition by an iron transporter. Molecular microbiology 2009, 72:1246-1259. [CrossRef]
- Bouvier B, Cézard C, Sonnet P: Selectivity of pyoverdine recognition by the FpvA receptor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from molecular dynamics simulations. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2015, 17:18022-18034. [CrossRef]
- Byun H, Jung I-J, Chen J, Larios Valencia J, Zhu J: Siderophore piracy enhances Vibrio cholerae environmental survival and pathogenesis. Microbiology 2020, 166:1038-1046. [CrossRef]
- Butaitė E, Baumgartner M, Wyder S, Kümmerli R: Siderophore cheating and cheating resistance shape competition for iron in soil and freshwater Pseudomonas communities. Nature communications 2017, 8:414. [CrossRef]
- Rutz J, Abdullah T, Singh S, Kalve V, Klebba P: Evolution of the ferric enterobactin receptor in gram-negative bacteria. Journal of bacteriology 1991, 173:5964-5974. [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio A, Crawford JM, Stewart EJ, Witt K, Gavrish E, Epstein S, Clardy J, Lewis K: Siderophores from neighboring organisms promote the growth of uncultured bacteria. Chemistry & biology 2010, 17:254-264. [CrossRef]
- Carrano CJ, Jordan M, Drechsel H, Schmid DG, Winkelmann G: Heterobactins: a new class of siderophores from Rhodococcus erythropolis IGTS8 containing both hydroxamate and catecholate donor groups. Biometals 2001, 14:119-125. [CrossRef]
- Raymond KN, Allred BE, Sia AK: Coordination chemistry of microbial iron transport. Accounts of chemical research 2015, 48:2496-2505. [CrossRef]
- Grandchamp GM, Caro L, Shank EA: Pirated Siderophores Promote Sporulation in. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2017, 83. [CrossRef]
- Dertz EA, Xu JD, Stintzi A, Raymond KN: Bacillibactin-mediated iron transport in. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2006, 128:22-23. [CrossRef]
- Zawadzka AM, Abergel RJ, Nichiporuk R, Andersen UN, Raymond KN: Siderophore-mediated iron acquisition systems in Bacillus cereus: identification of receptors for anthrax virulence-associated petrobactin. Biochemistry 2009, 48:3645-3657. [CrossRef]
- Moynié L, Milenkovic S, Mislin GLA, Gasser V, Malloci G, Baco E, McCaughan RP, Page MGP, Schalk IJ, Ceccarelli M, Naismith JH: The complex of ferric-enterobactin with its transporter from Pseudomonas aeruginosa suggests a two-site model. Nature Communications 2019, 10. [CrossRef]
- Ankenbauer RG, Quan HN: FptA, the Fe (III)-pyochelin receptor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a phenolate siderophore receptor homologous to hydroxamate siderophore receptors. Journal of bacteriology 1994, 176:307-319. [CrossRef]
- Chan DC, Burrows LL: Pseudomonas aeruginosa FpvB is a high-affinity transporter for xenosiderophores ferrichrome and ferrioxamine B. Mbio 2023, 14:e03149-03122. [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulou A, Theologidis I, Benaki D, Koukounia M, Zervakou A, Tzima A, Diallinas G, Hatzinikolaou DG, Skandalis NJM: Direct antibiotic activity of bacillibactin broadens the biocontrol range of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MBI600. 2021, 6:10.1128/msphere. 00376-00321. [CrossRef]
- Bodilis J, Ghysels B, Osayande J, Matthijs S, Pirnay JP, Denayer S, De Vos D, Cornelis PJEM: Distribution and evolution of ferripyoverdine receptors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 2009, 11:2123-2135. [CrossRef]
- Visca P, Imperi F, Lamont IL: Pyoverdine siderophores: from biogenesis to biosignificance. Trends in microbiology 2007, 15:22-30. [CrossRef]
- Crits-Christoph A, Bhattacharya N, Olm MR, Song YS, Banfield JFJGr: Transporter genes in biosynthetic gene clusters predict metabolite characteristics and siderophore activity. 2021, 31:239-250. [CrossRef]
- Barelmann I, Taraz K, Budzikiewicz H, Geoffroy V, Meyer J-MJZfNC: The structures of the pyoverdins from two Pseudomonas fluorescens strains accepted mutually by their respective producers. 2002, 57:9-16. [CrossRef]
- Costea PI, Hildebrand F, Arumugam M, Bäckhed F, Blaser MJ, Bushman FD, De Vos WM, Ehrlich SD, Fraser CM, Hattori M: Enterotypes in the landscape of gut microbial community composition. Nature microbiology 2018, 3:8-16. [CrossRef]
- Meyer J-M, Geoffroy VA, Baida N, Gardan L, Izard D, Lemanceau P, Achouak W, Palleroni NJJA, Microbiology E: Siderophore typing, a powerful tool for the identification of fluorescent and nonfluorescent pseudomonads. 2002, 68:2745-2753. [CrossRef]
- Li C, Pan D, Li M, Wang Y, Song L, Yu D, Zuo Y, Wang K, Liu Y, Wei ZJFim: Aerobactin-mediated iron acquisition enhances biofilm formation, oxidative stress resistance, and virulence of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. 2021, 12:699913. [CrossRef]
- Carroll CS, Moore MMJCrib, biology m: Ironing out siderophore biosynthesis: a review of non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS)-independent siderophore synthetases. 2018, 53:356-381. [CrossRef]
- Griffin AS, West SA, Buckling AJN: Cooperation and competition in pathogenic bacteria. 2004, 430:1024-1027. [CrossRef]
- Kramer J, Özkaya Ö, Kümmerli RJNRM: Bacterial siderophores in community and host interactions. 2020, 18:152-163. [CrossRef]
- Patel P, Song L, Challis GLJB: Distinct extracytoplasmic siderophore binding proteins recognize ferrioxamines and ferricoelichelin in Streptomyces coelicolor A3 (2). 2010, 49:8033-8042. [CrossRef]
- Coderre PE, Earhart CF: The entD gene of the Escherichia coli K12 enterobactin gene cluster. Microbiology 1989, 135:3043-3055. [CrossRef]
- Gu S, Shao Z, Qu Z, Zhu S, Shao Y, Zhang D, Allen R, He R, Shao J, Xiong GJb: Siderophore-receptor coevolution analysis reveals habitat-and pathogen-specific bacterial iron interaction networks. 2023:2023.2011. 2005.565711. [CrossRef]
- Hotta K, Kim C-Y, Fox DT, Koppisch AT: Siderophore-mediated iron acquisition in Bacillus anthracis and related strains. Microbiology 2010, 156:1918-1925. [CrossRef]
- Abramson J, Adler J, Dunger J, Evans R, Green T, Pritzel A, Ronneberger O, Willmore L, Ballard AJ, Bambrick J: Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024:1-3. [CrossRef]
- Zhu J, Gu Z, Pei J, Lai L: DiffBindFR: an SE (3) equivariant network for flexible protein–ligand docking. Chemical Science 2024, 15:7926-7942. [CrossRef]
- Wensel CR, Pluznick JL, Salzberg SL, Sears CLJTJoci: Next-generation sequencing: insights to advance clinical investigations of the microbiome. 2022, 132. [CrossRef]
- Shao J, Rong N, Wu Z, Gu S, Liu B, Shen N, Li Z: Siderophore-mediated iron partition promotes dynamical coexistence between cooperators and cheaters. Iscience 2023, 26. [CrossRef]
- Wu Z, Shao J, Zheng J, Liu B, Li Z, Shen N: A zero-sum game or an interactive frame? Iron competition between bacteria and humans in infection war. Chinese Medical Journal 2022, 135:1917-1926. [CrossRef]
- Hibbing ME, Fuqua C, Parsek MR, Peterson SB: Bacterial competition: surviving and thriving in the microbial jungle. Nature reviews microbiology 2010, 8:15-25. [CrossRef]
- Niehus R, Picot A, Oliveira NM, Mitri S, Foster KR: The evolution of siderophore production as a competitive trait. Evolution 2017, 71:1443-1455. [CrossRef]
- Smith P, Schuster M: Public goods and cheating in microbes. Current biology 2019, 29:R442-R447. [CrossRef]
- Gu S, Yang T, Shao Z, Wang T, Cao K, Jousset A, Friman V-P, Mallon C, Mei X, Wei ZJM: Siderophore-mediated interactions determine the disease suppressiveness of microbial consortia. 2020, 5:10.1128/msystems. 00811-00819. [CrossRef]
- Shao J, Li Y, Lu J, Gu S, Li Z: Siderophore Piracy Promotes Dynamical Coexistence in Microbial Community. bioRxiv 2023:2023.2011. 2021.568182. [CrossRef]
- Li Z, Liu B, Li SH-J, King CG, Gitai Z, Wingreen NS: Modeling microbial metabolic trade-offs in a chemostat. PLoS computational biology 2020, 16:e1008156. [CrossRef]
- Kerr B, Riley MA, Feldman MW, Bohannan BJ: Local dispersal promotes biodiversity in a real-life game of rock–paper–scissors. Nature 2002, 418:171-174. [CrossRef]
- Liao MJ, Din MO, Tsimring L, Hasty J: Rock-paper-scissors: Engineered population dynamics increase genetic stability. Science 2019, 365:1045-1049. [CrossRef]
- Kirkup BC, Riley MA: Antibiotic-mediated antagonism leads to a bacterial game of rock–paper–scissors in vivo. Nature 2004, 428:412-414. [CrossRef]
- Bushley KE, Ripoll DR, Turgeon BG: Module evolution and substrate specificity of fungal nonribosomal peptide synthetases involved in siderophore biosynthesis. BMC Evolutionary Biology 2008, 8:1-24. [CrossRef]
- Baunach M, Chowdhury S, Stallforth P, Dittmann E: The landscape of recombination events that create nonribosomal peptide diversity. Molecular Biology and Evolution 2021, 38:2116-2130. [CrossRef]
- Fan J, Ren J, He R, Wei P-L, Li Y, Li W, Chen D, Druzhinina IS, Li Z, Yin W-B: Biosynthetic diversification of peptaibol mediates fungus-mycohost interactions. bioRxiv 2022:2022.2006. 2005.494846. [CrossRef]
- Fischbach MA, Walsh CT: Assembly-line enzymology for polyketide and nonribosomal peptide antibiotics: logic, machinery, and mechanisms. Chemical reviews 2006, 106:3468-3496. [CrossRef]
- Bruns H, Crüsemann M, Letzel A-C, Alanjary M, McInerney JO, Jensen PR, Schulz S, Moore BS, Ziemert N: Function-related replacement of bacterial siderophore pathways. The ISME journal 2018, 12:320-329. [CrossRef]
- Soutar CD, Stavrinides J: The evolution of three siderophore biosynthetic clusters in environmental and host-associating strains of Pantoea. Molecular genetics and genomics 2018, 293:1453-1467. [CrossRef]
- Cimermancic P, Medema MH, Claesen J, Kurita K, Brown LCW, Mavrommatis K, Pati A, Godfrey PA, Koehrsen M, Clardy J: Insights into secondary metabolism from a global analysis of prokaryotic biosynthetic gene clusters. Cell 2014, 158:412-421. [CrossRef]
- Wang X, Zhou H, Ren X, Chen H, Zhong L, Bai X, Bian X: Recombineering enables genome mining of novel siderophores in a non-model Burkholderiales strain. Engineering Microbiology 2023, 3:100106. [CrossRef]
- Brown AS, Calcott MJ, Owen JG, Ackerley DF: Structural, functional and evolutionary perspectives on effective re-engineering of non-ribosomal peptide synthetase assembly lines. Natural product reports 2018, 35:1210-1228. [CrossRef]
- Bozhüyük KA, Präve L, Kegler C, Schenk L, Kaiser S, Schelhas C, Shi Y-N, Kuttenlochner W, Schreiber M, Kandler J: Evolution-inspired engineering of nonribosomal peptide synthetases. Science 2024, 383:eadg4320. [CrossRef]
- Barona-Gómez F, Chevrette MG, Hoskisson PA: On the evolution of natural product biosynthesis. In Advances in Microbial Physiology. Volume 83: Elsevier; 2023: 309-349. [CrossRef]
- Martiny AC, Treseder K, Pusch GJTIj: Phylogenetic conservatism of functional traits in microorganisms. 2013, 7:830-838. [CrossRef]
- Smith EE, Sims EH, Spencer DH, Kaul R, Olson MVJJob: Evidence for diversifying selection at the pyoverdine locus of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 2005, 187:2138-2147. [CrossRef]
- Lee W, van Baalen M, Jansen VAJEl: An evolutionary mechanism for diversity in siderophore-producing bacteria. 2012, 15:119-125. [CrossRef]
- Rütschlin S, Gunesch S, Böttcher TJACB: One enzyme to build them all: ring-size engineered siderophores inhibit the swarming motility of Vibrio. 2018, 13:1153-1158. [CrossRef]
- Thulasiraman P, Newton SM, Xu J, Raymond KN, Mai C, Hall A, Montague MA, Klebba PEJJob: Selectivity of ferric enterobactin binding and cooperativity of transport in gram-negative bacteria. 1998, 180:6689-6696. [CrossRef]
- Chan DC, Burrows LLJM: Pseudomonas aeruginosa FpvB is a high-affinity transporter for xenosiderophores ferrichrome and ferrioxamine B. 2023, 14:e03149-03122. [CrossRef]
- Winkelmann G, Braun VJFML: Stereoselective recognition of ferrichrome by fungi and bacteria. 1981, 11:237-241. [CrossRef]
- Denayer S, Matthijs S, Cornelis PJJob: Pyocin S2 (Sa) kills Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains via the FpvA type I ferripyoverdine receptor. 2007, 189:7663-7668. [CrossRef]
- Bonnain C, Breitbart M, Buck KNJFiMS: The Ferrojan horse hypothesis: iron-virus interactions in the ocean. 2016, 3:82. [CrossRef]
- Rabsch W, Ma L, Wiley G, Najar FZ, Kaserer W, Schuerch DW, Klebba JE, Roe BA, Gomez JAL, Schallmey MJJob: FepA-and TonB-dependent bacteriophage H8: receptor binding and genomic sequence. 2007, 189:5658-5674. [CrossRef]
- Vasse M, Torres-Barceló C, Hochberg MEJPotRSBBS: Phage selection for bacterial cheats leads to population decline. 2015, 282:20152207. [CrossRef]
- Ge H, Hu M, Zhao G, Du Y, Xu N, Chen XJMr: The” fighting wisdom and bravery” of tailed phage and host in the process of adsorption. 2020, 230:126344. [CrossRef]
- Murdoch CC, Skaar EPJNRM: Nutritional immunity: the battle for nutrient metals at the host–pathogen interface. 2022, 20:657-670. [CrossRef]
- Sargun A, Gerner RR, Raffatellu M, Nolan EMJTJoID: Harnessing iron acquisition machinery to target Enterobacteriaceae. 2021, 223:S307-S313. [CrossRef]
- Fischbach MA, Walsh CT, Clardy J: The evolution of gene collectives: How natural selection drives chemical innovation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2008, 105:4601-4608. [CrossRef]
- Kauffman SA: Reinventing the sacred: A new view of science, reason, and religion. Basic Books; 2008.
- Mizuno K, Mizuno M, Yamauchi M, Takemura AJ, Medrano Romero V, Morikawa K: Adjacent-possible ecological niche: growth of Lactobacillus species co-cultured with Escherichia coli in a synthetic minimal medium. Scientific reports 2017, 7:12880. [CrossRef]
- Testa B, Vistoli G, Pedretti A: Small Molecules as Exemplars of Emergent Properties and Diversification into the ‘Adjacent Possible’. Chemistry & Biodiversity 2014, 11:1309-1329. [CrossRef]
- Pearl Mizrahi S, Goyal A, Gore J: Community interactions drive the evolution of antibiotic tolerance in bacteria. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2023, 120:e2209043119. [CrossRef]
- Lee H, Bloxham B, Gore J: Resource competition can explain simplicity in microbial community assembly. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2023, 120:e2212113120. [CrossRef]
- Pilosof S, Alcala-Corona SA, Wang T, Kim T, Maslov S, Whitaker R, Pascual M: The network structure and eco-evolutionary dynamics of CRISPR-induced immune diversification. Nature Ecology & Evolution 2020, 4:1650-1660. [CrossRef]
- Puig S, Ramos-Alonso L, Romero AM, Martínez-Pastor MT: The elemental role of iron in DNA synthesis and repair. Metallomics 2017, 9:1483-1500. [CrossRef]
- Pau MY, Lipscomb JD, Solomon EI: Substrate activation for O2 reactions by oxidized metal centers in biology. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2007, 104:18355-18362. [CrossRef]
- Gu S, Wei Z, Shao Z, Friman V-P, Cao K, Yang T, Kramer J, Wang X, Li M, Mei XJNM: Competition for iron drives phytopathogen control by natural rhizosphere microbiomes. 2020, 5:1002-1010. [CrossRef]
- Sargun A, Gerner RR, Raffatellu M, Nolan EM: Harnessing iron acquisition machinery to target Enterobacteriaceae. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 2021, 223:S307-S313. [CrossRef]
- Ellermann M, Arthur JC: Siderophore-mediated iron acquisition and modulation of host-bacterial interactions. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2017, 105:68-78. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




